| Revision as of 23:21, 24 January 2017 editUgog Nizdast (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers30,127 edits Undid revision 761707681 by 213.210.205.27 (talk): WP:UNSOURCED, individual articles (Semitic, Urdu) don't make the claim← Previous edit | Revision as of 04:48, 29 January 2017 edit undoफ़िलप्रो (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users9,818 edits Undid revision 761794077 by 110.227.108.193 (talk)Next edit → | ||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| {{Use Indian English|date=May 2016}} | {{Use Indian English|date=May 2016}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The ] designates the ] of the ] as ] |
The ] designates the ] of the ] as ] written in the ] script, as well as ].<ref name="rajbhasha.nic.in">{{cite web|url=http://rajbhasha.nic.in/en/constitutional-provisions|title=Constitutional Provisions: Official Language Related Part-17 of The Constitution Of India|publisher=Department of Official Language, ]|accessdate=1 July 2015}}</ref> There is no ] as declared by the Constitution of ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/hindi-not-a-national-language-court/article94695.ece|title=Hindi, not a national language: Court|publisher='']''|date=25 January 2010}}</ref> ] and ] are used for official purposes such as parliamentary proceedings, judiciary, communications between the Central Government and a State Government.<ref name="rajbhasha.nic.in"/> States within India have the liberty and powers to specify their own official language(s) through legislation and therefore there are 22 officially recognized languages in India. The number of native ] speakers ranges between 14.5 and 24.5% in total Indian population, however, other dialects of Hindi termed as ] are spoken by nearly 45% of Indians, mostly accounted from the states falling under the ]. Other Indian languages are each spoken by around 10% or less of the population.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/Census_Data_Online/Language/Statement4.aspx|title=Scheduled Languages in descending order of speaker's strength - 2001|publisher=Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India|accessdate=1 July 2015}}</ref> | ||
| States specify their own official language(s) through legislation. The section of the Constitution of India dealing with official languages therefore includes detailed provisions which deal not just with the languages used for the official purposes of the union, but also with the languages that are to be used for the official purposes of each ] in the country, and the languages that are to be used for communication between the union and the states ''inter se''. | States specify their own official language(s) through legislation. The section of the Constitution of India dealing with official languages therefore includes detailed provisions which deal not just with the languages used for the official purposes of the union, but also with the languages that are to be used for the official purposes of each ] in the country, and the languages that are to be used for communication between the union and the states ''inter se''. | ||
| During the ], ] was used for purposes at the ] level.<ref>{{cite book|last=Mollin|first=Sandra|title=Euro-English: assessing variety status|year=2006|publisher=Gunter Narr Verlag|isbn=978-3-8233-6250-0|page=17|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qPhULmMmqJMC&pg=PA17}}</ref> The Indian constitution adopted in 1950 envisaged that ] would be gradually phased in to replace English over a fifteen-year period, but gave ] the power to, by law, provide for the continued use of English even thereafter.<ref></ref> Plans to make Hindi the sole official language of the |
During the ], ] was used for purposes at the ] level.<ref>{{cite book|last=Mollin|first=Sandra|title=Euro-English: assessing variety status|year=2006|publisher=Gunter Narr Verlag|isbn=978-3-8233-6250-0|page=17|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qPhULmMmqJMC&pg=PA17}}</ref> The Indian constitution adopted in 1950 envisaged that ] would be gradually phased in to replace English over a fifteen-year period, but gave ] the power to, by law, provide for the continued use of English even thereafter.<ref></ref> Plans to make Hindi the sole official language of the Republic met with ] in some parts of the country. Hindi continues to be used today, in combination with other (at the central level and in some states) State official languages at the state level. | ||
| The legal framework governing the use of languages for official purpose currently includes the ], the Official Languages Act, 1963, Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) Rules, 1976, and various state ]s, as well as ] made by the central government and the states. | The legal framework governing the use of languages for official purpose currently includes the ], the Official Languages Act, 1963, Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) Rules, 1976, and various state ]s, as well as ] made by the central government and the states. | ||
Revision as of 04:48, 29 January 2017
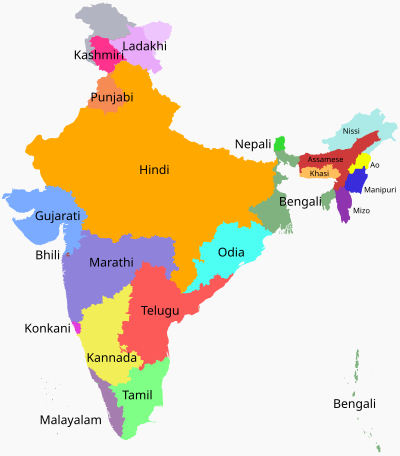
The Constitution of India designates the official language of the Government of India as Hindi written in the Devanagari script, as well as English. There is no national language as declared by the Constitution of India. Hindi and English are used for official purposes such as parliamentary proceedings, judiciary, communications between the Central Government and a State Government. States within India have the liberty and powers to specify their own official language(s) through legislation and therefore there are 22 officially recognized languages in India. The number of native Hindi speakers ranges between 14.5 and 24.5% in total Indian population, however, other dialects of Hindi termed as Hindi languages are spoken by nearly 45% of Indians, mostly accounted from the states falling under the Hindi belt. Other Indian languages are each spoken by around 10% or less of the population.
States specify their own official language(s) through legislation. The section of the Constitution of India dealing with official languages therefore includes detailed provisions which deal not just with the languages used for the official purposes of the union, but also with the languages that are to be used for the official purposes of each state and union territory in the country, and the languages that are to be used for communication between the union and the states inter se.
During the British Raj, English was used for purposes at the federal level. The Indian constitution adopted in 1950 envisaged that Hindi would be gradually phased in to replace English over a fifteen-year period, but gave Parliament the power to, by law, provide for the continued use of English even thereafter. Plans to make Hindi the sole official language of the Republic met with resistance in some parts of the country. Hindi continues to be used today, in combination with other (at the central level and in some states) State official languages at the state level.
The legal framework governing the use of languages for official purpose currently includes the Constitution, the Official Languages Act, 1963, Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) Rules, 1976, and various state laws, as well as rules and regulations made by the central government and the states.
Official languages of the Union
The Indian constitution, in 1950, declared Hindi in Devanagari script to be the official language of the union. Unless Parliament decided otherwise, the use of English for official purposes was to cease 15 years after the constitution came into effect, i.e., on 26 January 1965. The prospect of the changeover, however, led to much alarm in the non Hindi-speaking areas of India, especially Dravidian-speaking states whose languages were not related to Hindi at all. As a result, Parliament enacted the Official Languages Act, 1963, which provided for the continued use of English for official purposes along with Hindi, even after 1965.
In late 1964, an attempt was made to expressly provide for an end to the use of English, but it was met with protests from states such as Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, West Bengal, Karnataka, Puducherry and Andhra Pradesh. Some of these protests also turned violent. As a result, the proposal was dropped, and the Act itself was amended in 1967 to provide that the use of English would not be ended until a resolution to that effect was passed by the legislature of every state that had not adopted Hindi as its official language, and by each house of the Indian Parliament.
The position was thus that the Union government continues to use English in addition to Hindi for its official purposes as a "subsidiary official language," but is also required to prepare and execute a programme to progressively increase its use of Hindi. The exact extent to which, and the areas in which, the Union government uses Hindi and English, respectively, is determined by the provisions of the Constitution, the Official Languages Act, 1963, the Official Languages Rules, 1976, and statutory instruments made by the Department of Official Language under these laws.
Parliamentary proceedings and laws
The Indian constitution draws a distinction between the language to be used in Parliamentary proceedings, and the language in which laws are to be made. Parliamentary business, according to the Constitution, may be conducted in either Hindi or English. The use of English in parliamentary proceedings was to be phased out at the end of fifteen years unless Parliament chose to extend its use, which Parliament did through the Official Languages Act, 1963. In addition, the constitution permits a person who is unable to express themselves in either Hindi or English to, with the permission of the Speaker of the relevant House, address the House in their mother tongue.
In contrast, the constitution requires the authoritative text of all laws, including Parliamentary enactments and statutory instruments, to be in English, until Parliament decides otherwise. Parliament has not exercised its power to so decide, instead merely requiring that all such laws and instruments, and all bills brought before it, also be translated into Hindi, though the English text remains authoritative.
Judiciary
The constitution provides that all proceedings in the Supreme Court of India, the country's highest court and the High Courts, shall be in English. Parliament has the power to alter this by law, but has not done so. However, in many high courts, there is, with consent from the president, allowance of the optional use of Hindi. Such proposals have been successful in the states of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar.
Administration
The Union government is required by law to progressively increase the use of Hindi in its official work, which it has sought to do through "persuasion, incentive and goodwill".
The Official Language Act provides that the Union government shall use both Hindi and English in most administrative documents that are intended for the public. The Official Languages Rules, in contrast, provide for a higher degree of use of Hindi in communications between offices of the central government (other than offices in Tamil Nadu, to which the rules do not apply). Communications between different departments within the central government may be in either Hindi or English, although a translation into the other language must be provided if required. Communications within offices of the same department, however, must be in Hindi if the offices are in Hindi-speaking states, and in either Hindi or English otherwise with Hindi being used in proportion to the percentage of staff in the receiving office who have a working knowledge of Hindi. Notes and memos in files may be in either Hindi or English, with the Government having a duty to provide a translation into the other language if required.
In addition, every person submitting a petition for the redress of a grievance to a government officer or authority has a constitutional right to submit it in any language used in India.
Implementation
Various steps have been taken by the Indian government to implement the use and familiarisation of Hindi extensively. Dakshina Bharat Hindi Prachar Sabha headquartered at Chennai was formed to spread Hindi in South Indian states. Regional Hindi implementation offices at Bengaluru, Thiruvananthapuram, Mumbai, Kolkata, Guwahati, Bhopal, Delhi and Ghaziabad have been established to monitor the implementation of Hindi in Central government offices and PSUs.
Annual targets are set by the Department of Official Language regarding the amount of correspondence being carried out in Hindi. A Parliament Committee on Official Language constituted in 1976 periodically reviews the progress in the use of Hindi and submits a report to the President. The governmental body which makes policy decisions and established guidelines for promotion of Hindi is the Kendriya Hindi Samiti (est. 1967). In every city that has more than ten central Government offices, a Town Official Language Implementation Committee is established and cash awards are given to government employees who write books in Hindi. All Central government offices and PSUs are to establish Hindi Cells for implementation of Hindi in their offices.
Recently, the Modi government announced plans to promote Hindi in government offices in Southern and Northeast India.
State level

The Indian constitution does not specify the official languages to be used by the states for the conduct of their official functions, and leaves each state free to, through its legislature, adopt Hindi or any language used in its territory as its official language or languages. The language need not be one of those listed in the Eighth Schedule, and several states have adopted official languages which are not so listed. Examples include Kokborok in Tripura; Mizo in Mizoram; Khasi and Garo in Meghalaya.
Legislature and administration
The constitutional provisions in relation to use of the official language in legislation at the State level largely mirror those relating to the official language at the central level, with minor variations. State legislatures may conduct their business in their official language, Hindi or (for a transitional period, which the legislature can extend if it so chooses) English, and members who cannot use any of these have the same rights to their mother tongue with the Speaker's permission. The authoritative text of all laws must be in English, unless Parliament passes a law permitting a state to use another language, and if the original text of a law is in a different language, an authoritative English translation of all laws must be prepared.
The state has the right to regulate the use of its official language in public administration, and in general, neither the constitution nor any central enactment imposes any restriction on this right. However, every person submitting a petition for the redress of a grievance to an officer or authority of the state government has a constitutional right to submit it in any language used in that state, regardless of its official status.
In addition, the constitution grants the central government, acting through the President, the power to issue certain directives to the government of a state in relation to the use of minority languages for official purposes. The President may direct a State to officially recognise a language spoken in its territory for specified purposes and in specified regions, if its speakers demand it and satisfy him that a substantial proportion of the State's population desire its use. Similarly, States and local authorities are required to endeavour to provide primary education in the mother tongue for all linguistic minorities, regardless of whether their language is official in that State, and the President has the power to issue directions he deems necessary to ensure that they are provided these facilities.
State judiciary
States have significantly less freedom in relation to determine the language in which judicial proceedings in their respective High Courts will be conducted. The constitution gives the power to authorise the use of Hindi, or the state's official language in proceedings of the High Court to the Governor, rather than the state legislature, and requires the Governor to obtain the consent of the President of India, who in these matters acts on the advice of the Government of India. The Official Languages Act gives the Governor a similar power, subject to similar conditions, in relation to the language in which the High Court's judgments will be delivered.
Four states—Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan— have been granted the right to conduct proceedings in their High Courts in their official language, which, for all of them, was Hindi. However, the only non-Hindi state to seek a similar power—Tamil Nadu, which sought the right to conduct proceedings in Tamil in its High Court—had its application rejected by the central government earlier, which said it was advised to do so by the Supreme Court. In 2006, the law ministry said that it would not object to Tamil Nadu state's desire to conduct Madras High Court proceedings in Tamil. In 2010, the Chief Justice of the Madras High Court allowed lawyers to argue cases in Tamil.
List
| No. | State | Official language(s) | Additional official language(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Andhra Pradesh | Telugu | ||
| 2. | Arunachal Pradesh | English | ||
| 3. | Assam | Assamese | Bengali in the three districts of Barak Valley | |
| 4. | Bihar | Hindi | Urdu (for specified areas and purposes) | |
| 5. | Chhattisgarh | Hindi | ||
| 6. | Goa | Konkani | Marathi | |
| 7. | Gujarat | Gujarati | Hindi | |
| 8. | Haryana | Hindi | Punjabi | |
| 9. | Himachal Pradesh | Hindi | English | |
| 10. | Jammu and Kashmir | Urdu | ||
| 11. | Jharkhand | Hindi | Urdu | |
| 12. | Karnataka | Kannada | ||
| 13. | Kerala | Malayalam | ||
| 14. | Madhya Pradesh | Hindi | ||
| 15. | Maharashtra | Marathi | ||
| 16. | Manipur | Meiteilon (Manipuri) | English | |
| 17. | Meghalaya | English | Khasi and Garo | |
| 18. | Mizoram | Mizo, English and Hindi | ||
| 19. | Nagaland | English | ||
| 20. | Odisha | Odia | English | |
| 21. | Punjab | Punjabi | ||
| 22. | Rajasthan | Hindi | English | |
| 23. | Sikkim | English | Additional ten local languages | |
| 24. | Tamil Nadu | Tamil | English | |
| 25. | Telangana | Telugu and Urdu | ||
| 26. | Tripura | Bengali, English and Kokborok | ||
| 27. | Uttar Pradesh | Hindi | Urdu | |
| 28. | Uttarakhand | Hindi | ||
| 29. | West Bengal | Bengali | Nepali |
| No. | Union territory | Official language(s) | Additional official language(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Hindi and English | |
| 2. | Chandigarh | English | |
| 3. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | Gujarati Marathi, and Hindi | |
| 4. | Daman and Diu | Gujarati and Konkani | |
| 5. | Delhi | Hindi | Punjabi and Urdu |
| 6. | Lakshadweep | Malayalam and English | |
| 7. | Puducherry | Tamil | Telugu and Malayalam |
Eighth Schedule to the Constitution
The Eighth Schedule to the Indian Constitution contains a list of 22 scheduled languages. At the time the constitution was enacted, inclusion in this list meant that the language was entitled to representation on the Official Languages Commission, and that the language would be one of the bases that would be drawn upon to enrich Hindi, the official language of the Union. The list has since, however, acquired further significance. The Government of India is now under an obligation to take measures for the development of these languages, such that "they grow rapidly in richness and become effective means of communicating modern knowledge." In addition, a candidate appearing in an examination conducted for public service at a higher level is entitled to use any of these languages as the medium in which he or she answers the paper.
Via the 92nd Constitutional amendment 2003, four new languages – Dogri, Maithili, Santali and Bodo – were added to the 8th Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
The table below lists the 22 languages set out in the Eighth Schedule as of May 2008, together with the regions where they are used.
Even though the English language is not included in the Eighth Schedule (as it is a foreign language), it is one of the official languages of the Union of India.
Of the 22 official languages, 15 are Indo-Aryan, four are Dravidian, two are Tibeto-Burman, and one is Munda.
Since 2003, a government committee has been looking into the feasibility of treating all languages in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution as "Official Languages of the Union".
Union–state and interstate communication
The language in which communications between different states, or from the union government to a state or a person in a state, shall be sent is regulated by the Official Languages Act and, for states other than Tamil Nadu, by the Official Languages Rules. Communication between states who use Hindi as their official language is required to be in Hindi, whereas communication between a state whose official language is Hindi and one whose is not is required to be in English, or in Hindi with an accompanying English translation (unless the receiving state agrees to dispense with the translation).
Communication between the union and states which use Hindi as their official language (classified by the Official Language Rules as "the states in Region A"), and with persons who live in those states, is generally in Hindi, except in certain cases. Communication with a second category of states "Region B", which do not use Hindi as their official language but have elected to communicate with the union in Hindi (currently Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Punjab) is usually in Hindi, whilst communications sent to an individual in those states may be in either Hindi or English. Communication with all other states "Region C", and with people living in them, is in English.
See also
- List of Indian languages by number of native speakers
- Names of the Indian Constitution in the official languages of India
Notes
- Some languages may be over- or underrepresented as the census data used is at the state-level. For example, while Urdu has 52 million speakers (2001), in no state is it a majority as the language itself is primarily limited to Indian Muslims.
- Bhutia, Gurung, Lepcha, Limboo, Mangar, Mukhia, Newari, Rai, Sherpa and Tamang are the Additional Official Languages for the purpose of preservation of culture and tradition.
- See Official languages of Puducherry
- Includes variants and dialects
References
- "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Retrieved 17 September 2016.
- ^ "Constitutional Provisions: Official Language Related Part-17 of The Constitution Of India". Department of Official Language, Government of India. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- "Hindi, not a national language: Court". The Hindu. 25 January 2010.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - "Scheduled Languages in descending order of speaker's strength - 2001". Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- Mollin, Sandra (2006). Euro-English: assessing variety status. Gunter Narr Verlag. p. 17. ISBN 978-3-8233-6250-0.
- Kanchan Chandra, "Ethnic Bargains, Group Instability, and Social Choice Theory," Politics and Society 29, 3: 337-62.
- ^ "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- Commissioner Linguistic Minorities Archived 8 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Language in India
- THE OFFICIAL LANGUAGES ACT, 1963 Archived 1 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- National Portal of India: Know India: Profile Archived 17 April 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Committee of Parliament on Official Language report Archived 20 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Hardgrave, Robert L. (August 1965). "The Riots in Tamilnadu: Problems and Prospects of India's Language Crisis". Asian Survey (University of California Press)
- "The force of words", Time, 19 February 1965, retrieved 5 June 2007
- Forrester, Duncan B. (Spring–Summer 1966), "The Madras Anti-Hindi Agitation, 1965: Political Protest and its Effects on Language Policy in India", Pacific Affairs, 39 (1/2): 19–36, doi:10.2307/2755179
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(5)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ^ "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(1)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- Notification No. 2/8/60-O.L. (Ministry of Home Affairs), dated 27 April 1960
- ^ "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 1". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(1b)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- Article 120(1) first proviso.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 5(1,2)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- www
.business-standard .com /article /government-press-release /use-of-hindi-language-in-courts-116042801074 _1 .html - "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Section 3(3)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015. names, amongst others, resolutions, general orders, rules, notifications, administrative or other reports or press communiques issued by a government department, agency or corporation; administrative and other reports and official papers laid before a House or the Houses of Parliament; and contracts and agreements executed, and licences, permits, notices and forms of tender issued by or on behalf of the government (including government companies).
