| Revision as of 05:29, 23 February 2009 view source208.1.29.101 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:00, 17 January 2025 view source Tkbrett (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users29,607 edits →top: MOS:DATERANGE | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|President of the United States from 1953 to 1961}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-vandalism|small=yes|expiry=February 20, 2009}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Redirect2|Dwight David Eisenhower|Eisenhower|his grandson|David Eisenhower||Eisenhower (disambiguation)}} | ||
| {{Pp-vandalism|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Infobox President | |||
| {{Use American English|date=July 2020}} | |||
| |nationality=] | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=September 2023}} | |||
| |image=Dwight D. Eisenhower, official photo portrait, May 29, 1959.jpg | |||
| {{Infobox officeholder | |||
| |order=] ] | |||
| | image = Dwight D. Eisenhower, official photo portrait, May 29, 1959 (cropped)(3).jpg | |||
| |term_start=January 20, 1953 | |||
| | alt = Official portrait of Dwight D. Eisenhower as president of the United States | |||
| |term_end=January 20, 1961 | |||
| | caption = Official portrait, 1959 | |||
| |predecessor=] | |||
| | order = 34th | |||
| |successor=] | |||
| | office = President of the United States | |||
| |office2=1st ] | |||
| | vicepresident = ] | |||
| |term_start2=April 2, 1951 | |||
| | term_start = January 20, 1953 | |||
| |term_end2=May 30, 1952 | |||
| | term_end = January 20, 1961 | |||
| |predecessor2=''Post Created'' | |||
| | predecessor = ] | |||
| |succeeded2=Gen. ] | |||
| | successor = ] | |||
| |order3=1st ] | |||
| | order2 = 1st | |||
| |term_start3=May 8 | |||
| | office2 = Supreme Allied Commander Europe | |||
| |term_end3=November 10, 1945 | |||
| | president2 = Harry S. Truman | |||
| |predecessor3=''Post Created'' | |||
| | deputy2 = ] | |||
| |succeeded3=Gen. ] (acting) | |||
| | term_start2 = April 2, 1951 | |||
| |birth_date={{birth date|mf=yes|1890|10|14}} | |||
| | term_end2 = May 30, 1952 | |||
| |birth_place=], ], ] | |||
| | predecessor2 = Position established | |||
| |birthname= David Dwight Eisenhower | |||
| | successor2 = ] | |||
| |death_date={{death date and age|mf=yes|1969|03|28|1890|10|14}} | |||
| | order3 = 13th | |||
| |death_place=], ] | |||
| | office3 = President of Columbia University | |||
| |spouse=] | |||
| | term_start3 = June 7, 1948 | |||
| |children=Doud Dwight Eisenhower,<br/>] | |||
| | term_end3 = January 19, 1953 | |||
| |alma_mater=]<br/>], ], ] | |||
| | predecessor3 = ] | |||
| |occupation=] | |||
| | successor3 = ] | |||
| |party=] | |||
| | office4 = 16th ] | |||
| |vicepresident=] | |||
| | president4 = Harry S. Truman | |||
| |religion=] | |||
| | deputy4 = ] | |||
| |signature=Dwight D. Eisenhower signature.png | |||
| | term_start4 = November 19, 1945 | |||
| |rank=] ] | |||
| | term_end4 = February 6, 1948 | |||
| |branch= ] | |||
| | predecessor4 = ] | |||
| |serviceyears=1915–1953, 1961–1969 | |||
| | successor4 = ] | |||
| |commands=] | |||
| | office5 = 1st ] of the ] | |||
| |battles=] | |||
| | president5 = Harry S. Truman | |||
| |awards=] with four oak leaf clusters,<br/>],<br/>],<br/>],<br/>]<br/>(partial list) | |||
| | term5 = May 8{{snd}}November 10, 1945 | |||
| | predecessor5 = Position established | |||
| | successor5 = ] (acting) | |||
| | office6 = ] | |||
| | appointer6 = ] | |||
| | deputy6 = ] | |||
| | term_start6 = December 24, 1943 | |||
| | term_end6 = July 14, 1945 | |||
| | predecessor6 = Position established | |||
| | successor6 = Position abolished | |||
| | birth_name = David Dwight Eisenhower | |||
| | birth_date = {{birth date|1890|10|14}} | |||
| | birth_place = ], U.S. | |||
| | death_date = {{death date and age|1969|3|28|1890|10|14}} | |||
| | death_place = ], U.S. | |||
| | resting_place = ] | |||
| | party = ] (from 1952) | |||
| | spouse = {{marriage|]|July 1, 1916}} | |||
| | children = {{hlist|]|]}} | |||
| | relatives = ] | |||
| | occupation = {{hlist|]|politician}} | |||
| | education = ] (]) | |||
| | signature = Dwight Eisenhower Signature.svg | |||
| | signature_alt = Cursive signature in ink | |||
| <!--Military service-->| nickname = "Ike"<ref>{{cite web |title=The Eisenhowers |url=https://www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov/eisenhowers |publisher=] |access-date=October 1, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210818155630/https://www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov/eisenhowers |archive-date=August 18, 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | allegiance = United States | |||
| | branch = ] | |||
| | serviceyears = {{plainlist| | |||
| * 1915–1953 | |||
| * 1961–1969<ref name=post>{{cite web |url=http://www.eisenhower.utexas.edu/all_about_ike/post_presidential.html |publisher=The Eisenhower Presidential Library and Museum |title=Post-presidential years |access-date=September 5, 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131023053144/http://www.eisenhower.utexas.edu/all_about_ike/post_presidential.html |archive-date=October 23, 2013}}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | rank = ] | |||
| ] of ] in 1916, where Eisenhower was at the time a football coach.]] | |||
| | battles = {{hidden | |||
| ] 2nd from right.]] | |||
| |''See battles'' | |||
| '''Dwight David “Ike” Eisenhower''' (October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the ] ] from 1953 until 1961 and a ] in the ]. During ], he served as ] of the ] in ], with responsibility for planning and supervising the successful ] and ] in 1944–45. In 1951, he became the first ].<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-2057/Dwight-D-Eisenhower|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| |{{tree list}} | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ****] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ****] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ****] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ****] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| ***] | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***] | |||
| **] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{tree list/end}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |headerstyle=background:#dbdbdb | |||
| |style=text-align:center; | |||
| }} | |||
| | mawards = {{Indented plainlist| | |||
| * ] (5) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{see below|{{slink||Awards and decorations}}}} | |||
| }} | |||
| | module = {{Listen|pos=center|embed=yes|filename=Dwight D. Eisenhower on Military enforcement of school integration in Little Rock.ogg|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower's voice|type=speech|description=Eisenhower on military enforcement of ] in ]<br />Recorded September 24, 1957}} | |||
| | otherparty = ] (1909)<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ferrell |first=Robert H. |title=Eisenhower Was a Democrat |journal=Kansas History |date=1990 |volume=13 |page=134 |url=http://npshistory.com/publications/eise/kh-v13n3-1990-1.pdf |access-date=2 June 2024}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Dwight David Eisenhower'''{{efn|Pronounced ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|aɪ|z|ən|h|aʊ|.|ər|audio=Dwight D. Eisenhower Pronunciation.ogg}} {{respell|EYE|zən|how|ər}}}} (born '''David Dwight Eisenhower''';<!-- Do not remove. His birth name is different from his legal name. It must be in the lead and bolded.--> October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969), also known by his nickname '''Ike''', was the 34th ], serving from 1953 to 1961. During ], he was ] in Europe and achieved the ] as ]. Eisenhower planned and supervised two of the most consequential military campaigns of ]: ] in the ] in 1942–1943 and the ] in 1944. | |||
| Eisenhower was born in ], and raised in ]. His family had a strong religious background, and his mother became a ]. Eisenhower, however, belonged to no organized church until 1952. He graduated from ] in 1915 and later married ], with whom he had two sons. During ], he was denied a request to serve in Europe and instead commanded a unit that trained ] crews. Between the wars he served in staff positions in the US and the Philippines, reaching the rank of ] shortly before the entry of the US into World War II in 1941. After further promotion Eisenhower oversaw the Allied invasions of North Africa and ] before supervising the invasions of ] and ]. After the war ended in Europe, he served as ] of the ] (1945), ] (1945–1948), ] (1948–1953), and as the first ] (1951–1952). | |||
| As President, he oversaw the cease-fire of the ], kept up the pressure on the ] during the ], made ] a higher defense priority, launched the ], enlarged the ] program, and began the ]. He was the last ] ] to serve as U.S. president. | |||
| In 1952, Eisenhower entered the presidential race as a ] to block the isolationist foreign policies of Senator ], who opposed ]. Eisenhower won ] and the ] in ], both times defeating ]. Eisenhower's main goals in office were to ] and reduce ]s. In 1953, he considered using ]s to end the ] and may have threatened China with ] if an armistice was not reached quickly. China did agree and ] resulted, which remains in effect. His ] of nuclear deterrence prioritized "inexpensive" nuclear weapons while reducing funding for expensive Army divisions. He continued ]'s policy of recognizing ] as the legitimate government of China, and he won congressional approval of the ]. His administration provided major aid to help the French fight off Vietnamese Communists in the ]. After the French left, he gave strong financial support to the new state of ]. | |||
| ==Early life and family== | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower was born '''David Dwight Eisenhower''' in ],<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/quick_links/DDE_Mamie_general_bio.html|title=Dwight and Mamie Eisenhower|publisher=]}}</ref> the first president born in that state. He was the third of seven sons<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.whitehouse.gov/history/presidents/de34.html |title=Biography of Dwight D. Eisenhower |accessdate=2008-09-06 |work=whitehouse.gov |publisher=The White House }}</ref> born to David Jacob Eisenhower and ], of German, English and Swiss ancestry. The house in which he was born has been preserved as ] and is operated by the ]. | |||
| He supported ] in ] and ] orchestrated by his own administration. During the ] of 1956, he condemned the Israeli, British, and French invasion of Egypt, and he forced them to withdraw. He also condemned the Soviet invasion during the ] but took no action. He deployed 15,000 soldiers during the ]. Near the end of his term, a summit meeting with the Soviet leader ] was cancelled when ] over the Soviet Union. Eisenhower approved the ], which was left to John F. Kennedy to carry out. | |||
| He was named David Dwight and was called Dwight; he reversed the order of his given names when he entered ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fpri.org/footnotes/129.200705.eisenhower.ww2meaningamericans.html |title=World War II and Its Meaning for Americans |accessdate=2008-09-06 |last=Eisenhower |first=David |authorlink=David Eisenhower |month=May |year=2007 |work=www.pfri.org |publisher=Foreign Policy Research Institute }}</ref>, which is also where he received his nickname, "Ike".<ref> from the website of the ]</ref> | |||
| On the domestic front, Eisenhower governed as a ] who continued ] agencies and expanded ]. He covertly opposed ] and contributed to the end of ] by openly invoking ]. He signed the ] and sent Army troops to enforce federal court orders which ]. His administration undertook the development and construction of the ], which remains the largest construction of roadways in American history. In 1957, following the Soviet launch of ], Eisenhower led the American response which included the ] and the establishment of a stronger, science-based education via the ]. The Soviet Union began to reinforce ], escalating the ]. His two terms saw ] except for a ]. In ], he expressed his concerns about the dangers of massive ], particularly ] and government contracts to private military manufacturers, which he dubbed "the ]". Historical evaluations of ] place him among the ]. | |||
| Eisenhower's paternal ancestors can be traced back to Hans Nicolas Eisenhauer, whose surname is German for "iron worker."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://genealogy.about.com/library/surnames/e/bl_name-EISENHOWER.htm |title=EISENHOWER - Name Meaning & Origin |accessdate=2008-09-06 |work=The New York Times Company|publisher=geneaology.about.com}}</ref> Hans Eisenhauer and his family emigrated from ] (]), Germany to ] in 1741. Descendants made their way west. Eisenhower's family settled in ] in 1892. His father David Eisenhower was a college-educated engineer.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=13–14}}</ref> Eisenhower graduated from ] in 1909.<ref name="gradyear">{{cite web |url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,865992,00.html|title=Public School Products|accessdate=2008-09-06|date=1959-09-14|publisher=] }}</ref> | |||
| == Family background == | |||
| Eisenhower married ] (1896–1979) of ] on July 1, 1916. The couple had two sons. Doud Dwight Eisenhower was born September 24, 1917, and died of ] on January 2, 1921, at the age of three.<ref>{{cite book|author=Berger-Knorr, Lawrence|title=The Pennsylvania Relations of Dwight D. Eisenhower|page=8}}</ref> Their second son, ], was born the following year on August 3, 1922; John served in the ] (retiring as a brigadier general from the Army reserve), became an author, and served as ] from 1969 to 1971. John, coincidentally, graduated from West Point on D-Day, June 6, 1944, and was married to Barbara Jean Thompson in a June wedding in 1947. John and Barbara had four children: ], Barbara Ann, ] and Mary Jean. David, after whom ] is named, married ]'s daughter ] in 1968. | |||
| {{Further|Family of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| The Eisenhauer (German for "iron hewer" or "iron miner") family migrated from the German village of ] to the ] in 1741.<ref name="barnett19421109">{{cite news | url={{GBurl|id=JUAEAAAAMBAJ|p=112}}| title=General "Ike" Eisenhower | magazine=Life | date=November 9, 1942 | access-date=May 31, 2011 | author=Barnett, Lincoln | page=112}}</ref> Accounts vary as to how and when the German name Eisenhauer was ].<ref>{{cite news | url={{GBurl|id=YVD0jK03EPEC}} | title=Ike: An American Hero | author=Korda, Michael | year=2007 | access-date=July 22, 2012 | page=63| publisher=Harper Collins | isbn=9780061744969 }}</ref> | |||
| David Jacob Eisenhower, Eisenhower's father, was a college-educated engineer, despite his own father's urging to stay on the family farm. Eisenhower's mother, ], of predominantly German Protestant ancestry, moved to Kansas from Virginia. She married David on September 23, 1885, in ], on the campus of their alma mater, ].<ref name="Ambrose 1983, pp. 16–8">{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=16–18}}</ref> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| David owned a general store in ], but the business failed due to economic conditions and the family became impoverished. The Eisenhowers lived in Texas from 1889 until 1892, and later returned to Kansas, with $24 ({{Inflation|US|24|1892|fmt=eq}}) to their name. David worked as a railroad mechanic and then at a creamery.<ref name="Ambrose 1983, pp. 16–8" /> By 1898, the parents made a decent living and provided a suitable home for their large family.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=19}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower's paternal ancestor, Hans Nicholas Eisenhauer, was probably of ] or Reformed Protestant practice.{{Fact|date=September 2008}} Eisenhower's mother, Ida E. Stover Eisenhower, previously a member of the ] sect of the ]s, joined the ] (now more commonly known as ]) between 1895 and 1900, when Eisenhower was a child.<ref name=SmithGS>Smith, Gary Scott, (2006). - ''Faith and the Presidency: From George Washington to George W. Bush''. - Oxford, England: ]. - ISBN 0195300602. - Retrieved: 2008-05-24</ref> The Eisenhower home served as the local meeting hall from 1896 to 1915. | |||
| == Early life and education == | |||
| When Eisenhower joined the ] at ], ] in 1911, his ties to Jehovah’s Witnesses were weakened because of the group's anti-].<ref>The Watchtower-2002, p.159 | "They Are No Part of the World" ''Worship the Only True God'' | © Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania </ref><ref>''Reasoning From the Scriptures'' –1985, p. 138 | “Neutrality” | © Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania</ref> By 1915, his parents' home no longer served as the meeting hall. All the men in the household abandoned the Witnesses as adults. Some hid their previous affiliation.<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.seanet.com/~raines/eisenhower.html|title=Why President Eisenhower Hid His Jehovah's Witness Upbringing|author=Bergman, Jerry|journal=JW Research Journal|volume=6|issue=2|date=December 1999}}</ref><ref name=DDEL-JWAC>. - Dwight D. Eisenhower Library. - ]. - (Adobe Acrobat *.PDF document). - Retrieved: 2008-05-23</ref> At his death in 1942, Eisenhower's father was given ] rites as though he remained a Jehovah's Witness. Eisenhower's mother continued as an active Jehovah's Witness until her death. Despite their differences in religious beliefs, Eisenhower enjoyed a close relationship with his mother. | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower was born David Dwight Eisenhower in Denison, Texas, on October 14, 1890, the third of seven sons born to Ida and David.<ref>{{cite book|last=D'Este|first=Carlo|title=Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life|year=2003|publisher=Macmillan|isbn=0805056874|pages=21–22|url={{GBurl|id=RCeteK7LEiYC|p=21}}|access-date=September 13, 2016}}</ref> His mother soon reversed his two forenames after his birth to avoid the confusion of having two Davids in the family.<ref name="A18">{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=18}}</ref> He was named Dwight after the evangelist ].<ref>, biography on World War II graves website</ref> All of the boys were nicknamed "Ike", such as "Big Ike" (]) and "Little Ike" (Dwight); the nickname was intended as an abbreviation of their last name.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=22}}</ref> By World War II, only Dwight was still called "Ike".{{r|barnett19421109}} | |||
| In 1892, the family moved to Abilene, Kansas, which Eisenhower considered his hometown.{{r|barnett19421109}} As a child, he was involved in an accident that cost his younger brother ] an eye, for which he was remorseful for the remainder of his life.<ref>{{cite book|last=D'Este|first=Carlo|title=Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life|year=2003|publisher=Macmillan|isbn=0805056874|page=31|url={{GBurl|id=RCeteK7LEiYC|p=21}}|access-date=June 12, 2020}}</ref> Eisenhower developed a keen and enduring interest in exploring the outdoors. He learned about hunting and fishing, cooking, and card playing from a man named Bob Davis who camped on the ].<ref name=ease /><ref>D'Este, Carlo (2002). ''Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life'', p. 25.</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://home.nps.gov/eise/forteachers/classrooms/upload/webed-Molding-of-a-Leader-Lesson-3-Materials.pdf |title=Getting on the Right TRRACC |work=Lesson Plans: The Molding of a Leader |publisher=Eisenhower National Historic Site |access-date=April 27, 2013 |quote=... Ike spent his weekends at Davis's camp on the Smoky Hill River. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140326175456/http://home.nps.gov/eise/forteachers/classrooms/upload/webed-Molding-of-a-Leader-Lesson-3-Materials.pdf |archive-date=March 26, 2014 |url-status=live }}</ref> While his mother was against war, it was her collection of history books that first sparked Eisenhower's interest in military history; he became a voracious reader on the subject. Other favorite subjects early in his education were arithmetic and spelling.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=32}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower was baptized, confirmed, and became a ] in the ] Church in a single ceremony on February 1, 1953, just 12 days after his first inauguration.<ref name="Trivia">. - | |||
| (c/o . - Archive Date: 2007-06-12). - ]. - Retrieved: 2008-05-24</ref> He is the only president known to have undertaken these rites while in office. Eisenhower was instrumental in the addition of the words "''under God''" to the ] in 1954, and the 1956 adoption of "'']''" as the ] of the US, and its 1957 introduction on paper currency. In his retirement years, he was a member of the ] Presbyterian Church.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.gettysburg.com/communit/gpc.htm|title=Gettysburg Presbyterian Church|publisher=Gettysburg}}</ref> The chapel at his presidential library is intentionally inter-denominational. | |||
| Eisenhower's parents set aside specific times at breakfast and at dinner for daily family Bible reading. Chores were regularly assigned and rotated among all the children, and misbehavior was met with unequivocal discipline, usually from David.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=25}}</ref> His mother, previously a member (with David) of the ] (]) sect of the ]s,<ref name="Time"/> joined the ], later known as ]. The Eisenhower home served as the local meeting hall from 1896 to 1915, though Dwight never joined.<ref>Bergman, Jerry. "Steeped in Religion: President Eisenhower and the Influence of the Jehovah's Witnesses", ''Kansas History'' (Autumn 1998).</ref> His later decision to attend West Point saddened his mother, who felt that warfare was "rather wicked", but she did not overrule his decision.<ref>D'Este, Carlo (2002). ''Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life'', p. 58.</ref> Speaking of himself in 1948, Eisenhower said he was "one of the most deeply religious men I know" though unattached to any "sect or organization". He was baptized in the ] in 1953.<ref name="Time"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100820072103/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,889614,00.html |date=August 20, 2010 }}, ''Time'', February 9, 1953.</ref> | |||
| He questioned ] about how people can be certain they are going to ] after death.<ref name=GibbsN-DuffyM>Gibbs, Nancy; and Michael Duffy. - . - '']''. - August 9, 2007. - Retrieved: 2008-06-07</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower attended ] and graduated in 1909.<ref name="gradyear">{{Cite news |title=Public School Products |date=September 14, 1959 |magazine=]}}</ref> As a freshman, he injured his knee and developed a leg infection that extended into his groin, which his doctor diagnosed as life-threatening. The doctor insisted that the leg be amputated but Dwight refused to allow it, and surprisingly recovered, though he had to repeat his freshman year.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=36}}</ref> He and brother ] both wanted to attend college, though they lacked the funds. They made a pact to take alternate years at college while the other worked to earn the tuitions.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=37}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower was sworn into office with his personal ''West Point Bible'', open to ] 33:12, at both his 1953 and 1957 ] ceremonies. Additionally for 1953, he included the Bible that ] had used in 1789 (belonging to St. John's Masonic Lodge No. 1), opened to ] 7:14.<ref>. - Joint Congressional Committee | |||
| on Inaugural Ceremonies. - U.S. Senate.</ref><ref>. - Joint Congressional Committee | |||
| on Inaugural Ceremonies. - U.S. Senate.</ref> | |||
| Edgar took the first turn at school, and Dwight was employed as a night supervisor at the Belle Springs Creamery.<ref>{{Cite news|access-date=May 23, 2008|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,839998-3,00.html|title=Eisenhower: Soldier of Peace|magazine=]|date=April 4, 1969|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080524105356/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,839998-3,00.html|archive-date=May 24, 2008|url-status=dead}}</ref> When Edgar asked for a second year, Dwight consented. At that time, a friend ] was applying to the ] and urged Dwight to apply, since no tuition was required. Eisenhower requested consideration for either Annapolis or West Point with his Senator, ]. Though Eisenhower was among the winners of the entrance-exam competition, he was beyond the age limit for the Naval Academy.<ref name="Education">{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://www.dwightdeisenhower.com/biodde.html |title=Biography: Dwight David Eisenhower |publisher=] |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080523224747/http://www.dwightdeisenhower.com/biodde.html |archive-date=May 23, 2008 }}</ref> He accepted an appointment to West Point in 1911.<ref name="Education" /> | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| Dwight D. Eisenhower attended ] in Abilene, Kansas and graduated with the class of 1909.<ref name="gradyear"/> He then took a job as a night foreman at the Belle Springs Creamery.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,839998-3,00.html|title=Eisenhower: Soldier of Peace|work=]|date=1969-04-04}}</ref> | |||
| At West Point, Eisenhower relished the emphasis on traditions and on sports, but was less enthusiastic about the hazing, though he willingly accepted it as a plebe. He was also a regular violator of the more detailed regulations and finished school with a less than stellar discipline rating. Academically, Eisenhower's best subject by far was English. Otherwise, his performance was average, though he thoroughly enjoyed the typical emphasis of engineering on science and mathematics.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=44–48}}</ref> | |||
| After Dwight worked for two years to support his brother ]'s college education, a friend urged him to apply to the ]. Though Eisenhower passed the entrance exam, he was beyond the age of eligibility for admission to the Naval Academy.<ref name="Education">{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.dwightdeisenhower.com/biodde.html|title=Biography: Dwight David Eisenhower |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| In athletics, Eisenhower later said that "not making the baseball team at West Point was one of the greatest disappointments of my life, maybe my greatest".<ref name="rayaip">{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008|url=http://www.baseball-almanac.com/prz_qde.shtml|title=President Dwight D. Eisenhower Baseball Related Quotations|publisher=Baseball Almanac|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080521164214/http://www.baseball-almanac.com/prz_qde.shtml|archive-date=May 21, 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> He made the ]<ref name="ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil">{{cite web|title=Eisenhower BOQ 1915 |url=http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/tour8.htm |access-date=August 23, 2012 |publisher=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070717161130/http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/tour8.htm |archive-date= July 17, 2007}}</ref><ref name="ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil 2">{{cite web|url=http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/eisen_football.htm |title=Lt Eisenhower and Football Team |access-date=August 23, 2012 |publisher=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070717161130/http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/eisen_football.htm |archive-date= July 17, 2007}}</ref> and was a starter at ] in 1912, when he tried to tackle the legendary ] of the ].<ref>{{Cite news |access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://www.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/europe/07/09/jim.thorpe/ |title=Roller-coaster life of Indian icon, sports' first star |publisher=CNN |date=July 15, 1912 |author=Botelho, Greg |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071114200705/http://www.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/europe/07/09/jim.thorpe/ |archive-date=November 14, 2007 |url-status=live }}</ref> Eisenhower suffered a torn knee while being tackled in the next game, which was the last he played; he reinjured his knee on horseback and in the boxing ring,{{r|barnett19421109}}<ref name=ease>Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1967). ''At Ease: Stories I Tell to Friends'', Garden City, New York, Doubleday & Company, Inc.</ref><ref>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://www.eisenhowermemorial.org/stories/Ike-and-team.htm |title=Ike and the Team |publisher=] |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080725054759/http://www.eisenhowermemorial.org/stories/Ike-and-team.htm |archive-date=July 25, 2008 }}</ref> so he turned to fencing and gymnastics.{{r|barnett19421109}} | |||
| Kansas ] ] recommended Dwight for an appointment to the Military Academy in 1911, which he received.<ref name="Education"/> Eisenhower graduated in the upper half of the class of 1915.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.ipl.org/div/potus/ddeisenhower.html|title=Dwight David Eisenhower|publisher=]}}</ref> The 1915 class was known as "]", because 59 members eventually became ]s. | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Athletic career=== | |||
| Eisenhower long had aspirations of playing ]: | |||
| {{cquote|When I was a small boy in Kansas, a friend of mine and I went fishing and as we sat there in the warmth of the summer afternoon on a river bank, we talked about what we wanted to do when we grew up. I told him that I wanted to be a real major league baseball player, a genuine professional like ]. My friend said that he'd like to be President of the United States. Neither of us got our wish.<ref name = "rayaip">{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.baseball-almanac.com/prz_qde.shtml|title=President Dwight D. Eisenhower Baseball Related Quotations|publisher=Baseball Almanac}}</ref>}} | |||
| Eisenhower later served as junior varsity football coach and cheerleader, which caught the attention of General ].<ref name="Team America">{{Cite book |last=O'Connell |first=Robert L. |title=Team America |publisher=] |year=2022 |isbn=9780062883322 |edition=1st |pages=117–119}}</ref> He graduated from West Point in the middle of the class of 1915,<ref>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008|url=http://www.ipl.org/div/potus/ddeisenhower.html|title=Dwight David Eisenhower|publisher=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080511153206/http://www.ipl.org/div/potus/ddeisenhower.html|archive-date=May 11, 2008|url-status=dead}}</ref> which became known as "]", because 59 members eventually became ]s. After graduation in 1915, Second Lieutenant Eisenhower requested an assignment in the Philippines, which was denied; because of the ongoing ], he was posted to ] in ], Texas, under the command of General Funston. In 1916, while stationed at Fort Sam Houston, Funston convinced him to become the football coach for ];<ref name="Team America"/> he later became the coach at St. Louis College, now ],<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=56}}</ref> and was an honorary member of the Sigma Beta Chi fraternity there.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://sigmabetachi.celect.org/we-remember |title=We Remember |website=Sigma Beta Chi |access-date=March 20, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180320110037/http://sigmabetachi.celect.org/we-remember |archive-date=March 20, 2018 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| At West Point, Eisenhower tried out for the baseball team but did not make it. He would later say that "not making the baseball team at West Point was one of the greatest disappointments of my life, maybe my greatest."<ref name = "rayaip"/> But Eisenhower did make the football team. He started as a varsity running back and linebacker in 1912. In a bit of a fabled match-up, he even tackled the legendary ] in a 1912 game.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/europe/07/09/jim.thorpe/|title=Roller-coaster life of Indian icon, sports' first star |publisher=]|date=1912-07-15|author=Botelho, Greg}}</ref> The next week however, Eisenhower would hurt his knee after being tackled around the ankles, which he would soon worsen and permanently damage on horseback and in the boxing ring.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.eisenhowermemorial.org/stories/Ike-and-team.htm|title=Ike and the Team |publisher=]}}</ref> He would later serve as junior varsity football coach and yell leader. | |||
| == Personal life == | |||
| ] over whether Eisenhower played minor league (semi-professional) baseball for ] in the Central Kansas League the year before he attended West Point and played amateur football there. | |||
| {{main|Family of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| While Eisenhower was stationed in Texas, he met Mamie Doud of ].{{r|barnett19421109}} They were immediately taken with each other. He proposed to her on ] in 1916.<ref>{{cite web | url =https://highways.dot.gov/public-roads/marchapril-2003/man-who-changed-america-part-i | title =The Man Who Changed America, Part I | first =Richard F. | last =Weingroff | publisher =] | date =March–April 2003 | access-date =April 17, 2013 | archive-url =https://web.archive.org/web/20130509120831/http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/publications/publicroads/03mar/05.cfm | archive-date =May 9, 2013 | url-status =live }}</ref> A November wedding date in Denver was moved up to July 1 due to the impending ]; Funston approved 10 days of leave for their wedding.<ref>{{Cite book |last=O'Connell |first=Robert L. |title=Team America |publisher=] |year=2022 |isbn=9780062883322 |edition=1st |page=122}}</ref> The Eisenhowers moved many times during their first 35 years of marriage.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=59–60}}</ref> | |||
| The Eisenhowers had two sons. In late 1917 while he was in charge of training at ] in ], his wife Mamie had their first son, ], who died of ] at the age of three.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Berger-Knorr, Lawrence|title=The Pennsylvania Relations of Dwight D. Eisenhower|page=8}}</ref> Eisenhower was mostly reluctant to discuss his death.{{r|beckett}} Their second son, ], was born in ], Colorado.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/national/john-sd-eisenhower-historian-and-presidents-son-dies-at-91/2013/12/21/2f344aae-6a9a-11e3-ae56-22de072140a2_story.html |title=John S.D. Eisenhower dies; historian and president's son was 91 |date=December 21, 2013 |newspaper=The Washington Post |access-date=August 16, 2017 |first1=Martin |last1=Weil |first2=Emily |last2=Langer |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170817082546/https://www.washingtonpost.com/national/john-sd-eisenhower-historian-and-presidents-son-dies-at-91/2013/12/21/2f344aae-6a9a-11e3-ae56-22de072140a2_story.html |archive-date=August 17, 2017 |url-status=live }}</ref> John served in the ], retired as a brigadier general, became an author and served as ] from 1969 to 1971. He married Barbara Jean Thompson and had four children: ], Barbara Ann, ] and ]. David, after whom ] is named,<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/research/online_documents/camp_david.html |title=Camp David |publisher=Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library, Museum, and Boyhood Home |quote=Ike re-named it 'Camp David' in honor of his grandson David Eisenhower |access-date=August 16, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170706063352/https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/research/online_documents/camp_david.html |archive-date=July 6, 2017 |url-status=live }}</ref> married ]'s daughter ] in 1968. | |||
| In 1916, while stationed at ], Eisenhower was football coach for St. Louis College, now ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/tour8.htm |title=Eisenhower BOQ 1915 |accessdate=2008-05-24 |publisher=] }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://ameddregiment.amedd.army.mil/fshmuse/eisen_football.htm |title=Lt Eisenhower and Football Team |accessdate=2008-05-24 |publisher=] }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Early military career== | |||
| {{Refimprove|section|date=August 2008}} | |||
| {{see also|Military career of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| Eisenhower enrolled at the United States Military Academy at West Point in June 1911. His parents were against militarism, but did not object to his entering West Point because they supported his education. Eisenhower was a strong athlete and enjoyed notable successes in his competitive endeavors. In 1912, a spectacular Eisenhower ] won praise from the sports reporter of the '']'', and he even managed, with the help of a ] teammate, to tackle the legendary ]. In the very next week, however, his promising sports career ended when he incurred a severe knee injury. | |||
| Eisenhower was a golf enthusiast later in life, and he joined the ] in 1948.<ref>{{harvnb|Owen|1999|pp=165–167}}</ref> He played golf frequently during and after his presidency and was unreserved in his passion for the game, to the point of golfing during winter; he ordered his golf balls painted black so he could see them better against snow. He had a basic golf facility installed at Camp David, and he became close friends with the Augusta National Chairman ], inviting Roberts to stay at the ] on numerous occasions.<ref>{{harvnb|Owen|1999|p=169}}</ref> Roberts, an investment broker, also handled the Eisenhower family's investments.<ref name="owen-172-173">{{harvnb|Owen|1999|pp=172–173}}</ref> | |||
| ].]] | |||
| He began ] while at Columbia University, after watching ] paint Mamie's portrait. Eisenhower painted about 260 oils during the last 20 years of his life. The images were mostly landscapes but also portraits of subjects such as Mamie, their grandchildren, General Montgomery, ], and ].<ref name="dodson19901117">{{cite news | url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1990-11-17-me-4317-story.html | title=New Exhibit Offers a Look at Eisenhower the Artist | work=Los Angeles Times | date=November 17, 1990 | access-date=January 13, 2012 | author=Dodson, Marcida | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120309135112/http://articles.latimes.com/1990-11-17/local/me-4317_1_nixon-library | archive-date=March 9, 2012 | url-status=live }}</ref> ] stated that Eisenhower's paintings, "simple and earnest", caused her to "wonder at the hidden depths of this reticent president". A conservative in both art and politics, Eisenhower in a 1962 speech denounced modern art as "a piece of canvas that looks like a broken-down ], loaded with paint, has been driven over it".<ref name="beckett">{{cite journal | url=http://www.whha.org/whha_publications/publications_documents/whitehousehistory_21.pdf | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120605042420/http://www.whha.org/whha_publications/publications_documents/whitehousehistory_21.pdf | url-status=dead | archive-date=June 5, 2012 | title=President Eisenhower: Painter | author=Beckett, Wendy | journal=White House History | issue=21 | pages=30–40 }}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower graduated in 1915. He served with the ] until 1918 at various camps in ] and ]. During ], Eisenhower became the #3 leader of the new tank corps and rose to temporary (]) ] in the ]. He spent the war training tank crews in ] and never saw combat. After the war, Eisenhower reverted to his regular rank of ] (and was promoted to ] a few days later) before assuming duties at ], ], where he remained until 1922. His interest in ] was strengthened by many conversations with ] and other senior tank leaders; however their ideas on tank warfare were strongly discouraged by superiors.<ref>{{harvnb|Sixsmith|1973|p=6}}</ref> | |||
| '']'' was Eisenhower's favorite movie.<ref>{{cite web|last=Erickson|first=Hal|title=Angels in the Outfield (1951): Review Summary|url=https://movies.nytimes.com/movie/83734/Angels-in-the-Outfield/overview|access-date=September 25, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130928092648/http://movies.nytimes.com/movie/83734/Angels-in-the-Outfield/overview|archive-date=September 28, 2013|department=Movies & TV Dept.|work=]|author-link=Hal Erickson (author)|date=2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> His favorite reading material for relaxation was the Western novels of ].<ref name="Rhodes Scholars">{{cite book|last=Schaeper|first=Thomas J.|title=Rhodes Scholars, Oxford, and the Creation of an American Elite|year=2010|publisher=Berghahn Books|isbn=978-1845457211|page=210}}</ref> With his excellent memory and ability to focus, Eisenhower was skilled at cards. He learned poker, which he called his "favorite indoor sport", in Abilene. Eisenhower recorded West Point classmates' poker losses for payment after graduation and later stopped playing because his opponents resented having to pay him. A friend reported that after learning to play ] at West Point, Eisenhower played the game six nights a week for five months.<ref name="smith20123132">{{cite book | title=Eisenhower in War and Peace | publisher=Random House | author=Smith, Jean Edward | year=2012 | pages=31–32, 38 | isbn=978-0679644293}}</ref> Eisenhower continued to play bridge throughout his military career. While stationed in the Philippines, he played regularly with President ], earning him the nickname the "Bridge Wizard of Manila".<ref name="Manuel L. Quezon: 15 Mesmerizing Facts About Philippines' 2nd President">{{cite web |title=Manuel L. Quezon: 15 Mesmerizing Facts About Philippines' 2nd President |url=https://filipiknow.net/facts-about-president-manuel-quezon/ |website=FilipiKnow |access-date=October 27, 2020 |date=June 3, 2019}}</ref> An unwritten qualification for an officer's appointment to Eisenhower's staff during World War II was the ability to play bridge. He played even during the stressful weeks leading up to the D-Day landings. His favorite partner was General ], considered the best player in the US Army; he appointed Gruenther his second-in-command at NATO partly because of his skill at bridge. Saturday night bridge games at the White House were a feature of his presidency. He was a strong player, though not an expert by modern standards. The great bridge player and popularizer ] described his game as classic and sound with "flashes of brilliance" and said that "you can always judge a man's character by the way he plays cards. Eisenhower is a calm and collected player and never whines at his losses. He is brilliant in victory but never commits the bridge player's worst crime of gloating when he wins." Bridge expert ] frequently participated in the White House games and said, "The President plays better bridge than golf. He tries to break 90 at golf. At bridge, you would say he plays in the 70s."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://advocate.district8acbl.com/jun09/ike.htm |title=D-Day Memories of the Bridge Player in Chief |first=Karen |last=Walker |website=] District 8 |date=June 2009 |access-date=May 25, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160630205253/http://advocate.district8acbl.com/jun09/ike.htm |archive-date=June 30, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower became executive officer to General ] in the ], where he served until 1924. Under Conner's tutelage, he studied military history and theory (including ]'s '']''), and later cited Conner's enormous influence on his military thinking. In 1925–26, he attended the ] at ], Kansas,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www-cgsc.army.mil/carl/resources/csi/bender/bender.asp |title=Watershed at Leavenworth |accessdate=2008-09-06 |last=Bender |first=Mark C. |year=1990 |publisher=U.S. Army Command and General Staff College }}</ref> and then served as a ] commander at ], Georgia until 1927. | |||
| == World War I (1914–1918) == | |||
| ], Philippines]] | |||
| {{See also|Military career of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| Eisenhower served initially in logistics and then the ] at various camps in Texas and ] until 1918. When the US entered ], he immediately requested an overseas assignment but was denied and assigned to ].<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=61–62}}</ref> In February 1918, he was transferred to ] in ] with the ]. His unit was later ordered to France, but, to his chagrin, he received orders for the new ], where he was promoted to ] ] in the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=62}}</ref> He commanded a unit that trained tank crews at ] – his first command. Though Eisenhower and his tank crews never saw combat, he displayed excellent organizational skills as well as an ability to accurately assess junior officers' strengths and make optimal placements of personnel.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=63}}</ref> | |||
| During the late 1920s and early 1930s Eisenhower's career in the peacetime Army stagnated; many of his friends resigned for high paying business jobs. He was assigned to the ], directed by General ], then to the ], and then served as executive officer to General George V. Mosely, Assistant Secretary of War, from 1929 to 1933. He then served as chief military aide to General ], Army ], until 1935, when he accompanied MacArthur to the ], where he served as assistant military adviser to the Philippine government. It is sometimes said that this assignment provided valuable preparation for handling the challenging personalities of ], ] and ] during World War II. Eisenhower was promoted to lieutenant colonel (in a non-brevet status) in 1936 after sixteen years as a major. He also learned to fly, although he was never rated as a military pilot. He made a solo flight over the Philippines in 1937. | |||
| His spirits were raised when the unit under his command received orders overseas to France. This time his wishes were thwarted when the ] was signed a week before his departure date.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=65}}</ref> Completely missing out on the warfront left him depressed and bitter for a time, despite receiving the ] for his work at home.<ref>{{cite web |title=Dwight David Eisenhower |url=https://valor.militarytimes.com/hero/17503 |website=MilitaryTimes.com |publisher=Sightline Media Group |access-date=January 30, 2021}}</ref> In World War II, rivals who had combat service in the Great War (led by Gen. ]) sought to denigrate Eisenhower for his previous lack of combat duty, despite his stateside experience establishing a camp for thousands of troops and developing a full combat training schedule.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=68}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower returned to the U.S. in 1939 and held a series of staff positions in ], ] and Texas. In June 1941, he was appointed Chief of Staff to General ], Commander of the ], at ] in ], Texas. He was promoted to ] on October 3, 1941<ref></ref>. Although his administrative abilities had been noticed, on the eve of the U.S. entry into World War II he had never held an active command and was far from being considered as a potential commander of major operations. | |||
| ==Between the Wars (1918–1939)== | |||
| ==World War II== | |||
| === In service of generals === | |||
| {{Refimprove|section|date=August 2008}} | |||
| ] | ] at ]]] | ||
| After the war, Eisenhower reverted to his regular rank of ] and a few days later was promoted to ], a rank he held for 16 years.<ref name="Ambrose 1983, p. 14">{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=14}}</ref> The major was assigned in 1919 to a ] to test vehicles and dramatize the need for improved roads. Indeed, the convoy averaged only {{convert|5|mph|km/h}} from Washington, D.C. to San Francisco; later the improvement of highways became a signature issue for Eisenhower as president.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=69}}</ref> | |||
| He assumed duties again at ], Maryland, commanding a battalion of tanks, where he remained until 1922. His schooling continued, focused on the nature of the next war and the role of the tank. His new expertise in ] was strengthened by a close collaboration with ], ], and other senior tank leaders. Their leading-edge ideas of speed-oriented offensive tank warfare were strongly discouraged by superiors, who considered the new approach too radical and preferred to continue using tanks in a strictly supportive role for the infantry. Eisenhower was even threatened with ] for continued publication of these proposed methods of tank deployment, and he relented.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Sixsmith |first1=E. K. G. |title=Eisenhower, His Life and Campaigns |year=1973 |page=6 |publisher=Conshohocken, PA Combined Publishing}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=70–73}}</ref> | |||
| After the ] ], Eisenhower was assigned to the General Staff in Washington, where he served until June 1942 with responsibility for creating the major war plans to defeat Japan and ]. He was appointed Deputy Chief in charge of Pacific Defenses under the Chief of War Plans Division, General ], and then succeeded Gerow as Chief of the War Plans Division. Then he was appointed Assistant Chief of Staff in charge of Operations Division under Chief of Staff General ]. It was his close association with Marshall that finally brought Eisenhower to senior command positions. Marshall recognized his great organizational and administrative abilities.<ref>{{cite book | |||
| |last=Hakim | |||
| |first=Joy | |||
| |title=A History of Us: War, Peace and all that Jazz | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |date=1995 | |||
| |location=] | |||
| |isbn=0-19-509514-6 }}</ref> | |||
| From 1920, Eisenhower served under a succession of talented generals – ], ], ] and ]. He first became executive officer to General Conner in the ], where, joined by Mamie, he served until 1924. Under Conner's tutelage, he studied military history and theory (including ]'s '']''), and later cited Conner's enormous influence on his military thinking, saying in 1962 that "Fox Conner was the ablest man I ever knew." Conner's comment on Eisenhower was, " is one of the most capable, efficient and loyal officers I have ever met."<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=73–76}}</ref> On Conner's recommendation, in 1925–1926 he attended the ] at ], Kansas, where he graduated first in a class of 245 officers.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www-cgsc.army.mil/carl/resources/csi/bender/bender.asp |title=Watershed at Leavenworth |access-date=September 6, 2008 |last=Bender |first=Mark C. |year=1990 |publisher=U.S. Army Command and General Staff College |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081029063505/http://www-cgsc.army.mil/carl/resources/csi/bender/bender.asp |archive-date=October 29, 2008 }}</ref><ref>American President: An Online Reference Resource, ''Dwight David Eisenhower (1890–1969)'', , {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110605065316/http://millercenter.org/president/eisenhower/essays/biography/2 |date=June 5, 2011 }} Miller Center of Public Affairs, University of Virginia.</ref> | |||
| In 1942, Eisenhower was appointed Commanding General, ] (ETOUSA) and was based in ]. In November, he was also appointed ] of the ] (NATOUSA) through the new operational Headquarters ]. The word "expeditionary" was dropped soon after his appointment for security reasons. In February 1943, his authority was extended as commander of AFHQ across the Mediterranean basin to include the ], commanded by General Bernard Law Montgomery. The ] had advanced across the ] from the east and was ready for the start of the ]. Eisenhower gained his fourth star and gave up command of ETOUSA to be commander of NATOUSA. After the capitulation of ] forces in ], Eisenhower remained in command of the renamed ] (MTO), keeping the operational title and continued in command of NATOUSA redesignated MTOUSA. In this position he oversaw the ] and the ]. | |||
| During the late 1920s and early 1930s, Eisenhower's career stalled somewhat, as military priorities diminished; many of his friends resigned for high-paying business jobs. He was assigned to the ] directed by General Pershing, and with the help of his brother ], then a journalist at the ], he produced a guide to American battlefields in Europe.<ref>{{cite book |first=Steven |last=Trout |title=On the Battlefield of Memory: The First World War and American Remembrance, 1919–1941 |year=2010 |pages=xv–xxxii }}</ref> He then was assigned to the ] and graduated in 1928. After a one-year assignment in France, Eisenhower served as executive officer to General ], ], from 1929 to February 1933.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=82}}</ref> Major Eisenhower graduated from the ] in 1933 and later served on the faculty (it was later expanded to become the Industrial College of the Armed Services and is now known as the Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy).<ref>{{cite web|url=https://armyhistory.org/general-of-the-army-dwight-david-eisenhower/|title=General of the Army Dwight David Eisenhower|access-date=March 16, 2016|publisher=Army Historical Foundation|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160324093918/https://armyhistory.org/general-of-the-army-dwight-david-eisenhower/|archive-date=March 24, 2016|url-status=live|date=January 22, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.history.army.mil/brochures/Ike/ike.htm|title=Dwight David Eisenhower, The Centennial|access-date=March 16, 2016|year=1990|publisher=U.S. Army Center of Military History|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305142924/http://www.history.army.mil/brochures/ike/ike.htm|archive-date=March 5, 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ], ] on the evening of June 5, 1944.]] | |||
| His primary duty was planning for the next war, which proved most difficult in the midst of the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=88}}</ref> He then was posted as chief military aide to General Douglas MacArthur, Army Chief of Staff. In 1932, he participated in the clearing of the ] encampment in Washington, D.C. Although he was against the actions taken against the veterans and strongly advised MacArthur against taking a public role in it, he later wrote the Army's official incident report, endorsing MacArthur's conduct.<ref name=Wukovits43>{{cite book |title=Eisenhower |last=Wukovits |first=John F. |year=2006 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=978-0-230-61394-2 |page=43 |url={{GBurl|id=om5ZykQFGrwC|p=43}} |access-date=June 15, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life |last=D'Este |first=Carlo |author-link=Carlo D'Este |year=2002 |publisher=Henry Holt & Co. |isbn=0-8050-5687-4 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/eisenhowersoldie00dest |url-access=registration |access-date=June 15, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| In December 1943, it was announced that Eisenhower would be Supreme Allied Commander in Europe. In January 1944, he resumed command of ETOUSA and the following month was officially designated as the ] (SHAEF), serving in a dual role until the end of hostilities in Europe in May 1945. In these positions he was charged with planning and carrying out the Allied ] in June 1944 under the code name ], the liberation of western Europe and the invasion of Germany. A month after the Normandy ] landings on June 6, 1944, the ] took place, and control of the forces which took part in the southern invasion passed from the AFHQ to the SHAEF. From then until the ] on May 8, 1945, Eisenhower through SHAEF had supreme command of all operational Allied forces<sup>]</sup>, and through his command of ETOUSA, administrative command of all U.S. forces, on the ] north of the ]. | |||
| ===Philippine tenure (1935–1939)=== | |||
| As recognition of his senior position in the Allied command, on December 20, 1944, he was promoted to ] equivalent to the rank of ] in most European armies. In this and the previous high commands he held, Eisenhower showed his great talents for leadership and diplomacy. Although he had never seen action himself, he won the respect of front-line commanders. He dealt skillfully with difficult subordinates such as ] and ], and allies such as ], Field Marshal ] and General ]. He had fundamental disagreements with Churchill and Montgomery over questions of strategy, but these rarely upset his relationships with them. He negotiated with ] ]<ref>Memoir of Eisenhower's translator for the ] meetings with Zhukov {{cite news|title=Ike and Zhukov|author=]|work=Collier's Magazine|date=1955-07-22}}</ref>, and such was the confidence that President ] had in him, he sometimes worked directly with ], much to the chagrin of the British High Command who disliked being bypassed. During the advance towards Berlin, he was notified by General Bradley that Allied forces would suffer an estimated 100,000 casualties before taking the city. The Soviet Army sustained 80,000 casualties during the fighting in and around Berlin, the last large number of casualties suffered in the war against Nazism.<ref>{{harvnb|D'Este|2002|pp=694–96}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Ambrose, Stephen E.|title=Eisenhower and Berlin, 1945: The Decision to Halt at the Elbe|date=2000}}</ref> | |||
| In 1935, he accompanied MacArthur to the Philippines, where he served as assistant military adviser to the ] in developing their army. MacArthur allowed Eisenhower to handpick an officer whom he thought would contribute to the mission. Hence he chose ], a classmate of his at West Point. Having been brought up in Mexico, which inculcated into him the Spanish culture which influenced both Mexico and the Philippines, Ord was deemed the right pick for the job. Eisenhower had strong philosophical disagreements with MacArthur regarding the role of the ] and the leadership qualities that an American army officer should exhibit and develop in his subordinates. The antipathy between Eisenhower and MacArthur lasted the rest of their lives.<ref>Irish, Kerry. "Dwight Eisenhower and Douglas MacArthur in the Philippines: There Must Be a Day of Reckoning", ''Journal of Military History'', April 2010, Vol. 74, Issue 2, pp. 439–473.</ref> | |||
| Historians have concluded that this assignment provided valuable preparation for handling the challenging personalities of ], George S. Patton, George Marshall, and Bernard Montgomery during World War II. Eisenhower later emphasized that too much had been made of the disagreements with MacArthur and that a positive relationship endured.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=94}}</ref> While in Manila, Mamie suffered a life-threatening stomach ailment but recovered fully. Eisenhower was promoted to the rank of permanent lieutenant colonel in 1936. He also learned to fly with the ] at the Zablan Airfield in ] under Capt. ], making a solo flight over the Philippines in 1937, and obtained his private pilot's license in 1939 at ].<ref name="Villamor">{{cite book |last1=Villamor |first1=Jesus |last2=Snyder |first2=Gerald |title=They Never Surrendered |date=1968 |publisher=Vera-Reyes, Inc. }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/research/finding_aids/pdf/Eisenhower_Dwight_Pre_Presidential_Papers/Principal_File.pdf |title=Dwight D. Eisenhower Pre-Presidential Papers, 1916–52 |publisher=Eisenhower Presidential Library |access-date=August 16, 2017 |year=1997 |page=74 |quote=references to Eisenhower's pilot's license |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170209201349/https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/Research/Finding_Aids/pdf/Eisenhower_Dwight_Pre_Presidential_Papers/Principal_File.pdf |archive-date=February 9, 2017 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|journal=Air Progress|date=August 1989|page=62|first=Nick|last=Komons|title=unknown title}}</ref> Also around this time, he was offered a post by the ] Government, namely by then Philippine President ] on recommendations by MacArthur, to become the chief of police of a new capital being planned, now named ], but he declined the offer.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Merrit, Jésus V.|title=Our presidents: profiles in history|page=77|year=1962}}</ref> | |||
| It was never certain that ] would succeed. The seriousness surrounding the entire decision, including the timing and the location of the Normandy invasion, might be summarized by a second shorter speech that Eisenhower wrote in advance, in case he needed it. Long after the successful landings on D-Day and the ] broadcast of Eisenhower's brief speech concerning them, the never-used second speech was found in a shirt pocket by an ]. It read: | |||
| == World War II (1939–1945) == | |||
| :Our landings in the Cherbourg-Havre area have failed to gain a satisfactory foothold and I have withdrawn the troops. My decision to attack at this time and place was based on the best information available. The troops, the air and the Navy did all that bravery and devotion to duty could do. If any blame or fault attaches to the attempt, it is mine alone. | |||
| Eisenhower returned to the United States in December 1939 and was assigned as ] of the 1st Battalion, ] at ], Washington, later becoming the regimental executive officer. In March 1941 he was promoted to colonel and assigned as chief of staff of the newly activated ] under Major General ]. In June 1941, he was appointed chief of staff to General ], Commander of the ], at Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas. After successfully participating in the ], he was promoted to brigadier general on October 3, 1941.<ref>Korda (2007), pp 239–243</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dwightdeisenhower.com/general.html |title=The Eisenhowers: The General |website=Dwightdeisenhower.com |access-date=May 3, 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101230101757/http://www.dwightdeisenhower.com/general.html |archive-date=December 30, 2010 }}</ref> | |||
| After the ], Eisenhower was assigned to the General Staff in ], where he served until June 1942 with responsibility for creating the major war plans to defeat Japan and Germany. He was appointed Deputy Chief in charge of Pacific Defenses under the Chief of War Plans Division (WPD), General ], and then succeeded Gerow as Chief of the War Plans Division. Next, he was appointed Assistant Chief of Staff in charge of the new Operations Division (which replaced WPD) under Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall, who spotted talent and promoted accordingly.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983}}</ref> | |||
| ==Aftermath of World War II== | |||
| ===Occupation of Germany=== | |||
| Eisenhower served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. Army from 1945–48. ] | |||
| [[Image:Bundesarchiv Bild 183-14059-0018, Berlin, Oberbefehlshaber der vier Verbündeten.jpg|thumb|The Supreme Commanders on June 5, 1945 in Berlin: | |||
| ], Dwight D. Eisenhower, ] and ].]] | |||
| Following the German ] on May 8, 1945, Eisenhower was appointed Military Governor of the ], based in ]. Germany was divided into four Occupation Zones, one each for the U.S., Britain, France, and the Soviet Union. Upon full discovery of the ]s that were part of the ] (]), he ordered camera crews to comprehensively document evidence of the atrocity for use in the ]s ]s. He made the decision to reclassify German ] (POWs) in U.S. custody as ] (DEFs), thus depriving them of the protection of the ]. As DEFs, their food rations could be lowered and they could be compelled to serve as ] (see '']''). Eisenhower was an early supporter of the ] to permanently remove Germany's industrial capacity to wage future wars. In November 1945 he approved the distribution of 1000 free copies of ]'s book ''Germany is Our Problem'', which promoted and described the plan in detail, to American military officials in occupied Germany. Historian ] draws the conclusion that, despite Eisenhower's later claims the act was not an endorsement of the Morgenthau plan, Eisenhower both approved of the plan and had previously given Morgenthau at least some of his ideas about how Germany should be treated.<ref>{{cite book|author=Ambrose, Stephen|title=Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect (1893–1952)|location=]|publisher=]|date=1983|page=422}}</ref> He also incorporated officials from Morgenthau's ] into the army of occupation. These were commonly called "Morgenthau boys" for their zeal in interpreting the occupation directive ], which had been heavily influenced by Morgenthau and his plan, as strictly as possible.<ref>{{cite book|author=Petrov, Vladimir|title=Money and conquest; allied occupation currencies in World War II.|location=]|publisher=]|date=1967|pages=228–229}}</ref> | |||
| At the end of May 1942, Eisenhower accompanied Lt. Gen. ], commanding general of the ], to London to assess the effectiveness of the theater commander in England, Maj. Gen. ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.af.mil/About-Us/Biographies/Display/Article/107447/major-general-james-e-chaney/ |title=Major General James E. Chaney |work=Air Force |access-date=August 16, 2017 |publisher=U.S. Air Force |quote=From January 1942 to June 1942, he was the commanding general, U.S. Army Forces in the British Isles. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180613062541/http://www.af.mil/About-Us/Biographies/Display/Article/107447/major-general-james-e-chaney/ |archive-date=June 13, 2018 |url-status=live }}</ref> He returned to Washington on June 3 with a pessimistic assessment, stating he had an "uneasy feeling" about Chaney and his staff. On June 23, 1942, he returned to London as Commanding General, ] (ETOUSA), based in London and with a house in ],<ref>Eisenhower lived in 'Telegraph Cottage', Warren Road, Coombe, from 1942 to 1944. In 1995, a plaque commemorating this was placed there by the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames. It can be seen at the north end of Warren Road.</ref> and took over command of ETOUSA from Chaney.<ref name="huston">{{cite book| author=Huston, John W.| title=American Airpower Comes of Age: General Henry H. "Hap" Arnold's World War II Diaries| editor=Maj. Gen. John W. Huston, USAF| publisher=Air University Press| isbn=1585660930| year=2002| pages=| url=https://archive.org/details/americanairpower01arno/page/288}}</ref> He was promoted to lieutenant general on July 7. | |||
| ===Columbia University and NATO=== | |||
| In 1948, Eisenhower became President of ].<ref>Stephen E. Ambrose, ''Eisenhower'', New York, Touchstone Books, 1990, pp 234–235, ISBN 0-671-70107-X</ref> In December 1950, he took leave from the university when he became the Supreme Commander of the ] (NATO), and given operational command of NATO forces in Europe. Eisenhower retired from active service on May 31, 1952, and resumed the university presidency, which he held until January 1953. | |||
| === Operations Torch and Avalanche === | |||
| 1948 also was the year that Eisenhower's memoir, '']'', was published.<ref>''Crusade in Europe'', Doubleday; 1st edition (1948), 559 pages, ISBN 1125300914</ref> It is widely regarded as one of the finest U.S. military memoirs. | |||
| ], 1942]] | |||
| In November 1942, Eisenhower was also appointed ] of the ] (NATOUSA) through the new operational Headquarters ] (A(E)FHQ). The word "expeditionary" was dropped soon after his appointment for security reasons.{{Failed verification|date=July 2016}} The campaign in North Africa was designated Operation Torch and was planned ] within the ]. Eisenhower was the first non-British person to command ] in 200 years.<ref name=gibraltar>{{cite news|last=Gallagher|first=Wes|title=Eisenhower Commanded Gibraltar|url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=1928&dat=19421222&id=h5c0AAAAIBAJ&pg=3799,6270005|access-date=April 29, 2013|newspaper=The Lewiston Daily Sun|date=December 1942|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150920042406/https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=1928&dat=19421222&id=h5c0AAAAIBAJ&sjid=rGgFAAAAIBAJ&pg=3799,6270005|archive-date=September 20, 2015|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Entry into politics=== | |||
| {{main|United States presidential election, 1952}} | |||
| After his many wartime successes, Eisenhower was a great hero in the U.S. He was unusual for a military hero as he never saw the front line in his life. The nearest he came to being under enemy fire was in 1944 when a German fighter strafed the ground while he was inspecting troops in Normandy. Eisenhower dove for cover like everyone else and after the plane flew off, a British brigadier helped him up and seemed very relieved he was not hurt. When Eisenhower thanked him for his solicitude, the brigadier deflated him by explaining "my concern was that you should not be injured in my sector."{{Fact|date=August 2008}} | |||
| ] was deemed necessary to the campaign and Eisenhower encountered a "preposterous situation"{{according to whom|date=March 2019}} with the multiple rival factions in France. His primary objective was to move forces successfully into ] and intending to facilitate that objective, he gave his support to ] as High Commissioner in North Africa, despite Darlan's previous high offices in ] and his continued role as commander-in-chief of the ]. The ] leaders were "thunderstruck"{{according to whom|date=March 2019}} by this from a political standpoint, though none had offered Eisenhower guidance with the problem in planning the operation. Eisenhower was severely criticized{{by whom|date=March 2019}} for the move. Darlan was assassinated on December 24 by ], a French antifascist monarchist.<ref>Atkinson, ''An Army at Dawn'', pp. 251–252.</ref> Eisenhower later appointed as High Commissioner General ], who had been installed by the Allies as Darlan's commander-in-chief.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=204–210}}</ref> | |||
| Not long after his return in 1952, a "]" movement in the Republican party persuaded him to declare his candidacy in the ] to counter the candidacy of ] Senator ]. (Eisenhower had been courted by both parties in 1948 and had declined to run then.) Eisenhower defeated Taft for the nomination but came to an agreement that Taft would stay out of foreign affairs while Eisenhower followed a conservative domestic policy. Eisenhower's campaign was noted for the simple but effective ] "]" and was a crusade against the ] administration's policies regarding "], ] and Corruption."<ref name="time 2008">{{cite news | |||
| |url=http://www.time.com/time/politics/article/0,8599,1857862,00.html | |||
| |publisher='']'' | |||
| |date=November 10, 2008 | |||
| |title=When New President Meets Old, It's Not Always Pretty |first= Nancy|last=Gibbs}}</ref> Truman, formerly a friend of Eisenhower's, never forgave him for not denouncing Senator ] during the 1952 campaign.<ref name="time 2008"/> Truman said he had previously thought Eisenhower would be a great President, but "he has betrayed almost everything I thought he stood for."<ref name="time 2008"/> | |||
| Operation Torch also served as a valuable training ground for Eisenhower's combat command skills; during the initial phase of '']'' ]'s move into the ], Eisenhower created some confusion in the ranks by interference with the execution of battle plans by his subordinates. He also was initially indecisive in his removal of ], commanding ]. He became more adroit in such matters in later campaigns.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=230–233}}</ref> In February 1943, his authority was extended as commander of ] across the ] to include the ], commanded by ] Sir Bernard Montgomery. The Eighth Army had ] from the east and was ready for the start of the ]. | |||
| Eisenhower promised during his campaign to go to Korea himself and end the war there. He also promised to maintain both a strong NATO commitment against Communism and a corruption-free frugal administration at home. He and his running mate ], whose daughter later married Eisenhower's grandson David, defeated Democrats ] and ] in a landslide, marking the first Republican return to the ] in 20 years,<ref name="time 2008"/> with Eisenhower becoming the last President born in the 19th century. Eisenhower, at 62, was the oldest man to be elected President since ] in 1856.<ref name="'70s">{{cite book |title= How We Got Here: The '70s|last= Frum|first= David|authorlink= David Frum|coauthors= |year= 2000|publisher= Basic Books|location= New York, New York|isbn= 0465041957|page= 7|pages= |url= }}</ref> Eisenhower was the only general to serve as President in the 20th century, and the most recent President to have never held elected office prior to the Presidency. The other Presidents not to have sought prior elected office were ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| After the capitulation of ] forces in North Africa, Eisenhower oversaw the ]. Once ], the ], had fallen in Italy, the Allies switched their attention to the mainland with ]. But while Eisenhower argued with President Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Churchill, who both insisted on unconditional surrender in exchange for helping the Italians, the Germans pursued an aggressive buildup of forces in the country. The Germans made the already tough battle more difficult by adding 19 ] and initially outnumbering the ] forces 2 to 1.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=254–255}}</ref> | |||
| ==Presidency 1953–1961== | |||
| {{main|Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| ], ] and Dwight Eisenhower at a state dinner in 1959]] | |||
| ] and President Dwight D. Eisenhower in Madrid in 1959]] | |||
| ] briefs President Eisenhower in front of a Saturn 1 vehicle at the ] dedication on September 8, 1960.]] | |||
| === Supreme Allied commander and Operation Overlord === | |||
| Throughout his presidency, Eisenhower preached a doctrine of dynamic conservatism.{{Fact|date=October 2008}} He continued all the major ] programs still in operation, especially ]. He expanded its programs and rolled them into a new cabinet-level agency, the ], while extending benefits to an additional ten million workers. His cabinet, consisting of several corporate executives and one labor leader, was dubbed by one journalist, "Eight millionaires and a plumber."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,900543-1,00.html |title=The Flavor of the New |accessdate=2008-05-28 |date=1969-01-24 |publisher=Time }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| In December 1943, President Roosevelt decided that Eisenhower – not Marshall – would be Supreme Allied Commander in Europe. The following month, he resumed command of ] and the following month was officially designated as the ] (SHAEF), serving in a dual role until the end of hostilities in Europe in May 1945.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=275–276}}</ref> He was charged in these positions with planning and carrying out the Allied ] in June 1944 under the code name Operation Overlord, the liberation of Western Europe and the invasion of Germany.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hitchcock |first=W |title=] |publisher=] |year=2018 |isbn=978-1439175668 |pages=21–23}}</ref> | |||
| ] (PIR), part of the ], on June 5, 1944, the day before the D-Day invasion. The officer Eisenhower is speaking to is First Lieutenant ].]] | |||
| Eisenhower won his second term in 1956 with 457 of 531 votes in the ], and 57.6% of the ]. | |||
| Eisenhower, as well as the officers and troops under him, had learned valuable lessons in their previous operations, and their skills had all strengthened in preparation for the next most difficult campaign against the Germans—a beach landing assault. His first struggles, however, were with Allied leaders and officers on matters vital to the success of the Normandy invasion; he argued with Roosevelt over an essential agreement with ] to use ] forces in covert operations against the Germans in advance of Operation Overlord.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=280–281}}</ref> Admiral ] fought with Eisenhower over King's refusal to provide additional landing craft from the Pacific.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=284}}</ref> Eisenhower also insisted that the British give him exclusive command over all strategic ] to facilitate Overlord, to the point of threatening to resign unless Churchill relented, which he did.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=286–288}}</ref> Eisenhower then designed a bombing plan in France in advance of Overlord and argued with Churchill over the latter's concern with civilian casualties; de Gaulle interjected that the casualties were justified, and Eisenhower prevailed.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=289}}</ref> He also had to skillfully manage to retain the services of the often unruly George S. Patton, by severely reprimanding him when Patton earlier had ], and then when Patton gave a speech in which he made improper comments about postwar policy.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=250, 298}}</ref> | |||
| ===Interstate Highway System=== | |||
| {{main|Interstate Highway System}} | |||
| One of Eisenhower's enduring achievements was championing and signing the bill that authorized the Interstate Highway System in 1956.<ref name="economist">{{cite news | |||
| | title = The cracks are showing | |||
| | publisher = ''The Economist'' | |||
| | date = ] | |||
| | url = http://www.economist.com/obituary/displaystory.cfm?story_id=8447241 | |||
| | accessdate = 2008-10-23 }}</ref> He justified the project through the ] as essential to American security during the Cold War. It was believed that large cities would be targets in a possible future war, and the highways were designed to evacuate them and allow the military to move in. | |||
| The D-Day Normandy landings on June 6, 1944, were costly but successful. Two months later (August 15), the ] took place, and control of forces in the southern invasion passed from the AFHQ to the SHAEF. Many thought that victory in Europe would come by summer's end, but the Germans did not capitulate for almost a year. From then until the ] on May 8, 1945, Eisenhower, through SHAEF, commanded all Allied forces, and through his command of ETOUSA had administrative command of all US forces on the ] north of the ]. He was ever mindful of the inevitable loss of life and suffering that would be experienced by the troops under his command and their families. This prompted him to make a point of visiting every division involved in the invasion.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=278}}</ref> Eisenhower's sense of responsibility was underscored by his draft of a statement to be issued if the invasion failed. It has been called one of the great speeches of history: | |||
| Eisenhower's goal to create improved highways was influenced by his involvement in the U.S. Army's 1919 ]. He was assigned as an observer for the mission, which involved sending a convoy of U.S. Army vehicles coast to coast.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.usswashington.com/dl30au39h1.htm|title=The Last Week - The Road to War|publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://usswashington.com/worldwar2plus55/index.htm|title=About the Author|publisher=]}}</ref> His subsequent experience with German ]s during World War II convinced him of the benefits of an Interstate Highway System. Noticing the improved ability to move logistics throughout the country, he thought an Interstate Highway System in the U.S. would not only be beneficial for military operations, but be the building block for continued economic growth.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/dl/InterstateHighways/InterstateHighwaysdocuments.html|title=“Interstate Highway System”|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{blockquote|Our landings in the Cherbourg-Havre area have failed to gain a satisfactory foothold and I have withdrawn the troops. My decision to attack at this time and place was based on the best information available. The troops, the air and the Navy did all that bravery and devotion to duty could do. If any blame or fault attaches to the attempt, it is mine alone.<ref>William Safire, ''Lend me your ears: great speeches in history'' (2004), p. 1143</ref>}} | |||
| ===Eisenhower Doctrine=== | |||
| After the ], the United States became the protector of most Western interests in the ]. As a result, Eisenhower proclaimed the "]" in January 1957. In relation to the Middle East, the U.S. would be "prepared to use armed force... aggression from any country controlled by international communism." On July 15, 1958, he sent just under 15,000 soldiers to Lebanon (a combined force of Army and Marine Corps) as part of '']'', a non-combat peace keeping mission to stabilize the pro-Western government. They left in October of the same year. | |||
| <!--needs proper reference format | |||
| Boyer, et al. ''The Enduring Vision''. Houghton Mifflin: 2000.--> | |||
| === Liberation of France and victory in Europe === | |||
| In addition, Eisenhower explored the option of supporting the French colonial forces in ] who were fighting an independence insurrection there. However, Chief of Staff ] dissuaded the President from intervening by presenting a comprehensive estimate of the massive military deployment that would be necessary. | |||
| ] at Reims]] | |||
| {{cquote|Every ground commander seeks the battle of annihilation; so far as conditions permit, he tries to duplicate in modern war the classic example of ].|source=Eisenhower{{sfn|Grant|2001}}}} | |||
| Once the coastal assault had succeeded, Eisenhower insisted on retaining personal control over the land battle strategy and was immersed in the command and supply of multiple assaults through France on Germany. Field Marshal Montgomery insisted priority be given to his ]'s attack being made in the north, while Generals ] (]) and ] (]) insisted they be given priority in the center and south of the front (respectively). Eisenhower worked tirelessly to address the demands of the rival commanders to optimize Allied forces, often by giving them tactical latitude; many historians conclude this delayed the Allied victory in Europe. However, due to Eisenhower's persistence, the pivotal supply port at ] was successfully, albeit belatedly, ].<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=340–354}}</ref> | |||
| ===Civil rights=== | |||
| Eisenhower supported the 1954 '']'' U.S. Supreme Court decision, in which segregated ("]") schools were ruled to be unconstitutional. The very next day he told District of Columbia officials to make Washington a model for the rest of the country in integrating black and white public school children.<ref>{{harvnb|Eisenhower|1963|p=230}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Parmet|1972|pp=438–439}}</ref> He proposed to Congress the Civil Rights Acts of ] and ] and signed those acts into law. Although both Acts were weaker than subsequent civil rights legislation, they constituted the first significant civil rights acts since the 1870s. | |||
| The "]" incident of 1957 involved the refusal by ] to honor a Federal court order to integrate the schools. Under {{EO|10730}}, Eisenhower placed the ] under Federal control and sent Army troops to escort nine black students into an all-white public school. The integration did not occur without violence. Eisenhower and Arkansas governor ] engaged in tense arguments. | |||
| In recognition of his senior position in the Allied command, on December 20, 1944, he was promoted to ], equivalent to the rank of ] in most European armies. In this and the previous high commands he held, Eisenhower showed his great talents for leadership and diplomacy. Although he had never seen action himself, he won the respect of front-line commanders. He interacted adeptly with allies such as ], Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery and General ]. He had serious disagreements with Churchill and Montgomery over questions of strategy, but these rarely upset his relationships with them. He dealt with Soviet ], his Russian counterpart, and they became good friends.<ref>Jean Edward Smith, ''Eisenhower in War and Peace'' (2012) p. 451.</ref> | |||
| ===Judicial appointments=== | |||
| ====Supreme Court==== | |||
| In December 1944, the Germans launched a surprise counteroffensive, the ], which the Allies turned back in early 1945 after Eisenhower repositioned his armies and improved weather allowed the ] to engage.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=375–380}}</ref> German defenses continued to deteriorate on both the ] with the ] and the ] with the Western Allies. The British wanted to capture ], but Eisenhower decided it would be a military mistake for him to attack Berlin and said orders to that effect would have to be explicit. The British backed down but then wanted Eisenhower to move into ] for political reasons. Washington refused to support Churchill's plan to use Eisenhower's army for political maneuvers against ]. The actual division of Germany followed the lines that Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin had previously agreed upon. The Soviet Red Army captured Berlin in a ], and the Germans finally surrendered on May 7, 1945.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=395–406}}</ref> | |||
| Throughout 1945, the allied armies liberated numerous ] throughout Europe. As the allies learned the full extend of the ], Eisenhower anticipated that, in the future, attempts to recharacterize ]s as propaganda (]) would be made, and took steps against it by demanding extensive photo and film documentation of ].<ref>{{harvnb|Hobbs|1999|p=223}}</ref> | |||
| == After World War II (1945–1953) == | |||
| === Military Governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany === | |||
| ] from May through November 1945.]] | |||
| Following the German unconditional surrender, Eisenhower was appointed military governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany, located primarily in ], and ] in ]. Upon discovery of the ], he ordered camera crews to document evidence for use in the ]. He reclassified German ] (POWs) in US custody as ] (DEFs), who were no longer subject to the ]. Eisenhower followed the orders laid down by the ] (JCS) in directive ] but softened them by bringing in 400,000 tons of food for civilians and allowing more ].<ref>Zink, Harold (1947). ''American Military Government in Germany'', pp. 39–86</ref><ref>Goedde, Petra. "From Villains to Victims: Fraternization and the Feminization of Germany, 1945–1947", ''Diplomatic History'', Winter 1999, Vol. 23, Issue 1, pp. 1–19</ref><ref>Tent, James F. (1982), ''Mission on the Rhine: Reeducation and Denazification in American-Occupied Germany''</ref> In response to the devastation in Germany, including food shortages and an influx of refugees, he arranged distribution of American food and medical equipment.<ref>Zink, Harold (1957). ''The United States in Germany, 1944–1955''</ref> His actions reflected the new American attitudes of the German people as Nazi victims not villains, while aggressively purging the ex-Nazis.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=421–425}}</ref><ref>Goedde, Petra (2002). ''GIs and Germans: Culture, Gender and Foreign Relations, 1945–1949''</ref> | |||
| ===Army Chief of Staff=== | |||
| In November 1945, Eisenhower returned to Washington to replace Marshall as ]. His main role was the rapid demobilization of millions of soldiers, which was delayed by lack of shipping. Eisenhower was convinced in 1946 that the Soviet Union did not want war and that friendly relations could be maintained; he strongly supported the new United Nations and favored its involvement in the control of atomic bombs. However, in formulating policies regarding the ] and relations with the Soviets, Truman was guided by the State Department and ignored Eisenhower and the ]. Indeed, Eisenhower had opposed the use of the atomic bomb against the Japanese, writing, "First, the Japanese were ready to surrender and it wasn't necessary to hit them with that awful thing. Second, I hated to see our country be the first to use such a weapon."<ref>Richard Rhodes, ''The Making of the Atomic Bomb,'' with Rhodes citing a 1963 profile called "Ike on Ike, in ''Newsweek'' November 11, 1963</ref> Initially, Eisenhower hoped for cooperation with the Soviets.<ref name=Ambrose>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=432–452}}</ref> He even visited ] in 1945. Invited by ] and decorated with the ], he was shocked by the scale of destruction in the city.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.polskieradio.pl/39/156/Artykul/747362,Dwight-Eisenhower-wielki-Amerykanin-i-wielki-zolnierz |title=Dwight Eisenhower in Poland |publisher=Polish Radio |access-date=April 3, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160420131100/http://www.polskieradio.pl/39/156/Artykul/747362,Dwight-Eisenhower-wielki-Amerykanin-i-wielki-zolnierz |archive-date=April 20, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> However, by mid-1947, as east–west tensions over economic recovery in Germany and the ] escalated, Eisenhower agreed with a ] to stop Soviet expansion.<ref name="Ambrose" /> | |||
| === 1948 presidential election === | |||
| In June 1943, a visiting politician had suggested to Eisenhower that he might become president after the war. Believing that a general should not participate in politics, ] wrote that "figuratively speaking, kicked his political-minded visitor out of his office". As others asked him about his political future, Eisenhower told one that he could not imagine wanting to be considered for any political job "from dogcatcher to Grand High Supreme King of the Universe", and another that he could not serve as Army Chief of Staff if others believed he had political ambitions. In 1945, Truman told Eisenhower during the ] that if desired, the president would help the general win the ],<ref name="pusey1956">{{cite book | url=https://archive.org/stream/eisenhowerthepre002645mbp#page/n11/mode/2up | title=Eisenhower, the President | publisher=Macmillan | author=Pusey, Merlo J. | year=1956 | pages=1–6 | access-date=November 7, 2013 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141021230806/https://archive.org/stream/eisenhowerthepre002645mbp#page/n11/mode/2up | archive-date=October 21, 2014 | url-status=live }}</ref> and in 1947 he offered to run as Eisenhower's running mate on the Democratic ticket if MacArthur won the Republican nomination.<ref name="nyt20030711">" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170603084430/http://www.nytimes.com/2003/07/11/us/truman-wrote-of-48-offer-to-eisenhower.html |date=June 3, 2017 }}" ''The New York Times'', July 11, 2003.</ref> | |||
| As the election approached, other prominent citizens and politicians from both parties urged Eisenhower to run. In January 1948, after learning of plans in ] to elect delegates supporting him for the forthcoming ], Eisenhower stated through the Army that he was "not available for and could not accept nomination to high political office"; "life-long professional soldiers", he wrote, "in the absence of some obvious and overriding reason, abstain from seeking high political office".{{r|pusey1956}} Eisenhower maintained no political party affiliation during this time. Many believed he was forgoing his only opportunity to be president as Republican ] was considered the probable winner and would presumably serve two terms, meaning that Eisenhower, at age 66 in 1956, would be too old to run.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=455–460}}</ref> | |||
| === President at Columbia University and NATO Supreme Commander === | |||
| ] | |||
| ]'' at Columbia in 1953]] | |||
| ], Eisenhower presents an honorary degree to ].]] | |||
| In 1948, Eisenhower became President of ], an ] university in ], where he was inducted into ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.pbk.org/WEB/pbkdocs/Phi%20Beta%20Kappa%20Presidents%20.pdf |title=ΦΒΚ U.S. Presidents |access-date=August 16, 2017 |publisher=Phi Beta Kappa |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161008021125/https://www.pbk.org/WEB/pbkdocs/Phi%20Beta%20Kappa%20Presidents%20.pdf |archive-date=October 8, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> The choice was subsequently characterized as not having been a good fit for either party.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|loc=ch. 24}}</ref> During that year, Eisenhower's memoir, '']'', was published.<ref>''Crusade in Europe'', Doubleday; 1st edition (1948), 559 pages, {{ISBN|1125300914}}</ref> It was a major financial success.<ref name="owen-171-172"/> Eisenhower sought the advice of Augusta National's Roberts about the tax implications of this,<ref name="owen-171-172">{{harvnb|Owen|1999|pp=171–172}}</ref> and in due course Eisenhower's profit on the book was substantially aided by what author ] calls "a ruling without precedent" by the ]. It held that Eisenhower was not a professional writer, but rather, marketing the lifetime asset of his experiences, and thus he had to pay only capital gains tax on his $635,000 advance instead of the much higher personal tax rate. This ruling saved Eisenhower about $400,000.<ref>Pietrusza, David, ''1948: Harry Truman's Victory and the Year That Transformed America'', Union Square Publishing, 2011, p. 201</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower's stint as the president of Columbia was punctuated by his activity within the ], a study group he led concerning the political and military implications of the ] and ], Eisenhower's "vision of a great cultural center where business, professional and governmental leaders could meet from time to time to discuss and reach conclusions concerning problems of a social and political nature".<ref name="warshaw-20"/> His biographer ] suggested that this period served his "the political education", since he had to prioritize wide-ranging educational, administrative, and financial demands for the university.<ref>{{harvnb|Cook|1981|loc=ch. 3}}</ref> Through his involvement in the Council on Foreign Relations, he also gained exposure to economic analysis, which became the bedrock of his understanding in economic policy. "Whatever General Eisenhower knows about economics, he has learned at the study group meetings," one Aid to Europe member claimed.<ref>{{harvnb|Cook|1981|p=79}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower accepted the presidency of the university to expand his ability to promote "the American form of democracy" through education.<ref name="warshaw-18">{{harvnb|Jacobs|1993|p=18}}</ref> He was clear on this point to the trustees on the search committee. He informed them that his main purpose was "to promote the basic concepts of education in a democracy".<ref name="warshaw-18"/> As a result, he was "almost incessantly" devoted to the idea of the American Assembly, a concept he developed into an institution by the end of 1950.<ref name="warshaw-20">{{harvnb|Jacobs|1993|p=20}}</ref> | |||
| Within months of becoming university president, Eisenhower was requested to advise Secretary of Defense ] on the unification of the armed services.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=140–141}}</ref> About six months after his appointment, he became the informal ] in Washington.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=145–146}}</ref> Two months later he fell ill with what was diagnosed as acute gastroenteritis, and he spent over a month in recovery at the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=162–164}}</ref> He returned to his post in New York in mid-May, and in July 1949 took a two-month vacation out-of-state.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=168–169, 175}}</ref> Because the American Assembly had begun to take shape, he traveled around the country during summer and fall 1950, building financial support for it, including from ], a recently created alumni and benefactor organization for which he had helped recruit members.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=152, 238–242, 245–249}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower was unknowingly building resentment and a reputation among the Columbia University faculty and staff as an absentee president who was using the university for his own interests. As a career military man, he naturally had little in common with the academics.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=479–483}}</ref> The contacts gained through university and American Assembly fundraising activities would later become important supporters in Eisenhower's bid for the Republican party nomination and the presidency. Meanwhile, Columbia University's liberal faculty members became disenchanted with the university president's ties to oilmen and businessmen.{{citation needed|date=July 2023}} | |||
| He did have some successes at Columbia. Puzzled as to why no American university had undertaken the "continuous study of the causes, conduct and consequences of war",<ref name="y-s-ix"/> Eisenhower undertook the creation of the ], a research facility to "study war as a tragic social phenomenon".<ref name="jacobs-235-236">{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=235–236}}</ref> Eisenhower was able to use his network of wealthy friends and acquaintances to secure initial funding for it.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=484–485}}</ref> Under its founding director, international relations scholar ], the institute began in 1951 and became a pioneer in ], one that would be emulated by other institutes in the United States and Britain later in the decade.<ref name="y-s-ix">{{harvnb|Young|Schilling|2019|p=ix}}</ref> The Institute of War and Peace Studies thus became one of the projects which Eisenhower considered his "unique contribution" to Columbia.<ref name="jacobs-235-236"/> As the president of Columbia, Eisenhower gave voice to his opinions about the supremacy and difficulties of American democracy. His tenure marked his transformation from military to civilian leadership. His biographer Travis Beal Jacobs also suggested that the alienation of the Columbia faculty contributed to sharp intellectual criticism of him for many years.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|1993|pp=17ff}}</ref> | |||
| The trustees of Columbia University declined to accept Eisenhower's offer to resign in December 1950, when he took an extended leave from the university to become the Supreme Commander of the ] (NATO), and he was given operational command of NATO forces in Europe.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|pp=251–254}}</ref> Eisenhower retired from active service as an army general on June 3, 1952,<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|p=279}}</ref> and he resumed his presidency of Columbia. Meanwhile, Eisenhower had become the Republican Party nominee for president of the United States, a contest that he won on November 4. Eisenhower tendered his resignation as university president on November 15, 1952, effective January 19, 1953, the day before his inauguration.<ref>{{harvnb|Jacobs|2001|p=299}}</ref> | |||
| At home, Eisenhower was more effective in making the case for NATO in Congress than the Truman administration had been. By the middle of 1951, with American and European support, NATO was a genuine military power. Nevertheless, Eisenhower thought that NATO would become a truly European alliance, with the American and Canadian commitments ending after about ten years.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=502–511}}</ref> | |||
| === Presidential campaign of 1952 === | |||
| {{Main|1952 United States presidential election}} | |||
| {{See also|Draft Eisenhower movement}} | |||
| ] | |||
| President Truman sensed a broad-based desire for an Eisenhower candidacy for president, and he again pressed him to run for the office as a Democrat in 1951. But Eisenhower voiced his disagreements with the ] and declared himself to be a Republican.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=512}}</ref> A "]" movement in the Republican Party persuaded him to declare his candidacy in the 1952 presidential election to counter the candidacy of non-interventionist Senator ]. The effort was a long struggle; Eisenhower had to be convinced that political circumstances had created a genuine duty to offer himself as a candidate and that there was a mandate from the public for him to be their president. ] and others succeeded in convincing him, and he resigned his command at NATO in June 1952 to campaign full-time.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=524–528}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower defeated Taft for the nomination, having won critical delegate votes from Texas. His campaign was noted for the simple slogan "]". It was essential to his success that Eisenhower express opposition to Roosevelt's policy at the ] and to Truman's policies in Korea and China—matters in which he had once participated.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=530}}</ref><ref name="time 2008">{{cite news|url=http://www.time.com/time/politics/article/0,8599,1857862,00.html|magazine=Time|date=November 10, 2008|title=When New President Meets Old, It's Not Always Pretty|first=Nancy|last=Gibbs|access-date=November 12, 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081111030347/http://www.time.com/time/politics/article/0,8599,1857862,00.html|archive-date=November 11, 2008|url-status=dead}}</ref> In defeating Taft for the nomination, it became necessary for Eisenhower to appease the right-wing Old Guard of the Republican Party; his selection of Richard Nixon as the vice-president on the ticket was designed in part for that purpose. Nixon also provided a strong ] reputation, as well as youth to counter Eisenhower's more advanced age.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=541–546}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower insisted on campaigning in the ] in the general election, against the advice of his campaign team, refusing to surrender the region to the Democrats. The campaign strategy was dubbed "K<sub>1</sub>C<sub>2</sub>" and was intended to focus on attacking the Truman administration on three failures: the Korean War, ], and ].<ref>Herbert H. Hyman, and Paul B. Sheatsley, "The political appeal of President Eisenhower." ''Public Opinion Quarterly'' 17.4 (1953): 443-460 .</ref> | |||
| Two controversies tested him and his staff, but they did not damage the campaign. One involved a report that Nixon had improperly received funds from a secret trust. Nixon ] to avoid potential damage, but the matter permanently alienated the two candidates. The second issue centered on Eisenhower's relented decision to confront the controversial methods of Joseph McCarthy on his home turf in a Wisconsin appearance.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|pp=556–567}}</ref> Eisenhower condemned "wickedness in government", an allusion to gay government employees who were ] during McCarthyism.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Lavender Scare |first=David K. |last=Johnson |date=March 22, 2023 |isbn=978-0226825724 |publisher=The University of Chicago Press |page=121 }}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower defeated Democratic candidate ] in a landslide, with an electoral margin of 442 to 89, marking the first Republican return to the White House in 20 years.<ref name="time 2008" /> He also brought a Republican majority in the House, by eight votes, and in the Senate, evenly divided with Vice President Nixon providing Republicans the majority.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1983|p=571}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower was the last president born in the 19th century, and he was the oldest president-elect at age 62 since ] in 1856.<ref name="'70s">{{harvnb|Frum|2000|p=7}}</ref> He was the third commanding general of the Army to serve as president, after ] and ], and the last not to have held political office prior to becoming president until ] entered office in January 2017.<ref>{{cite web| last=Crockett| first=Zachary| title=Donald Trump is the only US president ever with no political or military experience| url=https://www.vox.com/policy-and-politics/2016/11/11/13587532/donald-trump-no-experience| website=vox.com| date=January 23, 2017| access-date=January 8, 2019| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170106051351/http://www.vox.com/policy-and-politics/2016/11/11/13587532/donald-trump-no-experience| archive-date=January 6, 2017| url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Election of 1956 === | |||
| {{Main|1956 United States presidential election}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In the United States presidential election of 1956, Eisenhower, the popular incumbent, was re-elected. The election was a re-match of 1952, as his opponent in 1956 was Stevenson, a former Illinois governor, whom Eisenhower had defeated four years earlier. Compared to the 1952 election, Eisenhower gained ], ], and ] from Stevenson, while losing ]. His voters were less likely to bring up his leadership record. Instead what stood out this time "was the response to personal qualities — to his sincerity, his integrity and sense of duty, his virtue as a family man, his religious devotion, and his sheer likeableness."<ref>{{cite book|first1=Angus|last1=Campbell|first2=Philip L.|last2=Converse|first3=Warren E.|last3=Miller|first4=Donald E.|last4=Stokes|title=The American Voter|url={{GBurl|id=JeYUrs_GOcMC|p=56}}|year=1960|page=56|publisher=University of Chicago Press |isbn=978-0226092546}}</ref> | |||
| == Presidency (1953–1961) == | |||
| {{Main|Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| {{for timeline|Timeline of the Dwight D. Eisenhower presidency}} | |||
| Truman and Eisenhower had minimal discussions about the transition of administrations due to a complete estrangement between them as a result of campaigning.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=14}}</ref> Eisenhower selected ] as his budget director, then asked ] and ] to make recommendations for his cabinet appointments. He accepted their recommendations without exception; they included ] and ] with whom he developed his closest relationships, as well as ]. His cabinet consisted of several corporate executives and one labor leader, and one journalist dubbed it "eight millionaires and a plumber".<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=24}}</ref> The cabinet was known for its lack of personal friends, office seekers, or experienced government administrators. He also upgraded the role of the ] in planning all phases of the Cold War.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=20–25}}</ref> | |||
| Before his inauguration, Eisenhower led a meeting of advisors at ] where they set goals for his first term: balance the budget, end the Korean War, defend vital interests at lower cost through nuclear deterrent, and end price and wage controls.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=32}}</ref> He also conducted the first pre-inaugural cabinet meeting in history in late 1952; he used this meeting to articulate his anti-communist Russia policy. His inaugural address was exclusively devoted to foreign policy and included this same philosophy as well as a commitment to foreign trade and the United Nations.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=43}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower made greater use of press conferences than any previous president, holding almost 200 over his two terms. He saw the benefit of maintaining a good relationship with the press, and he saw value in them as a means of direct communication with the American people.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=52}}</ref> | |||
| Throughout his presidency, Eisenhower adhered to a political philosophy of dynamic conservatism.<ref name="allida">{{cite web |editor-last1=Black |editor-first1=Allida |editor-last2=Hopkins |editor-first2=June |display-editors=etal |year=2003 |work=Eleanor Roosevelt National Historic Site |title=Teaching Eleanor Roosevelt: Dwight Eisenhower |access-date=November 26, 2011 |url=http://www.nps.gov/archive/elro/glossary/eisenhower-dwight.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070105034523/http://www.nps.gov/archive/elro/glossary/eisenhower-dwight.htm |archive-date=January 5, 2007}}</ref> He described himself as a "]"<ref name="EisenhowerEisenhower2011">{{cite book|first1=David|last1=Eisenhower|author2=Julie Nixon Eisenhower|title=Going Home To Glory: A Memoir of Life with Dwight D. Eisenhower, 1961–1969|url={{GBurl|id=yawcVhHVwNsC|p=126}}|date=October 11, 2011|publisher=Simon and Schuster|isbn=978-1439190913|page=126}}</ref> and used terms such as "progressive moderate" and "dynamic conservatism" to describe his approach.<ref>{{cite book |url={{GBurl|id=CW3VAwAAQBAJ|p=270}} |title=Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States: Dwight D. Eisenhower |isbn=978-1623768300 |last=Eisenhower |first=Dwight D. |year=1959 |page=270 |publisher=Best Books on }}</ref> He continued all the major ] programs still in operation, especially ]. He expanded its programs and rolled them into the new Cabinet-level agency of the ], while extending benefits to an additional ten million workers. He implemented ] in two years, which had not been completed under Truman.<ref name="Miller">{{cite news |author=Miller, James A. |date=November 21, 2007 |title=An inside look at Eisenhower's civil rights record |newspaper=The Boston Globe |url=http://articles.boston.com/2007-11-21/news/29228077_1_civil-rights-nichols-truman-s-executive-order |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120107182758/http://articles.boston.com/2007-11-21/news/29228077_1_civil-rights-nichols-truman-s-executive-order |archive-date=January 7, 2012 }}</ref> | |||
| In a private letter, Eisenhower wrote: | |||
| {{blockquote|Should any party attempt to abolish social security and eliminate labor laws and farm programs, you would not hear of that party again in our political history. There is a tiny splinter group of course, that believes you can do these things Their number is negligible and they are stupid.<ref>{{cite book|last=Mayer|first=Michael S.|url=https://archive.org/details/eisenhoweryears0000maye|title=The Eisenhower Years|year=2009|isbn=978-0-8160-5387-2|page=xii|publisher=Facts On File }}</ref>}} | |||
| When the ] approached, it became evident that the Republicans were in danger of losing their thin majority in both houses. Eisenhower was among those who blamed the Old Guard for the losses, and he took up the charge to stop suspected efforts by the right wing to take control of the GOP. He then articulated his position as a moderate, progressive Republican: "I have just one purpose ... and that is to build up a strong progressive Republican Party in this country. If the right wing wants a fight, they are going to get it ... before I end up, either this Republican Party will reflect progressivism or I won't be with them anymore."<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=220}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower initially planned on serving only one term, but he remained flexible in case leading Republicans wanted him to run again. He was recovering from a heart attack late in September 1955 when he met with his closest advisors to evaluate the GOP's potential candidates; the group concluded that a second term was well advised, and he announced that he would run again in February 1956.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=285–288}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Jean Edward Smith|title=Eisenhower in War and Peace|url={{GBurl|id=jO2gLXNNa2wC|p=674}}|year=2012|publisher=Random House|pages=674–683|isbn=978-0679644293|access-date=June 27, 2015}}</ref> Eisenhower was publicly noncommittal about having Nixon as the Vice President on his ticket; the question was an especially important one in light of his heart condition. He personally favored ], a Democrat who rejected his offer, so Eisenhower resolved to leave the matter in the hands of the party, which chose Nixon nearly unanimously.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=321–325}}</ref> In 1956, Eisenhower faced Adlai Stevenson again and won by an even larger landslide, with 457 of 531 electoral votes and 57.6 percent of the popular vote. His campaigning was curtailed out of health considerations.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=297}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower made full use of his valet, chauffeur, and secretarial support; he rarely drove or even dialed a phone number. He was an avid fisherman, golfer, painter, and bridge player.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=25}}</ref> On August 26, 1959, he was aboard the maiden flight of ], which replaced the ''Columbine'' as the presidential aircraft.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=537}}</ref> | |||
| ===Atoms for Peace=== | |||
| {{See also|History of nuclear power|History of nuclear weapons}} | |||
| Eisenhower gave the ] speech to the ] on 8 December 1953, advocating for constructive use of ] for ] and ] instead of ] ]. The speech led to the ] which allowed the civilian world to develop nuclear fission technology for peaceful and prosperous purposes.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.iaea.org/about/history/atoms-for-peace-speech | title=Atoms for Peace Speech | date=July 16, 2014 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-atomic-energy-act | title=Summary of the Atomic Energy Act | date=February 22, 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| === Interstate Highway System === | |||
| {{Main|Interstate Highway System}} | |||
| {{listen | |||
| | filename = Cadillacsquareexcerpt.ogg | |||
| | title = Remarks in Cadillac Square, Detroit | |||
| | description = President Eisenhower delivered remarks about the need for a new highway program at Cadillac Square in Detroit on October 29, 1954<br /> | |||
| }} | |||
| Eisenhower championed and signed the bill that authorized the ] in 1956.<ref name="economist">{{cite news|title=The cracks are showing|newspaper=The Economist|date=June 26, 2008|url=http://www.economist.com/obituary/displaystory.cfm?story_id=8447241|access-date=October 23, 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071120044855/http://www.economist.com/obituary/displaystory.cfm?story_id=8447241|archive-date=November 20, 2007|url-status=live}}</ref> He justified the project through the ] as essential to American security during the ]. | |||
| Eisenhower's goal to create improved highways was influenced by his involvement in the Army's 1919 ]. He was assigned as an observer for the mission, which involved sending a convoy of Army vehicles coast to coast.<ref>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://www.usswashington.com/dl30au39h1.htm |title=The Last Week – The Road to War |publisher=] |url-status=usurped |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070323225351/http://www.usswashington.com/dl30au39h1.htm |archive-date=March 23, 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://usswashington.com/worldwar2plus55/index.htm |title=About the Author |publisher=] |url-status=usurped |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080513084502/http://www.usswashington.com/worldwar2plus55/index.htm |archive-date=May 13, 2008 }}</ref> His subsequent experience with the German ] convinced him of the benefits of an Interstate Highway System. The system could also be used as a runway for airplanes, which would be beneficial to war efforts. Franklin D. Roosevelt put this system into place with the ]. He thought that an interstate highway system would be beneficial for military operations and would support continued economic growth.<ref name=archivesIHS>{{cite web|access-date=August 21, 2012|url=https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/research/online_documents/interstate_highway_system.html|title=Interstate Highway System|publisher=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130117094324/http://eisenhower.archives.gov/research/online_documents/interstate_highway_system.html|archive-date=January 17, 2013|url-status=live}}</ref> The legislation initially stalled in Congress over the issuance of bonds to finance the project, but the legislative effort was renewed and Eisenhower signed the law in June 1956.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=301, 326}}</ref> | |||
| ===ARPA=== | |||
| The ] was put together by Eisenhower and his ] in early 1958 in response to the successful launch of the first orbital satellite from the Soviet Union ]. ARPA eventually created the ] which was a predecessor to the ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.weber.edu/digitalhistory/internet_history.html | title=Internet History }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://engines.egr.uh.edu/episode/3144 | title=The Birth of the Internet | the Engines of Our Ingenuity }}</ref> | |||
| === Foreign policy === | |||
| ] during Nasser's visit to United Nations in New York, September 1960.]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ] in Taipei.]] | |||
| {{Excerpt|Foreign policy of the Dwight D. Eisenhower administration|templates=no}} | |||
| ==== Space Race ==== | |||
| {{Further|Space Race}} | |||
| ] celebrated America's Moon landings, which began 11 years after NASA was created during Eisenhower's presidency]] | |||
| Eisenhower and the CIA had known since at least January 1957, nine months before ], that Russia had the capability to launch a small payload into orbit and was likely to do so within a year.<ref>John M. Logsdon, "Exploring the Unknown: Selected Documents in the History of the U.S. Civil Space Program" (NASA; 1995)</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower's support of the nation's fledgling ] was officially modest until the Soviet launch of ] in 1957, gaining the Cold War enemy enormous prestige. He then launched a national campaign that funded not just space exploration but a major strengthening of science and higher education. The Eisenhower administration determined to adopt a non-aggressive policy that would allow "space-crafts of any state to overfly all states, a region free of military posturing and launch Earth satellites to explore space".<ref>Logsdon, John M., and Lear, Linda J. Exploring the Unknown:Selected Documents in the History of the U.S. Civil Space Program/ Washington D.C.</ref> His ] Policy attempted to legitimize illegal ] flyovers and ] while paving the way for spy satellite technology to orbit over sovereign territory,<ref>W. D. Kay, Defining NASA The Historical Debate Over the Agency's Mission, 2005.</ref> but ] and ] declined Eisenhower's proposal at the Geneva conference in July 1955.<ref>Parmet, Herbert S. Eisenhower and the American Crusades (New York: The Macmillan Company, 1972)</ref> In response to Sputnik being launched in October 1957, Eisenhower created ] as a civilian space agency in October 1958, signed a landmark science education law, and improved relations with American scientists.<ref>Yankek Mieczkowski, ''Eisenhower's Sputnik Moment: The Race for Space and World Prestige'' (Cornell University Press; 2013)</ref> | |||
| Fear spread through the United States that the Soviet Union would invade and spread ], so Eisenhower wanted to not only create a ] to detect any threats but ]s that would protect the United States. In strategic terms, it was Eisenhower who devised the American basic strategy of ] based upon the ] of ]s, land-based ]s (ICBMs), and ]s (SLBMs).<ref>Peter J. Roman, ''Eisenhower and the Missile Gap'' (1996)</ref> | |||
| NASA planners projected that ] would pull the United States ahead in the Space Race; however, in 1960, an Ad Hoc Panel on Man-in-Space concluded that "man-in-space can not be justified" and was too costly.<ref>The Presidents's Science Advisory Committee, "Report of the Ad Hoc Panel on Man-in-Space" December 16, 1960. NASA Historical Collection</ref> Eisenhower later resented the space program and its gargantuan price tag—he was quoted as saying, "Anyone who would spend $40 billion in a race to the moon for national prestige is nuts."<ref>Greg Ward, "A Rough Guide History of the USA" (Penguin Group: London, 2003)</ref> | |||
| ==== Korean War, Free China and Red China ==== | |||
| In late 1952, Eisenhower went to Korea and discovered a military and political stalemate. Once in office, when the Chinese ] began a buildup in the ] sanctuary, he considered using nuclear weapons if an armistice was not reached. Whether China was informed of the potential for nuclear force is unknown.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Jackson|first=Michael Gordon|date=2005|title=Beyond Brinkmanship: Eisenhower, Nuclear War Fighting, and Korea, 1953–1968|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/27552659|journal=Presidential Studies Quarterly|volume=35|issue=1|pages=52–75|doi=10.1111/j.1741-5705.2004.00235.x|jstor=27552659|issn=0360-4918}}</ref> His earlier military reputation in Europe was effective with the Chinese communists.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=51}}</ref> The National Security Council, the ], and the ] (SAC) devised detailed plans for nuclear war against Red China.<ref>{{cite journal|first=Matthew|last=Jones|title=Targeting China: U.S. Nuclear Planning and 'Massive Retaliation' in East Asia, 1953–1955|journal=Journal of Cold War Studies|year=2008|volume=10|issue=4|pages=37–65 |doi=10.1162/jcws.2008.10.4.37|s2cid=57564482 |issn = 1520-3972 }}</ref> With the death of Stalin in March 1953, Russian support for a Chinese communist hard-line weakened and China decided to compromise on the prisoner issue.<ref name="Ambrose 1984, p. 106–7">{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=106–107}}</ref> | |||
| ], and ], 1952]] | |||
| In July 1953, an armistice took effect with Korea divided along ]. The armistice and boundary remain in effect today. The armistice, which concluded despite opposition from Secretary Dulles, South Korean President ], and also within Eisenhower's party, has been described by biographer ] as the greatest achievement of the administration. Eisenhower had the insight to realize that unlimited war in the nuclear age was unthinkable, and limited war unwinnable.<ref name="Ambrose 1984, p. 106–7" /> | |||
| A point of emphasis in Eisenhower's campaign had been his endorsement of a policy of liberation from communism as opposed to a policy of containment. This remained his preference despite the armistice with Korea.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=173}}</ref> Throughout his terms Eisenhower took a hard-line attitude toward China, as demanded by conservative Republicans, with the goal of driving a wedge between China and the Soviet Union.<ref>{{cite journal|first=Qiang|last=Zhai|title=Crisis and Confrontations: Chinese-American Relations during the Eisenhower Administration|journal=Journal of American-East Asian Relations|year=2000|volume=9|issue=3/4|pages=221–249|doi=10.1163/187656100793645921|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower continued Truman's policy of recognizing the Republic of China (Taiwan) as the legitimate government of China, not the Peking (Beijing) regime. There were localized flare-ups when the People's Liberation Army began shelling the islands of ] and ] in September 1954. Eisenhower received recommendations embracing every variation of response; he thought it essential to have every possible option available to him as the crisis unfolded.<ref name="Ambrose 1984, p. 231">{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=231}}</ref> | |||
| The ] with the Republic of China was signed in December 1954. He requested and secured from Congress their "Free China Resolution" in January 1955, which gave Eisenhower unprecedented power in advance to use military force at any level in defense of Free China and the Pescadores. The Resolution bolstered the morale of the Chinese nationalists and signaled to Beijing that the US was committed to holding the line.<ref name="Ambrose 1984, p. 231" /> | |||
| During the ], Eisenhower threatened to use nuclear weapons against PRC military targets in ].<ref name=":17">{{Cite book |last=Crean |first=Jeffrey |title=The Fear of Chinese Power: an International History |date=2024 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-350-23394-2 |edition= |series=New Approaches to International History series |location=London, UK}}</ref>{{Rp|page=89}} These threats prompted Mao Zedong to launch ].<ref name=":17" />{{Rp|pages=89–90}} He authorized a series of bomb tests labeled ]. Nevertheless, he left the Chinese communists guessing as to the exact nature of his nuclear response. This allowed Eisenhower to accomplish all of his objectives—the end of this communist encroachment, the retention of the Islands by the Chinese nationalists and continued peace.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=245, 246}}</ref> Defense of the Republic of China from an invasion remains a core American policy.<ref>{{cite journal|first=Robert|last=Accinelli|title=Eisenhower, Congress, and the 1954–55 offshore island crisis|journal=Presidential Studies Quarterly|year=1990|volume=20|issue=2|pages=329–348|jstor=27550618}}</ref> | |||
| China invited some American reporters to China in 1956, having previously ousted American reporters after the PRC's founding.<ref name=":Minami2">{{Cite book |last=Minami |first=Kazushi |title=People's Diplomacy: How Americans and Chinese Transformed US-China Relations during the Cold War |date=2024 |publisher=] |isbn=9781501774157 |location=Ithaca, NY}}</ref>{{Rp|pages=115–116}} Eisenhower upheld the U.S. ban on travel to China.<ref name=":Minami2" />{{Rp|page=116}} U.S. newspapers, including ] and ] criticized the Eisenhower's administration decision as antithetical to the free press.<ref name=":Minami2" />{{Rp|page=116}} | |||
| ==== Southeast Asia ==== | |||
| {{further|United States in the Vietnam War}} | |||
| Early in 1953, the French asked Eisenhower for help in ] against the Communists, supplied from China, who were fighting the ]. Eisenhower sent Lt. General ] to Vietnam to assess the French forces there.<ref>Dunnigan, James and ] (1999), ''Dirty Little Secrets of the Vietnam War''. St. Martins Press, p. 85.</ref> Chief of Staff ] dissuaded the President from intervening by presenting a comprehensive estimate of the massive military deployment that would be necessary. Eisenhower stated prophetically that "this war would absorb our troops by divisions."<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=175}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower did provide France with bombers and non-combat personnel. After a few months with no success by the French, he added other aircraft to drop ] for clearing purposes. Further requests for assistance from the French were agreed to but only on conditions Eisenhower knew were impossible to meet – allied participation and congressional approval.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=175–157}}</ref> When the French fortress of ] fell to the Vietnamese Communists in May 1954, Eisenhower refused to intervene despite urging from the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs, the Vice President and the head of NCS.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=185}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower responded to the French defeat with the formation of the ] (Southeast Asia Treaty Organization) Alliance with the UK, France, New Zealand and Australia in defense of Vietnam against communism. At that time the French and Chinese reconvened the Geneva peace talks; Eisenhower agreed the US would participate only as an observer. After France and the Communists agreed to a partition of Vietnam, Eisenhower rejected the agreement, offering military and economic aid to southern Vietnam.<ref name="Nofi Albert p 257">Dunnigan, James and Nofi, Albert (1999), ''Dirty Little Secrets of the Vietnam War'', p. 257</ref> Ambrose argues that Eisenhower, by not participating in the Geneva agreement, had kept the US out of Vietnam; nevertheless, with the formation of SEATO, he had put the US back into the conflict.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=204–209}}</ref> | |||
| In late 1954, ] was made ambassador to "Free Vietnam", effectively elevating the country to sovereign status. Collins' instructions were to support the leader ] in subverting communism, by helping him to build an army and wage a military campaign.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=215}}</ref> In February 1955, Eisenhower dispatched the first American soldiers to Vietnam as military advisors to Diem's army. After Diem announced the formation of the Republic of Vietnam (commonly known as ]) in October, Eisenhower immediately recognized the new state and offered military, economic, and technical assistance.<ref>{{cite book|first=David L.|last=Anderson|title=Trapped by Success: The Eisenhower Administration and Vietnam, 1953–1961|url={{GBurl|id=tM88nZNx2J8C}}|year=1991|publisher=Columbia U.P.|isbn=978-0231515337}}</ref> | |||
| In the years that followed, Eisenhower increased the number of US military advisors in South Vietnam to 900.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.swarthmore.edu/library/peace/conscientiousobjection/OverviewVietnamWar.htm |title=Vietnam War |publisher=Swarthmore College Peace Collection |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160803124531/http://www.swarthmore.edu/library/peace/conscientiousobjection/OverviewVietnamWar.htm |archive-date=August 3, 2016 }}</ref> This was due to ]'s support of "uprisings" in the south and concern the nation would fall.<ref name="Nofi Albert p 257" /> In May 1957 Diem, then ], ] to the United States. Eisenhower pledged his continued support, and a parade was held in Diem's honor in New York City. Although Diem was publicly praised, in private Secretary of State John Foster Dulles conceded that Diem had been selected because there were no better alternatives.<ref>Karnow, Stanley. (1991), ''Vietnam, A History'', p. 230.</ref> | |||
| After the election of November 1960, Eisenhower, in a briefing with John F. Kennedy, pointed out the communist threat in Southeast Asia as requiring prioritization in the next administration. Eisenhower told Kennedy he considered Laos "the cork in the bottle" with regard to the regional threat.<ref>Reeves, Richard (1993), ''President Kennedy: Profile of Power'', p. 75.</ref> | |||
| ==== Legitimation of Francoist Spain ==== | |||
| {{Main|Pact of Madrid}} | |||
| ] and Eisenhower in ] in 1959]] | |||
| The Pact of Madrid, signed on September 23, 1953, by ] and the United States, was a significant effort to break ] of Spain, together with the ]. This development came at a time when other victorious Allies and much of the rest of the world remained hostile{{efn|For the 1946 United Nations condemnation<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.derechoshumanos.net/memoriahistorica/1946-Resolucion-ONU.htm|title=Resolution 39 (I) of the UN General Assembly on the Spanish question.}}</ref> of the Francoist regime, see "]"}} to a ] regime sympathetic to the cause of the former ] and ]. This accord took the form of three separate executive agreements that pledged the United States to furnish ] and ] to Spain. | |||
| ==== Middle East and Eisenhower doctrine ==== | |||
| ] (1959)]] | |||
| Even before he was inaugurated Eisenhower accepted a request from the British government to restore the Shah of Iran (Mohammad Reza Pahlavi) to power. He therefore ] to overthrow Prime Minister ].<ref>Eisenhower gave verbal approval to Secretary of State ] and to Director of Central Intelligence ] to proceed with the coup; Ambrose, ''Eisenhower, Vol. 2: The President'' p. 111; Ambrose (1990), ''Eisenhower: Soldier and President'', New York: Simon and Schuster, p. 333.</ref> This resulted in increased strategic control over Iranian oil by ].<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=129}}</ref> | |||
| In November 1956, Eisenhower forced an end to the combined British, French and Israeli invasion of Egypt in response to the ], receiving praise from Egyptian president ]. Simultaneously he condemned the brutal Soviet invasion of ] in response to the ]. He publicly disavowed his allies at the United Nations and used financial and diplomatic pressure to make them withdraw from Egypt.<ref>Kingseed, Cole (1995), ''Eisenhower and the Suez Crisis of 1956'', ch. 6</ref> Eisenhower explicitly defended his strong position against Britain and France in his memoirs, published in 1965.<ref>Dwight D. Eisenhower, ''Waging Peace: 1956–1961'' (1965) p. 99</ref> | |||
| After the Suez Crisis, the United States became the protector of unstable friendly governments in the Middle East via the "]".<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Lahav|first=Pnina|title=The Suez Crisis of 1956 and Its Aftermath: A Comparative Study of Constitutions, Use of Force, Diplomacy and International Relations|url=https://scholarship.law.bu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1199&context=faculty_scholarship|journal=Boston University Law Review|volume=95}}</ref> Designed by Secretary of State Dulles, it held the US would be "prepared to use armed force ... aggression from any country controlled by international communism". Further, the US would provide economic and military aid and, if necessary, use military force to stop the spread of communism in the Middle East.<ref>Isaac Alteras, ''Eisenhower and Israel: U.S.–Israeli Relations, 1953–1960'' (1993), p. 296.</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower applied the doctrine in 1957–1958 by dispensing economic aid to Jordan, and by encouraging Syria's neighbors to consider military operations against it. More dramatically, in July 1958, he sent 15,000 ] and soldiers to Lebanon as part of ], a non-combat peacekeeping mission to stabilize the pro-Western government and to prevent a radical revolution.<ref name="Little 1996 27–54">{{cite journal|last=Little|first=Douglas|title=His finest hour? Eisenhower, Lebanon, and the 1958 Middle East Crisis|journal=Diplomatic History|year=1996|volume=20|issue=1|pages=27–54|doi=10.1111/j.1467-7709.1996.tb00251.x}}</ref> The Marines departed three months later. Washington considered the military intervention successful since it brought about regional stability, weakened Soviet influence, and intimidated the Egyptian and Syrian governments, whose anti-West political position had hardened after the Suez Crisis.<ref name="Little 1996 27–54" /> | |||
| Most Arab countries were skeptical about the "Eisenhower doctrine" because they considered "Zionist imperialism" the real danger. However, they did take the opportunity to obtain free money and weapons. Egypt and Syria, supported by the Soviet Union, openly opposed the initiative. However, Egypt received American aid until the ] in 1967.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hahn|first=Peter L.|title=Securing the Middle East: The Eisenhower Doctrine of 1957|journal=Presidential Studies Quarterly|year=2006|volume=36|issue=1|pages=38–47|doi=10.1111/j.1741-5705.2006.00285.x}}</ref> | |||
| As the ] deepened, Dulles sought to isolate the ] by building regional alliances against it. Critics sometimes called it "]".<ref>{{cite book|last=Navari|first=Cornelia|year=2000|title=Internationalism and the State in the Twentieth Century|publisher=Routledge|page=316|isbn=978-0415097475}}</ref> | |||
| ==== 1960 U-2 incident ==== | |||
| {{Excerpt|1960 U-2 incident|templates=no|files=no}} | |||
| === Civil rights === | |||
| While President Truman's 1948 ] had begun the process of ], actual implementation had been slow. Eisenhower made clear his stance in his first ] in February 1953, saying "I propose to use whatever authority exists in the office of the President to end segregation in the District of Columbia, including the ], and any segregation in the Armed Forces".<ref>State of the Union Address, February 2, 1953, Public Papers, 1953 pp. 30–31.</ref> When he encountered opposition from the services, he used government control of military spending to force the change through, stating "Wherever Federal Funds are expended ..., I do not see how any American can justify ... a discrimination in the expenditure of those funds".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/ws/index.php?pid=9798|title=Eisenhower Press Conference, March 19, 1953|publisher=The American Presidency Project|access-date=October 17, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130131044238/http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/ws/index.php?pid=9798|archive-date=January 31, 2013|url-status=live}}</ref> When ], Eisenhower's first ], argued that the ] must recognize the "customs and usages prevailing in certain geographic areas of our country which the Navy had no part in creating," Eisenhower overruled him: "We have not taken and we shall not take a single backward step. There must be no second class citizens in this country."<ref>Byrnes to DDE, August 27, 1953, Eisenhower Library"</ref> | |||
| The administration declared ] a ] issue, as Communists around the world used the racial discrimination and history of violence in the US as a point of propaganda attack.<ref>] (2002), ''Cold War Civil Rights: Race and the Image of American Democracy''</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower told ] officials to make the city a model for the rest of the country in integrating black and white public-school children.<ref>{{harvnb|Eisenhower|1963|p=230}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Parmet|1972|pp=438–439}}</ref> He proposed to Congress the ] and ] and signed those acts into law. The 1957 act for the first time established a permanent civil rights office inside the ] and a ] to hear testimony about abuses of voting rights. Although both acts were much weaker than subsequent civil rights legislation, they constituted the first significant civil rights acts ].<ref>{{cite journal|first=Michael S.|last=Mayer|title=The Eisenhower Administration and the Civil Rights Act of 1957|journal=Congress & the Presidency|year=1989|volume=16|issue=2|pages=137–154|doi=10.1080/07343468909507929}}</ref> | |||
| In 1957, ] refused to honor a federal court order to integrate their public school system stemming from the '']'' decision. Eisenhower demanded that Arkansas governor ] obey the court order. When Faubus balked, the president placed the ] under federal control and sent in the ]. They protected ]' entry to ], an all-white public school, marking the first time since the ] the federal government had used federal troops in the South to enforce the Constitution.<ref>{{cite book|first=David|last=Nichol|title=A Matter of Justice: Eisenhower and the Beginning of the Civil Rights Revolution|year=2007|publisher=Simon & Schuster|isbn=978-1416541509|url=https://archive.org/details/matterofjusticee00nich}}</ref> ] wrote to Eisenhower to thank him for his actions, writing "The overwhelming majority of southerners, Negro and white, stand firmly behind your resolute action to restore law and order in ]".<ref>to DDE, September 25, 1957, Eisenhower Library</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower's administration contributed to the McCarthyist ]<ref>{{cite web|title=An interview with David K. Johnson author of The Lavender Scare: The Cold War Persecution of Gays and Lesbians in the Federal Government|url=http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/404811in.html|website=press.uchicago.edu|publisher=The University of Chicago|date=2004|access-date=December 16, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171220210821/http://www.press.uchicago.edu/Misc/Chicago/404811in.html|archive-date=December 20, 2017|url-status=live}}</ref> with Eisenhower issuing ] in 1953.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Adkins|first1=Judith|title='These People Are Frightened to Death' Congressional Investigations and the Lavender Scare|url=https://www.archives.gov/publications/prologue/2016/summer/lavender.html|website=archives.gov|publisher=The U.S. National Archives and Records Administration|quote=Most significantly, the 1950 congressional investigations and the Hoey committee's final report helped institutionalize discrimination by laying the groundwork for President Dwight D. Eisenhower's 1953 Executive Order #10450, 'Security Requirements for Government Employment.' That order explicitly added sexuality to the criteria used to determine suitability for federal employment.|access-date=January 15, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180116083139/https://www.archives.gov/publications/prologue/2016/summer/lavender.html|archive-date=January 16, 2018|url-status=live|date=August 15, 2016}}</ref> During Eisenhower's presidency thousands of ] applicants were barred from federal employment and over 5,000 federal employees were fired under suspicions of being homosexual.<ref name=documenting>{{cite book|last1=Sears|first1=Brad|last2=Hunter|first2=Nan D.|last3=Mallory|first3=Christy|title=Documenting Discrimination on the Basis of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in State Employment|date=September 2009|publisher=The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Law and Public Policy at the University of California Los Angeles School of Law|pages=5–3|url=https://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/5_History.pdf#page=3|quote=From 1947 to 1961, more than 5,000 allegedly homosexual federal civil servants lost their jobs in the purges for no reason other than sexual orientation, and thousands of applicants were also rejected for federal employment for the same reason. During this period, more than 1,000 men and women were fired for suspected homosexuality from the State Department alone—a far greater number than were dismissed for their membership in the Communist party.|access-date=January 15, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170206215755/http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/5_History.pdf#page=3|archive-date=February 6, 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Adkins|first1=Judith|title='These People Are Frightened to Death' Congressional Investigations and the Lavender Scare|url=https://www.archives.gov/publications/prologue/2016/summer/lavender.html|website=archives.gov|publisher=The U.S. National Archives and Records Administration|quote=Historians estimate that somewhere between 5,000 and tens of thousands of gay workers lost their jobs during the Lavender Scare.|access-date=January 15, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180116083139/https://www.archives.gov/publications/prologue/2016/summer/lavender.html|archive-date=January 16, 2018|url-status=live|date=August 15, 2016}}</ref> From 1947 to 1961 the number of firings based on sexual orientation were far greater than those for membership in the ],<ref name=documenting /> and government officials intentionally campaigned to make "homosexual" synonymous with "Communist traitor" such that LGBT people were treated as a national security threat.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Sears|first1=Brad|last2=Hunter|first2=Nan D.|last3=Mallory|first3=Christy|title=Documenting Discrimination on the Basis of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in State Employment|date=September 2009|publisher=The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Law and Public Policy at the University of California Los Angeles School of Law|pages=5–3|url=https://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/5_History.pdf#page=3|quote=Johnson has demonstrated that during this era government officials intentionally engaged in campaigns to associate homosexuality with Communism: 'homosexual' and 'pervert' became synonyms for 'Communist' and 'traitor.'|access-date=January 15, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170206215755/http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/5_History.pdf#page=3|archive-date=February 6, 2017|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| === Relations with Congress === | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower had a Republican Congress for only his first two years in office; in the Senate, Republicans held the majority by a one-vote margin. Despite being Eisenhower's political opponent for the 1952 Republican presidential nomination, Senator Majority Leader Robert A. Taft assisted Eisenhower a great deal by promoting the President's proposals among the "Old Guard" Republican Senators. Taft's death in July 1953—six months into Eisenhower's presidency—affected Eisenhower both personally and professionally. The President noted he had lost "a dear friend" with Taft's passing. Eisenhower disliked Taft's successor as Majority Leader, Senator ], and the relationship between the two men led to tension between the Senate and the White House.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=118–119}}</ref> | |||
| This prevented Eisenhower from openly condemning Joseph McCarthy's highly criticized methods against communism. To facilitate relations with Congress, Eisenhower decided to ignore McCarthy's controversies and thereby deprive them of more energy from the involvement of the White House. This position drew criticism from a number of corners.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=56–62}}</ref> In late 1953, McCarthy declared on national television that the employment of communists within the government was a menace and would be a pivotal issue in the ]. Eisenhower was urged to respond directly and specify the various measures he had taken to purge the government of communists.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=140}}</ref> | |||
| Among Eisenhower's objectives in not directly confronting McCarthy was to prevent McCarthy from dragging the ] (AEC) into McCarthy's witchhunt, which might interfere with the AEC's work on ]s and other weapons programs.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=167}}</ref><ref name="y-s-132">{{harvnb|Young|Schilling|2019|p=132}}</ref> In December 1953, Eisenhower learned that nuclear scientist ] had been accused of being a spy for the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Bundy|1988|pp=305–306}}</ref> Although Eisenhower never really believed these allegations,<ref>{{harvnb|Bundy|1988|p=305}}</ref> in January 1954 he ordered that "a blank wall" be placed between Oppenheimer and all defense-related activities.<ref>{{harvnb|Young|Schilling|2019|p=128}}</ref> The ] later that year resulted in the physicist losing his security clearance.<ref>{{harvnb|Bundy|1988|pp=310–311}}</ref> The matter was controversial at the time and remained so in later years, with Oppenheimer achieving a certain martyrdom.<ref name="y-s-132"/> The case would reflect poorly on Eisenhower, but the president had never examined it in any detail and had instead relied excessively upon the advice of his subordinates, especially that of AEC chairman ].<ref>{{harvnb|Bundy|1988|pp=316–317}}</ref> Eisenhower later suffered a major political defeat when his nomination of Strauss to be Secretary of Commerce was defeated in the Senate in 1959, in part due to Strauss's role in the Oppenheimer matter.<ref>{{harvnb|Young|Schilling|2019|pp=147, 150}}</ref> | |||
| In May 1955, McCarthy threatened to issue subpoenas to White House personnel. Eisenhower was furious, and issued an order as follows: "It is essential to efficient and effective administration that employees of the Executive Branch be in a position to be completely candid in advising with each other on official matters ... it is not in the public interest that any of their conversations or communications, or any documents or reproductions, concerning such advice be disclosed." This was an unprecedented step by Eisenhower to protect communication beyond the confines of a cabinet meeting, and soon became a tradition known as ]. Eisenhower's denial of McCarthy's access to his staff reduced McCarthy's hearings to rants about trivial matters and contributed to his ultimate downfall.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|pp=188–189}}</ref> | |||
| In early 1954, the Old Guard put forward a constitutional amendment, called the ], which would curtail international agreements by the Chief Executive, such as the ]s. Eisenhower opposed the measure.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=154}}</ref> The Old Guard agreed with Eisenhower on the development and ownership of nuclear reactors by private enterprises, which the Democrats opposed. The President succeeded in getting legislation creating a system of licensure for nuclear plants by the AEC.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=157}}</ref> | |||
| The Democrats gained a majority in both houses in the 1954 election.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=219}}</ref> Eisenhower had to work with the Democratic Majority Leader ] (later US president) in the Senate and Speaker ] in the House. ], the Republican Speaker from 1947 to 1949 and again from 1953 to 1955, wrote that Eisenhower "never surrounded himself with assistants who could solve political problems with professional skill. There were exceptions, ], for example, who as chairman of the ] tried to open the administration's eyes to the political facts of life, with occasional success. However, these exceptions were not enough to right the balance."<ref name=martin>Joseph W. Martin as told to Donavan, Robert J. (1960), ''My First Fifty Years in Politics'', New York: McGraw Hill, p. 227</ref> | |||
| Speaker Martin concluded that Eisenhower worked too much through subordinates in dealing with Congress, with results, "often the reverse of what he has desired" because Members of Congress, "resent having some young fellow who was picked up by the White House without ever having been elected to office himself coming around and telling them 'The Chief wants this'. The administration never made use of many Republicans of consequence whose services in one form or another would have been available for the asking."<ref name=martin /> | |||
| Eisenhower was relatively active with ], with 181 vetoes of which only two were overridden.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.senate.gov/legislative/vetoes/EisenhowerDD.htm | title=U.S. Senate: Vetoes by President Dwight D. Eisenhower }}</ref> | |||
| === Judicial appointments === | |||
| ==== Supreme Court ==== | |||
| {{Main|Dwight D. Eisenhower Supreme Court candidates|Dwight D. Eisenhower judicial appointments}} | |||
| Eisenhower appointed the following ] to the ]: | Eisenhower appointed the following ] to the ]: | ||
| * ], 1953 (]) | |||
| * ], 1954 | |||
| * ], 1956 | |||
| * ], 1957 | |||
| * ], 1958 | |||
| Whittaker was unsuited for the role and retired in 1962, after Eisenhower's presidency had ended. Stewart and Harlan were conservative Republicans, while Brennan was a Democrat who became a leading voice for liberalism.<ref>Newton, ''Eisenhower'' (2011) pp. 356–357</ref> In selecting a Chief Justice, Eisenhower looked for an experienced jurist who could appeal to liberals in the party as well as law-and-order conservatives, noting privately that Warren "represents the kind of political, economic, and social thinking that I believe we need on the Supreme Court ... He has a national name for integrity, uprightness, and courage that, again, I believe we need on the Court".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eisenhowermemorial.org/presidential-papers/first-term/documents/460.cfm |last1=Eisenhower |first1=Dwight D. |title=Personal and confidential To Milton Stover Eisenhower |date=9 October 1953 |work=Papers of Dwight David Eisenhower |id=doc. 460 |publisher=Eisenhower Memorial |access-date=January 26, 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120118180711/http://www.eisenhowermemorial.org/presidential-papers/first-term/documents/460.cfm |archive-date=January 18, 2012 }}</ref> | |||
| *], 1953 (Chief Justice) | |||
| *], 1954 | |||
| *], 1956 | |||
| *], 1957 | |||
| *], 1958 | |||
| === States admitted to the Union === | |||
| ====Other courts==== | |||
| Two states were ] during Eisenhower's presidency. | |||
| {{main|Dwight D. Eisenhower judicial appointments}} | |||
| * ] – January 3, 1959 (49th state) | |||
| In addition to his five Supreme Court appointments, Eisenhower appointed 45 judges to the ], and 129 judges to the ]. | |||
| * Hawaii – August 21, 1959 (50th state) | |||
| === |
=== Health issues === | ||
| Eisenhower began ] cigarettes at West Point, often three or four packs a day. He joked that he "gave an order" to stop ] in 1949. However, ] says the true story was more complex. At first, he removed cigarettes and ]s, but that did not work. He told a friend: | |||
| *] – January 3, 1959 <small>49th state</small> | |||
| {{blockquote|I decided to make a game of the whole business and try to achieve a feeling of some superiority ... So I stuffed cigarettes in every pocket, put them around my office on the desk ... made it a practice to offer a cigarette to anyone who came in ... while mentally reminding myself as I sat down, "I do not have to do what that poor fellow is doing."<ref>{{cite book|first=Evan|last=Thomas|title=Ike's Bluff: President Eisenhower's Secret Battle to Save the World|url=https://archive.org/details/ikesbluffpreside0000thom|url-access=registration|page=|year=2012|publisher=Little, Brown|isbn=978-0316217279|access-date=April 28, 2017}}</ref>}} | |||
| *] – August 21, 1959 <small>50th state</small> | |||
| He was the first president to release information about his health and medical records while in office, but people around him deliberately misled the public about his health. On September 24, 1955, while vacationing in ], he had a serious ]. While ] at ]<ref>Newton, ''Eisenhower'' pp. 196–199.</ref> ], his personal physician, misdiagnosed the symptoms as ], and failed to call in help that was urgently needed. Snyder later falsified his own records to cover his blunder and to allow Eisenhower to imply that he was healthy enough to do his job.<ref>Clarence G. Lasby, ''Eisenhower's Heart Attack: How Ike Beat Heart Disease and Held on to the Presidency'' (1997) pp. 57–113.</ref><ref>Robert P. Hudson, "Eisenhower's Heart Attack: How Ike Beat Heart Disease and Held on to the Presidency (review)" ''Bulletin of the History of Medicine'' 72#1 (1998) pp. 161–162 {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170429000309/https://muse.jhu.edu/article/4010 |date=April 29, 2017 }}.</ref><ref>R.H. Ferrell, ''Ill-Advised: Presidential Health & Public Trust'' (1992), pp. 53–150</ref> | |||
| ===End of presidency=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The heart attack required six weeks' hospitalization, during which time Nixon, Dulles, and ] assumed administrative duties and provided communication with the president.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=272}}</ref> He was treated by ], a ] with a national reputation, who regularly informed the press of the president's progress. His physician recommended a second presidential term as essential to his recovery.<ref>{{harvnb|Ambrose|1984|p=281}}</ref> | |||
| In 1961, Eisenhower became the first U.S. president to be "constitutionally forced" from office, having served the maximum two terms allowed by the ]. The amendment was ratified in 1951, during Harry S. Truman's term, but it stipulated that Truman would not be affected by the amendment. | |||
| As a consequence of his heart attack Eisenhower developed a left ventricular ], which caused a mild stroke during a cabinet meeting on November 25, 1957, when Eisenhower suddenly found himself unable to move his right hand or to speak. The president also suffered from ],<ref>{{cite news |title=Butler Criticizes Illness Reports: Says News Has Been Handled in Terms of Propaganda—Hagerty Denies It |first=Richard J. H. |last=Johnston |work=The New York Times |date=June 13, 1956 |page=32A |url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/113576174/ |quote=Paul M. Butler, the Democratic National Chairman, ... declared that the physicians who operated on and attended the President in his most recent illness 'have done a terrific job of trying to convince the American people that a man who has had a heart attack and then was afflicted with Crohn's disease is a better man physically.' He added: 'Whether the American people will buy that, I don't know.' |access-date=December 22, 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=President's Heart Reported Sound; Surgery Is Indicated: Inflamed, Obstructed, Intestine Is Blamed |last=Clark |first=Robert E |work=Atlanta Daily World |date=June 9, 1956 |page=1 |url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/491087844/ |access-date=December 22, 2016}}</ref> which necessitated surgery for a bowel obstruction on June 9, 1956.<ref>{{cite news |title=President Undergoes Surgery on Intestine Block at 2:59 A.M.: Doctors Pronounce It Success : Condition Is Good: Operation Lasts Hour and 53 Minutes–13 Attend Him |first=Anthony |last=Leviero |work=The New York Times |date=June 9, 1956 |page=1 |url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/113808030/ |quote=President Eisenhower was operated on at 2:59 A.M. today for relief of an intestinal obstruction. At 4:55 A.M., the operation was pronounced a success by the surgeons. ... The President's condition was diagnosed as ileitis. This is an inflamation of the ileum—the lowest portion of the small intestine, where it joins the large intestine. ... The President first felt ill shortly after midnight yesterday. He had attended a dinner of the White House News Photographers Association Thursday night and had returned to the White House at 11. Mrs. Eisenhower called Maj. Gen. Howard McC. Snyder, the President's personal physician, at 12:45 A.M. yesterday, telling him the President had some discomfort in his stomach. He recommended a slight dose of milk of magnesia. At 1:20 Mrs. Eisenhower called again, saying the President was still complaining of not feeling well. This time she asked Dr. Snyder to come to the White House from his home about a mile away on Connecticut Avenue. He arrived at 2 A.M. and has not left the President's side since. |access-date=December 22, 2016}}</ref> To treat the intestinal block, surgeons bypassed about ten inches of his ].<ref>{{cite news |title=Eisenhower Out Of Danger; Will Be Able To Resume Duties And Seek Reelection: Doctors See Prospect of Full Return to Job in Four to Six Weeks: Operation Performed to Prevent Gangrene of Bowel: Signing of Official Papers Viewed as Likely by Tomorrow or Tuesday | last=Knighton | first=William Jr. |work=The Baltimore Sun |date=June 10, 1956 |page=1 |url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/541066565/ |access-date=December 22, 2016 }}</ref> His scheduled meeting with Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was postponed so he could recover at his farm.<ref>{{cite news |title=Out of Hospital Visit Postponed |work=The New York Times |date=July 1, 1956 |page=E2 |url=https://www.proquest.com/docview/113842058/ |access-date=December 22, 2016 }}</ref> He was still recovering from this operation during the Suez Crisis. Eisenhower's health issues forced him to give up smoking and make some changes to his diet, but he still drank alcohol. During a visit to England, he complained of dizziness and had to have his blood pressure checked on August 29, 1959; however, before dinner at prime ministerial manor house ] on the next day his physician, General Howard Snyder, recalled that Eisenhower "drank several ], and one or two gins on the rocks ... three or four wines with the dinner".<ref>Williams, Charles ''Harold Macmillan'' (2009) p. 345</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower was also the first outgoing President to come under the protection of the ] (two then living former Presidents, ] and ], left office before the Act was passed). Under the act, Eisenhower was entitled to receive a lifetime pension, state-provided staff and a ] detail.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.archives.gov/about/laws/former-presidents.html|title=Former Presidents Act|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| Eisenhower's health during the last three years of his second term in office was relatively good. After leaving the White House, he suffered several additional and ultimately crippling heart attacks.<ref name="drzebra">{{cite web|url=http://www.doctorzebra.com/prez/g34.htm|title=President Dwight Eisenhower: Health & Medical History|publisher=doctorzebra.com|access-date=January 22, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130117084840/http://www.doctorzebra.com/prez/g34.htm|archive-date=January 17, 2013|url-status=live}}</ref> A severe heart attack in August 1965 largely ended his participation in public affairs.<ref name=post/> On December 12, 1966, his ] was removed, containing 16 ]s.<ref name="drzebra" /> After Eisenhower's death in 1969, an autopsy revealed an undiagnosed adrenal ],<ref>Messerli F. H., Loughlin K. R., Messerli A. W., Welch W. R.: The President and the pheochromocytoma. ''Am J Cardiol'' 2007; 99: 1325–1329.</ref> a ] adrenalin-secreting tumor that may have made him more vulnerable to ]. Eisenhower had seven heart attacks from 1955 until his death.<ref name="drzebra" /> | |||
| In the 1960 election to choose his successor, Eisenhower endorsed his own Vice-President, Republican Richard Nixon against Democrat ]. He thoroughly supported Nixon over Kennedy, telling friends: "I will do almost anything to avoid turning my chair and country over to Kennedy."<ref name="time 2008"/> However, he only campaigned for Nixon in the campaign's final days and even did Nixon some harm. When asked by reporters at the end of a televised press conference to list one of Nixon's policy ideas he had adopted, he joked, "If you give me a week, I might think of one." Kennedy's campaign used the quote in one of its campaign commercials. Nixon lost narrowly to Kennedy. Eisenhower, who was the oldest elected President in history at that time, thus handed power over to the youngest elected President.<ref name="time 2008"/> | |||
| === End of presidency === | |||
| On January 17, 1961, Eisenhower gave his final televised Address to the Nation from the ].<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.usa-presidents.info/speeches/eisenhower-farewell.html|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower Farewell Address|publisher=USA Presidents}}</ref> In his farewell speech to the nation, Eisenhower raised the issue of the Cold War and role of the U.S. armed forces. He described the Cold War saying: "We face a hostile ideology global in scope, atheistic in character, ruthless in purpose and insidious in method..." and warned about what he saw as unjustified government spending proposals and continued with a warning that "we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the ]... Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together." | |||
| The ], which set a ] on the presidency, was ratified in 1951. Eisenhower was the first president constitutionally prevented from serving a third term. | |||
| Eisenhower was also the first outgoing president to come under the protection of the ]. Under the act, Eisenhower was entitled to a lifetime pension, state-provided staff and a ] security detail.<ref>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008|url=https://www.archives.gov/about/laws/former-presidents.html|title=Former Presidents Act|publisher=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080614024342/http://www.archives.gov/about/laws/former-presidents.html|archive-date=June 14, 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Because of legal issues related to holding a military rank while in a civilian office, Eisenhower resigned his permanent commission as ] before entering the office of President of the United States. Upon completion of his Presidential term, his commission on the retired list was reactivated and Eisenhower again was commissioned a five-star general in the United States Army.{{Fact|date=January 2009}} | |||
| In the ] to choose his successor, Eisenhower endorsed Nixon over Democrat John F. Kennedy. He told friends, "I will do almost anything to avoid turning my chair and country over to Kennedy."<ref name="time 2008" /> He actively campaigned for Nixon in the final days, although he may have done Nixon some harm. When asked by reporters at the end of a televised press conference to list one of Nixon's policy ideas he had adopted, Eisenhower joked, "If you give me a week, I might think of one. I don't remember." Kennedy's campaign used the quote in one of its campaign commercials. Nixon narrowly lost to Kennedy. Eisenhower, who was, at 70, the oldest president to date, was succeeded by 43-year-old Kennedy, the youngest elected president.<ref name="time 2008" /> | |||
| ==Post-presidency== | |||
| Eisenhower retired to the place where he and Mamie had spent much of their post-war time, a working farm adjacent to the battlefield at ], ]. In 1967, the Eisenhowers donated the farm to the ] and since 1980 it has been open to the public as the ]<ref></ref>. In retirement, he did not completely retreat from political life; he spoke at the ] and appeared with ] in a Republican campaign commercial from Gettysburg.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://livingroomcandidate.movingimage.us/election/index.php?nav_action=election&nav_subaction=overview&campaign_id=168|title=Johnson vs. Goldwater|publisher=The Living Room Candidate}}</ref> | |||
| ] in 1967]] | |||
| It was originally intended for Eisenhower to have a more active role in the campaign as he wanted to respond to attacks Kennedy made on his administration. However, First Lady Mamie Eisenhower expressed concern to Second Lady ] about the strain campaigning would put on his heart, and wanted the president to withdraw, without letting him know of her intervention. Vice President Nixon himself was informed by White House physician Major General Howard Snyder that he could not approve a heavy campaign schedule for the president, whose health problems had been exacerbated by Kennedy's attacks. Nixon then convinced Eisenhower not to go ahead with the expanded campaign schedule and limit himself to the original schedule. Nixon reflected that if Eisenhower had carried out his expanded campaign schedule, he might have had a decisive impact on the outcome of the election, especially in states that Kennedy won with razor-thin margins. Mamie did not tell Dwight why Nixon changed his mind on Dwight's campaigning until years later.<ref>Nixon, Richard, The Memoirs of Richard Nixon, 1978, pp. 222–223.</ref> | |||
| ===Death and funeral=== | |||
| [[File:MEETING BETWEEN PRESIDENT DWIGHT D. EISENHOWER (DDE) AND PRESIDENT-ELECT KENNEDY-AR6180-C.jpg|thumb|Eisenhower sharing a light moment | |||
| Eisenhower died of ] on March 28, 1969 at ] in Washington D.C. The following day his body was moved to the ]'s Bethlehem Chapel where he lay in repose for twenty-eight hours. On March 30, his body was brought by ] to the ] where he lay in state in the ]. On March 31, Eisenhower's body was returned to the ] where he was given an ] funeral service. That evening, Eisenhower's body was placed onto a train en route to ], ]. His body arrived on April 2, and was interred later that day in a small chapel on the grounds of the ]. Eisenhower is buried alongside his son Doud who died at age 3 in 1921, and his wife, Mamie, who died in 1979.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/quick_links/funeral/DDE_funeral.html|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| with President-elect ] during their meeting in the Oval Office at White House]] | |||
| ] | |||
| On January 17, 1961, Eisenhower gave his final televised Address to the Nation from the ].<ref name=DDEFarewell>{{cite web|access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=http://www.usa-presidents.info/speeches/eisenhower-farewell.html |title=Dwight D. Eisenhower Farewell Address |date=January 17, 1961 |publisher=USA Presidents |url-status=usurped |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080513222105/http://www.usa-presidents.info/speeches/eisenhower-farewell.html |archive-date=May 13, 2008 }}</ref> In his ], Eisenhower raised the issue of the Cold War and role of the armed forces. He described the Cold War: "We face a hostile ideology global in scope, atheistic in character, ruthless in purpose and insidious in method ..." and warned about what he saw as unjustified government spending proposals. He continued with a warning that "we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military–industrial complex."<ref name=DDEFarewell /> Eisenhower elaborated, "we recognize the imperative need for this development ... the potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist ... Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together."<ref name=DDEFarewell /> | |||
| Because of legal issues related to holding a military rank while in a civilian office, Eisenhower had resigned his permanent commission as ] before assuming the presidency. Upon completion of his presidential term, his commission was reactivated by Congress.<ref name=post/><ref>{{cite web|title= A Chronology from ''The New York Times'', March 1961 |website=John F. Kennedy Presidential Library & Museum |url=http://www.jfklibrary.org/Historical+Resources/Archives/Reference+Desk/New+York+Times+Chronology/1961/March.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060503063950/http://www.jfklibrary.org/Historical+Resources/Archives/Reference+Desk/New+York+Times+Chronology/1961/March.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 3, 2006 |date=March 23, 1961 |access-date=May 30, 2009 |quote=Mr. Kennedy signed into law the act of Congress restoring the five-star rank of General of the Army to his predecessor, Dwight D. Eisenhower. (15:5) }}</ref> | |||
| ===Legacy=== | |||
| After Eisenhower left office, his reputation declined and he was seen as having been a "do-nothing" President. This was partly because of the contrast between Eisenhower and his young activist successor, ]. He was criticized for his reluctance to support the ] movement to the degree which activists wanted, his handling of the ] and the international embarrassment,<ref name="'70s 27">{{cite book |title= How We Got Here: The '70s|last= Frum|first= David|authorlink= David Frum|coauthors= |year= 2000|publisher= Basic Books|location= New York, New York|isbn= 0465041957|page= 27|pages= |url= }}</ref><ref name="us news">{{cite news |title= Presidential Lies and Deceptions|last= Walsh|first= Kenneth T.|authorlink= |coauthors= |date= 2008-06-06|publisher= ''US News and World Report|pages= |url=http://www.usnews.com/articles/news/politics/2008/06/06/presidential-lies-and-deceptions.html }}</ref> the Soviet Union's perceived leadership in the ] and the ], and his failure publicly to oppose ]. In particular, Eisenhower was criticized for failing to defend ] from attacks by ], though he privately deplored McCarthy's tactics and claims.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/presidents/34_eisenhower/eisenhower_politics.html|title=Presidential Politics|publisher=]}}</ref> Such omissions were held against him during the ] climate of the 1960s and 1970s. Since that time, however, Eisenhower's reputation has risen. In ] of historians, Eisenhower often is ranked in the top 10 among all US Presidents. | |||
| == Post-presidency (1961–1969) == | |||
| ==Tributes and memorials== | |||
| ] with Eisenhower aboard ] in October 1965]] | |||
| ] as part of the ]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aoc.gov/cc/art/nsh/eisenhower.cfm |title=Dwight D. Eisenhower |accessdate=November 29, 2008 |work=www.aoc.gov |publisher=Architect of the Capitol }}</ref>]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Eisenhower's picture was on the ] from 1971 to 1978. Nearly 700 million of the copper-nickel clad coins were minted for general circulation, and far smaller numbers of uncirculated and ] issues (in both copper-nickel and 40% silver varieties) were produced for collectors. He reappeared on a ] silver dollar issued in 1990, celebrating the 100th anniversary of his birth, which with a double image of him showed his two roles, as both a soldier and a statesman. As part of the ], Eisenhower will be featured on a gold-colored dollar coin in 2015.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://usmint.gov/mint_programs/$1coin/index.cfm?action=schedule |title=Presidential Dollar Coin Release Schedule |accessdate=2008-05-24 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Following the presidency, Eisenhower moved to the place where he and Mamie had spent much of their post-war time, a working farm adjacent to the ], {{convert|70|mi}} from his ancestral home in Elizabethville, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://articles.sun-sentinel.com/1985-08-08/news/8502010850_1_ambulance-service-steady-growth-post-office |title=Tiny Pennsylvania Town An Escape From Modernity |newspaper=] |date=August 8, 1985 |first=Mary |last=Klaus |access-date=January 4, 2016 |quote=From this farm the family migrated to Kansas in the summer of 1878. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160225045723/http://articles.sun-sentinel.com/1985-08-08/news/8502010850_1_ambulance-service-steady-growth-post-office |archive-date=February 25, 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://civilwar.gratzpa.org/2010/11/eisenhower-family-civil-war-veterans/ |title=Eisenhower Family Civil War Veterans |first=Norman |last=Gasbarro |date=November 29, 2010 |access-date=January 4, 2016 |quote=a stately old home, identified as the ancestral home of President Dwight D. Eisenhower |website=Civil War Blog |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160225182344/http://civilwar.gratzpa.org/2010/11/eisenhower-family-civil-war-veterans/ |archive-date=February 25, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> They also maintained a retirement home in ].<ref>{{cite book|last=Historical Society of Palm Desert |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7SntPkI-6qUC&pg=PA103 |title=Palm Desert|year=2009|publisher=Arcadia Publishing|isbn=978-0738559643|page=103|author2=Rover, Hal |author3=Kousken, Kim |author4= Romer, Brett }}</ref> | |||
| He is remembered for ending the ]. ], the second ] ], was named in his honor. | |||
| After leaving office, Eisenhower did not completely retreat from political life. He flew to San Antonio, where he had been stationed years earlier, to support ], the unsuccessful Republican candidate against the Democrat ] for ] seat.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.lib.utexas.edu/taro/utsa/00306/00306-P.html|title=Inventory of the San Antonio Express-News Photograph Collection, 1960-1969 |quote= Eisenhower, Dwight D.: visit to San Antonio in behalf of John Goode and Henry Catto, Jr.; downtown S.A. 10/29/1961 |publisher=University of Texas Library |access-date=May 17, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160602031931/http://www.lib.utexas.edu/taro/utsa/00306/00306-P.html|archive-date=June 2, 2016|url-status=dead }}</ref> He addressed the ], in San Francisco, and appeared with party nominee ] in a campaign commercial.<ref>{{cite web|access-date=January 20, 2011 |url=http://www.livingroomcandidate.org/commercials/1964/ike-at-gettysburg |title=Ike at Gettysburg (Goldwater, 1964) |work=1964: Johnson vs. Goldwater |publisher=Museum of the Moving Image |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131019120627/http://www.livingroomcandidate.org/commercials/1964/ike-at-gettysburg |archive-date=October 19, 2013 }}</ref> That endorsement came somewhat reluctantly, because Goldwater had in the late 1950s criticized Eisenhower's administration as "a dime-store New Deal".<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.newsday.com/long-island/politics/dwight-eisenhower-helped-barry-goldwater-s-failed-1964-election-bid-1.11783516 |newspaper=] |title=When an ex-president helped an 'extreme' Republican candidate |date=May 11, 2016 |access-date=December 9, 2016 |first=William |last=Goldschlag |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161220141200/http://www.newsday.com/long-island/politics/dwight-eisenhower-helped-barry-goldwater-s-failed-1964-election-bid-1.11783516 |archive-date=December 20, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> On January 20, 1969, ], Eisenhower issued a statement praising his former vice president and calling it a "day for rejoicing".<ref>{{cite news|url=http://archives.chicagotribune.com/1969/01/21/page/5/article/inauguration-is-a-day-for-rejoicing-ike|title=Inauguration Is a Day For Rejoicing: Ike|newspaper=Chicago Tribune|date=January 21, 1969|access-date=August 19, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170819103946/http://archives.chicagotribune.com/1969/01/21/page/5/article/inauguration-is-a-day-for-rejoicing-ike/|archive-date=August 19, 2017|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] (Interstate 290), a {{convert|30|mi|km|sing=on}} long expressway in the ] area, was renamed after him. | |||
| === Death === | |||
| The British A4 class steam locomotive No. 4496 (renumbered 60008) ''Golden Shuttle'' was renamed ''Dwight D. Eisenhower'' in 1946. It is preserved at the ] in ], ]. | |||
| At 12:25 p.m. on March 28, 1969, Eisenhower died from ] at ] in Washington, D.C., at age 78. His last words:{{blockquote|"I've always loved my wife, my children, and my grandchildren, and I've always loved my country. I want to go. God, take me."}} <ref> {{cite news|title = Eisenhower Dead at 78 as Ailing Heart Fails; Rites Will Start Today|last = Belair|first = Felix Jr.|date = March 29, 1969|newspaper = ]|page= 1}} </ref> The following day, his body was moved to the ]'s Bethlehem Chapel, where he lay in repose for 28 hours.<ref name="FinalPost">{{cite web|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower – Final Post|url=https://eisenhower.archives.gov/all_about_ike/final_post.html|publisher=Presidential Libraries System, National Archives and Records Administration|access-date=May 19, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190308051349/https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/all_about_ike/final_post.html|archive-date=March 8, 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> He was then transported to the ], where he ] in the ] on March 30 and 31.<ref>{{cite web|title=Lying in State or in Honor|url=https://www.aoc.gov/nations-stage/lying-state-honor|publisher=Architect of the Capitol|accessdate=May 19, 2019|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20190518015734/https://www.aoc.gov/nations-stage/lying-state-honor|archivedate=May 18, 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> A ] was conducted at the Washington National Cathedral on March 31.<ref name="Funeral">{{cite news |title=World's Leaders Join in Services for Eisenhower |first=Felix Jr. |last=Belair |newspaper=The New York Times |date=April 1, 1969 |page=1}}</ref> The president and First Lady, Richard and Pat Nixon, attended, as did former president Lyndon B. Johnson. Former President Harry S. Truman was unable to attend due to having vacation. Also among the 2,000 guests that were invited were the UN Secretary-General ] and 191 foreign delegates from 78 countries, including 10 foreign ]. Guests included President ] of France, who was in the United States for the first time since the ],<ref>{{cite news|title=Nixon will Meet with De Gaulle Today|first=Peter|last=Grose|newspaper=The New York Times|date=March 31, 1969|page=1|quote=President de Gaulle arrived by plane from Paris, on his first visit to the United States since the funeral of President Kennedy in 1963.}}</ref> Chancellor ] of West Germany, ] of Belgium and Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi of Iran.<ref name="Funeral" /> | |||
| The service included the singing of ] "The Palms", and the playing of the hymn "]".<ref>{{cite news|author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.-->|title=For A Modest Man: A Simple Funeral Honors Ike|url=https://cdnc.ucr.edu/cgi-bin/cdnc?a=d&d=DS19690401.2.4&e=-------en--20--1--txt-txIN--------1|work=]|agency=]|date=April 1, 1969|volume=42|issue=205|via=], Center for Bibliographical Studies and Research at the University of California Riverside|access-date=May 19, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ] was a small, liberal arts college chartered in ], ] in 1965, with classes beginning in 1968. Financial problems forced the school to fall under the management of the ] in 1979. Its last class graduated in 1983. | |||
| That evening, Eisenhower's body was placed onto a special ] for its journey from the capital to his hometown of ]. First incorporated into President ] in 1865, a funeral train would not be part of a US state funeral again until ].<ref>{{cite web|last1=Weissert|first1=Will|last2=Phillip|first2=David J.|agency=The Associated Press|url=https://www.militarytimes.com/news/pentagon-congress/2018/12/06/bushes-depart-on-first-presidential-funeral-train-since-1969/|title=Bushes depart on first presidential funeral train since 1969|date=December 6, 2018|website=MilitaryTimes.com|publisher=Sightline Media Group|access-date=May 19, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190809220531/https://www.militarytimes.com/news/pentagon-congress/2018/12/06/bushes-depart-on-first-presidential-funeral-train-since-1969/|archive-date=August 9, 2019|url-status=live}}</ref> on 2 April 1969 Eisenhower is buried inside the Place of Meditation, the chapel on the grounds of the ] in Abilene. As requested, he was buried in a ] casket, wearing his ], decorated with Army Distinguished Service Medal with three oak leaf clusters, Navy Distinguished Service Medal, and the Legion of Merit. Buried alongside Eisenhower are his son Doud, who died at age 3 in 1921, and wife Mamie, who died in 1979.<ref name=FinalPost/> | |||
| The ] in ], ] was named after the President in 1971. | |||
| President Richard Nixon eulogized Eisenhower in 1969, saying: | |||
| The ], located at ] near ], ], was named in his honor.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ddeamc.amedd.army.mil/Visitor/history.htm |title=History of Eisenhower Army Medical Center |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070203232831/http://www.ddeamc.amedd.army.mil/Visitor/history.htm|publisher=] |archivedate=2007-02-03|accessdate=2008-05-23}}</ref> | |||
| {{blockquote|Some men are considered great because they lead great armies or they lead powerful nations. For eight years now, Dwight Eisenhower has neither commanded an army nor led a nation; and yet he remained through his final days the world's most admired and respected man, truly the first citizen of the world.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.upi.com/Archives/Audio/1969/Eisenhower-Judy-Garland-Die/|title=1969 Year in Review: Eisenhower, Judy Garland die|publisher=UPI|date=October 25, 2005|access-date=December 19, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161010085652/http://www.upi.com/Archives/Audio/1969/Eisenhower-Judy-Garland-Die/|archive-date=October 10, 2016|url-status=live}}</ref>}} | |||
| In February 1971, ''Dwight D. Eisenhower School'' of ], ] was officially opened.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.freeholdtwp.k12.nj.us/eisenhower/history.htm|title=Eisenhower Middle School History|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| == Legacy and memory == | |||
| The ] was completed in 1979; it conveys westbound traffic on ] through the ], {{convert|60|mi|km}} west of ], ]. | |||
| === Public and scholarly assessments === | |||
| ] by ] stands in ] of the ] in Washington, D.C.]] | |||
| During his two terms as president, Eisenhower's ]s were consistently high, only briefly falling below 50 percent in 1958 and again in 1960.<ref>Lippman, Theo Jr. (September 19, 1979). . '']''. Retrieved November 25, 2024.</ref> His overall average of 63 percent in the ] remains the second highest in history.<ref name="brrt45">Reddy, Patrick (July 2, 2006). . '']''. Retrieved November 24, 2024.</ref> With the popularity of his successor, John F. Kennedy, Eisenhower's reputation declined in the years after he left office. He was widely seen by critics as an inactive, uninspiring, golf-playing president, which was in stark contrast to Kennedy, who was 26 years his junior. Critics also compared Eisenhower with the likes of ] as a "do nothing president".<ref>Alsop, Joseph (July 28, 1966). . '']''. Retrieved November 30, 2024.</ref> Despite his unprecedented use of Army troops to enforce a federal desegregation order at ] in Little Rock, Eisenhower was criticized for his reluctance to support the ] to the degree that activists wanted. Eisenhower also attracted criticism for his handling of the ] and the associated international embarrassment,<ref name="'70s 27">{{harvnb|Frum|2000|p=27}}</ref><ref name="us news">{{Cite news|title=Presidential Lies and Deceptions |last=Walsh |first=Kenneth T. |date=June 6, 2008 |work=U.S. News & World Report |url=https://www.usnews.com/articles/news/politics/2008/06/06/presidential-lies-and-deceptions.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080929194001/http://www.usnews.com/articles/news/politics/2008/06/06/presidential-lies-and-deceptions.html |archive-date=September 29, 2008 }}</ref> for the Soviet Union's perceived leadership in the ] and the ], and for his failure to publicly oppose ].<ref>{{Cite book |title=Presidents and Civil Liberties from Wilson to Obama |date=2012 |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/presidents-and-civil-liberties-from-wilson-to-obama/presidents-and-civil-liberties-from-wilson-to-obama/B0B615B2C365EF2387554EF9E1DB3790 |pages=i–ii |editor-last=Walker |editor-first=Samuel |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-107-01660-6 |access-date=February 26, 2023}}</ref> In particular, Eisenhower was criticized for failing to defend ] from attacks by ], though he privately deplored McCarthy's tactics.<ref>{{cite web |access-date=May 23, 2008 |url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/presidents/34_eisenhower/eisenhower_politics.html |title=Presidential Politics |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080606222418/http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/presidents/34_eisenhower/eisenhower_politics.html |archive-date=June 6, 2008 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Following the access of Eisenhower's private papers, his reputation changed amongst presidential historians.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=McMahon |first=Robert J. |date=1986 |title=Eisenhower and Third World Nationalism: A Critique of the Revisionists |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/2151625 |journal=Political Science Quarterly |volume=101 |issue=3 |pages=453–473 |doi=10.2307/2151625 |jstor=2151625 |issn=0032-3195}}</ref><ref name="millerlegacy">{{cite web |last1=Pach |first1=Chester J. Jr. |date=October 4, 2016 |title=Dwight D. Eisenhower: Impact and Legacy |url=https://millercenter.org/president/eisenhower/impact-and-legacy |access-date=February 26, 2023 |website=Miller Center}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=RABE |first=STEPHEN G. |date=1993 |title=Eisenhower Revisionism: A Decade of Scholarship |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/24912261 |journal=Diplomatic History |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=97–115 |doi=10.1111/j.1467-7709.1993.tb00160.x |jstor=24912261 |issn=0145-2096}}</ref> Historian ] has summarized a more recent turnaround in evaluations by historians: | |||
| In 1983, ] was founded in Washington, D.C., as a policy institute to advance Eisenhower's intellectual and leadership legacies. | |||
| {{blockquote|Historians long ago abandoned the view that Eisenhower's was a failed presidency. He did, after all, end the Korean War without getting into any others. He stabilized, and did not escalate, the Soviet–American rivalry. He strengthened European alliances while withdrawing support from European colonialism. He rescued the Republican Party from isolationism and McCarthyism. He maintained prosperity, balanced the budget, promoted technological innovation, facilitated (if reluctantly) the civil rights movement and warned, in the most memorable farewell address since Washington's, of a "military–industrial complex" that could endanger the nation's liberties. Not until Reagan would another president leave office with so strong a sense of having accomplished what he set out to do.<ref>John Lewis Gaddis, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170206184614/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/22/books/review/eisenhower-in-war-and-peace-by-jean-edward-smith.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220101/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/22/books/review/eisenhower-in-war-and-peace-by-jean-edward-smith.html |archive-date=2022-01-01 |url-access=limited |date=February 6, 2017 }}{{cbignore}}, ''New York Times Book Review'', April 20, 2012.</ref>}} | |||
| In 1999, the ] created the ] Commission, which is in the planning stages of creating an enduring ] in Washington, D.C., across the street from the ] on the ]. | |||
| Since 1982, scholars and historians have typically ranked Eisenhower among the ten best U.S. presidents.<ref>. ]. ''The World''. February 4, 1982. Retrieved November 24, 2024.</ref> ], a top aide to Franklin Roosevelt, referred to Eisenhower as "the least partisan president since ]." Historian ] called Eisenhower "a political genius" for making difficult foreign policy goals "look easy" to the general public to prevent further stress.<ref name="brrt45"/> | |||
| On May 7, 2002, the ] was officially renamed the Eisenhower Executive Office Building. This building is part of the ], west of the ]. It currently houses a number of executive offices, including ones for the Vice President and his or her spouse.<ref></ref> | |||
| ], April 22, 1961, three days after the failed ].]] | |||
| A county park in ], ] (]) is named in his honor.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.nassaucountyny.gov/agencies/Parks/WhereToGo/active/eisenhower.html|title=Eisenhower Park|publisher=]}}</ref> In addition, ] on ] near his birthplace of Denison is named in his honor; his actual birthplace is currently operated by the State of Texas as ]. | |||
| === Political practice === | |||
| Many public ] and ] in the U.S. are named after Eisenhower. | |||
| Although conservatism in politics was strong during the 1950s, and Eisenhower generally espoused conservative sentiments, his administration concerned itself mostly with foreign affairs and pursued a hands-off domestic policy. Eisenhower looked to moderation and cooperation as a means of governance, which he dubbed "The Middle Way".<ref name="jstor.org">{{cite journal|jstor=1863309|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower and the Corporate Commonwealth|first=Robert|last=Griffith|date=January 1, 1982|journal=The American Historical Review|volume=87|issue=1|pages=87–122|doi=10.2307/1863309}}</ref><ref>{{cite magazine |magazine=] |title=The President and His Decision |date=March 12, 1956 }}</ref> | |||
| Although he sought to slow or contain the ] and other federal programs, he did not attempt to repeal them outright. In doing so, Eisenhower was popular among the liberal wing of the Republican Party.<ref name="jstor.org" /> Conservative critics of his administration thought that he did not do enough to advance the goals of the right; according to ], "Eisenhower's victories were but accidents without consequence in the history of the Republican party."<ref>Morgenthau, Hans J.: "Goldwater – The Romantic Regression", in ''Commentary'', September 1964.</ref> | |||
| There is a ] in the ] of the ] in ]. | |||
| Since the 19th century, many if not all presidents were assisted by a central figure or "gatekeeper", sometimes described as the president's private secretary, sometimes with no official title.<ref name=medved>{{cite book|last=Medved|first=Michael|title=The Shadow Presidents: The Secret History of the Chief Executives and Their Top Aides|year=1979|publisher=Times Books|isbn=0812908163|url=https://archive.org/details/shadowpresidents00medv}}</ref> Eisenhower formalized this role, introducing the office of ] – an idea he borrowed from the United States Army. Every president after ] has appointed staff to this position. | |||
| A tree overhanging the 17th hole that always gave him trouble at Augusta National, where he was a member, is named in his honor. | |||
| As president, Eisenhower also initiated the "]" policy that still prevails in the US military. Officers who are passed over for promotion twice are then usually honorably but quickly discharged to make way for younger and more able officers. | |||
| The Eisenhower Golf Club at the ], a 36-hole facility featuring the Blue and Silver courses and which is ranked #1 among ] courses, is named in Eisenhower's honor. | |||
| On December 20, 1944, Eisenhower was appointed to the rank of ], placing him in the company of George Marshall, ], and ], the only four men to achieve the rank in World War II. Along with Omar Bradley, they were the only five men to achieve the rank since the August 5, 1888, death of ], and the only five men to hold the rank of ]. The rank was created by an ] on a temporary basis, when ] ] was passed on December 14, 1944,<ref name="PL78-482">{{cite web | |||
| ==Awards and decorations== | |||
| | url= http://en.wikisource.org/Public_Law_78-482 | |||
| ===United States awards=== | |||
| | title= Public Law 482 | |||
| ] in 1969 commemorating Dwight D. Eisenhower]] | |||
| | access-date= April 29, 2008 | |||
| ] from 1971–78 commemorating Eisenhower]] | |||
| | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20071013204129/http://en.wikisource.org/Public_Law_78-482 | |||
| ] World Citizenship Award in 1966]] | |||
| | archive-date= October 13, 2007 | |||
| In Order of Precedence | |||
| | url-status= live | |||
| *] with four ] | |||
| }} This law allowed only 75% of pay and allowances to the grade for those on the retired list.</ref> as a temporary rank, subject to reversion to permanent rank six months after the end of the war. The temporary rank was declared permanent on March 23, 1946, by Public Law 333 of the ], which also awarded full pay and allowances in the grade to those on the retired list.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| *] | |||
| |url=http://www.history.navy.mil/faqs/faq36-6.htm | |||
| *] | |||
| |title=Public Law 333, 79th Congress | |||
| *] | |||
| |date=April 11, 2007 | |||
| *] | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| *] | |||
| |access-date=October 22, 2007 | |||
| *] | |||
| |url-status=dead | |||
| *] with one silver and four bronze ] | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071013212055/http://history.navy.mil/faqs/faq36-6.htm | |||
| *] | |||
| |archive-date=October 13, 2007 | |||
| *] with "Germany" clasp | |||
| }} The retirement provisions were also applied to the World War II ] and the ], both of whom held four-star rank.</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Public Law 79-333|url=http://legisworks.org/congress/79/publaw-333.pdf|website=legisworks.org|publisher=Legis Works|access-date=October 19, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151121013632/http://legisworks.org/congress/79/publaw-333.pdf|archive-date=November 21, 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> It was created to give the most senior American commanders parity of rank with their British counterparts holding the ranks of ] and ]. | |||
| *] (2 awards) | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| He was offered the ], but turned it down. | |||
| | align = right | |||
| He was also an honorary member of the ]'s ]. | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | header_align = center | |||
| | footer = ]'s obverse design (left) and reverse design (right) of the Presidential Medal of Appreciation award during Eisenhower's official visit to the State of Hawaii from June 20 to 25, 1960 | |||
| | image1 = Dwight D. Eisenhower POTUS Appreciation Medal Hawaii Obverse.jpg|thumb|center|200x200 | |||
| | width1 = 120 | |||
| | image2 = Dwight D. Eisenhower POTUS Appreciation Medal Hawaii Reverse.jpg|thumb center|200x200 | |||
| | width2 = 120 | |||
| }} | |||
| Eisenhower founded ] in 1956, believing that citizen interaction would promote cultural interaction and ]. The program includes a ], which sends American youth on educational trips to other countries.<ref>{{cite web |title=Our Heritage |url=http://www.peopletopeople.com/AboutUs/Pages/OurHeritage.aspx |publisher=People to People International |access-date=September 29, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090301050108/http://www.peopletopeople.com/AboutUs/Pages/OurHeritage.aspx |archive-date=March 1, 2009 }}</ref> | |||
| ===International awards=== | |||
| List of citations bestowed by other countries.<ref>{{cite web|accessdate=2008-05-23|url=http://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/quick_links/military/decorations_awards_medals/Eisenhower_decorations_awards.html|title=Eisenhower Decorations and Awards|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| *Argentine Order of the Liberator San Martin, Great Cross | |||
| *Belgian ] | |||
| *Belgian ] | |||
| *Brazil Campaign Medal | |||
| *Brazil War Medal | |||
| *Brazilian Order of Military Merit, Grand Cross | |||
| *Brazilian Order of Aeronautical Merit, Grand Cross | |||
| *Brazilian National ] | |||
| *British ], Knight Grand Cross | |||
| *British ] | |||
| *British ] with "8" and "1" numerical devices. | |||
| *Chilean Chief Commander of the Order of Merit | |||
| *Chinese Order of Yun Hui, Grand Cordon | |||
| *Chinese Order of Yun Fei, Grand Cordon | |||
| *] | |||
| *Czechoslovakian Golden Star of Victory | |||
| *] | |||
| *Ecuadorian Star of Abdon Calderon | |||
| *Egyptian Order of Ismal, Grand Cordon | |||
| *Ethiopian Order of Solomon | |||
| *] | |||
| *].<ref>{{cite book|title=Allies|author=Eisenhower, John S. D.}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] ] with ]s | |||
| *Guatemalan Cross of Military Merit, First Class | |||
| *Haitian Order of Honor and Merit, Grand Cross | |||
| *Italy ], Knight Grand Cross | |||
| *Italy Order of Malta | |||
| *Luxembourg Medal of Merit | |||
| *] | |||
| *Mexican ], First Class | |||
| *Mexican Medal of Civic Merit | |||
| *Mexican Order of Military Merit | |||
| *Moroccan ] | |||
| *Netherlands: ], Knight Grand Cross | |||
| *Norwegian ] | |||
| *Pakistani '']'', or Order of Pakistan, First Class | |||
| *Panama Order of Vasco Nunez de Balboa, Grand Cross | |||
| *Panama Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero, Grand Master (collar grade) | |||
| *Philippines Distinguished Service Star | |||
| *Philippines Shield of Honor Medal, Chief Commander | |||
| *Philippines ], Raja (First Class) | |||
| *Polish ] | |||
| *Polish ] | |||
| *Polish ] | |||
| *Soviet ] | |||
| *Soviet ] | |||
| *Tunisian Order of Nichan Iftikhar, Gand Cordon | |||
| During his second term as president, Eisenhower awarded a series of specially designed US Mint presidential appreciation medals. Eisenhower presented the medal to individuals as an expression of his appreciation.<ref name=Gomez>{{cite book|last=Gomez|first=Darryl|title=Authoritative Numismatic Reference: Presidential Medal of Appreciation Award Medals 1958–1963 |year=2015 |publisher=CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform |isbn=978-1511786744}}</ref> The development of the appreciation medals was initiated by the White House and executed by the ], through the ]. The medals were struck from September 1958 through October 1960. A total of twenty designs are cataloged with a total mintage of 9,858. Prior to the end of his second term as president, 1,451 medals were turned in to the Bureau of the Mint and destroyed.<ref name="Gomez" /> The Eisenhower appreciation medals are part of the Presidential Medal of Appreciation Award Medal Series.<ref name="Gomez" /> | |||
| ===Other honors=== | |||
| *In 1966, Eisenhower was the second person to be awarded ]'s World Citizenship Award.<ref>{{cite book |last=Armbrester |first=Margaret E. |title=The Civitan Story |year=1992 |publisher=Ebsco Media |location=Birmingham, AL |pages=97 }}</ref> | |||
| *Eisenhower's name was given to a variety of streets, avenues, etc., in cities around the world, including ], ]. | |||
| *In December 1999, Eisenhower was listed on ]. | |||
| === Tributes and memorials === | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Main|List of memorials to Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| {{portal|World War I}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{portal|World War II}} | |||
| The Interstate Highway System is officially known as the "Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways". It was inspired in part by Eisenhower's experiences in World War II, where he recognized the advantages of the ] system in Germany.<ref name=archivesIHS /> Commemorative signs reading "Eisenhower Interstate System" and bearing Eisenhower's permanent ] insignia were introduced in 1993 and now are displayed throughout the Interstate System. Several highways are also named for him, including the ] (Interstate 290) near Chicago, the ] on ] west of ], and ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower Highway|url=https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/infrastructure/ddehwy.cfm|website=Federal Highway Administration|access-date=August 22, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160825182935/https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/infrastructure/ddehwy.cfm|archive-date=August 25, 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *], wife of Dwight D. Eisenhower | |||
| *], a speech to the U.N. General Assembly in December 1953 | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *], a term made popular by Eisenhower | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] Portrait painter (Gallery of Presidents, ]) and friend of Eisenhower | |||
| ] is a senior war college of the Department of Defense's ] in Washington, DC. Eisenhower graduated from this school when it was known as the Army Industrial College. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Specific references: | |||
| {{reflist|3}} | |||
| General references: | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| *{{citation|first=Stephen|last=Ambrose|title=Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect (1893–1952)|location=]|publisher=]|year=1983}}. | |||
| *{{citation|first=Carlo|last=D'Este |authorlink=Carlo D'Este |title=Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life|year=2002}}. | |||
| *{{citation|first=Dwight D.|last=Eisenhower|title=Mandate for Change, 1953–1956|year=1963}}. | |||
| *{{citation|first=Herbert S.|last=Parmet|title=Eisenhower and the American Crusades|year=1972}}. | |||
| *{{citation|first=E. K. G.|last=Sixsmith|title=Eisenhower, His Life and Campaigns|year=1973}}. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| Eisenhower was honored on the ], minted from 1971 to 1978. His centenary was honored on the ] issued in 1990. | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| ===Military career=== | |||
| *Ambrose, Stephen E. ''Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect, 1890–1952'' (1983);' | |||
| *Bacque, James. ''Other Losses'' (2d. rev. ed., 1999) | |||
| *Eisenhower, David. ''Eisenhower at War 1943–1945'' (1986), detailed study by his grandson | |||
| *Irish, Kerry E. "Apt Pupil: Dwight Eisenhower and the 1930 Industrial Mobilization Plan", ''The Journal of Military History'' 70.1 (2006) 31–61 online in Project Muse. | |||
| *Pogue, Forrest C. ''The Supreme Command'' (1996) official Army history of SHAEF | |||
| *Weigley, Russell. ''Eisenhower's Lieutenants.'' Indiana University Press, 1981. Ike's dealings with his key generals in WW2 | |||
| ===Civilian career=== | |||
| *Albertson, Dean, ed. ''Eisenhower as President'' (1963). | |||
| *Alexander, Charles C. ''Holding the Line: The Eisenhower Era, 1952–1961'' (1975). | |||
| *Ambrose, Stephen E. ''Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect, 1890–1952'' (1983); ''Eisenhower. The President'' (1984); one volume edition titled ''Eisenhower: Soldier and President'' (2003). Standard biography. | |||
| *Bowie, Robert R. and Richard H. Immerman; ''Waging Peace: How Eisenhower Shaped an Enduring Cold War Strategy'', Oxford University Press, 1998. | |||
| *Damms, Richard V. ''The Eisenhower Presidency, 1953–1961'' (2002). | |||
| *David Paul T. (ed.), ''Presidential Nominating Politics in 1952''. 5 vols., Johns Hopkins Press, 1954. | |||
| *Divine, Robert A. ''Eisenhower and the Cold War'' (1981). | |||
| *Greenstein, Fred I. ''The Hidden-Hand Presidency: Eisenhower as Leader'' (1991). | |||
| *Harris, Douglas B. "Dwight Eisenhower and the New Deal: The Politics of Preemption" ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'', Vol. 27, 1997. | |||
| *Harris, Seymour E. ''The Economics of the Political Parties, with Special Attention to Presidents Eisenhower and Kennedy'' (1962). | |||
| *Krieg, Joann P. ed. ''Dwight D. Eisenhower, Soldier, President, Statesman'' (1987). 24 essays by scholars. | |||
| *McAuliffe, Mary S. "Eisenhower, the President", ''Journal of American History'' 68 (1981), pp. 625–632. | |||
| *Medhurst, Martin J. ''Dwight D. Eisenhower: Strategic Communicator'' Greenwood Press, 1993. | |||
| *Pach, Chester J. and Elmo Richardson. ''Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower'' (1991). Standard scholarly survey. | |||
| ===Primary sources=== | |||
| *Boyle, Peter G., ed. ''The Churchill-Eisenhower Correspondence, 1953–1955'' University of North Carolina Press, 1990. | |||
| *Eisenhower, Dwight D. ''Crusade in Europe'' (1948), his war memoirs. | |||
| *Eisenhower, Dwight D. ''The White House Years: Waging Peace 1956-1961'', Doubleday and Co., 1965. | |||
| * 21 volume scholarly edition; complete for 1940–1961. | |||
| *Summersby, Kay. ''Eisenhower was my boss'' (1948) New York: Prentice Hall; (1949) Dell paperback. | |||
| In 1969 four major record companies – ], ], ] and ] – released tribute albums in Eisenhower's honor.<ref>{{cite news |url={{GBurl|id=ySgEAAAAMBAJ|p=3}} |title=Record Companies Run With Eisenhower Tribute Albums |magazine=Billboard |date=April 12, 1969 |access-date=December 2, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{external links}} | |||
| {{portal|United States Army|United States Department of the Army Seal.svg}} | |||
| {{sisterlinks|Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| * | |||
| * (with shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the Miller Center of Public Affairs) | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *] (Wikisource) | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * by B. C. Mossman and M. W. Stark | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *{{gutenberg author|id=Dwight+D.+Eisenhower|name=Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| *, lecture overview of EIsenhower's presidency by ], ], March 18, 2008 (available in text, audio and video formats). | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| In 1999, the ] created the ] Commission, to create an enduring ] in Washington, D.C. In 2009 the commission chose the architect ] to design the memorial.<ref>{{Cite news | title=Frank Gehry to design Eisenhower Memorial | url=https://www.bizjournals.com/albuquerque/stories/2009/03/30/daily41.html | work=] | date=April 1, 2009 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090404031334/http://www.bizjournals.com/albuquerque/stories/2009/03/30/daily41.html | archive-date=April 4, 2009 | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="WPmemorial">{{Cite news|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/04/01/AR2009040101880.html | |||
| |title=Architect Gehry Gets Design Gig For Eisenhower Memorial | |||
| |last=Trescott | |||
| |first=Jacqueline | |||
| |date=April 2, 2009 | |||
| |newspaper=The Washington Post | |||
| |access-date=August 26, 2017 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170703034223/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/04/01/AR2009040101880.html | |||
| |archive-date=July 3, 2017 | |||
| |url-status=live | |||
| }}</ref> The groundbreaking ceremony of the memorial was held on November 3, 2017, and was dedicated on September 17, 2020.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Horan|first=Tim|date=May 8, 2020|title=Eisenhower Memorial in D.C. is complete. Coronavirus delays dedication to September|work=The Wichita Eagle|url=https://www.kansas.com/news/coronavirus/article242601951.html#adnrb=900000|access-date=May 8, 2020}}</ref><ref name=program>{{Cite web |title=Dedication Of Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial |url=https://eisenhowermemorial.gov/sites/default/files/public/press/Dedication%20Ceremony%20Program_FINAL_200915_0.pdf |website=Eisenhower Memorial Commission |access-date=April 9, 2023 |archive-date=October 22, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201022183641/https://eisenhowermemorial.gov/sites/default/files/public/press/Dedication%20Ceremony%20Program_FINAL_200915_0.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> It stands on a {{convert|4|acre|adj=on}} site near the ] on Maryland Avenue, across the street from the ].<ref>{{Cite news | url=https://www.bizjournals.com/washington/stories/2010/01/18/daily80.html | title=Gilbane to manage design and construction of Eisenhower Memorial | last=Plumb | first=Tiereny | date=January 22, 2010 | work=]}}</ref> | |||
| In December 1999 he was listed on ]. In 2009 he was named to the ] in the Lifetime Achievement category for his contributions to the sport.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pgatour.com/2009/r/06/26/wghof_eisenhower/index.html |title=President Eisenhower named to World Golf Hall of Fame |publisher=PGA Tour |access-date=May 3, 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090629071851/http://www.pgatour.com/2009/r/06/26/wghof_eisenhower/index.html |archive-date=June 29, 2009 }}</ref> In 1973, he was inducted into the ] of the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Hall of Great Westerners |url=https://nationalcowboymuseum.org/hall-of-great-westerners/ |website=National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum |access-date=November 22, 2019}}</ref> On 27 October 2023, Fort Gordon was redesignated ].{{efn| name=fortEisenhower27Oct23 |1= Redesignation to Fort Eisenhower was on 27 October 2023.<ref name= redesignationCeremony ></ref>}}<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/us/plans-are-coming-together-for-fort-gordon-renaming-ceremony/ar-AA18FB63 |title=Plans are coming together for Fort Gordon renaming ceremony |work=MSN |access-date=27 April 2023 |archive-date=17 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230317004022/https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/us/plans-are-coming-together-for-fort-gordon-renaming-ceremony/ar-AA18FB63 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name= redesignation >{{cite news |first=Herb |last=Scribner |url=https://www.axios.com/2023/03/25/fort-hood-new-name-name-fort-cavazos |date=25 March 2023 |title=6 Army bases named after Confederate leaders get dates for new names |work=Axios |access-date=27 April 2023 |archive-date=18 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230418113618/https://www.axios.com/2023/03/25/fort-hood-new-name-name-fort-cavazos |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| == Honors == | |||
| === Awards and decorations === | |||
| ] awarded to Eisenhower<ref>Prince Bernhard of the Netherlands in an interview with H.G. Meijer, published in "Het Vliegerkruis", Amsterdam 1997, {{ISBN|9067073474}}. p. 92.</ref>]] | |||
| ] granted to Eisenhower upon his incorporation as a knight of the Danish ] in 1950.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Arms of Dwight D. Eisenhower |publisher=American Heraldry Society |url=http://www.americanheraldry.org/pages/index.php?n=President.Eisenhower |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150202002218/http://www.americanheraldry.org/pages/index.php?n=President.Eisenhower |archive-date=February 2, 2015 }}</ref> The anvil represents the fact that his name is derived from the German for "iron hewer", making these an example of ].|alt=]] | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- style="background:#ccf; text-align:center;" | |||
| | colspan=2 |'''US military decorations'''<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov/eisenhowers/awards-medals|title=Awards & Medals {{!}} Eisenhower Presidential Library|website=www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov|access-date=April 28, 2020}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|number=4|type=oak|ribbon=Distinguished Service Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] w/ 4 ]s | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Navy Distinguished Service ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Legion of Merit ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- style="background:#ccf; text-align:center;" | |||
| | colspan=2 |'''US service medals<ref name=":0" />''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Mexican Border Service Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=World War I Victory Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=American Defense Service Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|number=7|type=service-star|ribbon=European-African-Middle Eastern Campaign ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] w/ 7 ]s | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=World War II Victory Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|number=0|type=service-star|ribbon=Army of Occupation ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] w/ "Germany" clasp | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|number=1|type=service-star|ribbon=National Defense Service Medal ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] w/ 1 ] | |||
| |- style="background:#ccf; text-align:center;" | |||
| | colspan=2 |'''International and foreign awards'''<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.eisenhower.archives.gov/all_about_ike/awards_medals.html|title=USA and Foreign Decorations of Dwight D. Eisenhower|publisher=]|access-date=June 10, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161118062616/https://eisenhower.archives.gov/all_about_ike/awards_medals.html|archive-date=November 18, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=ARG Order of the Liberator San Martin - Grand Cross BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Argentina) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=AUT Honour for Services to the Republic of Austria - 2nd Class BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] (Austria)<ref>{{cite web | title=Questions to the Chancellor | year=2012 | publisher=Austrian Parliament | url=http://www.parlament.gv.at/PAKT/VHG/XXIV/AB/AB_10542/imfname_251156.pdf | page=194 | access-date=September 30, 2012 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121022192702/http://www.parlament.gv.at/PAKT/VHG/XXIV/AB/AB_10542/imfname_251156.pdf | archive-date=October 22, 2012 | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BEL - Order of Leopold - Grand Cordon bar.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cordon (Belgium) – 1945 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Croix de Guerre 1940-1945 with palm (Belgium) - ribbon bar.png|width=60}} | |||
| |{{Lang|fr|]|italic=no}} w/ palm (Belgium) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BRA - Order of the Southern Cross - Grand Cross BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Brazil) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BRA Ordem do Merito Militar Gra-cruz.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BRA Ordem do Mérito Aeronáutico Grã-Cruz.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Brazil) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BRA War Medal.png|width=60}} | |||
| |War Medal (Brazil) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=BRA Campaign Medal.png|width=60}} | |||
| |Campaign Medal (Brazil) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=CHL Order of Merit of Chile - Grand Cross BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Chile) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of the Cloud and Banner 1st.gif|width=60}} | |||
| |], with Special Grand Cordon, (China) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=TCH CS Vojensky Rad Bileho Lva 1st %281945%29 BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Czechoslovakia) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Czechoslovak War Cross 1939-1945 Ribbon.png|width=60}} | |||
| |] (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of the Elephant Ribbon bar.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight (Denmark) – December 15, 1945 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of Abdon Calderon First Class.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], First Class (Ecuador) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=EGY Order of Ismail.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cordon (Egypt) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=ETH Order of Solomon BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross with Cordon (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of The Queen of Sheba (Ethiopia) ribbon.gif|width=60}} | |||
| |], Member (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Legion Honneur GC ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (France) – 1943 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ordre de la Liberation 2nd ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Companion (France) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Medaille militaire ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] (France)<ref>{{Cite book|title=Allies|author=Eisenhower, John S. D.}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Croix de guerre 1939–1945 stripe bronsepalme.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] w/ palm (France) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=GRE Order of George I - Grand Cross BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross with Swords (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=GRE Order Redeemer 1Class.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Guatemalan Armed Forces Cross.jpg|width=60}} | |||
| |], First Class (Guatemala) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Orden Nacional de Honor y Mérito, Gran Cruz.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross with Gold Badge (Haiti) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=OESSG Cavaliere di Gran Croce BAR.jpg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Cavaliere di gran Croce BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross (Italy) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=JPN Daikun'i kikkasho BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Collar (Japan) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ordre de la couronne de Chene GC ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Luxembourg) | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=OPMM-gcX.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], KGC (]) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=MEX Order of the Aztec Eagle 1Class BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Collar (Mexico) – 1945 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=MEX Condecoracion al Merito Militar Primera Clase.png|width=60}} | |||
| |] (Mexico) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Noribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |Medal of Civic Merit (Mexico) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Noribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], (Morocco) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ordre de l'Ouissam Alaouite GC ribbon (Maroc).svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Morocco) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=NLD Order of the Dutch Lion - Grand Cross BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross (Netherlands) – October 6, 1945 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=St Olavs Orden storkors stripe.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Norway) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ord.Nishan-i-Pakistan.ribbon.gif|width=60}} | |||
| |], First Class (Pakistan) – December 7, 1957 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=PAN Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero - Grand Officer BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Officer (Panama) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=PAN Order of Vasco Nunez de Balboa - Grand Cross BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Panama) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=PHL Order of Sikatuna - Grand Collar BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Collar (Philippines) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=PHL Legion of Honor - Chief Commander BAR.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], Chief Commander (Philippines) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=PHL Distinguished Service Star BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], (Philippines) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=POL Polonia Restituta Wielki BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cross (Poland) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=POL Virtuti Militari Wielki BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], First Class (Poland) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=POL Order Krzyża Grunwaldu 1 Klasy BAR.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], First Class (Poland) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of the Royal House of Chakri (Thailand) ribbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight (Thailand) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ordre du Nichan Iftikhar GC ribbon (Tunisia).svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Grand Cordon (Tunisia) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of the Bath (ribbon).svg|width=60}} | |||
| |], Knight Grand Cross (United Kingdom) | |||
| * Military Division 1945 | |||
| * Civil Division 1957 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Galó de l'Orde del Mèrit (UK).svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] (United Kingdom) | |||
| * Member Military Division June 12, 1945 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Ribbon - Africa Star & 8.png|width=60}} | |||
| |], with 8th Army clasp (United Kingdom) | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |] (United Kingdom) | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=OrderVictoryRibbon.svg|width=60}} | |||
| |] (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics)<ref name="Empric">{{citation |last=Empric |first=Bruce E. |title=Uncommon Allies: U.S. Army Recipients of Soviet Military Decorations in World War II |publisher=Teufelsberg Press |pages=36, 46 |year=2024 |isbn=979-8-3444-6807-5}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=Order of Suvorov 106x30.png|width=60}} | |||
| |] (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics)<ref name="Empric"/> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{ribbon devices|ribbon=The Royal Yugoslav Commemorative War Cross rib.png|width=60}} | |||
| |The Royal Yugoslav Commemorative War Cross (]) | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Freedom of the City=== | |||
| Eisenhower received the ] honor from several locations, including: | |||
| * {{flagicon|England}} ] on June 12, 1945<ref>{{cite news |title=Eisenhower to get honor | work=The New York Times | date=June 10, 1945 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1945/06/10/archives/eisenhower-to-get-honor-city-of-london-to-give-limited-freedom-and.html |url-access=limited |access-date=August 26, 2020 }}</ref><ref>{{cite AV media |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wQHM9oqufv0 | archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211027/wQHM9oqufv0| archive-date=October 27, 2021|year=1945 |title=London Welcomes Her Newest Citizen |time=1:18 |type=Newsreel |via=Associated Press and YouTube |publisher=] |access-date=August 26, 2020 }}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|Northern Ireland}} ] of ] on August 24, 1945<ref name=":1">{{cite news |url=https://www.belfasttelegraph.co.uk/imported/eisenhower-in-ulster-28370627.html |title=Eisenhower in Ulster |date=July 5, 2008 |newspaper=Belfast Telegraph |access-date=August 26, 2020 }}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|Scotland}} Freedom of the City of ] in 1946<ref>{{cite AV media |url=https://www.britishpathe.com/video/eisenhowers-scottish-diary-aka-eisenhowers/query/Eisenhowers+Scottish+Diary |title=Eisenhower's Scottish Diary |time=0:13 |type=Newsreel |publisher=] |access-date=August 26, 2020 }}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|Scotland}} Freedom of the Burgh of ] in October 1946<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.maybole.org/news/2014/April/president_eisenhower_in_carrick.htm |title=President Eisenhower in Carrick |website=maybole.org |access-date=August 26, 2020 |archive-date=October 25, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201025053932/https://www.maybole.org/news/2014/April/president_eisenhower_in_carrick.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Honorary degrees=== | |||
| Eisenhower received many honorary degrees from universities and colleges around the world. These included: | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | |||
| ! style="width:20%;"| Location | |||
| ! style="width:20%;"| Date | |||
| ! style="width:40%;"| School | |||
| ! style="width:20%;"| Degree | |||
| ! style="width:20%;"| Gave commencement address | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Northern Ireland}} || '''August 24, 1945''' || ] || ] (LL.D)<ref name=":1"/><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.qub.ac.uk/about/Leadership-and-structure/Registrars-Office/FileStore/Filetoupload,837203,en.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200804121308/https://www.qub.ac.uk/about/Leadership-and-structure/Registrars-Office/FileStore/Filetoupload,837203,en.pdf |archive-date=August 4, 2020 |url-status=live |title=Honorary Degrees 1871–2018 |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|England}} || '''1945''' || ] || ] (DCL)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.britishpathe.com/video/oxford-degrees-for-war-leaders |title=Oxford Degrees for War Leaders |date=1945 |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Massachusetts}} || '''1946''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.harvard.edu/on-campus/commencement/honorary-degrees |title=Honorary Degrees |date= |website=] |access-date=August 26, 2020 |archive-date=November 4, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171104152828/https://www.harvard.edu/on-campus/commencement/honorary-degrees |url-status=dead }}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Pennsylvania}} || '''1946''' || ] || Doctorate<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.gettysburg.edu/commencement/traditions/honorary-degree-recipients |title=Honorary degree recipients |website=] |access-date=August 26, 2020 |archive-date=September 9, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190909202548/https://www.gettysburg.edu/commencement/traditions/honorary-degree-recipients |url-status=dead }}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Ontario}} || '''1946''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://governingcouncil.utoronto.ca/sites/default/files/2020-01/CHD%20recipients%20-%20Chrono%20-%201850-2019.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200401055346/https://governingcouncil.utoronto.ca/sites/default/files/2020-01/CHD%20recipients%20-%20Chrono%20-%201850-2019.pdf |archive-date=April 1, 2020 |url-status=live |title=Honorary Degree Recipients, 1850–2021 |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Pennsylvania}} || '''1947''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://secretary.upenn.edu/sites/default/files/Chronological-Penn-HDR-Listing_0.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190629122212/https://secretary.upenn.edu/sites/default/files/Chronological-Penn-HDR-Listing_0.pdf |archive-date=June 29, 2019 |url-status=live |title=Chronological Listing of Honorary Degree Recipients |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Connecticut}} || '''1948''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://secretary.yale.edu/programs-services/honorary-degrees/since-1702?field_degrees_value=All&field_year_value=All&keys=Eisenhower |title=Honorary Degrees Since 1702 |website=Office of the Secretary and Vice President for University Life, ]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|New York|1909}} || '''1950''' || ] || Doctorate<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.hofstra.edu/about/about_hondegrees.html |title=About: Honorary Degrees |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|New Hampshire}} || '''June 14, 1953''' || ] || Doctorate || Yes<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://250.dartmouth.edu/highlights/president-eisenhowers-commencement-address |title=President Eisenhower's Commencement Address |date=November 28, 2018 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Washington, D.C.}} || '''November 19, 1953''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://commencement.catholic.edu/_media/docs/master-listing-of-all-honorary-degrees.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201122092636/https://commencement.catholic.edu/_media/docs/master-listing-of-all-honorary-degrees.pdf |archive-date=November 22, 2020 |url-status=live |title=Honorary Degrees Conferred by The Catholic University of America |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Virginia}} || '''1953''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D) || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Illinois}} || '''1954''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.northwestern.edu/provost/committees/administrative/honorary-degrees/honorary-degree-recipients.html |title=Honorary Degree Recipients |website=Office of the Provost, ]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Maryland}} || '''June 7, 1954''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite speech |last=Eisenhower |first=Dwight D. |author-link=Dwight D. Eisenhower |title=Remarks at Washington College on Receiving an Honorary Doctor of Laws Degree |date=June 7, 1954 |location=Washington College, Maryland |publisher=] |url=https://staging.washcoll.edu/centers/starr/revcollege/presidential/deisenhower.html |access-date=January 9, 2022 |language=en-US |archive-date=October 20, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201020172825/https://staging.washcoll.edu/centers/starr/revcollege/presidential/deisenhower.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> || Yes | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Maryland}} || '''1958''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://commencement.jhu.edu/our-history/honorary-degrees-awarded/ |title=Honorary Degrees Awarded |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|India}} || '''December 17, 1959''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.britishpathe.com/video/india-likes-ike |title=India Likes Ike |date=1959 |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Indiana}} || '''June 5, 1960''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://commencement.nd.edu/assets/385863/honorary_degrees_archive_by_date.pdf |title=Honorary Degree Recipients, 1844–2019 |date=November 2019 |website=] |access-date=August 26, 2020 |archive-date=October 22, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201022055700/https://commencement.nd.edu/assets/385863/honorary_degrees_archive_by_date.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|New York|1909}} || '''June 20, 1964''' || ] || Doctor of Laws (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1964/06/21/archives/eisenhower-given-honorary-degree-at-bard-college.html |title=Eisenhower Given Honorary Degree at Bard College |newspaper=] |date=June 21, 1964}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Iowa}} || '''1965''' || ] || ] (LL.D)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.grinnell.edu/about/offices-services/conference-operations/commencement/archives/honorary-degrees |title=Past Honorary Degrees |website=]}}</ref> || | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{Flagu|Ohio}} || '''October 5, 1965''' || ] || ] (DHL)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://media.library.ohio.edu/digital/collection/archives/id/47827/ |title=U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower with commemorative plaque at Ohio University Memorial Auditorium |date=October 5, 1965 |website=] Libraries}}</ref> || Yes | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| == Promotions == | |||
| {|class="wikitable" style="background:white" | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|No insignia | |||
| |], United States Military Academy: June 14, 1911 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|No pin insignia in 1915 | |||
| |], ]: June 12, 1915 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: July 1, 1916 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: May 15, 1917 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], ]: June 17, 1918 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], National Army: October 20, 1918 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: June 30, 1920<br />(Reverted to permanent rank.) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: July 2, 1920 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: November 4, 1922<br />(Discharged as major and appointed as captain due to reduction of Army.) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: August 26, 1924 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: July 1, 1936 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], ]: March 6, 1941 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Army of the United States: September 29, 1941<br />(temporary) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Army of the United States: March 27, 1942<br />(temporary) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Army of the United States: July 7, 1942<br />(temporary) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Army of the United States: February 11, 1943<br />(temporary) | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: August 30, 1943 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: August 30, 1943 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Army of the United States: December 20, 1944 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="text-align:center;"|] | |||
| |], Regular Army: April 11, 1946 | |||
| |} | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * "]", phrase on religion by Eisenhower, 1952 | |||
| * ], speech to the UN General Assembly, 1953 | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] for time management | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'', American television film, 2004 | |||
| * ], chauffeur and secretary | |||
| * ] | |||
| '''General''': | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| === Citations === | |||
| {{Reflist|25em}} | |||
| === Print sources === | |||
| {{Main|Bibliography of Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| ==== General biographies ==== | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Stephen|last=Ambrose|title=Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect (1893–1952) |volume=I |publisher=] |year=1983 |author-link=Stephen E. Ambrose }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Stephen|last=Ambrose|title=Eisenhower: The President (1952–1969) |volume=II|publisher=]|year=1984 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Peter G.|last=Boyle|title=Eisenhower|publisher=Pearson/Longman|year=2005|isbn=0582287200}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Carlo|last=D'Este|author-link=Carlo D'Este|title=Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life|year=2002|publisher=Macmillan |isbn=0805056866|url=https://archive.org/details/eisenhowersoldie00dest}} | |||
| * Krieg, Joann P. ed. (1987). ''Dwight D. Eisenhower, Soldier, President, Statesman''. 24 essays by scholars. {{ISBN|0313259550}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Jim|last=Newton|title=Eisenhower: The White House Years|year=2011|publisher=Doubleday|isbn=978-0-385-52353-0|url=https://archive.org/details/eisenhowerwhiteh00newt}}, popular history. | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Herbert S.|last=Parmet|title=Eisenhower and the American Crusades|year=1972|oclc=482017}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Jean Edward|last=Smith|title=Eisenhower in War and Peace|publisher=Random House|year=2012|isbn=978-1400066933}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Tom|last=Wicker|title=Dwight D. Eisenhower|publisher=Times Books|year=2002|isbn=0805069070|url=https://archive.org/details/rutherfordbhayes00tref}}, popular history | |||
| ==== Military career ==== | |||
| * {{cite book |url={{GBurl|id=F9zBvoVavjQC}} |title = The Supreme Commander|isbn = 9780307946638|last1 = Ambrose|first1 = Stephen E.|date = January 17, 2012| publisher=Knopf Doubleday Publishing }} | |||
| * {{cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/victorseisenhowe00step |url-access=registration |publisher=Simon & Schuster |title=The Victors: Eisenhower and His Boys the Men of World War II |isbn=9780684864549 |last=Ambrose |first=Stephen E. |date=July 15, 1999 }} | |||
| * Eisenhower, David (1986). ''Eisenhower at War 1943–1945'', Random House. {{ISBN|0394412370}}. A detailed study by his grandson. | |||
| * ] (2003). ''General Ike'', Free Press. {{ISBN|0743244745}}, by his son. | |||
| * Hatch, Alden. ''General Eisenhower'' (1944) , early popular biography. | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Hobbs|first=Joseph Patrick|title=Dear General: Eisenhower's Wartime Letters to Marshall |url={{GBurl|id=3O5-bYg1g28C}} |date=1999|publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press |isbn=0801862191}} | |||
| * Irish, Kerry E. "Apt Pupil: Dwight Eisenhower and the 1930 Industrial Mobilization Plan", ''The Journal of Military History'' 70.1 (2006) 31–61 online in Project Muse. | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Jordan|first=Jonathan W.|title=Brothers Rivals Victors: Eisenhower, Patton, Bradley, and the Partnership that Drove the Allied Conquest in Europe|publisher=NAL/Caliber|date=2011|isbn=978-0451232120|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/brothersrivalsvi0000jord}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Jordan|first=Jonathan W. |title=American Warlords: How Roosevelt's High Command Led America to Victory in World War II|publisher = NAL/Caliber|date=2015|isbn = 978-0451414571 |url={{GBurl|id=qeSoBAAAQBAJ}} }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Pogue |first=Forrest C.|author-link=Forrest Pogue|title= The Supreme Command|publisher = ], Dept. of the Army|date=1954|oclc= 1247005}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last= Weigley|first=Russell|author-link=Russell Weigley|title= Eisenhower's Lieutenants: the Campaign of France and Germany, 1944–1945|publisher = Indiana University Press |year=1981 |url={{GBurl|id=W12mDwAAQBAJ}} |isbn=0253133335}} | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Sixsmith|first=Major General E. K. G.|author-link=Eric Sixsmith|title=Eisenhower as Military Commander|publisher=]|year=1973|isbn=978-0713412123}} | |||
| ==== Civilian career ==== | |||
| * {{cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/wagingpeacehowei00robe |url-access=registration |publisher=Oxford University Press |title=Waging Peace: How Eisenhower Shaped an Enduring Cold War Strategy |isbn=9780199879083 |last1=Bowie |first1=Robert R. |author1-link=Robert R. Bowie |last2=Immerman |first2=Richard H. |author2-link=Richard H. Immerman |date=February 12, 1998 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Chernus |first=Ira |author-link=Ira Chernus |title=Apocalypse Management: Eisenhower and the Discourse of National Insecurity| year=2008 |publisher=Stanford University Press |isbn=978-0804758079 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | author-first=Blanche Wiesen | author-last=Cook | title=The Declassified Eisenhower: A Divided Legacy | publisher=Doubleday | year=1981 }} | |||
| * Damms, Richard V. (2002). ''The Eisenhower Presidency, 1953–1961'' | |||
| * David Paul T., ed. (1954). ''Presidential Nominating Politics in 1952''. 5 vols., Johns Hopkins Press. {{OCLC|519846}} | |||
| * Divine, Robert A. (1981). ''Eisenhower and the Cold War''. | |||
| * Gellman, Irwin F. (2015). ''The President and the Apprentice: Eisenhower and Nixon, 1952–1961.'' New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. {{ISBN|978-0300181050}} | |||
| * ] (1991). ''The Hidden-Hand Presidency: Eisenhower as Leader''. Basic Books. {{ISBN|0465029485}} | |||
| * Harris, Douglas B. "Dwight Eisenhower and the New Deal: The Politics of Preemption", ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'', Vol. 27, 1997. | |||
| * Harris, Seymour E. (1962). ''The Economics of the Political Parties, with Special Attention to Presidents Eisenhower and Kennedy''. {{OCLC|174566}} | |||
| * {{cite book | author-first= Travis Beal | author-last=Jacobs | chapter=Eisenhower, the American Assembly, and the 1952 Elections | editor-last= Warshaw | editor-first=Shirley Anne | title=Reexamining the Eisenhower presidency | publisher= Greenwood Press | year= 1993 | isbn=0313287929 | pages=17–32 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | author-first=Travis Beal | author-last=Jacobs | title=Eisenhower at Columbia | publisher=Transaction Publishers | year=2001 | isbn=0-7658-0036-5 }} | |||
| * Mason, Robert. "War Hero in the White House: Dwight Eisenhower and the Politics of Peace, Prosperity, and Party." in ''Profiles in Power'' (Brill, 2020) pp. 112–128. | |||
| * Medhurst, Martin J. (1993). ''Dwight D. Eisenhower: Strategic Communicator.'' Greenwood Press. {{ISBN|0313261407}} | |||
| * Mayer, Michael S. (2009). ''The Eisenhower Years'' Facts on File. {{ISBN|0816053871}} | |||
| * Newton, Jim. (2011) ''Eisenhower: The White House Years'' {{ISBN|978-0385523530}} | |||
| * Pach, Chester J., and Richardson, Elmo (1991). ''Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower''. University Press of Kansas. {{ISBN|0700604367}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pickett |first=William B. |author-link=William B. Pickett |title=Eisenhower Decides to Run: Presidential Politics and Cold War Strategy |publisher=Ivan R. Dee |year=2000 |isbn=1-56-663787-2 |title-link=Eisenhower Decides To Run }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pickett |first=William B. |author-link=William B. Pickett |title= Dwight David Eisenhower and American Power|publisher=Harlan Davidson |year=1995 |isbn=0-88-295918-2 |title-link=Dwight David Eisenhower and American Power }} | |||
| * Watry, David M. (2014). ''Diplomacy at the Brink: Eisenhower, Churchill and Eden in the Cold War''. Louisiana State University Press. | |||
| ==== General history ==== | |||
| * {{cite book | author-first=McGeorge | author-last=Bundy | title=Danger and Survival: Choices About the Bomb in the First Fifty Years | publisher=Random House | date=1988 | isbn=0-394-52278-8 }} | |||
| * {{cite book| title=How We Got Here: The 70s The Decade That Brought You Modern Life – For Better Or Worse| url=https://archive.org/details/howwegothere70sd00frum| url-access=registration| last=Frum| first=David| author-link=David Frum| year=2000| publisher=Basic Books| isbn=0-465-04196-5}} | |||
| * {{cite news |last1=Grant |first1=Rebecca |title=Deep Strife |url=https://www.airandspaceforces.com/article/0601airland/ |work=Air & Space Forces Magazine |date=June 1, 2001}} | |||
| * {{cite book | author-link=David Owen (author)|author-last=Owen | author-first=David | year=1999 | title=The Making of the Masters: Clifford Roberts, Augusta National, and Golf's Most Prestigious Tournament | publisher= Simon and Schuster | isbn=0684857294 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | author1-first=Ken | author1-last=Young | author2-first=Warner R. | author2-last=Schilling | title=Super Bomb: Organizational Conflict and the Development of the Hydrogen Bomb | publisher=Cornell University Press | year=2019 | isbn=978-1-5017-4516-4 }} | |||
| ==== Primary sources ==== | |||
| * Boyle, Peter G., ed. (1990). ''The Churchill–Eisenhower Correspondence, 1953–1955''. University of North Carolina Press. | |||
| * Boyle, Peter G., ed. (2005). ''The Eden–Eisenhower correspondence, 1955–1957''. University of North Carolina Press. {{ISBN|0807829358}} | |||
| * Butcher, Harry C. (1946). ''My Three Years With Eisenhower The Personal Diary of Captain Harry C. Butcher, USNR'', candid memoir by a top aide. | |||
| * Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1948). '']'', his war memoirs. | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Dwight D.|last=Eisenhower|title=Mandate for Change, 1953–1956|year=1963}} | |||
| * Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1965). ''The White House Years: Waging Peace 1956–1961'', Doubleday and Co. | |||
| * ''Eisenhower Papers'' 21-volume scholarly edition; complete for 1940–1961. | |||
| * Summersby, Kay (1948). ''Eisenhower Was My Boss'', Prentice Hall; (1949) Dell paperback. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Sister project links |wikt=no |b=no |n=no |s=Author:Dwight D. Eisenhower |v=no}} | |||
| <!--===============================================================================--> | |||
| <!--| WIKIPEDIA IS NOT A COLLECTION OF LINKS. Only a limited number of new links |--> | |||
| <!--| should be added to this article. Consider adding links to the appropriate |--> | |||
| <!--| category at the Open Directory Project (www.dmoz.org) and link back to that |--> | |||
| <!--| category using the {{dmoz}} template. |--> | |||
| <!--| See ] and ] for further details |--> | |||
| <!--===============================================================================--> | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * {{New York Times topic|new_id=person/dwight-david-eisenhower|name=Dwight David Eisenhower}} | |||
| * from the Library of Congress | |||
| * and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the ] | |||
| * , from ]'s '']'', October 25, 1999 | |||
| * {{Gutenberg author | id=1665| name=Dwight David Eisenhower}} | |||
| * {{Internet Archive author |sname=Eisenhower}} | |||
| * {{C-SPAN|3465}} | |||
| {{Dwight D. Eisenhower}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title=Offices and distinctions | |||
| |list1= | |||
| {{s-start}} | {{s-start}} | ||
| {{s-mil}} | {{s-mil}} | ||
| {{s-bef|before= |
{{s-bef|before=]<br />]}} | ||
| {{s-ttl|title=Commanding General of |
{{s-ttl|title=Commanding General of the ]|years=1942–1943<br />1944–1945}} | ||
| {{s-aft|after= |
{{s-aft|after=]<br />]}} | ||
| {{s-bef|before=Gen. ]}} | |||
| {{s-new|office|rows=2}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=Commanding General of U.S. Army Europe|years=1944 – 1945}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1944–1945}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=Gen. ]}} | |||
| {{s-non|reason=Office abolished}} | |||
| {{s-new}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1945}} | |||
| {{s-break}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=Gen. ]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=Gen. ]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1945 |
{{s-ttl|title=]|years=1945}} | ||
| {{s-aft|after= |
{{s-aft|after=]|as=acting governor}} | ||
| {{s-new}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] (])|years=1949 – 1952}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1945–1948}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=Gen. ]}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | |||
| {{s-new|office}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1951–1952}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | |||
| {{s-aca}} | {{s-aca}} | ||
| {{s-bef|before=] |
{{s-bef|before=]|as=acting president}} | ||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years= |
{{s-ttl|title=]|years=1948–1953}} | ||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | {{s-aft|after=]}} | ||
| {{s-ppo}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] ] for President of the United States|years=], ]}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | |||
| {{s-off}} | {{s-off}} | ||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | {{s-bef|before=]}} | ||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years= |
{{s-ttl|title=]|years=1953–1961}} | ||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | {{s-aft|after=]}} | ||
| {{s-ppo}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=], ]}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | |||
| {{s-hon}} | {{s-hon}} | ||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | {{s-bef|before=]}} | ||
| {{s-ttl|title=People who have ] |
{{s-ttl|title=People who have ] in the ]|years=1969}} | ||
| {{s-aft|after=]}} | {{s-aft|after=]}} | ||
| {{s-end}} | |||
| {{s-ref|}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title= Articles related to Dwight D. Eisenhower | |||
| |list1= | |||
| {{St. Mary's Rattlers football coach navbox}} | |||
| {{US Army Chiefs of Staff}} | {{US Army Chiefs of Staff}} | ||
| {{SACEUR}} | |||
| {{USRepPresNominees}} | |||
| {{Republican Party (United States)}} | |||
| {{US Presidents}} | |||
| {{ |
{{US presidents}} | ||
| {{Eisenhower cabinet}} | |||
| {{Columbia University presidents}} | |||
| {{1952 United States presidential election}} | |||
| {{1956 United States presidential election}} | |||
| {{NCAA Theodore Roosevelt Award}} | |||
| {{National Football Foundation Gold Medal Winners}} | |||
| {{Time Persons of the Year|state1=uncollapsed|state2=uncollapsed}} | {{Time Persons of the Year|state1=uncollapsed|state2=uncollapsed}} | ||
| {{Philippine Legion of Honor recipients}} | |||
| {{Order of Sikatuna recipients}} | |||
| {{Lifetime|1890|1969|Eisenhower, Dwight D.}} | |||
| {{Lain in State (USA)|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Persondata | |||
| |NAME=Eisenhower, Dwight David | |||
| |ALTERNATIVE NAMES=Ike (common referent) | |||
| |SHORT DESCRIPTION=United States general and President | |||
| |DATE OF BIRTH={{birth date|mf=yes|1890|10|14|mf=y}} | |||
| |PLACE OF BIRTH=], ] | |||
| |DATE OF DEATH={{death date|mf=yes|1969|3|28|mf=y}} | |||
| |PLACE OF DEATH=] | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Portal bar|1940s|1950s|Biography|Kansas|Law|Politics|Texas|United States}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Eisenhower, Dwight D.}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Eisenhower, Dwight D.}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|sv}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:00, 17 January 2025
President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 "Dwight David Eisenhower" and "Eisenhower" redirect here. For his grandson, see David Eisenhower. For other uses, see Eisenhower (disambiguation).
| Dwight D. Eisenhower | |
|---|---|
 Official portrait, 1959 Official portrait, 1959 | |
| 34th President of the United States | |
| In office January 20, 1953 – January 20, 1961 | |
| Vice President | Richard Nixon |
| Preceded by | Harry S. Truman |
| Succeeded by | John F. Kennedy |
| 1st Supreme Allied Commander Europe | |
| In office April 2, 1951 – May 30, 1952 | |
| President | Harry S. Truman |
| Deputy | Bernard Montgomery |
| Preceded by | Position established |
| Succeeded by | Matthew Ridgway |
| 13th President of Columbia University | |
| In office June 7, 1948 – January 19, 1953 | |
| Preceded by | Nicholas Murray Butler |
| Succeeded by | Grayson L. Kirk |
| 16th Chief of Staff of the Army | |
| In office November 19, 1945 – February 6, 1948 | |
| President | Harry S. Truman |
| Deputy | J. Lawton Collins |
| Preceded by | George C. Marshall |
| Succeeded by | Omar Bradley |
| 1st Military Governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany | |
| In office May 8 – November 10, 1945 | |
| President | Harry S. Truman |
| Preceded by | Position established |
| Succeeded by | George S. Patton (acting) |
| Supreme Commander Allied Expeditionary Force | |
| In office December 24, 1943 – July 14, 1945 | |
| Appointed by | Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| Deputy | Arthur Tedder |
| Preceded by | Position established |
| Succeeded by | Position abolished |
| Personal details | |
| Born | David Dwight Eisenhower (1890-10-14)October 14, 1890 Denison, Texas, U.S. |
| Died | March 28, 1969(1969-03-28) (aged 78) Washington, D.C., U.S. |
| Resting place | Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library, Museum and Boyhood Home |
| Political party | Republican (from 1952) |
| Other political affiliations | Democratic (1909) |
| Spouse |
Mamie Doud (m. 1916) |
| Children | |
| Relatives | Eisenhower family |
| Education | United States Military Academy (BS) |
| Occupation |
|
| Signature | |
| Nickname | "Ike" |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | United States |
| Branch/service | United States Army |
| Years of service |
|
| Rank | General of the Army |
| Battles/wars | See battles |
| Awards | |
|
Dwight D. Eisenhower's voice
Eisenhower on military enforcement of school integration in Little Rock Recorded September 24, 1957 | |
Dwight David Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969), also known by his nickname Ike, was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force in Europe and achieved the five-star rank as General of the Army. Eisenhower planned and supervised two of the most consequential military campaigns of World War II: Operation Torch in the North Africa campaign in 1942–1943 and the invasion of Normandy in 1944.
Eisenhower was born in Denison, Texas, and raised in Abilene, Kansas. His family had a strong religious background, and his mother became a Jehovah's Witness. Eisenhower, however, belonged to no organized church until 1952. He graduated from West Point in 1915 and later married Mamie Doud, with whom he had two sons. During World War I, he was denied a request to serve in Europe and instead commanded a unit that trained tank crews. Between the wars he served in staff positions in the US and the Philippines, reaching the rank of brigadier general shortly before the entry of the US into World War II in 1941. After further promotion Eisenhower oversaw the Allied invasions of North Africa and Sicily before supervising the invasions of France and Germany. After the war ended in Europe, he served as military governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany (1945), Army Chief of Staff (1945–1948), president of Columbia University (1948–1953), and as the first supreme commander of NATO (1951–1952).
In 1952, Eisenhower entered the presidential race as a Republican to block the isolationist foreign policies of Senator Robert A. Taft, who opposed NATO. Eisenhower won that year's election and the 1956 election in landslides, both times defeating Adlai Stevenson II. Eisenhower's main goals in office were to contain the spread of communism and reduce federal deficits. In 1953, he considered using nuclear weapons to end the Korean War and may have threatened China with nuclear attack if an armistice was not reached quickly. China did agree and an armistice resulted, which remains in effect. His New Look policy of nuclear deterrence prioritized "inexpensive" nuclear weapons while reducing funding for expensive Army divisions. He continued Harry S. Truman's policy of recognizing Taiwan as the legitimate government of China, and he won congressional approval of the Formosa Resolution. His administration provided major aid to help the French fight off Vietnamese Communists in the First Indochina War. After the French left, he gave strong financial support to the new state of South Vietnam.
He supported regime-changing military coups in Iran and Guatemala orchestrated by his own administration. During the Suez Crisis of 1956, he condemned the Israeli, British, and French invasion of Egypt, and he forced them to withdraw. He also condemned the Soviet invasion during the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 but took no action. He deployed 15,000 soldiers during the 1958 Lebanon crisis. Near the end of his term, a summit meeting with the Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev was cancelled when a US spy plane was shot down over the Soviet Union. Eisenhower approved the Bay of Pigs Invasion, which was left to John F. Kennedy to carry out.
On the domestic front, Eisenhower governed as a moderate conservative who continued New Deal agencies and expanded Social Security. He covertly opposed Joseph McCarthy and contributed to the end of McCarthyism by openly invoking executive privilege. He signed the Civil Rights Act of 1957 and sent Army troops to enforce federal court orders which integrated schools in Little Rock, Arkansas. His administration undertook the development and construction of the Interstate Highway System, which remains the largest construction of roadways in American history. In 1957, following the Soviet launch of Sputnik, Eisenhower led the American response which included the creation of NASA and the establishment of a stronger, science-based education via the National Defense Education Act. The Soviet Union began to reinforce their own space program, escalating the Space Race. His two terms saw unprecedented economic prosperity except for a minor recession in 1958. In his farewell address, he expressed his concerns about the dangers of massive military spending, particularly deficit spending and government contracts to private military manufacturers, which he dubbed "the military–industrial complex". Historical evaluations of his presidency place him among the upper tier of American presidents.
Family background
Further information: Family of Dwight D. EisenhowerThe Eisenhauer (German for "iron hewer" or "iron miner") family migrated from the German village of Karlsbrunn to the Province of Pennsylvania in 1741. Accounts vary as to how and when the German name Eisenhauer was anglicized.
David Jacob Eisenhower, Eisenhower's father, was a college-educated engineer, despite his own father's urging to stay on the family farm. Eisenhower's mother, Ida Elizabeth (Stover) Eisenhower, of predominantly German Protestant ancestry, moved to Kansas from Virginia. She married David on September 23, 1885, in Lecompton, Kansas, on the campus of their alma mater, Lane University. David owned a general store in Hope, Kansas, but the business failed due to economic conditions and the family became impoverished. The Eisenhowers lived in Texas from 1889 until 1892, and later returned to Kansas, with $24 (equivalent to $814 in 2023) to their name. David worked as a railroad mechanic and then at a creamery. By 1898, the parents made a decent living and provided a suitable home for their large family.
Early life and education

