| Revision as of 19:36, 1 May 2011 editKen keisel (talk | contribs)2,987 edits updated entry← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:15, 4 May 2011 edit undoRlandmann (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators54,016 edits reformat Godall referencesNext edit → | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| ==Operational history== | ==Operational history== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Redesignated as AF-2W (TB3F-1S) and AF-2S (TB3F-2S), the Guardian entered service in October 1950,<ref name="Swan2"/> with VS-25,<ref |
Redesignated as AF-2W (TB3F-1S) and AF-2S (TB3F-2S), the Guardian entered service in October 1950,<ref name="Swan2"/> with VS-25,<ref name="wagner"/> and was the largest (though not the heaviest) single-engine, piston-engined aircraft ever operated by the US Navy.<ref name="VS">Goebel, Greg. ''VectorSite,'' 2009. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref><ref>Thruelsen 1976, p. 242.</ref> A total of 193 AF-2S Guardians were built.<ref name="Swan2"/> In 1952, the "hunter" AF-3S was introduced, fitting a ] (MAD) for the detection of submerged submarines; 40 of this variant were built.<ref name="Swan2"/> The last Guardian was delivered to the Navy in March 1953,<ref name="Swan2"/> with a total of 389 built.<ref name="VS"/> | ||
| The Guardian saw service in the maritime patrol role during the ], however it proved unpopular with pilots, being underpowered and heavy on the controls; the aircraft suffered from a severely high accident rate.<ref name="VS"/> Shortly after the end of the war, it began to be replaced by the Grumman S2F Tracker,<ref name="Swan2"/> with the last AF retired from active service on 31 August 1955.<ref name="VS"/> It remained in service with the US Naval Air Reserve until 1957.<ref name="VS"/> | The Guardian saw service in the maritime patrol role during the ], however it proved unpopular with pilots, being underpowered and heavy on the controls; the aircraft suffered from a severely high accident rate.<ref name="VS"/> Shortly after the end of the war, it began to be replaced by the Grumman S2F Tracker,<ref name="Swan2"/> with the last AF retired from active service on 31 August 1955.<ref name="VS"/> It remained in service with the US Naval Air Reserve until 1957.<ref name="VS"/> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| After disposal by the U.S. Navy five Guardians saw many years service with Aero Union based at ] California in the forest fire-fighting role, the last being retired in 1978.<ref> ''Pima Air & Space Museum''. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | After disposal by the U.S. Navy five Guardians saw many years service with Aero Union based at ] California in the forest fire-fighting role, the last being retired in 1978.<ref> ''Pima Air & Space Museum''. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | ||
| * An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123088, civil registration N3143G, is currently dismantled, and in storage in ]. While owned by Aero Union this aircraft was converted into a fire-bomber, but never saw service in that role. It is owned by Aero-Trans Corporation. This is the same aircraft advertised for sale by Aero Union in July 2003.<ref>Godall |
* An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123088, civil registration N3143G, is currently dismantled, and in storage in ]. While owned by Aero Union this aircraft was converted into a fire-bomber, but never saw service in that role. It is owned by Aero-Trans Corporation. This is the same aircraft advertised for sale by Aero Union in July 2003.<ref>Godall 2005, p.</ref> | ||
| * An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126731, civil registration N9993Z, is currently owned by the ]. The aircraft was restored in 1997, and flew briefly with the CAF as "Navy 126731/SM/10". The aircraft is currently on static display with its wings folded at the CAF's Mesa facility in ].<ref>Godall |
* An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126731, civil registration N9993Z, is currently owned by the ]. The aircraft was restored in 1997, and flew briefly with the CAF as "Navy 126731/SM/10". The aircraft is currently on static display with its wings folded at the CAF's Mesa facility in ].<ref>Godall 2005, p.</ref><ref></ref> | ||
| * An AF-2S, BuNo 126759, civil registration N3144G, is in open storage in ].<ref>Godall |
* An AF-2S, BuNo 126759, civil registration N3144G, is in open storage in ].<ref>Godall 2005, p.</ref> | ||
| * An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126792, civil registration N9995Z, is currently in the collection of Jimmy Leeward, and located at the Leeward Air Ranch at ]. This aircraft had flown as Tanker #E21 with Aero Union until 1977. It was owned by the EAA Aviation Foundation in ] from 1984 until 1986, when it was acquired by Jimmy Leeward. It currently flies as "Navy 126792".<ref>Godall |
* An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126792, civil registration N9995Z, is currently in the collection of Jimmy Leeward, and located at the Leeward Air Ranch at ]. This aircraft had flown as Tanker #E21 with Aero Union until 1977. It was owned by the EAA Aviation Foundation in ] from 1984 until 1986, when it was acquired by Jimmy Leeward. It currently flies as "Navy 126792".<ref>Godall 2005, p.</ref> | ||
