| Revision as of 19:07, 6 October 2002 editInfrogmation (talk | contribs)Administrators88,163 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:16, 15 January 2025 edit undo50.219.60.8 (talk) →Nuclear threats | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Decade of the Gregorian calendar (1960–1969)}} | |||
| ]: ] - ''']''' - ] | |||
| {{Redirect-multi|4|Sixties|'60s|The Sixties|The 60s|decades comprising years 60–69 of other centuries |List of decades|other uses|The Sixties (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=February 2023}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=February 2023}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | image_style = border:none;b | |||
| | perrow = 3/5/3/3 | |||
| | image1 = P-2H Neptune over Soviet ship Oct 1962 (1x2 crop).jpg | |||
| | image2 = Six-Day War. IDF forces organizing in secret behind trees (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image3 = Patient Package Insert for Oral Contraceptives (FDA 079) (8249451687).jpg | |||
| | image4 = Starved girl (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image5 = Aldrin Apollo 11 16x9 crop.jpg | |||
| | image6 = Gateway to space 2016, Budapest, SK-1 spacesuit 4 (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image7 = Mao Zedong in 1965 Color (3x2 close cropped).png | |||
| | image8 = Martin Luther King - March on Washington.jpg | |||
| | image9 = Valdivia after earthquake, 1960 (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image10 = JFK limousine.png | |||
| | image11 = The Beatles arrive at JFK Airport.jpg | |||
| | image12 = The National Archives UK - CO 1069-124-8.jpg | |||
| | image13 = DakToVietnam1966.jpg | |||
| | image14 = 10 Soviet Invasion of Czechoslovakia - Flickr - The Central Intelligence Agency.jpg | |||
| | total_width = 400 | |||
| | footer = From top left, clockwise: A US Navy plane flies over a Soviet cargo ship during the ''']'''; Israeli tanks advancing on the ] during the ''']'''; the ''']''' is first introduced, sparking the ] and the ] movement; During the ''']''' , ] delivers his ''']''' speech; ''']''' led the ] of the U.S. music market and became the ]; the ] unfolds before the ] and was part of the ''']'''; A U.S. infantry patrol during the ''']'''; During the ''']''', in which 16 ]n countries ] from their ]; Damaged homes in ] following the 9.4–9.6 {{m|w|link=y}} ''']'''; Biafran child starving from the mass famine caused by the ''']'''; The ''']''' mission lands the first humans on the Moon; ] became the first human to enter ] and ] by ''']'''; China's ] initiates the ''']''' plan which fails and brings mass starvation in which ] by 1961, and in 1966, Mao starts the ''']''', which purged traditional Chinese practices and ideas; ] is ''']''' in 1963. | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Decadebox|196}} | |||
| The '''1960s''' (pronounced "nineteen-sixties", shortened to the "'''{{'}}60s'''" or the "'''Sixties'''") was a decade that began on January 1, 1960, and ended on December 31, 1969.<ref name="Zeitz"> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100106144139/http://www.americanheritage.com/articles/magazine/ah/2006/5/2006_5_32.shtml |date=6 January 2010 }} "1964: The Year the Sixties Began", ''American Heritage'', Oct. 2006.</ref> | |||
| While the achievements of humans being ], ], ] and ] extended exploration, the Sixties are known as the "]" in the United States and other Western countries. There was a revolution in social norms, including clothing, music, drugs, dress, ], formalities, ], precepts of military duty, and schooling. Some people denounce the decade as one of irresponsible excess, flamboyance, the decay of social order, and the fall or relaxation of social taboos. A wide range of music emerged; from popular music inspired by and including the ] (in the United States known as the ]), the ], to the poetic lyrics of ]. In the United States the Sixties were also called the "cultural decade" while in the United Kingdom (especially London) it was called the ]. | |||
| ]: ] ] ] ] ] ] - '''1960s''' - ] ] ] ] ] | |||
| The United States had four presidents that served during the decade; ], ], ] and ]. Eisenhower was near the end of his term and left office in January 1961, and ]<ref name="Barth84Exhaustion">] (1984) intro to '']'', in ''The Friday Book''.</ref><ref>{{cite news | url= https://www.nytimes.com/2007/11/05/books/05masl.html | work= ] | title= Brokaw Explores Another Turning Point, the '60s | date= 5 November 2007 | access-date= 26 August 2011 | author= ] | archive-date= 20 July 2019 | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20190720205838/https://www.nytimes.com/2007/11/05/books/05masl.html | url-status= live }}</ref> in 1963. Kennedy had wanted ]<ref>{{cite magazine|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,842353-7,00.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070921004504/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,842353-7,00.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=21 September 2007|title=The Economy: We Are All Keynesians Now|date=31 December 1965|access-date=1 January 2011|magazine=]|quote=Keynesianism made its biggest breakthrough under John Kennedy, who, as Arthur Schlesinger reports in A Thousand Days, "was unquestionably the first Keynesian President."}}</ref> and staunch ] social reforms. These were passed under Johnson including civil rights for African Americans and health care for ] and ]. Despite his large-scale ] programs, Johnson was increasingly disliked by the ] at home and abroad. For some, May 1968 meant the end of traditional collective action and the beginning of a new era to be dominated mainly by the so-called ].<ref>Staricco, Juan Ignacio (2012) https://www.scribd.com/doc/112409042/The-French-May-and-the-Roots-of-Postmodern-Politics {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160306160322/https://www.scribd.com/doc/112409042/The-French-May-and-the-Roots-of-Postmodern-Politics |date=6 March 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| Years: ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] | |||
| After the ] led by ], the United States attempted to depose the new leader by training Cuban exiles and ] the island of ]. This led to Cuba to ally itself to the Soviet Union, a hostile enemy to the United States, resulting in an ] when Cuba hosted Soviet ballistic missiles similar to Turkey hosting American missiles, which brought the ] of causing ]. However, after negotiations between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R, both agreed to withdraw their weapons averting potential ]. | |||
| ----- | |||
| '''Events and Trends''' | |||
| After U.S. president ], direct tensions between the superpower countries of the United States and the Soviet Union developed into a contest with ], insurgency funding, puppet governments and other overall influence mainly in ], Africa, and ]. This "]" dominated the world's geopolitics during the decade. Construction of the ] by ] began in 1961. Africa was in a period of radical political change as 32 countries ] from their ]. The heavy-handed American role in the ] lead to an ] with outraged student protestors around the globe culminating in the ]. | |||
| The '''1960s''' was a turbulent decade of change around the world. Many of the trends of the 1960s were due to the ] changes brought about by the ] generation and the dissolution of European colonial empires. | |||
| * ]; many new or previously occupied contries achieve independance in ], ]. | |||
| ] saw the end of ] ] in 1962 that led to many Chinese to die from ] and the start of the ] from 1966 to 1976. Its stated goal was to preserve ] by ] remnants of ] and ] elements from ], leading to the arrests of a many Chinese politicians, the killings of millions of civilians and ethnic minorities, and the destruction of many historical and cultural buildings, artifacts and materials all of which would last until the ]. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]; end of racial ] and disenfranchisment of ] | |||
| By the end of the ], post-war reconstructed Europe began ]. World War II had closed up social classes with remnants of the old feudal gentry disappearing. A developing upper-working-class (a newly redefined middle-class) in Western Europe could afford a radio, television, refrigerator and motor vehicles. The ] and other ] countries were improving quickly after rebuilding from WWII. Real GDP growth averaged 6% a year during the second half of the decade; overall, the worldwide economy prospered in the 1960s with expansion of the middle class and the increase of new domestic technology. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] assassinated in ]; his brother ] assassinated in ]. | |||
| In the United Kingdom, the ] gained power in 1964 with ] as prime minister through most of the decade.<ref>Arthur Marwick, ''The Sixties: Cultural Revolution in Britain, France, Italy, and the United States, c.1958-c.1974'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998, {{ISBN|978-0-19-210022-1}}), 247–248.</ref> In France, the ] led to President ] temporarily fleeing the country.<ref name="Erlanger 2008">{{cite news|last=Erlanger|first=Steven|title=May 1968 – a watershed in French life|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2008/04/29/world/europe/29iht-france.4.12440504.html|access-date=31 August 2012|newspaper=The New York Times|date=29 April 2008|archive-date=16 April 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110416072914/http://www.nytimes.com/2008/04/29/world/europe/29iht-france.4.12440504.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Italy formed its first left-of-center government in March 1962 with ] becoming prime minister in 1963. Soviet leaders during the decade were ] until 1964 and ]. | |||
| * ] assassinated on ], ]. | |||
| * ]'s ] program | |||
| During the 1960s, the world population increased from 3.0 to 3.7 billion people. There were approximately 1.15 billion births and 500 million deaths. | |||
| * ], ] & ] converge at the ] Festival & Concert, ]. | |||
| * Worldwide expansion of ]. | |||
| ==Politics and wars== | |||
| * Students protesting percieved problems with the status-quo surpressed with violence by police and soldiers in ], ], ], ]. | |||
| {{See also|List of sovereign states in the 1960s}} | |||
| * Increase in ], Los Angeles ], ], Chicago riot, Democratic National Convention, 1968 | |||
| * Rise of the ] generation to adulthood; ] debuts on ]. | |||
| ===Wars=== | |||
| * First widespread availibily of practical ] pill for women; ] | |||
| ] (1955–1975)]] | |||
| * The rise of ] | |||
| ], after the ] of 1959 and before the official ] of 1961]] | |||
| * Growing popularity of religions other than Christianity in the West, and of ]; ] asks: "Is God Dead?" | |||
| {{Main|List of wars 1945–1989#1960–1969}} | |||
| * The ] and protests, leading to ] shootings in May, ] | |||
| * The ] (1947–1991) | |||
| * Growing hegemony of ] and ] ideology in some universities; Reassesment of the ] | |||
| ** The ] (1955–1975) | |||
| * ] develops, diversifies, and becomes very hip. The ] eclipse ]. | |||
| *** 1961 – Substantial (approximately 700) American advisory forces first arrive in ]. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *** 1962 – By mid-1962, the number of U.S. military advisers in ] had risen from 900 to 12,000. | |||
| * ] | |||
| *** 1963 – By the time of U.S. president ]'s death there were 16,000 American military personnel in South Vietnam, up from Eisenhower's 900 advisors to cope with rising guerrilla activity in Vietnam.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.swarthmore.edu/library/peace/conscientiousobjection/OverviewVietnamWar.htm |title=Brief Overview of Vietnam War |publisher=Swarthmore College Peace Collection |access-date=8 February 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160803124531/http://www.swarthmore.edu/library/peace/conscientiousobjection/OverviewVietnamWar.htm |archive-date=3 August 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| * ] abandons driving on the left side. | |||
| *** 1964 – In direct response to the minor naval engagement known as the ] which occurred on 2 August 1964, the ], a ] of the ], was passed on 10 August 1964. The resolution gave U.S. president ] authorization, without a formal ] by Congress, for the use of military force in Southeast Asia. The Johnson administration subsequently cited the resolution as legal authority for its rapid escalation of U.S. military involvement in the Vietnam War.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1970/06/25/archives/gulf-of-tonkin-measure-voted-in-haste-and-confusion-in-1964.html |title=Gulf of Tonkin Measure Voted in Haste and Confusion in 1964 |work=] |date=25 June 1970 |access-date=23 July 2018 |archive-date=23 July 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180723212757/https://www.nytimes.com/1970/06/25/archives/gulf-of-tonkin-measure-voted-in-haste-and-confusion-in-1964.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| * The ] puts man on ]'s ]; ]s revolutionize global communications. | |||
| *** 1966 – After 1966, with the draft in place more than 500,000 troops are sent to ] by the Johnson administration and college attendance soars. | |||
| * Start of the development of ] | |||
| ** The ] (1961) – an unsuccessful attempt by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba with support from U.S. government armed forces, to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro. | |||
| ** ] (1961–1974) – the war was fought between ] and the emerging nationalist movements in ]. It was a decisive ideological struggle and armed conflict of the ] in African (Portuguese Africa and surrounding nations) and European (mainland Portugal) scenarios. Unlike other European nations, the ] did not leave its African colonies, or the overseas provinces, during the 1950s and 1960s. During the 1960s, various armed independence movements, most prominently led by ]-led parties who cooperated under the ] umbrella and pro-U.S. groups, became active in these areas, most notably in ], ], and ]. During the war, several atrocities were committed by all forces involved in the conflict. | |||
| * The ] began in January 1963 and ended in August 1966. | |||
| * ] of 1962 occurred between ] and ] over a border dispute. | |||
| * The ] began in September. | |||
| * ] (early-20th century-present) | |||
| ** ] (June 1967) – a war between Israel and the neighboring states of ], ], and ]. The Arab states of ], ], ], ], ] and ] also contributed troops and arms.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/05/17/AR2007051701976.html |newspaper=] |title=Prelude to the Six Days |first=Charles |last=Krauthammer |date=18 May 2007 |access-date=20 April 2010 |archive-date=24 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190724024352/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/05/17/AR2007051701976.html |url-status=live }}</ref> At the war's end, Israel had gained control of the ], the ], the ], ], and the ]. The results of the war affect the ] of the region to this day. | |||
| ] during the Nigerian blockade of ] 1967–1970.]] | |||
| * The ] came to a close in 1962. | |||
| * The ] began in 1967. | |||
| * Civil wars in ] and ] rage on throughout the decade. | |||
| * The ] was a military conflict which broke out on 27 November 1969, between ] and ]. | |||
| ===Internal conflicts=== | |||
| * The massive ] in Japan against the ] were the largest and longest protests in Japan's history.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Kapur|first=Nick|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Re5hDwAAQBAJ|title=Japan at the Crossroads: Conflict and Compromise after Anpo|publisher=]|year=2018|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts|pages=1|isbn=9780674988484|access-date=26 July 2021|archive-date=16 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201216035041/https://books.google.com/books?id=Re5hDwAAQBAJ|url-status=live}}</ref> Although they ultimately failed to stop the treaty, they forced the resignation of Japanese prime minister ] and the cancellation of a planned visit to Japan by U.S. president ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Kapur|first=Nick|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Re5hDwAAQBAJ|title=Japan at the Crossroads: Conflict and Compromise after Anpo|publisher=]|year=2018|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts|pages=4–6|isbn=9780674988484|access-date=26 July 2021|archive-date=16 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201216035041/https://books.google.com/books?id=Re5hDwAAQBAJ|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| * The ] was a period of ] and ] in the ] between 1960 and 1965 that ended with the establishment of a unitary state led by ]. | |||
| * The ] leads to a brief international occupation of the country and the election of ] as president. | |||
| * The ] occurred as part of the ] that marked the beginning of Suharto's 31-year presidency. | |||
| * ] (1966–1976) – a period of widespread social and political upheaval in the People's Republic of China which was launched by ], the chairman of the ]. Mao alleged that "liberal bourgeois" elements were permeating the party and society at large and that they wanted to restore ]. Mao insisted that these elements be removed through post-revolutionary ] by mobilizing the thoughts and actions of China's youth, who formed ] groups around the country. The movement subsequently spread into the military, urban workers, and the party leadership itself. Although Mao himself officially declared the Cultural Revolution to have ended in 1969, the power struggles and political instability between 1969 and the arrest of the ] in 1976 are now also widely regarded as part of the Revolution. | |||
| *The ] movement in India began in 1967 with an ] of tribals against local landlords in the village of ], West Bengal, led by certain leaders of the ]. The movement was influenced by ] and spread to many tribal districts in Eastern India, gaining strong support among the radical urban youth. After counter-insurgency operations by the police, military and paramilitary forces, the movement fragmented but is still active in many districts. | |||
| * ] in Northern Ireland began with the rise of the ] in the mid-1960s, the conflict continued into the later 1990s. | |||
| * The ] in Bangladesh (at the time East Pakistan). The movement gave way to the ] mass uprising, which released ] from prison and put the country on the road to ] in the early 1970s. | |||
| * The ] occurred in August 1966 in the ] district of San Francisco. This incident was one of the first recorded ] riots in United States history, preceding the more famous 1969 Stonewall Riots in New York City by three years. | |||
| * The ] occurred in June 1969 in New York City. The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent demonstrations against a police raid that took place in the ], in the ] neighborhood of New York City. They are frequently cited as the first instance in American history when people in the homosexual community fought back against a government-sponsored system that persecuted sexual minorities, and they have become the defining event that marked the start of the ] in the United States and around the world. | |||
| * In 1967, the ] withheld milk supplies for 15 days as part of an effort to induce a quota system to stabilize prices. | |||
| * ]. | |||
| * Mass socialist or Communist movement in most European countries (particularly France and Italy), with which the student-based new left was involved. The most spectacular manifestation of this was the ] student revolt of 1968 in Paris that linked up with a general strike of ten million workers called by the trade unions; and for a few days seemed capable of overthrowing the government of ]. De Gaulle went off to visit French troops in Germany to check on their loyalty. Major concessions were won for trade union rights, higher minimum wages and better working conditions. | |||
| * University students protested in the hundreds of thousands against the Vietnam War in London, Paris, Berlin and Rome. | |||
| * In Eastern Europe students also drew inspiration from the protests in the West. In Poland and ] they protested against restrictions on free speech by ] regimes. | |||
| * The ] – was a government massacre of student and civilian protesters and bystanders that took place during the afternoon and night of 2 October 1968, in the ] in the ] section of Mexico City. | |||
| ===Coups=== | |||
| {{Main|List of coups d'état and coup attempts#1960–1969}} | |||
| Prominent ] of the decade included: | |||
| * On 27 May 1960, a coup in ] led by ] and ] overthrew the government of ]. | |||
| * On 16 May 1961, a coup in ] led by army officer ] made the establishment of temporary military rule. | |||
| * In 1963, a ] in ] leads to the death of President ] and the establishment of temporary military rule. | |||
| * On 31 March and 1 April 1964, a ] in Brazil overthrows President João Goulart and starts a 21-year period of ]. | |||
| * On 21 April 1967, in Greece a group of colonels established a ] for seven years. | |||
| * In 1968, a ] led to the overthrow of ] by the ] ]. | |||
| * On 1 September 1969, a small group of military officers led by the army officer ] ] monarchy in ]. | |||
| ===Nuclear threats=== | |||
| ], taken by United States spy planes on 1 November 1962.]] | |||
| * The ] (16–28 October 1962) – a near-military confrontation between the U.S. and the Soviet Union about the presence of Soviet missiles in ]. After an American ] (quarantine) blockade of Cuba the Soviet Union under the leadership of ] agreed to remove their missiles from Cuba in exchange for the U.S. removing its missiles from Turkey. | |||
| * On 13 February 1960, ]. France possessed a ] by 1968. | |||
| * On 16 October 1964, ]. China possessed a ] by 1967. | |||
| ===Decolonization and independence=== | |||
| * The transformation of Africa from ] to independence in what is known as the ] dramatically accelerated during the decade, with 32 countries gaining independence between 1960 and 1968, marking the end of the European empires that once dominated the African continent. However, many of these new post-colonial states would struggle with internal and external issues including famine, corruption, genocide, disease, and violent conflicts in the 1960s and succeeding decades.<ref>{{Cite journal|url=https://doi.org/10.1080/14623528.2014.936700|title=The Nigeria–Biafra war: postcolonial conflict and the question of genocide|first1=Lasse|last1=Heerten|first2=A. Dirk|last2=Moses|date=3 July 2014|journal=Journal of Genocide Research|volume=16|issue=2–3|pages=169–203|via=Taylor and Francis+NEJM|doi=10.1080/14623528.2014.936700|s2cid=143878825 | issn = 1462-3528 }}</ref> Many of these issues were caused or exacerbated by American and Soviet involvement during the ] with each side supporting various strongmen, dictators, and guerillas favorable to their causes in these countries.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.atomicheritage.org/history/proxy-wars-during-cold-war-africa|title=Proxy Wars During the Cold War: Africa|website=Atomic Heritage Foundation}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://history.state.gov/milestones/1961-1968/congo-decolonization|title=Milestones: 1961–1968 – Office of the Historian|website=history.state.gov}}</ref> ] on the continent has been difficult, but many nations who decolonized in the 1960s began to see a rebound and unprecedented growth in the first quarter of the 21st century. As a whole, Africa's GDP rose by an average of over 6% a year between 2013 and 2022, a rate only outpaced by China.<ref>{{cite news|title=Africa rising A hopeful continent|url=https://www.economist.com/news/special-report/21572377-african-lives-have-already-greatly-improved-over-past-decade-says-oliver-august|newspaper=The Economist|publisher=The Economist Newspaper Limited|access-date=15 December 2013|author=Oliver August|date=2 March 2013}}</ref><ref>{{Citation|last=Ocran|first=Matthew Kofi|title=Post-Independence African Economies: 1960–2015|date=2019|url=https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10770-3_9|work=Economic Development in the Twenty-first Century: Lessons for Africa Throughout History|pages=301–372|editor-last=Ocran|editor-first=Matthew Kofi|series=Palgrave Studies in Economic History|place=Cham|publisher=Springer International Publishing|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-3-030-10770-3_9|isbn=978-3-030-10770-3|s2cid=159395862 |access-date=2021-07-07}}</ref> | |||
| ===Prominent political events=== | |||
| ====North America==== | |||
| =====United States===== | |||
| ] and others at the ] in 1963]] | |||
| * 1960 – ] – The very close campaign was the series of four Kennedy–Nixon debates; they were the first presidential debates held on television. Kennedy won a close election. | |||
| * 1961 – President ] promised some more aggressive confrontation with the Soviet Union; he also established the ]. | |||
| * 1963 – ] published the book '']'', reawakening the feminist movement and being largely responsible for its second wave. | |||
| * 1963 – Civil rights becomes a central issue as the ] and ] lead to President Kennedy's ], ]'s "]" speech at the ] on 6 August and the ]. | |||
| * 1963 – Kennedy was assassinated and replaced by Vice President ]. The nation was in shock. For the next half-century, conspiracy theorists concocted numerous alternative explanations to the official report that a lone gunman killed Kennedy. | |||
| * 1964 – Johnson pressed for ] legislation. ] signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. This landmark piece of legislation in the United States outlawed ] in schools, public places, and employment. The first black riots erupt in major cities. | |||
| * 1964 – Johnson was reelected over Conservative spokesman Senator ] by a wide landslide; Liberals gained full control of Congress. | |||
| * 1964 – The ] was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on 3 September. | |||
| * 1965 – After the events of the ], the ] was lobbied for (and then signed into law) by President Lyndon B. Johnson. The Voting Rights Act outlawed discriminatory voting practices that had caused the widespread disenfranchisement of African Americans in the United States. | |||
| * 1968 – U.S. president ] was elected, defeating Vice President ], in November. | |||
| * 1969 – U.S. president ] was inaugurated in January 1969; he promised "peace with honor" to end the ]. | |||
| =====Canada===== | |||
| * ] in Quebec altered the province-city-state into a more secular society. The Jean Lesage ] government created a welfare state (''État-Providence'') and fomented the rise of active nationalism among Francophone French-speaking Quebecer Québécois. | |||
| * On 15 February 1965, the new ] was adopted in Canada after a much-anticipated debate known as the ]. | |||
| * In 1960, the ] becomes law and suffrage (as well as the right for any Canadian citizen to vote) was finally adopted by John Diefenbaker's Progressive Conservative government. The new election act allowed ] people to vote for the first time. | |||
| =====Mexico===== | |||
| * The student and ] protests in 1968 coincided with political upheavals in a number of other countries. Although these events often sprung from completely different causes, they were influenced by reports and images of what was happening in the United States and France.<ref>Jaime Pensado, "The (forgotten) Sixties in Mexico." ''The Sixties: A Journal of History, Politics and Culture'' (2008) 1#1: 83–90.</ref> | |||
| ]'s ] had become a popular symbol of rebellion for the New Left]] | |||
| ====Europe==== | |||
| ] | |||
| * British prime minister ] delivered his "]" speech in 1960. | |||
| * The government of the ] authorized construction of the ] on 13 August 1961 to prevent East Germans from leaving ] to ].<ref>Curtis Cate, ''The Ides of August: The Berlin Wall Crisis–1961'' (1978).</ref> | |||
| * ] calls the ] of the Catholic Church, continued by ] (after John XXIII died in 1963), which met from 11 October 1962 until 8 December 1965.<ref>Giuseppe Alberigo, and Matthew Sherry, ''A Brief History of Vatican II'' (2006)</ref> | |||
| * In October 1964, Soviet leader ] was expelled from office due to his increasingly erratic and authoritarian behavior. ] and ] then became the new leaders of the Soviet Union.<ref>William Taubman, ''Khrushchev: The Man and His Era'' (2003),</ref> | |||
| * In ], 1968 was the year of ]'s ], a source of inspiration to many Western leftists who admired Dubček's "socialism with a human face". The Soviet ] in August ended these hopes and also fatally damaged the chances of the orthodox communist parties drawing many recruits from the student protest movement.<ref>Günter, et al. eds. Bischof, ''The Prague Spring and the Warsaw Pact Invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968'' (Lexington Books, 2010)</ref> | |||
| ====Asia==== | |||
| =====China===== | |||
| * The ] (1966–1976) and the ] (1961–1989) | |||
| **1966 marked the beginning of the Cultural Revolution that was launched by Mao Zedong and lasted until his death in 1976. The goal of the revolution was to preserve Chinese communism by purging Chinese society of its traditional and remaining capitalist elements. Though it failed to achieve its main objectives, the revolution marked the effective return of Mao to the center of power. | |||
| ** Following Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev's removal from power in 1964, Sino-Soviet relations devolved into ]. The Chinese were deeply disturbed by the Soviet suppression of the ] in 1968 as the latter now claimed the right to intervene in any country it saw as deviating from the correct path of socialism. In March 1969, armed clashes took place along the ] in the former Manchuria and this finally drove the Chinese to restore relations with the U.S. as Mao Zedong decided that the Soviet Union posed the bigger threat to China. | |||
| =====India===== | |||
| * A literary and cultural movement started in ], ] and other cities by a group of writers and painters who called themselves "Hungryalists", or members of the ]. The band of writers wanted to change virtually everything and were arrested with several cases filed against them on various charges; they ultimately won these cases.<ref>{{cite book|author=Krishna Dutta|title=Calcutta: A Cultural History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=59wfjyIIJAkC&pg=PA220|year=2008|publisher=Interlink Books|page=220|isbn=978-1-56656-721-3|access-date=10 October 2016|archive-date=27 June 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140627142825/http://books.google.com/books?id=59wfjyIIJAkC&pg=PA220|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| =====Indonesia===== | |||
| * President ] banned the ] on 15 August 1960 and caused a tension the between government and Islamist groups.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Akbarzadeh |first=Shahram |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8a8wefN4bd8C&q=political+islam+sukarno&pg=PA160 |title=Islam and Political Legitimacy |last2=Saeed |first2=Abdullah |date=2003-09-02 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-134-38056-5 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| * The ] (1965–1968) | |||
| ** In the early hours of 1 October 1965, ] launched a coup d'état attempt in ], assassinated six senior ] generals and a junior army officer. They also seized ] and proclaimed the establishment of "the Revolutionary Council" through a radio broadcast later in the morning, with ] as its leader. | |||
| ** On the same day, ] successfully persuaded the soldiers on Merdeka Square to join forces with the Indonesian ] divisions and launched a counterattack on the movement, ending the coup attempt. Three days later, the bodies of seven army officers were found buried in an old well in ] and the bodies were recovered. | |||
| ** In the aftermath of the coup d'état attempt, the people blamed the attempt on the ], prompting a ] against leftists and communist sympathizers across the country. Around 500,000-1,000,000 casualties were massacred. The killings were mostly done by the locals with the help of the Army. | |||
| ** Soon, mass demonstrations and protests from the ] against ] occurred. President Sukarno was notorious for his friendly approach towards the leftists, particularly the Communist Party of Indonesia. | |||
| ** In the climax of the protests, President Sukarno signed the ] on 11 March 1966, effectively transferring authority to Major General Suharto to restore order and ensure security in the country. On 12 March 1967, President Sukarno was stripped of his political power by the ] (MPRS) and Major General Suharto became ]. Later, he became president ] on 27 March 1968. Sukarno lived under house arrest until his death in June 1970. | |||
| =====Japan and South Korea===== | |||
| * The ] (1960s–1990s) | |||
| ** Japan's remarkable economic growth between the post-] era and the end of the ]. During the economic boom, Japan rapidly became the world's ] at the time (after the United States). | |||
| ** In 1960, Japan was wracked by the massive ] against the revision of the ], resulting in the resignation of Prime Minister ]; Kishi's successor, ], began implementing economic policies, known as the ] removed most of Japan's anti-monopoly laws and promised to double the size of Japan's economy within 10 years. ] became Prime Minister of Japan four years later, succeeding Ikeda due to health issues. | |||
| ** The ] were held in Japan, the first time the country hosted them and the first time that the ] were held in Asia. The world's first bullet train (the ] between ] and ]) commences operations; it is the oldest high-speed rail system in the world. | |||
| * The ] and ] (1960–1972) | |||
| ** The ] were mass protests in ] against President ] and the ] from 11 to 26 April 1960, which led to Rhee's resignation. The Second Republic was established as a ] under President ] and Prime Minister ]. The Second Republic ended the First Republic, formed a liberal democracy, and formulated the first ] to develop the formerly-neglected economy. | |||
| ** The ] and the establishment of the ], led by Major General ] on 16 May 1961, put an effective end to the Second Republic. Park was one of a group of military leaders who had been pushing for the de-politicization of the military. | |||
| ** The ] began with the ], a series of economic development projects implemented by President Park Chung Hee. South Korea received US$800 million from Japan under property claims and was mostly dependent on ] (largely from the U.S. in exchange for South Korea's involvement in the ]). | |||
| ** South Korea's first diplomatic relations with Japan were established under the Third Republic and ] were normalized in the ] signed on 22 July 1965 and in an agreement ratified on 14 August 1965. Japan agreed to provide a large amount of compensation, grants, and loans to South Korea and the two countries began economic and political cooperation. | |||
| ====Africa==== | |||
| ], African leader]] | |||
| * On 1 September 1969, the ] monarchy was overthrown and a radical, revolutionary government headed by dictator ] took power. | |||
| * On 1 October 1960, ] gained its independence from Great Britain. | |||
| ====South America==== | |||
| * In 1964, a ] against the democratically elected government of ] president ] initiated a military dictatorship that caused over 20 years of oppression. | |||
| * The ] revolutionary ] travelled to Africa and then ] in his campaign to spread worldwide revolution. He was captured and executed in 1967 by the Bolivian army and afterwards became an iconic figure for leftists around the world. | |||
| * ] took power by means of a coup in ] in 1968. | |||
| ==Economics== | |||
| {{Globalize|article|USA|date=July 2018}} | |||
| ===The United States=== | |||
| During the 1960s the United States was in the ]. The 1960s are remembered as a time period of rapid workforce growth (roughly 33% between February 1961 and December 1969),<ref>U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, All Employees, Total Nonfarm , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PAYEMS, January 3, 2024.</ref> ], low unemployment,<ref>Holland, Susan S. “Long-Term Unemployment in the 1960’s.” Monthly Labor Review, vol. 88, no. 9, 1965, pp. 1069–76. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/41836225. Accessed 4 Jan. 2024.</ref><ref>U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Unemployment Rate , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/UNRATE, January 3, 2024</ref> rapid GDP growth, gains in productivity and generally low inflation. After the ] the United States experienced sustained rapid economic growth which began in February 1961 and ended with the ]. It lasted a total of 106 months, which made it the longest recorded economic expansion in the history of the United States until the ]. | |||
| On January 20, 1961, John F. Kennedy became the president of the United States. In his campaign, John F. Kennedy promised to "get America moving again." His goal was economic growth of 4–6% per year and unemployment below 4%.{{citation needed|date=January 2024}}To do this, he proposed a wide range of policies which embraced ] (which he is the first president to do so). Among these policies included a 7% tax credit for businesses that invest in new plants and equipment,{{citation needed|date=January 2024}} Income ] and an increase in the federal minimum wage. | |||
| Although, the 1960s were not perfect. The government routinely produced fiscal deficits (as a result of the tax cuts and increased expenditure embarked under Kennedy), with only one surplus during this time period (as opposed to the 1950s which produced 3).<ref>U.S. Office of Management and Budget and Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Federal Surplus or Deficit as Percent of Gross Domestic Product , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FYFSGDA188S, January 3, 2024.</ref> Furthermore, by 1966 inflation began to climb, which is a general trend that continued into the ]. By the end of the decade under Nixon, the combined inflation and unemployment rate known as the ] had exploded to nearly 10% with inflation at 6.2% and unemployment at 3.5% and by 1975 the misery index was almost 20%.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://inflationdata.com/articles/inflation-cpi-consumer-price-index-1960-1969/|title=Inflation and CPI Consumer Price Index 1960–1969|website=InflationData.com|access-date=9 October 2020|archive-date=9 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201009192240/https://inflationdata.com/articles/inflation-cpi-consumer-price-index-1960-1969/|url-status=live}}</ref> By the end of the decade, median family income had risen from $8,540 in 1963 to $10,770 by 1969.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://elcoushistory.tripod.com/economics1960.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070606123915/http://elcoushistory.tripod.com/economics1960.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=6 June 2007|title=U.S. History – 1960s}}</ref> | |||
| ==Assassinations and attempts== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Prominent assassinations, targeted killings, and assassination attempts include: | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable mw-collapsible" | |||
| ! style="width:120px;"| Date | |||
| ! Description | |||
| |- | |||
| |12 October 1960 | |||
| |], leader of the Japan Socialist Party, was ] by ] ] while speaking in a televised political debate in Tokyo.<ref name=chun>{{cite book |title=A Nation of a Hundred Million Idiots?: A Social History of Japanese Television, 1953–1973 |last=Chun |first=Jayson Makoto |publisher=Routledge |year=2006 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9miRAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA184 |pages=184–185 |isbn=978-0-415-97660-2 |access-date=22 March 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Japan's Foreign Policy |last=Langdon |first=Frank |year=1973 |publisher=] |location=Vancouver |isbn=0774800151 |page=19 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9qqdRRfwj-EC&pg=PA19 |access-date=18 August 2012 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |17 January 1961 | |||
| |], the Prime Minister of the ]; ], Minister of Youth and Sports; ], vice-president of the Senate, were ] by a Belgian and Congolese firing squad outside ].<ref>{{Cite news|title=Katanga's Communique on the Killing of Lumumba|date=14 February 1961|work=]|id = {{ProQuest|115317883}}}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |30 May 1961 | |||
| |], dictator of the Dominican Republic for 31 years, was ] in a plot led by members of his general staff.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.moreorless.au.com/killers/trujillo.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111115223630/http://www.moreorless.au.com/killers/trujillo.html | archive-date=15 November 2011 | title=Rafael Trujillo killer file }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |13 January 1963 | |||
| |], the Prime Minister of ], was killed during the ]. His body was dumped in front of the U.S. embassy in ].<ref>{{cite news |title=Togo's President Slain in Coup: Insurgents Seize Most Of Cabinet |newspaper=The Washington Post |date=14 January 1963 |page=A11}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |2 November 1963 | |||
| |], 1st president of South Vietnam, along with his brother and chief political adviser ], was ] in a ] led by elements of the South Vietnamese ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://millercenter.org/the-presidency/educational-resources/diem-coup | title=The Diem coup | Miller Center | date=18 September 2017 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |22 November 1963 | |||
| |], 35th president of the United States, was ] while riding in a motorcade through ] in ], Texas. His assassin, ], was himself ] by ] two days later.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.archives.gov/research/jfk/warren-commission-report/chapter-1#conclusions | title=Chapter 1 | date=15 August 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |21 February 1965 | |||
| |], an American civil rights leader, was ] in ]. The perpetrators of the killing are disputed.<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.nytimes.com/1965/02/22/archives/malcolm-x-shot-to-death-at-rally-here-three-other-negroes-wounded.html | title=Malcolm X Shot to Death at Rally | work=The New York Times | date=22 February 1965 | last1=Kihss | first1=Peter }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |6 September 1966 | |||
| |], Prime Minister of South Africa and architect of ], was stabbed to death by ], a parliamentary messenger, at the South African ].<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,836363-1,00.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070424173033/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,836363-1,00.html | archive-date=24 April 2007 | title=Death to the Architect }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |9 October 1967 | |||
| |], an Argentine-Cuban Marxist revolutionary, was ] by the CIA and Bolivian army.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7027619.stm|title=CIA man recounts Che Guevara's death|date=8 October 2007|newspaper=BBC|access-date=24 June 2016|archive-date=28 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170628161656/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7027619.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |4 April 1968 | |||
| |], American ] leader, was ] in ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://kinginstitute.stanford.edu/encyclopedia/assassination-martin-luther-king-jr | title=Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr | date=24 April 2017 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |5 June 1968 | |||
| |], former Attorney General and a leading ], was ] in Los Angeles following a speech regarding his victory in California.<ref></ref> | |||
| |} | |||
| == Disasters == | |||
| '''Natural:''' | |||
| * The ], also known as the Great Chilean earthquake, is to date the most powerful earthquake ever recorded, rating 9.5 on the moment magnitude scale. It caused localized tsunamis that severely battered the Chilean coast, with waves up to 25 meters (82 ft). The main tsunami raced across the Pacific Ocean and devastated ]. | |||
| * ] was a 6.1 moment magnitude earthquake which occurred in Skopje, SR Macedonia (present-day Republic of Macedonia) on 26 July 1963, which killed over 1,070 people, injured between 3,000 and 4,000 and left more than 200,000 people homeless. About 80% of the city was destroyed. | |||
| * 1963 – ] – The Vajont dam flood in Italy was caused by a mountain sliding in the dam and causing a flood wave that killed approximately 2,000 people in the towns in its path. | |||
| * 1964 – The ], the most powerful earthquake recorded in the U.S. and North America, struck ] and killed 143 people. | |||
| * 1965 – ] caused severe damage to the U.S. Gulf Coast, especially in the state of ]. | |||
| * 1969 – The ] caught fire in Ohio. Fires had erupted on the river many times, including 22 June 1969, when a river fire captured the attention of Time magazine, which described the Cuyahoga as the river that "oozes rather than flows" and in which a person "does not drown but decays." This helped spur legislative action on water pollution control resulting in the Clean Water Act, Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement, and the creation of the federal Environmental Protection Agency. | |||
| * 1969 – ] hit the U.S. Gulf Coast at Category 5 Status. It peaked and made landfall with 175 mph (280 km/h) winds and caused $1.42 billion (1969 USD) in damages. | |||
| '''Non-natural:''' | |||
| * On 16 December 1960, a ] DC-8 and a ] Lockheed Constellation ] and crashed, killing 134 people. | |||
| * On 15 February 1961, ] crashed on its way to Brussels, Belgium, killing all 72 passengers on board and 1 person on the ground. Among those killed were all 18 members of the US figure skating team, on their way to the World Championships. | |||
| * On 16 March 1962, ], a Lockheed Super Constellation, inexplicably disappeared over the Western Pacific, leaving all 107 on board presumed dead. Since the wreckage of the aircraft is lost to this day, the cause of the crash remains a mystery. | |||
| * On 3 June 1962, ], a Boeing 707, crashed on takeoff from Paris. 130 people were killed in the crash while 2 survived. | |||
| * On 20 May 1965, ] crashed on approach to ], Egypt. 121 died while 6 survived. | |||
| * On 4 February 1966, ], a Boeing 727, plunged into ] for reasons unknown. All 133 people on board died. | |||
| * On 5 March 1966, ] broke up in mid-air and crashed on the slopes of ]. All 124 aboard died. | |||
| * On 8 December 1966, the car ferry ] sank in the ] during a storm, killing 217 people. | |||
| * On 16 March 1969, a DC-9 operating ] crashed in the Venezuelan city of ]. A total of 155 people died in the crash. | |||
| ==Social and political movements== | |||
| ===Counterculture and social revolution=== | |||
| {{See also|Counterculture of the 1960s | Timeline of 1960s counterculture}} | |||
| In the second half of the decade, young people began to revolt against the conservative norms of the old time, as well as remove themselves from mainstream liberalism, in particular the high level of materialism which was so common during the era. This created a "counterculture" that sparked a social revolution throughout much of the Western world. It began in the United States as a reaction against the conservatism and social ] of the 1950s, and the U.S. government's extensive military intervention in Vietnam. The youth involved in the popular social aspects of the movement became known as ]. These groups created a movement toward liberation in society, including the ], questioning authority and government, and demanding more freedoms and rights for women and minorities. The ], a widespread, eclectic collection of newspapers served as a unifying medium for the counterculture. The movement was also marked by the first widespread, socially accepted drug use (including ] and ]) and ] music. | |||
| ===Anti-war movement=== | |||
| {{main|Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War}} | |||
| ] during the ]'s 21 October 1967 ]]] | |||
| The war in Vietnam would eventually lead to a commitment of over half a million American troops, resulting in over 58,500 American deaths and producing a large-scale antiwar movement in the United States. As late as the end of 1965, few Americans protested the American involvement in Vietnam, but as the war dragged on and the body count continued to climb, civil unrest escalated. Students became a powerful and disruptive force and university campuses sparked a national debate over the war. As the movement's ideals spread beyond college campuses, doubts about the war also began to appear within the administration itself. A mass movement began rising in opposition to the ], including the ]'s 1967 march to the United Nations and its ], the ] at which the slogan "]" became famous, and continuing in the massive ] protests in 1969 as well as the movement of resistance to ] ("the Draft") for the war.{{Citation needed|date=November 2009}} | |||
| The ] was initially based on the older 1950s ], heavily influenced by the ], but by the mid-1960s it outgrew this and became a broad-based mass movement centered in universities and churches: one kind of protest was called a "]". Other terms heard in the United States included "]", "]", "]", and "]". Voter age-limits were challenged by the phrase: "If you're old enough to die for your country, you're old enough to vote." | |||
| ===Civil rights movement=== | |||
| {{Main|Civil rights movement}} | |||
| ]'s 28 August 1963, ] in front of the ]]] | |||
| Beginning in the mid-1950s and continuing into the late 1960s, ] in the United States organized a movement to end legalized ] and obtain ]. This article covers the phase of the movement between 1955 and 1968, particularly in the South. The emergence of the ], which lasted roughly from 1966 to 1975, enlarged the aims of the civil rights movement to include racial dignity, ] and ] ], and ]. | |||
| The movement was characterized by major campaigns of ]. Between 1955 and 1968, acts of ] and ] protest produced crisis situations between activists and government authorities. Federal, state, and local governments, businesses, and communities often had to respond immediately to these situations that highlighted the inequities faced by African Americans. Forms of protest and/or civil disobedience included boycotts such as the successful ] (1955–1956) in Alabama, ]s such as the influential ] (1960) in North Carolina, ] such as the ] (1965) in Alabama, and other nonviolent activities. | |||
| Noted legislative achievements during this phase of the civil rights movement were passage of ]<ref name="cra64">{{cite web|url=http://finduslaw.com/civil_rights_act_of_1964_cra_title_vii_equal_employment_opportunities_42_us_code_chapter_21|title=Civil Rights Act of 1964 – CRA – Title VII – Equal Employment Opportunities – 42 US Code Chapter 21|access-date=22 December 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101021141154/http://finduslaw.com/civil_rights_act_of_1964_cra_title_vii_equal_employment_opportunities_42_us_code_chapter_21|archive-date=21 October 2010|url-status=dead}}</ref> that banned discrimination based on "race, color, religion, or national origin" in employment practices and public accommodations, the ] that restored and protected voting rights, the ] that dramatically opened entry to the U.S. to immigrants other than traditional European groups, and the ] that banned discrimination in the sale or rental of housing. | |||
| ===Hispanic and Chicano movement=== | |||
| Another large ethnic minority group, the ], are among other ] in the U.S. who fought to end racial discrimination and socioeconomic disparity. The largest Mexican-American populations were in the Southwestern United States, such as California with over 1 million '']'' in Los Angeles alone, and ] where ] laws included Mexican-Americans as "non-white" in some instances to be legally segregated. | |||
| Socially, the ] addressed what it perceived to be negative ]s of Mexicans in mass media and the American consciousness. It did so through the creation of works of literary and visual art that validated Mexican-American ethnicity and culture. Chicanos fought to end social stigmas such as the usage of the Spanish language and advocated official ] in federal and state governments. | |||
| The Chicano Movement also addressed discrimination in public and private institutions. Early in the twentieth century, Mexican Americans formed organizations to protect themselves from discrimination. One of those organizations, the ], was formed in 1929 and remains active today.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://lulac.org/about/history/ |title=LULAC History{{snd}}All for One and One for All |website=] |access-date=22 March 2023}}</ref> | |||
| The movement gained momentum after World War II when groups such as the ], which was formed by returning Mexican American veterans, joined in the efforts by other civil rights organizations.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.americangiforum.org/about.cfm |title=americangiforum.org |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150706223234/http://www.americangiforum.org/about.cfm |archive-date=6 July 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| Mexican-American civil-rights activists achieved several major legal victories including the 1947 '']'' ] ruling which declared that segregating children of "Mexican and Latin descent" was unconstitutional and the 1954 '']'' ruling which declared that Mexican Americans and other racial groups in the United States were entitled to equal protection under the ] of the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.latinola.com/story.php?story=432|title=LatinoLA – Hollywood :: Mendez v. Westminster|work=LatinoLA|access-date=17 March 2008|archive-date=16 April 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080416202512/http://www.latinola.com/story.php?story=432|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.oyez.org/cases/1950%E2%80%931959/1953/1953_406/|title=Hernandez v. Texas – The Oyez Project at IIT Chicago-Kent College of Law|work=oyez.org|access-date=27 June 2017|archive-date=7 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160307034040/https://www.oyez.org/cases/1950%E2%80%931959/1953/1953_406/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The most prominent civil-rights organization in the Mexican-American community, the ] (MALDEF), was founded in 1968.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.maldef.org/about/index.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080422002948/http://www.maldef.org/about/index.htm|url-status=dead|title=MALDEF{{spaced ndash}} About Us<!-- Bot generated title -->|archive-date=22 April 2008}}</ref> Although modeled after the ], MALDEF has also taken on many of the functions of other organizations, including political advocacy and training of local leaders. | |||
| Meanwhile, ] in the U.S. mainland fought against racism, police brutality and socioeconomic problems affecting the three million Puerto Ricans residing in the 50 states. The main concentration of the population was in New York City. | |||
| In the 1960s and the following 1970s, Hispanic-American culture was on the rebound like ethnic music, foods, culture and identity both became popular and assimilated into the American mainstream. Spanish-language television networks, radio stations and newspapers increased in presence across the country, especially in U.S.–Mexican border towns and East Coast cities like New York City, and the growth of the ] community in Miami, Florida. | |||
| The multitude of discrimination at this time represented an inhuman side to a society that in the 1960s was upheld as a world and industry leader. The issues of civil rights and warfare became major points of reflection of virtue and democracy, what once was viewed as traditional and inconsequential was now becoming the significance in the turning point of a culture. A document known as the Port Huron Statement exemplifies these two conditions perfectly in its first hand depiction, "while these and other problems either directly oppressed us or rankled our consciences and became our own subjective concerns, we began to see complicated and disturbing paradoxes in our surrounding America. The declaration "all men are created equal..." rang hollow before the facts of Negro life in the South and the big cities of the North. The proclaimed peaceful intentions of the United States contradicted its economic and military investments in the Cold War status quo." These intolerable issues became too visible to ignore therefore its repercussions were feared greatly, the realization that we as individuals take the responsibility for encounter and resolution in our lives issues was an emerging idealism of the 1960s. | |||
| ===Second-wave feminism=== | |||
| {{Main|Second-wave feminism}} | |||
| A second wave of feminism in the United States and around the world gained momentum in the early 1960s. While the first wave of the early 20th century was centered on gaining suffrage and overturning ''de jure'' inequalities, the second wave was focused on changing cultural and social norms and ''de facto'' inequalities associated with women. At the time, a woman's place was generally seen as being in the home, and they were excluded from many jobs and professions. In the U.S., a ] found discrimination against women in the workplace and every other aspect of life, a revelation which launched two decades of prominent women-centered legal reforms (i.e., the ], ], etc.) which broke down the last remaining legal barriers to women's personal freedom and professional success. | |||
| Feminists took to the streets, marching and protesting, authoring books and debating to change social and political views that limited women. In 1963, with ]'s book, '']'', the role of women in society, and in public and private life was questioned. By 1966, the movement was beginning to grow in size and power as women's group spread across the country and Friedan, along with other feminists, founded the ]. In 1968, "]" became a household term as, for the first time, the new women's movement eclipsed the ] when ], led by ], ] in ]. The movement continued throughout the next decades. ] was a key feminist. | |||
| ===Gay rights movement=== | |||
| {{Main|Gay liberation|LGBT social movements}} | |||
| The United States, in the middle of a social revolution, led the world in LGBT rights in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Inspired by the civil-rights movement and the women's movement, early gay-rights pioneers had begun, by the 1960s, to build a movement. These groups were rather conservative in their practices, emphasizing that ''gay men and women are no different from those who are straight'' and deserve full equality. This philosophy would be dominant again after AIDS, but by the very end of the 1960s, the movement's goals would change and become more radical, demanding a right to be different, and encouraging ]. | |||
| The symbolic birth of the ] would not come until the decade had almost come to a close. Gays were not allowed by law to congregate. Gay establishments such as the ] in New York City were routinely raided by the police to arrest gay people. On a night in late June 1969, LGBT people resisted, for the first time, a police raid, and rebelled openly in the streets. This uprising called the ] began a new period of the LGBT rights movement that in the next decade would cause dramatic change both inside the LGBT community and in the mainstream American culture. | |||
| ===New Left=== | |||
| The rapid rise of a "]" applied the class perspective of ] to postwar America but had little organizational connection with older Marxist organizations such as the ], and even went as far as to reject organized labor as the basis of a unified left-wing movement. Sympathetic to the ideology of ], the New Left differed from the traditional left in its resistance to dogma and its emphasis on personal as well as societal change. ] (SDS) became the organizational focus of the New Left and was the prime mover behind the opposition to the War in Vietnam. The 1960s left also consisted of ephemeral campus-based ], ] and ] groups, some of which by the end of the 1960s had turned to ]. | |||
| ===Crime=== | |||
| The 1960s was also associated with a large increase in crime and urban unrest of all types. Between 1960 and 1969 reported incidence of violent crime per 100,000 people in the United States nearly doubled and have yet to return to the levels of the early 1960s.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/statab/hist/HS-23.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924134627/http://www.census.gov/statab/hist/HS-23.pdf|url-status=dead|title=U.S. Census Bureau Data |archive-date=24 September 2015}}</ref> Large riots broke out in many cities like Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York City, ], ] and Washington, D.C. By the end of the decade, politicians like ] and ] campaigned on restoring law and order to a nation troubled with the new unrest. | |||
| ==Science and technology== | |||
| ===Science=== | |||
| ====Space exploration==== | |||
| ] crew took a picture, for the first time in history, of the entire Earth]] | |||
| ] mission landed the first humans on the Moon in July 1969.]] | |||
| The ] between the United States and the Soviet Union dominated the 1960s. The Soviets sent the first man, ], into ] during the ] mission on 12 April 1961, and scored a host of other successes, but by the middle of the decade the U.S. was taking the lead. In May 1961, President Kennedy set the goal for the United States of landing a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s. | |||
| In June 1963, ] became the first woman in space during the ] mission. In 1965, Soviets launched the first probe to hit another planet of the ] (]), ], and the first probe to make a soft landing on and transmit from the surface of the Moon, ]. In March 1966, the Soviet Union launched ], which became the first ] to enter orbit around the Moon, and in September 1968, ] flew the first terrestrial beings, including two tortoises, to circumnavigate the Moon. | |||
| The deaths of astronauts ], ], and ] in the ] fire on 27 January 1967, put a temporary hold on the U.S. space program, but afterward progress was steady, with the ] crew (], ], ]) being the first crewed mission to orbit another celestial body (the Moon) during Christmas of 1968. | |||
| On 20 July 1969, the ]. The ] mission, launched on 16 July 1969, carried mission Commander ], Command Module Pilot ], and Lunar Module Pilot ], and Aldrin and Armstrong flew the Lunar Module '']'' to the lunar surface. Apollo 11 fulfilled President ]'s goal of reaching the Moon by the end of the 1960s, which he had expressed during a speech given before a joint session of Congress on 25 May 1961: "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth." | |||
| The Soviet program lost its sense of direction with the death of chief designer ] in 1966. Political pressure, conflicts between different design bureaus, and engineering problems caused by an inadequate budget would doom the Soviet attempt to land men on the Moon. Shortly after the American Apollo 1 disaster, tragedy struck the Soviet program when cosmonaut ] was killed when the parachutes on his ] flight failed. | |||
| A succession of uncrewed American and Soviet probes traveled to the Moon, ], and ] during the 1960s, and commercial satellites also came into use. | |||
| ====Other scientific developments==== | |||
| ] was introduced in 1960.]] | |||
| * 1960 – The oral female birth-control contraceptive, ], was released in the United States after ] (FDA) approval. | |||
| * 1963 – The measles vaccine was released after being approved by the FDA | |||
| * 1963 – ] is awarded the Nobel prize for discovering the ] of the ] | |||
| * 1964 – The discovery and confirmation of the ] in 1964 secured the Big Bang as the best theory of the origin and evolution of the universe. | |||
| * 1965 – ] introduced. | |||
| * 1967 – First ] operation by Professor ] in South Africa. | |||
| * 1967 – Discovery of the first known ] (a rapidly spinning ]) by ] | |||
| * During the late 1960s, the ] achieved a major leap in agricultural production, mitigating a potential famine situation.<ref>{{cite book|author=Peter B.R. Hazell|title=The Asian Green Revolution|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=frNfVx-KZOcC&pg=PA1|year=2009|work=IFPRI Discussion Paper|publisher=Intl Food Policy Res Inst|access-date=2022-02-18|archive-date=28 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201028040330/https://books.google.com/books?id=frNfVx-KZOcC&pg=PA1|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Technology=== | |||
| ] | |||
| * ], the world's first ] service began in 1964. | |||
| ====Automobiles and Motorcycles==== | |||
| As the 1960s began, American cars showed a rapid rejection of 1950s styling excess, and would remain relatively clean and boxy for the entire decade. The horsepower race reached its climax in the late 1960s, with ] sold by most makes. The compact ], launched in 1964, was one of the decade's greatest successes. The "]" American automakers enjoyed their highest ever sales and profitability in the 1960s, but the demise of ] in 1966 left ] as the last significant independent. The decade would see the car market split into different size classes for the first time, and model lineups now included ] and ] cars in addition to ] ones. | |||
| The popular modern hatchback, with front-wheel-drive and a two-box configuration, was born in 1965 with the introduction of the ], many of this car's design principles live on in its modern counterparts: a large rear opening incorporating the rear window, foldable rear seats to extend boot space. The ], released in 1959, had first popularised the front wheel drive two-box configuration, but technically was not a hatchback as it had a fold-down bootlid. | |||
| Japanese cars also began to gain acceptance in the Western market, and popular economy models such as the ], ], and the first popular Japanese sports car, the ], were released in the mid- to late-1960s. | |||
| Mopeds and Scooters gains popularity in these decade, with ] in United States, Japan and Europe, ] in Japan and ], ],] and ] mopeds in Western Europe. | |||
| ====Electronics and communications==== | |||
| ] | |||
| * 1960 – The first working laser was demonstrated in May by ] at ]. | |||
| * 1960 – ] announces the ] ], the most common sorter on computers. | |||
| * 1961 – ], the first ], was introduced. | |||
| * 1962 – First transatlantic satellite broadcast via the ] satellite. | |||
| * 1962 – The ] coding language was invented by ] | |||
| * 1962 – The first computer video game, '']'', was invented. | |||
| * 1962 – Red ]s were developed. | |||
| * 1963 – The first ], '']'', is launched. | |||
| * 1963 – First transpacific satellite broadcast via the ] satellite. | |||
| * 1963 – ] telephones introduced. | |||
| * 1963 – ] was the first touch interactive ] program. | |||
| * 1963 – The ] Electronic Valve company produced the first home ] called the "Telcan". | |||
| * 1964 – ] audio format was developed. | |||
| * 1964 – The ] was introduced. | |||
| * 1964 – The first successful ], ]'s 12-bit ], was marketed. | |||
| * 1964 – The ] ] was created. | |||
| * 1964 – The world's first ], the ], was introduced. | |||
| * 1964 – ] released ]s with ]. | |||
| * 1967 – ] and ] broadcast color television systems started publicly transmitting in Europe. | |||
| * 1967 – The first ] was opened in ], London. | |||
| * 1967 – The ] coding language was invented by ] | |||
| * 1968 – ] developed his ] (a working prototype of the Magnavox Odyssey). | |||
| * 1968 – The ] of the ], the ] ], ], ], email, and ]. | |||
| * 1969 – ], the research-oriented prototype of the Internet, was introduced. | |||
| * 1969 – ] invented at AT&T ], used as the electronic imager in still and video cameras. | |||
| ==Additional notable worldwide events== | |||
| * The ] occurred between 8–10 August 1969 when actress ], coffee heiress ] and several others were brutally murdered in the Tate residence by ]'s "family." ] and ] were also murdered by the Manson family the following night. | |||
| * ] celebrated its 100th anniversary of ] in 1967 by hosting ] in ], ]. During the anniversary celebrations, French president ] visited Canada and caused a considerable uproar by declaring his support for Québécois independence. | |||
| * The ] first became active after murdering five known victims in the San Francisco Bay Area between December 1968 and October 1969, operating in rural, urban and suburban settings. | |||
| ==Popular culture== | |||
| <gallery widths="190" perrow="5"> | |||
| File:Doctor Who logo 1963-1967.jpg|TV shows like '']'', '']'', ''],'' '']'', ''],'' and ]'s '']'' were popular in the 1960s (the latter garnering a much wider audience in the following decades and becoming a ]). | |||
| File:Beatles ad 1965 just the beatles crop.jpg|] (consisting of ], ], ], and ]) released music throughout the 1960s, and are often considered the most popular band in global history. ] was/is the fanaticism surrounding The Beatles. The Beatles experienced intense fan worship during the '60s era. | |||
| File:Bob Dylan in November 1963-2.jpg|] is often considered to be one of the greatest songwriters of all time, and through a process of mutual influence with The Beatles and other artists, helped define the explosion of musical ideas in the 1960s. | |||
| File:PeaceAndLoveBus.svg|] and ] were an aesthetic of the ] and ] movements of the 1960s and later in the 1970s. | |||
| File:19680810 20 Anti-War March.jpg|]s like the ] were ] and ]s against various forms of governmental jurisdiction and ]. These protests were a major part of 1960s and 1970s popular culture. | |||
| File:1969-NBC.jpg|] cartoons such as '']'', '']'', ''], ], ]'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']'' were popular in the 1960s. | |||
| File:Woodstock redmond stage.JPG|Crowds at the stage during the ], two months after the ] in June 1969. | |||
| File:TokyoOlympics1964Opening.jpg|Six Olympic Games were held in the 1960s, ] and ], ] and ], ] and ] (all during the Cold War). | |||
| File:Buzz salutes the U.S. Flag.jpg|The 1960s were the height of the ] and space aesthetics in popular culture. In 1969, humans ] for the first time. | |||
| File:1960s Batmobile (FMC).jpg|The superhero boom of the decade saw in media and popular culture, TV series like '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']'' were more popular. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| The ] dominated the second half of the 1960s, its most famous moments being the ] in San Francisco in 1967, and the ] in ] in 1969. ], especially ], were widely used medicinally, spiritually and recreationally throughout the late 1960s, and were popularized by ] with his slogan "]". ] and the ] also played a part in the role of "turning heads on". ] influenced the music, artwork and films of the decade, and a number of prominent musicians died of drug overdoses (see ]). There was a growing interest in Eastern religions and philosophy, and many attempts were made to found communes, which varied from supporting free love to religious puritanism. | |||
| === Music === | |||
| ] pictured in 1962. Known as ]'s "] supergroup", The Miracles were one of the first commercially successful acts of the 1960s and propelled both Motown and its ] label to international fame.]] | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | image1 = The Beatles i Hötorgscity 1963.jpg | |||
| | width1 = 179 | |||
| | alt1 = Beatles | |||
| | caption1 = The arrival of ] in the U.S. during 1964, and particularly their appearance on television's '']'', marked the beginning of the ] in the history of music, in which a large number of rock and pop music acts from the United Kingdom gained enormous popularity in the U.S. | |||
| | image2 = Joan Baez Bob Dylan crop.jpg | |||
| | width2 = 165 | |||
| | alt2 = Dylan | |||
| | caption2 = ] was the face of the ] of the 1960s. In 1964, Dylan was shifting his focus to more abstract and introspective themes, and eventually would ], alienating many in the folk crowd. | |||
| | footer_align = | |||
| | footer = | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| | quote = "The 60s were a leap in human consciousness. ], ], ], ], ], they led a revolution of conscience. ], ], ] created revolution and evolution themes. The music was like ], with many colors and revolutionary ways. The youth of today must go there to find themselves." | |||
| | source = – ]<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101223045640/http://puntodigital.com/carlos-santana-im-immortal/224228/ |date=23 December 2010 }} interview by ''Punto Digital'', 13 October 2010</ref> | |||
| | width = 30% | |||
| }} | |||
| The rock 'n' roll movement of the 1950s quickly came to an end in 1959 with ] (as explained in the song "]"), the scandal of ]' marriage to his 13-year-old cousin, and the induction of ] into the ]. As the 1960s began, the major rock 'n' roll stars of the '50s such as ] and ] had dropped off the charts and popular music in the U.S. came to be dominated by girl groups, ], novelty pop songs, clean-cut teen idols, and ] music. Another important change in music during the early 1960s was the ] which introduced ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and many other singer-songwriters to the public. | |||
| Girl groups and female singers, such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] dominated the charts in the early 1960s. This style consisted typically of light pop themes about teenage romance and lifestyles, backed by vocal harmonies and a strong rhythm. Most girl groups were African-American, but white girl groups and singers, such as ], ], and ] also emerged during this period. | |||
| Around the same time, record producer ] began producing girl groups and created a new kind of pop music production that came to be known as the ]. This style emphasized higher budgets and more elaborate arrangements, and more melodramatic musical themes in place of a simple, light-hearted pop sound. Spector's innovations became integral to the growing sophistication of popular music from 1965 onward. | |||
| Also during the early 1960s, ] emerged, a rock subgenre that was centered in Southern California and based on beach and surfing themes, in addition to the usual songs about teenage romance and innocent fun. ] quickly became the premier surf rock band and almost completely and single-handedly overshadowed the many lesser-known artists in the subgenre. Surf rock reached its peak in 1963–1965 before gradually being overtaken by bands influenced by the ] and the counterculture movement. | |||
| The ] also emerged as a rock subgenre in the early 1960s, which focused on teenagers' fascination with ]. The Beach Boys also dominated this subgenre, along with the duo ]. Such notable songs include "]", "]", and "]", all by the Beach Boys; ]'s "]" and "]", ]' "]", and many others. Like girl groups and surf rock, car songs also became overshadowed by the British Invasion and the counterculture movement. | |||
| The early 1960s also saw the golden age of another rock subgenre, the ], which focused on lost teen romance caused by sudden death, mainly in ]. Such songs included ]'s "]", ]'s "]", ]'s "]", ]' "]", and perhaps the subgenre's most popular, "]" by ]. | |||
| In the early 1960s, Britain became a hotbed of rock 'n' roll activity during this time. In late 1963, the Beatles embarked on their first US tour and cult singer ] released her first solo single. A few months later, rock 'n' roll founding father ] emerged from a {{frac|2|1|2}}-year prison stint and resumed recording and touring. The stage was set for the spectacular revival of rock music. | |||
| In the UK, the Beatles played raucous rock 'n' roll – as well as doo wop, girl-group songs, show tunes – and wore leather jackets. Their manager ] encouraged the group to wear suits. ] abruptly exploded after the group's appearance on '']'' in 1964. Late in 1965, the Beatles released the album '']'' which marked the beginning of their transition to a sophisticated power pop group with elaborate studio arrangements and production, and a year after that, they gave up touring entirely to focus only on albums. A host of imitators followed the Beatles in the so-called British Invasion, including groups like ], ] and ] who would become legends in their own right. | |||
| As the counterculture movement developed, artists began making new kinds of music influenced by the use of psychedelic drugs. Guitarist ] emerged onto the scene in 1967 with a radically new approach to electric guitar that replaced Chuck Berry, previously seen as the gold standard of rock guitar. Rock artists began to take on serious themes and social commentary/protest instead of simplistic pop themes. | |||
| A major development in popular music during the mid-1960s was the movement away from singles and towards albums. Previously, popular music was based around the 45 single (or even earlier, the 78 single) and albums such as they existed were little more than a hit single or two backed with filler tracks, instrumentals, and covers. The development of the AOR (album-oriented rock) format was complicated and involved several concurrent events such as Phil Spector's Wall of Sound, the introduction by Bob Dylan of "serious" lyrics to rock music, and the Beatles' new studio-based approach. In any case, after 1965 the vinyl LP had definitively taken over as the primary format for all popular music styles. | |||
| Blues also continued to develop strongly during the '60s, but after 1965, it increasingly shifted to the young white rock audience and away from its traditional black audience, which moved on to other styles such as soul and funk. | |||
| ] music and ] during the first half of the 1960s was largely a continuation of 1950s styles, retaining its core audience of young, urban, college-educated whites. By 1967, the death of several important jazz figures such as ] and ] precipitated a decline in the genre. The takeover of rock in the late 1960s largely spelled the end of jazz and standards as mainstream forms of music, after they had dominated much of the first half of the 20th century. | |||
| ] gained popularity on the ], due in large part to the ], led by ] and ]. Female country artists were also becoming more mainstream (in a genre dominated by men in previous decades), with such acts as ], ], and ]. | |||
| Late 1960s also was the beginning of ], which became more popular in 1970s. | |||
| ====Significant events in music in the 1960s==== | |||
| * ] returned to civilian life in the U.S. after two years away in the ]. He resumes his musical career by recording "]" and "]" in March 1960.<ref>Jorgensen, Ernst (1998). ''Elvis Presley: A life in music. The complete recording sessions'', p.120. St. Martin's Press. {{ISBN|0-312-18572-3}}</ref> | |||
| * Country music stars ], ] and ] were killed when their plane ] in Camden, Tennessee while returning home from a ] benefit show in March 1963. | |||
| * In July 1964, a plane crash claimed the life of another country music legend, ], when the plane he was piloting crashed in a turbulent thunderstorm while on final approach to ]. | |||
| * ] was shot and killed at a motel (at the age of 33) in Los Angeles, California on 11 December 1964, under suspicious circumstances. | |||
| * ] was founded in 1960. Its first ] hit was "]" by the Miracles in 1960. "Shop Around" peaked at number-two on the ] and was Motown's first million-selling record. | |||
| * Newcastle-born ] and his band "]" hit the No. 1 in charts in the U.S. with their hit single "]" in 1964. | |||
| * Folk singer and activist ] released her ] on ] in December 1960. | |||
| * ] scored Motown's first U.S. No. 1 pop hit, "]", in 1961. Motown would score 110 ''Billboard'' Top 10 hits during its run. | |||
| * ] released three straight number one hits. | |||
| * In a widely anticipated and publicized event, ] arrive in America in February 1964, spearheading the ]. | |||
| * The '']'' original soundtrack tops record charts. ] receive ] and double ]. | |||
| * ] hits number one on ''Billboard'' with "]" and number two with "You Don't Own Me" at the age of 17 (behind "]" by The Beatles). | |||
| * ] scored twelve number-one hit singles between 1964 and 1969, beginning with "]". | |||
| * ] release "]" in August 1964, which tops the British charts; it is regarded as the first ] hit and a blueprint for related genres such as ].<ref name="YRGM All">{{cite web|title=You Really Got Me|url=https://www.allmusic.com/song/t630847|website=AllMusic|last=Sullivan|first=Denise|access-date=25 November 2009|archive-date=13 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220913055439/https://www.allmusic.com/song/you-really-got-me-mt0033940816|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| * ] released '']'' in late 1964, considered one of the most acclaimed jazz albums of the era. | |||
| * The ] was formed in 1965 (originally The Warlocks), thus paving the way for the emergence of ]. | |||
| * ] went ] at the 1965 ]. | |||
| * ]'s number-one hit "]" still remains the top-selling single by a female artist in the UK from 1964. | |||
| * ] had a huge No. 1 hit with their song "]" in the summer of 1965. | |||
| * ] released a cover of Bob Dylan's "]", which reached No. 1 on the U.S. charts and repeated the feat in the U.K. shortly thereafter. The extremely influential track effectively creates the musical subgenre of ]. | |||
| * Bob Dylan's "]" is a top-five hit on both sides of the Atlantic during the summer of 1965. | |||
| * Bob Dylan's 1965 albums '']'' and '']'' ushered in album-focused rock and the ] genre. | |||
| ] were a popular musical duo of the era]] | |||
| * ] released the single "]" in 1965. | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1966, which significantly influenced The Beatles' '']'' album released the following year. | |||
| * Bob Dylan was called "Judas" by an audience member during the ] ]; the start of the ] industry follows, with recordings of this concert circulating for 30 years – wrongly labeled as ''The Royal Albert Hall Concert'' – before a legitimate release in 1998 as ''].'' | |||
| * In February 1966, Nancy Sinatra's song "]{{thin space}}" became very popular. | |||
| * In 1966, '']'' was the first album by a female group to reach the top position of the ] in the United States. | |||
| * ] were the first Australian group to have a number one with "]" in 1966. | |||
| * ] released the influential '']'' in 1967. | |||
| * ] released its self-titled debut album, '']'', in 1967. | |||
| * ] released its self-titled debut album, '']'', in January 1967. | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1967. | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1967. | |||
| * ] released "]" in 1967. | |||
| ] launched the mainstream career of Jimi Hendrix, one of the most influential electric guitarists in history]] | |||
| * ] released two successful albums during 1967 ('']'' and '']'') that innovate both guitar, trio and recording techniques. | |||
| * ] released the album '']'' in November 1967. | |||
| * R&B legend ] has his first No. 1 hit with "]". He also played at the ] in 1967 just before he died in a plane crash. | |||
| * ] released its debut record, '']''. | |||
| * ] released the ] album '']'' in December 1967. | |||
| * The ] released their international debut album, '']'', in July 1967; it included the pop standard "]". | |||
| * The ] in 1967 was the beginning of the "]". | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1967. It was nicknamed "The Soundtrack of the Summer of Love". | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1968. | |||
| * After ] folded, ] was formed by ] and manager ] in 1968 with ], ], ], and Page as members; they released their debut album, '']'', the next year. | |||
| * ], with ] as lead singer, became an overnight sensation after their performance at the ] in 1967 and released their second album '']'' in 1968. | |||
| * ] with ] released the influential LP '']'' in late 1968, forming the basis for ]. | |||
| * ] released the influential double LP '']'' in 1968 that furthered the guitar and studio innovations of his previous two albums. | |||
| * ] released the single "]" in 1968, featured in the film '']''. | |||
| * Country music newcomer ] released the country and pop hit "]" in 1968, which is about a ]-wearing mother of a teenage girl who was criticized by the local ] for supposedly setting a bad example for her daughter but turns the tables by exposing some of the PTA members' wrongdoings. The song, along with Riley's ] persona in connection with it, apparently gave country music a "sexual revolution" of its own as hemlines of other female country artists' stage dresses began rising in the years that followed. | |||
| * ] revolutionized black music with their 1968 hit single "]" and became international sensations by 1969 with the release of their hit record '']''. The band cemented their position as a vital counterculture band when they performed at the ]. | |||
| * ] released "Race with the Devil" in October 1968. | |||
| * After a long performance drought, ] made a successful return to TV and live performances after spending most of the decade making movies, beginning with his '']'' in December 1968 on ], followed by a summer engagement in ] in 1969. Presley's return to live performing set the stage for his many concert tours and continued Vegas engagements throughout the 1970s until his death in 1977. | |||
| * ] released "]" in December 1968. | |||
| * The Rolling Stones filmed the TV special '']'' in December 1968 but the film was not released for transmission. It was considered a fabled "lost" performance for decades until it was released in North America on ] and ] in 1996. The special features performances from ], ] (featuring ], ] and ]), ] and ]. | |||
| * ] released their second album, '']'', in March 1969. The album was an important hard rock milestone. | |||
| * The ] (and the ] four months later) in 1969. | |||
| * ] released and toured the first rock opera, '']'', in 1969. | |||
| * Proto-punk band ] released the live album '']'' in 1969. | |||
| * ] released the ] '']'' in 1969. | |||
| * ] released "]" in 1969. The song amassed popularity with the ] at the time and would later be used in films, TV shows and video games depicting the ] or the ] during the late 1960s and early 1970s. | |||
| * ] released their debut album in 1969. | |||
| * ] released '']'' in 1969. | |||
| * ] released their debut album, '']'', in 1969. | |||
| * ] released two of their self-titled debut albums, '']'' and '']'', in 1969. | |||
| ===Film=== | |||
| {{See also|History of film#1960s|1960s in film}} | |||
| ] in '']'' (1962)]] | |||
| The highest-grossing film of the decade was 20th Century Fox's '']'' (1965).<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010710051059/https://boxofficemojo.com/alltime/adjusted.htm|date=10 July 2001}}. ].</ref> | |||
| Some of Hollywood's most notable ] of the 1960s include: | |||
| <!--at August 2012, unclear order. probably year of release? research before alphabetizing. probably best to leave release-year order with year of release appended following title--> | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| The counterculture movement had a significant effect on cinema. Movies began to break social taboos such as ] and ] causing both controversy and fascination. They turned increasingly dramatic, unbalanced, and hectic as the cultural revolution was starting. This was the beginning of the ] era that dominated the next decade in theatres and revolutionized the film industry. Films of this time also focused on the changes happening in the world. ]'s '']'' (1969) focused on the ] of the time. Movies also became more sexually explicit, such as ]'s'' ]'' (1968), as the ] progressed. | |||
| In Europe, ] gained wider distribution and saw movements like ] (The French New Wave), which featured French filmmakers such as ], ], ], and ]; the ] documentary movement took place in Canada, France and the United States; ] ], ] ] and ] ] and ] produced original and offbeat masterpieces and the high-point of ] with ] and ] making some of their most known films during this period. Notable films from this period include: '']'', '']''; '']''; '']'', '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; ''];'' '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; '']''; and the ] '']''. | |||
| ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] in ]'s '']'', 1960]] | |||
| In Japan, '']'' a film version of the story of the ] directed by ], was released in 1962; the legendary story was also remade as a television series in Japan. Academy Award-winning ] director ] produced '']'' (1961) and '']'' (1962), which both starred ] as a mysterious ] swordsman for hire. Like his previous films both had a profound influence around the world. The '']'' genre was a direct outgrowth of the Kurosawa films. The influence of these films is most apparent in ]'s '']'' (1964) starring ] and ]'s '']'' (1996). ''Yojimbo'' was also the origin of the "]" trend which included Sergio Leone's '']'', and '']'' both also starring Clint Eastwood, and arguably continued through his 1968 opus '']'', starring ], ], ], and ]. '']'' a 1960 American ] directed by ] was a ] of ]'s 1954 film, '']''. Another popular figure in this genre was ], with films from the 60s such as '']'' (1962), '']'' (1966), '']'' (1969) and others. | |||
| The 1960s were also about experimentation. With the explosion of lightweight and affordable cameras, the underground ] movement thrived. The movement's notable figures include Canada's ] and Americans ], ], ], and ]. Notable films in this genre include '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. | |||
| ], the founder of ], died on 15 December 1966 from a major tumor in his left lung. Alongside '']'', '']'' and '']'' (some of his most important blockbusters), animated feature films of the decade that are of notable status include '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'' and '']''. | |||
| ====Significant events in the film industry in the 1960s==== | |||
| *Removal of the ]'s ] in 1967. | |||
| *The MPA's establishment of the ] in 1968. | |||
| *The decline and end of the ]. | |||
| *The rise of ] films and theaters. | |||
| *The end of the ] era. | |||
| *The beginning of the ] Era due to the counterculture. | |||
| *The rise of independent producers that worked outside the studio system. | |||
| *Move to all-color production in Hollywood films. | |||
| *The invention of the ] 1/4", sync-sound, portable open-reel tape deck. | |||
| *New film formats like ] are invented and new ways of displaying film are tested at ]. | |||
| *Flat-bed film editing tables (like the ]) appear; they eventually replace the ] editing platform. | |||
| *The ] reaches its peak. | |||
| *] and ] documentaries. | |||
| *The beginning of the ] in 1969, which continued throughout the 1970s and into the first half of the 1980s. | |||
| ===Television=== | |||
| {{Main|1960s in television}} | |||
| The most prominent TV series of the 1960s include '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. ''The Flintstones'' was a popular show, receiving 40 million views an episode with an average of 3 million views a day. ''Doctor Who'' is the longest-running science-fiction show of all time according to the '']''. Some programming (such as '']'') became controversial by challenging the foundations of America's corporate and governmental controls, making fun of world leaders and questioning U.S. involvement in (as well as escalation of) the ]. | |||
| ===Fashion=== | |||
| {{Main|1960s in fashion}} | |||
| Significant fashion trends of the 1960s include: | |||
| * ] exerted an enormous influence on young men's fashions and hairstyles in the 1960s which included most notably the ], the ] and the ]. | |||
| * The ] movement late in the decade also had a strong influence on clothing styles, including ], ] and ] fabrics, as well as ] prints. | |||
| * The ] came into fashion in 1963 after being featured in the film '']''. | |||
| * ] popularised the ], which became one of the most popular fashion rages in the late 1960s among young women and teenage girls. Its popularity continued throughout the first half of the 1970s and then disappeared temporarily from mainstream fashion before making a comeback in the mid-1980s. | |||
| * Men's mainstream hairstyles ranged from the ], the ], the ] hairstyle, the tapered hairstyle, and short, parted hair in the early part of the decade, to longer parted hairstyles with ] towards the latter half of the decade. | |||
| * Women's mainstream hairstyles ranged from ], the bird's nest hairstyle, and the ] hairstyle in the early part of the decade, to very short styles popularized by ] and ] in ] towards the latter half of the decade. | |||
| * African-American hairstyles for men and women included the ]. | |||
| <gallery widths="190" perrow="5"> | |||
| File:Mop-top hair.jpg|Members of Argentine rock band ] sporting ]s, which were considered at the time a rebellious hairstyle. | |||
| File:On the Beach at Tiberias.jpg|The ] became a fashionable item in the Western world during the decade | |||
| File:Londons_Carnaby_Street,_1966.jpg|"Swinging London" fashions on ], {{Circa|1966}} | |||
| File:Tie dye T-shirts.jpg|] shirts of all colors were at their height and worn by many during the 1960s. | |||
| File:Lava lamps (16136876840).jpg|]s (released in the late 1940s) became very prevalent in the 1960s and were used as decorations. | |||
| File:Go-go boots by Andre Courreges, 1965.jpg|]s were a popular piece of fashion, worn by many. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ===Literature=== | |||
| {{see also|List of years in literature#1960s}} | |||
| * ] by S.E. Hinton was a massively popular novel during the decade. It illustrated the difficult life for the working class at the time.<ref>{{Cite web |last=August |first=Jude |date=2022-05-02 |title=How "The Outsiders" Became the Origin of YA Literature |url=https://medium.com/@judeaugust/how-the-outsiders-became-the-origin-of-ya-literature-d8636a971ea6 |access-date=2023-12-27 |website=Medium |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Sports === | |||
| The first ever Super bowl had happened in 1967 in Los Angeles, California | |||
| ====Olympics==== | |||
| There were six ] held during the decade. These were: | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 25 August – 11 September 1960, in Rome, Italy | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 18–28 February 1960, in ], California, United States | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 10–24 October 1964, in Tokyo, Japan | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 29 January – 9 February 1964, in ], Austria | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 12–27 October 1968, in ], Mexico | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} 6–18 February 1968, in ], France | |||
| ====Association football==== | |||
| There were two ]s during the decade: | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} hosted in Chile, won by Brazil | |||
| * ]{{spaced ndash}} hosted and won by England | |||
| ====Baseball==== | |||
| The first wave of ] expansion in 1961 included the formation of the ], the move to Minnesota to become the ] by the ] and the formation of a ]. Major League Baseball sanctioned both the ] and the ] as new ] franchises in 1962. | |||
| In 1969, the ] expanded when the ] and ], were admitted to the league prompting the expansion of the post-season (in the form of the ]) for the first time since the creation of the World Series. The Pilots stayed just one season in Seattle before moving and becoming the ] in 1970. The National League also added two teams in 1969, the ] and ]. By 1969, the New York Mets won the ] in only the 8th year of the team's existence. | |||
| ====Basketball==== | |||
| The ] tournaments during the 1960s were dominated by the ], who won eight straight titles from 1959 to 1966 and added two more consecutive championships in 1968 and 1969, aided by such players as ], ] and ]. Other notable NBA players included ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| At the ] level, the ] also proved dominant. Coached by ], they were helped by ] and by ] to win championships and dominate the American college basketball landscape during the decade. | |||
| ====Disc sports (Frisbee)==== | |||
| Alternative sports, using the flying disc, began in the mid-sixties. As numbers of young people became alienated from social norms, they resisted and looked for alternatives. They would form what would become known as the ]. The forms of escape and resistance would manifest in many ways including social activism, alternative lifestyles, experimental living through foods, dress, music and alternative recreational activities, including that of throwing a ].<ref>{{cite book|title=Countercultural Sports in America: The History and Meaning of Ultimate Frisbee|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qycPRAAACAAJ|author=Jordan Holtzman-Conston|publisher=Waltham, Mass|year=2010|isbn=978-3838311951|access-date=28 December 2017|archive-date=24 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200724120036/https://books.google.com/books?id=qycPRAAACAAJ|url-status=live}}</ref> Starting with promotional efforts from ] and ] (Canada), a few tournaments and professionals using ] show tours to perform at universities, fairs and sporting events, disc sports such as ], ], ], ] and ] became this sports first events.<ref>{{cite web|title=World Flying Disc Federation|url=http://wfdf.org/|work=WFDF Official Website|access-date=19 October 2013|archive-date=18 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131018043512/http://wfdf.org/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=World Flying Disc Federation |url=http://wfdf.org/history-stats/history-of-fyling-disc |work=History of the Flying Disc |access-date=20 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131019095944/http://wfdf.org/history-stats/history-of-fyling-disc |archive-date=19 October 2013 }}</ref> Two sports, the team sport of ] and ] are very popular worldwide and are now being played semiprofessionally.<ref>{{cite web|title=Professional Disc Golf Association|url=http://www.pdga.com/|work=PDGA Official Website|access-date=19 October 2013|archive-date=9 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210509023305/https://www.pdga.com/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=American Ultimate Disc League|url=http://theaudl.com/|work=AUDL Official Website|access-date=20 October 2013|archive-date=21 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151021064303/http://theaudl.com/|url-status=live}}</ref> The ], ] and the Freestyle Players Association are the official rules and sanctioning organizations for flying disc sports worldwide. ] (MLU) and the ] (AUDL) are the first semi-professional ultimate leagues. | |||
| ====Racing==== | |||
| In ], the ] and ] series were both established in 1966. The ] won outright in the ]. Graham Hill edged out Jackie Stewart and Denny Hulme for the World Championship in Formula One. | |||
| == People == | |||
| ===Activists=== | |||
| Some activist leaders of the 1960s period include: | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=18em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Joan Baez 1963.jpg|] | |||
| File:Dick Gregory.jpg|] | |||
| File:John Lewis 1964-04-16 (cropped).jpg|] | |||
| File:Jerry Rubin (edit) - Spectrum 13Mar1970.jpg|] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Actors and entertainers=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=18em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery widths="160px" heights="150px" perrow="5"> | |||
| File:Brigitte_Bardot_-_1962.jpg|], 1962 | |||
| File:Audrey Hepburn (cropped).jpg|], 1963 | |||
| File:Clint Eastwood - 1960s (cropped).JPG|], 1964 | |||
| File:Sean Connery 1964.png|], 1964 | |||
| Image:Paul Newman Harper.jpg|], 1966 | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Filmmakers=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=18em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery widths="160px" heights="160px" perrow="4"> | |||
| Image:Hitchcock,_Alfred_02.jpg|] | |||
| File:Ingmar Bergman Smultronstallet.jpg|] | |||
| File:Federico Fellini NYWTS 2.jpg|] | |||
| File:Kubrick on the set of Barry Lyndon (1975 publicity photo).jpg|] | |||
| File:Jean-Luc Godard at Berkeley, 1968.jpg|] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Musicians and singers=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery widths="160px" heights="160px" perrow="4"> | |||
| File:Willie Nelson Grand Ole Opry publicity - cropped.jpg|], 1965 | |||
| File:Aretha Franklin 1968.jpg|], 1968 | |||
| File:JohnnyCash1969.jpg|], 1969 | |||
| File:Janis Joplin seated 1970.JPG|], 1969 | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Bands=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery widths="160px" heights="160px" perrow="4"> | |||
| File:The_Beatles_performing_at_The_Ed_Sullivan_Show_(cropped_2).jpg|], 1964 | |||
| File:Sullivan Beach Boys (cropped).jpg|], 1964 | |||
| File:The Doors in Copenhagen 1968.jpg|], 1968 | |||
| File:CreamDutchTV1968.jpg|], 1968 | |||
| File:The Temptations on the Ed Sullivan Show.JPG|], 1969 | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Writers=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Isaac.Asimov01.jpg|] | |||
| File:James Baldwin 37 Allan Warren (cropped).jpg|] | |||
| File:Arthur C. Clarke 1965.jpg|] | |||
| File:Philip K Dick in early 1960s (photo by Arthur Knight) 02 (cropped).jpg|] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Sports figures=== | |||
| ], 1966]] | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=18em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{portal|1960s}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (the younger members of that demographic had matured in the early part of the decade). | |||
| * ] (the decade when the older members of the Boomer generation had become of age). | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'' (book) | |||
| ===Timelines=== | |||
| The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade: | |||
| ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] • ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * Anastakis, Dimitry, ed. ''The Sixties: passion, politics, and style'' (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2008.) Canadian emphasis | |||
| * Baugess, James S., and Abbe Debolt, eds. ''Encyclopedia of the Sixties: A Decade of Culture and Counterculture'' (2 vol, 2012; also E-book) 871pp; 500 entries by scholars ; | |||
| * Berton, Pierre. ''1967: the Last Good Year'' (Toronto: Doubleday Canada, 1997). Canadian events | |||
| * Brooks, Victor. ''Last Season of Innocence: The Teen Experience in the 1960s'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2012) 207 pp. | |||
| * Brown, Timothy Scott. ''West Germany and the Global Sixties'' (2013) | |||
| * Christiansen, Samantha and Zachary Scarlett, ed. ''The Third World and the Global 1960s'' (New York: Berghahn, 2013) | |||
| * Farber, David, and Beth Bailey, eds. ''The Columbia guide to America in the 1960s'' (Columbia University Press, 2003). | |||
| * Farber, David, ed. ''The Sixties: From Memory to History'' (1994), Scholarly essays on the United States | |||
| * Flamm, Michael W. and David Steigerwald. ''Debating the 1960s: Liberal, Conservative, and Radical Perspectives'' (2007) on USA | |||
| * Isserman, Maurice, and Michael Kazin. ''America divided: The civil war of the 1960s'' (6th ed. Oxford UP, 2020). | |||
| * Marwick, Arthur. ''The Sixties: Cultural Revolution in Britain, France, Italy, and the United States, c.1958-c.1974'' (Oxford University Press, 1998, {{ISBN|978-0-19-210022-1}}) | |||
| * Matusow, Allen, ''The Unraveling of America: A History of Liberalism in the 1960s'' (1984) | |||
| * Padva, Gilad. Animated Nostalgia and Invented Authenticity in Arte's ''Summer of the Sixties''. In Padva, Gilad, ''Queer Nostalgia in Cinema and Pop Culture'', pp. 13–34 (Palgrave Macmillan, 2014, {{ISBN|978-1-137-26633-0}}). | |||
| * Palmer, Bryan D. ''Canada's 1960s: The Ironies of Identity in a Rebellious Era''. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2009. | |||
| * Sandbrook, Dominic. ''Never Had It So Good: A History of Britain from Suez to the Beatles'' (2006) 928pp; | |||
| * Sandbrook, Dominic. ''White Heat: A History of Britain in the Swinging Sixties'' (2 vol 2007) | |||
| * Strain, Christopher B. ''The Long Sixties: America, 1955–1973'' (Wiley, 2017). xii, 204 pp. | |||
| * Unger, Debi, and Irwin Unger, eds. '' The Times Were a Changin': The Sixties Reader'' (1998) | |||
| ===Historiography=== | |||
| * DeKoven, Marianne. ''The Sixties and the Emergence of the Postmodern'' (Duke University Press, 2004) | |||
| * Farber, David R. ''The Sixties: From Memory to History'' (1994) | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Heale |first=Michael J. |title=The Sixties as History: A Review of the Political Historiography |journal=Reviews in American History |date=March 2005 |volume=33 |issue=1 |pages=133–152 |doi=10.1353/rah.2005.0009 |jstor=30031497 |s2cid=145537005 }} | |||
| * Hunt, Andrew. "When Did the Sixties Happen? Searching for New Directions", ''Journal of Social History'' (1999) 33#1 pp 147–161. | |||
| * Meyer, James. ''The Art of Return: The Sixties and Contemporary Culture'' (University of Chicago Press, 2019). {{isbn|9780226521558}} | |||
| * Pensado, Jaime. "The (forgotten) Sixties in Mexico." ''The Sixties: A Journal of History, Politics and Culture''(2008) 1#1: 83–90. | |||
| * Rising, George Goodwin. "Stuck in the sixties: Conservatives and the legacies of the 1960s." (PhD U. of Arizona, 2003). {{hdl|10150/280496}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite news|last1=Zurawik|first1=David|title=On PBS, Six Hours of The '60s|url=https://www.baltimoresun.com/1991/01/20/on-pbs-six-hours-of-the-60s/|access-date=22 September 2015|work=The Baltimore Sun Times|date=20 January 1991|archive-date=4 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304101705/http://articles.baltimoresun.com/1991-01-20/features/1991020182_1_boomers-sixties-obsession|url-status=live}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180315063443/http://www.public.iastate.edu/~rjackson/webbibl.html |date=15 March 2018 }} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{spaced ndash}} slideshow by '']'' | |||
| * , exhibit at the ], Library, Special Collections. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite web |publisher= ] |url= http://www.vam.ac.uk/collections/fashion/features/1960s/index.html |title= 1960s Fashion Feature, including biographies, interviews, clothing and resources |url-status= dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080509050501/http://www.vam.ac.uk/collections/fashion/features/1960s/index.html |archive-date= 9 May 2008 |df= dmy-all }} | |||
| * {{spaced ndash}} articles, video, pictures, and facts | |||
| {{Events by month links}} | |||
| {{20th century}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:16, 15 January 2025
Decade of the Gregorian calendar (1960–1969) "Sixties", "'60s", "The Sixties", and "The 60s" redirect here. For decades comprising years 60–69 of other centuries, see List of decades. For other uses, see The Sixties (disambiguation).