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 1(ii)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 4(a)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 4(b,c)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 4(d)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 8". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "Official Language - Constitutional/Statutory Provisions". Government of India. Archived from the original on 17 April 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Centre to promote use of Hindi in South India, Northeast: Jitendra Singh". The Indian Express. 9 June 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- "Govt to promote use of Hindi in routine conversation, NE - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- Constitution of India, Article 345
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Section 7". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- Language in Courts - a bridge or a barrier?
- Special Correspondent (12 March 2007), "Karunanidhi stands firm on Tamil in High Court", The Hindu, p. 1
{{citation}}:|last=has generic name (help) - The Hindu: Tamil Nadu / Thanjavur News: No objection to Tamil as court language: A.P. Shah
- Silobreaker: Make Tamil the language of Madras High Court: Karu Archived 30 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- The Hindu: Tamil Nadu News: Karunanidhi hopeful of Centre’s announcement
- indianexpress.com
- Tamil Nadu government press release
- "Advocate argues in Tamil in High Court". The New Indian Express. 23 June 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- "Languages". APOnline. 2002. Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- "The Assam Official Language Act, 1960". Northeast Portal. 19 December 1960. Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ANI (10 September 2014). "Assam government withdraws Assamese as official language in Barak Valley, restores Bengali". DNA India. Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- "The Bihar Official Language Act, 1950" (PDF). National Commission for Linguistic Minorities. 29 November 1950. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- ^ Benedikter, Thomas (2009). Language Policy and Linguistic Minorities in India: An Appraisal of the Linguistic Rights of Minorities in India. LIT Verlag Münster. p. 89. ISBN 978-3-643-10231-7. Cite error: The named reference "Benedikter2009" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- The National Commission for Linguistic Minorities, 1950 (ibid) makes no mention of Chhattisgarhi as an additional state language, despite the 2007 notification of the State Govt, presumably because Chhattisgarhi is considered as a dialect of Hindi.
- "The Goa, Daman and Diu Official Language Act, 1987" (PDF). U.T. Administration of Daman & Diu. 19 December 1987. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- Kurzon, Dennis (2004). "3. The Konkani-Marathi Controversy : 2000-01 version". Where East Looks West: Success in English in Goa and on the Konkan Coast. Multilingual Matters. pp. 42–58. ISBN 978-1-85359-673-5. Retrieved 26 December 2014. Dated, but gives a good overview of the controversy to give Marathi full "official status".
- "The Haryana Official Language Act, 1969" (PDF). acts.gov.in (server). 15 March 1969. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- "Haryana grants second language status to Punjabi". Hindustan Times. 28 January 2010.
- "The Himachal Pradesh Official Language Act, 1975" (PDF). 21 February 1975. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- "Language and Literature", Official website of Government of Madhya Pradesh, Government of Madhya Pradesh, retrieved 16 July 2007
- Section 2(f) of the Manipur Official Language Act, 1979 states that the official language of Manipur is the Manipuri language (an older English name for the Meitei language) written in the Bengali script. The Sangai Express, Mayek body threatens to stall proceeding, retrieved 16 July 2007
- Commissioner Linguistic Minorities, 42nd report: July 2003 - June 2004, p. para 25.5, archived from the original on 8 October 2007, retrieved 16 July 2007
- Commissioner Linguistic Minorities, 43rd report: July 2004 - June 2005, p. para 25.1, archived from the original on 10 April 2009, retrieved 16 July 2007
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help). On 21 March 2006, the Chief Minister of Meghalaya stated in the State Assembly that a notification to this effect had been issued. Meghalaya Legislative Assembly, Budget session: Starred Questions and Answers - Tuesday, the 21st March 2006., retrieved 16 July 2007 - "Oriya to be official language in Orissa - Indian Express". archive.indianexpress.com. 2 January 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2016.
- Government of Sikkim, Introduction to Sikkim, retrieved 16 July 2007
- Eleven other languages — Bhutia, Lepcha, Limboo, Newari, Gurung, Mangar, Mukhia, Rai, Sherpa and Tamang - are termed "official", but only for the purposes of the preservation of culture and tradition. Commissioner Linguistic Minorities, 43rd report: July 2004 - June 2005, pp. paras 27.3–27.4, archived from the original on 10 April 2009, retrieved 16 July 2007
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help). See also Commissioner Linguistic Minorities, 41st report: July 2002 - June 2003, p. paras 28.4, 28.9, archived from the original on 24 February 2007, retrieved 16 July 2007 - "Bengali and Kokborok are the state/official language, English, Hindi, Manipuri and Chakma are other languages". Tripura Official government website. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- Tripura Official Language Act, 1964
- Commissioner Linguistic Minorities, 43rd report: July 2004 - June 2005, pp. paras 6.1–6.2, archived from the original on 10 April 2009, retrieved 16 July 2007
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Urdu and Punjabi are the two secondary official languages of Delhi under the Delhi Official Language Bill, 2000 Punjabi, Urdu made official languages in Delhi, The Times of India, 25 June 2003, retrieved 17 July 2007
- There are three primary languages used for official purposes - Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam. Only, English is recognized for official uses as per the official language policy. The official language policy of the union territory states that the Tamil language should be the primary language used for all or any of the official purposes of the union territory. In case of Mahe and Yanam, Malayalam and Telugu, respectively, may be used instead of or in conjunction with Tamil. The English language may also be used for official purposes. (ACT 28, Gazetteer, Pondicherry Vol. 1, P. II)Multilingualism and second language acquisition and learning in Pondicherry
- Office of the Chief Electoral Officer, Puducherry, General Information on Pondicherry, archived from the original on 28 September 2007, retrieved 6 June 2007
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Constitution of India, Article 344(1).
- Constitution of India, Article 351.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 2". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 4". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- National Portal of India: Government: Constitution of India Archived 31 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Constitution of India Archived 9 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine, page 330, EIGHTH SCHEDULE, Articles 344 (1) and 351]. Languages.
- "Statement 1 - Abstract of Speakers' Strength of Languages and Mother Tongues - 2001". Government of India. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2016.
- http://www.bihardays.com/jharkhands-11-second-languages-will-create-new-jobs-enrich-national-culture/
- "The Origins of the Konkani Language". www.kamat.com. 15 August 1997 – 15 January 2016.
- "Indian Languages: Konkani Language". iloveindia.com.
- "Oriya gets its due in neighbouring state- Orissa- IBNLive". Ibnlive.in.com. 4 September 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- Naresh Chandra Pattanayak Sep 1, 2011, 08.04am IST (1 September 2011). "Oriya second language in Jharkhand - Times Of India". Articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - "Bengali, Oriya among 12 dialects as 2nd language in Jharkhand". daily.bhaskar.com. 31 August 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- "A Committee has been constituted under the Chairmanship of Shri Sita Kant Mohapatra to make recommendation, inter-alia on the feasibility of treating all languages in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution, including Tamil, as Official Languages of the Union. The Government will consider the recommendations of the Committee and take a suitable decision in the matter."Indian parliament Archived 21 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(1)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 2(g)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(2)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- "The Official Languages (Use for Official Purpose of the Union) - Rules 1976 (As Amended, 1987) - Paragraph 3(3)". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
External links
- Department of Official Language (DOL) – Official webpage explains the chronological events related to Official Languages Act and amendments
- Central Institute of Indian Languages – A comprehensive federal government site that offers complete info on Indian Languages
- Reconciling Linguistic Diversity: The History and the Future of Language Policy in India by Jason Baldridge
- Multi-lingualism and language policy in India
- Words and phrases in more than 30 Indian languages
| Languages of India | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official languages |
| ||||||||||
| Major unofficial languages |
| ||||||||||
| Major languages of South Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Languages of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contemporary languages |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scripts |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prestige language- influence | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activism | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||