| * An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 129233, civil registration N9994Z, is preserved at the ], Tucson, Arizona. The aircraft is displayed in incorrect Aero Union fire-fighting markings as "N9995Z Tanker E21", the aircraft that is now at the Leeward Air Ranch (see above).<ref> ''Pima Air & Space Museum''. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | * An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 129233, civil registration N9994Z, is preserved at the ], Tucson, Arizona. The aircraft is displayed in incorrect Aero Union fire-fighting markings as "N9995Z Tanker E21", the aircraft that is now at the Leeward Air Ranch (see above).<ref> ''Pima Air & Space Museum''. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | ||
| * Another ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123100, civil registration N3144G, is on display at the ] in ]. It was the seventh AF-2S produced. The aircraft was operated as a firefighter until 1978. It was acquired by the museum in 1980. It is displayed in the colors of its first Navy assignment, though still carries the non-historical number "30" on the cowling, for many years the aircraft's call-sign while operating as a fire fighting aircraft;<ref> ''National Museum of Naval Aviation.'' Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | * Another ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123100, civil registration N3144G, is on display at the ] in ]. It was the seventh AF-2S produced. The aircraft was operated as a firefighter until 1978. It was acquired by the museum in 1980. It is displayed in the colors of its first Navy assignment, though still carries the non-historical number "30" on the cowling, for many years the aircraft's call-sign while operating as a fire fighting aircraft;<ref> ''National Museum of Naval Aviation.'' Retrieved: 16 January 2011.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 4 May 2011
| AF Guardian | |
|---|---|

| |
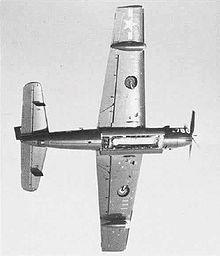
| Hunter-Killer team of AF-2W (lower) and AF-2S | |
| Role | Anti-submarine aircraftType of aircraft |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Grumman |
| First flight | 19 December 1945 |
| Introduction | October 1950 |
| Retired | 31 August 1955 |
| Status | Replaced by S-2 Tracker |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | 389 |
The Grumman AF Guardian was the first purpose-built anti-submarine warfare (ASW) aircraft system to enter service in the United States Navy. It consisted of two airframes, one for detection gear, the other for weapons. The Guardian remained in service until August 1955, when it was replaced by the twin-engine Grumman S-2 Tracker, the first purpose-built single airframe ASW airplane to serve the U.S. Navy. The Guardian was the largest single-engine aircraft ever to operate from a U.S. aircraft carrier.
Design and development

The original design concept for the aircraft that would become the Guardian, the XTB2F of 1944, was to be a twin-engined aircraft with a 3,600 lb (1,633 kg) warload and a range of 3,700 mi (5,950 km). This was considered to be too large for practical use from an Essex class aircraft carrier, and was canceled in 1945, replaced by a modified F7F Tigercat, the XTSF-1.
However, this too was considered impractible; and another alternative, the internally-developed Grumman Model G-70, was selected instead, being given the Navy designation XTB3F. This was designed as mixed-power aircraft, with a Pratt & Whitney Double Wasp radial engine in the nose and a Westinghouse 19XB turbojet in the tail. This was found to be unsuitable and the jet engine was removed without ever having been used in flight. The XTB3F-1S carried a crew of two seated side-by-side and an armament of two 20 mm cannon and 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs, torpedoes and/or rockets, and made its first flight on 19 December 1945.
On 24 December 1945, the Navy changed the role of the aircraft from torpedo-bomber to anti-submarine warfare. All the required equipment could not be fitted into a single aircraft, consequently two variants would be produced, one as a "hunter" and another as a "killer." The "hunter" aircraft would not carry any armament, but instead two additional crew members and a ventral radome for APS-20 search radar. This aircraft, the XTB3F-1S, first flew in November 1948. The "killer" deleted the cannon of the torpedo bomber, but retained the bomb bay, added a third crewmember, a searchlight, and short-range radar, and (as the XTB3F-2S) first flew in January 1949.
Operational history

Redesignated as AF-2W (TB3F-1S) and AF-2S (TB3F-2S), the Guardian entered service in October 1950, with VS-25, and was the largest (though not the heaviest) single-engine, piston-engined aircraft ever operated by the US Navy. A total of 193 AF-2S Guardians were built. In 1952, the "hunter" AF-3S was introduced, fitting a magnetic anomaly detector (MAD) for the detection of submerged submarines; 40 of this variant were built. The last Guardian was delivered to the Navy in March 1953, with a total of 389 built.
The Guardian saw service in the maritime patrol role during the Korean War, however it proved unpopular with pilots, being underpowered and heavy on the controls; the aircraft suffered from a severely high accident rate. Shortly after the end of the war, it began to be replaced by the Grumman S2F Tracker, with the last AF retired from active service on 31 August 1955. It remained in service with the US Naval Air Reserve until 1957.
Survivors
After disposal by the U.S. Navy five Guardians saw many years service with Aero Union based at Chico California in the forest fire-fighting role, the last being retired in 1978.
- An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123088, civil registration N3143G, is currently dismantled, and in storage in Ocala, Florida. While owned by Aero Union this aircraft was converted into a fire-bomber, but never saw service in that role. It is owned by Aero-Trans Corporation. This is the same aircraft advertised for sale by Aero Union in July 2003.