Eisenhower was born David Dwight Eisenhower in Denison, Texas, on October 14, 1890, the third of seven sons born to Ida and David. His mother soon reversed his two forenames after his birth to avoid the confusion of having two Davids in the family. He was named Dwight after the evangelist Dwight L. Moody. All of the boys were nicknamed "Ike", such as "Big Ike" (Edgar) and "Little Ike" (Dwight); the nickname was intended as an abbreviation of their last name. By World War II, only Dwight was still called "Ike".
In 1892, the family moved to Abilene, Kansas, which Eisenhower considered his hometown. As a child, he was involved in an accident that cost his younger brother Earl an eye, for which he was remorseful for the remainder of his life. Eisenhower developed a keen and enduring interest in exploring the outdoors. He learned about hunting and fishing, cooking, and card playing from a man named Bob Davis who camped on the Smoky Hill River. While his mother was against war, it was her collection of history books that first sparked Eisenhower's interest in military history; he became a voracious reader on the subject. Other favorite subjects early in his education were arithmetic and spelling.
Eisenhower's parents set aside specific times at breakfast and at dinner for daily family Bible reading. Chores were regularly assigned and rotated among all the children, and misbehavior was met with unequivocal discipline, usually from David. His mother, previously a member (with David) of the River Brethren (Brethren in Christ Church) sect of the Mennonites, joined the International Bible Students Association, later known as Jehovah's Witnesses. The Eisenhower home served as the local meeting hall from 1896 to 1915, though Dwight never joined. His later decision to attend West Point saddened his mother, who felt that warfare was "rather wicked", but she did not overrule his decision. Speaking of himself in 1948, Eisenhower said he was "one of the most deeply religious men I know" though unattached to any "sect or organization". He was baptized in the Presbyterian Church in 1953.
Eisenhower attended Abilene High School and graduated in 1909. As a freshman, he injured his knee and developed a leg infection that extended into his groin, which his doctor diagnosed as life-threatening. The doctor insisted that the leg be amputated but Dwight refused to allow it, and surprisingly recovered, though he had to repeat his freshman year. He and brother Edgar both wanted to attend college, though they lacked the funds. They made a pact to take alternate years at college while the other worked to earn the tuitions.
Edgar took the first turn at school, and Dwight was employed as a night supervisor at the Belle Springs Creamery. When Edgar asked for a second year, Dwight consented. At that time, a friend Edward "Swede" Hazlett was applying to the Naval Academy and urged Dwight to apply, since no tuition was required. Eisenhower requested consideration for either Annapolis or West Point with his Senator, Joseph L. Bristow. Though Eisenhower was among the winners of the entrance-exam competition, he was beyond the age limit for the Naval Academy. He accepted an appointment to West Point in 1911.
At West Point, Eisenhower relished the emphasis on traditions and on sports, but was less enthusiastic about the hazing, though he willingly accepted it as a plebe. He was also a regular violator of the more detailed regulations and finished school with a less than stellar discipline rating. Academically, Eisenhower's best subject by far was English. Otherwise, his performance was average, though he thoroughly enjoyed the typical emphasis of engineering on science and mathematics.
In athletics, Eisenhower later said that "not making the baseball team at West Point was one of the greatest disappointments of my life, maybe my greatest". He made the varsity football team and was a starter at halfback in 1912, when he tried to tackle the legendary Jim Thorpe of the Carlisle Indians. Eisenhower suffered a torn knee while being tackled in the next game, which was the last he played; he reinjured his knee on horseback and in the boxing ring, so he turned to fencing and gymnastics.

Eisenhower later served as junior varsity football coach and cheerleader, which caught the attention of General Frederick Funston. He graduated from West Point in the middle of the class of 1915, which became known as "the class the stars fell on", because 59 members eventually became general officers. After graduation in 1915, Second Lieutenant Eisenhower requested an assignment in the Philippines, which was denied; because of the ongoing Mexican Revolution, he was posted to Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas, under the command of General Funston. In 1916, while stationed at Fort Sam Houston, Funston convinced him to become the football coach for Peacock Military Academy; he later became the coach at St. Louis College, now St. Mary's University, and was an honorary member of the Sigma Beta Chi fraternity there.
Personal life
Main article: Family of Dwight D. EisenhowerWhile Eisenhower was stationed in Texas, he met Mamie Doud of Boone, Iowa. They were immediately taken with each other. He proposed to her on Valentine's Day in 1916. A November wedding date in Denver was moved up to July 1 due to the impending American entry into World War I; Funston approved 10 days of leave for their wedding. The Eisenhowers moved many times during their first 35 years of marriage.
The Eisenhowers had two sons. In late 1917 while he was in charge of training at Fort Oglethorpe in Georgia, his wife Mamie had their first son, Doud Dwight "Icky" Eisenhower, who died of scarlet fever at the age of three. Eisenhower was mostly reluctant to discuss his death. Their second son, John Eisenhower, was born in Denver, Colorado. John served in the United States Army, retired as a brigadier general, became an author and served as Ambassador to Belgium from 1969 to 1971. He married Barbara Jean Thompson and had four children: David, Barbara Ann, Susan Elaine and Mary Jean. David, after whom Camp David is named, married Richard Nixon's daughter Julie in 1968.

Eisenhower was a golf enthusiast later in life, and he joined the Augusta National Golf Club in 1948. He played golf frequently during and after his presidency and was unreserved in his passion for the game, to the point of golfing during winter; he ordered his golf balls painted black so he could see them better against snow. He had a basic golf facility installed at Camp David, and he became close friends with the Augusta National Chairman Clifford Roberts, inviting Roberts to stay at the White House on numerous occasions. Roberts, an investment broker, also handled the Eisenhower family's investments.
He began oil painting while at Columbia University, after watching Thomas E. Stephens paint Mamie's portrait. Eisenhower painted about 260 oils during the last 20 years of his life. The images were mostly landscapes but also portraits of subjects such as Mamie, their grandchildren, General Montgomery, George Washington, and Abraham Lincoln. Wendy Beckett stated that Eisenhower's paintings, "simple and earnest", caused her to "wonder at the hidden depths of this reticent president". A conservative in both art and politics, Eisenhower in a 1962 speech denounced modern art as "a piece of canvas that looks like a broken-down Tin Lizzie, loaded with paint, has been driven over it".
Angels in the Outfield was Eisenhower's favorite movie. His favorite reading material for relaxation was the Western novels of Zane Grey. With his excellent memory and ability to focus, Eisenhower was skilled at cards. He learned poker, which he called his "favorite indoor sport", in Abilene. Eisenhower recorded West Point classmates' poker losses for payment after graduation and later stopped playing because his opponents resented having to pay him. A friend reported that after learning to play contract bridge at West Point, Eisenhower played the game six nights a week for five months. Eisenhower continued to play bridge throughout his military career. While stationed in the Philippines, he played regularly with President Manuel Quezon, earning him the nickname the "Bridge Wizard of Manila". An unwritten qualification for an officer's appointment to Eisenhower's staff during World War II was the ability to play bridge. He played even during the stressful weeks leading up to the D-Day landings. His favorite partner was General Alfred Gruenther, considered the best player in the US Army; he appointed Gruenther his second-in-command at NATO partly because of his skill at bridge. Saturday night bridge games at the White House were a feature of his presidency. He was a strong player, though not an expert by modern standards. The great bridge player and popularizer Ely Culbertson described his game as classic and sound with "flashes of brilliance" and said that "you can always judge a man's character by the way he plays cards. Eisenhower is a calm and collected player and never whines at his losses. He is brilliant in victory but never commits the bridge player's worst crime of gloating when he wins." Bridge expert Oswald Jacoby frequently participated in the White House games and said, "The President plays better bridge than golf. He tries to break 90 at golf. At bridge, you would say he plays in the 70s."
World War I (1914–1918)
See also: Military career of Dwight D. EisenhowerEisenhower served initially in logistics and then the infantry at various camps in Texas and Georgia until 1918. When the US entered World War I, he immediately requested an overseas assignment but was denied and assigned to Ft. Leavenworth, Kansas. In February 1918, he was transferred to Camp Meade in Maryland with the 65th Engineers. His unit was later ordered to France, but, to his chagrin, he received orders for the new tank corps, where he was promoted to brevet lieutenant colonel in the National Army. He commanded a unit that trained tank crews at Camp Colt – his first command. Though Eisenhower and his tank crews never saw combat, he displayed excellent organizational skills as well as an ability to accurately assess junior officers' strengths and make optimal placements of personnel.
His spirits were raised when the unit under his command received orders overseas to France. This time his wishes were thwarted when the armistice was signed a week before his departure date. Completely missing out on the warfront left him depressed and bitter for a time, despite receiving the Distinguished Service Medal for his work at home. In World War II, rivals who had combat service in the Great War (led by Gen. Bernard Montgomery) sought to denigrate Eisenhower for his previous lack of combat duty, despite his stateside experience establishing a camp for thousands of troops and developing a full combat training schedule.
Between the Wars (1918–1939)
In service of generals