 From top left, clockwise: A US Navy plane flies over a Soviet cargo ship during the Cuban Missile Crisis; Israeli tanks advancing on the Golan Heights during the Six-Day War; the Birth control pill is first introduced, sparking the sexual revolution and the hippie movement; During the Civil rights movement , Martin Luther King Jr. delivers his I Have a Dream speech; the Beatles led the British Invasion of the U.S. music market and became the most influential band in popular music history; the Prague Spring unfolds before the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia and was part of the Protests of 1968; A U.S. infantry patrol during the Vietnam War; During the Year of Africa, in which 16 African countries gained independence from their European colonial rulers; Damaged homes in Chile following the 9.4–9.6 Mw Valdivia earthquake; Biafran child starving from the mass famine caused by the Nigerian Civil War; The Apollo 11 mission lands the first humans on the Moon; Yuri Gagarin became the first human to enter outer space and orbit the Earth by Vostok 1; China's Mao Zedong initiates the Great Leap Forward plan which fails and brings mass starvation in which 15 to 55 million people died by 1961, and in 1966, Mao starts the Cultural Revolution, which purged traditional Chinese practices and ideas; John F. Kennedy is assassinated in 1963.
From top left, clockwise: A US Navy plane flies over a Soviet cargo ship during the Cuban Missile Crisis; Israeli tanks advancing on the Golan Heights during the Six-Day War; the Birth control pill is first introduced, sparking the sexual revolution and the hippie movement; During the Civil rights movement , Martin Luther King Jr. delivers his I Have a Dream speech; the Beatles led the British Invasion of the U.S. music market and became the most influential band in popular music history; the Prague Spring unfolds before the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia and was part of the Protests of 1968; A U.S. infantry patrol during the Vietnam War; During the Year of Africa, in which 16 African countries gained independence from their European colonial rulers; Damaged homes in Chile following the 9.4–9.6 Mw Valdivia earthquake; Biafran child starving from the mass famine caused by the Nigerian Civil War; The Apollo 11 mission lands the first humans on the Moon; Yuri Gagarin became the first human to enter outer space and orbit the Earth by Vostok 1; China's Mao Zedong initiates the Great Leap Forward plan which fails and brings mass starvation in which 15 to 55 million people died by 1961, and in 1966, Mao starts the Cultural Revolution, which purged traditional Chinese practices and ideas; John F. Kennedy is assassinated in 1963.
| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
The 1960s (pronounced "nineteen-sixties", shortened to the "'60s" or the "Sixties") was a decade that began on January 1, 1960, and ended on December 31, 1969.
While the achievements of humans being launched into space, orbiting Earth, perform spacewalk and walking on the Moon extended exploration, the Sixties are known as the "countercultural decade" in the United States and other Western countries. There was a revolution in social norms, including clothing, music, drugs, dress, sexuality, formalities, civil rights, precepts of military duty, and schooling. Some people denounce the decade as one of irresponsible excess, flamboyance, the decay of social order, and the fall or relaxation of social taboos. A wide range of music emerged; from popular music inspired by and including the Beatles (in the United States known as the British Invasion), the folk music revival, to the poetic lyrics of Bob Dylan. In the United States the Sixties were also called the "cultural decade" while in the United Kingdom (especially London) it was called the Swinging Sixties.
The United States had four presidents that served during the decade; Dwight D. Eisenhower, John F. Kennedy, Lyndon B. Johnson and Richard Nixon. Eisenhower was near the end of his term and left office in January 1961, and Kennedy was assassinated in 1963. Kennedy had wanted Keynesian and staunch anti-communist social reforms. These were passed under Johnson including civil rights for African Americans and health care for the elderly and the poor. Despite his large-scale Great Society programs, Johnson was increasingly disliked by the New Left at home and abroad. For some, May 1968 meant the end of traditional collective action and the beginning of a new era to be dominated mainly by the so-called new social movements.
After the Cuban Revolution led by Fidel Castro, the United States attempted to depose the new leader by training Cuban exiles and invading the island of Cuba. This led to Cuba to ally itself to the Soviet Union, a hostile enemy to the United States, resulting in an international crisis when Cuba hosted Soviet ballistic missiles similar to Turkey hosting American missiles, which brought the possibility of causing World War III. However, after negotiations between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R, both agreed to withdraw their weapons averting potential nuclear warfare.
After U.S. president Kennedy's assassination, direct tensions between the superpower countries of the United States and the Soviet Union developed into a contest with proxy wars, insurgency funding, puppet governments and other overall influence mainly in Latin America, Africa, and Asia. This "Cold War" dominated the world's geopolitics during the decade. Construction of the Berlin Wall by East Germany began in 1961. Africa was in a period of radical political change as 32 countries gained independence from their European colonial rulers. The heavy-handed American role in the Vietnam War lead to an anti-Vietnam War movement with outraged student protestors around the globe culminating in the protests of 1968.
China saw the end of Mao's Great Leap Forward in 1962 that led to many Chinese to die from the deadliest famine in human history and the start of the Cultural Revolution from 1966 to 1976. Its stated goal was to preserve Chinese communism by purging remnants of capitalist and traditional elements from Chinese society, leading to the arrests of a many Chinese politicians, the killings of millions of civilians and ethnic minorities, and the destruction of many historical and cultural buildings, artifacts and materials all of which would last until the death of Mao Zedong.
By the end of the 1950s, post-war reconstructed Europe began an economic boom. World War II had closed up social classes with remnants of the old feudal gentry disappearing. A developing upper-working-class (a newly redefined middle-class) in Western Europe could afford a radio, television, refrigerator and motor vehicles. The Soviet Union and other Warsaw Pact countries were improving quickly after rebuilding from WWII. Real GDP growth averaged 6% a year during the second half of the decade; overall, the worldwide economy prospered in the 1960s with expansion of the middle class and the increase of new domestic technology.
In the United Kingdom, the Labour Party gained power in 1964 with Harold Wilson as prime minister through most of the decade. In France, the protests of 1968 led to President Charles de Gaulle temporarily fleeing the country. Italy formed its first left-of-center government in March 1962 with Aldo Moro becoming prime minister in 1963. Soviet leaders during the decade were Nikita Khrushchev until 1964 and Leonid Brezhnev.
During the 1960s, the world population increased from 3.0 to 3.7 billion people. There were approximately 1.15 billion births and 500 million deaths.
Politics and wars
See also: List of sovereign states in the 1960sWars

- The Cold War (1947–1991)
- The Vietnam War (1955–1975)
- 1961 – Substantial (approximately 700) American advisory forces first arrive in Vietnam.
- 1962 – By mid-1962, the number of U.S. military advisers in South Vietnam had risen from 900 to 12,000.
- 1963 – By the time of U.S. president John F. Kennedy's death there were 16,000 American military personnel in South Vietnam, up from Eisenhower's 900 advisors to cope with rising guerrilla activity in Vietnam.
- 1964 – In direct response to the minor naval engagement known as the Gulf of Tonkin incident which occurred on 2 August 1964, the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, a joint resolution of the U.S. Congress, was passed on 10 August 1964. The resolution gave U.S. president Lyndon B. Johnson authorization, without a formal declaration of war by Congress, for the use of military force in Southeast Asia. The Johnson administration subsequently cited the resolution as legal authority for its rapid escalation of U.S. military involvement in the Vietnam War.
- 1966 – After 1966, with the draft in place more than 500,000 troops are sent to Vietnam by the Johnson administration and college attendance soars.
- The Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) – an unsuccessful attempt by a CIA-trained force of Cuban exiles to invade southern Cuba with support from U.S. government armed forces, to overthrow the Cuban government of Fidel Castro.
- Portuguese Colonial War (1961–1974) – the war was fought between Portugal's military and the emerging nationalist movements in Portugal's African colonies. It was a decisive ideological struggle and armed conflict of the Cold War in African (Portuguese Africa and surrounding nations) and European (mainland Portugal) scenarios. Unlike other European nations, the Portuguese regime did not leave its African colonies, or the overseas provinces, during the 1950s and 1960s. During the 1960s, various armed independence movements, most prominently led by communist-led parties who cooperated under the CONCP umbrella and pro-U.S. groups, became active in these areas, most notably in Angola, Mozambique, and Portuguese Guinea. During the war, several atrocities were committed by all forces involved in the conflict.
- The Vietnam War (1955–1975)
- The Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation began in January 1963 and ended in August 1966.
- Sino-Indian War of 1962 occurred between China and India over a border dispute.
- The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 began in September.
- Arab–Israeli conflict (early-20th century-present)
- Six-Day War (June 1967) – a war between Israel and the neighboring states of Egypt, Jordan, and Syria. The Arab states of Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Tunisia, Morocco and Algeria also contributed troops and arms. At the war's end, Israel had gained control of the Sinai Peninsula, the Gaza Strip, the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights. The results of the war affect the geopolitics of the region to this day.
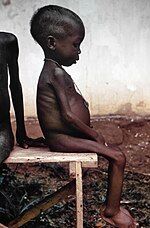
- The Algerian War came to a close in 1962.
- The Nigeria Civil War began in 1967.
- Civil wars in Laos and Sudan rage on throughout the decade.
- The Al-Wadiah War was a military conflict which broke out on 27 November 1969, between Saudi Arabia and the People's Republic of South Yemen.
Internal conflicts
- The massive 1960 Anpo protests in Japan against the U.S.-Japan Security Treaty were the largest and longest protests in Japan's history. Although they ultimately failed to stop the treaty, they forced the resignation of Japanese prime minister Nobusuke Kishi and the cancellation of a planned visit to Japan by U.S. president Dwight D. Eisenhower.
- The Congo Crisis was a period of political upheaval and conflict in the Republic of the Congo between 1960 and 1965 that ended with the establishment of a unitary state led by Mobutu Sese Seko.
- The Dominican Civil War leads to a brief international occupation of the country and the election of Joaquín Balaguer as president.
- The Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66 occurred as part of the Transition to the New Order that marked the beginning of Suharto's 31-year presidency.
- Cultural Revolution in China (1966–1976) – a period of widespread social and political upheaval in the People's Republic of China which was launched by Mao Zedong, the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party. Mao alleged that "liberal bourgeois" elements were permeating the party and society at large and that they wanted to restore capitalism. Mao insisted that these elements be removed through post-revolutionary class struggle by mobilizing the thoughts and actions of China's youth, who formed Red Guards groups around the country. The movement subsequently spread into the military, urban workers, and the party leadership itself. Although Mao himself officially declared the Cultural Revolution to have ended in 1969, the power struggles and political instability between 1969 and the arrest of the Gang of Four in 1976 are now also widely regarded as part of the Revolution.
- The Naxalite movement in India began in 1967 with an armed uprising of tribals against local landlords in the village of Naxalbari, West Bengal, led by certain leaders of the Communist Party of India (Marxist). The movement was influenced by Mao Zedong's ideology and spread to many tribal districts in Eastern India, gaining strong support among the radical urban youth. After counter-insurgency operations by the police, military and paramilitary forces, the movement fragmented but is still active in many districts.
- The Troubles in Northern Ireland began with the rise of the Northern Ireland civil rights movement in the mid-1960s, the conflict continued into the later 1990s.
- The Six-Point movement in Bangladesh (at the time East Pakistan). The movement gave way to the 1969 East Pakistan mass uprising, which released Sheikh Mujibur Rahman from prison and put the country on the road to liberation in the early 1970s.
- The Compton's Cafeteria Riot occurred in August 1966 in the Tenderloin district of San Francisco. This incident was one of the first recorded transgender riots in United States history, preceding the more famous 1969 Stonewall Riots in New York City by three years.
- The Stonewall riots occurred in June 1969 in New York City. The Stonewall riots were a series of spontaneous, violent demonstrations against a police raid that took place in the Stonewall Inn, in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of New York City. They are frequently cited as the first instance in American history when people in the homosexual community fought back against a government-sponsored system that persecuted sexual minorities, and they have become the defining event that marked the start of the gay rights movement in the United States and around the world.
- In 1967, the National Farmers Organization withheld milk supplies for 15 days as part of an effort to induce a quota system to stabilize prices.
- The May 1968 student and worker uprisings in France.
- Mass socialist or Communist movement in most European countries (particularly France and Italy), with which the student-based new left was involved. The most spectacular manifestation of this was the May student revolt of 1968 in Paris that linked up with a general strike of ten million workers called by the trade unions; and for a few days seemed capable of overthrowing the government of Charles de Gaulle. De Gaulle went off to visit French troops in Germany to check on their loyalty. Major concessions were won for trade union rights, higher minimum wages and better working conditions.
- University students protested in the hundreds of thousands against the Vietnam War in London, Paris, Berlin and Rome.
- In Eastern Europe students also drew inspiration from the protests in the West. In Poland and Yugoslavia they protested against restrictions on free speech by communist regimes.
- The Tlatelolco massacre – was a government massacre of student and civilian protesters and bystanders that took place during the afternoon and night of 2 October 1968, in the Plaza de las Tres Culturas in the Tlatelolco section of Mexico City.
Coups
Main article: List of coups d'état and coup attempts § 1960–1969Prominent coups d'état of the decade included:
- On 27 May 1960, a coup in Turkey led by Cemal Gürsel and Cemal Madanoğlu overthrew the government of Adnan Menderes.
- On 16 May 1961, a coup in South Korea led by army officer Park Chung Hee made the establishment of temporary military rule.
- In 1963, a coup in South Vietnam leads to the death of President Ngô Đình Diệm and the establishment of temporary military rule.
- On 31 March and 1 April 1964, a military coup in Brazil overthrows President João Goulart and starts a 21-year period of military dictatorship.
- On 21 April 1967, in Greece a group of colonels established a military dictatorship for seven years.
- In 1968, a coup in Iraq led to the overthrow of Abdul Rahman Arif by the Arab Socialist Baath Party.
- On 1 September 1969, a small group of military officers led by the army officer Muammar Gaddafi overthrows monarchy in Libya.
Nuclear threats

- The Cuban Missile Crisis (16–28 October 1962) – a near-military confrontation between the U.S. and the Soviet Union about the presence of Soviet missiles in Cuba. After an American Naval (quarantine) blockade of Cuba the Soviet Union under the leadership of Nikita Khrushchev agreed to remove their missiles from Cuba in exchange for the U.S. removing its missiles from Turkey.
- On 13 February 1960, France detonated its first atomic bomb. France possessed a hydrogen bomb by 1968.
- On 16 October 1964, China detonated its first atomic bomb. China possessed a hydrogen bomb by 1967.
Decolonization and independence
- The transformation of Africa from colonialism to independence in what is known as the decolonisation of Africa dramatically accelerated during the decade, with 32 countries gaining independence between 1960 and 1968, marking the end of the European empires that once dominated the African continent. However, many of these new post-colonial states would struggle with internal and external issues including famine, corruption, genocide, disease, and violent conflicts in the 1960s and succeeding decades. Many of these issues were caused or exacerbated by American and Soviet involvement during the Cold War with each side supporting various strongmen, dictators, and guerillas favorable to their causes in these countries. Economic development on the continent has been difficult, but many nations who decolonized in the 1960s began to see a rebound and unprecedented growth in the first quarter of the 21st century. As a whole, Africa's GDP rose by an average of over 6% a year between 2013 and 2022, a rate only outpaced by China.
Prominent political events
North America
United States

- 1960 – 1960 United States presidential election – The very close campaign was the series of four Kennedy–Nixon debates; they were the first presidential debates held on television. Kennedy won a close election.
- 1961 – President John F. Kennedy promised some more aggressive confrontation with the Soviet Union; he also established the Peace Corps.
- 1963 – Betty Friedan published the book The Feminine Mystique, reawakening the feminist movement and being largely responsible for its second wave.
- 1963 – Civil rights becomes a central issue as the Birmingham campaign and Birmingham riot lead to President Kennedy's Civil Rights Address, Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech at the March on Washington on 6 August and the 16th Street Baptist Church bombing.
- 1963 – Kennedy was assassinated and replaced by Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson. The nation was in shock. For the next half-century, conspiracy theorists concocted numerous alternative explanations to the official report that a lone gunman killed Kennedy.
- 1964 – Johnson pressed for civil rights legislation. Civil Rights Act of 1964 signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. This landmark piece of legislation in the United States outlawed racial segregation in schools, public places, and employment. The first black riots erupt in major cities.
- 1964 – Johnson was reelected over Conservative spokesman Senator Barry Goldwater by a wide landslide; Liberals gained full control of Congress.
- 1964 – The Wilderness Act was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on 3 September.
- 1965 – After the events of the Selma to Montgomery marches, the National Voting Rights Act of 1965 was lobbied for (and then signed into law) by President Lyndon B. Johnson. The Voting Rights Act outlawed discriminatory voting practices that had caused the widespread disenfranchisement of African Americans in the United States.
- 1968 – U.S. president Richard M. Nixon was elected, defeating Vice President Hubert H. Humphrey, in November.
- 1969 – U.S. president Richard Nixon was inaugurated in January 1969; he promised "peace with honor" to end the Vietnam War.
Canada
- The Quiet Revolution in Quebec altered the province-city-state into a more secular society. The Jean Lesage Liberal government created a welfare state (État-Providence) and fomented the rise of active nationalism among Francophone French-speaking Quebecer Québécois.
- On 15 February 1965, the new flag of Canada was adopted in Canada after a much-anticipated debate known as the Great Canadian flag debate.
- In 1960, the Canadian Bill of Rights becomes law and suffrage (as well as the right for any Canadian citizen to vote) was finally adopted by John Diefenbaker's Progressive Conservative government. The new election act allowed First Nations people to vote for the first time.
Mexico
- The student and New Left protests in 1968 coincided with political upheavals in a number of other countries. Although these events often sprung from completely different causes, they were influenced by reports and images of what was happening in the United States and France.

Europe

- British prime minister Harold Macmillan delivered his "Wind of Change" speech in 1960.
- The government of the East Germany authorized construction of the Berlin Wall on 13 August 1961 to prevent East Germans from leaving East Berlin to West Berlin.
- Pope John XXIII calls the Second Vatican Council of the Catholic Church, continued by Pope Paul VI (after John XXIII died in 1963), which met from 11 October 1962 until 8 December 1965.
- In October 1964, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev was expelled from office due to his increasingly erratic and authoritarian behavior. Leonid Brezhnev and Alexei Kosygin then became the new leaders of the Soviet Union.
- In Czechoslovakia, 1968 was the year of Alexander Dubček's Prague Spring, a source of inspiration to many Western leftists who admired Dubček's "socialism with a human face". The Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia in August ended these hopes and also fatally damaged the chances of the orthodox communist parties drawing many recruits from the student protest movement.
Asia
China
- The Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) and the Sino-Soviet split (1961–1989)
- 1966 marked the beginning of the Cultural Revolution that was launched by Mao Zedong and lasted until his death in 1976. The goal of the revolution was to preserve Chinese communism by purging Chinese society of its traditional and remaining capitalist elements. Though it failed to achieve its main objectives, the revolution marked the effective return of Mao to the center of power.
- Following Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev's removal from power in 1964, Sino-Soviet relations devolved into open hostility. The Chinese were deeply disturbed by the Soviet suppression of the Prague Spring in 1968 as the latter now claimed the right to intervene in any country it saw as deviating from the correct path of socialism. In March 1969, armed clashes took place along the Sino-Soviet border in the former Manchuria and this finally drove the Chinese to restore relations with the U.S. as Mao Zedong decided that the Soviet Union posed the bigger threat to China.
India
- A literary and cultural movement started in Calcutta, Patna and other cities by a group of writers and painters who called themselves "Hungryalists", or members of the Hungry generation. The band of writers wanted to change virtually everything and were arrested with several cases filed against them on various charges; they ultimately won these cases.
Indonesia
- President Sukarno banned the Masyumi Party on 15 August 1960 and caused a tension the between government and Islamist groups.
- The Transition to the New Order (1965–1968)
- In the early hours of 1 October 1965, a group of army officers launched a coup d'état attempt in Jakarta, assassinated six senior Indonesian Army generals and a junior army officer. They also seized Merdeka Square and proclaimed the establishment of "the Revolutionary Council" through a radio broadcast later in the morning, with Lieutenant Colonel Untung Syamsuri as its leader.
- On the same day, Major General Suharto successfully persuaded the soldiers on Merdeka Square to join forces with the Indonesian Army Strategic Reserve Command divisions and launched a counterattack on the movement, ending the coup attempt. Three days later, the bodies of seven army officers were found buried in an old well in Lubang Buaya and the bodies were recovered.
- In the aftermath of the coup d'état attempt, the people blamed the attempt on the Communist Party of Indonesia, prompting a mass purge against leftists and communist sympathizers across the country. Around 500,000-1,000,000 casualties were massacred. The killings were mostly done by the locals with the help of the Army.
- Soon, mass demonstrations and protests from the Indonesian Students' Action Front against President Sukarno's government occurred. President Sukarno was notorious for his friendly approach towards the leftists, particularly the Communist Party of Indonesia.
- In the climax of the protests, President Sukarno signed the Supersemar on 11 March 1966, effectively transferring authority to Major General Suharto to restore order and ensure security in the country. On 12 March 1967, President Sukarno was stripped of his political power by the Provisional People's Consultative Assembly (MPRS) and Major General Suharto became acting president. Later, he became president formally on 27 March 1968. Sukarno lived under house arrest until his death in June 1970.
Japan and South Korea
- The Japanese economic miracle (1960s–1990s)
- Japan's remarkable economic growth between the post-World War II era and the end of the Cold War. During the economic boom, Japan rapidly became the world's second-largest economy at the time (after the United States).
- In 1960, Japan was wracked by the massive Anpo protests against the revision of the U.S.-Japan Security Treaty, resulting in the resignation of Prime Minister Nobusuke Kishi; Kishi's successor, Hayato Ikeda, began implementing economic policies, known as the Income Doubling Plan removed most of Japan's anti-monopoly laws and promised to double the size of Japan's economy within 10 years. Eisaku Satō became Prime Minister of Japan four years later, succeeding Ikeda due to health issues.
- The 1964 Summer Olympics were held in Japan, the first time the country hosted them and the first time that the Olympic Games were held in Asia. The world's first bullet train (the Tōkaidō Shinkansen between Tokyo Station and Shin-Ōsaka Station) commences operations; it is the oldest high-speed rail system in the world.
- The Second and Third Republics of Korea (1960–1972)
- The April Revolution were mass protests in South Korea against President Syngman Rhee and the First Republic from 11 to 26 April 1960, which led to Rhee's resignation. The Second Republic was established as a parliamentary government under President Yun Bo-seon and Prime Minister Chang Myon. The Second Republic ended the First Republic, formed a liberal democracy, and formulated the first Five-Year Plans to develop the formerly-neglected economy.
- The May 16 coup and the establishment of the SCNR, led by Major General Park Chung Hee on 16 May 1961, put an effective end to the Second Republic. Park was one of a group of military leaders who had been pushing for the de-politicization of the military.
- The Miracle on the Han River began with the Five-Year Plans of South Korea, a series of economic development projects implemented by President Park Chung Hee. South Korea received US$800 million from Japan under property claims and was mostly dependent on foreign aid (largely from the U.S. in exchange for South Korea's involvement in the Vietnam War).
- South Korea's first diplomatic relations with Japan were established under the Third Republic and South Korea-Japan relations were normalized in the Treaty on Basic Relations signed on 22 July 1965 and in an agreement ratified on 14 August 1965. Japan agreed to provide a large amount of compensation, grants, and loans to South Korea and the two countries began economic and political cooperation.
Africa

- On 1 September 1969, the Libyan monarchy was overthrown and a radical, revolutionary government headed by dictator Muammar Gaddafi took power.
- On 1 October 1960, Nigeria gained its independence from Great Britain.
South America
- In 1964, a successful coup against the democratically elected government of Brazilian president João Goulart initiated a military dictatorship that caused over 20 years of oppression.
- The Argentine revolutionary Ernesto "Che" Guevara travelled to Africa and then Bolivia in his campaign to spread worldwide revolution. He was captured and executed in 1967 by the Bolivian army and afterwards became an iconic figure for leftists around the world.
- Juan Velasco Alvarado took power by means of a coup in Peru in 1968.
Economics
| The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (July 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The United States
During the 1960s the United States was in the postwar economic boom. The 1960s are remembered as a time period of rapid workforce growth (roughly 33% between February 1961 and December 1969), tax cuts, low unemployment, rapid GDP growth, gains in productivity and generally low inflation. After the Recession of 1960–1961 the United States experienced sustained rapid economic growth which began in February 1961 and ended with the Recession of 1969–1970. It lasted a total of 106 months, which made it the longest recorded economic expansion in the history of the United States until the 1990s United States boom.
On January 20, 1961, John F. Kennedy became the president of the United States. In his campaign, John F. Kennedy promised to "get America moving again." His goal was economic growth of 4–6% per year and unemployment below 4%.To do this, he proposed a wide range of policies which embraced Keynesian economics (which he is the first president to do so). Among these policies included a 7% tax credit for businesses that invest in new plants and equipment, Income tax cuts and an increase in the federal minimum wage.
Although, the 1960s were not perfect. The government routinely produced fiscal deficits (as a result of the tax cuts and increased expenditure embarked under Kennedy), with only one surplus during this time period (as opposed to the 1950s which produced 3). Furthermore, by 1966 inflation began to climb, which is a general trend that continued into the 1970's. By the end of the decade under Nixon, the combined inflation and unemployment rate known as the misery index (economics) had exploded to nearly 10% with inflation at 6.2% and unemployment at 3.5% and by 1975 the misery index was almost 20%. By the end of the decade, median family income had risen from $8,540 in 1963 to $10,770 by 1969.
Assassinations and attempts



Prominent assassinations, targeted killings, and assassination attempts include:
| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| 12 October 1960 | Inejiro Asanuma, leader of the Japan Socialist Party, was stabbed to death by far-right ultranationalist Otoya Yamaguchi while speaking in a televised political debate in Tokyo. |
| 17 January 1961 | Patrice Lumumba, the Prime Minister of the Democratic Republic of the Congo; Maurice Mpolo, Minister of Youth and Sports; Joseph Okito, vice-president of the Senate, were assassinated by a Belgian and Congolese firing squad outside Lubumbashi. |
| 30 May 1961 | Rafael Trujillo, dictator of the Dominican Republic for 31 years, was assassinated in a plot led by members of his general staff. |
| 13 January 1963 | Sylvanus Olympio, the Prime Minister of Togo, was killed during the 1963 Togolese coup d'état. His body was dumped in front of the U.S. embassy in Lomé. |
| 2 November 1963 | Ngô Đình Diệm, 1st president of South Vietnam, along with his brother and chief political adviser Ngô Đình Nhu, was assassinated in a coup led by elements of the South Vietnamese Army. |
| 22 November 1963 | John F. Kennedy, 35th president of the United States, was shot to death while riding in a motorcade through Dealey Plaza in Dallas, Texas. His assassin, Lee Harvey Oswald, was himself murdered by Jack Ruby two days later. |
| 21 February 1965 | Malcolm X, an American civil rights leader, was shot to death in Manhattan. The perpetrators of the killing are disputed. |
| 6 September 1966 | Hendrik Verwoerd, Prime Minister of South Africa and architect of apartheid, was stabbed to death by Dimitri Tsafendas, a parliamentary messenger, at the South African House of Assembly. |
| 9 October 1967 | Che Guevara, an Argentine-Cuban Marxist revolutionary, was executed by the CIA and Bolivian army. |
| 4 April 1968 | Martin Luther King Jr., American civil rights leader, was shot to death in Memphis, Tennessee. |
| 5 June 1968 | Robert F. Kennedy, former Attorney General and a leading 1968 Democratic presidential candidate, was shot to death in Los Angeles following a speech regarding his victory in California. |
Disasters
Natural:
- The 1960 Valdivia earthquake, also known as the Great Chilean earthquake, is to date the most powerful earthquake ever recorded, rating 9.5 on the moment magnitude scale. It caused localized tsunamis that severely battered the Chilean coast, with waves up to 25 meters (82 ft). The main tsunami raced across the Pacific Ocean and devastated Hilo, Hawaii.
- 1963 Skopje earthquake was a 6.1 moment magnitude earthquake which occurred in Skopje, SR Macedonia (present-day Republic of Macedonia) on 26 July 1963, which killed over 1,070 people, injured between 3,000 and 4,000 and left more than 200,000 people homeless. About 80% of the city was destroyed.
- 1963 – Vajont dam disaster – The Vajont dam flood in Italy was caused by a mountain sliding in the dam and causing a flood wave that killed approximately 2,000 people in the towns in its path.
- 1964 – The Good Friday earthquake, the most powerful earthquake recorded in the U.S. and North America, struck Alaska and killed 143 people.
- 1965 – Hurricane Betsy caused severe damage to the U.S. Gulf Coast, especially in the state of Louisiana.
- 1969 – The Cuyahoga River caught fire in Ohio. Fires had erupted on the river many times, including 22 June 1969, when a river fire captured the attention of Time magazine, which described the Cuyahoga as the river that "oozes rather than flows" and in which a person "does not drown but decays." This helped spur legislative action on water pollution control resulting in the Clean Water Act, Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement, and the creation of the federal Environmental Protection Agency.
- 1969 – Hurricane Camille hit the U.S. Gulf Coast at Category 5 Status. It peaked and made landfall with 175 mph (280 km/h) winds and caused $1.42 billion (1969 USD) in damages.
Non-natural:
- On 16 December 1960, a United Airlines DC-8 and a Trans World Airlines Lockheed Constellation collided over New York City and crashed, killing 134 people.
- On 15 February 1961, Sabena Flight 548 crashed on its way to Brussels, Belgium, killing all 72 passengers on board and 1 person on the ground. Among those killed were all 18 members of the US figure skating team, on their way to the World Championships.
- On 16 March 1962, Flying Tiger Line Flight 739, a Lockheed Super Constellation, inexplicably disappeared over the Western Pacific, leaving all 107 on board presumed dead. Since the wreckage of the aircraft is lost to this day, the cause of the crash remains a mystery.
- On 3 June 1962, Air France Flight 007, a Boeing 707, crashed on takeoff from Paris. 130 people were killed in the crash while 2 survived.
- On 20 May 1965, PIA Flight 705 crashed on approach to Cairo, Egypt. 121 died while 6 survived.
- On 4 February 1966, All Nippon Airways Flight 60, a Boeing 727, plunged into Tokyo Bay for reasons unknown. All 133 people on board died.
- On 5 March 1966, BOAC Flight 911 broke up in mid-air and crashed on the slopes of Mount Fuji. All 124 aboard died.
- On 8 December 1966, the car ferry SS Heraklion sank in the Aegean Sea during a storm, killing 217 people.
- On 16 March 1969, a DC-9 operating Viasa Flight 742 crashed in the Venezuelan city of Maracaibo. A total of 155 people died in the crash.
Social and political movements
Counterculture and social revolution
See also: Counterculture of the 1960s and Timeline of 1960s countercultureIn the second half of the decade, young people began to revolt against the conservative norms of the old time, as well as remove themselves from mainstream liberalism, in particular the high level of materialism which was so common during the era. This created a "counterculture" that sparked a social revolution throughout much of the Western world. It began in the United States as a reaction against the conservatism and social conformity of the 1950s, and the U.S. government's extensive military intervention in Vietnam. The youth involved in the popular social aspects of the movement became known as hippies. These groups created a movement toward liberation in society, including the sexual revolution, questioning authority and government, and demanding more freedoms and rights for women and minorities. The Underground Press, a widespread, eclectic collection of newspapers served as a unifying medium for the counterculture. The movement was also marked by the first widespread, socially accepted drug use (including LSD and marijuana) and psychedelic music.
Anti-war movement
Main article: Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War
The war in Vietnam would eventually lead to a commitment of over half a million American troops, resulting in over 58,500 American deaths and producing a large-scale antiwar movement in the United States. As late as the end of 1965, few Americans protested the American involvement in Vietnam, but as the war dragged on and the body count continued to climb, civil unrest escalated. Students became a powerful and disruptive force and university campuses sparked a national debate over the war. As the movement's ideals spread beyond college campuses, doubts about the war also began to appear within the administration itself. A mass movement began rising in opposition to the Vietnam War, including the National Mobilization to End the War in Vietnam's 1967 march to the United Nations and its March on the Pentagon, the 1968 Democratic National Convention protests at which the slogan "The whole world is watching" became famous, and continuing in the massive Moratorium protests in 1969 as well as the movement of resistance to conscription ("the Draft") for the war.
The antiwar movement was initially based on the older 1950s Peace movement, heavily influenced by the American Communist Party, but by the mid-1960s it outgrew this and became a broad-based mass movement centered in universities and churches: one kind of protest was called a "sit-in". Other terms heard in the United States included "the Draft", "draft dodger", "conscientious objector", and "Vietnam vet". Voter age-limits were challenged by the phrase: "If you're old enough to die for your country, you're old enough to vote."
Civil rights movement
Main article: Civil rights movement
Beginning in the mid-1950s and continuing into the late 1960s, African Americans in the United States organized a movement to end legalized racial discrimination and obtain voting rights. This article covers the phase of the movement between 1955 and 1968, particularly in the South. The emergence of the Black Power movement, which lasted roughly from 1966 to 1975, enlarged the aims of the civil rights movement to include racial dignity, economic and political self-sufficiency, and anti-imperialism.
The movement was characterized by major campaigns of civil resistance. Between 1955 and 1968, acts of civil disobedience and nonviolent protest produced crisis situations between activists and government authorities. Federal, state, and local governments, businesses, and communities often had to respond immediately to these situations that highlighted the inequities faced by African Americans. Forms of protest and/or civil disobedience included boycotts such as the successful Montgomery bus boycott (1955–1956) in Alabama, sit-ins such as the influential Greensboro sit-ins (1960) in North Carolina, marches such as the Selma to Montgomery marches (1965) in Alabama, and other nonviolent activities.
Noted legislative achievements during this phase of the civil rights movement were passage of Civil Rights Act of 1964 that banned discrimination based on "race, color, religion, or national origin" in employment practices and public accommodations, the Voting Rights Act of 1965 that restored and protected voting rights, the Immigration and Nationality Services Act of 1965 that dramatically opened entry to the U.S. to immigrants other than traditional European groups, and the Fair Housing Act of 1968 that banned discrimination in the sale or rental of housing.
Hispanic and Chicano movement
Another large ethnic minority group, the Mexican-Americans, are among other Hispanics in the U.S. who fought to end racial discrimination and socioeconomic disparity. The largest Mexican-American populations were in the Southwestern United States, such as California with over 1 million Chicanos in Los Angeles alone, and Texas where Jim Crow laws included Mexican-Americans as "non-white" in some instances to be legally segregated.
Socially, the Chicano Movement addressed what it perceived to be negative ethnic stereotypes of Mexicans in mass media and the American consciousness. It did so through the creation of works of literary and visual art that validated Mexican-American ethnicity and culture. Chicanos fought to end social stigmas such as the usage of the Spanish language and advocated official bilingualism in federal and state governments.
The Chicano Movement also addressed discrimination in public and private institutions. Early in the twentieth century, Mexican Americans formed organizations to protect themselves from discrimination. One of those organizations, the League of United Latin American Citizens, was formed in 1929 and remains active today.
The movement gained momentum after World War II when groups such as the American G.I. Forum, which was formed by returning Mexican American veterans, joined in the efforts by other civil rights organizations.
Mexican-American civil-rights activists achieved several major legal victories including the 1947 Mendez v. Westminster U.S. Supreme Court ruling which declared that segregating children of "Mexican and Latin descent" was unconstitutional and the 1954 Hernandez v. Texas ruling which declared that Mexican Americans and other racial groups in the United States were entitled to equal protection under the 14th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution.
The most prominent civil-rights organization in the Mexican-American community, the Mexican American Legal Defense and Educational Fund (MALDEF), was founded in 1968. Although modeled after the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund, MALDEF has also taken on many of the functions of other organizations, including political advocacy and training of local leaders.
Meanwhile, Puerto Ricans in the U.S. mainland fought against racism, police brutality and socioeconomic problems affecting the three million Puerto Ricans residing in the 50 states. The main concentration of the population was in New York City.
In the 1960s and the following 1970s, Hispanic-American culture was on the rebound like ethnic music, foods, culture and identity both became popular and assimilated into the American mainstream. Spanish-language television networks, radio stations and newspapers increased in presence across the country, especially in U.S.–Mexican border towns and East Coast cities like New York City, and the growth of the Cuban American community in Miami, Florida.
The multitude of discrimination at this time represented an inhuman side to a society that in the 1960s was upheld as a world and industry leader. The issues of civil rights and warfare became major points of reflection of virtue and democracy, what once was viewed as traditional and inconsequential was now becoming the significance in the turning point of a culture. A document known as the Port Huron Statement exemplifies these two conditions perfectly in its first hand depiction, "while these and other problems either directly oppressed us or rankled our consciences and became our own subjective concerns, we began to see complicated and disturbing paradoxes in our surrounding America. The declaration "all men are created equal..." rang hollow before the facts of Negro life in the South and the big cities of the North. The proclaimed peaceful intentions of the United States contradicted its economic and military investments in the Cold War status quo." These intolerable issues became too visible to ignore therefore its repercussions were feared greatly, the realization that we as individuals take the responsibility for encounter and resolution in our lives issues was an emerging idealism of the 1960s.
Second-wave feminism
Main article: Second-wave feminismA second wave of feminism in the United States and around the world gained momentum in the early 1960s. While the first wave of the early 20th century was centered on gaining suffrage and overturning de jure inequalities, the second wave was focused on changing cultural and social norms and de facto inequalities associated with women. At the time, a woman's place was generally seen as being in the home, and they were excluded from many jobs and professions. In the U.S., a Presidential Commission on the Status of Women found discrimination against women in the workplace and every other aspect of life, a revelation which launched two decades of prominent women-centered legal reforms (i.e., the Equal Pay Act of 1963, Title IX, etc.) which broke down the last remaining legal barriers to women's personal freedom and professional success.
Feminists took to the streets, marching and protesting, authoring books and debating to change social and political views that limited women. In 1963, with Betty Friedan's book, The Feminine Mystique, the role of women in society, and in public and private life was questioned. By 1966, the movement was beginning to grow in size and power as women's group spread across the country and Friedan, along with other feminists, founded the National Organization for Women. In 1968, "Women's Liberation" became a household term as, for the first time, the new women's movement eclipsed the civil rights movement when New York Radical Women, led by Robin Morgan, protested the annual Miss America pageant in Atlantic City, New Jersey. The movement continued throughout the next decades. Gloria Steinem was a key feminist.
Gay rights movement
Main articles: Gay liberation and LGBT social movementsThe United States, in the middle of a social revolution, led the world in LGBT rights in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Inspired by the civil-rights movement and the women's movement, early gay-rights pioneers had begun, by the 1960s, to build a movement. These groups were rather conservative in their practices, emphasizing that gay men and women are no different from those who are straight and deserve full equality. This philosophy would be dominant again after AIDS, but by the very end of the 1960s, the movement's goals would change and become more radical, demanding a right to be different, and encouraging gay pride.
The symbolic birth of the gay rights movement would not come until the decade had almost come to a close. Gays were not allowed by law to congregate. Gay establishments such as the Stonewall Inn in New York City were routinely raided by the police to arrest gay people. On a night in late June 1969, LGBT people resisted, for the first time, a police raid, and rebelled openly in the streets. This uprising called the Stonewall riots began a new period of the LGBT rights movement that in the next decade would cause dramatic change both inside the LGBT community and in the mainstream American culture.
New Left
The rapid rise of a "New Left" applied the class perspective of Marxism to postwar America but had little organizational connection with older Marxist organizations such as the Communist Party, and even went as far as to reject organized labor as the basis of a unified left-wing movement. Sympathetic to the ideology of C. Wright Mills, the New Left differed from the traditional left in its resistance to dogma and its emphasis on personal as well as societal change. Students for a Democratic Society (SDS) became the organizational focus of the New Left and was the prime mover behind the opposition to the War in Vietnam. The 1960s left also consisted of ephemeral campus-based Trotskyist, Maoist and anarchist groups, some of which by the end of the 1960s had turned to militancy.
Crime
The 1960s was also associated with a large increase in crime and urban unrest of all types. Between 1960 and 1969 reported incidence of violent crime per 100,000 people in the United States nearly doubled and have yet to return to the levels of the early 1960s. Large riots broke out in many cities like Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York City, Newark, New Jersey, Oakland, California and Washington, D.C. By the end of the decade, politicians like George Wallace and Richard Nixon campaigned on restoring law and order to a nation troubled with the new unrest.
Science and technology
Science
Space exploration


The Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union dominated the 1960s. The Soviets sent the first man, Yuri Gagarin, into outer space during the Vostok 1 mission on 12 April 1961, and scored a host of other successes, but by the middle of the decade the U.S. was taking the lead. In May 1961, President Kennedy set the goal for the United States of landing a man on the Moon by the end of the 1960s.
In June 1963, Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space during the Vostok 6 mission. In 1965, Soviets launched the first probe to hit another planet of the Solar System (Venus), Venera 3, and the first probe to make a soft landing on and transmit from the surface of the Moon, Luna 9. In March 1966, the Soviet Union launched Luna 10, which became the first space probe to enter orbit around the Moon, and in September 1968, Zond 5 flew the first terrestrial beings, including two tortoises, to circumnavigate the Moon.
The deaths of astronauts Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger B. Chaffee in the Apollo 1 fire on 27 January 1967, put a temporary hold on the U.S. space program, but afterward progress was steady, with the Apollo 8 crew (Frank Borman, Jim Lovell, William Anders) being the first crewed mission to orbit another celestial body (the Moon) during Christmas of 1968.
On 20 July 1969, the first humans landed on the Moon. The Apollo 11 mission, launched on 16 July 1969, carried mission Commander Neil Armstrong, Command Module Pilot Michael Collins, and Lunar Module Pilot Buzz Aldrin, and Aldrin and Armstrong flew the Lunar Module Eagle to the lunar surface. Apollo 11 fulfilled President John F. Kennedy's goal of reaching the Moon by the end of the 1960s, which he had expressed during a speech given before a joint session of Congress on 25 May 1961: "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth."
The Soviet program lost its sense of direction with the death of chief designer Sergey Korolyov in 1966. Political pressure, conflicts between different design bureaus, and engineering problems caused by an inadequate budget would doom the Soviet attempt to land men on the Moon. Shortly after the American Apollo 1 disaster, tragedy struck the Soviet program when cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov was killed when the parachutes on his Soyuz 1 flight failed.
A succession of uncrewed American and Soviet probes traveled to the Moon, Venus, and Mars during the 1960s, and commercial satellites also came into use.
Other scientific developments

- 1960 – The oral female birth-control contraceptive, the pill, was released in the United States after Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval.
- 1963 – The measles vaccine was released after being approved by the FDA
- 1963 – Maria Goeppert Mayer is awarded the Nobel prize for discovering the nuclear shell of the atomic nucleus
- 1964 – The discovery and confirmation of the Cosmic microwave background in 1964 secured the Big Bang as the best theory of the origin and evolution of the universe.
- 1965 – AstroTurf introduced.
- 1967 – First heart transplantation operation by Professor Christiaan Barnard in South Africa.
- 1967 – Discovery of the first known pulsar (a rapidly spinning neutron star) by Jocelyn Bell Burnell
- During the late 1960s, the Green Revolution achieved a major leap in agricultural production, mitigating a potential famine situation.
Technology

- Shinkansen, the world's first high-speed rail service began in 1964.
Automobiles and Motorcycles
As the 1960s began, American cars showed a rapid rejection of 1950s styling excess, and would remain relatively clean and boxy for the entire decade. The horsepower race reached its climax in the late 1960s, with muscle cars sold by most makes. The compact Ford Mustang, launched in 1964, was one of the decade's greatest successes. The "Big Three" American automakers enjoyed their highest ever sales and profitability in the 1960s, but the demise of Studebaker in 1966 left American Motors Corporation as the last significant independent. The decade would see the car market split into different size classes for the first time, and model lineups now included compact and mid-sized cars in addition to full-sized ones.
The popular modern hatchback, with front-wheel-drive and a two-box configuration, was born in 1965 with the introduction of the Renault 16, many of this car's design principles live on in its modern counterparts: a large rear opening incorporating the rear window, foldable rear seats to extend boot space. The Mini, released in 1959, had first popularised the front wheel drive two-box configuration, but technically was not a hatchback as it had a fold-down bootlid.
Japanese cars also began to gain acceptance in the Western market, and popular economy models such as the Toyota Corolla, Datsun 510, and the first popular Japanese sports car, the Datsun 240Z, were released in the mid- to late-1960s.
Mopeds and Scooters gains popularity in these decade, with Honda Super Cub in United States, Japan and Europe, Mitsubishi Silver Pigeon in Japan and Vespa, Kreidler Florett,Zundapp and Sachs mopeds in Western Europe.
Electronics and communications

- 1960 – The first working laser was demonstrated in May by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories.
- 1960 – Tony Hoare announces the Quicksort algorithm, the most common sorter on computers.
- 1961 – Unimate, the first industrial robot, was introduced.
- 1962 – First transatlantic satellite broadcast via the Telstar satellite.
- 1962 – The FORMAC coding language was invented by Jean Sammet
- 1962 – The first computer video game, Spacewar!, was invented.
- 1962 – Red LEDs were developed.
- 1963 – The first geosynchronous communications satellite, Syncom 2, is launched.
- 1963 – First transpacific satellite broadcast via the Relay 1 satellite.
- 1963 – Touch-Tone telephones introduced.
- 1963 – Sketchpad was the first touch interactive computer graphics program.
- 1963 – The Nottingham Electronic Valve company produced the first home video recorder called the "Telcan".
- 1964 – 8-track tape audio format was developed.
- 1964 – The Compact Cassette was introduced.
- 1964 – The first successful Minicomputer, Digital Equipment Corporation's 12-bit PDP-8, was marketed.
- 1964 – The programming language BASIC was created.
- 1964 – The world's first supercomputer, the CDC 6600, was introduced.
- 1964 – Fairchild Semiconductor released ICs with dual in-line packaging.
- 1967 – PAL and SECAM broadcast color television systems started publicly transmitting in Europe.
- 1967 – The first Automatic Teller Machine was opened in Barclays Bank, London.
- 1967 – The Logo coding language was invented by Cynthia Solomon
- 1968 – Ralph Baer developed his Brown Box (a working prototype of the Magnavox Odyssey).
- 1968 – The first public demonstration of the computer mouse, the paper paradigm Graphical user interface, video conferencing, teleconferencing, email, and hypertext.
- 1969 – ARPANET, the research-oriented prototype of the Internet, was introduced.
- 1969 – CCD invented at AT&T Bell Labs, used as the electronic imager in still and video cameras.
Additional notable worldwide events
- The Manson murders occurred between 8–10 August 1969 when actress Sharon Tate, coffee heiress Abigail Folger and several others were brutally murdered in the Tate residence by Charles Manson's "family." Rosemary LaBianca and Leno LaBianca were also murdered by the Manson family the following night.
- Canada celebrated its 100th anniversary of Confederation in 1967 by hosting Expo 67 in Montreal, Quebec. During the anniversary celebrations, French president Charles De Gaulle visited Canada and caused a considerable uproar by declaring his support for Québécois independence.
- The Zodiac killer first became active after murdering five known victims in the San Francisco Bay Area between December 1968 and October 1969, operating in rural, urban and suburban settings.
Popular culture
-
 TV shows like Doctor Who, The Ed Sullivan Show, The Andy Griffith Show, The Addams Family, The Fugitive, and Gene Roddenberry's Star Trek: The Original Series were popular in the 1960s (the latter garnering a much wider audience in the following decades and becoming a global phenomenon).
TV shows like Doctor Who, The Ed Sullivan Show, The Andy Griffith Show, The Addams Family, The Fugitive, and Gene Roddenberry's Star Trek: The Original Series were popular in the 1960s (the latter garnering a much wider audience in the following decades and becoming a global phenomenon).
-
 The Beatles (consisting of John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison, and Ringo Starr) released music throughout the 1960s, and are often considered the most popular band in global history. Beatlemania was/is the fanaticism surrounding The Beatles. The Beatles experienced intense fan worship during the '60s era.
The Beatles (consisting of John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison, and Ringo Starr) released music throughout the 1960s, and are often considered the most popular band in global history. Beatlemania was/is the fanaticism surrounding The Beatles. The Beatles experienced intense fan worship during the '60s era.
-
 Bob Dylan is often considered to be one of the greatest songwriters of all time, and through a process of mutual influence with The Beatles and other artists, helped define the explosion of musical ideas in the 1960s.
Bob Dylan is often considered to be one of the greatest songwriters of all time, and through a process of mutual influence with The Beatles and other artists, helped define the explosion of musical ideas in the 1960s.
-
 Peace symbols and flowers were an aesthetic of the counterculture and hippie movements of the 1960s and later in the 1970s.
Peace symbols and flowers were an aesthetic of the counterculture and hippie movements of the 1960s and later in the 1970s.
-
 Anti-war movements like the protests of 1968 were demonstrations and revolts against various forms of governmental jurisdiction and corruption. These protests were a major part of 1960s and 1970s popular culture.
Anti-war movements like the protests of 1968 were demonstrations and revolts against various forms of governmental jurisdiction and corruption. These protests were a major part of 1960s and 1970s popular culture.
-
 Hanna-Barbera cartoons such as The Flintstones, The Jetsons, The Huckleberry Hound Show, The Quick Draw McGraw Show, The Yogi Bear Show, Wacky Races, Top Cat, Scooby-Doo, and Jonny Quest were popular in the 1960s.
Hanna-Barbera cartoons such as The Flintstones, The Jetsons, The Huckleberry Hound Show, The Quick Draw McGraw Show, The Yogi Bear Show, Wacky Races, Top Cat, Scooby-Doo, and Jonny Quest were popular in the 1960s.
-
Crowds at the stage during the Woodstock Music Festival, two months after the Stonewall riots in June 1969.
-
 Six Olympic Games were held in the 1960s, Squaw Valley and Rome in 1960, Innsbruck and Tokyo in 1964, Grenoble and Mexico City in 1968 (all during the Cold War).
Six Olympic Games were held in the 1960s, Squaw Valley and Rome in 1960, Innsbruck and Tokyo in 1964, Grenoble and Mexico City in 1968 (all during the Cold War).
-
 The 1960s were the height of the Space Age and space aesthetics in popular culture. In 1969, humans landed on the Moon for the first time.
The 1960s were the height of the Space Age and space aesthetics in popular culture. In 1969, humans landed on the Moon for the first time.
-
 The superhero boom of the decade saw in media and popular culture, TV series like Batman, The Green Hornet, The Marvel Super Heroes, and Spider-Man were more popular.
The superhero boom of the decade saw in media and popular culture, TV series like Batman, The Green Hornet, The Marvel Super Heroes, and Spider-Man were more popular.
The counterculture movement dominated the second half of the 1960s, its most famous moments being the Summer of Love in San Francisco in 1967, and the Woodstock Festival in upstate New York in 1969. Psychedelic drugs, especially LSD, were widely used medicinally, spiritually and recreationally throughout the late 1960s, and were popularized by Timothy Leary with his slogan "Turn on, tune in, drop out". Ken Kesey and the Merry Pranksters also played a part in the role of "turning heads on". Psychedelic influenced the music, artwork and films of the decade, and a number of prominent musicians died of drug overdoses (see 27 Club). There was a growing interest in Eastern religions and philosophy, and many attempts were made to found communes, which varied from supporting free love to religious puritanism.
Music

 The arrival of the Beatles in the U.S. during 1964, and particularly their appearance on television's The Ed Sullivan Show, marked the beginning of the British Invasion in the history of music, in which a large number of rock and pop music acts from the United Kingdom gained enormous popularity in the U.S.
The arrival of the Beatles in the U.S. during 1964, and particularly their appearance on television's The Ed Sullivan Show, marked the beginning of the British Invasion in the history of music, in which a large number of rock and pop music acts from the United Kingdom gained enormous popularity in the U.S. Bob Dylan was the face of the American folk music revival of the 1960s. In 1964, Dylan was shifting his focus to more abstract and introspective themes, and eventually would adapt the use of electric instrumentation, alienating many in the folk crowd.
Bob Dylan was the face of the American folk music revival of the 1960s. In 1964, Dylan was shifting his focus to more abstract and introspective themes, and eventually would adapt the use of electric instrumentation, alienating many in the folk crowd.
– Carlos Santana"The 60s were a leap in human consciousness. Mahatma Gandhi, Malcolm X, Martin Luther King, Che Guevara, Mother Teresa, they led a revolution of conscience. The Beatles, The Doors, Jimi Hendrix created revolution and evolution themes. The music was like Dalí, with many colors and revolutionary ways. The youth of today must go there to find themselves."
The rock 'n' roll movement of the 1950s quickly came to an end in 1959 with the Day the Music Died (as explained in the song "American Pie"), the scandal of Jerry Lee Lewis' marriage to his 13-year-old cousin, and the induction of Elvis Presley into the United States Army. As the 1960s began, the major rock 'n' roll stars of the '50s such as Chuck Berry and Little Richard had dropped off the charts and popular music in the U.S. came to be dominated by girl groups, surf music, novelty pop songs, clean-cut teen idols, and Motown music. Another important change in music during the early 1960s was the American folk music revival which introduced Bob Dylan, Joan Baez, Pete Seeger, The Kingston Trio, Harry Belafonte, Odetta, Phil Ochs, and many other singer-songwriters to the public.
Girl groups and female singers, such as the Shirelles, Betty Everett, Little Eva, the Dixie Cups, the Ronettes, Martha and the Vandellas and the Supremes dominated the charts in the early 1960s. This style consisted typically of light pop themes about teenage romance and lifestyles, backed by vocal harmonies and a strong rhythm. Most girl groups were African-American, but white girl groups and singers, such as Lesley Gore, the Angels, and the Shangri-Las also emerged during this period.
Around the same time, record producer Phil Spector began producing girl groups and created a new kind of pop music production that came to be known as the Wall of Sound. This style emphasized higher budgets and more elaborate arrangements, and more melodramatic musical themes in place of a simple, light-hearted pop sound. Spector's innovations became integral to the growing sophistication of popular music from 1965 onward.
Also during the early 1960s, surf rock emerged, a rock subgenre that was centered in Southern California and based on beach and surfing themes, in addition to the usual songs about teenage romance and innocent fun. The Beach Boys quickly became the premier surf rock band and almost completely and single-handedly overshadowed the many lesser-known artists in the subgenre. Surf rock reached its peak in 1963–1965 before gradually being overtaken by bands influenced by the British Invasion and the counterculture movement.
The car song also emerged as a rock subgenre in the early 1960s, which focused on teenagers' fascination with car culture. The Beach Boys also dominated this subgenre, along with the duo Jan and Dean. Such notable songs include "Little Deuce Coupe", "409", and "Shut Down", all by the Beach Boys; Jan and Dean's "Little Old Lady from Pasadena" and "Drag City", Ronny and the Daytonas' "Little GTO", and many others. Like girl groups and surf rock, car songs also became overshadowed by the British Invasion and the counterculture movement.
The early 1960s also saw the golden age of another rock subgenre, the teen tragedy song, which focused on lost teen romance caused by sudden death, mainly in traffic accidents. Such songs included Mark Dinning's "Teen Angel", Ray Peterson's "Tell Laura I Love Her", Jan and Dean's "Dead Man's Curve", the Shangri-Las' "Leader of the Pack", and perhaps the subgenre's most popular, "Last Kiss" by J. Frank Wilson and the Cavaliers.
In the early 1960s, Britain became a hotbed of rock 'n' roll activity during this time. In late 1963, the Beatles embarked on their first US tour and cult singer Dusty Springfield released her first solo single. A few months later, rock 'n' roll founding father Chuck Berry emerged from a 2+1⁄2-year prison stint and resumed recording and touring. The stage was set for the spectacular revival of rock music.
In the UK, the Beatles played raucous rock 'n' roll – as well as doo wop, girl-group songs, show tunes – and wore leather jackets. Their manager Brian Epstein encouraged the group to wear suits. Beatlemania abruptly exploded after the group's appearance on The Ed Sullivan Show in 1964. Late in 1965, the Beatles released the album Rubber Soul which marked the beginning of their transition to a sophisticated power pop group with elaborate studio arrangements and production, and a year after that, they gave up touring entirely to focus only on albums. A host of imitators followed the Beatles in the so-called British Invasion, including groups like the Rolling Stones, the Who and the Kinks who would become legends in their own right.
As the counterculture movement developed, artists began making new kinds of music influenced by the use of psychedelic drugs. Guitarist Jimi Hendrix emerged onto the scene in 1967 with a radically new approach to electric guitar that replaced Chuck Berry, previously seen as the gold standard of rock guitar. Rock artists began to take on serious themes and social commentary/protest instead of simplistic pop themes.
A major development in popular music during the mid-1960s was the movement away from singles and towards albums. Previously, popular music was based around the 45 single (or even earlier, the 78 single) and albums such as they existed were little more than a hit single or two backed with filler tracks, instrumentals, and covers. The development of the AOR (album-oriented rock) format was complicated and involved several concurrent events such as Phil Spector's Wall of Sound, the introduction by Bob Dylan of "serious" lyrics to rock music, and the Beatles' new studio-based approach. In any case, after 1965 the vinyl LP had definitively taken over as the primary format for all popular music styles.
Blues also continued to develop strongly during the '60s, but after 1965, it increasingly shifted to the young white rock audience and away from its traditional black audience, which moved on to other styles such as soul and funk.
Jazz music and pop standards during the first half of the 1960s was largely a continuation of 1950s styles, retaining its core audience of young, urban, college-educated whites. By 1967, the death of several important jazz figures such as John Coltrane and Nat King Cole precipitated a decline in the genre. The takeover of rock in the late 1960s largely spelled the end of jazz and standards as mainstream forms of music, after they had dominated much of the first half of the 20th century.
Country music gained popularity on the West Coast, due in large part to the Bakersfield sound, led by Buck Owens and Merle Haggard. Female country artists were also becoming more mainstream (in a genre dominated by men in previous decades), with such acts as Patsy Cline, Loretta Lynn, and Tammy Wynette.
Late 1960s also was the beginning of disco music, which became more popular in 1970s.
Significant events in music in the 1960s
- Elvis Presley returned to civilian life in the U.S. after two years away in the U.S. Army. He resumes his musical career by recording "It's Now or Never" and "Are You Lonesome Tonight?" in March 1960.
- Country music stars Patsy Cline, Cowboy Copas and Hawkshaw Hawkins were killed when their plane crashed in Camden, Tennessee while returning home from a Kansas City benefit show in March 1963.
- In July 1964, a plane crash claimed the life of another country music legend, Jim Reeves, when the plane he was piloting crashed in a turbulent thunderstorm while on final approach to Nashville International Airport.
- Sam Cooke was shot and killed at a motel (at the age of 33) in Los Angeles, California on 11 December 1964, under suspicious circumstances.
- Motown was founded in 1960. Its first Top Ten hit was "Shop Around" by the Miracles in 1960. "Shop Around" peaked at number-two on the Billboard Hot 100 and was Motown's first million-selling record.
- Newcastle-born Eric Burdon and his band "The Animals" hit the No. 1 in charts in the U.S. with their hit single "The House of the Rising Sun" in 1964.
- Folk singer and activist Joan Baez released her debut album on Vanguard Records in December 1960.
- The Marvelettes scored Motown's first U.S. No. 1 pop hit, "Please Mr. Postman", in 1961. Motown would score 110 Billboard Top 10 hits during its run.
- The Four Seasons released three straight number one hits.
- In a widely anticipated and publicized event, The Beatles arrive in America in February 1964, spearheading the British Invasion.
- The Mary Poppins original soundtrack tops record charts. Sherman Brothers receive Grammys and double Oscars.
- Lesley Gore hits number one on Billboard with "It's My Party" and number two with "You Don't Own Me" at the age of 17 (behind "I Want To Hold Your Hand" by The Beatles).
- The Supremes scored twelve number-one hit singles between 1964 and 1969, beginning with "Where Did Our Love Go".
- The Kinks release "You Really Got Me" in August 1964, which tops the British charts; it is regarded as the first hard rock hit and a blueprint for related genres such as heavy metal.
- John Coltrane released A Love Supreme in late 1964, considered one of the most acclaimed jazz albums of the era.
- The Grateful Dead was formed in 1965 (originally The Warlocks), thus paving the way for the emergence of acid rock.
- Bob Dylan went electric at the 1965 Newport Folk Festival.
- Cilla Black's number-one hit "Anyone Who Had a Heart" still remains the top-selling single by a female artist in the UK from 1964.
- The Rolling Stones had a huge No. 1 hit with their song "(I Can't Get No) Satisfaction" in the summer of 1965.
- The Byrds released a cover of Bob Dylan's "Mr. Tambourine Man", which reached No. 1 on the U.S. charts and repeated the feat in the U.K. shortly thereafter. The extremely influential track effectively creates the musical subgenre of folk rock.
- Bob Dylan's "Like a Rolling Stone" is a top-five hit on both sides of the Atlantic during the summer of 1965.
- Bob Dylan's 1965 albums Bringing It All Back Home and Highway 61 Revisited ushered in album-focused rock and the folk rock genre.

- Simon and Garfunkel released the single "The Sound of Silence" in 1965.
- The Beach Boys released Pet Sounds in 1966, which significantly influenced The Beatles' Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band album released the following year.
- Bob Dylan was called "Judas" by an audience member during the Manchester Free Trade Hall concert; the start of the bootleg recording industry follows, with recordings of this concert circulating for 30 years – wrongly labeled as The Royal Albert Hall Concert – before a legitimate release in 1998 as The Bootleg Series Vol. 4: Bob Dylan Live 1966, The "Royal Albert Hall" Concert.
- In February 1966, Nancy Sinatra's song "These Boots Are Made for Walkin' " became very popular.
- In 1966, The Supremes A' Go-Go was the first album by a female group to reach the top position of the Billboard magazine pop albums chart in the United States.
- The Seekers were the first Australian group to have a number one with "Georgy Girl" in 1966.
- Jefferson Airplane released the influential Surrealistic Pillow in 1967.
- The Velvet Underground released its self-titled debut album, The Velvet Underground & Nico, in 1967.
- The Doors released its self-titled debut album, The Doors, in January 1967.
- Love released Forever Changes in 1967.
- The Procol Harum released A Whiter Shade of Pale in 1967.
- Cream released "Disraeli Gears" in 1967.

- The Jimi Hendrix Experience released two successful albums during 1967 (Are You Experienced and Axis: Bold as Love) that innovate both guitar, trio and recording techniques.
- The Moody Blues released the album Days of Future Passed in November 1967.
- R&B legend Otis Redding has his first No. 1 hit with "Sitting on the Dock of the Bay". He also played at the Monterey International Pop Festival in 1967 just before he died in a plane crash.
- Pink Floyd released its debut record, The Piper at the Gates of Dawn.
- Bob Dylan released the country rock album John Wesley Harding in December 1967.
- The Bee Gees released their international debut album, Bee Gees 1st, in July 1967; it included the pop standard "To Love Somebody".
- The Monterey International Pop Festival in 1967 was the beginning of the "Summer of Love".
- The Beatles released Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band in 1967. It was nicknamed "The Soundtrack of the Summer of Love".
- Johnny Cash released At Folsom Prison in 1968.
- After The Yardbirds folded, Led Zeppelin was formed by Jimmy Page and manager Peter Grant in 1968 with Robert Plant, John Bonham, John Paul Jones, and Page as members; they released their debut album, Led Zeppelin, the next year.
- Big Brother and the Holding Company, with Janis Joplin as lead singer, became an overnight sensation after their performance at the Monterey International Pop Festival in 1967 and released their second album Cheap Thrills in 1968.
- Gram Parsons with The Byrds released the influential LP Sweetheart of the Rodeo in late 1968, forming the basis for country rock.
- The Jimi Hendrix Experience released the influential double LP Electric Ladyland in 1968 that furthered the guitar and studio innovations of his previous two albums.
- Simon and Garfunkel released the single "Mrs. Robinson" in 1968, featured in the film The Graduate.
- Country music newcomer Jeannie C. Riley released the country and pop hit "Harper Valley PTA" in 1968, which is about a miniskirt-wearing mother of a teenage girl who was criticized by the local PTA for supposedly setting a bad example for her daughter but turns the tables by exposing some of the PTA members' wrongdoings. The song, along with Riley's mod persona in connection with it, apparently gave country music a "sexual revolution" of its own as hemlines of other female country artists' stage dresses began rising in the years that followed.
- Sly & the Family Stone revolutionized black music with their 1968 hit single "Dance to the Music" and became international sensations by 1969 with the release of their hit record Stand!. The band cemented their position as a vital counterculture band when they performed at the Woodstock Festival.
- The Gun released "Race with the Devil" in October 1968.
- After a long performance drought, Elvis Presley made a successful return to TV and live performances after spending most of the decade making movies, beginning with his '68 Comeback Special in December 1968 on NBC, followed by a summer engagement in Las Vegas in 1969. Presley's return to live performing set the stage for his many concert tours and continued Vegas engagements throughout the 1970s until his death in 1977.
- The Foundations released "Build Me Up Buttercup" in December 1968.
- The Rolling Stones filmed the TV special The Rolling Stones Rock and Roll Circus in December 1968 but the film was not released for transmission. It was considered a fabled "lost" performance for decades until it was released in North America on Laserdisc and VHS in 1996. The special features performances from The Who, The Dirty Mac (featuring John Lennon, Eric Clapton and Mitch Mitchell), Jethro Tull and Taj Mahal.
- Spooky Tooth released their second album, Spooky Two, in March 1969. The album was an important hard rock milestone.
- The Woodstock Festival (and the Altamont Free Concert four months later) in 1969.
- The Who released and toured the first rock opera, Tommy, in 1969.
- Proto-punk band MC5 released the live album Kick Out the Jams in 1969.
- Captain Beefheart and his Magic Band released the avant-garde Trout Mask Replica in 1969.
- Creedence Clearwater Revival released "Fortunate Son" in 1969. The song amassed popularity with the anti-war movement at the time and would later be used in films, TV shows and video games depicting the Vietnam War or the U.S during the late 1960s and early 1970s.
- The Stooges released their debut album in 1969.
- The Beatles released Abbey Road in 1969.
- King Crimson released their debut album, In the Court of the Crimson King, in 1969.
- Led Zeppelin released two of their self-titled debut albums, Led Zeppelin I and Led Zeppelin II, in 1969.
Film
See also: History of film § 1960s, and 1960s in film
The highest-grossing film of the decade was 20th Century Fox's The Sound of Music (1965).
Some of Hollywood's most notable blockbuster films of the 1960s include:
- 2001: A Space Odyssey
- The Apartment
- The Birds
- I Am Curious (Yellow)
- Bonnie and Clyde
- Breakfast at Tiffany's
- Bullitt
- Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid
- Carnival of Souls
- Cleopatra
- Cool Hand Luke
- The Dirty Dozen
- Doctor Zhivago
- Dr. Strangelove
- Easy Rider
- Exodus
- Faces
- Funny Girl
- Goldfinger
- The Graduate
- Guess Who's Coming to Dinner
- Head
- How the West Was Won
- The Hustler
- Ice Station Zebra
- In the Heat of the Night
- The Italian Job
- It's a Mad, Mad, Mad, Mad World
- Jason and the Argonauts
- Judgment at Nuremberg
- The Jungle Book
- Lawrence of Arabia
- The Lion in Winter
- The Longest Day
- The Love Bug
- A Man for All Seasons
- The Manchurian Candidate
- Mary Poppins
- Medium Cool
- Midnight Cowboy
- My Fair Lady
- Night of the Living Dead
- The Pink Panther
- The Odd Couple
- Oliver!
- One Hundred and One Dalmatians
- One Million Years B.C.
- Planet of the Apes
- Psycho
- Romeo and Juliet
- Rosemary's Baby
- The Sound of Music
- Spartacus
- Swiss Family Robinson
- The Sword in the Stone
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Valley of the Dolls
- West Side Story
- Who's Afraid of Virginia Woolf?
- The Wild Bunch
The counterculture movement had a significant effect on cinema. Movies began to break social taboos such as sex and violence causing both controversy and fascination. They turned increasingly dramatic, unbalanced, and hectic as the cultural revolution was starting. This was the beginning of the New Hollywood era that dominated the next decade in theatres and revolutionized the film industry. Films of this time also focused on the changes happening in the world. Dennis Hopper's Easy Rider (1969) focused on the drug culture of the time. Movies also became more sexually explicit, such as Roger Vadim's Barbarella (1968), as the counterculture progressed.
In Europe, art cinema gained wider distribution and saw movements like la Nouvelle Vague (The French New Wave), which featured French filmmakers such as Roger Vadim, François Truffaut, Alain Resnais, and Jean-Luc Godard; the cinéma vérité documentary movement took place in Canada, France and the United States; Swedish filmmaker Ingmar Bergman, Chilean filmmaker Alexandro Jodorowsky and Polish filmmakers Roman Polanski and Wojciech Jerzy Has produced original and offbeat masterpieces and the high-point of Italian filmmaking with Michelangelo Antonioni and Federico Fellini making some of their most known films during this period. Notable films from this period include: La Dolce Vita, 8+1⁄2; La Notte; L'Eclisse, The Red Desert; Blowup; Fellini Satyricon; Accattone; The Gospel According to St. Matthew; Theorem; Winter Light; The Silence; Persona; Shame; A Passion; Au hasard Balthazar; Mouchette; Last Year at Marienbad; Chronique d'un été; Titicut Follies; High School; Salesman; La jetée; Warrendale; Knife in the Water; Repulsion; The Saragossa Manuscript; El Topo; A Hard Day's Night; and the cinéma vérité Dont Look Back.

In Japan, Chūshingura: Hana no Maki, Yuki no Maki a film version of the story of the forty-seven rōnin directed by Hiroshi Inagaki, was released in 1962; the legendary story was also remade as a television series in Japan. Academy Award-winning Japanese director Akira Kurosawa produced Yojimbo (1961) and Sanjuro (1962), which both starred Toshiro Mifune as a mysterious samurai swordsman for hire. Like his previous films both had a profound influence around the world. The Spaghetti Western genre was a direct outgrowth of the Kurosawa films. The influence of these films is most apparent in Sergio Leone's A Fistful of Dollars (1964) starring Clint Eastwood and Walter Hill's Last Man Standing (1996). Yojimbo was also the origin of the "Man with No Name" trend which included Sergio Leone's For a Few Dollars More, and The Good, The Bad and The Ugly both also starring Clint Eastwood, and arguably continued through his 1968 opus Once Upon a Time in the West, starring Henry Fonda, Charles Bronson, Claudia Cardinale, and Jason Robards. The Magnificent Seven a 1960 American western film directed by John Sturges was a remake of Akira Kurosawa's 1954 film, Seven Samurai. Another popular figure in this genre was John Wayne, with films from the 60s such as The Man Who Shot Liberty Valance (1962), El Dorado (1966), True Grit (1969) and others.
The 1960s were also about experimentation. With the explosion of lightweight and affordable cameras, the underground avant-garde film movement thrived. The movement's notable figures include Canada's Michael Snow and Americans Kenneth Anger, Stan Brakhage, Andy Warhol, and Jack Smith. Notable films in this genre include Dog Star Man, Scorpio Rising, Wavelength, Chelsea Girls, Blow Job, Vinyl, and Flaming Creatures.
Walt Disney, the founder of The Walt Disney Company, died on 15 December 1966 from a major tumor in his left lung. Alongside One Hundred and One Dalmatians, The Sword in the Stone and The Jungle Book (some of his most important blockbusters), animated feature films of the decade that are of notable status include Gay Purr-ee, Hey There, It's Yogi Bear!, The Man Called Flintstone, Mad Monster Party?, Yellow Submarine and A Boy Named Charlie Brown.
Significant events in the film industry in the 1960s
- Removal of the Motion Picture Association of America's Production Code in 1967.
- The MPA's establishment of the film ratings system in 1968.
- The decline and end of the studio system.
- The rise of arthouse films and theaters.
- The end of the classical Hollywood cinema era.
- The beginning of the New Hollywood Era due to the counterculture.
- The rise of independent producers that worked outside the studio system.
- Move to all-color production in Hollywood films.
- The invention of the Nagra 1/4", sync-sound, portable open-reel tape deck.
- New film formats like IMAX are invented and new ways of displaying film are tested at Expo 67.
- Flat-bed film editing tables (like the Steenbeck) appear; they eventually replace the Moviola editing platform.
- The French New Wave reaches its peak.
- Direct cinema and cinéma vérité documentaries.
- The beginning of the Golden Age of Porn in 1969, which continued throughout the 1970s and into the first half of the 1980s.
Television
Main article: 1960s in televisionThe most prominent TV series of the 1960s include Doctor Who, The Ed Sullivan Show, Coronation Street, Star Trek, Peyton Place, The Twilight Zone, The Outer Limits, The Andy Williams Show, The Dean Martin Show, The Wonderful World of Disney, Alfred Hitchcock Presents, The Beverly Hillbillies, Bonanza, Batman, McHale's Navy, Rowan and Martin's Laugh-In, The Dick Van Dyke Show, The Fugitive, The Tonight Show, Gunsmoke, The Andy Griffith Show, Gilligan's Island, Mission: Impossible, The Flintstones, The Adventures of Ozzie and Harriet, Lassie, The Danny Thomas Show, The Lucy Show, My Three Sons, The Red Skelton Show, Bewitched, and I Dream of Jeannie. The Flintstones was a popular show, receiving 40 million views an episode with an average of 3 million views a day. Doctor Who is the longest-running science-fiction show of all time according to the Guinness World Records. Some programming (such as The Smothers Brothers Comedy Hour) became controversial by challenging the foundations of America's corporate and governmental controls, making fun of world leaders and questioning U.S. involvement in (as well as escalation of) the Vietnam War.
Fashion
Main article: 1960s in fashionSignificant fashion trends of the 1960s include:
- The Beatles exerted an enormous influence on young men's fashions and hairstyles in the 1960s which included most notably the mop-top haircut, the Beatle boots and the Nehru jacket.
- The hippie movement late in the decade also had a strong influence on clothing styles, including bell-bottom jeans, tie-dye and batik fabrics, as well as paisley prints.
- The bikini came into fashion in 1963 after being featured in the film Beach Party.
- Mary Quant popularised the miniskirt, which became one of the most popular fashion rages in the late 1960s among young women and teenage girls. Its popularity continued throughout the first half of the 1970s and then disappeared temporarily from mainstream fashion before making a comeback in the mid-1980s.
- Men's mainstream hairstyles ranged from the pompadour, the crew cut, the flattop hairstyle, the tapered hairstyle, and short, parted hair in the early part of the decade, to longer parted hairstyles with sideburns towards the latter half of the decade.
- Women's mainstream hairstyles ranged from beehive hairdos, the bird's nest hairstyle, and the chignon hairstyle in the early part of the decade, to very short styles popularized by Twiggy and Mia Farrow in Rosemary's Baby towards the latter half of the decade.
- African-American hairstyles for men and women included the afro.
-
 Members of Argentine rock band Los Gatos sporting mop-top haircuts, which were considered at the time a rebellious hairstyle.
Members of Argentine rock band Los Gatos sporting mop-top haircuts, which were considered at the time a rebellious hairstyle.
-
 The bikini became a fashionable item in the Western world during the decade
The bikini became a fashionable item in the Western world during the decade
-
 "Swinging London" fashions on Carnaby Street, c. 1966
"Swinging London" fashions on Carnaby Street, c. 1966
-
 Tie-dye shirts of all colors were at their height and worn by many during the 1960s.
Tie-dye shirts of all colors were at their height and worn by many during the 1960s.
-
 Lava lamps (released in the late 1940s) became very prevalent in the 1960s and were used as decorations.
Lava lamps (released in the late 1940s) became very prevalent in the 1960s and were used as decorations.
-
 Go-go boots were a popular piece of fashion, worn by many.
Go-go boots were a popular piece of fashion, worn by many.
Literature
See also: List of years in literature § 1960s- The Outsiders by S.E. Hinton was a massively popular novel during the decade. It illustrated the difficult life for the working class at the time.
Sports
The first ever Super bowl had happened in 1967 in Los Angeles, California
Olympics
There were six Olympic Games held during the decade. These were:
- 1960 Summer Olympics – 25 August – 11 September 1960, in Rome, Italy
- 1960 Winter Olympics – 18–28 February 1960, in Squaw Valley, California, United States
- 1964 Summer Olympics – 10–24 October 1964, in Tokyo, Japan
- 1964 Winter Olympics – 29 January – 9 February 1964, in Innsbruck, Austria
- 1968 Summer Olympics – 12–27 October 1968, in Mexico City, Mexico
- 1968 Winter Olympics – 6–18 February 1968, in Grenoble, France
Association football
There were two FIFA World Cups during the decade:
- 1962 FIFA World Cup – hosted in Chile, won by Brazil
- 1966 FIFA World Cup – hosted and won by England
Baseball
The first wave of Major League Baseball expansion in 1961 included the formation of the Los Angeles Angels, the move to Minnesota to become the Minnesota Twins by the former Washington Senators and the formation of a new franchise called the Washington Senators. Major League Baseball sanctioned both the Houston Colt .45s and the New York Mets as new National League franchises in 1962.
In 1969, the American League expanded when the Kansas City Royals and Seattle Pilots, were admitted to the league prompting the expansion of the post-season (in the form of the League Championship Series) for the first time since the creation of the World Series. The Pilots stayed just one season in Seattle before moving and becoming the Milwaukee Brewers in 1970. The National League also added two teams in 1969, the Montreal Expos and San Diego Padres. By 1969, the New York Mets won the World Series in only the 8th year of the team's existence.
Basketball
The NBA tournaments during the 1960s were dominated by the Boston Celtics, who won eight straight titles from 1959 to 1966 and added two more consecutive championships in 1968 and 1969, aided by such players as Bob Cousy, Bill Russell and John Havlicek. Other notable NBA players included Wilt Chamberlain, Elgin Baylor, Jerry West and Oscar Robertson.
At the NCAA level, the UCLA Bruins also proved dominant. Coached by John Wooden, they were helped by Lew Alcindor and by Bill Walton to win championships and dominate the American college basketball landscape during the decade.
Disc sports (Frisbee)
Alternative sports, using the flying disc, began in the mid-sixties. As numbers of young people became alienated from social norms, they resisted and looked for alternatives. They would form what would become known as the counterculture. The forms of escape and resistance would manifest in many ways including social activism, alternative lifestyles, experimental living through foods, dress, music and alternative recreational activities, including that of throwing a Frisbee. Starting with promotional efforts from Wham-O and Irwin Toy (Canada), a few tournaments and professionals using Frisbee show tours to perform at universities, fairs and sporting events, disc sports such as freestyle, double disc court, guts, disc ultimate and disc golf became this sports first events. Two sports, the team sport of disc ultimate and disc golf are very popular worldwide and are now being played semiprofessionally. The World Flying Disc Federation, Professional Disc Golf Association and the Freestyle Players Association are the official rules and sanctioning organizations for flying disc sports worldwide. Major League Ultimate (MLU) and the American Ultimate Disc League (AUDL) are the first semi-professional ultimate leagues.
Racing
In motorsports, the Can-Am and Trans-Am series were both established in 1966. The Ford GT40 won outright in the 24 Hours of Le Mans. Graham Hill edged out Jackie Stewart and Denny Hulme for the World Championship in Formula One.
People
Activists
Some activist leaders of the 1960s period include:
- Joan Baez
- James Baldwin
- Harry Belafonte
- James Bevel
- Stokely Carmichael
- Rennie Davis
- David Dellinger
- Bob Dylan
- Medgar Evers
- Michael Farrell
- Lawrence Ferlinghetti
- Allen Ginsberg
- Dick Gregory
- Abbie Hoffman
- Jesse Jackson
- Barbara Jordan
- Bernard Lafayette
- Timothy Leary
- John Lennon
- John Lewis
- Martin Luther King Jr.
- James Meredith
- Diane Nash
- Phil Ochs
- Yoko Ono
- Rosa Parks
- Jerry Rubin
- Mario Savio
- Fred Shuttlesworth
- Gloria Steinem
- Malcolm X
- Andrew Young
Actors and entertainers
- Eddie Albert
- Jack Albertson
- Steve Allen
- Woody Allen
- Julie Andrews
- James Arness
- Fred Astaire
- Richard Attenborough
- Stéphane Audran
- Charles Aznavour
- Carroll Baker
- Barbara Bain
- Lucille Ball
- Martin Balsam
- Anne Bancroft
- Brigitte Bardot
- Richard Basehart
- Alan Bates
- Anne Baxter
- Warren Beatty
- Jean-Paul Belmondo
- Jane Birkin
- Robert Blake
- Mel Blanc
- Dirk Bogarde
- Richard Boone
- Shirley Booth
- Ernest Borgnine
- Tom Bosley
- Stephen Boyd
- Marlon Brando
- Lloyd Bridges
- Charles Bronson
- Mel Brooks
- Jim Brown
- Lenny Bruce
- Yul Brynner
- Richard Burton
- Raymond Burr
- Sid Caesar
- Michael Caine
- Rory Calhoun
- Claudia Cardinale
- Yvonne De Carlo
- Leslie Caron
- John Carradine
- Diahann Carroll
- Johnny Carson
- John Cassavetes
- George Chakiris
- Charlie Chaplin
- Julie Christie
- Lee Van Cleef
- Montgomery Clift
- Lee J. Cobb
- James Coburn
- Joan Collins
- Sean Connery
- Chuck Connors
- Robert Conrad
- Bill Cosby
- Tom Courtenay
- Bob Crane
- Bing Crosby
- Robert Culp
- Tony Curtis
- Peter Cushing
- Sammy Davis Jr.
- Doris Day
- Ruby Dee
- Sandra Dee
- Alain Delon
- Catherine Deneuve
- Brandon deWilde
- Angie Dickinson
- Troy Donahue
- Diana Dors
- Kirk Douglas
- James Drury
- Patty Duke
- Faye Dunaway
- Robert Duvall
- Dick Van Dyke
- Clint Eastwood
- Barbara Eden
- Anita Ekberg
- Peter Falk
- Mia Farrow
- Mel Ferrer
- José Ferrer
- Peter Finch
- Albert Finney
- Jo Van Fleet
- Henry Fonda
- Jane Fonda
- Peter Fonda
- June Foray
- Glenn Ford
- John Forsythe
- Anthony Franciosa
- Louis de Funès
- Clark Gable
- Eva Gabor
- Zsa Zsa Gabor
- James Garner
- Judy Garland
- Vittorio Gassman
- Jackie Gleason
- Cary Grant
- Stewart Granger
- Lorne Greene
- Andy Griffith
- Alec Guinness
- Fred Gwynne
- Gene Hackman
- Larry Hagman
- Jonathan Harris
- Richard Harris
- William Hartnell
- Tippi Hedren
- Van Heflin
- Audrey Hepburn
- Katharine Hepburn
- Charlton Heston
- Dustin Hoffman
- William Holden
- James Hong
- Dennis Hopper
- Bob Hope
- Rock Hudson
- Jeffrey Hunter
- Tab Hunter
- John Ireland
- Burl Ives
- Glynis Johns
- Carolyn Jones
- Shirley Jones
- Katy Jurado
- Anna Karina
- Danny Kaye
- Brian Keith
- George Kennedy
- Gene Kelly
- Grace Kelly
- Jack Kelly
- Eartha Kitt
- Jack Klugman
- Don Knotts
- Martin Landau
- Burt Lancaster
- Angela Lansbury
- Peter Lawford
- Cloris Leachman
- Bruce Lee
- Christopher Lee
- Janet Leigh
- Jack Lemmon
- Jerry Lewis
- Robert Loggia
- Gina Lollobrigida
- Sophia Loren
- Peter Lorre
- Darren McGavin
- David McCallum
- Fred MacMurray
- Shirley MacLaine
- Jayne Mansfield
- Karl Malden
- Dorothy Malone
- Ann-Margret
- Dean Martin
- Steve Martin
- Lee Marvin
- James Mason
- Marcello Mastroianni
- David McCallum
- Roddy McDowall
- Steve McQueen
- Burgess Meredith
- Toshiro Mifune
- Vera Miles
- Sal Mineo
- Robert Mitchum
- Elizabeth Montgomery
- Roger Moore
- Marilyn Monroe
- Jeanne Moreau
- Rita Moreno
- Harry Morgan
- Robert Morse
- Don Murray
- Patricia Neal
- Paul Newman
- Julie Newmar
- Barbara Nichols
- Leslie Nielsen
- Leonard Nimoy
- David Niven
- Kim Novak
- Maureen O'Hara
- Laurence Olivier
- Peter O'Toole
- Geraldine Page
- Janis Paige
- Eleanor Parker
- Jack Palance
- Gregory Peck
- George Peppard
- Anthony Perkins
- Michel Piccoli
- Donald Pleasence
- Suzanne Pleshette
- Christopher Plummer
- Sidney Poitier
- Paula Prentiss
- Elvis Presley
- Vincent Price
- Anthony Quayle
- Anthony Quinn
- Tony Randall
- Lynn Redgrave
- Michael Redgrave
- Vanessa Redgrave
- Oliver Reed
- Robert Reed
- Carl Reiner
- Lee Remick
- Don Rickles
- Diana Rigg
- Thelma Ritter
- Robert Redford
- Burt Reynolds
- Debbie Reynolds
- Jason Robards
- Cliff Robertson
- Edward G. Robinson
- Cesar Romero
- Mickey Rooney
- Barbara Rush
- Eva Marie Saint
- George Sanders
- Telly Savalas
- John Saxon
- Maximilian Schell
- George C. Scott
- George Segal
- Jean Seberg
- Peter Sellers
- Omar Sharif
- William Shatner
- Jean Simmons
- Frank Sinatra
- Ann Sothern
- Robert Stack
- Terence Stamp
- James Stewart
- Barbra Streisand
- Woody Strode
- Barry Sullivan
- Ed Sullivan
- Donald Sutherland
- Max von Sydow
- Sharon Tate
- Elizabeth Taylor
- Rod Taylor
- Jean-Louis Trintignant
- Patrick Troughton
- Cicely Tyson
- Raf Vallone
- Robert Vaughn
- Robert Wagner
- Eli Wallach
- Burt Ward
- John Wayne
- Raquel Welch
- Adam West
- Betty White
- Stuart Whitman
- Richard Widmark
- Gene Wilder
- Jonathan Winters
- Shelley Winters
- Natalie Wood
- Joanne Woodward
- Keenan Wynn
- Efrem Zimbalist Jr.
-
 Brigitte Bardot, 1962
Brigitte Bardot, 1962
-
 Audrey Hepburn, 1963
Audrey Hepburn, 1963
-
Clint Eastwood, 1964
-
 Sean Connery, 1964
Sean Connery, 1964
-
 Paul Newman, 1966
Paul Newman, 1966
Filmmakers
- Alfred Hitchcock
- Stanley Kubrick
- Ingmar Bergman
- Federico Fellini
- Orson Welles
- Roman Polanski
- Akira Kurosawa
- Ishiro Honda
- Jean-Luc Godard
- Pier Paolo Pasolini
- François Truffaut
- Sergio Leone
- David Lean
- Sidney Lumet
- John Ford
- Dennis Hopper
- John Huston
- John Sturges
- Sam Peckinpah
- Billy Wilder
- Blake Edwards
- Arthur Penn
- Michelangelo Antonioni
- Alain Resnais
- Claude Chabrol
- George A. Romero
- Eric Rohmer
- Don Siegel
- Jean Rouch
- Robert Mulligan
- Andreï Tarkovsky
- Luchino Visconti
- Jerry Lewis
- Luis Buñuel
- Joseph Losey
- Richard Fleisher
- Joseph L. Mankiewicz
- John Huston
- Luigi Comencini
- Elia Kazan
- Stuart Rosenberg
- Woody Allen
- Mike Nichols
- Robert Wise
- Norman Jewison
- Mario Bava
- Lucio Fulci
- Robert Aldrich
- Stanley Kramer
- Howard Hawks
- Jacques Tati
- Lewis Milestone
- Mikhaïl Kalatozov
- Stanley Donen
- George Cukor
- John Frankenheimer
- Sydney Pollack
- Ken Loach
- Michael Powell
- Anthony Mann
- Jack Clayton
- Vittorio De Sica
- Gene Roddenberry
- Steven Spielberg
Musicians and singers
- Paul Anka
- Richard Anthony
- Louis Armstrong
- Eddy Arnold
- Chet Atkins
- Burt Bacharach
- Joan Baez
- Pearl Bailey
- Bee Gees
- Tony Bennett
- Chuck Berry
- Art Blakey
- Bobby Bland
- Pat Boone
- David Bowie
- James Brown
- Solomon Burke
- Jerry Butler
- Glen Campbell
- Johnny Cash
- Ray Charles
- Chubby Checker
- Lou Christie
- Eric Clapton
- Dee Clark
- Petula Clark
- Patsy Cline
- Rosemary Clooney
- Joe Cocker
- Nat "King" Cole
- Sam Cooke
- Leonard Cohen
- John Coltrane
- King Crimson
- Bing Crosby
- Bobby Darin
- Miles Davis
- Sammy Davis Jr.
- Delia Derbyshire
- Neil Diamond
- Bo Diddley
- Dion DiMucci
- Fats Domino
- Bob Dylan
- Duke Ellington
- Art Farmer
- Eddie Fisher
- Ella Fitzgerald
- Tennessee Ernie Ford
- Aretha Franklin
- Marvin Gaye
- Robin Gibb
- Dizzy Gillespie
- Lesley Gore
- Eydie Gormé
- Buddy Guy
- Merle Haggard
- Johnny Hallyday
- Jimi Hendrix
- Eddie Hodges
- Lena Horne
- Burl Ives
- Etta James
- Sonny James
- Waylon Jennings
- George Jones
- Quincy Jones
- Tom Jones
- Janis Joplin
- B.B. King
- Ben E. King
- Freddie King
- Eartha Kitt
- Frankie Laine
- Brenda Lee
- Peggy Lee
- Jerry Lee Lewis
- Loretta Lynn
- Scott McKenzie
- Manfred Mann
- Bob Marley
- Dean Martin
- Johnny Mathis
- Curtis Mayfield
- Barry McGuire
- Roger Miller
- Charles Mingus
- Guy Mitchell
- Joni Mitchell
- Thelonious Monk
- Bill Monroe
- Wes Montgomery
- Jim Morrison
- Ricky Nelson
- Sandy Nelson
- Willie Nelson
- Phil Ochs
- Roy Orbison
- Buck Owens
- Dolly Parton
- Elvis Presley
- Ray Price
- Charley Pride
- Lou Rawls
- Jerry Reed
- Jimmy Reed
- Lou Reed
- Della Reese
- Otis Redding
- Cliff Richard
- Little Richard
- Jeannie C. Riley
- Tex Ritter
- Max Roach
- Marty Robbins
- Jimmy Rodgers
- Sonny Rollins
- Demis Roussos
- Kyu Sakamoto
- Neil Sedaka
- Pete Seeger
- Nina Simone
- Frank Sinatra
- Hank Snow
- Dusty Springfield
- Rod Stewart
- Joan Sutherland
- Hank Thompson
- Conway Twitty
- Ernest Tubb
- Big Joe Turner
- Ike & Tina Turner
- Sarah Vaughan
- Bobby Vee
- Gene Vincent
- Porter Wagoner
- Dionne Warwick
- Dinah Washington
- Muddy Waters
- Kitty Wells
- Dottie West
- Howlin' Wolf
- Andy Williams
- Jackie Wilson
- Nancy Wilson
- Stevie Wonder
- Faron Young
- Neil Young
- Frank Zappa
- Cass Elliot
-
 Willie Nelson, 1965
Willie Nelson, 1965
-
 Aretha Franklin, 1968
Aretha Franklin, 1968
-
 Johnny Cash, 1969
Johnny Cash, 1969
-
Janis Joplin, 1969
Bands
- The Animals
- The Beach Boys
- The Beatles
- Bee Gees
- Blood, Sweat and Tears
- The Cascades
- Cream
- Creedence Clearwater Revival
- The Doors
- The Four Tops
- Gladys Knight & the Pips
- Grateful Dead
- Herb Alpert & the Tijuana Brass
- The Hollies
- The Impressions
- Iron Butterfly
- The Jackson 5
- Jefferson Airplane
- The Jimi Hendrix Experience
- The Kinks
- Led Zeppelin
- The Mamas & the Papas
- The Marvelettes
- The Miracles
- The Monkees
- Moody Blues
- The Ohio Express
- Pink Floyd
- Procol Harum
- The Righteous Brothers
- The Rolling Stones
- The Ronettes
- Santana
- The Shadows
- Simon and Garfunkel
- The Stooges
- The Supremes
- The Temptations
- The Velvet Underground
- The Who
- The Yardbirds
- The Zombies
-
 The Beatles, 1964
The Beatles, 1964
-
 Beach Boys, 1964
Beach Boys, 1964
-
 The Doors, 1968
The Doors, 1968
-
 Cream, 1968
Cream, 1968
-
The Temptations, 1969
Writers
- Kurt Vonnegut
- Isaac Asimov
- Ray Bradbury
- Dr. Seuss
- Gabriel García Márquez
- Arthur Miller
- Sylvia Plath
- Philip K. Dick
- Carlos Castaneda
- Truman Capote
- John Steinbeck
- Arthur C. Clarke
- Harper Lee
- Jack Kerouac
- Robert Heinlein
- Ken Kesey
- Joseph Heller
- Henry Miller
- Hunter S. Thompson
- Edward Albee
- Gore Vidal
- William S. Burroughs
- Frank Herbert
- Charles M. Schultz
- Anthony Burgess
- Thomas Pinchon
- Tom Stoppard
- Seamus Heaney
- Joseph Campbell
- Edward Abbey
- Norman Podhoretz
- Amiri Baraka
- James Graham Ballard
- Noël Coward
- Philip Larkin
- Agatha Christie
- James Baldwin
- Lorraine Hansberry
Sports figures

- Hank Aaron
- Muhammad Ali
- Ernie Banks
- Gordon Banks
- Elgin Baylor
- Yogi Berra
- George Best
- Abebe Bikila
- Jack Brabham
- Lou Brock
- Jim Brown
- Giacomo Bulgarelli
- Matt Busby
- Dick Butkus
- John Carlos
- Věra Čáslavská
- Wilt Chamberlain
- Bobby Charlton
- Jack Charlton
- Jim Clark
- Roberto Clemente
- Otis Davis
- Alfredo Di Stefano
- Yukio Endō
- Lee Evans
- Eusebio
- Dick Fosbury
- Garrincha
- Bob Gibson
- Charles Greene
- Dan Gurney
- John Havlicek
- Mike Hailwood
- Bob Hayes
- Phil Hill
- Jim Hines
- Geoff Hurst
- Giacinto Facchetti
- Peggy Fleming
- Paul Hornung
- Vince Lombardi
- Rafer Johnson
- Sam Jones
- K. C. Jones
- Kipchoge Keino
- Mickey Mantle
- Vincent Matthews
- Willie Mays
- Willie McCovey
- Bruce McLaren
- Bobby Moore
- Pedro Morales
- Joe Namath
- Jack Nicklaus
- Ray Nitschke
- Chuck Norris
- Al Oerter
- Arnold Palmer
- Pelé
- Richard Petty
- Brian Piccolo
- Ferenc Puskás
- Alf Ramsey
- Jochen Rindt
- Oscar Robertson
- Frank Robinson
- Bobby Robson
- Bill Russell
- Satch Sanders
- Gale Sayers
- Arnold Schwarzenegger
- Bill Shankly
- Ronnie Ray Smith
- Tommie Smith
- Bart Starr
- John Surtees
- Giovanni Trapattoni
- Johnny Unitas
- Jerry West
- Fred Williamson
- Mamo Wolde
- Lev Yashin
See also
- List of decades
- 1960s decor
- Silent Generation (the younger members of that demographic had matured in the early part of the decade).
- Baby Boomers (the decade when the older members of the Boomer generation had become of age).
- List of underground newspapers of the 1960s counterculture
- The Sixties Unplugged (book)
Timelines
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:
1960 • 1961 • 1962 • 1963 • 1964 • 1965 • 1966 • 1967 • 1968 • 1969 • Timeline of 1960s counterculture
References
- Joshua Zeitz Archived 6 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine "1964: The Year the Sixties Began", American Heritage, Oct. 2006.
- John Barth (1984) intro to The Literature of Exhaustion, in The Friday Book.
- Maslin, Janet (5 November 2007). "Brokaw Explores Another Turning Point, the '60s". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 July 2019. Retrieved 26 August 2011.
- "The Economy: We Are All Keynesians Now". Time. 31 December 1965. Archived from the original on 21 September 2007. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
Keynesianism made its biggest breakthrough under John Kennedy, who, as Arthur Schlesinger reports in A Thousand Days, "was unquestionably the first Keynesian President."
- Staricco, Juan Ignacio (2012) https://www.scribd.com/doc/112409042/The-French-May-and-the-Roots-of-Postmodern-Politics Archived 6 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Arthur Marwick, The Sixties: Cultural Revolution in Britain, France, Italy, and the United States, c.1958-c.1974 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998, ISBN 978-0-19-210022-1), 247–248.
- Erlanger, Steven (29 April 2008). "May 1968 – a watershed in French life". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 16 April 2011. Retrieved 31 August 2012.
- "Brief Overview of Vietnam War". Swarthmore College Peace Collection. Archived from the original on 3 August 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- "Gulf of Tonkin Measure Voted in Haste and Confusion in 1964". The New York Times. 25 June 1970. Archived from the original on 23 July 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- Krauthammer, Charles (18 May 2007). "Prelude to the Six Days". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 24 July 2019. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- Kapur, Nick (2018). Japan at the Crossroads: Conflict and Compromise after Anpo. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 1. ISBN 9780674988484. Archived from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 26 July 2021.
- Kapur, Nick (2018). Japan at the Crossroads: Conflict and Compromise after Anpo. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. pp. 4–6. ISBN 9780674988484. Archived from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 26 July 2021.
- Heerten, Lasse; Moses, A. Dirk (3 July 2014). "The Nigeria–Biafra war: postcolonial conflict and the question of genocide". Journal of Genocide Research. 16 (2–3): 169–203. doi:10.1080/14623528.2014.936700. ISSN 1462-3528. S2CID 143878825 – via Taylor and Francis+NEJM.
- "Proxy Wars During the Cold War: Africa". Atomic Heritage Foundation.
- "Milestones: 1961–1968 – Office of the Historian". history.state.gov.
- Oliver August (2 March 2013). "Africa rising A hopeful continent". The Economist. The Economist Newspaper Limited. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- Ocran, Matthew Kofi (2019), Ocran, Matthew Kofi (ed.), "Post-Independence African Economies: 1960–2015", Economic Development in the Twenty-first Century: Lessons for Africa Throughout History, Palgrave Studies in Economic History, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 301–372, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-10770-3_9, ISBN 978-3-030-10770-3, S2CID 159395862, retrieved 7 July 2021
- Jaime Pensado, "The (forgotten) Sixties in Mexico." The Sixties: A Journal of History, Politics and Culture (2008) 1#1: 83–90.
- Curtis Cate, The Ides of August: The Berlin Wall Crisis–1961 (1978).
- Giuseppe Alberigo, and Matthew Sherry, A Brief History of Vatican II (2006)
- William Taubman, Khrushchev: The Man and His Era (2003),
- Günter, et al. eds. Bischof, The Prague Spring and the Warsaw Pact Invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968 (Lexington Books, 2010)
- Krishna Dutta (2008). Calcutta: A Cultural History. Interlink Books. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-56656-721-3. Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 10 October 2016.
- Akbarzadeh, Shahram; Saeed, Abdullah (2 September 2003). Islam and Political Legitimacy. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-38056-5.
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, All Employees, Total Nonfarm , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PAYEMS, January 3, 2024.
- Holland, Susan S. “Long-Term Unemployment in the 1960’s.” Monthly Labor Review, vol. 88, no. 9, 1965, pp. 1069–76. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/41836225. Accessed 4 Jan. 2024.
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Unemployment Rate , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/UNRATE, January 3, 2024
- U.S. Office of Management and Budget and Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Federal Surplus or Deficit as Percent of Gross Domestic Product , retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/FYFSGDA188S, January 3, 2024.
- "Inflation and CPI Consumer Price Index 1960–1969". InflationData.com. Archived from the original on 9 October 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- "U.S. History – 1960s". Archived from the original on 6 June 2007.
- Chun, Jayson Makoto (2006). A Nation of a Hundred Million Idiots?: A Social History of Japanese Television, 1953–1973. Routledge. pp. 184–185. ISBN 978-0-415-97660-2. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
- Langdon, Frank (1973). Japan's Foreign Policy. Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press. p. 19. ISBN 0774800151. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- "Katanga's Communique on the Killing of Lumumba". The New York Times. 14 February 1961. ProQuest 115317883.
- "Rafael Trujillo killer file". Archived from the original on 15 November 2011.
- "Togo's President Slain in Coup: Insurgents Seize Most Of Cabinet". The Washington Post. 14 January 1963. p. A11.
- "The Diem coup | Miller Center". 18 September 2017.
- "Chapter 1". 15 August 2016.
- Kihss, Peter (22 February 1965). "Malcolm X Shot to Death at Rally". The New York Times.
- "Death to the Architect". Archived from the original on 24 April 2007.
- "CIA man recounts Che Guevara's death". BBC. 8 October 2007. Archived from the original on 28 June 2017. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- "Assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr". 24 April 2017.
- Sirhan Reverse Decision
- "Civil Rights Act of 1964 – CRA – Title VII – Equal Employment Opportunities – 42 US Code Chapter 21". Archived from the original on 21 October 2010. Retrieved 22 December 2012.
- "LULAC History – All for One and One for All". League of United Latin American Citizens. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- "americangiforum.org". Archived from the original on 6 July 2015.
- "LatinoLA – Hollywood :: Mendez v. Westminster". LatinoLA. Archived from the original on 16 April 2008. Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- "Hernandez v. Texas – The Oyez Project at IIT Chicago-Kent College of Law". oyez.org. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 27 June 2017.
- "MALDEF – About Us". Archived from the original on 22 April 2008.
- "U.S. Census Bureau Data" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015.
- Peter B.R. Hazell (2009). The Asian Green Revolution. Intl Food Policy Res Inst. Archived from the original on 28 October 2020. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - Carlos Santana: I'm Immortal Archived 23 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine interview by Punto Digital, 13 October 2010
- Jorgensen, Ernst (1998). Elvis Presley: A life in music. The complete recording sessions, p.120. St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-312-18572-3
- Sullivan, Denise. "You Really Got Me". AllMusic. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 25 November 2009.
- Archived 10 July 2001 at the Wayback Machine. Box Office Mojo.
- August, Jude (2 May 2022). "How "The Outsiders" Became the Origin of YA Literature". Medium. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- Jordan Holtzman-Conston (2010). Countercultural Sports in America: The History and Meaning of Ultimate Frisbee. Waltham, Mass. ISBN 978-3838311951. Archived from the original on 24 July 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "World Flying Disc Federation". WFDF Official Website. Archived from the original on 18 October 2013. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- "World Flying Disc Federation". History of the Flying Disc. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- "Professional Disc Golf Association". PDGA Official Website. Archived from the original on 9 May 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- "American Ultimate Disc League". AUDL Official Website. Archived from the original on 21 October 2015. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
Further reading
- Anastakis, Dimitry, ed. The Sixties: passion, politics, and style (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2008.) Canadian emphasis
- Baugess, James S., and Abbe Debolt, eds. Encyclopedia of the Sixties: A Decade of Culture and Counterculture (2 vol, 2012; also E-book) 871pp; 500 entries by scholars excerpt and text search; online review
- Berton, Pierre. 1967: the Last Good Year (Toronto: Doubleday Canada, 1997). Canadian events
- Brooks, Victor. Last Season of Innocence: The Teen Experience in the 1960s (Rowman & Littlefield, 2012) 207 pp.
- Brown, Timothy Scott. West Germany and the Global Sixties (2013)
- Christiansen, Samantha and Zachary Scarlett, ed. The Third World and the Global 1960s (New York: Berghahn, 2013) Introduction
- Farber, David, and Beth Bailey, eds. The Columbia guide to America in the 1960s (Columbia University Press, 2003).
- Farber, David, ed. The Sixties: From Memory to History (1994), Scholarly essays on the United States
- Flamm, Michael W. and David Steigerwald. Debating the 1960s: Liberal, Conservative, and Radical Perspectives (2007) on USA
- Isserman, Maurice, and Michael Kazin. America divided: The civil war of the 1960s (6th ed. Oxford UP, 2020).
- Marwick, Arthur. The Sixties: Cultural Revolution in Britain, France, Italy, and the United States, c.1958-c.1974 (Oxford University Press, 1998, ISBN 978-0-19-210022-1)
- Matusow, Allen, The Unraveling of America: A History of Liberalism in the 1960s (1984) excerpt
- Padva, Gilad. Animated Nostalgia and Invented Authenticity in Arte's Summer of the Sixties. In Padva, Gilad, Queer Nostalgia in Cinema and Pop Culture, pp. 13–34 (Palgrave Macmillan, 2014, ISBN 978-1-137-26633-0).
- Palmer, Bryan D. Canada's 1960s: The Ironies of Identity in a Rebellious Era. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2009.
- Sandbrook, Dominic. Never Had It So Good: A History of Britain from Suez to the Beatles (2006) 928pp; excerpt and text search
- Sandbrook, Dominic. White Heat: A History of Britain in the Swinging Sixties (2 vol 2007)
- Strain, Christopher B. The Long Sixties: America, 1955–1973 (Wiley, 2017). xii, 204 pp.
- Unger, Debi, and Irwin Unger, eds. The Times Were a Changin': The Sixties Reader (1998) excerpt and text search
Historiography
- DeKoven, Marianne. The Sixties and the Emergence of the Postmodern (Duke University Press, 2004)
- Farber, David R. The Sixties: From Memory to History (1994) excerpt and text search
- Heale, Michael J. (March 2005). "The Sixties as History: A Review of the Political Historiography". Reviews in American History. 33 (1): 133–152. doi:10.1353/rah.2005.0009. JSTOR 30031497. S2CID 145537005.
- Hunt, Andrew. "When Did the Sixties Happen? Searching for New Directions", Journal of Social History (1999) 33#1 pp 147–161.
- Meyer, James. The Art of Return: The Sixties and Contemporary Culture (University of Chicago Press, 2019). ISBN 9780226521558
- Pensado, Jaime. "The (forgotten) Sixties in Mexico." The Sixties: A Journal of History, Politics and Culture(2008) 1#1: 83–90.
- Rising, George Goodwin. "Stuck in the sixties: Conservatives and the legacies of the 1960s." (PhD U. of Arizona, 2003). hdl:10150/280496
- Ira Chernus, "When Did "the '60s" Begin? A Cautionary Tale for Historians" 4 Feb 2014, History News Network
- "1964" (PBS documentary, 2013)
- Zurawik, David (20 January 1991). "On PBS, Six Hours of The '60s". The Baltimore Sun Times. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
External links
- The 1960s: A Bibliography Archived 15 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- CBC Digital Archives – 1960s a GoGo
- The Sixties Project
- Heroes of the 1960s – slideshow by Life magazine
- The 60s: Literary Tradition and Social Change, exhibit at the University of Virginia, Library, Special Collections.
- 1960s protest movements in America
- The 1960s in Europe (Online Teaching and Research Guide)
- "1960s Fashion Feature, including biographies, interviews, clothing and resources". Victoria and Albert Museum. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008.
- The 1960s – articles, video, pictures, and facts
| Events by month | |
|---|---|
| 1969 | |
| 1968 | |
| 1967 | |
| 1966 | |
| 1965 | |
| 1964 | |
| 1963 | |
| 1962 | |
| 1961 | |
| 1960 | |
| History of the 20th century | |
|---|---|
| Topics | |
| Lists |
|