- An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126731, civil registration N9993Z, is currently owned by the Commrative Air Force. The aircraft was restored in 1997, and flew briefly with the CAF as "Navy 126731/SM/10". The aircraft is currently on static display with its wings folded at the CAF's Mesa facility in Mesa, Arizona.
- An AF-2S, BuNo 126759, civil registration N3144G, is in open storage in Tulare, California.
- An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 126792, civil registration N9995Z, is currently in the collection of Jimmy Leeward, and located at the Leeward Air Ranch at Ocala, Florida. This aircraft had flown as Tanker #E21 with Aero Union until 1977. It was owned by the EAA Aviation Foundation in Oshkosh, Wisconsin from 1984 until 1986, when it was acquired by Jimmy Leeward. It currently flies as "Navy 126792".
- An ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 129233, civil registration N9994Z, is preserved at the Pima Air Museum, Tucson, Arizona. The aircraft is displayed in incorrect Aero Union fire-fighting markings as "N9995Z Tanker E21", the aircraft that is now at the Leeward Air Ranch (see above).
- Another ex Aero Union AF-2S, BuNo 123100, civil registration N3144G, is on display at the National Museum of Naval Aviation in Pensacola, Florida. It was the seventh AF-2S produced. The aircraft was operated as a firefighter until 1978. It was acquired by the museum in 1980. It is displayed in the colors of its first Navy assignment, though still carries the non-historical number "30" on the cowling, for many years the aircraft's call-sign while operating as a fire fighting aircraft;
Variants

- XTB3F-1
- Prototypes of two-seat torpedo bomber powered by two 2,300 hp R-2800-46 engines and a Westinghouse turbojet; one built.
- XTB3F-1S
- Two modified XTB3F-1 prototypes with turbojet removed and ventral radome , later re-designated as XAF-1.
- AF-2S
- Production variant with 2,400 hp R-2800-48 engines, 193 built.
- AF-2W
- Hunter variant with search radar in a ventral radome, 153 built.
- AF-3S
- Hunter/Killer variant similar to AF-2S with retractable MAD boom, 40 built.
Operators
Specifications (AF-2S Guardian)
Data from United States Navy Aircraft since 1911
General characteristics
- Crew: 3 (4 in AF-2W variant)
Performance
Armament
- Rockets: 16× 5 in (127 mm) unguided High velocity aircraft rocket (HVAR) rockets
- Bombs: 4,000 lb (1,814 kg) of bombs, torpedoes, and depth charges
See also
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
- Notes
- ^ Wagner 1982, p. 498
- ^ Goebel, Greg. "Grumman AF Guardian." VectorSite, 2009. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.
- Norton 2008, p. 120.
- Donald and March 2001, p. 46.
- ^ Swanborough and Bowers 1990, p. 246.
- Thruelsen 1976, p. 242.
- "Aircraft Collection." Pima Air & Space Museum. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.
- Godall 2005, p.
- Godall 2005, p.
- AF2S Guardian at Arizona Wing Commemerative Airforce
- Godall 2005, p.
- Godall 2005, p.
- "Aircraft Collection." Pima Air & Space Museum. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.
- "AF-2S Aircraft, Bureau Number 123100." National Museum of Naval Aviation. Retrieved: 16 January 2011.
- Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 228.
- Bibliography
- Donald, David and Daniel J. March. Carrier Aviation Air Power Directory. Norwalk, CT: AIRtime Publishing, 2001. ISBN 1-880588-43-9.
- Godall, Geoffrey. Warbirds Directory, 4th Edition. Victoria, Australia: Victoria Publishing, 2005
- Gunston, Bill. Grumman: Sixty Years of Excellence. New York: Orion Books, 1988. ISBN 0-517-56796-2.
- Swanborough, Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. United States Navy Aircraft since 1911. London: Putnam, Second edition, 1976. ISBN 0-370-10054-9.
- Swanborough, Gordon and Peter M. Bowers. United States Navy Aircraft since 1911. London: Putnam, Third edition, 1990. ISBN 978-0870217920.
- Thruelsen, Richard. The Grumman Story. New York: Praeger Publishers, Inc., 1976. ISBN 0-275-54260-2.
- Wagner, Ray (1982). American Combat Planes, Third Edition. USA: Doubleday & Company. ISBN 0-385-13120-8.
External links
- Grumman AF Guardian at Greg Goebel's Air Vectors
- AF2S Guardian at Arizona Wing Commemerative Airforce
| USN/USMC attack aircraft designations 1946–1962 by manufacturer | |
|---|---|
| Douglas | |
| Grumman | |
| McDonnell Douglas | |
| North American | |
| Martin | |
| Vought | |
| USN/USMC torpedo aircraft designations pre-1962 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torpedo |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Torpedo Bomber |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Torpedo Scout |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Patrol Torpedo Bomber |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Aviation lists | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Military | |
| Accidents / incidents | |
| Records | |
Categories: