| Revision as of 01:29, 26 July 2023 editSlik357 (talk | contribs)94 edits Cleaned up grammar for the initial paragraph explaining enzyme secretion and the resulting damage to pancreatic ducts.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 23:35, 7 January 2025 edit undoKaltenmeyer (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users120,061 editsm clean upTag: AWB | ||
| (41 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| | image = 3D Medical Animation Acute Pancreatitis.jpg | | image = 3D Medical Animation Acute Pancreatitis.jpg | ||
| | caption = Still from 3D medical animation of acute ] | | caption = Still from 3D medical animation of acute ] | ||
| | pronounce = |
| pronounce = | ||
| | field = ], ] | | field = ], ] | ||
| | symptoms = |
| symptoms = | ||
| | complications = |
| complications = | ||
| | onset = |
| onset = | ||
| | duration = |
| duration = | ||
| | types = |
| types = | ||
| | causes = |
| causes = | ||
| | risks = |
| risks = | ||
| | diagnosis = |
| diagnosis = | ||
| | differential = |
| differential = | ||
| | prevention = |
| prevention = | ||
| | treatment = |
| treatment = | ||
| | medication = |
| medication = | ||
| | prognosis = |
| prognosis = | ||
| | frequency = | | frequency = | ||
| | deaths = |
| deaths = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Acute pancreatitis''' (AP) is a sudden ] of the ]. Causes |
'''Acute pancreatitis''' (AP) is a sudden ] of the ]. Causes include a ] impacted in the ] or the ], heavy ], ], ], ], ] (with triglycerides usually being very elevated, over 1000 mg/dL), certain medications, hereditary causes and, in children, ]. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event, it may be ], or it may progress to ] and/or ] (the term pancreatic dysfunction includes cases of acute or chronic pancreatitis where the pancreas is measurably damaged, even if it has not failed). | ||
| In all cases of acute pancreatitis, early ] hydration and early enteral (nutrition delivered to the gut, either by mouth or via a ]) feeding are associated with lower mortality and complications.<ref name="Mederos 2021">{{cite journal |last1=Mederos |first1=Michael A. |last2=Reber |first2=Howard A. |last3=Girgis |first3=Mark D. |title=Acute Pancreatitis: A Review |journal=JAMA |date=26 January 2021 |volume=325 |issue=4 |pages=382–390 |doi=10.1001/jama.2020.20317|pmid=33496779 }}</ref> Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures such as hospitalization with intravenous fluid infusion, pain control, and early enteral feeding. If a person is not able to tolerate feeding by mouth, feeding via ] or nasojejunal tubes are frequently used which provide nutrition directly to the stomach or intestines respectively.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> Severe cases often require admission to an ]. Severe pancreatitis, which by definition includes organ damage other than the pancreas, is associated with a mortality rate of 20%.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> The condition is characterized by the pancreas secreting active enzymes such as ], ] and ], instead of their inactive forms, leading to auto-digestion of the pancreas. Calcium helps to convert trypsinogen to the active trypsin, thus elevated calcium (of any cause) is a potential cause of pancreatitis.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> Damage to the pancreatic ducts can occur as a result of this. Long term complications include ] (pancreatogenic diabetes), in which the pancreas is unable to secrete enough insulin due to structural damage.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> 35% develop ] in which the pancreas is unable to secrete digestive enzymes due to structural damage, leading to malabsorption.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, ], intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an ] to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. For people with this condition, the pancreas will begin to secrete active enzymes such as Trypsin, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase instead of their inactive forms. Damage to the pancreatic ducts can occur as a result of this. | |||
| {{TOC limit|3}} | {{TOC limit|3}} | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| ===Common=== | ===Common=== | ||
| Common symptoms of acute pancreatitis include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and low to moderate grade fever.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /><ref>{{cite web|title=Pancreatitis|publisher=Mayo Clinic|url=https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20360227|access-date=14 October 2020}}</ref> The abdominal pain is the most common symptom and it is usually described as being in the left upper quadrant, epigastric area or around the umbilicus, with radiation throughout the abdomen, or to the chest or back.<ref name="Quinlan 2014">{{cite journal |last1=Quinlan |first1=JD |title=Acute pancreatitis. |journal=American Family Physician |date=1 November 2014 |volume=90 |issue=9 |pages=632–9 |pmid=25368923}}</ref> The abdominal pain initially may worsen with eating or drinking but may become constant as the disease progresses.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /><ref name="Quinlan 2014" /> Less common symptoms include ], abdominal bloating and indigestion.<ref name="Quinlan 2014" /> Although these are common symptoms, frequently they are not all present; and epigastric pain may be the only symptom.<ref>{{cite web|title=Symptoms & Causes of Pancreatitis|publisher=The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases|url=https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes|access-date=4 October 2020}}</ref> | |||
| *severe ] (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases | |||
| *]<ref>{{cite web|title=Pancreatitis|publisher=Mayo Clinic|url=https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20360227|access-date=14 October 2020}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] (shivering) | |||
| *] instability, including ] | |||
| *] (rapid heartbeat) | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| Although these are common symptoms, frequently they are not all present; and epigastric pain may be the only symptom.<ref>{{cite web|title=Symptoms & Causes of Pancreatitis|publisher=The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases|url=https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes|access-date=4 October 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ] (hemorrhagic discoloration of the flanks) or ] (hemorrhagic discoloration of the umbilicus) are associated with severe disease. However both signs are rare (occurring in less than 1% of cases of acute pancreatitis) and are not specific nor sensitive for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.<ref name="Wright 2016">{{cite journal |last1=Wright |first1=William F. |title=Cullen Sign and Grey Turner Sign Revisited |journal=Journal of Osteopathic Medicine |date=1 June 2016 |volume=116 |issue=6 |pages=398–401 |doi=10.7556/jaoa.2016.081}}</ref> ] (fluid in the lung cavity) may occur in up to 34% of people with acute pancreatitis and are associated with a poor prognosis.<ref name="Zeng 2023">{{cite journal |last1=Zeng |first1=Tingting |last2=An |first2=Jing |last3=Wu |first3=Yanqiu |last4=Hu |first4=Xueru |last5=An |first5=Naer |last6=Gao |first6=Lijuan |last7=Wan |first7=Chun |last8=Liu |first8=Lian |last9=Shen |first9=Yongchun |title=Incidence and prognostic role of pleural effusion in patients with acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis |journal=Annals of Medicine |date=12 December 2023 |volume=55 |issue=2 |doi=10.1080/07853890.2023.2285909|pmc=10880572 }}</ref> The Mayo-Robson's sign (pain while pressing at the top of the angle lateral to the ] and below the left 12th rib (left ] (CVA)) is also associated with acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite book|author=Sriram Bhat M|title=SRB's Clinical Methods in Surgery|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WK52DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA488|date=2018-10-31|publisher=JP Medical Ltd|isbn=978-93-5270-545-0|pages=488–}}</ref> | |||
| ===Uncommon=== | |||
| The following are associated with severe disease: | |||
| *] (hemorrhagic discoloration of the flanks) | |||
| *] (hemorrhagic discoloration of the umbilicus) | |||
| *Pleural effusions (fluid in the bases of the pleural cavity) | |||
| * Grünwald sign (appearance of ], large bruise, around the umbilicus due to local toxic lesion of the vessels) | |||
| * Körte's sign (pain or resistance in the zone where the head of pancreas is located (in ], 6–7 cm above the umbilicus)) | |||
| * Kamenchik's sign (pain with pressure under the ]) | |||
| * Mayo-Robson's sign (pain while pressing at the top of the angle lateral to the ] and below the left 12th rib (left ] (CVA))<ref>{{cite book|author=Sriram Bhat M|title=SRB's Clinical Methods in Surgery|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WK52DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA488|date=2018-10-31|publisher=JP Medical Ltd|isbn=978-93-5270-545-0|pages=488–}}</ref> | |||
| * Mayo-Robson's point – a point on border of inner 2/3 with the external 1/3 of the line that represents the bisection of the left upper abdominal quadrant, where tenderness on pressure exists in disease of the pancreas. At this point the tail of pancreas is projected on the abdominal wall. | |||
| === Complications === | === Complications === | ||
| Complications of acute pancreatitis may occur. Necrotic pancreatitis occurs when inflammation of the pancreas progresses to cell death. Acute fluid collections may form adjacent to the pancreas or necrotic collections (discrete areas of dead tissue) may also form adjacent to or within the pancreas. These may progress to ]s and walled off areas of dead tissue which may persist for longer than 4 weeks. Both can become secondarily infected.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> Other complications include ] splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, hemorrhage from erosions into splenic artery and vein, blood clot of the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein and portal veins, duodenal obstruction, common bile duct obstruction, progression to chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic ascites, or pleural effusion.<ref>{{Cite book | chapter-url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6978/ | chapter = Early complications of severe acute pancreatitis | vauthors = Bassi C, Falconi M, Butturini G, Pederzoli P | title = Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. | veditors = Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA | location = Munich | publisher = Zuckschwerdt |date=2001 }}</ref><ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Systemic complications include ] (ARDS), ], ] (DIC), ] (from fat saponification), ] and ] (from pancreatic insulin-producing ] damage), and ] due to exocrine failure.{{Citation needed|date=October 2024}} | |||
| Locoregional complications include ] (most common, occurring in up to 25% of all cases, typically after 4–6 weeks) and phlegmon/abscess formation, splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, hemorrhage from erosions into splenic artery and vein, thrombosis of the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein and portal veins (in descending order of frequency), duodenal obstruction, common bile duct obstruction, progression to chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion, sterile/infected pancreatic necrosis.<ref>{{Cite book | chapter-url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK6978/ | chapter = Early complications of severe acute pancreatitis | vauthors = Bassi C, Falconi M, Butturini G, Pederzoli P | title = Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. | veditors = Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA | location = Munich | publisher = Zuckschwerdt |date=2001 }}</ref> | |||
| Tobacco use, recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic tissue death, alcoholic pancreatitis are all risk factors for developing chronic pancreatitis.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Systemic complications include ] (ARDS), ], ] (DIC), ] (from fat saponification), ] and ] (from pancreatic insulin-producing ] damage), ] due to exocrine failure | |||
| * '''Metabolic''' | |||
| **], ], ] | |||
| * '''Respiratory''' | |||
| **], ], ], ], ] | |||
| * '''Renal''' | |||
| ** Renal artery or vein thrombosis | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * '''Circulatory''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] and ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * '''Gastrointestinal''' | |||
| ** Gastrointestinal hemorrhage from stress ulceration | |||
| ** Gastric varices (secondary to splenic vein thrombosis) | |||
| ** Gastrointestinal obstruction | |||
| *''' Hepatobiliary''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * '''Neurologic''' | |||
| ** ] or ] (confusion, delusion and coma) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] (angiopathic retinopathy with hemorrhage) | |||
| * '''Hematologic''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *'''Dermatologic''' | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *'''Miscellaneous''' | |||
| ** Subcutaneous fat necrosis | |||
| ** Arthalgia | |||
| == Causes == | == Causes == | ||
| Line 101: | Line 49: | ||
| * Idiopathic in 15–25% of cases | * Idiopathic in 15–25% of cases | ||
| * Metabolic disorders: ], ], ], ] | * Metabolic disorders: ], ], ], ] | ||
| * May occur after instrumentation of the pancreatic duct or its opening to the duodenum (ampula of Vater) in procedures such as an ] or ] (ERCP). The risk after EUS is less than 1% and the risk after ERCP is 5-10%.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| * Post-] retrograde cholangiopancreatography | |||
| * Abdominal trauma | * Abdominal trauma | ||
| * Penetrating ulcers | * Penetrating ulcers | ||
| * ] of the ], and other ] | * ] of the ], and other ] | ||
| * Drugs: ] |
* Drugs: ] with or without ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], estrogen containing products or hormones, ], ], ], ], ], ]<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | ||
| * Infections: ], ], ], ], '']'', '']'' | * Infections: ], ], ], ], '']'', '']'' | ||
| *Structural abnormalities: |
* Structural abnormalities: ], pancreatic masses or cysts that block the ducts.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ]<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | ||
| * Severe ]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rawla P, Sunkara T, Thandra KC, Gaduputi V | title = Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: updated review of current treatment and preventive strategies | journal = Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 11 | issue = 6 | pages = 441–448 | date = December 2018 | pmid = 29923163 | doi = 10.1007/s12328-018-0881-1 | s2cid = 49311482 }}</ref> | * Severe ]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rawla P, Sunkara T, Thandra KC, Gaduputi V | title = Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: updated review of current treatment and preventive strategies | journal = Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 11 | issue = 6 | pages = 441–448 | date = December 2018 | pmid = 29923163 | doi = 10.1007/s12328-018-0881-1 | s2cid = 49311482 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 121: | Line 69: | ||
| * ]s other than mumps, including ]<ref name="Review of Infectious Etiology of Ac"/> | * ]s other than mumps, including ]<ref name="Review of Infectious Etiology of Ac"/> | ||
| * Hyperparathyroidism | * Hyperparathyroidism | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] or ] | * ] or ] | ||
| * ] reaction<ref name="A new source of drug-induced acute pancreatitis: codeine">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hastier P, Buckley MJ, Peten EP, Demuth N, Dumas R, Demarquay JF, Caroli-Bosc FX, Delmont JP | title = A new source of drug-induced acute pancreatitis: codeine | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 95 | issue = 11 | pages = 3295–8 | date = November 2000 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03213.x | pmid = 11095359 | s2cid = 22261058 }}</ref><ref name="Pancreatitis due to codeine">{{cite journal | vauthors = Moreno Escobosa MC, Amat López J, Cruz Granados S, Moya Quesada MC | title = Pancreatitis due to codeine | journal = Allergologia et Immunopathologia | volume = 33 | issue = 3 | pages = 175–7 | year = 2005 | pmid = 15946633 | doi = 10.1157/13075703 }}</ref> | |||
| == Pathology == | == Pathology == | ||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=October 2024}} | |||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| ===Pathogenesis=== | ===Pathogenesis=== | ||