After the war, Eisenhower reverted to his regular rank of captain and a few days later was promoted to major, a rank he held for 16 years. The major was assigned in 1919 to a transcontinental Army convoy to test vehicles and dramatize the need for improved roads. Indeed, the convoy averaged only 5 miles per hour (8.0 km/h) from Washington, D.C. to San Francisco; later the improvement of highways became a signature issue for Eisenhower as president.
He assumed duties again at Camp Meade, Maryland, commanding a battalion of tanks, where he remained until 1922. His schooling continued, focused on the nature of the next war and the role of the tank. His new expertise in tank warfare was strengthened by a close collaboration with George S. Patton, Sereno E. Brett, and other senior tank leaders. Their leading-edge ideas of speed-oriented offensive tank warfare were strongly discouraged by superiors, who considered the new approach too radical and preferred to continue using tanks in a strictly supportive role for the infantry. Eisenhower was even threatened with court-martial for continued publication of these proposed methods of tank deployment, and he relented.
From 1920, Eisenhower served under a succession of talented generals – Fox Conner, John J. Pershing, Douglas MacArthur and George Marshall. He first became executive officer to General Conner in the Panama Canal Zone, where, joined by Mamie, he served until 1924. Under Conner's tutelage, he studied military history and theory (including Carl von Clausewitz's On War), and later cited Conner's enormous influence on his military thinking, saying in 1962 that "Fox Conner was the ablest man I ever knew." Conner's comment on Eisenhower was, " is one of the most capable, efficient and loyal officers I have ever met." On Conner's recommendation, in 1925–1926 he attended the Command and General Staff College at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, where he graduated first in a class of 245 officers.
During the late 1920s and early 1930s, Eisenhower's career stalled somewhat, as military priorities diminished; many of his friends resigned for high-paying business jobs. He was assigned to the American Battle Monuments Commission directed by General Pershing, and with the help of his brother Milton Eisenhower, then a journalist at the Agriculture Department, he produced a guide to American battlefields in Europe. He then was assigned to the Army War College and graduated in 1928. After a one-year assignment in France, Eisenhower served as executive officer to General George V. Moseley, Assistant Secretary of War, from 1929 to February 1933. Major Eisenhower graduated from the Army Industrial College in 1933 and later served on the faculty (it was later expanded to become the Industrial College of the Armed Services and is now known as the Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy).
His primary duty was planning for the next war, which proved most difficult in the midst of the Great Depression. He then was posted as chief military aide to General Douglas MacArthur, Army Chief of Staff. In 1932, he participated in the clearing of the Bonus March encampment in Washington, D.C. Although he was against the actions taken against the veterans and strongly advised MacArthur against taking a public role in it, he later wrote the Army's official incident report, endorsing MacArthur's conduct.
Philippine tenure (1935–1939)
In 1935, he accompanied MacArthur to the Philippines, where he served as assistant military adviser to the Philippine government in developing their army. MacArthur allowed Eisenhower to handpick an officer whom he thought would contribute to the mission. Hence he chose James Ord, a classmate of his at West Point. Having been brought up in Mexico, which inculcated into him the Spanish culture which influenced both Mexico and the Philippines, Ord was deemed the right pick for the job. Eisenhower had strong philosophical disagreements with MacArthur regarding the role of the Philippine Army and the leadership qualities that an American army officer should exhibit and develop in his subordinates. The antipathy between Eisenhower and MacArthur lasted the rest of their lives.
Historians have concluded that this assignment provided valuable preparation for handling the challenging personalities of Winston Churchill, George S. Patton, George Marshall, and Bernard Montgomery during World War II. Eisenhower later emphasized that too much had been made of the disagreements with MacArthur and that a positive relationship endured. While in Manila, Mamie suffered a life-threatening stomach ailment but recovered fully. Eisenhower was promoted to the rank of permanent lieutenant colonel in 1936. He also learned to fly with the Philippine Army Air Corps at the Zablan Airfield in Camp Murphy under Capt. Jesus Villamor, making a solo flight over the Philippines in 1937, and obtained his private pilot's license in 1939 at Fort Lewis. Also around this time, he was offered a post by the Philippine Commonwealth Government, namely by then Philippine President Manuel L. Quezon on recommendations by MacArthur, to become the chief of police of a new capital being planned, now named Quezon City, but he declined the offer.
World War II (1939–1945)
Eisenhower returned to the United States in December 1939 and was assigned as commanding officer of the 1st Battalion, 15th Infantry Regiment at Fort Lewis, Washington, later becoming the regimental executive officer. In March 1941 he was promoted to colonel and assigned as chief of staff of the newly activated IX Corps under Major General Kenyon Joyce. In June 1941, he was appointed chief of staff to General Walter Krueger, Commander of the Third Army, at Fort Sam Houston in San Antonio, Texas. After successfully participating in the Louisiana Maneuvers, he was promoted to brigadier general on October 3, 1941.
After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Eisenhower was assigned to the General Staff in Washington, where he served until June 1942 with responsibility for creating the major war plans to defeat Japan and Germany. He was appointed Deputy Chief in charge of Pacific Defenses under the Chief of War Plans Division (WPD), General Leonard T. Gerow, and then succeeded Gerow as Chief of the War Plans Division. Next, he was appointed Assistant Chief of Staff in charge of the new Operations Division (which replaced WPD) under Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall, who spotted talent and promoted accordingly.
At the end of May 1942, Eisenhower accompanied Lt. Gen. Henry H. Arnold, commanding general of the Army Air Forces, to London to assess the effectiveness of the theater commander in England, Maj. Gen. James E. Chaney. He returned to Washington on June 3 with a pessimistic assessment, stating he had an "uneasy feeling" about Chaney and his staff. On June 23, 1942, he returned to London as Commanding General, European Theater of Operations (ETOUSA), based in London and with a house in Coombe, Kingston upon Thames, and took over command of ETOUSA from Chaney. He was promoted to lieutenant general on July 7.
Operations Torch and Avalanche

In November 1942, Eisenhower was also appointed Supreme Commander Allied Expeditionary Force of the North African Theater of Operations (NATOUSA) through the new operational Headquarters Allied (Expeditionary) Force Headquarters (A(E)FHQ). The word "expeditionary" was dropped soon after his appointment for security reasons. The campaign in North Africa was designated Operation Torch and was planned in the underground headquarters within the Rock of Gibraltar. Eisenhower was the first non-British person to command Gibraltar in 200 years.
French cooperation was deemed necessary to the campaign and Eisenhower encountered a "preposterous situation" with the multiple rival factions in France. His primary objective was to move forces successfully into Tunisia and intending to facilitate that objective, he gave his support to François Darlan as High Commissioner in North Africa, despite Darlan's previous high offices in Vichy France and his continued role as commander-in-chief of the French armed forces. The Allied leaders were "thunderstruck" by this from a political standpoint, though none had offered Eisenhower guidance with the problem in planning the operation. Eisenhower was severely criticized for the move. Darlan was assassinated on December 24 by Fernand Bonnier de La Chapelle, a French antifascist monarchist. Eisenhower later appointed as High Commissioner General Henri Giraud, who had been installed by the Allies as Darlan's commander-in-chief.
Operation Torch also served as a valuable training ground for Eisenhower's combat command skills; during the initial phase of Generalfeldmarschall Erwin Rommel's move into the Kasserine Pass, Eisenhower created some confusion in the ranks by interference with the execution of battle plans by his subordinates. He also was initially indecisive in his removal of Lloyd Fredendall, commanding II Corps. He became more adroit in such matters in later campaigns. In February 1943, his authority was extended as commander of AFHQ across the Mediterranean basin to include the British Eighth Army, commanded by General Sir Bernard Montgomery. The Eighth Army had advanced across the Western Desert from the east and was ready for the start of the Tunisia Campaign.
After the capitulation of Axis forces in North Africa, Eisenhower oversaw the invasion of Sicily. Once Mussolini, the Italian leader, had fallen in Italy, the Allies switched their attention to the mainland with Operation Avalanche. But while Eisenhower argued with President Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Churchill, who both insisted on unconditional surrender in exchange for helping the Italians, the Germans pursued an aggressive buildup of forces in the country. The Germans made the already tough battle more difficult by adding 19 divisions and initially outnumbering the Allied forces 2 to 1.
Supreme Allied commander and Operation Overlord
In December 1943, President Roosevelt decided that Eisenhower – not Marshall – would be Supreme Allied Commander in Europe. The following month, he resumed command of ETOUSA and the following month was officially designated as the Supreme Allied Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF), serving in a dual role until the end of hostilities in Europe in May 1945. He was charged in these positions with planning and carrying out the Allied assault on the coast of Normandy in June 1944 under the code name Operation Overlord, the liberation of Western Europe and the invasion of Germany.

Eisenhower, as well as the officers and troops under him, had learned valuable lessons in their previous operations, and their skills had all strengthened in preparation for the next most difficult campaign against the Germans—a beach landing assault. His first struggles, however, were with Allied leaders and officers on matters vital to the success of the Normandy invasion; he argued with Roosevelt over an essential agreement with De Gaulle to use French resistance forces in covert operations against the Germans in advance of Operation Overlord. Admiral Ernest J. King fought with Eisenhower over King's refusal to provide additional landing craft from the Pacific. Eisenhower also insisted that the British give him exclusive command over all strategic air forces to facilitate Overlord, to the point of threatening to resign unless Churchill relented, which he did. Eisenhower then designed a bombing plan in France in advance of Overlord and argued with Churchill over the latter's concern with civilian casualties; de Gaulle interjected that the casualties were justified, and Eisenhower prevailed. He also had to skillfully manage to retain the services of the often unruly George S. Patton, by severely reprimanding him when Patton earlier had slapped a subordinate, and then when Patton gave a speech in which he made improper comments about postwar policy.
The D-Day Normandy landings on June 6, 1944, were costly but successful. Two months later (August 15), the invasion of Southern France took place, and control of forces in the southern invasion passed from the AFHQ to the SHAEF. Many thought that victory in Europe would come by summer's end, but the Germans did not capitulate for almost a year. From then until the end of the war in Europe on May 8, 1945, Eisenhower, through SHAEF, commanded all Allied forces, and through his command of ETOUSA had administrative command of all US forces on the Western Front north of the Alps. He was ever mindful of the inevitable loss of life and suffering that would be experienced by the troops under his command and their families. This prompted him to make a point of visiting every division involved in the invasion. Eisenhower's sense of responsibility was underscored by his draft of a statement to be issued if the invasion failed. It has been called one of the great speeches of history:
Our landings in the Cherbourg-Havre area have failed to gain a satisfactory foothold and I have withdrawn the troops. My decision to attack at this time and place was based on the best information available. The troops, the air and the Navy did all that bravery and devotion to duty could do. If any blame or fault attaches to the attempt, it is mine alone.
Liberation of France and victory in Europe

Every ground commander seeks the battle of annihilation; so far as conditions permit, he tries to duplicate in modern war the classic example of Cannae.
— Eisenhower
Once the coastal assault had succeeded, Eisenhower insisted on retaining personal control over the land battle strategy and was immersed in the command and supply of multiple assaults through France on Germany. Field Marshal Montgomery insisted priority be given to his 21st Army Group's attack being made in the north, while Generals Bradley (12th US Army Group) and Devers (Sixth US Army Group) insisted they be given priority in the center and south of the front (respectively). Eisenhower worked tirelessly to address the demands of the rival commanders to optimize Allied forces, often by giving them tactical latitude; many historians conclude this delayed the Allied victory in Europe. However, due to Eisenhower's persistence, the pivotal supply port at Antwerp was successfully, albeit belatedly, opened in late 1944.
In recognition of his senior position in the Allied command, on December 20, 1944, he was promoted to General of the Army, equivalent to the rank of Field Marshal in most European armies. In this and the previous high commands he held, Eisenhower showed his great talents for leadership and diplomacy. Although he had never seen action himself, he won the respect of front-line commanders. He interacted adeptly with allies such as Winston Churchill, Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery and General Charles de Gaulle. He had serious disagreements with Churchill and Montgomery over questions of strategy, but these rarely upset his relationships with them. He dealt with Soviet Marshal Zhukov, his Russian counterpart, and they became good friends.
In December 1944, the Germans launched a surprise counteroffensive, the Battle of the Bulge, which the Allies turned back in early 1945 after Eisenhower repositioned his armies and improved weather allowed the Army Air Force to engage. German defenses continued to deteriorate on both the Eastern Front with the Red Army and the Western Front with the Western Allies. The British wanted to capture Berlin, but Eisenhower decided it would be a military mistake for him to attack Berlin and said orders to that effect would have to be explicit. The British backed down but then wanted Eisenhower to move into Czechoslovakia for political reasons. Washington refused to support Churchill's plan to use Eisenhower's army for political maneuvers against Moscow. The actual division of Germany followed the lines that Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin had previously agreed upon. The Soviet Red Army captured Berlin in a very bloody large-scale battle, and the Germans finally surrendered on May 7, 1945.
Throughout 1945, the allied armies liberated numerous Nazi concentration camps throughout Europe. As the allies learned the full extend of the Holocaust, Eisenhower anticipated that, in the future, attempts to recharacterize Nazi crimes as propaganda (Holocaust denial) would be made, and took steps against it by demanding extensive photo and film documentation of Nazi death camps.
After World War II (1945–1953)
Military Governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany
Following the German unconditional surrender, Eisenhower was appointed military governor of the American-occupied zone of Germany, located primarily in Southern Germany, and headquartered in Frankfurt am Main. Upon discovery of the Nazi concentration camps, he ordered camera crews to document evidence for use in the Nuremberg Trials. He reclassified German prisoners of war (POWs) in US custody as Disarmed Enemy Forces (DEFs), who were no longer subject to the Geneva Convention. Eisenhower followed the orders laid down by the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) in directive JCS 1067 but softened them by bringing in 400,000 tons of food for civilians and allowing more fraternization. In response to the devastation in Germany, including food shortages and an influx of refugees, he arranged distribution of American food and medical equipment. His actions reflected the new American attitudes of the German people as Nazi victims not villains, while aggressively purging the ex-Nazis.
Army Chief of Staff
In November 1945, Eisenhower returned to Washington to replace Marshall as Chief of Staff of the Army. His main role was the rapid demobilization of millions of soldiers, which was delayed by lack of shipping. Eisenhower was convinced in 1946 that the Soviet Union did not want war and that friendly relations could be maintained; he strongly supported the new United Nations and favored its involvement in the control of atomic bombs. However, in formulating policies regarding the atomic bomb and relations with the Soviets, Truman was guided by the State Department and ignored Eisenhower and the Pentagon. Indeed, Eisenhower had opposed the use of the atomic bomb against the Japanese, writing, "First, the Japanese were ready to surrender and it wasn't necessary to hit them with that awful thing. Second, I hated to see our country be the first to use such a weapon." Initially, Eisenhower hoped for cooperation with the Soviets. He even visited Warsaw in 1945. Invited by Bolesław Bierut and decorated with the highest military decoration, he was shocked by the scale of destruction in the city. However, by mid-1947, as east–west tensions over economic recovery in Germany and the Greek Civil War escalated, Eisenhower agreed with a containment policy to stop Soviet expansion.
1948 presidential election
In June 1943, a visiting politician had suggested to Eisenhower that he might become president after the war. Believing that a general should not participate in politics, Merlo J. Pusey wrote that "figuratively speaking, kicked his political-minded visitor out of his office". As others asked him about his political future, Eisenhower told one that he could not imagine wanting to be considered for any political job "from dogcatcher to Grand High Supreme King of the Universe", and another that he could not serve as Army Chief of Staff if others believed he had political ambitions. In 1945, Truman told Eisenhower during the Potsdam Conference that if desired, the president would help the general win the 1948 election, and in 1947 he offered to run as Eisenhower's running mate on the Democratic ticket if MacArthur won the Republican nomination.
As the election approached, other prominent citizens and politicians from both parties urged Eisenhower to run. In January 1948, after learning of plans in New Hampshire to elect delegates supporting him for the forthcoming Republican National Convention, Eisenhower stated through the Army that he was "not available for and could not accept nomination to high political office"; "life-long professional soldiers", he wrote, "in the absence of some obvious and overriding reason, abstain from seeking high political office". Eisenhower maintained no political party affiliation during this time. Many believed he was forgoing his only opportunity to be president as Republican Thomas E. Dewey was considered the probable winner and would presumably serve two terms, meaning that Eisenhower, at age 66 in 1956, would be too old to run.
President at Columbia University and NATO Supreme Commander



In 1948, Eisenhower became President of Columbia University, an Ivy League university in New York City, where he was inducted into Phi Beta Kappa. The choice was subsequently characterized as not having been a good fit for either party. During that year, Eisenhower's memoir, Crusade in Europe, was published. It was a major financial success. Eisenhower sought the advice of Augusta National's Roberts about the tax implications of this, and in due course Eisenhower's profit on the book was substantially aided by what author David Pietrusza calls "a ruling without precedent" by the Department of the Treasury. It held that Eisenhower was not a professional writer, but rather, marketing the lifetime asset of his experiences, and thus he had to pay only capital gains tax on his $635,000 advance instead of the much higher personal tax rate. This ruling saved Eisenhower about $400,000.
Eisenhower's stint as the president of Columbia was punctuated by his activity within the Council on Foreign Relations, a study group he led concerning the political and military implications of the Marshall Plan and The American Assembly, Eisenhower's "vision of a great cultural center where business, professional and governmental leaders could meet from time to time to discuss and reach conclusions concerning problems of a social and political nature". His biographer Blanche Wiesen Cook suggested that this period served his "the political education", since he had to prioritize wide-ranging educational, administrative, and financial demands for the university. Through his involvement in the Council on Foreign Relations, he also gained exposure to economic analysis, which became the bedrock of his understanding in economic policy. "Whatever General Eisenhower knows about economics, he has learned at the study group meetings," one Aid to Europe member claimed.
Eisenhower accepted the presidency of the university to expand his ability to promote "the American form of democracy" through education. He was clear on this point to the trustees on the search committee. He informed them that his main purpose was "to promote the basic concepts of education in a democracy". As a result, he was "almost incessantly" devoted to the idea of the American Assembly, a concept he developed into an institution by the end of 1950.
Within months of becoming university president, Eisenhower was requested to advise Secretary of Defense James Forrestal on the unification of the armed services. About six months after his appointment, he became the informal Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff in Washington. Two months later he fell ill with what was diagnosed as acute gastroenteritis, and he spent over a month in recovery at the Augusta National Golf Club. He returned to his post in New York in mid-May, and in July 1949 took a two-month vacation out-of-state. Because the American Assembly had begun to take shape, he traveled around the country during summer and fall 1950, building financial support for it, including from Columbia Associates, a recently created alumni and benefactor organization for which he had helped recruit members. Eisenhower was unknowingly building resentment and a reputation among the Columbia University faculty and staff as an absentee president who was using the university for his own interests. As a career military man, he naturally had little in common with the academics. The contacts gained through university and American Assembly fundraising activities would later become important supporters in Eisenhower's bid for the Republican party nomination and the presidency. Meanwhile, Columbia University's liberal faculty members became disenchanted with the university president's ties to oilmen and businessmen.
He did have some successes at Columbia. Puzzled as to why no American university had undertaken the "continuous study of the causes, conduct and consequences of war", Eisenhower undertook the creation of the Institute of War and Peace Studies, a research facility to "study war as a tragic social phenomenon". Eisenhower was able to use his network of wealthy friends and acquaintances to secure initial funding for it. Under its founding director, international relations scholar William T. R. Fox, the institute began in 1951 and became a pioneer in international security studies, one that would be emulated by other institutes in the United States and Britain later in the decade. The Institute of War and Peace Studies thus became one of the projects which Eisenhower considered his "unique contribution" to Columbia. As the president of Columbia, Eisenhower gave voice to his opinions about the supremacy and difficulties of American democracy. His tenure marked his transformation from military to civilian leadership. His biographer Travis Beal Jacobs also suggested that the alienation of the Columbia faculty contributed to sharp intellectual criticism of him for many years.
The trustees of Columbia University declined to accept Eisenhower's offer to resign in December 1950, when he took an extended leave from the university to become the Supreme Commander of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and he was given operational command of NATO forces in Europe. Eisenhower retired from active service as an army general on June 3, 1952, and he resumed his presidency of Columbia. Meanwhile, Eisenhower had become the Republican Party nominee for president of the United States, a contest that he won on November 4. Eisenhower tendered his resignation as university president on November 15, 1952, effective January 19, 1953, the day before his inauguration.
At home, Eisenhower was more effective in making the case for NATO in Congress than the Truman administration had been. By the middle of 1951, with American and European support, NATO was a genuine military power. Nevertheless, Eisenhower thought that NATO would become a truly European alliance, with the American and Canadian commitments ending after about ten years.
Presidential campaign of 1952
Main article: 1952 United States presidential election See also: Draft Eisenhower movement
President Truman sensed a broad-based desire for an Eisenhower candidacy for president, and he again pressed him to run for the office as a Democrat in 1951. But Eisenhower voiced his disagreements with the Democrats and declared himself to be a Republican. A "Draft Eisenhower" movement in the Republican Party persuaded him to declare his candidacy in the 1952 presidential election to counter the candidacy of non-interventionist Senator Robert A. Taft. The effort was a long struggle; Eisenhower had to be convinced that political circumstances had created a genuine duty to offer himself as a candidate and that there was a mandate from the public for him to be their president. Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. and others succeeded in convincing him, and he resigned his command at NATO in June 1952 to campaign full-time.
Eisenhower defeated Taft for the nomination, having won critical delegate votes from Texas. His campaign was noted for the simple slogan "I Like Ike". It was essential to his success that Eisenhower express opposition to Roosevelt's policy at the Yalta Conference and to Truman's policies in Korea and China—matters in which he had once participated. In defeating Taft for the nomination, it became necessary for Eisenhower to appease the right-wing Old Guard of the Republican Party; his selection of Richard Nixon as the vice-president on the ticket was designed in part for that purpose. Nixon also provided a strong anti-communist reputation, as well as youth to counter Eisenhower's more advanced age.
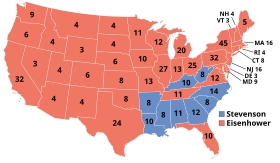
Eisenhower insisted on campaigning in the South in the general election, against the advice of his campaign team, refusing to surrender the region to the Democrats. The campaign strategy was dubbed "K1C2" and was intended to focus on attacking the Truman administration on three failures: the Korean War, Communism, and corruption.
Two controversies tested him and his staff, but they did not damage the campaign. One involved a report that Nixon had improperly received funds from a secret trust. Nixon spoke out adroitly to avoid potential damage, but the matter permanently alienated the two candidates. The second issue centered on Eisenhower's relented decision to confront the controversial methods of Joseph McCarthy on his home turf in a Wisconsin appearance. Eisenhower condemned "wickedness in government", an allusion to gay government employees who were conflated with communism during McCarthyism.
Eisenhower defeated Democratic candidate Adlai Stevenson II in a landslide, with an electoral margin of 442 to 89, marking the first Republican return to the White House in 20 years. He also brought a Republican majority in the House, by eight votes, and in the Senate, evenly divided with Vice President Nixon providing Republicans the majority.
Eisenhower was the last president born in the 19th century, and he was the oldest president-elect at age 62 since James Buchanan in 1856. He was the third commanding general of the Army to serve as president, after George Washington and Ulysses S. Grant, and the last not to have held political office prior to becoming president until Donald Trump entered office in January 2017.
Election of 1956
Main article: 1956 United States presidential election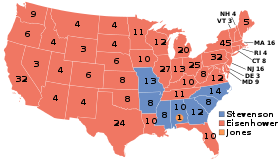
In the United States presidential election of 1956, Eisenhower, the popular incumbent, was re-elected. The election was a re-match of 1952, as his opponent in 1956 was Stevenson, a former Illinois governor, whom Eisenhower had defeated four years earlier. Compared to the 1952 election, Eisenhower gained Kentucky, Louisiana, and West Virginia from Stevenson, while losing Missouri. His voters were less likely to bring up his leadership record. Instead what stood out this time "was the response to personal qualities — to his sincerity, his integrity and sense of duty, his virtue as a family man, his religious devotion, and his sheer likeableness."
Presidency (1953–1961)
Main article: Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower For a chronological guide, see Timeline of the Dwight D. Eisenhower presidency.Truman and Eisenhower had minimal discussions about the transition of administrations due to a complete estrangement between them as a result of campaigning. Eisenhower selected Joseph M. Dodge as his budget director, then asked Herbert Brownell Jr. and Lucius D. Clay to make recommendations for his cabinet appointments. He accepted their recommendations without exception; they included John Foster Dulles and George M. Humphrey with whom he developed his closest relationships, as well as Oveta Culp Hobby. His cabinet consisted of several corporate executives and one labor leader, and one journalist dubbed it "eight millionaires and a plumber". The cabinet was known for its lack of personal friends, office seekers, or experienced government administrators. He also upgraded the role of the National Security Council in planning all phases of the Cold War.
Before his inauguration, Eisenhower led a meeting of advisors at Pearl Harbor where they set goals for his first term: balance the budget, end the Korean War, defend vital interests at lower cost through nuclear deterrent, and end price and wage controls. He also conducted the first pre-inaugural cabinet meeting in history in late 1952; he used this meeting to articulate his anti-communist Russia policy. His inaugural address was exclusively devoted to foreign policy and included this same philosophy as well as a commitment to foreign trade and the United Nations.

Eisenhower made greater use of press conferences than any previous president, holding almost 200 over his two terms. He saw the benefit of maintaining a good relationship with the press, and he saw value in them as a means of direct communication with the American people.
Throughout his presidency, Eisenhower adhered to a political philosophy of dynamic conservatism. He described himself as a "progressive conservative" and used terms such as "progressive moderate" and "dynamic conservatism" to describe his approach. He continued all the major New Deal programs still in operation, especially Social Security. He expanded its programs and rolled them into the new Cabinet-level agency of the Department of Health, Education and Welfare, while extending benefits to an additional ten million workers. He implemented racial integration in the Armed Services in two years, which had not been completed under Truman.
In a private letter, Eisenhower wrote:
Should any party attempt to abolish social security and eliminate labor laws and farm programs, you would not hear of that party again in our political history. There is a tiny splinter group of course, that believes you can do these things Their number is negligible and they are stupid.
When the 1954 Congressional elections approached, it became evident that the Republicans were in danger of losing their thin majority in both houses. Eisenhower was among those who blamed the Old Guard for the losses, and he took up the charge to stop suspected efforts by the right wing to take control of the GOP. He then articulated his position as a moderate, progressive Republican: "I have just one purpose ... and that is to build up a strong progressive Republican Party in this country. If the right wing wants a fight, they are going to get it ... before I end up, either this Republican Party will reflect progressivism or I won't be with them anymore."
Eisenhower initially planned on serving only one term, but he remained flexible in case leading Republicans wanted him to run again. He was recovering from a heart attack late in September 1955 when he met with his closest advisors to evaluate the GOP's potential candidates; the group concluded that a second term was well advised, and he announced that he would run again in February 1956. Eisenhower was publicly noncommittal about having Nixon as the Vice President on his ticket; the question was an especially important one in light of his heart condition. He personally favored Robert B. Anderson, a Democrat who rejected his offer, so Eisenhower resolved to leave the matter in the hands of the party, which chose Nixon nearly unanimously. In 1956, Eisenhower faced Adlai Stevenson again and won by an even larger landslide, with 457 of 531 electoral votes and 57.6 percent of the popular vote. His campaigning was curtailed out of health considerations.
Eisenhower made full use of his valet, chauffeur, and secretarial support; he rarely drove or even dialed a phone number. He was an avid fisherman, golfer, painter, and bridge player. On August 26, 1959, he was aboard the maiden flight of Air Force One, which replaced the Columbine as the presidential aircraft.
Atoms for Peace
See also: History of nuclear power and History of nuclear weaponsEisenhower gave the Atoms for Peace speech to the United Nations General Assembly on 8 December 1953, advocating for constructive use of nuclear fission for electrical energy and nuclear medicine instead of nuclear arms race proliferation. The speech led to the Atomic Energy Act of 1954 which allowed the civilian world to develop nuclear fission technology for peaceful and prosperous purposes.
Interstate Highway System
Main article: Interstate Highway System
Text of speech excerpt
Problems playing this file? See media help.
Eisenhower championed and signed the bill that authorized the Interstate Highway System in 1956. He justified the project through the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956 as essential to American security during the Cold War.
Eisenhower's goal to create improved highways was influenced by his involvement in the Army's 1919 Transcontinental Motor Convoy. He was assigned as an observer for the mission, which involved sending a convoy of Army vehicles coast to coast. His subsequent experience with the German autobahn convinced him of the benefits of an Interstate Highway System. The system could also be used as a runway for airplanes, which would be beneficial to war efforts. Franklin D. Roosevelt put this system into place with the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1944. He thought that an interstate highway system would be beneficial for military operations and would support continued economic growth. The legislation initially stalled in Congress over the issuance of bonds to finance the project, but the legislative effort was renewed and Eisenhower signed the law in June 1956.
ARPA
The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) was put together by Eisenhower and his Science Advisory Committee in early 1958 in response to the successful launch of the first orbital satellite from the Soviet Union Sputnik 1. ARPA eventually created the ARPANET which was a predecessor to the internet.
Foreign policy



The United States foreign policy of the Dwight D. Eisenhower administration, from 1953 to 1961, focused on the Cold War with the Soviet Union and its satellites. The United States built up a stockpile of nuclear weapons and nuclear delivery systems to deter military threats and save money while cutting back on expensive Army combat units. A major uprising broke out in Hungary in 1956; the Eisenhower administration did not become directly involved, but condemned the military invasion by the Soviet Union. Eisenhower sought to reach a nuclear test ban treaty with the Soviet Union, but following the 1960 U-2 incident the Kremlin canceled a scheduled summit in Paris.
As he promised, Eisenhower quickly ended the fighting in Korea, leaving it divided North and South. The U.S. has kept major forces there ever since to deter North Korea. In 1954, he played a key role in the Senate's defeat of the Bricker Amendment, which would have limited the president's treaty making power and ability to enter into executive agreements with foreign leaders. The Eisenhower administration used propaganda and covert action extensively, and the Central Intelligence Agency supported two military coups: the 1953 Iranian coup d'état and the 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état. The administration did not approve the partition of Vietnam at the 1954 Geneva Conference, and directed economic and military aid and advice to South Vietnam. Washington led the establishment of the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization as an alliance of anti-Communist states in Southeast Asia. It ended two crises with China over Taiwan.
In 1956, Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal, sparking the Suez Crisis, in which a coalition of France, Britain, and Israel attacked Egypt. Concerned about the economic and political impacts of the invasion, Eisenhower had warned the three against any such action. When they invaded anyway he used heavy financial and diplomatic pressures to force a withdrawal. In the aftermath of the crisis, Eisenhower announced the Eisenhower Doctrine, under which any country in the Middle East could request American economic assistance or aid from American military forces.
The Cuban Revolution broke out during Eisenhower's second term, resulting in the replacement of pro-U.S. military dictator Fulgencio Batista with Fidel Castro. In response to the revolution, the Eisenhower administration broke ties with Cuba and Eisenhower approved a CIA operation to carry out a campaign of terrorist attacks and sabotage, kill civilians, and cause economic damage. The CIA also trained and commanded pilots to bomb civilian airfields. The CIA began preparations for an invasion of Cuba by Cuban expatriates, ultimately resulting in the failed Bay of Pigs Invasion after Eisenhower left office.Space Race
Further information: Space Race
Eisenhower and the CIA had known since at least January 1957, nine months before Sputnik, that Russia had the capability to launch a small payload into orbit and was likely to do so within a year.
Eisenhower's support of the nation's fledgling space program was officially modest until the Soviet launch of Sputnik in 1957, gaining the Cold War enemy enormous prestige. He then launched a national campaign that funded not just space exploration but a major strengthening of science and higher education. The Eisenhower administration determined to adopt a non-aggressive policy that would allow "space-crafts of any state to overfly all states, a region free of military posturing and launch Earth satellites to explore space". His Open Skies Policy attempted to legitimize illegal Lockheed U-2 flyovers and Project Genetrix while paving the way for spy satellite technology to orbit over sovereign territory, but Nikolai Bulganin and Nikita Khrushchev declined Eisenhower's proposal at the Geneva conference in July 1955. In response to Sputnik being launched in October 1957, Eisenhower created NASA as a civilian space agency in October 1958, signed a landmark science education law, and improved relations with American scientists.
Fear spread through the United States that the Soviet Union would invade and spread communism, so Eisenhower wanted to not only create a surveillance satellite to detect any threats but ballistic missiles that would protect the United States. In strategic terms, it was Eisenhower who devised the American basic strategy of nuclear deterrence based upon the triad of strategic bombers, land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), and submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs).
NASA planners projected that human spaceflight would pull the United States ahead in the Space Race; however, in 1960, an Ad Hoc Panel on Man-in-Space concluded that "man-in-space can not be justified" and was too costly. Eisenhower later resented the space program and its gargantuan price tag—he was quoted as saying, "Anyone who would spend $40 billion in a race to the moon for national prestige is nuts."
Korean War, Free China and Red China
In late 1952, Eisenhower went to Korea and discovered a military and political stalemate. Once in office, when the Chinese People's Volunteer Army began a buildup in the Kaesong sanctuary, he considered using nuclear weapons if an armistice was not reached. Whether China was informed of the potential for nuclear force is unknown. His earlier military reputation in Europe was effective with the Chinese communists. The National Security Council, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the Strategic Air Command (SAC) devised detailed plans for nuclear war against Red China. With the death of Stalin in March 1953, Russian support for a Chinese communist hard-line weakened and China decided to compromise on the prisoner issue.

In July 1953, an armistice took effect with Korea divided along approximately the same boundary as in 1950. The armistice and boundary remain in effect today. The armistice, which concluded despite opposition from Secretary Dulles, South Korean President Syngman Rhee, and also within Eisenhower's party, has been described by biographer Stephen E. Ambrose as the greatest achievement of the administration. Eisenhower had the insight to realize that unlimited war in the nuclear age was unthinkable, and limited war unwinnable.
A point of emphasis in Eisenhower's campaign had been his endorsement of a policy of liberation from communism as opposed to a policy of containment. This remained his preference despite the armistice with Korea. Throughout his terms Eisenhower took a hard-line attitude toward China, as demanded by conservative Republicans, with the goal of driving a wedge between China and the Soviet Union. Eisenhower continued Truman's policy of recognizing the Republic of China (Taiwan) as the legitimate government of China, not the Peking (Beijing) regime. There were localized flare-ups when the People's Liberation Army began shelling the islands of Quemoy and Matsu in September 1954. Eisenhower received recommendations embracing every variation of response; he thought it essential to have every possible option available to him as the crisis unfolded.
The Sino-American Mutual Defense Treaty with the Republic of China was signed in December 1954. He requested and secured from Congress their "Free China Resolution" in January 1955, which gave Eisenhower unprecedented power in advance to use military force at any level in defense of Free China and the Pescadores. The Resolution bolstered the morale of the Chinese nationalists and signaled to Beijing that the US was committed to holding the line.
During the First Taiwan Strait crisis, Eisenhower threatened to use nuclear weapons against PRC military targets in Fujian. These threats prompted Mao Zedong to launch China's nuclear weapons program. He authorized a series of bomb tests labeled Operation Teapot. Nevertheless, he left the Chinese communists guessing as to the exact nature of his nuclear response. This allowed Eisenhower to accomplish all of his objectives—the end of this communist encroachment, the retention of the Islands by the Chinese nationalists and continued peace. Defense of the Republic of China from an invasion remains a core American policy.
China invited some American reporters to China in 1956, having previously ousted American reporters after the PRC's founding. Eisenhower upheld the U.S. ban on travel to China. U.S. newspapers, including The New York Times and The Washington Post criticized the Eisenhower's administration decision as antithetical to the free press.
Southeast Asia
Further information: United States in the Vietnam WarEarly in 1953, the French asked Eisenhower for help in French Indochina against the Communists, supplied from China, who were fighting the First Indochina War. Eisenhower sent Lt. General John W. O'Daniel to Vietnam to assess the French forces there. Chief of Staff Matthew Ridgway dissuaded the President from intervening by presenting a comprehensive estimate of the massive military deployment that would be necessary. Eisenhower stated prophetically that "this war would absorb our troops by divisions."
Eisenhower did provide France with bombers and non-combat personnel. After a few months with no success by the French, he added other aircraft to drop napalm for clearing purposes. Further requests for assistance from the French were agreed to but only on conditions Eisenhower knew were impossible to meet – allied participation and congressional approval. When the French fortress of Dien Bien Phu fell to the Vietnamese Communists in May 1954, Eisenhower refused to intervene despite urging from the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs, the Vice President and the head of NCS.
Eisenhower responded to the French defeat with the formation of the SEATO (Southeast Asia Treaty Organization) Alliance with the UK, France, New Zealand and Australia in defense of Vietnam against communism. At that time the French and Chinese reconvened the Geneva peace talks; Eisenhower agreed the US would participate only as an observer. After France and the Communists agreed to a partition of Vietnam, Eisenhower rejected the agreement, offering military and economic aid to southern Vietnam. Ambrose argues that Eisenhower, by not participating in the Geneva agreement, had kept the US out of Vietnam; nevertheless, with the formation of SEATO, he had put the US back into the conflict.
In late 1954, Gen. J. Lawton Collins was made ambassador to "Free Vietnam", effectively elevating the country to sovereign status. Collins' instructions were to support the leader Ngo Dinh Diem in subverting communism, by helping him to build an army and wage a military campaign. In February 1955, Eisenhower dispatched the first American soldiers to Vietnam as military advisors to Diem's army. After Diem announced the formation of the Republic of Vietnam (commonly known as South Vietnam) in October, Eisenhower immediately recognized the new state and offered military, economic, and technical assistance.
In the years that followed, Eisenhower increased the number of US military advisors in South Vietnam to 900. This was due to North Vietnam's support of "uprisings" in the south and concern the nation would fall. In May 1957 Diem, then President of South Vietnam, made a state visit to the United States. Eisenhower pledged his continued support, and a parade was held in Diem's honor in New York City. Although Diem was publicly praised, in private Secretary of State John Foster Dulles conceded that Diem had been selected because there were no better alternatives.
After the election of November 1960, Eisenhower, in a briefing with John F. Kennedy, pointed out the communist threat in Southeast Asia as requiring prioritization in the next administration. Eisenhower told Kennedy he considered Laos "the cork in the bottle" with regard to the regional threat.
Legitimation of Francoist Spain
Main article: Pact of Madrid
The Pact of Madrid, signed on September 23, 1953, by Francoist Spain and the United States, was a significant effort to break international isolation of Spain, together with the Concordat of 1953. This development came at a time when other victorious Allies and much of the rest of the world remained hostile to a fascist regime sympathetic to the cause of the former Axis powers and established with Nazi assistance. This accord took the form of three separate executive agreements that pledged the United States to furnish economic and military aid to Spain.
Middle East and Eisenhower doctrine

Even before he was inaugurated Eisenhower accepted a request from the British government to restore the Shah of Iran (Mohammad Reza Pahlavi) to power. He therefore authorized the CIA to overthrow Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh. This resulted in increased strategic control over Iranian oil by US and British companies.
In November 1956, Eisenhower forced an end to the combined British, French and Israeli invasion of Egypt in response to the Suez Crisis, receiving praise from Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser. Simultaneously he condemned the brutal Soviet invasion of Hungary in response to the Hungarian Revolution of 1956. He publicly disavowed his allies at the United Nations and used financial and diplomatic pressure to make them withdraw from Egypt. Eisenhower explicitly defended his strong position against Britain and France in his memoirs, published in 1965.
After the Suez Crisis, the United States became the protector of unstable friendly governments in the Middle East via the "Eisenhower Doctrine". Designed by Secretary of State Dulles, it held the US would be "prepared to use armed force ... aggression from any country controlled by international communism". Further, the US would provide economic and military aid and, if necessary, use military force to stop the spread of communism in the Middle East.
Eisenhower applied the doctrine in 1957–1958 by dispensing economic aid to Jordan, and by encouraging Syria's neighbors to consider military operations against it. More dramatically, in July 1958, he sent 15,000 Marines and soldiers to Lebanon as part of Operation Blue Bat, a non-combat peacekeeping mission to stabilize the pro-Western government and to prevent a radical revolution. The Marines departed three months later. Washington considered the military intervention successful since it brought about regional stability, weakened Soviet influence, and intimidated the Egyptian and Syrian governments, whose anti-West political position had hardened after the Suez Crisis.
Most Arab countries were skeptical about the "Eisenhower doctrine" because they considered "Zionist imperialism" the real danger. However, they did take the opportunity to obtain free money and weapons. Egypt and Syria, supported by the Soviet Union, openly opposed the initiative. However, Egypt received American aid until the Six-Day War in 1967.
As the Cold War deepened, Dulles sought to isolate the Soviet Union by building regional alliances against it. Critics sometimes called it "pacto-mania".
1960 U-2 incident
This section is an excerpt from 1960 U-2 incident.
On 1 May 1960, a United States U-2 spy plane was shot down by the Soviet Air Defence Forces while conducting photographic aerial reconnaissance deep inside Soviet territory. Flown by American pilot Francis Gary Powers, the aircraft had taken off from Peshawar, Pakistan, and crashed near Sverdlovsk (present-day Yekaterinburg), after being hit by a surface-to-air missile. Powers parachuted to the ground and was captured.
Initially, American authorities acknowledged the incident as the loss of a civilian weather research aircraft operated by NASA, but were forced to admit the mission's true purpose a few days later after the Soviet government produced the captured pilot and parts of the U-2's surveillance equipment, including photographs of Soviet military bases.
The incident occurred during the tenures of American president Dwight D. Eisenhower and Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev, around two weeks before the scheduled opening of an east–west summit in Paris, France. Khrushchev and Eisenhower had met face-to-face at Camp David in Maryland in September 1959, and the seeming thaw in U.S.-Soviet relations had raised hopes globally for a peaceful resolution to the Cold War. The U-2 incident shattered the amiable "Spirit of Camp David" that had prevailed for eight months, prompting the cancellation of the summit in Paris and embarrassing the U.S. on the international stage. The Pakistani government issued a formal apology to the Soviet Union for its role in the mission.
Following his capture, Powers was convicted of espionage and sentenced to three years of imprisonment plus seven years of hard labour; he was released two years later, in February 1962, in a prisoner exchange for Soviet intelligence officer Rudolf Abel.Civil rights
While President Truman's 1948 Executive Order 9981 had begun the process of desegregating the Armed Forces, actual implementation had been slow. Eisenhower made clear his stance in his first State of the Union address in February 1953, saying "I propose to use whatever authority exists in the office of the President to end segregation in the District of Columbia, including the Federal Government, and any segregation in the Armed Forces". When he encountered opposition from the services, he used government control of military spending to force the change through, stating "Wherever Federal Funds are expended ..., I do not see how any American can justify ... a discrimination in the expenditure of those funds". When Robert B. Anderson, Eisenhower's first Secretary of the Navy, argued that the US Navy must recognize the "customs and usages prevailing in certain geographic areas of our country which the Navy had no part in creating," Eisenhower overruled him: "We have not taken and we shall not take a single backward step. There must be no second class citizens in this country."
The administration declared racial discrimination a national security issue, as Communists around the world used the racial discrimination and history of violence in the US as a point of propaganda attack.
Eisenhower told Washington, D.C. officials to make the city a model for the rest of the country in integrating black and white public-school children. He proposed to Congress the Civil Rights Act of 1957 and of 1960 and signed those acts into law. The 1957 act for the first time established a permanent civil rights office inside the Justice Department and a Civil Rights Commission to hear testimony about abuses of voting rights. Although both acts were much weaker than subsequent civil rights legislation, they constituted the first significant civil rights acts since 1875.
In 1957, Arkansas refused to honor a federal court order to integrate their public school system stemming from the Brown decision. Eisenhower demanded that Arkansas governor Orval Faubus obey the court order. When Faubus balked, the president placed the Arkansas National Guard under federal control and sent in the 101st Airborne Division. They protected nine black students' entry to Little Rock Central High School, an all-white public school, marking the first time since the Reconstruction Era the federal government had used federal troops in the South to enforce the Constitution. Martin Luther King Jr. wrote to Eisenhower to thank him for his actions, writing "The overwhelming majority of southerners, Negro and white, stand firmly behind your resolute action to restore law and order in Little Rock".
Eisenhower's administration contributed to the McCarthyist Lavender Scare with Eisenhower issuing Executive Order 10450 in 1953. During Eisenhower's presidency thousands of lesbian and gay applicants were barred from federal employment and over 5,000 federal employees were fired under suspicions of being homosexual. From 1947 to 1961 the number of firings based on sexual orientation were far greater than those for membership in the Communist Party, and government officials intentionally campaigned to make "homosexual" synonymous with "Communist traitor" such that LGBT people were treated as a national security threat.
Relations with Congress

Eisenhower had a Republican Congress for only his first two years in office; in the Senate, Republicans held the majority by a one-vote margin. Despite being Eisenhower's political opponent for the 1952 Republican presidential nomination, Senator Majority Leader Robert A. Taft assisted Eisenhower a great deal by promoting the President's proposals among the "Old Guard" Republican Senators. Taft's death in July 1953—six months into Eisenhower's presidency—affected Eisenhower both personally and professionally. The President noted he had lost "a dear friend" with Taft's passing. Eisenhower disliked Taft's successor as Majority Leader, Senator William Knowland, and the relationship between the two men led to tension between the Senate and the White House.
This prevented Eisenhower from openly condemning Joseph McCarthy's highly criticized methods against communism. To facilitate relations with Congress, Eisenhower decided to ignore McCarthy's controversies and thereby deprive them of more energy from the involvement of the White House. This position drew criticism from a number of corners. In late 1953, McCarthy declared on national television that the employment of communists within the government was a menace and would be a pivotal issue in the 1954 Senate elections. Eisenhower was urged to respond directly and specify the various measures he had taken to purge the government of communists.
Among Eisenhower's objectives in not directly confronting McCarthy was to prevent McCarthy from dragging the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) into McCarthy's witchhunt, which might interfere with the AEC's work on hydrogen bombs and other weapons programs. In December 1953, Eisenhower learned that nuclear scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer had been accused of being a spy for the Soviet Union. Although Eisenhower never really believed these allegations, in January 1954 he ordered that "a blank wall" be placed between Oppenheimer and all defense-related activities. The Oppenheimer security hearing later that year resulted in the physicist losing his security clearance. The matter was controversial at the time and remained so in later years, with Oppenheimer achieving a certain martyrdom. The case would reflect poorly on Eisenhower, but the president had never examined it in any detail and had instead relied excessively upon the advice of his subordinates, especially that of AEC chairman Lewis Strauss. Eisenhower later suffered a major political defeat when his nomination of Strauss to be Secretary of Commerce was defeated in the Senate in 1959, in part due to Strauss's role in the Oppenheimer matter.
In May 1955, McCarthy threatened to issue subpoenas to White House personnel. Eisenhower was furious, and issued an order as follows: "It is essential to efficient and effective administration that employees of the Executive Branch be in a position to be completely candid in advising with each other on official matters ... it is not in the public interest that any of their conversations or communications, or any documents or reproductions, concerning such advice be disclosed." This was an unprecedented step by Eisenhower to protect communication beyond the confines of a cabinet meeting, and soon became a tradition known as executive privilege. Eisenhower's denial of McCarthy's access to his staff reduced McCarthy's hearings to rants about trivial matters and contributed to his ultimate downfall.
In early 1954, the Old Guard put forward a constitutional amendment, called the Bricker Amendment, which would curtail international agreements by the Chief Executive, such as the Yalta Agreements. Eisenhower opposed the measure. The Old Guard agreed with Eisenhower on the development and ownership of nuclear reactors by private enterprises, which the Democrats opposed. The President succeeded in getting legislation creating a system of licensure for nuclear plants by the AEC.
The Democrats gained a majority in both houses in the 1954 election. Eisenhower had to work with the Democratic Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson (later US president) in the Senate and Speaker Sam Rayburn in the House. Joe Martin, the Republican Speaker from 1947 to 1949 and again from 1953 to 1955, wrote that Eisenhower "never surrounded himself with assistants who could solve political problems with professional skill. There were exceptions, Leonard W. Hall, for example, who as chairman of the Republican National Committee tried to open the administration's eyes to the political facts of life, with occasional success. However, these exceptions were not enough to right the balance."
Speaker Martin concluded that Eisenhower worked too much through subordinates in dealing with Congress, with results, "often the reverse of what he has desired" because Members of Congress, "resent having some young fellow who was picked up by the White House without ever having been elected to office himself coming around and telling them 'The Chief wants this'. The administration never made use of many Republicans of consequence whose services in one form or another would have been available for the asking."
Eisenhower was relatively active with legislative vetoes, with 181 vetoes of which only two were overridden.
Judicial appointments
Supreme Court
Main articles: Dwight D. Eisenhower Supreme Court candidates and Dwight D. Eisenhower judicial appointmentsEisenhower appointed the following Justices to the Supreme Court of the United States:
- Earl Warren, 1953 (Chief Justice)
- John Marshall Harlan II, 1954
- William J. Brennan, 1956
- Charles Evans Whittaker, 1957
- Potter Stewart, 1958
Whittaker was unsuited for the role and retired in 1962, after Eisenhower's presidency had ended. Stewart and Harlan were conservative Republicans, while Brennan was a Democrat who became a leading voice for liberalism. In selecting a Chief Justice, Eisenhower looked for an experienced jurist who could appeal to liberals in the party as well as law-and-order conservatives, noting privately that Warren "represents the kind of political, economic, and social thinking that I believe we need on the Supreme Court ... He has a national name for integrity, uprightness, and courage that, again, I believe we need on the Court".
States admitted to the Union
Two states were admitted to the Union during Eisenhower's presidency.
- Alaska – January 3, 1959 (49th state)
- Hawaii – August 21, 1959 (50th state)
Health issues
Eisenhower began chain smoking cigarettes at West Point, often three or four packs a day. He joked that he "gave an order" to stop cold turkey in 1949. However, Evan Thomas says the true story was more complex. At first, he removed cigarettes and ashtrays, but that did not work. He told a friend:
I decided to make a game of the whole business and try to achieve a feeling of some superiority ... So I stuffed cigarettes in every pocket, put them around my office on the desk ... made it a practice to offer a cigarette to anyone who came in ... while mentally reminding myself as I sat down, "I do not have to do what that poor fellow is doing."
He was the first president to release information about his health and medical records while in office, but people around him deliberately misled the public about his health. On September 24, 1955, while vacationing in Colorado, he had a serious heart attack. While convalescing at Building 500 Howard McCrum Snyder, his personal physician, misdiagnosed the symptoms as indigestion, and failed to call in help that was urgently needed. Snyder later falsified his own records to cover his blunder and to allow Eisenhower to imply that he was healthy enough to do his job.
The heart attack required six weeks' hospitalization, during which time Nixon, Dulles, and Sherman Adams assumed administrative duties and provided communication with the president. He was treated by Paul Dudley White, a cardiologist with a national reputation, who regularly informed the press of the president's progress. His physician recommended a second presidential term as essential to his recovery.
As a consequence of his heart attack Eisenhower developed a left ventricular aneurysm, which caused a mild stroke during a cabinet meeting on November 25, 1957, when Eisenhower suddenly found himself unable to move his right hand or to speak. The president also suffered from Crohn's disease, which necessitated surgery for a bowel obstruction on June 9, 1956. To treat the intestinal block, surgeons bypassed about ten inches of his small intestine. His scheduled meeting with Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was postponed so he could recover at his farm. He was still recovering from this operation during the Suez Crisis. Eisenhower's health issues forced him to give up smoking and make some changes to his diet, but he still drank alcohol. During a visit to England, he complained of dizziness and had to have his blood pressure checked on August 29, 1959; however, before dinner at prime ministerial manor house Chequers on the next day his physician, General Howard Snyder, recalled that Eisenhower "drank several gin-and-tonics, and one or two gins on the rocks ... three or four wines with the dinner".
Eisenhower's health during the last three years of his second term in office was relatively good. After leaving the White House, he suffered several additional and ultimately crippling heart attacks. A severe heart attack in August 1965 largely ended his participation in public affairs. On December 12, 1966, his gallbladder was removed, containing 16 gallstones. After Eisenhower's death in 1969, an autopsy revealed an undiagnosed adrenal pheochromocytoma, a benign adrenalin-secreting tumor that may have made him more vulnerable to heart disease. Eisenhower had seven heart attacks from 1955 until his death.
End of presidency
The 22nd Amendment to the US Constitution, which set a two-term limit on the presidency, was ratified in 1951. Eisenhower was the first president constitutionally prevented from serving a third term.
Eisenhower was also the first outgoing president to come under the protection of the Former Presidents Act. Under the act, Eisenhower was entitled to a lifetime pension, state-provided staff and a Secret Service security detail.
In the 1960 election to choose his successor, Eisenhower endorsed Nixon over Democrat John F. Kennedy. He told friends, "I will do almost anything to avoid turning my chair and country over to Kennedy." He actively campaigned for Nixon in the final days, although he may have done Nixon some harm. When asked by reporters at the end of a televised press conference to list one of Nixon's policy ideas he had adopted, Eisenhower joked, "If you give me a week, I might think of one. I don't remember." Kennedy's campaign used the quote in one of its campaign commercials. Nixon narrowly lost to Kennedy. Eisenhower, who was, at 70, the oldest president to date, was succeeded by 43-year-old Kennedy, the youngest elected president.
It was originally intended for Eisenhower to have a more active role in the campaign as he wanted to respond to attacks Kennedy made on his administration. However, First Lady Mamie Eisenhower expressed concern to Second Lady Pat Nixon about the strain campaigning would put on his heart, and wanted the president to withdraw, without letting him know of her intervention. Vice President Nixon himself was informed by White House physician Major General Howard Snyder that he could not approve a heavy campaign schedule for the president, whose health problems had been exacerbated by Kennedy's attacks. Nixon then convinced Eisenhower not to go ahead with the expanded campaign schedule and limit himself to the original schedule. Nixon reflected that if Eisenhower had carried out his expanded campaign schedule, he might have had a decisive impact on the outcome of the election, especially in states that Kennedy won with razor-thin margins. Mamie did not tell Dwight why Nixon changed his mind on Dwight's campaigning until years later.

On January 17, 1961, Eisenhower gave his final televised Address to the Nation from the Oval Office. In his farewell speech, Eisenhower raised the issue of the Cold War and role of the armed forces. He described the Cold War: "We face a hostile ideology global in scope, atheistic in character, ruthless in purpose and insidious in method ..." and warned about what he saw as unjustified government spending proposals. He continued with a warning that "we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military–industrial complex." Eisenhower elaborated, "we recognize the imperative need for this development ... the potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist ... Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together."
Because of legal issues related to holding a military rank while in a civilian office, Eisenhower had resigned his permanent commission as General of the Army before assuming the presidency. Upon completion of his presidential term, his commission was reactivated by Congress.
Post-presidency (1961–1969)



Following the presidency, Eisenhower moved to the place where he and Mamie had spent much of their post-war time, a working farm adjacent to the battlefield at Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, 70 miles (110 km) from his ancestral home in Elizabethville, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania. They also maintained a retirement home in Palm Desert, California.
After leaving office, Eisenhower did not completely retreat from political life. He flew to San Antonio, where he had been stationed years earlier, to support John W. Goode, the unsuccessful Republican candidate against the Democrat Henry B. Gonzalez for Texas's 20th congressional district seat. He addressed the 1964 Republican National Convention, in San Francisco, and appeared with party nominee Barry Goldwater in a campaign commercial. That endorsement came somewhat reluctantly, because Goldwater had in the late 1950s criticized Eisenhower's administration as "a dime-store New Deal". On January 20, 1969, the day Nixon was inaugurated as President, Eisenhower issued a statement praising his former vice president and calling it a "day for rejoicing".
Death
At 12:25 p.m. on March 28, 1969, Eisenhower died from congestive heart failure at Walter Reed Army Medical Center in Washington, D.C., at age 78. His last words:
"I've always loved my wife, my children, and my grandchildren, and I've always loved my country. I want to go. God, take me."
The following day, his body was moved to the Washington National Cathedral's Bethlehem Chapel, where he lay in repose for 28 hours. He was then transported to the United States Capitol, where he lay in state in the Capitol Rotunda on March 30 and 31. A state funeral was conducted at the Washington National Cathedral on March 31. The president and First Lady, Richard and Pat Nixon, attended, as did former president Lyndon B. Johnson. Former President Harry S. Truman was unable to attend due to having vacation. Also among the 2,000 guests that were invited were the UN Secretary-General U Thant and 191 foreign delegates from 78 countries, including 10 foreign heads of state and government. Guests included President Charles de Gaulle of France, who was in the United States for the first time since the state funeral of John F. Kennedy, Chancellor Kurt-Georg Kiesinger of West Germany, King Baudouin of Belgium and Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi of Iran.
The service included the singing of Faure's "The Palms", and the playing of the hymn "Onward, Christian Soldiers".
That evening, Eisenhower's body was placed onto a special funeral train for its journey from the capital to his hometown of Abilene, Kansas. First incorporated into President Abraham Lincoln's funeral in 1865, a funeral train would not be part of a US state funeral again until 2018. on 2 April 1969 Eisenhower is buried inside the Place of Meditation, the chapel on the grounds of the Eisenhower Presidential Center in Abilene. As requested, he was buried in a Government Issue casket, wearing his World War II uniform, decorated with Army Distinguished Service Medal with three oak leaf clusters, Navy Distinguished Service Medal, and the Legion of Merit. Buried alongside Eisenhower are his son Doud, who died at age 3 in 1921, and wife Mamie, who died in 1979.
President Richard Nixon eulogized Eisenhower in 1969, saying:
Some men are considered great because they lead great armies or they lead powerful nations. For eight years now, Dwight Eisenhower has neither commanded an army nor led a nation; and yet he remained through his final days the world's most admired and respected man, truly the first citizen of the world.
Legacy and memory
Public and scholarly assessments

During his two terms as president, Eisenhower's approval ratings were consistently high, only briefly falling below 50 percent in 1958 and again in 1960. His overall average of 63 percent in the Gallup poll remains the second highest in history. With the popularity of his successor, John F. Kennedy, Eisenhower's reputation declined in the years after he left office. He was widely seen by critics as an inactive, uninspiring, golf-playing president, which was in stark contrast to Kennedy, who was 26 years his junior. Critics also compared Eisenhower with the likes of Calvin Coolidge as a "do nothing president". Despite his unprecedented use of Army troops to enforce a federal desegregation order at Central High School in Little Rock, Eisenhower was criticized for his reluctance to support the civil rights movement to the degree that activists wanted. Eisenhower also attracted criticism for his handling of the 1960 U-2 incident and the associated international embarrassment, for the Soviet Union's perceived leadership in the nuclear arms race and the Space Race, and for his failure to publicly oppose McCarthyism. In particular, Eisenhower was criticized for failing to defend George C. Marshall from attacks by Joseph McCarthy, though he privately deplored McCarthy's tactics.
Following the access of Eisenhower's private papers, his reputation changed amongst presidential historians. Historian John Lewis Gaddis has summarized a more recent turnaround in evaluations by historians:
Historians long ago abandoned the view that Eisenhower's was a failed presidency. He did, after all, end the Korean War without getting into any others. He stabilized, and did not escalate, the Soviet–American rivalry. He strengthened European alliances while withdrawing support from European colonialism. He rescued the Republican Party from isolationism and McCarthyism. He maintained prosperity, balanced the budget, promoted technological innovation, facilitated (if reluctantly) the civil rights movement and warned, in the most memorable farewell address since Washington's, of a "military–industrial complex" that could endanger the nation's liberties. Not until Reagan would another president leave office with so strong a sense of having accomplished what he set out to do.
Since 1982, scholars and historians have typically ranked Eisenhower among the ten best U.S. presidents. Rexford Tugwell, a top aide to Franklin Roosevelt, referred to Eisenhower as "the least partisan president since George Washington." Historian Garry Wills called Eisenhower "a political genius" for making difficult foreign policy goals "look easy" to the general public to prevent further stress.

Political practice
Although conservatism in politics was strong during the 1950s, and Eisenhower generally espoused conservative sentiments, his administration concerned itself mostly with foreign affairs and pursued a hands-off domestic policy. Eisenhower looked to moderation and cooperation as a means of governance, which he dubbed "The Middle Way".
Although he sought to slow or contain the New Deal and other federal programs, he did not attempt to repeal them outright. In doing so, Eisenhower was popular among the liberal wing of the Republican Party. Conservative critics of his administration thought that he did not do enough to advance the goals of the right; according to Hans Morgenthau, "Eisenhower's victories were but accidents without consequence in the history of the Republican party."
Since the 19th century, many if not all presidents were assisted by a central figure or "gatekeeper", sometimes described as the president's private secretary, sometimes with no official title. Eisenhower formalized this role, introducing the office of White House Chief of Staff – an idea he borrowed from the United States Army. Every president after Lyndon Johnson has appointed staff to this position.
As president, Eisenhower also initiated the "up or out" policy that still prevails in the US military. Officers who are passed over for promotion twice are then usually honorably but quickly discharged to make way for younger and more able officers.
On December 20, 1944, Eisenhower was appointed to the rank of General of the Army, placing him in the company of George Marshall, Henry "Hap" Arnold, and Douglas MacArthur, the only four men to achieve the rank in World War II. Along with Omar Bradley, they were the only five men to achieve the rank since the August 5, 1888, death of Philip Sheridan, and the only five men to hold the rank of five-star general. The rank was created by an Act of Congress on a temporary basis, when Public Law 78-482 was passed on December 14, 1944, as a temporary rank, subject to reversion to permanent rank six months after the end of the war. The temporary rank was declared permanent on March 23, 1946, by Public Law 333 of the 79th Congress, which also awarded full pay and allowances in the grade to those on the retired list. It was created to give the most senior American commanders parity of rank with their British counterparts holding the ranks of field marshal and admiral of the fleet.

 Frank Gasparro's obverse design (left) and reverse design (right) of the Presidential Medal of Appreciation award during Eisenhower's official visit to the State of Hawaii from June 20 to 25, 1960
Frank Gasparro's obverse design (left) and reverse design (right) of the Presidential Medal of Appreciation award during Eisenhower's official visit to the State of Hawaii from June 20 to 25, 1960
Eisenhower founded People to People International in 1956, believing that citizen interaction would promote cultural interaction and world peace. The program includes a student ambassador component, which sends American youth on educational trips to other countries.
During his second term as president, Eisenhower awarded a series of specially designed US Mint presidential appreciation medals. Eisenhower presented the medal to individuals as an expression of his appreciation. The development of the appreciation medals was initiated by the White House and executed by the United States Mint, through the Philadelphia Mint. The medals were struck from September 1958 through October 1960. A total of twenty designs are cataloged with a total mintage of 9,858. Prior to the end of his second term as president, 1,451 medals were turned in to the Bureau of the Mint and destroyed. The Eisenhower appreciation medals are part of the Presidential Medal of Appreciation Award Medal Series.
Tributes and memorials
Main article: List of memorials to Dwight D. Eisenhower
The Interstate Highway System is officially known as the "Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways". It was inspired in part by Eisenhower's experiences in World War II, where he recognized the advantages of the autobahn system in Germany. Commemorative signs reading "Eisenhower Interstate System" and bearing Eisenhower's permanent 5-star rank insignia were introduced in 1993 and now are displayed throughout the Interstate System. Several highways are also named for him, including the Eisenhower Expressway (Interstate 290) near Chicago, the Eisenhower Tunnel on Interstate 70 west of Denver, and Interstate 80 in California.
Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy is a senior war college of the Department of Defense's National Defense University in Washington, DC. Eisenhower graduated from this school when it was known as the Army Industrial College.
Eisenhower was honored on the Eisenhower dollar, minted from 1971 to 1978. His centenary was honored on the Eisenhower commemorative dollar issued in 1990.
In 1969 four major record companies – ABC Records, MGM Records, Buddha Records and Caedmon Audio – released tribute albums in Eisenhower's honor.
In 1999, the United States Congress created the Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial Commission, to create an enduring national memorial in Washington, D.C. In 2009 the commission chose the architect Frank Gehry to design the memorial. The groundbreaking ceremony of the memorial was held on November 3, 2017, and was dedicated on September 17, 2020. It stands on a 4-acre (1.6 ha) site near the National Mall on Maryland Avenue, across the street from the National Air and Space Museum.
In December 1999 he was listed on Gallup's List of Most Widely Admired People of the 20th century. In 2009 he was named to the World Golf Hall of Fame in the Lifetime Achievement category for his contributions to the sport. In 1973, he was inducted into the Hall of Great Westerners of the National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum. On 27 October 2023, Fort Gordon was redesignated Fort Eisenhower.
Honors
Awards and decorations


Freedom of the City
Eisenhower received the Freedom honor from several locations, including:
 Freedom of the City of London on June 12, 1945
Freedom of the City of London on June 12, 1945 Freedom of the City of Belfast on August 24, 1945
Freedom of the City of Belfast on August 24, 1945 Freedom of the City of Edinburgh in 1946
Freedom of the City of Edinburgh in 1946 Freedom of the Burgh of Maybole in October 1946
Freedom of the Burgh of Maybole in October 1946
Honorary degrees
Eisenhower received many honorary degrees from universities and colleges around the world. These included:
| Location | Date | School | Degree | Gave commencement address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| August 24, 1945 | Queen's University Belfast | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1945 | University of Oxford | Doctor of Civil Law (DCL) | ||
| 1946 | Harvard University | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1946 | Gettysburg College | Doctorate | ||
| 1946 | University of Toronto | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1947 | University of Pennsylvania | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1948 | Yale University | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1950 | Hofstra University | Doctorate | ||
| June 14, 1953 | Dartmouth College | Doctorate | Yes | |
| November 19, 1953 | Catholic University of America | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1953 | College of William and Mary | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1954 | Northwestern University | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| June 7, 1954 | Washington College | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | Yes | |
| 1958 | Johns Hopkins University | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| December 17, 1959 | University of Delhi | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| June 5, 1960 | University of Notre Dame | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| June 20, 1964 | Bard College | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| 1965 | Grinnell College | Doctor of Laws (LL.D) | ||
| October 5, 1965 | Ohio University | Doctor of Humane Letters (DHL) | Yes |
Promotions
| No insignia | Cadet, United States Military Academy: June 14, 1911 |
| No pin insignia in 1915 | Second Lieutenant, Regular Army: June 12, 1915 |
| First Lieutenant, Regular Army: July 1, 1916 | |
| Captain, Regular Army: May 15, 1917 | |
| Major, National Army: June 17, 1918 | |
| Lieutenant Colonel, National Army: October 20, 1918 | |
| Captain, Regular Army: June 30, 1920 (Reverted to permanent rank.) | |
| Major, Regular Army: July 2, 1920 | |
| Captain, Regular Army: November 4, 1922 (Discharged as major and appointed as captain due to reduction of Army.) | |
| Major, Regular Army: August 26, 1924 | |
| Lieutenant Colonel, Regular Army: July 1, 1936 | |
| Colonel, Army of the United States: March 6, 1941 | |
| Brigadier General, Army of the United States: September 29, 1941 (temporary) | |
| Major General, Army of the United States: March 27, 1942 (temporary) | |
| Lieutenant General, Army of the United States: July 7, 1942 (temporary) | |
| General, Army of the United States: February 11, 1943 (temporary) | |
| Brigadier General, Regular Army: August 30, 1943 | |
| Major General, Regular Army: August 30, 1943 | |

|
General of the Army, Army of the United States: December 20, 1944 |

|
General of the Army, Regular Army: April 11, 1946 |
See also
- "And I don't care what it is", phrase on religion by Eisenhower, 1952
- Atoms for Peace, speech to the UN General Assembly, 1953
- Committee on Scientists and Engineers
- Eisenhower baseball controversy
- Eisenhower method for time management
- Eisenhower National Historic Site
- Eisenhower Presidential Center
- Ike: Countdown to D-Day, American television film, 2004
- Kay Summersby, chauffeur and secretary
- People to People Student Ambassador Program
General:
- Historical rankings of presidents of the United States
- History of the United States (1945–1964)
- List of presidents of the United States
- List of presidents of the United States by previous experience
Notes
- Pronounced (/ˈaɪzənhaʊ.ər/ EYE-zən-how-ər
- For the 1946 United Nations condemnation of the Francoist regime, see "Spanish Question"
- Redesignation to Fort Eisenhower was on 27 October 2023.
References
Citations
- Ferrell, Robert H. (1990). "Eisenhower Was a Democrat" (PDF). Kansas History. 13: 134. Retrieved June 2, 2024.
- "The Eisenhowers". Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library, Museum and Boyhood Home. Archived from the original on August 18, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2021.
- ^ "Post-presidential years". The Eisenhower Presidential Library and Museum. Archived from the original on October 23, 2013. Retrieved September 5, 2012.
- ^ Barnett, Lincoln (November 9, 1942). "General "Ike" Eisenhower". Life. p. 112. Retrieved May 31, 2011.
- Korda, Michael (2007). "Ike: An American Hero". Harper Collins. p. 63. ISBN 9780061744969. Retrieved July 22, 2012.
- ^ Ambrose 1983, pp. 16–18
- Ambrose 1983, p. 19
- D'Este, Carlo (2003). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life. Macmillan. pp. 21–22. ISBN 0805056874. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 18
- Eisenhower, Dwight David "Ike"., biography on World War II graves website
- Ambrose 1983, p. 22
- D'Este, Carlo (2003). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life. Macmillan. p. 31. ISBN 0805056874. Retrieved June 12, 2020.
- ^ Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1967). At Ease: Stories I Tell to Friends, Garden City, New York, Doubleday & Company, Inc.
- D'Este, Carlo (2002). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life, p. 25.
- "Getting on the Right TRRACC" (PDF). Lesson Plans: The Molding of a Leader. Eisenhower National Historic Site. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 26, 2014. Retrieved April 27, 2013.
... Ike spent his weekends at Davis's camp on the Smoky Hill River.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 32
- Ambrose 1983, p. 25
- ^ "Faith Staked Down" Archived August 20, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, Time, February 9, 1953.
- Bergman, Jerry. "Steeped in Religion: President Eisenhower and the Influence of the Jehovah's Witnesses", Kansas History (Autumn 1998).
- D'Este, Carlo (2002). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life, p. 58.
- "Public School Products". Time. September 14, 1959.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 36
- Ambrose 1983, p. 37
- "Eisenhower: Soldier of Peace". Time. April 4, 1969. Archived from the original on May 24, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ "Biography: Dwight David Eisenhower". Eisenhower Foundation. Archived from the original on May 23, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 44–48
- "President Dwight D. Eisenhower Baseball Related Quotations". Baseball Almanac. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- "Eisenhower BOQ 1915". Fort Sam Houston. Archived from the original on July 17, 2007. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
- "Lt Eisenhower and Football Team". Fort Sam Houston. Archived from the original on July 17, 2007. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
- Botelho, Greg (July 15, 1912). "Roller-coaster life of Indian icon, sports' first star". CNN. Archived from the original on November 14, 2007. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- "Ike and the Team". Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ O'Connell, Robert L. (2022). Team America (1st ed.). HarperCollins. pp. 117–119. ISBN 9780062883322.
- "Dwight David Eisenhower". Internet Public Library. Archived from the original on May 11, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 56
- "We Remember". Sigma Beta Chi. Archived from the original on March 20, 2018. Retrieved March 20, 2018.
- Weingroff, Richard F. (March–April 2003). "The Man Who Changed America, Part I". Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- O'Connell, Robert L. (2022). Team America (1st ed.). HarperCollins. p. 122. ISBN 9780062883322.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 59–60
- Berger-Knorr, Lawrence. The Pennsylvania Relations of Dwight D. Eisenhower. p. 8.
- ^ Beckett, Wendy. "President Eisenhower: Painter" (PDF). White House History (21): 30–40. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 5, 2012.
- Weil, Martin; Langer, Emily (December 21, 2013). "John S.D. Eisenhower dies; historian and president's son was 91". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on August 17, 2017. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- "Camp David". Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library, Museum, and Boyhood Home. Archived from the original on July 6, 2017. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
Ike re-named it 'Camp David' in honor of his grandson David Eisenhower
- Owen 1999, pp. 165–167
- Owen 1999, p. 169
- Owen 1999, pp. 172–173
- Dodson, Marcida (November 17, 1990). "New Exhibit Offers a Look at Eisenhower the Artist". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on March 9, 2012. Retrieved January 13, 2012.
- Erickson, Hal (2013). "Angels in the Outfield (1951): Review Summary". Movies & TV Dept. The New York Times. Archived from the original on September 28, 2013. Retrieved September 25, 2013.
- Schaeper, Thomas J. (2010). Rhodes Scholars, Oxford, and the Creation of an American Elite. Berghahn Books. p. 210. ISBN 978-1845457211.
- Smith, Jean Edward (2012). Eisenhower in War and Peace. Random House. pp. 31–32, 38. ISBN 978-0679644293.
- "Manuel L. Quezon: 15 Mesmerizing Facts About Philippines' 2nd President". FilipiKnow. June 3, 2019. Retrieved October 27, 2020.
- Walker, Karen (June 2009). "D-Day Memories of the Bridge Player in Chief". ACBL District 8. Archived from the original on June 30, 2016. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 61–62
- Ambrose 1983, p. 62
- Ambrose 1983, p. 63
- Ambrose 1983, p. 65
- "Dwight David Eisenhower". MilitaryTimes.com. Sightline Media Group. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 68
- Ambrose 1983, p. 14
- Ambrose 1983, p. 69
- Sixsmith, E. K. G. (1973). Eisenhower, His Life and Campaigns. Conshohocken, PA Combined Publishing. p. 6.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 70–73
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 73–76
- Bender, Mark C. (1990). "Watershed at Leavenworth". U.S. Army Command and General Staff College. Archived from the original on October 29, 2008. Retrieved September 6, 2008.
- American President: An Online Reference Resource, Dwight David Eisenhower (1890–1969), "Life Before the Presidency", Archived June 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Miller Center of Public Affairs, University of Virginia.
- Trout, Steven (2010). On the Battlefield of Memory: The First World War and American Remembrance, 1919–1941. pp. xv–xxxii.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 82
- "General of the Army Dwight David Eisenhower". Army Historical Foundation. January 22, 2015. Archived from the original on March 24, 2016. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- "Dwight David Eisenhower, The Centennial". U.S. Army Center of Military History. 1990. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 88
- Wukovits, John F. (2006). Eisenhower. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-230-61394-2. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- D'Este, Carlo (2002). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life. Henry Holt & Co. p. 223. ISBN 0-8050-5687-4. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- Irish, Kerry. "Dwight Eisenhower and Douglas MacArthur in the Philippines: There Must Be a Day of Reckoning", Journal of Military History, April 2010, Vol. 74, Issue 2, pp. 439–473.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 94
- Villamor, Jesus; Snyder, Gerald (1968). They Never Surrendered. Vera-Reyes, Inc.
- "Dwight D. Eisenhower Pre-Presidential Papers, 1916–52" (PDF). Eisenhower Presidential Library. 1997. p. 74. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 9, 2017. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
references to Eisenhower's pilot's license
- Komons, Nick (August 1989). "unknown title". Air Progress: 62.
- Merrit, Jésus V. (1962). Our presidents: profiles in history. p. 77.
- Korda (2007), pp 239–243
- "The Eisenhowers: The General". Dwightdeisenhower.com. Archived from the original on December 30, 2010. Retrieved May 3, 2010.
- Ambrose 1983
- "Major General James E. Chaney". Air Force. U.S. Air Force. Archived from the original on June 13, 2018. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
From January 1942 to June 1942, he was the commanding general, U.S. Army Forces in the British Isles.
- Eisenhower lived in 'Telegraph Cottage', Warren Road, Coombe, from 1942 to 1944. In 1995, a plaque commemorating this was placed there by the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames. It can be seen at the north end of Warren Road.
- Huston, John W. (2002). Maj. Gen. John W. Huston, USAF (ed.). American Airpower Comes of Age: General Henry H. "Hap" Arnold's World War II Diaries. Air University Press. pp. 288, 312. ISBN 1585660930.
- Gallagher, Wes (December 1942). "Eisenhower Commanded Gibraltar". The Lewiston Daily Sun. Archived from the original on September 20, 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2013.
- Atkinson, An Army at Dawn, pp. 251–252.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 204–210
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 230–233
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 254–255
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 275–276
- Hitchcock, W (2018). The Age of Eisenhower. Simon & Schuster. pp. 21–23. ISBN 978-1439175668.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 280–281
- Ambrose 1983, p. 284
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 286–288
- Ambrose 1983, p. 289
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 250, 298
- Ambrose 1983, p. 278
- William Safire, Lend me your ears: great speeches in history (2004), p. 1143
- Grant 2001.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 340–354
- Jean Edward Smith, Eisenhower in War and Peace (2012) p. 451.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 375–380
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 395–406
- Hobbs 1999, p. 223
- Zink, Harold (1947). American Military Government in Germany, pp. 39–86
- Goedde, Petra. "From Villains to Victims: Fraternization and the Feminization of Germany, 1945–1947", Diplomatic History, Winter 1999, Vol. 23, Issue 1, pp. 1–19
- Tent, James F. (1982), Mission on the Rhine: Reeducation and Denazification in American-Occupied Germany
- Zink, Harold (1957). The United States in Germany, 1944–1955
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 421–425
- Goedde, Petra (2002). GIs and Germans: Culture, Gender and Foreign Relations, 1945–1949
- Richard Rhodes, The Making of the Atomic Bomb, with Rhodes citing a 1963 profile called "Ike on Ike, in Newsweek November 11, 1963
- ^ Ambrose 1983, pp. 432–452
- "Dwight Eisenhower in Poland". Polish Radio. Archived from the original on April 20, 2016. Retrieved April 3, 2016.
- ^ Pusey, Merlo J. (1956). Eisenhower, the President. Macmillan. pp. 1–6. Archived from the original on October 21, 2014. Retrieved November 7, 2013.
- "Truman Wrote of '48 Offer to Eisenhower Archived June 3, 2017, at the Wayback Machine" The New York Times, July 11, 2003.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 455–460
- "ΦΒΚ U.S. Presidents" (PDF). Phi Beta Kappa. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2016. Retrieved August 16, 2017.
- Ambrose 1983, ch. 24
- Crusade in Europe, Doubleday; 1st edition (1948), 559 pages, ISBN 1125300914
- ^ Owen 1999, pp. 171–172
- Pietrusza, David, 1948: Harry Truman's Victory and the Year That Transformed America, Union Square Publishing, 2011, p. 201
- ^ Jacobs 1993, p. 20
- Cook 1981, ch. 3
- Cook 1981, p. 79
- ^ Jacobs 1993, p. 18
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 140–141
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 145–146
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 162–164
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 168–169, 175
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 152, 238–242, 245–249
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 479–483
- ^ Young & Schilling 2019, p. ix
- ^ Jacobs 2001, pp. 235–236
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 484–485
- Jacobs 1993, pp. 17ff
- Jacobs 2001, pp. 251–254
- Jacobs 2001, p. 279
- Jacobs 2001, p. 299
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 502–511
- Ambrose 1983, p. 512
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 524–528
- Ambrose 1983, p. 530
- ^ Gibbs, Nancy (November 10, 2008). "When New President Meets Old, It's Not Always Pretty". Time. Archived from the original on November 11, 2008. Retrieved November 12, 2008.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 541–546
- Herbert H. Hyman, and Paul B. Sheatsley, "The political appeal of President Eisenhower." Public Opinion Quarterly 17.4 (1953): 443-460 online.
- Ambrose 1983, pp. 556–567
- Johnson, David K. (March 22, 2023). The Lavender Scare. The University of Chicago Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-0226825724.
- Ambrose 1983, p. 571
- Frum 2000, p. 7
- Crockett, Zachary (January 23, 2017). "Donald Trump is the only US president ever with no political or military experience". vox.com. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- Campbell, Angus; Converse, Philip L.; Miller, Warren E.; Stokes, Donald E. (1960). The American Voter. University of Chicago Press. p. 56. ISBN 978-0226092546.
- Ambrose 1984, p. 14
- Ambrose 1984, p. 24
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 20–25
- Ambrose 1984, p. 32
- Ambrose 1984, p. 43
- Ambrose 1984, p. 52
- Black, Allida; Hopkins, June; et al., eds. (2003). "Teaching Eleanor Roosevelt: Dwight Eisenhower". Eleanor Roosevelt National Historic Site. Archived from the original on January 5, 2007. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- Eisenhower, David; Julie Nixon Eisenhower (October 11, 2011). Going Home To Glory: A Memoir of Life with Dwight D. Eisenhower, 1961–1969. Simon and Schuster. p. 126. ISBN 978-1439190913.
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1959). Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States: Dwight D. Eisenhower. Best Books on. p. 270. ISBN 978-1623768300.
- Miller, James A. (November 21, 2007). "An inside look at Eisenhower's civil rights record". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on January 7, 2012.
- Mayer, Michael S. (2009). The Eisenhower Years. Facts On File. p. xii. ISBN 978-0-8160-5387-2.
- Ambrose 1984, p. 220
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 285–288
- Jean Edward Smith (2012). Eisenhower in War and Peace. Random House. pp. 674–683. ISBN 978-0679644293. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 321–325
- Ambrose 1984, p. 297
- Ambrose 1984, p. 25
- Ambrose 1984, p. 537
- "Atoms for Peace Speech". July 16, 2014.
- "Summary of the Atomic Energy Act". February 22, 2013.
- "The cracks are showing". The Economist. June 26, 2008. Archived from the original on November 20, 2007. Retrieved October 23, 2008.
- "The Last Week – The Road to War". USS Washington (BB-56). Archived from the original on March 23, 2007. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- "About the Author". USS Washington (BB-56). Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ "Interstate Highway System". Eisenhower Presidential Center. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved August 21, 2012.
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 301, 326
- "Internet History".
- "The Birth of the Internet | the Engines of Our Ingenuity".
- John M. Logsdon, "Exploring the Unknown: Selected Documents in the History of the U.S. Civil Space Program" (NASA; 1995)
- Logsdon, John M., and Lear, Linda J. Exploring the Unknown:Selected Documents in the History of the U.S. Civil Space Program/ Washington D.C.
- W. D. Kay, Defining NASA The Historical Debate Over the Agency's Mission, 2005.
- Parmet, Herbert S. Eisenhower and the American Crusades (New York: The Macmillan Company, 1972)
- Yankek Mieczkowski, Eisenhower's Sputnik Moment: The Race for Space and World Prestige (Cornell University Press; 2013)
- Peter J. Roman, Eisenhower and the Missile Gap (1996)
- The Presidents's Science Advisory Committee, "Report of the Ad Hoc Panel on Man-in-Space" December 16, 1960. NASA Historical Collection
- Greg Ward, "A Rough Guide History of the USA" (Penguin Group: London, 2003)
- Jackson, Michael Gordon (2005). "Beyond Brinkmanship: Eisenhower, Nuclear War Fighting, and Korea, 1953–1968". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 35 (1): 52–75. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5705.2004.00235.x. ISSN 0360-4918. JSTOR 27552659.
- Ambrose 1984, p. 51
- Jones, Matthew (2008). "Targeting China: U.S. Nuclear Planning and 'Massive Retaliation' in East Asia, 1953–1955". Journal of Cold War Studies. 10 (4): 37–65. doi:10.1162/jcws.2008.10.4.37. ISSN 1520-3972. S2CID 57564482.
- ^ Ambrose 1984, pp. 106–107
- Ambrose 1984, p. 173
- Zhai, Qiang (2000). "Crisis and Confrontations: Chinese-American Relations during the Eisenhower Administration". Journal of American-East Asian Relations. 9 (3/4): 221–249. doi:10.1163/187656100793645921.
- ^ Ambrose 1984, p. 231
- ^ Crean, Jeffrey (2024). The Fear of Chinese Power: an International History. New Approaches to International History series. London, UK: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1-350-23394-2.
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 245, 246
- Accinelli, Robert (1990). "Eisenhower, Congress, and the 1954–55 offshore island crisis". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 20 (2): 329–348. JSTOR 27550618.
- ^ Minami, Kazushi (2024). People's Diplomacy: How Americans and Chinese Transformed US-China Relations during the Cold War. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 9781501774157.
- Dunnigan, James and Nofi, Albert (1999), Dirty Little Secrets of the Vietnam War. St. Martins Press, p. 85.
- Ambrose 1984, p. 175
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 175–157
- Ambrose 1984, p. 185
- ^ Dunnigan, James and Nofi, Albert (1999), Dirty Little Secrets of the Vietnam War, p. 257
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 204–209
- Ambrose 1984, p. 215
- Anderson, David L. (1991). Trapped by Success: The Eisenhower Administration and Vietnam, 1953–1961. Columbia U.P. ISBN 978-0231515337.
- "Vietnam War". Swarthmore College Peace Collection. Archived from the original on August 3, 2016.
- Karnow, Stanley. (1991), Vietnam, A History, p. 230.
- Reeves, Richard (1993), President Kennedy: Profile of Power, p. 75.
- "Resolution 39 (I) of the UN General Assembly on the Spanish question".
- Eisenhower gave verbal approval to Secretary of State John Foster Dulles and to Director of Central Intelligence Allen Dulles to proceed with the coup; Ambrose, Eisenhower, Vol. 2: The President p. 111; Ambrose (1990), Eisenhower: Soldier and President, New York: Simon and Schuster, p. 333.
- Ambrose 1984, p. 129
- Kingseed, Cole (1995), Eisenhower and the Suez Crisis of 1956, ch. 6
- Dwight D. Eisenhower, Waging Peace: 1956–1961 (1965) p. 99
- Lahav, Pnina. "The Suez Crisis of 1956 and Its Aftermath: A Comparative Study of Constitutions, Use of Force, Diplomacy and International Relations". Boston University Law Review. 95.
- Isaac Alteras, Eisenhower and Israel: U.S.–Israeli Relations, 1953–1960 (1993), p. 296.
- ^ Little, Douglas (1996). "His finest hour? Eisenhower, Lebanon, and the 1958 Middle East Crisis". Diplomatic History. 20 (1): 27–54. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7709.1996.tb00251.x.
- Hahn, Peter L. (2006). "Securing the Middle East: The Eisenhower Doctrine of 1957". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 36 (1): 38–47. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5705.2006.00285.x.
- Navari, Cornelia (2000). Internationalism and the State in the Twentieth Century. Routledge. p. 316. ISBN 978-0415097475.
- State of the Union Address, February 2, 1953, Public Papers, 1953 pp. 30–31.
- "Eisenhower Press Conference, March 19, 1953". The American Presidency Project. Archived from the original on January 31, 2013. Retrieved October 17, 2012.
- Byrnes to DDE, August 27, 1953, Eisenhower Library"
- Dudziak, Mary L. (2002), Cold War Civil Rights: Race and the Image of American Democracy
- Eisenhower 1963, p. 230
- Parmet 1972, pp. 438–439
- Mayer, Michael S. (1989). "The Eisenhower Administration and the Civil Rights Act of 1957". Congress & the Presidency. 16 (2): 137–154. doi:10.1080/07343468909507929.
- Nichol, David (2007). A Matter of Justice: Eisenhower and the Beginning of the Civil Rights Revolution. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1416541509.
- to DDE, September 25, 1957, Eisenhower Library
- "An interview with David K. Johnson author of The Lavender Scare: The Cold War Persecution of Gays and Lesbians in the Federal Government". press.uchicago.edu. The University of Chicago. 2004. Archived from the original on December 20, 2017. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- Adkins, Judith (August 15, 2016). "'These People Are Frightened to Death' Congressional Investigations and the Lavender Scare". archives.gov. The U.S. National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on January 16, 2018. Retrieved January 15, 2018.
Most significantly, the 1950 congressional investigations and the Hoey committee's final report helped institutionalize discrimination by laying the groundwork for President Dwight D. Eisenhower's 1953 Executive Order #10450, 'Security Requirements for Government Employment.' That order explicitly added sexuality to the criteria used to determine suitability for federal employment.
- ^ Sears, Brad; Hunter, Nan D.; Mallory, Christy (September 2009). Documenting Discrimination on the Basis of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in State Employment (PDF). The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Law and Public Policy at the University of California Los Angeles School of Law. pp. 5–3. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 6, 2017. Retrieved January 15, 2018.
From 1947 to 1961, more than 5,000 allegedly homosexual federal civil servants lost their jobs in the purges for no reason other than sexual orientation, and thousands of applicants were also rejected for federal employment for the same reason. During this period, more than 1,000 men and women were fired for suspected homosexuality from the State Department alone—a far greater number than were dismissed for their membership in the Communist party.
- Adkins, Judith (August 15, 2016). "'These People Are Frightened to Death' Congressional Investigations and the Lavender Scare". archives.gov. The U.S. National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on January 16, 2018. Retrieved January 15, 2018.
Historians estimate that somewhere between 5,000 and tens of thousands of gay workers lost their jobs during the Lavender Scare.
- Sears, Brad; Hunter, Nan D.; Mallory, Christy (September 2009). Documenting Discrimination on the Basis of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in State Employment (PDF). The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Law and Public Policy at the University of California Los Angeles School of Law. pp. 5–3. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 6, 2017. Retrieved January 15, 2018.
Johnson has demonstrated that during this era government officials intentionally engaged in campaigns to associate homosexuality with Communism: 'homosexual' and 'pervert' became synonyms for 'Communist' and 'traitor.'
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 118–119
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 56–62
- Ambrose 1984, p. 140
- Ambrose 1984, p. 167
- ^ Young & Schilling 2019, p. 132
- Bundy 1988, pp. 305–306
- Bundy 1988, p. 305
- Young & Schilling 2019, p. 128
- Bundy 1988, pp. 310–311
- Bundy 1988, pp. 316–317
- Young & Schilling 2019, pp. 147, 150
- Ambrose 1984, pp. 188–189
- Ambrose 1984, p. 154
- Ambrose 1984, p. 157
- Ambrose 1984, p. 219
- ^ Joseph W. Martin as told to Donavan, Robert J. (1960), My First Fifty Years in Politics, New York: McGraw Hill, p. 227
- "U.S. Senate: Vetoes by President Dwight D. Eisenhower".
- Newton, Eisenhower (2011) pp. 356–357
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (October 9, 1953). "Personal and confidential To Milton Stover Eisenhower". Papers of Dwight David Eisenhower. Eisenhower Memorial. doc. 460. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- Thomas, Evan (2012). Ike's Bluff: President Eisenhower's Secret Battle to Save the World. Little, Brown. p. 175. ISBN 978-0316217279. Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- Newton, Eisenhower pp. 196–199.
- Clarence G. Lasby, Eisenhower's Heart Attack: How Ike Beat Heart Disease and Held on to the Presidency (1997) pp. 57–113.
- Robert P. Hudson, "Eisenhower's Heart Attack: How Ike Beat Heart Disease and Held on to the Presidency (review)" Bulletin of the History of Medicine 72#1 (1998) pp. 161–162 online Archived April 29, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
- R.H. Ferrell, Ill-Advised: Presidential Health & Public Trust (1992), pp. 53–150
- Ambrose 1984, p. 272
- Ambrose 1984, p. 281
- Johnston, Richard J. H. (June 13, 1956). "Butler Criticizes Illness Reports: Says News Has Been Handled in Terms of Propaganda—Hagerty Denies It". The New York Times. p. 32A. Retrieved December 22, 2016.
Paul M. Butler, the Democratic National Chairman, ... declared that the physicians who operated on and attended the President in his most recent illness 'have done a terrific job of trying to convince the American people that a man who has had a heart attack and then was afflicted with Crohn's disease is a better man physically.' He added: 'Whether the American people will buy that, I don't know.'
- Clark, Robert E (June 9, 1956). "President's Heart Reported Sound; Surgery Is Indicated: Inflamed, Obstructed, Intestine Is Blamed". Atlanta Daily World. p. 1. Retrieved December 22, 2016.
- Leviero, Anthony (June 9, 1956). "President Undergoes Surgery on Intestine Block at 2:59 A.M.: Doctors Pronounce It Success : Condition Is Good: Operation Lasts Hour and 53 Minutes–13 Attend Him". The New York Times. p. 1. Retrieved December 22, 2016.
President Eisenhower was operated on at 2:59 A.M. today for relief of an intestinal obstruction. At 4:55 A.M., the operation was pronounced a success by the surgeons. ... The President's condition was diagnosed as ileitis. This is an inflamation of the ileum—the lowest portion of the small intestine, where it joins the large intestine. ... The President first felt ill shortly after midnight yesterday. He had attended a dinner of the White House News Photographers Association Thursday night and had returned to the White House at 11. Mrs. Eisenhower called Maj. Gen. Howard McC. Snyder, the President's personal physician, at 12:45 A.M. yesterday, telling him the President had some discomfort in his stomach. He recommended a slight dose of milk of magnesia. At 1:20 Mrs. Eisenhower called again, saying the President was still complaining of not feeling well. This time she asked Dr. Snyder to come to the White House from his home about a mile away on Connecticut Avenue. He arrived at 2 A.M. and has not left the President's side since.
- Knighton, William Jr. (June 10, 1956). "Eisenhower Out Of Danger; Will Be Able To Resume Duties And Seek Reelection: Doctors See Prospect of Full Return to Job in Four to Six Weeks: Operation Performed to Prevent Gangrene of Bowel: Signing of Official Papers Viewed as Likely by Tomorrow or Tuesday". The Baltimore Sun. p. 1. Retrieved December 22, 2016.
- "Out of Hospital Visit Postponed". The New York Times. July 1, 1956. p. E2. Retrieved December 22, 2016.
- Williams, Charles Harold Macmillan (2009) p. 345
- ^ "President Dwight Eisenhower: Health & Medical History". doctorzebra.com. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- Messerli F. H., Loughlin K. R., Messerli A. W., Welch W. R.: The President and the pheochromocytoma. Am J Cardiol 2007; 99: 1325–1329.
- "Former Presidents Act". National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on June 14, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- Nixon, Richard, The Memoirs of Richard Nixon, 1978, pp. 222–223.
- ^ "Dwight D. Eisenhower Farewell Address". USA Presidents. January 17, 1961. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- "A Chronology from The New York Times, March 1961". John F. Kennedy Presidential Library & Museum. March 23, 1961. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2009.
Mr. Kennedy signed into law the act of Congress restoring the five-star rank of General of the Army to his predecessor, Dwight D. Eisenhower. (15:5)
- Klaus, Mary (August 8, 1985). "Tiny Pennsylvania Town An Escape From Modernity". Sun-Sentinel. Archived from the original on February 25, 2016. Retrieved January 4, 2016.
From this farm the family migrated to Kansas in the summer of 1878.
- Gasbarro, Norman (November 29, 2010). "Eisenhower Family Civil War Veterans". Civil War Blog. Archived from the original on February 25, 2016. Retrieved January 4, 2016.
a stately old home, identified as the ancestral home of President Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Historical Society of Palm Desert; Rover, Hal; Kousken, Kim; Romer, Brett (2009). Palm Desert. Arcadia Publishing. p. 103. ISBN 978-0738559643.
- "Inventory of the San Antonio Express-News Photograph Collection, 1960-1969". University of Texas Library. Archived from the original on June 2, 2016. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
Eisenhower, Dwight D.: visit to San Antonio in behalf of John Goode and Henry Catto, Jr.; downtown S.A. 10/29/1961
- "Ike at Gettysburg (Goldwater, 1964)". 1964: Johnson vs. Goldwater. Museum of the Moving Image. Archived from the original on October 19, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2011.
- Goldschlag, William (May 11, 2016). "When an ex-president helped an 'extreme' Republican candidate". Newsday. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- "Inauguration Is a Day For Rejoicing: Ike". Chicago Tribune. January 21, 1969. Archived from the original on August 19, 2017. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- Belair, Felix Jr. (March 29, 1969). "Eisenhower Dead at 78 as Ailing Heart Fails; Rites Will Start Today". The New York Times. p. 1.
- ^ "Dwight D. Eisenhower – Final Post". Presidential Libraries System, National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on March 8, 2019. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- "Lying in State or in Honor". Architect of the Capitol. Archived from the original on May 18, 2019. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- ^ Belair, Felix Jr. (April 1, 1969). "World's Leaders Join in Services for Eisenhower". The New York Times. p. 1.
- Grose, Peter (March 31, 1969). "Nixon will Meet with De Gaulle Today". The New York Times. p. 1.
President de Gaulle arrived by plane from Paris, on his first visit to the United States since the funeral of President Kennedy in 1963.
- "For A Modest Man: A Simple Funeral Honors Ike". The Desert Sun. Vol. 42, no. 205. UPI. April 1, 1969. Retrieved May 19, 2019 – via California Digital Newspaper Collection, Center for Bibliographical Studies and Research at the University of California Riverside.
- Weissert, Will; Phillip, David J. (December 6, 2018). "Bushes depart on first presidential funeral train since 1969". MilitaryTimes.com. Sightline Media Group. The Associated Press. Archived from the original on August 9, 2019. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- "1969 Year in Review: Eisenhower, Judy Garland die". UPI. October 25, 2005. Archived from the original on October 10, 2016. Retrieved December 19, 2016.
- Lippman, Theo Jr. (September 19, 1979). RUNNING AGAINST CARTER. The Baltimore Sun. Retrieved November 25, 2024.
- ^ Reddy, Patrick (July 2, 2006). Is Bush like Ike?. The Buffalo News. Retrieved November 24, 2024.
- Alsop, Joseph (July 28, 1966). Assaying the Presidents. The Calgary Albertan. Retrieved November 30, 2024.
- Frum 2000, p. 27
- Walsh, Kenneth T. (June 6, 2008). "Presidential Lies and Deceptions". U.S. News & World Report. Archived from the original on September 29, 2008.
- Walker, Samuel, ed. (2012). Presidents and Civil Liberties from Wilson to Obama. Cambridge University Press. pp. i–ii. ISBN 978-1-107-01660-6. Retrieved February 26, 2023.
- "Presidential Politics". Public Broadcasting Service. Archived from the original on June 6, 2008. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- McMahon, Robert J. (1986). "Eisenhower and Third World Nationalism: A Critique of the Revisionists". Political Science Quarterly. 101 (3): 453–473. doi:10.2307/2151625. ISSN 0032-3195. JSTOR 2151625.
- Pach, Chester J. Jr. (October 4, 2016). "Dwight D. Eisenhower: Impact and Legacy". Miller Center. Retrieved February 26, 2023.
- RABE, STEPHEN G. (1993). "Eisenhower Revisionism: A Decade of Scholarship". Diplomatic History. 17 (1): 97–115. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7709.1993.tb00160.x. ISSN 0145-2096. JSTOR 24912261.
- John Lewis Gaddis, "He Made It Look Easy: 'Eisenhower in War and Peace', by Jean Edward Smith" Archived February 6, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, New York Times Book Review, April 20, 2012.
- Presidents rated: Truman, Ike near the top. The Chicago Tribune. The World. February 4, 1982. Retrieved November 24, 2024.
- ^ Griffith, Robert (January 1, 1982). "Dwight D. Eisenhower and the Corporate Commonwealth". The American Historical Review. 87 (1): 87–122. doi:10.2307/1863309. JSTOR 1863309.
- "The President and His Decision". Life. March 12, 1956.
- Morgenthau, Hans J.: "Goldwater – The Romantic Regression", in Commentary, September 1964.
- Medved, Michael (1979). The Shadow Presidents: The Secret History of the Chief Executives and Their Top Aides. Times Books. ISBN 0812908163.
- "Public Law 482". Archived from the original on October 13, 2007. Retrieved April 29, 2008. This law allowed only 75% of pay and allowances to the grade for those on the retired list.
- "Public Law 333, 79th Congress". Naval Historical Center. April 11, 2007. Archived from the original on October 13, 2007. Retrieved October 22, 2007. The retirement provisions were also applied to the World War II Commandant of the Marine Corps and the Commandant of the Coast Guard, both of whom held four-star rank.
- "Public Law 79-333" (PDF). legisworks.org. Legis Works. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 21, 2015. Retrieved October 19, 2015.
- "Our Heritage". People to People International. Archived from the original on March 1, 2009. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- ^ Gomez, Darryl (2015). Authoritative Numismatic Reference: Presidential Medal of Appreciation Award Medals 1958–1963. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 978-1511786744.
- "Dwight D. Eisenhower Highway". Federal Highway Administration. Archived from the original on August 25, 2016. Retrieved August 22, 2016.
- "Record Companies Run With Eisenhower Tribute Albums". Billboard. April 12, 1969. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- "Frank Gehry to design Eisenhower Memorial". American City Business Journals. April 1, 2009. Archived from the original on April 4, 2009.
- Trescott, Jacqueline (April 2, 2009). "Architect Gehry Gets Design Gig For Eisenhower Memorial". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 3, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- Horan, Tim (May 8, 2020). "Eisenhower Memorial in D.C. is complete. Coronavirus delays dedication to September". The Wichita Eagle. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- "Dedication Of Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial" (PDF). Eisenhower Memorial Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 22, 2020. Retrieved April 9, 2023.
- Plumb, Tiereny (January 22, 2010). "Gilbane to manage design and construction of Eisenhower Memorial". American City Business Journals.
- "President Eisenhower named to World Golf Hall of Fame". PGA Tour. Archived from the original on June 29, 2009. Retrieved May 3, 2010.
- "Hall of Great Westerners". National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum. Retrieved November 22, 2019.
- (27 Oct 2023) Fort Eisenhower redesignation ceremony
- "Plans are coming together for Fort Gordon renaming ceremony". MSN. Archived from the original on March 17, 2023. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- Scribner, Herb (March 25, 2023). "6 Army bases named after Confederate leaders get dates for new names". Axios. Archived from the original on April 18, 2023. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- Prince Bernhard of the Netherlands in an interview with H.G. Meijer, published in "Het Vliegerkruis", Amsterdam 1997, ISBN 9067073474. p. 92.
- "The Arms of Dwight D. Eisenhower". American Heraldry Society. Archived from the original on February 2, 2015.
- ^ "Awards & Medals | Eisenhower Presidential Library". www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- "USA and Foreign Decorations of Dwight D. Eisenhower". Eisenhower Presidential Center. Archived from the original on November 18, 2016. Retrieved June 10, 2012.
- "Questions to the Chancellor" (PDF). Austrian Parliament. 2012. p. 194. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 22, 2012. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- Eisenhower, John S. D. Allies.
- ^ Empric, Bruce E. (2024), Uncommon Allies: U.S. Army Recipients of Soviet Military Decorations in World War II, Teufelsberg Press, pp. 36, 46, ISBN 979-8-3444-6807-5
- "Eisenhower to get honor". The New York Times. June 10, 1945. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- London Welcomes Her Newest Citizen (Newsreel). British Movietone News. 1945. Event occurs at 1:18. Archived from the original on October 27, 2021. Retrieved August 26, 2020 – via Associated Press and YouTube.
- ^ "Eisenhower in Ulster". Belfast Telegraph. July 5, 2008. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- Eisenhower's Scottish Diary (Newsreel). British Pathé. Event occurs at 0:13. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "President Eisenhower in Carrick". maybole.org. Archived from the original on October 25, 2020. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Honorary Degrees 1871–2018" (PDF). Queen's University Belfast. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 4, 2020.
- "Oxford Degrees for War Leaders". British Pathé. 1945.
- "Honorary Degrees". Harvard University. Archived from the original on November 4, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Honorary degree recipients". Gettysburg College. Archived from the original on September 9, 2019. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Honorary Degree Recipients, 1850–2021" (PDF). University of Toronto. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 1, 2020.
- "Chronological Listing of Honorary Degree Recipients" (PDF). University of Pennsylvania. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 29, 2019.
- "Honorary Degrees Since 1702". Office of the Secretary and Vice President for University Life, Yale University.
- "About: Honorary Degrees". Hofstra University.
- "President Eisenhower's Commencement Address". Dartmouth College. November 28, 2018.
- "Honorary Degrees Conferred by The Catholic University of America" (PDF). Catholic University of America. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 22, 2020.
- "Honorary Degree Recipients". Office of the Provost, Northwestern University.
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (June 7, 1954). Remarks at Washington College on Receiving an Honorary Doctor of Laws Degree (Speech). Washington College, Maryland: Washington College. Archived from the original on October 20, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
- "Honorary Degrees Awarded". Johns Hopkins University.
- "India Likes Ike". British Pathé. 1959.
- "Honorary Degree Recipients, 1844–2019" (PDF). University of Notre Dame. November 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 22, 2020. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Eisenhower Given Honorary Degree at Bard College". The New York Times. June 21, 1964.
- "Past Honorary Degrees". Grinnell College.
- "U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower with commemorative plaque at Ohio University Memorial Auditorium". Ohio University Libraries. October 5, 1965.
Print sources
Main article: Bibliography of Dwight D. EisenhowerGeneral biographies
- Ambrose, Stephen (1983). Eisenhower: Soldier, General of the Army, President-Elect (1893–1952). Vol. I. Simon & Schuster.
- Ambrose, Stephen (1984). Eisenhower: The President (1952–1969). Vol. II. Simon & Schuster.
- Boyle, Peter G. (2005). Eisenhower. Pearson/Longman. ISBN 0582287200.
- D'Este, Carlo (2002). Eisenhower: A Soldier's Life. Macmillan. ISBN 0805056866.
- Krieg, Joann P. ed. (1987). Dwight D. Eisenhower, Soldier, President, Statesman. 24 essays by scholars. ISBN 0313259550
- Newton, Jim (2011). Eisenhower: The White House Years. Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-52353-0., popular history.
- Parmet, Herbert S. (1972). Eisenhower and the American Crusades. OCLC 482017.
- Smith, Jean Edward (2012). Eisenhower in War and Peace. Random House. ISBN 978-1400066933.
- Wicker, Tom (2002). Dwight D. Eisenhower. Times Books. ISBN 0805069070., popular history
Military career
- Ambrose, Stephen E. (January 17, 2012). The Supreme Commander. Knopf Doubleday Publishing. ISBN 9780307946638.
- Ambrose, Stephen E. (July 15, 1999). The Victors: Eisenhower and His Boys the Men of World War II. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 9780684864549.
- Eisenhower, David (1986). Eisenhower at War 1943–1945, Random House. ISBN 0394412370. A detailed study by his grandson.
- Eisenhower, John S. D. (2003). General Ike, Free Press. ISBN 0743244745, by his son.
- Hatch, Alden. General Eisenhower (1944) online, early popular biography.
- Hobbs, Joseph Patrick (1999). Dear General: Eisenhower's Wartime Letters to Marshall. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0801862191.
- Irish, Kerry E. "Apt Pupil: Dwight Eisenhower and the 1930 Industrial Mobilization Plan", The Journal of Military History 70.1 (2006) 31–61 online in Project Muse.
- Jordan, Jonathan W. (2011). Brothers Rivals Victors: Eisenhower, Patton, Bradley, and the Partnership that Drove the Allied Conquest in Europe. NAL/Caliber. ISBN 978-0451232120.
- Jordan, Jonathan W. (2015). American Warlords: How Roosevelt's High Command Led America to Victory in World War II. NAL/Caliber. ISBN 978-0451414571.
- Pogue, Forrest C. (1954). The Supreme Command. Office of the Chief of Military History, Dept. of the Army. OCLC 1247005.
- Weigley, Russell (1981). Eisenhower's Lieutenants: the Campaign of France and Germany, 1944–1945. Indiana University Press. ISBN 0253133335.
- Sixsmith, Major General E. K. G. (1973). Eisenhower as Military Commander. B. C. T. Batsford Limited. ISBN 978-0713412123.
Civilian career
- Bowie, Robert R.; Immerman, Richard H. (February 12, 1998). Waging Peace: How Eisenhower Shaped an Enduring Cold War Strategy. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199879083.
- Chernus, Ira (2008). Apocalypse Management: Eisenhower and the Discourse of National Insecurity. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0804758079.
- Cook, Blanche Wiesen (1981). The Declassified Eisenhower: A Divided Legacy. Doubleday.
- Damms, Richard V. (2002). The Eisenhower Presidency, 1953–1961
- David Paul T., ed. (1954). Presidential Nominating Politics in 1952. 5 vols., Johns Hopkins Press. OCLC 519846
- Divine, Robert A. (1981). Eisenhower and the Cold War.
- Gellman, Irwin F. (2015). The President and the Apprentice: Eisenhower and Nixon, 1952–1961. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300181050
- Greenstein, Fred I. (1991). The Hidden-Hand Presidency: Eisenhower as Leader. Basic Books. ISBN 0465029485
- Harris, Douglas B. "Dwight Eisenhower and the New Deal: The Politics of Preemption", Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 27, 1997.
- Harris, Seymour E. (1962). The Economics of the Political Parties, with Special Attention to Presidents Eisenhower and Kennedy. OCLC 174566
- Jacobs, Travis Beal (1993). "Eisenhower, the American Assembly, and the 1952 Elections". In Warshaw, Shirley Anne (ed.). Reexamining the Eisenhower presidency. Greenwood Press. pp. 17–32. ISBN 0313287929.
- Jacobs, Travis Beal (2001). Eisenhower at Columbia. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 0-7658-0036-5.
- Mason, Robert. "War Hero in the White House: Dwight Eisenhower and the Politics of Peace, Prosperity, and Party." in Profiles in Power (Brill, 2020) pp. 112–128.
- Medhurst, Martin J. (1993). Dwight D. Eisenhower: Strategic Communicator. Greenwood Press. ISBN 0313261407
- Mayer, Michael S. (2009). The Eisenhower Years Facts on File. ISBN 0816053871
- Newton, Jim. (2011) Eisenhower: The White House Years ISBN 978-0385523530
- Pach, Chester J., and Richardson, Elmo (1991). Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0700604367
- Pickett, William B. (2000). Eisenhower Decides to Run: Presidential Politics and Cold War Strategy. Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1-56-663787-2.
- Pickett, William B. (1995). Dwight David Eisenhower and American Power. Harlan Davidson. ISBN 0-88-295918-2.
- Watry, David M. (2014). Diplomacy at the Brink: Eisenhower, Churchill and Eden in the Cold War. Louisiana State University Press.
General history
- Bundy, McGeorge (1988). Danger and Survival: Choices About the Bomb in the First Fifty Years. Random House. ISBN 0-394-52278-8.
- Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The 70s The Decade That Brought You Modern Life – For Better Or Worse. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-04196-5.
- Grant, Rebecca (June 1, 2001). "Deep Strife". Air & Space Forces Magazine.
- Owen, David (1999). The Making of the Masters: Clifford Roberts, Augusta National, and Golf's Most Prestigious Tournament. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0684857294.
- Young, Ken; Schilling, Warner R. (2019). Super Bomb: Organizational Conflict and the Development of the Hydrogen Bomb. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-1-5017-4516-4.
Primary sources
- Boyle, Peter G., ed. (1990). The Churchill–Eisenhower Correspondence, 1953–1955. University of North Carolina Press.
- Boyle, Peter G., ed. (2005). The Eden–Eisenhower correspondence, 1955–1957. University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0807829358
- Butcher, Harry C. (1946). My Three Years With Eisenhower The Personal Diary of Captain Harry C. Butcher, USNR, candid memoir by a top aide. online
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1948). Crusade in Europe, his war memoirs.
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1963). Mandate for Change, 1953–1956.
- Eisenhower, Dwight D. (1965). The White House Years: Waging Peace 1956–1961, Doubleday and Co.
- Eisenhower Papers 21-volume scholarly edition; complete for 1940–1961.
- Summersby, Kay (1948). Eisenhower Was My Boss, Prentice Hall; (1949) Dell paperback.
External links
- White House biography
- Eisenhower Presidential Library and Museum
- Eisenhower National Historic Site
- Eisenhower Foundation
- Major speeches of Dwight Eisenhower
- Dwight David Eisenhower collected news and commentary at The New York Times
- Dwight D. Eisenhower: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Extensive essays on Dwight Eisenhower and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the Miller Center of Public Affairs
- "Life Portrait of Dwight D. Eisenhower", from C-SPAN's American Presidents: Life Portraits, October 25, 1999
- Works by Dwight David Eisenhower at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Dwight D. Eisenhower at the Internet Archive
- Appearances on C-SPAN
| Offices and distinctions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Articles related to Dwight D. Eisenhower | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Dwight D. Eisenhower
- 1890 births
- 1969 deaths
- 20th-century Presbyterians
- 20th-century presidents of the United States
- American anti-communists
- American anti-fascists
- American five-star officers
- American football halfbacks
- American people of Pennsylvania Dutch descent
- American people of the Korean War
- American Presbyterians
- Army Black Knights football players
- Candidates in the 1952 United States presidential election
- Candidates in the 1956 United States presidential election
- Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
- Companions of the Liberation
- Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy alumni
- Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy
- Eisenhower family
- Graduates of the United States Military Academy Class of 1915
- Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour
- Grand Crosses of the Order of George I with Swords
- Grand Crosses of the Order of Polonia Restituta
- Grand Crosses of the Order of the Liberator General San Martin
- Grand Crosses of the Order of the White Lion
- Grand Crosses of the Virtuti Militari
- Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath
- Honorary members of the Order of Merit
- Kansas Republicans
- Knights Grand Cross of the Military Order of Savoy
- Members of the Order of the Holy Sepulchre
- Military personnel from Kansas
- Military personnel from Pennsylvania
- Military personnel from Texas
- NATO Supreme Allied Commanders
- New York (state) Republicans
- Pennsylvania Republicans
- People from Abilene, Kansas
- People from Denison, Texas
- People from Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
- People of the Cold War
- People of the Congo Crisis
- People with Crohn's disease
- Presidents of Columbia University
- Presidents of the United States
- American recipients of the Croix de guerre (Belgium)
- American recipients of the Croix de Guerre 1939–1945 (France)
- Recipients of the Czechoslovak War Cross 1939–1945
- Recipients of the Distinguished Service Medal (US Army)
- Recipients of the Distinguished Service Star
- Recipients of the Grand Decoration with Sash for Services to the Republic of Austria
- Recipients of the Legion of Merit
- Recipients of the National Order of Merit (Malta)
- Recipients of the Navy Distinguished Service Medal
- Recipients of the Order of Military Merit (Brazil)
- Recipients of the Order of Suvorov, 1st class
- Recipients of the Order of the Cross of Grunwald, 1st class
- Recipients of the Order of Victory
- Republican Party (United States) presidential nominees
- Republican Party presidents of the United States
- Residents of Thatched House Lodge
- Members of the Sons of the American Revolution
- St. Mary's Rattlers football coaches
- Time Person of the Year
- United States Army Chiefs of Staff
- United States Army Command and General Staff College alumni
- United States Army generals of World War II
- United States Army generals
- United States Army personnel of World War I
- United States Army War College alumni
- United States Military Academy alumni
- United States military governors
- World Golf Hall of Fame inductees
- Writers from Kansas
- Writers from Pennsylvania
- Writers from Texas
- Players of American football from Kansas
- Coaches of American football from Kansas
- United States Army Infantry Branch personnel
- Centrism in the United States
- Recipients of orders, decorations, and medals of Ethiopia
- Deaths from congestive heart failure
- 20th-century American farmers
- Progressive conservatism