| Acute pancreatitis occurs when there is abnormal activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas. This occurs through inappropriate activation of inactive enzyme precursors called ] (or proenzymes) inside the pancreas, most notably ]. Normally, trypsinogen is converted to its active form (]) in the first part of the small intestine (]), where the enzyme assists in the digestion of proteins. During an episode of acute pancreatitis, trypsinogen comes into contact with lysosomal enzymes (specifically ]), which activate trypsinogen to trypsin. The active form trypsin then leads to further activation of other molecules of trypsinogen. The activation of these digestive enzymes lead to inflammation, edema, vascular injury, and even cellular death. The death of pancreatic cells occurs via two main mechanisms: |
Acute pancreatitis occurs when there is abnormal activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas. This occurs through inappropriate activation of inactive enzyme precursors called ] (or proenzymes) inside the pancreas, most notably ]. Normally, trypsinogen is converted to its active form (]) in the first part of the small intestine (]), where the enzyme assists in the digestion of proteins. During an episode of acute pancreatitis, trypsinogen comes into contact with lysosomal enzymes (specifically ]), which activate trypsinogen to trypsin. The active form trypsin then leads to further activation of other molecules of trypsinogen. The activation of these digestive enzymes lead to inflammation, edema, vascular injury, and even cellular death. The death of pancreatic cells occurs via two main mechanisms: ], which is physiologically controlled, and ], which is less organized and more damaging. The balance between these two mechanisms of cellular death is mediated by ] which regulate apoptosis and have important anti-necrosis functions during pancreatitis: preventing trypsinogen activation, preventing ATP depletion through inhibiting polyADP-ribose polymerase, and by inhibiting the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs). If, however, the caspases are depleted due to either chronic ethanol exposure or through a severe insult then necrosis can predominate. | ||
| ===Pathophysiology=== | ===Pathophysiology=== | ||
| Line 142: | Line 88: | ||
| == Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
| Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed using ] and ] |
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed using ] and ] findings supporting the diagnosis with imaging and pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase). The Revised Atlanta Classification requires two out of three of the following findings for the diagnosis: abdominal pain consistent with pancreatitis, elevated amylase or lipase levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal, and imaging consistent with acute pancreatitis.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /><ref name=ACG_Gudielines_2013>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS | title = American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 108 | issue = 9 | pages = 1400–15; 1416 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23896955 | doi = 10.1038/ajg.2013.218 | s2cid = 12610145 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Additional labs may be used to identify organ failure for prognostic purposes or to guide fluid resuscitation rate.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> If the lipase level is about 2.5 to 3 times that of amylase, it is an indication of pancreatitis due to alcohol.<ref name="pmid1718808">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gumaste VV, Dave PB, Weissman D, Messer J | title = Lipase/amylase ratio. A new index that distinguishes acute episodes of alcoholic from nonalcoholic acute pancreatitis | journal = Gastroenterology | volume = 101 | issue = 5 | pages = 1361–6 | date = November 1991 | pmid = 1718808 | doi = 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90089-4 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Serum lipase is more sensitive and specific than serum amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis, and is the preferred test in the diagnosis.<ref name="pmid17032204">{{cite journal | vauthors = Banks PA, Freeman ML | title = Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 101 | issue = 10 | pages = 2379–400 | date = October 2006 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00856.x | pmid = 17032204 | s2cid = 1837007 | collaboration = Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid15831893">{{cite journal |author=UK Working Party on Acute Pancreatitis | title = UK guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis | journal = Gut | volume = 54 | issue = Suppl 3 | pages = iii1–9 | date = May 2005 | pmid = 15831893 | pmc = 1867800 | doi = 10.1136/gut.2004.057026 }}</ref> | ||
| Most, but not all individual studies support favor the diagnostic utility of lipase.<ref>{{synthesis inline|date=September 2014}}In support of the superiority of the lipase: | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D | title = Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis? | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 75 | issue = 6 | pages = 399–404 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15943725 | doi = 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x | s2cid = 35768001 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Treacy J, Williams A, Bais R, Willson K, Worthley C, Reece J, Bessell J, Thomas D | title = Evaluation of amylase and lipase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 71 | issue = 10 | pages = 577–82 | date = October 2001 | pmid = 11552931 | doi = 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2001.02220.x | s2cid = 30880859 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Keim V, Teich N, Fiedler F, Hartig W, Thiele G, Mössner J | title = A comparison of lipase and amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in patients with abdominal pain | journal = Pancreas | volume = 16 | issue = 1 | pages = 45–9 | date = January 1998 | pmid = 9436862 | doi = 10.1097/00006676-199801000-00008 | s2cid = 21285537 }} | |||
| Without support for the superiority of the lipase: | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Ignjatović S, Majkić-Singh N, Mitrović M, Gvozdenović M | title = Biochemical evaluation of patients with acute pancreatitis | journal = Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine | volume = 38 | issue = 11 | pages = 1141–4 | date = November 2000 | pmid = 11156345 | doi = 10.1515/CCLM.2000.173 | s2cid = 34932274 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Sternby B, O'Brien JF, Zinsmeister AR, DiMagno EP | title = What is the best biochemical test to diagnose acute pancreatitis? A prospective clinical study | journal = Mayo Clinic Proceedings | volume = 71 | issue = 12 | pages = 1138–44 | date = December 1996 | pmid = 8945483 | doi = 10.4065/71.12.1138 }}</ref> In one large study, there were no patients with pancreatitis who had an elevated amylase with a normal lipase.<ref name="pmid15943725">{{cite journal | vauthors = Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D | title = Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis? | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 75 | issue = 6 | pages = 399–404 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15943725 | doi = 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x | s2cid = 35768001 }}</ref> Another study found that the amylase could add diagnostic value to the lipase, but only if the results of the two tests were combined with a discriminant function equation.<ref name="pmid7504593">{{cite journal | vauthors = Corsetti JP, Cox C, Schulz TJ, Arvan DA | title = Combined serum amylase and lipase determinations for diagnosis of suspected acute pancreatitis | journal = Clinical Chemistry | volume = 39 | issue = 12 | pages = 2495–9 | date = December 1993 | doi = 10.1093/clinchem/39.12.2495 | pmid = 7504593 | url = http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7504593 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Reduced lipase clearance due to kidney disease, gastrointestinal or hepatobiliary cancers, pancreatic enzyme hypersecretion, critical illness including due to neurosurgical causes have been shown to increase serum lipase and may complicate the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hameed AM, Lam VW, Pleass HC | title = Significant elevations of serum lipase not caused by pancreatitis: a systematic review | journal = HPB | volume = 17 | issue = 2 | pages = 99–112 | date = February 2015 | pmid = 24888393 | pmc = 4299384 | doi = 10.1111/hpb.12277 }}</ref> | |||
| * Blood investigations – ], ], liver function, serum calcium, serum amylase and lipase | |||
| * Imaging – A triple phase abdominal CT and abdominal ultrasound are together considered the gold standard for the evaluation of acute pancreatitis. Other modalities including the abdominal x-ray lack sensitivity and are not recommended. An important caveat is that imaging during the first 12 hours may be falsely reassuring as the inflammatory and necrotic process usually requires 48 hours to fully manifest. | |||
| === Differential diagnosis === | === Differential diagnosis === | ||
| Line 155: | Line 108: | ||
| * ] pain | * ] pain | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| === Biochemical === | |||
| * Elevated serum ] and ] levels, in combination with severe abdominal pain, often trigger the initial diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. However, they have no role in assessing disease severity. | |||
| * Serum lipase rises 4 to 8 hours from the onset of symptoms and normalizes within 7 to 14 days after treatment. | |||
| * Serum amylase may be normal (in 10% of cases) for cases of acute or chronic pancreatitis (depleted acinar cell mass) and hypertriglyceridemia. | |||
| * Reasons for false positive elevated serum amylase include salivary gland disease (elevated salivary amylase), bowel obstruction, infarction, cholecystitis, and a perforated ulcer. | |||
| * If the lipase level is about 2.5 to 3 times that of amylase, it is an indication of pancreatitis due to alcohol.<ref name="pmid1718808">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gumaste VV, Dave PB, Weissman D, Messer J | title = Lipase/amylase ratio. A new index that distinguishes acute episodes of alcoholic from nonalcoholic acute pancreatitis | journal = Gastroenterology | volume = 101 | issue = 5 | pages = 1361–6 | date = November 1991 | pmid = 1718808 | doi = 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90089-4 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| **Decreased serum calcium | |||
| **Glycosuria | |||
| Regarding selection on these tests, two practice guidelines state: | |||
| : "It is usually not necessary to measure both serum amylase and lipase. Serum lipase may be preferable because it remains normal in some nonpancreatic conditions that increase serum amylase including macroamylasemia, parotitis, and some carcinomas. In general, serum lipase is thought to be more sensitive and specific than serum amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis"<ref name="pmid17032204">{{cite journal | vauthors = Banks PA, Freeman ML | title = Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 101 | issue = 10 | pages = 2379–400 | date = October 2006 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00856.x | pmid = 17032204 | s2cid = 1837007 | collaboration = Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology }}</ref> | |||
| : "Although amylase is widely available and provides acceptable accuracy of diagnosis, where lipase is available it is preferred for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis (recommendation grade A)"<ref name="pmid15831893">{{cite journal |author=UK Working Party on Acute Pancreatitis | title = UK guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis | journal = Gut | volume = 54 Suppl 3 | issue = Suppl 3 | pages = iii1–9 | date = May 2005 | pmid = 15831893 | pmc = 1867800 | doi = 10.1136/gut.2004.057026 }}</ref> | |||
| Most, but not all individual studies support the superiority of the lipase.<ref>{{synthesis inline|date=September 2014}}In support of the superiority of the lipase: | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D | title = Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis? | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 75 | issue = 6 | pages = 399–404 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15943725 | doi = 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x | s2cid = 35768001 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Treacy J, Williams A, Bais R, Willson K, Worthley C, Reece J, Bessell J, Thomas D | title = Evaluation of amylase and lipase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 71 | issue = 10 | pages = 577–82 | date = October 2001 | pmid = 11552931 | doi = 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2001.02220.x | s2cid = 30880859 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Steinberg WM, Goldstein SS, Davis ND, Shamma'a J, Anderson K | title = Diagnostic assays in acute pancreatitis. A study of sensitivity and specificity | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | volume = 102 | issue = 5 | pages = 576–80 | date = May 1985 | pmid = 2580467 | doi = 10.7326/0003-4819-102-5-576 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Lin XZ, Wang SS, Tsai YT, Lee SD, Shiesh SC, Pan HB, Su CH, Lin CY | title = Serum amylase, isoamylase, and lipase in the acute abdomen. Their diagnostic value for acute pancreatitis | journal = Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 47–52 | date = February 1989 | pmid = 2466075 | doi = 10.1097/00004836-198902000-00011 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Keim V, Teich N, Fiedler F, Hartig W, Thiele G, Mössner J | title = A comparison of lipase and amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in patients with abdominal pain | journal = Pancreas | volume = 16 | issue = 1 | pages = 45–9 | date = January 1998 | pmid = 9436862 | doi = 10.1097/00006676-199801000-00008 | s2cid = 21285537 }} | |||
| Without support for the superiority of the lipase: | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Ignjatović S, Majkić-Singh N, Mitrović M, Gvozdenović M | title = Biochemical evaluation of patients with acute pancreatitis | journal = Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine | volume = 38 | issue = 11 | pages = 1141–4 | date = November 2000 | pmid = 11156345 | doi = 10.1515/CCLM.2000.173 | s2cid = 34932274 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Sternby B, O'Brien JF, Zinsmeister AR, DiMagno EP | title = What is the best biochemical test to diagnose acute pancreatitis? A prospective clinical study | journal = Mayo Clinic Proceedings | volume = 71 | issue = 12 | pages = 1138–44 | date = December 1996 | pmid = 8945483 | doi = 10.4065/71.12.1138 }}</ref> In one large study, there were no patients with pancreatitis who had an elevated amylase with a normal lipase.<ref name="pmid15943725">{{cite journal | vauthors = Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D | title = Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis? | journal = ANZ Journal of Surgery | volume = 75 | issue = 6 | pages = 399–404 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15943725 | doi = 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x | s2cid = 35768001 }}</ref> Another study found that the amylase could add diagnostic value to the lipase, but only if the results of the two tests were combined with a discriminant function equation.<ref name="pmid7504593">{{cite journal | vauthors = Corsetti JP, Cox C, Schulz TJ, Arvan DA | title = Combined serum amylase and lipase determinations for diagnosis of suspected acute pancreatitis | journal = Clinical Chemistry | volume = 39 | issue = 12 | pages = 2495–9 | date = December 1993 | doi = 10.1093/clinchem/39.12.2495 | pmid = 7504593 | url = http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7504593 }}</ref> | |||
| While often quoted lipase levels of 3 or more times the upper-limit of normal is diagnostic of pancreatitis, there are also other differential diagnosis to be considered relating to this rise.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hameed AM, Lam VW, Pleass HC | title = Significant elevations of serum lipase not caused by pancreatitis: a systematic review | journal = HPB | volume = 17 | issue = 2 | pages = 99–112 | date = February 2015 | pmid = 24888393 | pmc = 4299384 | doi = 10.1111/hpb.12277 }}</ref> | |||
| === Computed tomography === | === Computed tomography === | ||
| Line 188: | Line 114: | ||
| CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if: | CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if: | ||
| *the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain | * the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain | ||
| *there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis | * there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis | ||
| *there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8 | * there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8 | ||
| *there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy | * there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy | ||
| *there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock | * there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock | ||
| CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations: | CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations: | ||
| *acute change in status | * acute change in status | ||
| *to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure | * to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure | ||
| *before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis | * before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis | ||
| Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings. | Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings. | ||
| CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall: | CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall: | ||
| * Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset) | |||
| * Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space | |||
| * Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed ], which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc. | |||
| The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalized areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging,<ref name="pmid2379000">{{cite journal | vauthors = Larvin M, Chalmers AG, McMahon MJ | title = Dynamic contrast enhanced computed tomography: a precise technique for identifying and localising pancreatic necrosis | journal = BMJ | volume = 300 | issue = 6737 | pages = 1425–8 | date = June 1990 | pmid = 2379000 | pmc = 1663140 | doi = 10.1136/bmj.300.6737.1425 }}</ref> and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated. | |||
| *Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset) | |||
| *Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space | |||
| *Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed ], which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc. | |||
| The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalised areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging,<ref name="pmid2379000">{{cite journal | vauthors = Larvin M, Chalmers AG, McMahon MJ | title = Dynamic contrast enhanced computed tomography: a precise technique for identifying and localising pancreatic necrosis | journal = BMJ | volume = 300 | issue = 6737 | pages = 1425–8 | date = June 1990 | pmid = 2379000 | pmc = 1663140 | doi = 10.1136/bmj.300.6737.1425 }}</ref> and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated. | |||
| === Magnetic resonance imaging === | === Magnetic resonance imaging === | ||
| Line 216: | Line 141: | ||
| === Ultrasound === | === Ultrasound === | ||
| ] of acute pancreatitis]] | ] of acute pancreatitis]] | ||
| Ultrasound is less preferred as a diagnostic test for acute pancreatitis, but it may be used in select cases. ] may be obtained if there is concern of a gallstone blocking the pancreatic duct leading to pancreatitis.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| On ], the finding of a hypoechoic and bulky pancreas is regarded as diagnostic of acute pancreatitis.{{citation needed|date=June 2021}} | |||
| == Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
| Early enteral (nutrition given directly to the gut, either by mouth or via feeding tube) nutrition and aggressive intravenous fluid hydration are indicated in all forms and severities of acute pancreatitis and are associated with lower mortality and complications.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Initial management of a patient with acute pancreatitis consists of supportive care with fluid resuscitation, pain control, nothing by mouth, and nutritional support. | |||
| === Fluid replacement === | === Fluid replacement === | ||
| The specific rate of intravenous fluid replacement in acute pancreatitis is not well established but some experts recommend an initial fluid infusion rate of 5-10 mL of IV fluids per kilogram of body weight per hour and adjusting the rate to meet physiologic parameters such as heart rate, ], urine output and ].<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Aggressive hydration at a rate of 5 to 10 mL/kg per hour of isotonic crystalloid solution (e.g., normal saline or lactated Ringer's solution) to all patients with acute pancreatitis, unless cardiovascular, renal, or other related comorbid factors preclude aggressive fluid replacement. In patients with severe volume depletion that manifests as hypotension and tachycardia, more rapid repletion with 20 mL/kg of intravenous fluid given over 30 minutes followed by 3 mL/kg/hour for 8 to 12 hours.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gardner TB, Vege SS, Pearson RK, Chari ST | title = Fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis | journal = Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology | volume = 6 | issue = 10 | pages = 1070–6 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18619920 | doi = 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.05.005 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Haydock MD, Mittal A, Wilms HR, Phillips A, Petrov MS, Windsor JA | title = Fluid therapy in acute pancreatitis: anybody's guess | journal = Annals of Surgery | volume = 257 | issue = 2 | pages = 182–8 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23207241 | doi = 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31827773ff | s2cid = 46381021 }}</ref> | |||
| Isotonic crystalloid solutions (such as ]) are preferred over ] for fluid resuscitation and are associated with a lower risk of developing ] (SIRS).<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Fluid requirements should be reassessed at frequent intervals in the first six hours of admission and for the next 24 to 48 hours. The rate of fluid resuscitation should be adjusted based on clinical assessment, hematocrit and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) values. | |||
| In the initial stages (within the first 12 to 24 hours) of acute pancreatitis, fluid replacement has been associated with a reduction in morbidity and mortality.<ref>{{cite journal | title = IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis | journal = Pancreatology | volume = 13 | issue = 4 Suppl 2 | pages = e1–15 | year = 2013 | pmid = 24054878 | doi = 10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063 | author1 = Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Talukdar R, Swaroop Vege S | title = Early management of severe acute pancreatitis | journal = Current Gastroenterology Reports | volume = 13 | issue = 2 | pages = 123–30 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 21243452 | doi = 10.1007/s11894-010-0174-4 | s2cid = 38955726 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Trikudanathan G, Navaneethan U, Vege SS | title = Current controversies in fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review | journal = Pancreas | volume = 41 | issue = 6 | pages = 827–34 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22781906 | doi = 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824c1598 | s2cid = 1864635 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gardner TB, Vege SS, Chari ST, Petersen BT, Topazian MD, Clain JE, Pearson RK, Levy MJ, Sarr MG | title = Faster rate of initial fluid resuscitation in severe acute pancreatitis diminishes in-hospital mortality | journal = Pancreatology | volume = 9 | issue = 6 | pages = 770–6 | year = 2009 | pmid = 20110744 | doi = 10.1159/000210022 | s2cid = 5614093 }}</ref> | In the initial stages (within the first 12 to 24 hours) of acute pancreatitis, fluid replacement has been associated with a reduction in morbidity and mortality.<ref>{{cite journal | title = IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis | journal = Pancreatology | volume = 13 | issue = 4 Suppl 2 | pages = e1–15 | year = 2013 | pmid = 24054878 | doi = 10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063 | author1 = Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines | doi-access = free | hdl = 1854/LU-8582111 | hdl-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Talukdar R, Swaroop Vege S | title = Early management of severe acute pancreatitis | journal = Current Gastroenterology Reports | volume = 13 | issue = 2 | pages = 123–30 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 21243452 | doi = 10.1007/s11894-010-0174-4 | s2cid = 38955726 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Trikudanathan G, Navaneethan U, Vege SS | title = Current controversies in fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review | journal = Pancreas | volume = 41 | issue = 6 | pages = 827–34 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22781906 | doi = 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824c1598 | s2cid = 1864635 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gardner TB, Vege SS, Chari ST, Petersen BT, Topazian MD, Clain JE, Pearson RK, Levy MJ, Sarr MG | title = Faster rate of initial fluid resuscitation in severe acute pancreatitis diminishes in-hospital mortality | journal = Pancreatology | volume = 9 | issue = 6 | pages = 770–6 | year = 2009 | pmid = 20110744 | doi = 10.1159/000210022 | s2cid = 5614093 }}</ref> | ||
| === Pain control === | === Pain control === | ||
| Line 233: | Line 158: | ||
| Opioids are safe and effective at providing pain control in patients with acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Basurto Ona X, Rigau Comas D, Urrútia G | title = Opioids for acute pancreatitis pain | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 7 | issue = 7 | pages = CD009179 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23888429 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD009179.pub2 }}</ref> Adequate pain control requires the use of intravenous opiates, usually in the form of a patient-controlled analgesia pump. ] or ] (intravenous) may be used for pain relief in acute pancreatitis. Fentanyl is being increasingly used due to its better safety profile, especially in renal impairment. As with other opiates, fentanyl can depress respiratory function. It can be given both as a bolus as well as constant infusion. | Opioids are safe and effective at providing pain control in patients with acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Basurto Ona X, Rigau Comas D, Urrútia G | title = Opioids for acute pancreatitis pain | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 7 | issue = 7 | pages = CD009179 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23888429 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD009179.pub2 }}</ref> Adequate pain control requires the use of intravenous opiates, usually in the form of a patient-controlled analgesia pump. ] or ] (intravenous) may be used for pain relief in acute pancreatitis. Fentanyl is being increasingly used due to its better safety profile, especially in renal impairment. As with other opiates, fentanyl can depress respiratory function. It can be given both as a bolus as well as constant infusion. | ||
| ] has been historically favored over ] because of the belief that morphine caused an increase in ] pressure. However, no clinical studies suggest that morphine can aggravate or cause pancreatitis or cholecystitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Helm JF, Venu RP, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Toouli J, Arndorfer RC | title = Effects of morphine on the human sphincter of Oddi | journal = Gut | volume = 29 | issue = 10 | pages = 1402–7 | date = October 1988 | pmid = 3197985 | pmc = 1434014 | doi = 10.1136/gut.29.10.1402 }}</ref> In addition, meperidine has a short half-life and repeated doses can lead to accumulation of the metabolite normeperidine, which causes neuromuscular side effects and, rarely, seizures. | ] has been historically favored over ] because of the belief that morphine caused an increase in ] pressure. However, no clinical studies suggest that morphine can aggravate or cause pancreatitis or cholecystitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Helm JF, Venu RP, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Toouli J, Arndorfer RC | title = Effects of morphine on the human sphincter of Oddi | journal = Gut | volume = 29 | issue = 10 | pages = 1402–7 | date = October 1988 | pmid = 3197985 | pmc = 1434014 | doi = 10.1136/gut.29.10.1402 }}</ref> In addition, meperidine has a short half-life and repeated doses can lead to accumulation of the metabolite normeperidine, which causes neuromuscular side effects and, rarely, seizures. | ||
| === Bowel rest === | |||
| In the management of acute pancreatitis, the treatment is to stop feeding the patient, giving them nothing by mouth, giving ] fluids to prevent ], and sufficient pain control. As the pancreas is stimulated to secrete ]s by the presence of food in the stomach, having no food pass through the system allows the pancreas to rest.{{Citation needed|date=July 2012}} Approximately 20% of patients have a relapse of pain during acute pancreatitis.<ref name="pmid17573797">{{cite journal | vauthors = Petrov MS, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Cirkel GA, Brink MA, Gooszen HG | title = Oral refeeding after onset of acute pancreatitis: a review of literature | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 102 | issue = 9 | pages = 2079–84; quiz 2085 | date = September 2007 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01357.x | pmid = 17573797 | hdl=1874/26559 | s2cid = 11581054 | hdl-access = free }}</ref> Approximately 75% of relapses occur within 48 hours of oral refeeding.{{Citation needed|date=July 2012}} | |||
| The incidence of relapse after oral refeeding may be reduced by post-pyloric ] rather than ] prior to oral refeeding.<ref name="pmid17573797" /> IMRIE scoring is also useful. | |||
| === Nutritional support === | === Nutritional support === | ||
| Acute pancreatitis is a catabolic state and with hemodynamic instability or fluid shifts or edema there may be reduced intravascular perfusion to the gut. This reduction in gut perfusion increases the risk of gut necrosis with bacterial translocation with the subsequent risk of sepsis or secondary infections.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> Enteral nutrition gives one needed caloric intake as well as enhances intestinal motility and blood flow to the gut, reducing these risks.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> Enteral nutrition (as compared to ], in which nutrients are given via intravenous infusion) is associated with reduced mortality, reduced risk of multi-organ failure and systemic infection in those with acute pancreatitis.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /><ref name="Al-Omran 2010">{{cite journal |last1=Al-Omran |first1=Mohammed |last2=AlBalawi |first2=Zaina H |last3=Tashkandi |first3=Mariam F |last4=Al-Ansary |first4=Lubna A |title=Enteral versus parenteral nutrition for acute pancreatitis |journal=Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews |date=20 January 2010 |issue=1 |pages=CD002837 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD002837.pub2|pmid=20091534 |pmc=7120370 }}</ref> In patients with acute pancreatitis, the ] (AGA) recommends early oral nutrition, within 24 hours, rather than keeping the patient fastng (or nothing by mouth). And in those unable to feed orally, the AGA recommends enteral nutrition (via a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube) rather than parenteral nutrition.<ref name="Crockett 2018">{{cite journal |last1=Crockett |first1=Seth D. |last2=Wani |first2=Sachin |last3=Gardner |first3=Timothy B. |last4=Falck-Ytter |first4=Yngve |last5=Barkun |first5=Alan N. |last6=Crockett |first6=Seth |last7=Falck-Ytter |first7=Yngve |last8=Feuerstein |first8=Joseph |last9=Flamm |first9=Steven |last10=Gellad |first10=Ziad |last11=Gerson |first11=Lauren |last12=Gupta |first12=Samir |last13=Hirano |first13=Ikuo |last14=Inadomi |first14=John |last15=Nguyen |first15=Geoffrey C. |last16=Rubenstein |first16=Joel H. |last17=Singh |first17=Siddharth |last18=Smalley |first18=Walter E. |last19=Stollman |first19=Neil |last20=Street |first20=Sarah |last21=Sultan |first21=Shahnaz |last22=Vege |first22=Santhi S. |last23=Wani |first23=Sachin B. |last24=Weinberg |first24=David |title=American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis |journal=Gastroenterology |date=March 2018 |volume=154 |issue=4 |pages=1096–1101 |doi=10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.032|pmid=29409760 }}</ref> | |||
| Recently, there has been a shift in the management paradigm from ] (TPN) to early, post-pyloric enteral feeding (in which a feeding tube is endoscopically or radiographically introduced to the third portion of the duodenum). The advantage of enteral feeding is that it is more physiological, prevents gut mucosal atrophy, and is free from the side effects of TPN (such as ]). The additional advantages of post-pyloric feeding are the inverse relationship of pancreatic exocrine secretions and distance of nutrient delivery from the pylorus, as well as reduced risk of aspiration. | |||
| Disadvantages of a naso-enteric feeding tube include increased risk of sinusitis (especially if the tube remains in place greater than two weeks) and a still-present risk of accidentally ] even in intubated patients (contrary to popular belief, the endotracheal tube cuff alone is not always sufficient to prevent NG tube entry into the trachea). | |||
| === Oxygen=== | |||
| Oxygen may be provided in some patients (about 30%) if Pao2 levels fall below 70mm of Hg. | |||
| === Antibiotics === | === Antibiotics === | ||
| Up to 20 percent of people with acute pancreatitis develop an infection outside the pancreas such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, or urinary tract infections.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Boermeester MA, Nieuwenhuijs VB, van Goor H, Dejong CH, Schaapherder AF, Gooszen HG | title = Timing and impact of infections in acute pancreatitis | journal = The British Journal of Surgery | volume = 96 | issue = 3 | pages = 267–73 | date = March 2009 | pmid = 19125434 | doi = 10.1002/bjs.6447 | s2cid = 2226746 }}</ref> These infections are associated with an increase in mortality.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu BU, Johannes RS, Kurtz S, Banks PA | title = The impact of hospital-acquired infection on outcome in acute pancreatitis | journal = Gastroenterology | volume = 135 | issue = 3 | pages = 816–20 | date = September 2008 | pmid = 18616944 | pmc = 2570951 | doi = 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.053 }}</ref> When an infection is suspected, antibiotics should be started while the source of the infection is being determined. However, if cultures are negative and no source of infection is identified, antibiotics should be discontinued. | Up to 20 percent of people with acute pancreatitis develop an infection outside the pancreas such as ], ], or ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Boermeester MA, Nieuwenhuijs VB, van Goor H, Dejong CH, Schaapherder AF, Gooszen HG | title = Timing and impact of infections in acute pancreatitis | journal = The British Journal of Surgery | volume = 96 | issue = 3 | pages = 267–73 | date = March 2009 | pmid = 19125434 | doi = 10.1002/bjs.6447 | s2cid = 2226746 | doi-access = free }}</ref> These infections are associated with an increase in mortality.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu BU, Johannes RS, Kurtz S, Banks PA | title = The impact of hospital-acquired infection on outcome in acute pancreatitis | journal = Gastroenterology | volume = 135 | issue = 3 | pages = 816–20 | date = September 2008 | pmid = 18616944 | pmc = 2570951 | doi = 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.053 }}</ref> Fluid collections around the pancreas or areas within the pancreas that experience tissue death (necrosis) may also become secondarily infected requiring the use of antibiotics.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> When an infection is suspected, antibiotics should be started while the source of the infection is being determined. However, if cultures are negative and no source of infection is identified, antibiotics should be discontinued. | ||
| Preventative antibiotics are not recommended in people with acute pancreatitis, regardless of the type (interstitial or necrotizing) or disease severity (mild, moderately severe, or severe)<ref name="ACG_Gudielines_2013"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jafri NS, Mahid SS, Idstein SR, Hornung CA, Galandiuk S | title = Antibiotic prophylaxis is not protective in severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = American Journal of Surgery | volume = 197 | issue = 6 | pages = 806–13 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19217608 | doi = 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.08.016 }}</ref> | Preventative antibiotics are not recommended in people with acute pancreatitis, regardless of the type (interstitial or necrotizing) or disease severity (mild, moderately severe, or severe)<ref name="ACG_Gudielines_2013"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jafri NS, Mahid SS, Idstein SR, Hornung CA, Galandiuk S | title = Antibiotic prophylaxis is not protective in severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = American Journal of Surgery | volume = 197 | issue = 6 | pages = 806–13 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19217608 | doi = 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.08.016 }}</ref> | ||
| ===Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography=== | ===Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography=== | ||
| In 30% of those with acute pancreatitis, no cause is identified. ] (ERCP) with empirical ] has an equal chance of causing complications and treating the underlying cause, therefore, is not recommended for treating acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Canlas KR, Branch MS | title = Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in acute pancreatitis | journal = World Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 13 | issue = 47 | pages = 6314–20 | date = December 2007 | pmid = 18081218 | pmc = 4205448 | doi = 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6314 }}</ref> If a gallstone is detected, ERCP, performed within 24 to 72 hours of presentation with successful removal of the stone, is known to reduce morbidity and mortality.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Intensive Care Manual | vauthors = Apostolakos MJ, Papadakos PJ |year=2001 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional |isbn=978-0-07-006696-0}}</ref> The indications for early ERCP are: | In 30% of those with acute pancreatitis, no cause is identified. ] (ERCP) with empirical ] has an equal chance of causing complications and treating the underlying cause, therefore, is not recommended for treating acute pancreatitis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Canlas KR, Branch MS | title = Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in acute pancreatitis | journal = World Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 13 | issue = 47 | pages = 6314–20 | date = December 2007 | pmid = 18081218 | pmc = 4205448 | doi = 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6314 | doi-access = free }}</ref> If a gallstone is detected, ERCP, performed within 24 to 72 hours of presentation with successful removal of the stone, is known to reduce morbidity and mortality.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Intensive Care Manual | vauthors = Apostolakos MJ, Papadakos PJ |year=2001 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional |isbn=978-0-07-006696-0}}</ref> The indications for early ERCP are: | ||
| * Clinical deterioration or lack of improvement after 24 hours | * Clinical deterioration or lack of improvement after 24 hours | ||
| * Detection of common bile duct stones or dilated intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts on abdominal CT | * Detection of common bile duct stones or dilated intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts on abdominal CT | ||
| Line 260: | Line 175: | ||
| === Surgery === | === Surgery === | ||
| In those with mild acute pancreatitis due to gallstones, ] (removal of the gallbladder) is recommended in the hospital and is associated with a reduced risk of pancreatitis recurrence.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> In those with gallstone pancreatitis who have severe disease, including the presence of peripancreatic fluid collections, cholecystectomy should be delayed as the fluid collections around the pancreas make surgery technically difficult. The peri-pancreatic fluids also carry a risk of becoming secondarily infected with surgery.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Surgery is indicated for (i) infected pancreatic necrosis and (ii) diagnostic uncertainty and (iii) complications. The most common cause of death in acute pancreatitis is secondary infection. Infection is diagnosed based on 2 criteria | |||
| *Gas bubbles on CT scan (present in 20 to 50% of infected necrosis) | |||
| *Positive bacterial culture on FNA (fine needle aspiration, usually CT or US guided) of the pancreas. | |||
| Surgery is indicated for (i) infected pancreatic necrosis and (ii) diagnostic uncertainty and (iii) complications.{{Citation needed|date=October 2024}} The most common cause of death in acute pancreatitis is secondary infection. Infection is diagnosed based on 2 criteria{{Citation needed|date=October 2024}} | |||
| Surgical options for infected necrosis include: | |||
| * Gas bubbles on CT scan (present in 20 to 50% of infected necrosis) | |||
| *Minimally invasive management – necrosectomy through small incision in skin (left flank) or abdomen | |||
| * Positive bacterial culture on FNA (fine needle aspiration, usually CT or US guided) of the pancreas. | |||
| *Conventional management – necrosectomy with simple drainage | |||
| *Closed management – necrosectomy with closed continuous postoperative lavage | |||
| Surgical options for infected necrosis include:{{Citation needed|date=October 2024}} | |||
| *Open management – necrosectomy with planned staged reoperations at definite intervals (up to 20+ reoperations in some cases) | |||
| * Minimally invasive management – necrosectomy through small incision in skin (left flank) or abdomen | |||
| * Conventional management – necrosectomy with simple drainage | |||
| * Closed management – necrosectomy with closed continuous postoperative lavage | |||
| * Open management – necrosectomy with planned staged reoperations at definite intervals (up to 20+ reoperations in some cases) | |||
| === Other measures === | === Other measures === | ||
| *Pancreatic enzyme inhibitors are proven not to work.<ref>{{cite book |title=Current Obstetric & Gynecologic Diagnosis & Treatment | vauthors = DeCherney AH, Lauren N |year=2003 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional |isbn=978-0-8385-1401-6}}</ref> | * Pancreatic enzyme inhibitors are proven not to work.<ref>{{cite book |title=Current Obstetric & Gynecologic Diagnosis & Treatment | vauthors = DeCherney AH, Lauren N |year=2003 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Professional |isbn=978-0-8385-1401-6}}</ref> | ||
| *The use of ] has been shown not to improve outcomes.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Trauma Manual: Trauma and Acute Care Surgery | vauthors = Peitzman AB, Schwab CW, Yealy DM, Fabian TC |year=2007 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |isbn=978-0-7817-6275-5}}</ref> | * The use of ] has been shown not to improve outcomes.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Trauma Manual: Trauma and Acute Care Surgery | vauthors = Peitzman AB, Schwab CW, Yealy DM, Fabian TC |year=2007 |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |isbn=978-0-7817-6275-5}}</ref> | ||
| == Classification by severity: prognostic scoring systems == | == Classification by severity: prognostic scoring systems == | ||
| Acute pancreatitis patients recover in majority of cases. Some may develop abscess, pseudocyst or duodenal obstruction. |
Acute pancreatitis patients recover in majority of cases. Some may develop abscess, pseudocyst or duodenal obstruction. About 20% of the acute pancreatitis are severe with a mortality of about 20%.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | ||
| Acute pancreatitis can be further divided into mild and severe pancreatitis. Several clinical scoring tools have been developed to determine prognostic information and may guide certain areas of clinical management, such as need for ICU admission.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| Two such scoring systems are the ] and ] (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation) indices. Most,<ref name="pmi2568529">{{cite journal | vauthors = Larvin M, McMahon MJ | title = APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis | journal = Lancet | volume = 2 | issue = 8656 | pages = 201–5 | date = July 1989 | pmid = 2568529 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(89)90381-4 | s2cid = 26047869 }}</ref><ref name="pmid16698595">{{cite journal | vauthors = Yeung YP, Lam BY, Yip AW | title = APACHE system is better than Ranson system in the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis | journal = Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 294–9 | date = May 2006 | pmid = 16698595 | url = http://www.hbpdint.com/text.asp?id=837 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20061026152338/http://hbpdint.com/text.asp?id=837 | archive-date = 2006-10-26 }}</ref> but not all<ref name="pmid12409825">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chatzicostas C, Roussomoustakaki M, Vlachonikolis IG, Notas G, Mouzas I, Samonakis D, Kouroumalis EA | title = Comparison of Ranson, APACHE II and APACHE III scoring systems in acute pancreatitis | journal = Pancreas | volume = 25 | issue = 4 | pages = 331–5 | date = November 2002 | pmid = 12409825 | doi = 10.1097/00006676-200211000-00002 | s2cid = 27166241 }}</ref> studies report that the Apache score may be more accurate. In the negative study of the APACHE-II, the APACHE-II 24-hour score was used rather than the 48-hour score.<ref name="pmid12409825" /> | |||
| Mostly the Ranson Criteria are used to determine severity of acute pancreatitis. In severe pancreatitis serious amounts of necrosis determine the further clinical outcome. About 20% of the acute pancreatitis are severe with a mortality of about 20%. This is an important classification as severe pancreatitis will need intensive care therapy whereas mild pancreatitis can be treated on the common ward. | |||
| Some experts recommend using the APACHE II score as well as a serum hematocrit level early during the admission as prognostic indicators.<ref name="pmid17032204" /> | |||
| Necrosis will be followed by a ] (SIRS) and will determine the immediate clinical course. The further clinical course is then determined by bacterial infection. SIRS is the cause of bacterial (Gram negative) translocation from the patients colon. | |||
| There are several ways to help distinguish between these two forms. One is the above-mentioned Ranson Score. | |||
| In predicting the prognosis, there are several scoring indices that have been used as predictors of survival. Two such scoring systems are the ] and ] (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation) indices. Most,<ref name="pmi2568529">{{cite journal | vauthors = Larvin M, McMahon MJ | title = APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis | journal = Lancet | volume = 2 | issue = 8656 | pages = 201–5 | date = July 1989 | pmid = 2568529 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(89)90381-4 | s2cid = 26047869 }}</ref><ref name="pmid16698595">{{cite journal | vauthors = Yeung YP, Lam BY, Yip AW | title = APACHE system is better than Ranson system in the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis | journal = Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 294–9 | date = May 2006 | pmid = 16698595 | url = http://www.hbpdint.com/text.asp?id=837 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20061026152338/http://hbpdint.com/text.asp?id=837 | archive-date = 2006-10-26 }}</ref> but not all<ref name="pmid12409825">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chatzicostas C, Roussomoustakaki M, Vlachonikolis IG, Notas G, Mouzas I, Samonakis D, Kouroumalis EA | title = Comparison of Ranson, APACHE II and APACHE III scoring systems in acute pancreatitis | journal = Pancreas | volume = 25 | issue = 4 | pages = 331–5 | date = November 2002 | pmid = 12409825 | doi = 10.1097/00006676-200211000-00002 | s2cid = 27166241 }} (comment=this study used an Apache cutoff of >=10)</ref> studies report that the Apache score may be more accurate. In the negative study of the APACHE-II,<ref name="pmid12409825" /> the APACHE-II 24-hour score was used rather than the 48-hour score. In addition, all patients in the study received an ultrasound twice which may have influenced allocation of co-interventions. Regardless, only the APACHE-II can be fully calculated upon admission. As the APACHE-II is more cumbersome to calculate, presumably patients whose only laboratory abnormality is an elevated lipase or amylase do not need assessment with the APACHE-II; however, this approach is not studied. The APACHE-II score can be calculated at . | |||
| Practice guidelines state: | |||
| :2006: "The two tests that are most helpful at admission in distinguishing mild from severe acute pancreatitis are APACHE-II score and serum hematocrit. It is recommended that APACHE-II scores be generated during the first 3 days of hospitalization and thereafter as needed to help in this distinction. It is also recommended that serum hematocrit be obtained at admission, 12 h after admission, and 24 h after admission to help gauge adequacy of fluid resuscitation."<ref name="pmid17032204" /> | |||
| :2005: "Immediate assessment should include clinical evaluation, particularly of any cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal compromise, body mass index, chest x ray, and APACHE II score"<ref name="pmid15831893"/> | |||
| ===Ranson score=== | ===Ranson score=== | ||
| Line 295: | Line 203: | ||
| ====At admission==== | ====At admission==== | ||
| * age in years > 55 years | * age in years > 55 years | ||
| * white blood cell count > 16000 cells/mm3 | * white blood cell count > 16000 cells/mm3 | ||
| Line 303: | Line 210: | ||
| ====At 48 hours==== | ====At 48 hours==== | ||
| * Calcium (serum calcium < 2.0 mmol/L (< 8.0 mg/dL) | * Calcium (serum calcium < 2.0 mmol/L (< 8.0 mg/dL) | ||
| * Hematocrit fall >10% | * Hematocrit fall >10% | ||
| Line 329: | Line 235: | ||
| Score 7 to 8 : 100% mortality | Score 7 to 8 : 100% mortality | ||
| === |
===APACHE II score=== | ||
| {{Main|APACHE II}} | {{Main|APACHE II}} | ||
| "Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation" (]) score > 8 points predicts 11% to 18% mortality<ref name="pmid17032204" /> | "Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation" (]) score > 8 points predicts 11% to 18% mortality<ref name="pmid17032204" /> | ||
| * Hemorrhagic peritoneal fluid | |||
| * ] | |||
| *Hemorrhagic peritoneal fluid | |||
| * Indicators of organ failure | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] (SBP <90 mmHG) or ] > 130 beat/min | |||
| *Indicators of organ failure | |||
| * PO<sub>2</sub> <60 mmHg | |||
| *] (SBP <90 mmHG) or ] > 130 beat/min | |||
| * ] (<50 mL/h) or increasing ] and ] | |||
| *PO<sub>2</sub> <60 mmHg | |||
| * Serum calcium < 1.90 mmol/L (<8.0 mg/dL) or serum albumin <33 g/L (<3.2.g/dL)> | |||
| *] (<50 mL/h) or increasing ] and ] | |||
| *Serum calcium < 1.90 mmol/L (<8.0 mg/dL) or serum albumin <33 g/L (<3.2.g/dL)> | |||
| ===Balthazar score=== | ===Balthazar score=== | ||
| Line 392: | Line 297: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| CTSI's staging of acute pancreatitis severity has been shown by a number of studies to provide more accurate assessment than APACHE II, Ranson, and ] (CRP) level.<ref name="pmid16944038">{{cite journal | vauthors = Knoepfli AS, Kinkel K, Berney T, Morel P, Becker CD, Poletti PA | title = Prospective study of 310 patients: can early CT predict the severity of acute pancreatitis? | journal = Abdominal Imaging | volume = 32 | issue = 1 | pages = 111–5 | year = 2007 | pmid = 16944038 | doi = 10.1007/s00261-006-9034-y | s2cid = 20809378 | url = http://doc.rero.ch/record/311512/files/261_2006_Article_9034.pdf }}</ref><ref name="pmid16273623">{{cite journal | vauthors = Leung TK, Lee CM, Lin SY, Chen HC, Wang HJ, Shen LK, Chen YY | title = Balthazar computed tomography severity index is superior to Ranson criteria and APACHE II scoring system in predicting acute pancreatitis outcome | journal = World Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 11 | issue = 38 | pages = 6049–52 | date = October 2005 | pmid = 16273623 | pmc = 4436733 | doi = 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.6049 }}</ref><ref name="pmid16183486">{{cite journal | vauthors = Vriens PW, van de Linde P, Slotema ET, Warmerdam PE, Breslau PJ | title = Computed tomography severity index is an early prognostic tool for acute pancreatitis | journal = Journal of the American College of Surgeons | volume = 201 | issue = 4 | pages = 497–502 | date = October 2005 | pmid = 16183486 | doi = 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.06.269 }}</ref> However, a few studies indicate that CTSI is not significantly associated with the prognosis of hospitalization in patients with pancreatic necrosis, nor is it an accurate predictor of AP severity.<ref name="pmid17895844">{{cite journal | vauthors = Triantopoulou C, Lytras D, Maniatis P, Chrysovergis D, Manes K, Siafas I, Papailiou J, Dervenis C | title = Computed tomography versus Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis: a prospective, comparative study with statistical evaluation | journal = Pancreas | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 238–42 | date = October 2007 | pmid = 17895844 | doi = 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3180619662 | s2cid = 24245362 }}</ref><ref name="pmid15380848">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mortelé KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Wiesner W, Cantisani V, Ernst MD, Kalantari BN, Ros PR | title = Peripancreatic vascular abnormalities complicating acute pancreatitis: contrast-enhanced helical CT findings | journal = European Journal of Radiology | volume = 52 | issue = 1 | pages = 67–72 | date = October 2004 | pmid = 15380848 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.10.006 }}</ref> | CTSI's staging of acute pancreatitis severity has been shown by a number of studies to provide more accurate assessment than APACHE II, Ranson, and ] (CRP) level.<ref name="pmid16944038">{{cite journal | vauthors = Knoepfli AS, Kinkel K, Berney T, Morel P, Becker CD, Poletti PA | title = Prospective study of 310 patients: can early CT predict the severity of acute pancreatitis? | journal = Abdominal Imaging | volume = 32 | issue = 1 | pages = 111–5 | year = 2007 | pmid = 16944038 | doi = 10.1007/s00261-006-9034-y | s2cid = 20809378 | url = http://doc.rero.ch/record/311512/files/261_2006_Article_9034.pdf }}</ref><ref name="pmid16273623">{{cite journal | vauthors = Leung TK, Lee CM, Lin SY, Chen HC, Wang HJ, Shen LK, Chen YY | title = Balthazar computed tomography severity index is superior to Ranson criteria and APACHE II scoring system in predicting acute pancreatitis outcome | journal = World Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 11 | issue = 38 | pages = 6049–52 | date = October 2005 | pmid = 16273623 | pmc = 4436733 | doi = 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.6049 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid16183486">{{cite journal | vauthors = Vriens PW, van de Linde P, Slotema ET, Warmerdam PE, Breslau PJ | title = Computed tomography severity index is an early prognostic tool for acute pancreatitis | journal = Journal of the American College of Surgeons | volume = 201 | issue = 4 | pages = 497–502 | date = October 2005 | pmid = 16183486 | doi = 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.06.269 }}</ref> However, a few studies indicate that CTSI is not significantly associated with the prognosis of hospitalization in patients with pancreatic necrosis, nor is it an accurate predictor of AP severity.<ref name="pmid17895844">{{cite journal | vauthors = Triantopoulou C, Lytras D, Maniatis P, Chrysovergis D, Manes K, Siafas I, Papailiou J, Dervenis C | title = Computed tomography versus Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis: a prospective, comparative study with statistical evaluation | journal = Pancreas | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 238–42 | date = October 2007 | pmid = 17895844 | doi = 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3180619662 | s2cid = 24245362 }}</ref><ref name="pmid15380848">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mortelé KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Wiesner W, Cantisani V, Ernst MD, Kalantari BN, Ros PR | title = Peripancreatic vascular abnormalities complicating acute pancreatitis: contrast-enhanced helical CT findings | journal = European Journal of Radiology | volume = 52 | issue = 1 | pages = 67–72 | date = October 2004 | pmid = 15380848 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.10.006 }}</ref> | ||
| === Glasgow score === | === Glasgow score === | ||
| The Glasgow score is valid for both gallstone and alcohol induced pancreatitis, whereas the Ranson score is only for alcohol induced pancreatitis{{Citation needed|reason=Can't find this established anywhere in the literature, there are two Ranson scoring systems depending on gallstone vs non-gallstone|date=November 2016}}. If a patient scores 3 or more it indicates severe pancreatitis and the patient should be considered for transfer to ITU. It is scored through the mnemonic, PANCREAS: | The Glasgow score is valid for both gallstone and alcohol induced pancreatitis, whereas the Ranson score is only for alcohol induced pancreatitis{{Citation needed|reason=Can't find this established anywhere in the literature, there are two Ranson scoring systems depending on gallstone vs non-gallstone|date=November 2016}}. If a patient scores 3 or more it indicates severe pancreatitis and the patient should be considered for transfer to ITU. It is scored through the mnemonic, PANCREAS: | ||
| * P – PaO2 <8kPa | |||
| * |
* A – Age >55-years-old | ||
| * |
* N – Neutrophilia: WCC >15x10(9)/L | ||
| * C – Calcium <2 mmol/L | |||
| *N – Neutrophilia: WCC >15x10(9)/L | |||
| * |
* R – Renal function: Urea >16 mmol/L | ||
| * |
* E – Enzymes: LDH >600iu/L; AST >200iu/L | ||
| * |
* A – Albumin <32g/L (serum) | ||
| * S – Sugar: blood glucose >10 mmol/L | |||
| *A – Albumin <32g/L (serum) | |||
| *S – Sugar: blood glucose >10 mmol/L | |||
| ===BISAP score=== | ===BISAP score=== | ||
| Predicts mortality risk in pancreatitis with fewer variables than Ranson's criteria. Data should be taken from the first 24 hours of the patient's evaluation. | Predicts mortality risk in pancreatitis with fewer variables than Ranson's criteria. Data should be taken from the first 24 hours of the patient's evaluation. | ||
| * BUN >25 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L) | |||
| * Abnormal mental status with a Glasgow coma score <15 | |||
| *BUN >25 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L) | |||
| * Evidence of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome) | |||
| *Abnormal mental status with a Glasgow coma score <15 | |||
| * Patient age >60 years old | |||
| *Evidence of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome) | |||
| * Imaging study reveals pleural effusion | |||
| *Patient age >60 years old | |||
| *Imaging study reveals pleural effusion | |||
| Patients with a score of zero had a mortality of less than one percent, whereas patients with a score of five had a mortality rate of 22 percent. In the validation cohort, the BISAP score had similar test performance characteristics for predicting mortality as the APACHE II score.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Papachristou GI, Muddana V, Yadav D, O'Connell M, Sanders MK, Slivka A, Whitcomb DC | title = Comparison of BISAP, Ranson's, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 105 | issue = 2 | pages = 435–41; quiz 442 | date = February 2010 | pmid = 19861954 | doi = 10.1038/ajg.2009.622 | s2cid = 41655611 }}</ref> As is a problem with many of the other scoring systems, the BISAP has not been validated for predicting outcomes such as length of hospital stay, need for ICU care, or need for intervention. | Patients with a score of zero had a mortality of less than one percent, whereas patients with a score of five had a mortality rate of 22 percent. In the validation cohort, the BISAP score had similar test performance characteristics for predicting mortality as the APACHE II score.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Papachristou GI, Muddana V, Yadav D, O'Connell M, Sanders MK, Slivka A, Whitcomb DC | title = Comparison of BISAP, Ranson's, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis | journal = The American Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 105 | issue = 2 | pages = 435–41; quiz 442 | date = February 2010 | pmid = 19861954 | doi = 10.1038/ajg.2009.622 | s2cid = 41655611 }}</ref> As is a problem with many of the other scoring systems, the BISAP has not been validated for predicting outcomes such as length of hospital stay, need for ICU care, or need for intervention. | ||
| == Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
| The worldwide incidence of acute pancreatitis has increasing from 1961 to 2016 with an average annual percentage increase of 3%, the increased incidence was seen in North America and Europe.<ref name="Ianuzzi 2022">{{cite journal |last1=Iannuzzi |first1=Jordan P. |last2=King |first2=James A. |last3=Leong |first3=Jessica Hope |last4=Quan |first4=Joshua |last5=Windsor |first5=Joseph W. |last6=Tanyingoh |first6=Divine |last7=Coward |first7=Stephanie |last8=Forbes |first8=Nauzer |last9=Heitman |first9=Steven J. |last10=Shaheen |first10=Abdel-Aziz |last11=Swain |first11=Mark |last12=Buie |first12=Michael |last13=Underwood |first13=Fox E. |last14=Kaplan |first14=Gilaad G. |title=Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |journal=Gastroenterology |date=January 2022 |volume=162 |issue=1 |pages=122–134 |doi=10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043|pmid=34571026 }}</ref> The incidence of acute pancreatitis in the United States is 110-140 cases per 100,000 people.<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| In the United States, the annual incidence is 18 cases of acute pancreatitis per 100,000 population, and it accounts for 220,000 hospitalizations in the US.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Whitcomb DC | title = Clinical practice. Acute pancreatitis | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 354 | issue = 20 | pages = 2142–50 | date = May 2006 | pmid = 16707751 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMcp054958 }}</ref> In a European cross-sectional study, incidence of acute pancreatitis increased from 12.4 to 15.9 per 100,000 annually from 1985 to 1995; however, mortality remained stable as a result of better outcomes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Eland IA, Sturkenboom MJ, Wilson JH, Stricker BH | title = Incidence and mortality of acute pancreatitis between 1985 and 1995 | journal = Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology | volume = 35 | issue = 10 | pages = 1110–6 | date = October 2000 | pmid = 11099067 | doi = 10.1080/003655200451261 | s2cid = 218906363 }}</ref> Another study showed a lower incidence of 9.8 per 100,000 but a similar worsening trend (increasing from 4.9 in 1963–74) over time.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Goldacre MJ, Roberts SE | title = Hospital admission for acute pancreatitis in an English population, 1963–98: database study of incidence and mortality | journal = BMJ | volume = 328 | issue = 7454 | pages = 1466–9 | date = June 2004 | pmid = 15205290 | pmc = 428514 | doi = 10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1466 }}</ref> | |||
| In the United States the most common causes include gallstones, which are responsible for 21-33% of cases, followed by alcohol (16-27%) and elevated triglycerides (2-5%).<ref name="Mederos 2021" /> | |||
| In Western countries, the most common cause is alcohol, accounting for 65 percent of acute pancreatitis cases in the US, 20 percent of cases in Sweden, and 5 percent of those in the United Kingdom.{{citation needed|date=January 2016}} In Eastern countries, ]s are the most common cause of acute pancreatitis. The causes of acute pancreatitis also varies across age groups, with trauma and systemic disease (such as infection) being more common in children. ] is a more common cause in adolescents and young adults than in other age groups. | |||
| == |
==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 431: | Line 334: | ||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| * Banks et al. Modified Marshall scoring system | |||
| * image. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Parikh |first1=RP |last2=Upadhyay |first2=KJ |title=Cullen's sign for acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis |journal=Indian J Med Res |date= Jul 4, 2013 |volume=137 |issue=6 |page=1210 |pmid=23852306 |pmc=3734730 |url=http://www.ijmr.org.in/text.asp?2013/137/6/1210/114397 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171223043557/http://www.ijmr.org.in/article.asp?issn=0971-5916;year=2013;volume=137;issue=6;spage=1210;epage=1210;aulast=Parikh |archive-date= Dec 23, 2017 }} | |||
| {{Gastroenterology}} | |||
| {{Medical resources | {{Medical resources | ||
| | DiseasesDB = 9539 |
| DiseasesDB = 9539 | ||
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|K|85||k|80}} |
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|K|85||k|80}} | ||
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|577.0}} |
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|577.0}} | ||
| | ICDO = |
| ICDO = | ||
| | OMIM = |
| OMIM = | ||
| | MedlinePlus = 000287 |
| MedlinePlus = 000287 | ||
| | eMedicineSubj = med |
| eMedicineSubj = med | ||
| | eMedicineTopic = 1720 |
| eMedicineTopic = 1720 | ||
| | eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|radio|521}} |
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|radio|521}} | ||
| | MeshID = | | MeshID = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| * Banks et al. Modified Marshall scoring system | |||
| * image. | |||
| * Parikh RP, Upadhyay KJ. Cullen's sign for acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Indian J Med Res 2013 ;137:1210 http://www.ijmr.org.in/text.asp?2013/137/6/1210/114397 | |||
| {{Gastroenterology}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Pancreatitis}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Acute Pancreatitis}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:35, 7 January 2025
Medical condition| Acute pancreatitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Acute pancreatic necrosis |
 | |
| Still from 3D medical animation of acute pancreatitis | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology, general surgery |
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes include a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct or the pancreatic duct, heavy alcohol use, systemic disease, trauma, elevated calcium levels, hypertriglyceridemia (with triglycerides usually being very elevated, over 1000 mg/dL), certain medications, hereditary causes and, in children, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event, it may be recurrent, or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis and/or pancreatic failure (the term pancreatic dysfunction includes cases of acute or chronic pancreatitis where the pancreas is measurably damaged, even if it has not failed).
In all cases of acute pancreatitis, early intravenous fluid hydration and early enteral (nutrition delivered to the gut, either by mouth or via a feeding tube) feeding are associated with lower mortality and complications. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures such as hospitalization with intravenous fluid infusion, pain control, and early enteral feeding. If a person is not able to tolerate feeding by mouth, feeding via nasogastric or nasojejunal tubes are frequently used which provide nutrition directly to the stomach or intestines respectively. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit. Severe pancreatitis, which by definition includes organ damage other than the pancreas, is associated with a mortality rate of 20%. The condition is characterized by the pancreas secreting active enzymes such as trypsin, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase, instead of their inactive forms, leading to auto-digestion of the pancreas. Calcium helps to convert trypsinogen to the active trypsin, thus elevated calcium (of any cause) is a potential cause of pancreatitis. Damage to the pancreatic ducts can occur as a result of this. Long term complications include type 3c diabetes (pancreatogenic diabetes), in which the pancreas is unable to secrete enough insulin due to structural damage. 35% develop exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in which the pancreas is unable to secrete digestive enzymes due to structural damage, leading to malabsorption.
Signs and symptoms
Common
Common symptoms of acute pancreatitis include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and low to moderate grade fever. The abdominal pain is the most common symptom and it is usually described as being in the left upper quadrant, epigastric area or around the umbilicus, with radiation throughout the abdomen, or to the chest or back. The abdominal pain initially may worsen with eating or drinking but may become constant as the disease progresses. Less common symptoms include hiccups, abdominal bloating and indigestion. Although these are common symptoms, frequently they are not all present; and epigastric pain may be the only symptom.
Grey-Turner's sign (hemorrhagic discoloration of the flanks) or Cullen's sign (hemorrhagic discoloration of the umbilicus) are associated with severe disease. However both signs are rare (occurring in less than 1% of cases of acute pancreatitis) and are not specific nor sensitive for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Pleural effusions (fluid in the lung cavity) may occur in up to 34% of people with acute pancreatitis and are associated with a poor prognosis. The Mayo-Robson's sign (pain while pressing at the top of the angle lateral to the erector spinae muscles and below the left 12th rib (left costovertebral angle (CVA)) is also associated with acute pancreatitis.
Complications
Complications of acute pancreatitis may occur. Necrotic pancreatitis occurs when inflammation of the pancreas progresses to cell death. Acute fluid collections may form adjacent to the pancreas or necrotic collections (discrete areas of dead tissue) may also form adjacent to or within the pancreas. These may progress to pancreatic pseudocysts and walled off areas of dead tissue which may persist for longer than 4 weeks. Both can become secondarily infected. Other complications include gastric outlet obstruction splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, hemorrhage from erosions into splenic artery and vein, blood clot of the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein and portal veins, duodenal obstruction, common bile duct obstruction, progression to chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic ascites, or pleural effusion.
Systemic complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), hypocalcemia (from fat saponification), hyperglycemia and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (from pancreatic insulin-producing beta cell damage), and malabsorption due to exocrine failure.
Tobacco use, recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic tissue death, alcoholic pancreatitis are all risk factors for developing chronic pancreatitis.
Causes
Most common
- Biliary pancreatitis due to gallstones or constriction of ampulla of Vater in 40% of cases
- Alcohol in 30% of cases
- Idiopathic in 15–25% of cases
- Metabolic disorders: hereditary pancreatitis, hypercalcemia, elevated triglycerides, malnutrition
- May occur after instrumentation of the pancreatic duct or its opening to the duodenum (ampula of Vater) in procedures such as an endoscopic ultrasound or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). The risk after EUS is less than 1% and the risk after ERCP is 5-10%.
- Abdominal trauma
- Penetrating ulcers
- Carcinoma of the head of pancreas, and other cancer
- Drugs: acetaminophen with or without codeine, amiodarone, azathioprine, carbamazepine, cimetidine, cisplatin, clomiphene, enalapril, estrogen containing products or hormones, furosemide, isoniazid, metronidazole, methyldopa, pravastatin, valproic acid
- Infections: mumps, viral hepatitis, coxsackie B virus, cytomegalovirus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Ascaris
- Structural abnormalities: pancreas divisum, pancreatic masses or cysts that block the ducts.
- Radiotherapy
- Autoimmune pancreatitis
- Severe hypertriglyceridemia
Less common
- Scorpion venom
- Chinese liver fluke
- Ischemia from bypass surgery
- Heart valve surgery
- Fat necrosis
- Pregnancy
- Infections other than mumps, including varicella zoster
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Cystic fibrosis
- Anorexia or bulimia
Pathology
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
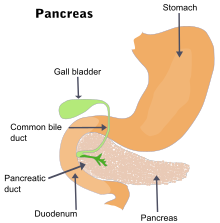
Pathogenesis
Acute pancreatitis occurs when there is abnormal activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas. This occurs through inappropriate activation of inactive enzyme precursors called zymogens (or proenzymes) inside the pancreas, most notably trypsinogen. Normally, trypsinogen is converted to its active form (trypsin) in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum), where the enzyme assists in the digestion of proteins. During an episode of acute pancreatitis, trypsinogen comes into contact with lysosomal enzymes (specifically cathepsin), which activate trypsinogen to trypsin. The active form trypsin then leads to further activation of other molecules of trypsinogen. The activation of these digestive enzymes lead to inflammation, edema, vascular injury, and even cellular death. The death of pancreatic cells occurs via two main mechanisms: apoptosis, which is physiologically controlled, and necrosis, which is less organized and more damaging. The balance between these two mechanisms of cellular death is mediated by caspases which regulate apoptosis and have important anti-necrosis functions during pancreatitis: preventing trypsinogen activation, preventing ATP depletion through inhibiting polyADP-ribose polymerase, and by inhibiting the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs). If, however, the caspases are depleted due to either chronic ethanol exposure or through a severe insult then necrosis can predominate.
Pathophysiology
The two types of acute pancreatitis are mild and severe, which are defined based on whether the predominant response to cell injury is inflammation (mild) or necrosis (severe). In mild pancreatitis, there is inflammation and edema of the pancreas. In severe pancreatitis, there is necrosis of the pancreas, and nearby organs may become injured.
As part of the initial injury there is an extensive inflammatory response due to pancreatic cells synthesizing and secreting inflammatory mediators: primarily TNF-alpha and IL-1. A hallmark of acute pancreatitis is a manifestation of the inflammatory response, namely the recruitment of neutrophils to the pancreas. The inflammatory response leads to the secondary manifestations of pancreatitis: hypovolemia from capillary permeability, acute respiratory distress syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulations, renal failure, cardiovascular failure, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Histopathology
The acute pancreatitis (acute hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis) is characterized by acute inflammation and necrosis of pancreas parenchyma, focal enzymic necrosis of pancreatic fat and vessel necrosis (hemorrhage). These are produced by intrapancreatic activation of pancreatic enzymes. Lipase activation produces the necrosis of fat tissue in pancreatic interstitium and peripancreatic spaces as well as vessel damage. Necrotic fat cells appear as shadows, contours of cells, lacking the nucleus, pink, finely granular cytoplasm. It is possible to find calcium precipitates (hematoxylinophilic). Digestion of vascular walls results in thrombosis and hemorrhage. Inflammatory infiltrate is rich in neutrophils. Due to the pancreas lacking a capsule, the inflammation and necrosis can extend to include fascial layers in the immediate vicinity of the pancreas.
Diagnosis
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed using clinical history and physical examination findings supporting the diagnosis with imaging and pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase). The Revised Atlanta Classification requires two out of three of the following findings for the diagnosis: abdominal pain consistent with pancreatitis, elevated amylase or lipase levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal, and imaging consistent with acute pancreatitis. Additional labs may be used to identify organ failure for prognostic purposes or to guide fluid resuscitation rate. If the lipase level is about 2.5 to 3 times that of amylase, it is an indication of pancreatitis due to alcohol. Serum lipase is more sensitive and specific than serum amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis, and is the preferred test in the diagnosis.
Most, but not all individual studies support favor the diagnostic utility of lipase. In one large study, there were no patients with pancreatitis who had an elevated amylase with a normal lipase. Another study found that the amylase could add diagnostic value to the lipase, but only if the results of the two tests were combined with a discriminant function equation.
Reduced lipase clearance due to kidney disease, gastrointestinal or hepatobiliary cancers, pancreatic enzyme hypersecretion, critical illness including due to neurosurgical causes have been shown to increase serum lipase and may complicate the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Perforated peptic ulcer
- Biliary colic
- Acute cholecystitis
- Pneumonia
- Pleuritic pain
- Myocardial infarction
Computed tomography

Regarding the need for computed tomography, practice guidelines state:
CT is an important common initial assessment tool for acute pancreatitis. Imaging is indicated during the initial presentation if:
- the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis is uncertain
- there is abdominal distension and tenderness, fever >102 F (38,9 C), or leukocytosis
- there is a Ranson score > 3 or APACHE score > 8
- there is no improvement after 72 hours of conservative medical therapy
- there has been an acute change in status: fever, pain, or shock
CT is recommended as a delayed assessment tool in the following situations:
- acute change in status
- to determine therapeutic response after surgery or interventional radiologic procedure
- before discharge in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
Abdominal CT should not be performed before the first 12 hours of onset of symptoms as early CT (<12 hours) may result in equivocal or normal findings.
CT findings can be classified into the following categories for easy recall:
- Intrapancreatic – diffuse or segmental enlargement, edema, gas bubbles, pancreatic pseudocysts and phlegmons/abscesses (which present 4 to 6 wks after initial onset)
- Peripancreatic / extrapancreatic – irregular pancreatic outline, obliterated peripancreatic fat, retroperitoneal edema, fluid in the lessar sac, fluid in the left anterior pararenal space
- Locoregional – Gerota's fascia sign (thickening of inflamed Gerota's fascia, which becomes visible), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion (seen on basal cuts of the pleural cavity), adynamic ileus, etc.
The principal value of CT imaging to the treating clinician is the capacity to identify devitalized areas of the pancreas which have become necrotic due to ischaemia. Pancreatic necrosis can be reliably identified by intravenous contrast-enhanced CT imaging, and is of value if infection occurs and surgical or percutaneous debridement is indicated.
Magnetic resonance imaging
While computed tomography is considered the gold standard in diagnostic imaging for acute pancreatitis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become increasingly valuable as a tool for the visualization of the pancreas, particularly of pancreatic fluid collections and necrotized debris. Additional utility of MRI includes its indication for imaging of patients with an allergy to CT's contrast material, and an overall greater sensitivity to hemorrhage, vascular complications, pseudoaneurysms, and venous thrombosis.
Another advantage of MRI is its utilization of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) sequences. MRCP provides useful information regarding the etiology of acute pancreatitis, i.e., the presence of tiny biliary stones (choledocholithiasis or cholelithiasis) and duct anomalies. Clinical trials indicate that MRCP can be as effective a diagnostic tool for acute pancreatitis with biliary etiology as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, but with the benefits of being less invasive and causing fewer complications.
Ultrasound

Ultrasound is less preferred as a diagnostic test for acute pancreatitis, but it may be used in select cases. Abdominal ultrasonography may be obtained if there is concern of a gallstone blocking the pancreatic duct leading to pancreatitis.
Treatment
Early enteral (nutrition given directly to the gut, either by mouth or via feeding tube) nutrition and aggressive intravenous fluid hydration are indicated in all forms and severities of acute pancreatitis and are associated with lower mortality and complications.
Fluid replacement
The specific rate of intravenous fluid replacement in acute pancreatitis is not well established but some experts recommend an initial fluid infusion rate of 5-10 mL of IV fluids per kilogram of body weight per hour and adjusting the rate to meet physiologic parameters such as heart rate, mean arterial pressure, urine output and hematocrit.
Isotonic crystalloid solutions (such as lactated ringers) are preferred over normal saline for fluid resuscitation and are associated with a lower risk of developing systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
In the initial stages (within the first 12 to 24 hours) of acute pancreatitis, fluid replacement has been associated with a reduction in morbidity and mortality.
Pain control
Abdominal pain is often the predominant symptom in patients with acute pancreatitis and should be treated with analgesics.
Opioids are safe and effective at providing pain control in patients with acute pancreatitis. Adequate pain control requires the use of intravenous opiates, usually in the form of a patient-controlled analgesia pump. Hydromorphone or fentanyl (intravenous) may be used for pain relief in acute pancreatitis. Fentanyl is being increasingly used due to its better safety profile, especially in renal impairment. As with other opiates, fentanyl can depress respiratory function. It can be given both as a bolus as well as constant infusion. Meperidine has been historically favored over morphine because of the belief that morphine caused an increase in sphincter of Oddi pressure. However, no clinical studies suggest that morphine can aggravate or cause pancreatitis or cholecystitis. In addition, meperidine has a short half-life and repeated doses can lead to accumulation of the metabolite normeperidine, which causes neuromuscular side effects and, rarely, seizures.
Nutritional support
Acute pancreatitis is a catabolic state and with hemodynamic instability or fluid shifts or edema there may be reduced intravascular perfusion to the gut. This reduction in gut perfusion increases the risk of gut necrosis with bacterial translocation with the subsequent risk of sepsis or secondary infections. Enteral nutrition gives one needed caloric intake as well as enhances intestinal motility and blood flow to the gut, reducing these risks. Enteral nutrition (as compared to parenteral nutrition, in which nutrients are given via intravenous infusion) is associated with reduced mortality, reduced risk of multi-organ failure and systemic infection in those with acute pancreatitis. In patients with acute pancreatitis, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) recommends early oral nutrition, within 24 hours, rather than keeping the patient fastng (or nothing by mouth). And in those unable to feed orally, the AGA recommends enteral nutrition (via a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube) rather than parenteral nutrition.
Antibiotics
Up to 20 percent of people with acute pancreatitis develop an infection outside the pancreas such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, or urinary tract infections. These infections are associated with an increase in mortality. Fluid collections around the pancreas or areas within the pancreas that experience tissue death (necrosis) may also become secondarily infected requiring the use of antibiotics. When an infection is suspected, antibiotics should be started while the source of the infection is being determined. However, if cultures are negative and no source of infection is identified, antibiotics should be discontinued.
Preventative antibiotics are not recommended in people with acute pancreatitis, regardless of the type (interstitial or necrotizing) or disease severity (mild, moderately severe, or severe)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
In 30% of those with acute pancreatitis, no cause is identified. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with empirical biliary sphincterotomy has an equal chance of causing complications and treating the underlying cause, therefore, is not recommended for treating acute pancreatitis. If a gallstone is detected, ERCP, performed within 24 to 72 hours of presentation with successful removal of the stone, is known to reduce morbidity and mortality. The indications for early ERCP are:
- Clinical deterioration or lack of improvement after 24 hours
- Detection of common bile duct stones or dilated intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts on abdominal CT
The risks of ERCP are that it may worsen pancreatitis, it may introduce an infection to otherwise sterile pancreatitis, and bleeding.
Surgery
In those with mild acute pancreatitis due to gallstones, cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) is recommended in the hospital and is associated with a reduced risk of pancreatitis recurrence. In those with gallstone pancreatitis who have severe disease, including the presence of peripancreatic fluid collections, cholecystectomy should be delayed as the fluid collections around the pancreas make surgery technically difficult. The peri-pancreatic fluids also carry a risk of becoming secondarily infected with surgery.
Surgery is indicated for (i) infected pancreatic necrosis and (ii) diagnostic uncertainty and (iii) complications. The most common cause of death in acute pancreatitis is secondary infection. Infection is diagnosed based on 2 criteria
- Gas bubbles on CT scan (present in 20 to 50% of infected necrosis)
- Positive bacterial culture on FNA (fine needle aspiration, usually CT or US guided) of the pancreas.
Surgical options for infected necrosis include:
- Minimally invasive management – necrosectomy through small incision in skin (left flank) or abdomen
- Conventional management – necrosectomy with simple drainage
- Closed management – necrosectomy with closed continuous postoperative lavage
- Open management – necrosectomy with planned staged reoperations at definite intervals (up to 20+ reoperations in some cases)
Other measures
- Pancreatic enzyme inhibitors are proven not to work.
- The use of octreotide has been shown not to improve outcomes.
Classification by severity: prognostic scoring systems
Acute pancreatitis patients recover in majority of cases. Some may develop abscess, pseudocyst or duodenal obstruction. About 20% of the acute pancreatitis are severe with a mortality of about 20%. Acute pancreatitis can be further divided into mild and severe pancreatitis. Several clinical scoring tools have been developed to determine prognostic information and may guide certain areas of clinical management, such as need for ICU admission.
Two such scoring systems are the Ranson criteria and APACHE II (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation) indices. Most, but not all studies report that the Apache score may be more accurate. In the negative study of the APACHE-II, the APACHE-II 24-hour score was used rather than the 48-hour score. Some experts recommend using the APACHE II score as well as a serum hematocrit level early during the admission as prognostic indicators.
Ranson score
Main article: Ranson criteriaThe Ranson score is used to predict the severity of acute pancreatitis. They were introduced in 1974.
At admission
- age in years > 55 years
- white blood cell count > 16000 cells/mm3
- blood glucose > 11.1 mmol/L (> 200 mg/dL)
- serum AST > 250 IU/L
- serum LDH > 350 IU/L
At 48 hours
- Calcium (serum calcium < 2.0 mmol/L (< 8.0 mg/dL)
- Hematocrit fall >10%
- Oxygen (hypoxemia PO2 < 60 mmHg)
- BUN increased by 1.8 or more mmol/L (5 or more mg/dL) after IV fluid hydration
- Base deficit (negative base excess) > 4 mEq/L
- Sequestration of fluids > 6 L
The criteria for point assignment is that a certain breakpoint be met at any time during that 48 hour period, so that in some situations it can be calculated shortly after admission. It is applicable to both gallstone and alcoholic pancreatitis.
Alternatively, pancreatitis can be diagnosed by meeting any of the following:
Alternative Ranson score
Ranson's score of ≥ 8 Organ failure Substantial pancreatic necrosis (at least 30% glandular necrosis according to contrast-enhanced CT)
Interpretation If the score ≥ 3, severe pancreatitis likely. If the score < 3, severe pancreatitis is unlikely Or
Score 0 to 2 : 2% mortality Score 3 to 4 : 15% mortality Score 5 to 6 : 40% mortality Score 7 to 8 : 100% mortality
APACHE II score
Main article: APACHE II"Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation" (APACHE II) score > 8 points predicts 11% to 18% mortality
- Hemorrhagic peritoneal fluid
- Obesity
- Indicators of organ failure
- Hypotension (SBP <90 mmHG) or tachycardia > 130 beat/min
- PO2 <60 mmHg
- Oliguria (<50 mL/h) or increasing BUN and creatinine
- Serum calcium < 1.90 mmol/L (<8.0 mg/dL) or serum albumin <33 g/L (<3.2.g/dL)>
Balthazar score
Developed in the early 1990s by Emil J. Balthazar et al., the Computed Tomography Severity Index (CTSI) is a grading system used to determine the severity of acute pancreatitis. The numerical CTSI has a maximum of ten points, and is the sum of the Balthazar grade points and pancreatic necrosis grade points:
Balthazar grade
| Balthazar grade | Appearance on CT | CT grade points |
|---|---|---|
| Grade A | Normal CT | 0 points |
| Grade B | Focal or diffuse enlargement of the pancreas | 1 point |
| Grade C | Pancreatic gland abnormalities and peripancreatic inflammation | 2 points |
| Grade D | Fluid collection in a single location | 3 points |
| Grade E | Two or more fluid collections and / or gas bubbles in or adjacent to pancreas | 4 points |
Necrosis score
| Necrosis percentage | Points |
|---|---|
| No necrosis | 0 points |
| 0 to 30% necrosis | 2 points |
| 30 to 50% necrosis | 4 points |
| Over 50% necrosis | 6 points |
CTSI's staging of acute pancreatitis severity has been shown by a number of studies to provide more accurate assessment than APACHE II, Ranson, and C-reactive protein (CRP) level. However, a few studies indicate that CTSI is not significantly associated with the prognosis of hospitalization in patients with pancreatic necrosis, nor is it an accurate predictor of AP severity.
Glasgow score
The Glasgow score is valid for both gallstone and alcohol induced pancreatitis, whereas the Ranson score is only for alcohol induced pancreatitis. If a patient scores 3 or more it indicates severe pancreatitis and the patient should be considered for transfer to ITU. It is scored through the mnemonic, PANCREAS:
- P – PaO2 <8kPa
- A – Age >55-years-old
- N – Neutrophilia: WCC >15x10(9)/L
- C – Calcium <2 mmol/L
- R – Renal function: Urea >16 mmol/L
- E – Enzymes: LDH >600iu/L; AST >200iu/L
- A – Albumin <32g/L (serum)
- S – Sugar: blood glucose >10 mmol/L
BISAP score
Predicts mortality risk in pancreatitis with fewer variables than Ranson's criteria. Data should be taken from the first 24 hours of the patient's evaluation.
- BUN >25 mg/dL (8.9 mmol/L)
- Abnormal mental status with a Glasgow coma score <15
- Evidence of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome)
- Patient age >60 years old
- Imaging study reveals pleural effusion
Patients with a score of zero had a mortality of less than one percent, whereas patients with a score of five had a mortality rate of 22 percent. In the validation cohort, the BISAP score had similar test performance characteristics for predicting mortality as the APACHE II score. As is a problem with many of the other scoring systems, the BISAP has not been validated for predicting outcomes such as length of hospital stay, need for ICU care, or need for intervention.
Epidemiology
The worldwide incidence of acute pancreatitis has increasing from 1961 to 2016 with an average annual percentage increase of 3%, the increased incidence was seen in North America and Europe. The incidence of acute pancreatitis in the United States is 110-140 cases per 100,000 people.
In the United States the most common causes include gallstones, which are responsible for 21-33% of cases, followed by alcohol (16-27%) and elevated triglycerides (2-5%).
See also
References
- Sommermeyer L (December 1935). "Acute Pancreatitis". American Journal of Nursing. 35 (12): 1157–1161. doi:10.2307/3412015. JSTOR 3412015.
- ^ Mederos, Michael A.; Reber, Howard A.; Girgis, Mark D. (26 January 2021). "Acute Pancreatitis: A Review". JAMA. 325 (4): 382–390. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.20317. PMID 33496779.
- "Pancreatitis". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ Quinlan, JD (1 November 2014). "Acute pancreatitis". American Family Physician. 90 (9): 632–9. PMID 25368923.
- "Symptoms & Causes of Pancreatitis". The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- Wright, William F. (1 June 2016). "Cullen Sign and Grey Turner Sign Revisited". Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. 116 (6): 398–401. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2016.081.
- Zeng, Tingting; An, Jing; Wu, Yanqiu; Hu, Xueru; An, Naer; Gao, Lijuan; Wan, Chun; Liu, Lian; Shen, Yongchun (12 December 2023). "Incidence and prognostic role of pleural effusion in patients with acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis". Annals of Medicine. 55 (2). doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2285909. PMC 10880572.
- Sriram Bhat M (2018-10-31). SRB's Clinical Methods in Surgery. JP Medical Ltd. pp. 488–. ISBN 978-93-5270-545-0.
- Bassi C, Falconi M, Butturini G, Pederzoli P (2001). "Early complications of severe acute pancreatitis". In Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA (eds.). Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Munich: Zuckschwerdt.
- Rawla P, Sunkara T, Thandra KC, Gaduputi V (December 2018). "Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: updated review of current treatment and preventive strategies". Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology. 11 (6): 441–448. doi:10.1007/s12328-018-0881-1. PMID 29923163. S2CID 49311482.
- ^ Rawla P, Bandaru SS, Vellipuram AR (June 2017). "Review of Infectious Etiology of Acute Pancreatitis". Gastroenterology Research. 10 (3): 153–158. doi:10.14740/gr858w. PMC 5505279. PMID 28725301.
- Chung JW, Ryu SH, Jo JH, Park JY, Lee S, Park SW, Song SY, Chung JB (January 2013). "Clinical implications and risk factors of acute pancreatitis after cardiac valve surgery". Yonsei Medical Journal. 54 (1): 154–9. doi:10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.154. PMC 3521256. PMID 23225812.
- ^ Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS (September 2013). "American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 108 (9): 1400–15, 1416. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.218. PMID 23896955. S2CID 12610145.
- Gumaste VV, Dave PB, Weissman D, Messer J (November 1991). "Lipase/amylase ratio. A new index that distinguishes acute episodes of alcoholic from nonalcoholic acute pancreatitis". Gastroenterology. 101 (5): 1361–6. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(91)90089-4. PMID 1718808.
- ^ Banks PA, Freeman ML, et al. (Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology) (October 2006). "Practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 101 (10): 2379–400. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00856.x. PMID 17032204. S2CID 1837007.
- UK Working Party on Acute Pancreatitis (May 2005). "UK guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis". Gut. 54 (Suppl 3): iii1–9. doi:10.1136/gut.2004.057026. PMC 1867800. PMID 15831893.
- In support of the superiority of the lipase:
- Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D (June 2005). "Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis?". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 75 (6): 399–404. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x. PMID 15943725. S2CID 35768001.
- Treacy J, Williams A, Bais R, Willson K, Worthley C, Reece J, Bessell J, Thomas D (October 2001). "Evaluation of amylase and lipase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 71 (10): 577–82. doi:10.1046/j.1445-2197.2001.02220.x. PMID 11552931. S2CID 30880859.
- Keim V, Teich N, Fiedler F, Hartig W, Thiele G, Mössner J (January 1998). "A comparison of lipase and amylase in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis in patients with abdominal pain". Pancreas. 16 (1): 45–9. doi:10.1097/00006676-199801000-00008. PMID 9436862. S2CID 21285537.
- Ignjatović S, Majkić-Singh N, Mitrović M, Gvozdenović M (November 2000). "Biochemical evaluation of patients with acute pancreatitis". Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. 38 (11): 1141–4. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2000.173. PMID 11156345. S2CID 34932274.
- Sternby B, O'Brien JF, Zinsmeister AR, DiMagno EP (December 1996). "What is the best biochemical test to diagnose acute pancreatitis? A prospective clinical study". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 71 (12): 1138–44. doi:10.4065/71.12.1138. PMID 8945483.
- Smith RC, Southwell-Keely J, Chesher D (June 2005). "Should serum pancreatic lipase replace serum amylase as a biomarker of acute pancreatitis?". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 75 (6): 399–404. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03391.x. PMID 15943725. S2CID 35768001.
- Corsetti JP, Cox C, Schulz TJ, Arvan DA (December 1993). "Combined serum amylase and lipase determinations for diagnosis of suspected acute pancreatitis". Clinical Chemistry. 39 (12): 2495–9. doi:10.1093/clinchem/39.12.2495. PMID 7504593.
- Hameed AM, Lam VW, Pleass HC (February 2015). "Significant elevations of serum lipase not caused by pancreatitis: a systematic review". HPB. 17 (2): 99–112. doi:10.1111/hpb.12277. PMC 4299384. PMID 24888393.
- Bailey & Love's/24th/1123
- Larvin M, Chalmers AG, McMahon MJ (June 1990). "Dynamic contrast enhanced computed tomography: a precise technique for identifying and localising pancreatic necrosis". BMJ. 300 (6737): 1425–8. doi:10.1136/bmj.300.6737.1425. PMC 1663140. PMID 2379000.
- Arvanitakis M, Koustiani G, Gantzarou A, Grollios G, Tsitouridis I, Haritandi-Kouridou A, Dimitriadis A, Arvanitakis C (May 2007). "Staging of severity and prognosis of acute pancreatitis by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging-a comparative study". Digestive and Liver Disease. 39 (5): 473–82. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2007.01.015. PMID 17363349.
- ^ Scaglione M, Casciani E, Pinto A, Andreoli C, De Vargas M, Gualdi GF (October 2008). "Imaging assessment of acute pancreatitis: a review". Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI. 29 (5): 322–40. doi:10.1053/j.sult.2008.06.009. PMID 18853839.
- Miller FH, Keppke AL, Dalal K, Ly JN, Kamler VA, Sica GT (December 2004). "MRI of pancreatitis and its complications: part 1, acute pancreatitis". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 183 (6): 1637–44. doi:10.2214/ajr.183.6.01831637. PMID 15547203.
- Testoni PA, Mariani A, Curioni S, Zanello A, Masci E (June 2008). "MRCP-secretin test-guided management of idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis: long-term outcomes". Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 67 (7): 1028–34. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2007.09.007. PMID 18179795.
- Khalid A, Peterson M, Slivka A (August 2003). "Secretin-stimulated magnetic resonance pancreaticogram to assess pancreatic duct outflow obstruction in evaluation of idiopathic acute recurrent pancreatitis: a pilot study". Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 48 (8): 1475–81. doi:10.1023/A:1024747319606. PMID 12924639. S2CID 3066587.
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines (2013). "IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis". Pancreatology. 13 (4 Suppl 2): e1–15. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063. hdl:1854/LU-8582111. PMID 24054878.
- Talukdar R, Swaroop Vege S (April 2011). "Early management of severe acute pancreatitis". Current Gastroenterology Reports. 13 (2): 123–30. doi:10.1007/s11894-010-0174-4. PMID 21243452. S2CID 38955726.
- Trikudanathan G, Navaneethan U, Vege SS (August 2012). "Current controversies in fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review". Pancreas. 41 (6): 827–34. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824c1598. PMID 22781906. S2CID 1864635.
- Gardner TB, Vege SS, Chari ST, Petersen BT, Topazian MD, Clain JE, Pearson RK, Levy MJ, Sarr MG (2009). "Faster rate of initial fluid resuscitation in severe acute pancreatitis diminishes in-hospital mortality". Pancreatology. 9 (6): 770–6. doi:10.1159/000210022. PMID 20110744. S2CID 5614093.
- Basurto Ona X, Rigau Comas D, Urrútia G (July 2013). "Opioids for acute pancreatitis pain". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7 (7): CD009179. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009179.pub2. PMID 23888429.
- Helm JF, Venu RP, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Toouli J, Arndorfer RC (October 1988). "Effects of morphine on the human sphincter of Oddi". Gut. 29 (10): 1402–7. doi:10.1136/gut.29.10.1402. PMC 1434014. PMID 3197985.
- Al-Omran, Mohammed; AlBalawi, Zaina H; Tashkandi, Mariam F; Al-Ansary, Lubna A (20 January 2010). "Enteral versus parenteral nutrition for acute pancreatitis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD002837. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002837.pub2. PMC 7120370. PMID 20091534.
- Crockett, Seth D.; Wani, Sachin; Gardner, Timothy B.; Falck-Ytter, Yngve; Barkun, Alan N.; Crockett, Seth; Falck-Ytter, Yngve; Feuerstein, Joseph; Flamm, Steven; Gellad, Ziad; Gerson, Lauren; Gupta, Samir; Hirano, Ikuo; Inadomi, John; Nguyen, Geoffrey C.; Rubenstein, Joel H.; Singh, Siddharth; Smalley, Walter E.; Stollman, Neil; Street, Sarah; Sultan, Shahnaz; Vege, Santhi S.; Wani, Sachin B.; Weinberg, David (March 2018). "American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis". Gastroenterology. 154 (4): 1096–1101. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.032. PMID 29409760.
- Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Boermeester MA, Nieuwenhuijs VB, van Goor H, Dejong CH, Schaapherder AF, Gooszen HG (March 2009). "Timing and impact of infections in acute pancreatitis". The British Journal of Surgery. 96 (3): 267–73. doi:10.1002/bjs.6447. PMID 19125434. S2CID 2226746.
- Wu BU, Johannes RS, Kurtz S, Banks PA (September 2008). "The impact of hospital-acquired infection on outcome in acute pancreatitis". Gastroenterology. 135 (3): 816–20. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.053. PMC 2570951. PMID 18616944.
- Jafri NS, Mahid SS, Idstein SR, Hornung CA, Galandiuk S (June 2009). "Antibiotic prophylaxis is not protective in severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis". American Journal of Surgery. 197 (6): 806–13. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.08.016. PMID 19217608.
- Canlas KR, Branch MS (December 2007). "Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in acute pancreatitis". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 13 (47): 6314–20. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6314. PMC 4205448. PMID 18081218.
- Apostolakos MJ, Papadakos PJ (2001). The Intensive Care Manual. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-006696-0.
- DeCherney AH, Lauren N (2003). Current Obstetric & Gynecologic Diagnosis & Treatment. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-8385-1401-6.
- Peitzman AB, Schwab CW, Yealy DM, Fabian TC (2007). The Trauma Manual: Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-6275-5.
- Larvin M, McMahon MJ (July 1989). "APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis". Lancet. 2 (8656): 201–5. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(89)90381-4. PMID 2568529. S2CID 26047869.
- Yeung YP, Lam BY, Yip AW (May 2006). "APACHE system is better than Ranson system in the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis". Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International. 5 (2): 294–9. PMID 16698595. Archived from the original on 2006-10-26.
- ^ Chatzicostas C, Roussomoustakaki M, Vlachonikolis IG, Notas G, Mouzas I, Samonakis D, Kouroumalis EA (November 2002). "Comparison of Ranson, APACHE II and APACHE III scoring systems in acute pancreatitis". Pancreas. 25 (4): 331–5. doi:10.1097/00006676-200211000-00002. PMID 12409825. S2CID 27166241.
- Balthazar EJ, Robinson DL, Megibow AJ, Ranson JH (February 1990). "Acute pancreatitis: value of CT in establishing prognosis". Radiology. 174 (2): 331–6. doi:10.1148/radiology.174.2.2296641. PMID 2296641.
- Knoepfli AS, Kinkel K, Berney T, Morel P, Becker CD, Poletti PA (2007). "Prospective study of 310 patients: can early CT predict the severity of acute pancreatitis?" (PDF). Abdominal Imaging. 32 (1): 111–5. doi:10.1007/s00261-006-9034-y. PMID 16944038. S2CID 20809378.
- Leung TK, Lee CM, Lin SY, Chen HC, Wang HJ, Shen LK, Chen YY (October 2005). "Balthazar computed tomography severity index is superior to Ranson criteria and APACHE II scoring system in predicting acute pancreatitis outcome". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 11 (38): 6049–52. doi:10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.6049. PMC 4436733. PMID 16273623.
- Vriens PW, van de Linde P, Slotema ET, Warmerdam PE, Breslau PJ (October 2005). "Computed tomography severity index is an early prognostic tool for acute pancreatitis". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 201 (4): 497–502. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.06.269. PMID 16183486.
- Triantopoulou C, Lytras D, Maniatis P, Chrysovergis D, Manes K, Siafas I, Papailiou J, Dervenis C (October 2007). "Computed tomography versus Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis: a prospective, comparative study with statistical evaluation". Pancreas. 35 (3): 238–42. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3180619662. PMID 17895844. S2CID 24245362.
- Mortelé KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Wiesner W, Cantisani V, Ernst MD, Kalantari BN, Ros PR (October 2004). "Peripancreatic vascular abnormalities complicating acute pancreatitis: contrast-enhanced helical CT findings". European Journal of Radiology. 52 (1): 67–72. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.10.006. PMID 15380848.
- Papachristou GI, Muddana V, Yadav D, O'Connell M, Sanders MK, Slivka A, Whitcomb DC (February 2010). "Comparison of BISAP, Ranson's, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 105 (2): 435–41, quiz 442. doi:10.1038/ajg.2009.622. PMID 19861954. S2CID 41655611.
- Iannuzzi, Jordan P.; King, James A.; Leong, Jessica Hope; Quan, Joshua; Windsor, Joseph W.; Tanyingoh, Divine; Coward, Stephanie; Forbes, Nauzer; Heitman, Steven J.; Shaheen, Abdel-Aziz; Swain, Mark; Buie, Michael; Underwood, Fox E.; Kaplan, Gilaad G. (January 2022). "Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Gastroenterology. 162 (1): 122–134. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043. PMID 34571026.
External links
- Banks et al. Modified Marshall scoring system online calculator
- Pathology Atlas image.
- Parikh, RP; Upadhyay, KJ (Jul 4, 2013). "Cullen's sign for acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis". Indian J Med Res. 137 (6): 1210. PMC 3734730. PMID 23852306. Archived from the original on Dec 23, 2017.
| Diseases of the human digestive system | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper GI tract |
| ||||||||||
| Lower GI tract Enteropathy |
| ||||||||||
| GI bleeding | |||||||||||
| Accessory |
| ||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |