| Revision as of 06:44, 18 March 2007 view source60.229.224.50 (talk) →Tomb of Nefertari← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:11, 13 January 2025 view source Cerebrality (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,052 edits →Sed festivals: Amun favorite god before first Sed festival | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty (1303–1213 BC)}} | |||
| {{Pharaoh Infobox | | |||
| {{redirect|Ramses II|the heavily modified Soviet T-55 main battle tank of the Egyptian military|Ramses II tank}} | |||
| Name=Ramesses II| | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| Image=].]] | | |||
| {{Protection padlock|small=yes}} | |||
| Nomen=<hiero><-i-mn:n:N36-ra:Z1-ms-s-sw-></hiero><br>Ramesses (meryamun)<br>''Born of Re, (Beloved of Amun)'' | | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2024}} | |||
| Pronomen=<hiero><-ra-wsr-mAat-ra*stp:n-></hiero><br>Usermaatre-setepenre<br>''The Justice of Re is Powerful,<br>Chosen of Re'' | | |||
| {{Infobox pharaoh | |||
| Golden=Userrenput-aanehktu | | |||
| | name = Ramesses II | |||
| Nebty=Mekkemetwafkhasut | | |||
| | alt_name = Ramesses the Great, Ozymandias | |||
| Horus=Kanakht Merymaa | | |||
| | image =Ramses II British Museum.jpg | |||
| Reign=66 years<br>1279 BC to 1213 BC | | |||
| | caption = The ] ({{circa|1250 BC}}), a statue depicting Ramesses II, from the ] in ]. Currently on display at the ] in ]. | |||
| Predecessor=] | | |||
| | reign = 1279–1213 BC | |||
| Successor=] | | |||
| | dynasty = ] | |||
| Spouse=], ]<br>] | | |||
| | predecessor = ] | |||
| Issues=], ], ], <br> ], ]<br /> see also: ] | | |||
| | successor = ] | |||
| Dynasty=] | | |||
| Father=] | | |||
| Mother=] | | |||
| Born=1302 BC | | |||
| Died=1213 BC | | |||
| Burial=] | | |||
| Monuments=], ], <br>],etc.| | |||
| Alt=Ramesses the Great <br>alternatively transcribed as Ramses and Rameses | | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Ramesses II''' (also known as '''Ramesses the Great''' and alternatively ] as '''Ramses''' and '''Rameses''' {{unicode|''*Riʕmīsisu''}}) was an ]ian ] of the ]. He is often regarded as Egypt's greatest and most powerful pharaoh.<ref>James Putnan,An introduction to egyptology,1990</ref> He was born ca. 1302 BC. At age fourteen, Ramesses was appointed Prince Regent by his father ].<ref>James Putnan,An introduction to egyptology, 1990</ref> He is believed to have taken the throne in his early 20s and to have ruled Egypt from 1279 BC to 1213 BC<ref>Michael Rice, Who's Who in Ancient Egypt, Routledge, 1999</ref> for a total of 66 years and 2 months, according to Manetho. He was once said to have lived to be 99 years old, but it is more likely that he died in his 90th or 91st year. ] writers such as ] attributed his accomplishments to the semi-mythical ], and he is traditionally believed to have been the Pharaoh of ] due to a tradition started by ]. If he became king in 1279 BC as most Egyptologists today believe, he would have assumed the throne on ], ] based on his known accession date of '''III Shemu day 27'''.<ref>J. von Beckerath, ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten'', Mainz, (1997), pp.108 & 190</ref><ref>Peter J. Brand, The Monuments of Seti I: Epigraphic, Historical and Art Historical Analysis, Brill, NV Leiden (2000), pp.302-305</ref> Ramesses II would celebrate an unprecedented total of 14 ]s during his reign--more than any other pharaoh.<ref>David O'Connor & Eric Cline, Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign, University of Michigan Press, 1998, p.16</ref> | |||
| | horus = ''Ka nakht, Mery maat''{{Sfnp|Leprohon|2013|pp=114-115}}<br>The strong bull, beloved of right (truth){{sfnp|Tyldesley|2001|p=xxiv}} | |||
| ==Life== | |||
| | horus_hiero = <hiero>E1:D44-C10-mr</hiero> | |||
| ] between ] of ] and Ramesses II of ], at the ].]] | |||
| | nebty = ''Mek kemet, waf khasut''{{Sfnp|Leprohon|2013|pp=114-115}}<br>Protector of Egypt who curbs foreign lands{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2001|p=xxiv}} | |||
| Ramesses II was the third king of the ], and the second child of ] and his ]. <ref>Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, Thames & Hudson (2004), p.164</ref> His only known sibling was ], though in the case of ], one of his Great Royal Wives, it is not clear whether she was a younger sister or a daughter of Ramesses. | |||
| | nebty_hiero = <hiero>G20-V31-I6-t:O49-G45-f:Z7</hiero><br><hiero>D44-N25-t:Z2</hiero> | |||
| | golden = ''User renput, aa nakhtu''{{Sfnp|Leprohon|2013|pp=114-115}}<br>Rich in years – great in victories{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2001|p=xxiv}} | |||
| | golden_hiero = <hiero>wsr-s-M4-M4-M4-O29:D44:Z2</hiero> | |||
| | prenomen = ''User maat Re, setep en Re''{{Sfnp|Leprohon|2013|pp=114-115}}<br>The justice of ] is powerful – chosen of Rê{{sfnp|Clayton|1994|p=146}} | |||
| | prenomen_hiero = <hiero>ra-wsr-mAat-ra*stp:n</hiero> | |||
| | nomen = ''Ra mes su, mery Amun''{{Sfnp|Leprohon|2013|pp=114-115}}<br>Rê is the one who bore him, beloved of ]{{sfnp|Clayton|1994|p=146}} | |||
| | nomen_hiero = <hiero>i-mn:n:N36-ra:Z1-ms-s-sw</hiero> | |||
| | consort = ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | |||
| The most memorable of Ramesses' wives was ]. During his long reign, eight women held the title ] Jimmy Dunn: The Queens of Ramesses II]</ref> (often simultaneously): ] and ], whom he married early in his reign; ], ] and ], his own daughters who replaced their mothers Nefertari and Isetnofret when they died or retired; ]; ], Princess of ]; another Hittite princess whose name did not survive.<ref>Dodson & Hilton, op.cit., pp. 170-172</ref> | |||
| | children = 88–103 ('']'') | |||
| | father = ] | |||
| | mother = ] | |||
| | birth_date = {{circa|1303 BC}} | |||
| | death_date = {{circa|1213 BC}} (aged 90–91) | |||
| | Burial = ] | |||
| | Monuments = ], ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.philae.nu/akhet/ARamsTempl.html |title=Mortuary temple of Ramesses II at Abydos |access-date=28 October 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081222024716/http://www.philae.nu/akhet/ARamsTempl.html |archive-date=22 December 2008 }}</ref> ], ],<ref name="Bart">{{cite web |url=http://euler.slu.edu/Dept/Faculty/bart/egyptianhtml/kings%20and%20Queens/Temples_of_Ramesses_II.html |title=Temples of Ramesses II |author=Anneke Bart |access-date=23 April 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080428001908/http://euler.slu.edu/Dept/Faculty/bart/egyptianhtml/kings%20and%20Queens/Temples_of_Ramesses_II.html |archive-date=28 April 2008 |url-status=dead}}</ref> ]<ref name="Bart" />}} | |||
| '''Ramesses II'''{{efn|Other ] include '''Rameses''' and '''Ramses''' (from {{langx|grc-x-koine|Ῥαμέσσης}}, {{Transliteration|grc|Rhaméssēs}}).<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |year=2004 |title=Rameses |encyclopedia=Webster's New World College Dictionary |publisher=Wiley Publishing |url=http://www.yourdictionary.com/Rameses |access-date=27 April 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111002183650/http://www.yourdictionary.com/Rameses |archive-date=2 October 2011 |url-status=live}}</ref>}} ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|r|æ|m|ə|s|iː|z|,_|ˈ|r|æ|m|s|iː|z|,_|ˈ|r|æ|m|z|iː|z}}; {{langx|egy|]}}, {{Transliteration|egy|Rīꜥa-masē-sə}},{{Efn|Meaning "] is the one who bore him" in the ].}} {{IPA|egy|ɾiːʕamaˈseːsə}}; {{nowrap|{{circa|1303 BC – 1213 BC}}}}),<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |year=2004 |title=Ramses |encyclopedia=Webster's New World College Dictionary |publisher=Wiley Publishing |url=http://www.yourdictionary.com/Ramses |access-date=27 April 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120124063401/http://www.yourdictionary.com/ramses |archive-date=24 January 2012 |url-status=live}}</ref> commonly known as '''Ramesses the Great''', was an ]. He was the third ruler of the ]. Along with ] of the ], he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the ], which itself was the most powerful period of ].{{sfnp|Putnam|1990|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the ], generally considered a stalemate.<ref>Kulkarni, P., Ji, Z., Xu, Y., Neskovic, M., & Nolan, K. (2023). ''Exploring Semantic Perturbations on Grover''. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.00509.</ref> | |||
| The writer ] stated in ] that Ramesses II had as many as 20 sons and 20 daughters but scholars today believe his offspring numbered over a hundred in total. In 2004, Dodson and Hilton noted that the monumental evidence "seems to indicate that Ramesses II had around 110 children-- 48-50 sons and 40-53 daughters."<ref>Dodson & Hilton, op.cit., p.166</ref> His children include ] and ] (princesses and their father's wives), Sethnakhte, ] the king's first born son, ] (who would eventually succeed him as Ramesses' 13th son), and Prince ]. Ramesses II's second born son, ]--sometimes called Ramesses Junior--became the crown prince from Year 25 to Year 50 of his father's reign after the death of Amen-her-khepesh.<ref>Dodson & Hilton, op. cit., p.173</ref> | |||
| In ], he is called '''Ozymandias''',{{efn|{{langx|grc-x-koine|Ὀσυμανδύας}}, {{Transliteration|grc|Osymandýas}}.}}<ref>{{cite web |author1=Diodorus Siculus |author-link1=Diodorus Siculus |title=Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca Historica, Books I-V, book 1, chapter 47, section 4 |website=www.perseus.tufts.edu |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A2008.01.0540%3Abook%3D1%3Achapter%3D47%3Asection%3D4 |access-date=10 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110506022136/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A2008.01.0540%3Abook%3D1%3Achapter%3D47%3Asection%3D4 |archive-date=6 May 2011 |url-status=live}}</ref> derived from the first part of his Egyptian-language regnal name: {{lang|egy-Latn|Usermaatre ]}}.{{efn|"The ] of ] is powerful—chosen of Ra."}}<ref name="pdsOzymandias">{{cite web |url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/egypt/explore/ramses.html |title=Ozymandias |website=] |access-date=30 March 2008|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071213185559/http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/egypt/explore/ramses.html |archive-date=13 December 2007}}</ref> Ramesses was also referred to as the "Great Ancestor" by successor pharaohs and the Egyptian people. | |||
| In his second year, Ramesses II decisively defeated the ] or Sherden sea pirates who were wreaking havoc along Egypt's Mediterranean coast by attacking cargo-ladden vessels travelling the sea routes to Egypt.<ref>N. Grimal, ''A History of Ancient Egypt'' (Oxford: Blackwell, 1992) pp.250-253</ref> The Sherden people came from the coast of ] or south-west Turkey, more likely Ionia. Ramesses posted troops and ships at strategic points along the coast and patiently allowed the pirates to attack their prey before skillfully catching them by surprise in a sea battle and capturing them all in one fell swoop.<ref>Joyce Tyldesley, ''Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh'', Viking/Penguin Books (2000), pp.53</ref> Ramesses would soon incorporate these skilled mercenaries into his army where they were to play a pivotal role at the battle of Kadesh. As king, Ramesses II led several expeditions north into the lands east of the ] (the location of the modern ], ] and ]). | |||
| For the early part of his reign, he focused on building cities, temples, and monuments. After establishing the city of ] in the ], he designated it as Egypt's new capital and used it as the main staging point for his campaigns in ]. Ramesses led several military expeditions into the ], where he reasserted Egyptian control over ] and ]; he also led a number of expeditions into ], all commemorated in inscriptions at ] and ]. He celebrated an unprecedented thirteen or fourteen ]s—more than any other pharaoh.{{sfnp|O'Connor|Cline|1998|p=16}} | |||
| ==Battle of Kadesh== | |||
| ], at the ], in a relief inside his ] temple.]] | |||
| After some preparations, Ramesses decided to attack territory in the Levant which belonged to a more substantial enemy: the Hittite Empire. At the ] in May 1274 BC towards the end of the Fourth year of his reign, Egyptian forces under his leadership marched through the coastal road through Canaan and south Syria through the ] and approached Kadesh from the south..<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.68</ref> Ramesses planned to seize the citadel of Kadesh which belonged to king ] of the ]. The battle almost turned into a disaster as Ramesses was initially tricked by two Bedouin spies in the pay of the Hittites to believe that Muwatallis and his massive army were still 120 miles north of Kadesh. Ramesses II only learned of the true nature of his dire predicament when a subsequent pair of Hittite spies were captured, beaten and forced to reveal the truth before him: | |||
| Estimates of his age at death vary, although 90 or 91 is considered to be the most likely figure.{{sfnp|von Beckerath|1997|pp=108, 190}}{{sfnp|Brand|2000|pp=302–305}} Upon his death, he was buried in a tomb (]) in the ];<ref>{{cite web |author=Leblanc |first=Christian |title=Gerard |url=http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/Gerard_Flament/ramstomb.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071204180741/http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/Gerard_Flament/ramstomb.htm <!-- Bot retrieved archive --> |archive-date=4 December 2007 |access-date=23 April 2008}}</ref> his body was later moved to the ], where it was discovered by archaeologists in 1881. Ramesses' ] is now on display at the ], located in the city of ].<ref name=Parisse>{{cite news |last=Parisse |first=Emmanuel |date=5 April 2021 |title=22 Ancient Pharaohs Have Been Carried Across Cairo in an Epic 'Golden Parade' |url=https://www.sciencealert.com/22-ancient-pharaohs-have-been-carried-across-cairo-in-an-epic-golden-parade |work=ScienceAlert |access-date=5 April 2021 |archive-date=27 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220327201021/https://www.sciencealert.com/22-ancient-pharaohs-have-been-carried-across-cairo-in-an-epic-golden-parade |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{cquote|When they had been brought before Pharaoh, His Majesty asked, 'Who are you?' They replied 'We belong to the king of ]. He has sent us to spy on you.' Then His Majesty said to them, 'Where is he, the enemy from Hatti? I had heard that he was in the land of Khaleb, north of Tunip.' They replied to His Majesty, 'Lo, the king of ] has already arrived, together with the many countries who are supporting him... They are armed with their infantry and their ]s. They have their weapons of war at the ready. They are more numerous than the grains of sand on the beach. Behold, they stand equipped and ready for battle behind the old city of ].'<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', pp.70-71</ref>}} | |||
| == Early life == | |||
| Ramesses had fallen into a well-laid trap by Muwatallis whose thousands of infantry and chariotry were hidden well behind the eastern bank of the ] river under the command of the king's brother, ]. The Egyptian army itself had been divided into two main forces – the Re and Amun brigades with Ramesses and the Ptah and Seth brigades – separated from each other by forests and the far side of the Orontes river.<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', pp.70-73</ref> The Re brigade was almost totally destroyed by the surprise initial Hittite chariot attack and Ramesses II had barely enough time to rally his own Amun brigade and secure reinforcements from the Ptah Army Brigade (who were just arriving upon the scene of battle) to turn the tide of battle against the Hittites. While Ramesses II had in theory 'won' the battle, Muwatallis had effectively won the war since the pharaoh could not secure victory due to his battlefield losses. Ramesses was compelled to retreat south with the Hittite commander ] relentlessly harrying the Egyptian forces through the Bekaa Valley; the Egyptian province of Upi was also captured according to the Hittite records at ].<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.73</ref> | |||
| Ramesses II was not born a prince. His grandfather ] was a vizier and military officer during the reign of pharaoh ], who appointed Ramesses I as his successor; at that time, Ramesses II was about eleven years old.<ref>Darnell, J. C., & Manassa, C. (2007). ''Tutankhamun's Armies: Battle and Conquest During Ancient Egypt's Late Eighteenth Dynasty''. John Wiley & Sons.</ref> | |||
| ] (])]] | |||
| After Ramesses I died, his son, ] became king, and designated his son Ramesses II as prince regent at about the age of fourteen.{{sfnp|Putnam|1990|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} | |||
| ==Aftermath== | |||
| Egypt's sphere of influence was now restricted to Canaan while Syria fell into Hittite hands. Over the ensuing years, Rameses II would return to campaign against the Hittites and even achieved several spectacular victories (at a time of Hittite weakness due to a dispute over Muwatallis' succession) to briefly capture the cities of ], where no Egyptian soldier had been seen since the time of ] almost 120 years previously and even Kadesh in his 8th and 9th Years.<ref>Grimal, op. cit., pp. 256f.</ref> However, neither power could decisively defeat the other in battle. Consequently, in the twenty-first year of his reign (]), Ramses decided to conclude an agreement with the new Hittite king at Kadesh, Hattusili III, to end the conflict. The ensuing document is the earliest known ] in world history. | |||
| ==Reign length== | |||
| Ramesses II also campaigned south of the ] into ]. He constructed many impressive monuments, including the renowned archeological complex of ], and the ] known as the ]. It is said that there are more statues of him in existence than of any other Egyptian pharaoh, not surprising as he was the second-longest reigning Pharaoh of Egypt after ]. Rameses may have used art as a means of propaganda and his victories over foreigners are depicted on numerous temple reliefs while he had more colossal statues than any other pharaoh. He also usurped many existing statues by inscribing his own ] on them. Many of these building projects date from his early years and it appears that there was considerable economic decline towards the end of his long 66-year reign. The colossal ] was reconstructed and erected on Ramses Square in Cairo in ]. | |||
| Ramesses date of accession to the throne is recorded as III ], day 27, which most ] believe to be 31 May 1279 BC.{{sfnp|von Beckerath|1997|pp=108, 190}}{{sfnp|Brand|2000|pp=302–305}} | |||
| <br clear=all> In August 2006, contractors moved the 3,200-year-old statue of him from Ramesses Square to save it from exhaust fumes that were causing the 83-ton statue to deteriorate.<ref></ref> The statue was originally taken from a temple in Memphis. The new site will be located near the future ]. | |||
| The Jewish historian ], in his book '']'' which included material from ]'s ''Aegyptiaca'', assigned Ramesses II ("Armesses Miamun") a reign of 66 years, 2 months.<ref> © 2011–2023 by Peter Lundström—Some Rights Reserved—V. 4.0.</ref> This is essentially confirmed by the calendar of Papyrus ] fragment L, where Year 67, I ] day 18 of Ramesses II is immediately followed by Year 1, II ] day 19 of ] (Ramesses II's son), meaning Ramesses II died about 2 months into his 67th Regnal year.<ref>A. H. Gardiner, Ramesside Administrative Documents, (Oxford, 1948), 30, 10, and 14.</ref> | |||
| {{pagenumbers|date=February 2007}} | |||
| ==Min Festival== | |||
| This ancient festival, dating back to pre-dynastic Egypt,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thekeep.org/~kunoichi/kunoichi/themestream/min.html|title=Min}}</ref> was still very popular during Ramesses II's time. It was connected with the worship of the king and was carried out in the last month of the summer.<ref name=Skliar>Ania Skliar, ''Grosse kulturen der welt-Ägypten'', 2005</ref> The festival was carried out by the king himself, followed by his wife, royal family, and the ].<ref name=Skliar/> When the king entered the ] of the god ], he brought ]s and burning incense.<ref name=Skliar/> Then, the standing god was carried out of the ] on a shield carried by 22 priests.<ref name=Skliar/> In front of the statue of the god there were also two small seated statues of the pharaoh. In front of the god Min there was a large ceremonial procession that included dancers and priests. In front of them was a king with a white bull that was wearing a solar disc between its horns.<ref name=Skliar/> When the god arrived at the end of the procession, he is given sacrificial offerings from the ]. At the end of the ], the pharaoh was given a bundle of ] that symbolised ].<ref name=Skliar/> | |||
| In 1994, A. J. Peden proposed that Ramesses II died between II Akhet day 3 and II Akhet day 13 on the basis of Theban graffito 854+855, equated to Merneptah's Year 1 II Akhet day 2.<ref>A. J. Peden, A Note on the Accession Date of Merenptah, p. 69.</ref> The workman's village of ] preserves a fragment of a mid-20th dynasty necropolis journal (P. Turin prov. nr. 8538 recto I, 5; unpublished) which records that the date II Akhet day 6 was a Free feast day for the "Sailing of UsimaRe-Setepenre." (for Ramesses II).<ref name="auto">R. J. Demarée, , JEOL 46 (2016), p. 125.</ref> As the Egyptologist Robert J. Demarée notes in a 2016 paper: | |||
| ==Building activity and monuments== | |||
| : The feast called ẖnw – ‘Sailing’ – was clearly observed in Thebes or at ] during the Ramesside Period in remembrance of the passing of deified royals. The ‘Sailing’ of ] was celebrated on II Shemu 15; the ‘Sailing’ of Seti I on III Shemu 24; and the ‘Sailing’ of Ramesses II on II Akhet 6.<ref name="auto"/> | |||
| In contrast to the buildings of other pharaohs, many of the monuments from the reign of Ramesses II are well preserved. There are accounts of his glory hewn on stone, statues, remains of palaces and temples,most notable the ] in the western ] and the rock temples of ]. He covered the land from the ] to ] with buildings in a way no ] before him had done.<ref>Wolfhart Westendorf,Das alte ägypten,1969</ref> | |||
| He also founded a new capital city in the Delta during his reign called ]; it had previously served as a summer palace during Seti I's reign. | |||
| The date of Ramesses II's recorded death on II Akhet day 6 falls perfectly within A. J. Peden's estimated timeline for the king's death in the interval between II Akhet day 3 and II Akhet day 13. This means that Ramesses II died on Year 67, II ] day 6 of his reign after ruling Egypt for 66 years 2 months and 9 days. | |||
| ===Ramesseum=== | |||
| {{further|]}} | |||
| ==Military campaigns== | |||
| ] courtyard]] | |||
| Early in his life, Ramesses II embarked on numerous campaigns to restore possession of previously held territories lost to the ]ns and ] and to secure Egypt's borders. He was also responsible for suppressing some Nubian revolts and carrying out a campaign in ]. Though the ] often dominates the scholarly view of Ramesses II's military prowess and power, he nevertheless enjoyed more than a few outright victories over Egypt's enemies. During his reign, the Egyptian army is estimated to have totaled some 100,000 men: a formidable force that he used to strengthen Egyptian influence.<ref name="Gabriel6">{{cite book |last=Gabriel |first=R. |year=2002 |title=The Great Armies of Antiquity |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |isbn=9780275978099 |page=6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y1ngxn_xTOIC}}</ref> | |||
| Ever since the 19th century, the temple complex known as the ], which was built by Ramesses II between ] and the desert, has been known by this name. The Greek ] ] marveled at his gigantic and famous temple which is now no more than a few ruins. | |||
| ===Battle against Sherden pirates=== | |||
| Oriented northwest and southeast, the temple itself was preceded by two courts. An enormous pylon stood before the first court, with the royal palace at the left and the gigantic statue of the king looming up at the back.<ref name=Skliar/> Only fragments of the base and torso remain of the syenite statue of the enthroned pharaoh, 17 meters high and weighing more than 1000 tons. The scenes of the great pharaoh and his army triumphing over the Hittite forces fleeing before ], represented in line with the canons of the "epic poem of Pentaur", can still be made out of the pylon.<ref name=Skliar/> Remains of the second court include part of the internal facade of the pylon and a portion of the Osiride portico on the right.<ref name=Skliar/> Scenes of war and the rout the ] at Kadesh are repeated on the walls.<ref name=Skliar/> In the upper registers, feast and honor of the phallic god ], god of fertility.<ref name=Skliar/> On the opposite side of the court the few Osiride pillars and columns still left can furnish an idea of the original grandeur.<ref name=Skliar/> Scattered remains of the two statues of the seated king can also be seen, one in pink granite and the other in black granite, which once flanked the entrance to the ].<ref name=Skliar/> Thirty-nine out of the forty-eight columns in the great ] (m 41x 31) still stand in the central rows. They are decorated with the usual scenes of the king before various gods. Part of the ceiling decorated with gold stars on a blue ground has also been preserved.<ref name=Skliar/> The sons and daughters of Ramesses appear in the procession on the few walls left. The sanctuary was composed of three consecutive rooms, with eight columns and the tetrastyle cell.<ref name=Skliar/> Part of the first room, with the ceiling decorated with astral scenes, and few remains of the second room are all that is left. Vast storerooms built in mud bricks stretched out around the temple.<ref name=Skliar/> Traces of a school for scribes were found among the ruins. | |||
| In his second year, Ramesses II decisively defeated the ] sea pirates who were wreaking havoc along Egypt's Mediterranean coast by attacking cargo-laden vessels travelling the sea routes to ].{{sfnp|Grimal|1992|pp=250–253}} The Sherden people probably came from the coast of ], from southwest ] or perhaps, also from the island of ].<ref>{{harvp|Drews|1993|p=54}}: "Already in the 1840s Egyptologists had debated the identity of the "northerners, coming from all lands," who assisted the Libyan King Meryre in his attack upon Merneptah. Some scholars believed that Meryre's auxiliaries were merely his neighbors on the Libyan coast, while others identified them as Indo-Europeans from north of the Caucasus. It was one of Maspero's most illustrious predecessors, Emmanuel de Rougé, who proposed that the names reflected the lands of the northern Mediterranean: the Lukka, Ekwesh, Tursha, Shekelesh, and Shardana were men from ], ], ] (western Italy), ], and ]." De Rougé and others regarded Meryre's auxiliaries—these "peoples de la mer Méditerranée"—as mercenary bands, since the ], at least, were known to have served as mercenaries already in the early years of Ramesses the Great. Thus the only "migration" that the Karnak Inscription seemed to suggest was an attempted encroachment by Libyans upon neighboring territory."</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Gale |first=N. H. |title=On Cooking Pots, Drinking Cups, Loomweights and Ethnicity in Bronze Age Cyprus and Neighbouring Regions |year=2011 |editor1=Karageorghis |editor-first=V. |location=Nicosia |chapter=Source of the Lead Metal used to make a Repair Clamp on a ] Vase recently excavated at Pyla-Kokkinokremos on Cyprus |editor2=O. Kouka}}</ref>{{sfnp|O'Connor|Cline|1998|pp=112–113}} Ramesses posted troops and ships at strategic points along the coast and patiently allowed the pirates to attack their perceived prey before skillfully catching them by surprise in a sea battle and capturing them all in a single action.{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2000|p=53}} A ] from ] speaks of their having come "in their war-ships from the midst of the sea, and none were able to stand before them". There probably was a naval battle somewhere near the mouth of the Nile, as shortly afterward, many Sherden are seen among the pharaoh's body-guard where they are conspicuous by their horned helmets having a ball projecting from the middle, their round shields, and the great ] with which they are depicted in inscriptions of the Battle of Kadesh.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.eclectichistorian.net/Griffzungenschwert |title=The Naue Type II Sword |access-date=30 May 2008|url-status=live|archive-date=20 July 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080720183900/http://www.eclectichistorian.net/Griffzungenschwert/}}</ref> In that sea battle, together with the Sherden, the pharaoh also defeated the ] (L'kkw, possibly the people later known as the ]), and the Šqrsšw (]) peoples. | |||
| === Syrian campaigns === | |||
| A temple of ], of which nothing is now left but the foundations, once stood to the right of the hypostyle hall. It consisted of a peristyle court with two chapel shrines. The entire complex was enclosed in mud brick walls which started at the gigantic southeast pylon. | |||
| ====First Syrian campaign==== | |||
| ] showing him capturing enemies: a Nubian, a Libyan and a Syrian, {{Circa|1250 BC}}. ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Richardson |first1=Dan |title=Cairo and the Pyramids (Rough Guides Snapshot Egypt) |date=2013 |publisher=Rough Guides UK |isbn=978-1-4093-3544-3 |page=14 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VgtCeNKcs-IC&pg=PT14 |language=en |access-date=4 July 2020 |archive-date=8 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200708230914/https://books.google.com/books?id=VgtCeNKcs-IC&pg=PT14 |url-status=live }}</ref>]] | |||
| The immediate antecedents to the Battle of Kadesh were the early campaigns of Ramesses II into ]. His first campaign seems to have taken place in the fourth year of his reign and was commemorated by the erection of what became the first of the ] near what is now ]. The inscription is almost totally illegible due to weathering. | |||
| In the fourth year of his reign, he captured the Hittite vassal state of the Amurru during his campaign in Syria.{{sfnp|Grimal|1992|pp=253 ff}} | |||
| ===Abu Simbel=== | |||
| {{further|]}} | |||
| The great temple of Ramesses II at ] was discovered in 1813 by the famous Swiss Orientalist and traveler ]. However, four years passed before anyone could enter the temple, because an enormous pile of sand almost completely covered the facade and its colossal statues, blocking the entranceway. This feat was achieved by the great Paduan explorer ], who managed to penetrate the interior on 4 August 1817.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref>] colossus]] | |||
| ====Second Syrian campaign==== | |||
| The Great Temple at Abu Simbel,which took about twenty years to build was completed around year 24 of the reign of Ramesses the Great(which corresponds to 1265 BC). It was dedicated to the gods ], ], and ], as well as to the deified Ramesses himself.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Battle of Kadesh}}The Battle of Kadesh in his fifth regnal year was the climactic engagement in a campaign that Ramesses fought in Syria, against the resurgent Hittite forces of ]. The pharaoh wanted a victory at ] both to expand Egypt's frontiers into Syria, and to emulate his father Seti I's triumphal entry into the city just a decade or so earlier. | |||
| He also constructed his new capital, ]. There he built factories to manufacture weapons, chariots, and shields, supposedly producing some 1,000 weapons in a week, about 250 chariots in two weeks, and 1,000 shields in a week and a half. After these preparations, Ramesses moved to attack territory in the ], which belonged to a more substantial enemy than any he had ever faced in war: the ].{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2000|p=68}} | |||
| Four colossal 20 meter statues of the pharaoh with the double crown of Upper and Lower Egypt decorate the facade of the temple which is 35 meters wide and is toped by a frieze with 22 baboons, worshippers of the sun and flank the entrance.<ref name=Skliar/> This latter is crowned by a bas-relief representing two images of the king worshiping Ra Harakhti, whose statue stands in a large niche.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> This god is holding the hieroglyph user in his right hand and a feather while ], the goddess of truth and justice) in on his left; this is nothing less than a gigantic cryptogram for Ramesses II`s throne nane, User-Maat-Re. Next to the legs of the colossi, there are other statues no higher than the knees of the pharaoh.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> These depict ], Ramesses`s chief wife and queen mother Mut-Tuy, princes ], Ramesses, and the princesses ], ] and ]. | |||
| After advancing through ] for exactly a month, according to the Egyptian sources, Ramesses arrived at Kadesh on 1 May 1274 BC.<ref>Obsomer 2012: 134; the date is Gregorian, equivalent to the Julian 12 May.</ref> Here, Ramesses' troops were caught in a Hittite ambush and were initially outnumbered by the enemy, whose chariotry smashed through the second division of Ramesses' forces and attacked his camp. Receiving reinforcements from other Egyptian divisions arriving on the battlefield, the Egyptians counterattacked and routed the Hittites, whose survivors abandoned their chariots and swam the ] to reach the safe city walls.<ref>Detailed analysis of the Egyptian sources in Obsomer 2012: 127–171; see also Bryce 2005: 234–239.</ref>{{Citation needed|date=October 2022|reason=Was sourced to the unreliable History Channel: https://web.archive.org/web/20080416015854/http://www.history.com/shows.do?action=detail&episodeId=211104}} Although left in possession of the battlefield, Ramesses, logistically unable to sustain a long siege, returned to Egypt.<ref name="hittites.info">. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131014163832/http://www.hittites.info/history.aspx?text=history%2FMiddle+Late+Empire.htm|date=14 October 2013}}.</ref><ref name="Dougherty">100 Battles, ''Decisive Battles that Shaped the World'', Dougherty, Martin, J., Parragon, pp. 10–11.</ref> While Ramesses claimed a great victory, and this was technically true in terms of the actual battle, it is generally considered that the Hittites were the ultimate victors as far as the overall campaign was concerned, since the Egyptians retreated after the battle, and Hittite forces invaded and briefly occupied the Egyptian possessions in the region of ].<ref>Bryce 2005. pp. 238–239.</ref> | |||
| The temple is complex in structure and quite unusual because of its many side chambers. The hypostyle hall (sometimes also called pronaos) is 18 meters long and 16,7 meters wide and is supported by eight huge Osirid pillars depicting the deified Ramesses linked to the god ], the god of the Underworld, to indicate the everlasting nature of the pharaoh. The colossal statues along the left-hand wall bear the white crown of ], while those on the opposite side are wearing the double crown of Upper and ](pschent).<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> The bas-reliefs on the walls of the pronaos depict battle scenes in the military campaigns the ruler waged. Much of the sculpture is given to the ], on the Orontes river in present-day ], in which the Egyptian king fought against the ].<ref name=Skliar/> The most famous relief shows the king on his chariot shooting arrows against his fleeing enemies, who are being taken prisoner.<ref name=Skliar/> From the hypostyle hall, one enters the second pillared hall, which has four pillars decorated with beautiful scenes of offerings to the gods. This hall gives access to a transverse vestibule in the middle of which is the entrance to the sanctuary. Here, on a black wall, are rock cut sculptures of four seated figures: ], the deified king Rameses,and the gods ] and ]. ], ] and ] were the main divinities in that period and their cult centers were at ], ] and ] respectively.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> | |||
| ====Third Syrian campaign==== | |||
| The axis of the temple was positioned by the ancient Egyptian architects in such a way that twice a year on October 20 and February 20, the rays of the sun would penetrate the sanctuary and illuminate the sculpture on the back wall, except for the statue of ], the god connected with the ], who always remained in the dark.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref><ref name=Skliar/> It is quite logical to assume that these dates had some relation to a great event, such as the jubilee celebrating the thirtieth anniversary of the ]'s rule. In fact, according to calculations made on the basis of the heliacal rising of the star ] (Sothis) and inscriptions found by archaeologists, this date must have been October 22. This image of the king was enhanced and revitalized by the energy of the solar star, and the deified Ramesses Great could take his place next to ] and ].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref><!-- Needs clarification: is it actually Oct 20 or 22? When was the other date determined, and why was it thought to be the right date? --> | |||
| Egypt's sphere of influence was now restricted to Canaan while ] fell into Hittite hands. Canaanite princes, seemingly encouraged by the Egyptian incapacity to impose their will and goaded on by the Hittites, began revolts against Egypt. Ramesses II was not willing to let this stand, and prepared to contest the Hittite advance with new military campaigns. Because they are recorded on his monuments with few indications of precise dates or the regnal year, the precise chronology of the subsequent campaigns is not clear.<ref>Obsomer 2012: 188, within a detailed discussion on 173-192.</ref> Late in the seventh year of his reign (April/May 1272 BC <ref name="Obsomer 2012: 530">Obsomer 2012: 530.</ref>), Ramesses II returned to Syria again. This time he proved more successful against his Hittite foes. During this campaign he split his army into two forces. One force was led by his son, ], and it chased warriors of the ] tribes across the ] as far as the ], capturing ]-]. It then marched on to capture ]. The other force, led by Ramesses himself, attacked ] and ]. He, too, then entered Moab, where he rejoined his son. The reunited army then marched on ], Damascus, on to ], and finally, recaptured Upi (the land around Damascus), reestablishing Egypt's former sphere of influence.{{sfnp|Grimal|1992|p=256}}<ref>Kitchen 1982: 67; Obsomer 2012: 189–190 doubts the dating of the Moabite campaign to Year 7–8 by Kitchen, on the grounds that Amun-her-khepshef might have been too young to carry out such an independent role.</ref> | |||
| ====Later Syrian campaigns==== | |||
| The temple of ] and ], also known as the Small Temple, was built about one hundred meters northeast of the temple of Ramesses II and was dedicated to the goddess ] and Ramesses II`s chief consort, Nefertari. This was in fact the first time in ancient ] that a temple was dedicated to a queen.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> The rock-cut facade is decorated with two groups of colossi that are separated by the large gateway. The statues, slightly more than ten meters high, are of the king and his queen. On the other side of the portal are two statues of the king, wearing the ] of ] (south colossus) and the ] (north colossus); these are flanked by statues of the queen and the king. What is truly surprising is that for the only time in ], the statues of the king and his consort are equal in size.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> Traditionally, the statues of the queens stood next to those of the ], but were never taller than his knees. This exception to such a long standing rule bears witness to the special importance attached to Nefertari by Ramesses, who went to ] with his beloved wife in the 24th year of his reign. As the Great temple of the king, there are small statues of princes and princesses next to their parents. In this case they are positioned symmetrically: on the south side (at left as you face the gateway) are, from left to right, princes Meryatum and Meryre, princesses Merytamun and Henttawi, and princes Rahirwenemef and ], while on the north side the same figures are in reverse order. The plan of the Small Temple is a simplified version of that of the Great Temple. | |||
| {{main|Siege of Dapur}} | |||
| ] (left) and ] (right) adoring Ramesses in the small temple at ] | |||
| ] fortress of ]|330x330px]] | |||
| ]] | |||
| Ramesses extended his military successes in his eighth and ninth years. He crossed the Dog River (]) and pushed north into ]. His armies managed to march as far north as Dapur,{{sfnp|Kitchen|1996|p=26}} where he had a statue of himself erected. The Egyptian pharaoh thus found himself in northern Amurru, well past Kadesh, in ], where no Egyptian soldier had been seen since the time of ], almost 120 years earlier. He laid siege to Dapur before capturing it, and returning to Egypt.<ref>Kitchen 1982: 68–70.</ref> By November 1272 BC, Ramesses was back in Egypt, at ].<ref name="Obsomer 2012: 530"/> His victory in the north proved ephemeral. After having reasserted his power over Canaan, Ramesses led his army north. A mostly illegible stele at the Dog River near ], (Lebanon), which appears to be dated to the king's second year, was probably set up there in his tenth year (1269 BC).{{sfnp|Kitchen|1979|pp=223–224}}<ref>Obsomer 2012: 531.</ref> The thin strip of territory pinched between Amurru and Kadesh did not make for a stable possession. Within a year, they had returned to the Hittite fold, so that Ramesses had to march against Dapur once more in his tenth year. This time he claimed to have fought the battle without even bothering to put on his ], until two hours after the fighting began. Six of Ramesses's youthful sons, still wearing their ], took part in this conquest. He took towns in ],{{sfnp|Kitchen|1996|p=33}} and Tunip in ],{{sfnp|Kitchen|1996|p=47}} later recorded on the walls of the ].{{sfnp|Kitchen|1996|p=46}} This second success at the location was equally as meaningless as his first, as neither power could decisively defeat the other in battle.{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|p=68}} In year eighteen, Ramesses erected a stele at ], on 19 January 1261 BC.<ref>Obsomer 2012: 190–192, 531.</ref> | |||
| ===Peace treaty with the Hittites=== | |||
| As the larger temple dedicated to the king, the hypostyle hall or ] is supported by six ]s; in this case, however, they are not Osirid pillars depicting the king, but are decorated with scenes with the queen playing the sinistrum (an instrument sacred to the goddess Hathor), together with the ]s ], ], ], and ], and the ]es ], ], ], Mut of Asher, ] and ]; in one scene Ramesses is presenting ]s or].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> The capitals of the pillars bear the face of the goddess Hathor; this type of column is known as Hathoric. The bas-reliefs in the pillared hall illustrate the deification of the ], the destruction of his enemies in the north and south (in this scenes the king is accompanied by his wife), and the queen making offerings to the goddess ] and ].<ref name=Skliar/> The hypostyle hall is followed by a vestibule, access to which is given by three large doors. On the south and the north walls of this chamber there are two graceful and poetic bes-reliefs of the king and his consort presenting ] plants to ], who is depicted as a cow on a boat sailing in a thicket of papyri. On the west wall, Ramesses II and Nefertari are depicted making offerings to god ] and the divinities of the Cataracts - ], ] and ]. | |||
| {{main|Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty}} | |||
| ] between ] of ] and Ramesses II of ], at the ]]] | |||
| In Year 21 of Ramesses's reign, he concluded a peace treaty with the Hittites known to modern scholars as the ''Treaty of Kadesh''. Though this treaty settled the disputes over Canaan, its immediate impetus seems to have been a diplomatic crisis that occurred following ]'s accession to the Hittite throne. Ḫattušili had come to power by deposing his nephew ] in the brief and bitter ]. Though the deposed king was initially sent into exile in Syria, he subsequently attempted to regain power and fled to Egypt once these attempts were discovered.<ref name="Bryce183195">{{cite book|last=Bryce|first=Trevor|author-link=Trevor Bryce|date=2023|title= Warriors of Anatolia: A Concise history of the Hittites|publisher=Bloomsbury|pages=183–195|isbn=978-1-3503-4885-1}}</ref> | |||
| The rock cut ] and the two side ] are connected to the transverse vestibule and are aligned with the axis of the temple. The bas-reliefs on the side walls of the small sanctuary represent scenes of ]s to various ]s made either by the ] or the ].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> On the back wall, which lies to the west along the axis of the ], there is a niche in which ], as a divine cow, seems to be coming out of the ]: the goddess is depicted as the ] of the temple dedicated to her and to queen ], who is intimately linked to the ].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> | |||
| Each temple has its own priest that represents the king in daily religious ceremonies. In theory, the Pharaoh should be the only celebrant in daily religious ceremonies performed in different temples throughout Egypt. In reality, the high priest also played that role. To reach that position, an extensive education in art and science was necessary, like the one pharaoh had. Reading, writing, engineering, arithmetic, geometry, astronomy, space measurement, time calculations, were all part of this learning. The priests of Heliopolis, for example, became guardians of sacred knowledge and earned the reputation of wise men. | |||
| When Ḫattušili demanded his extradition, Ramesses II denied any knowledge of his whereabouts. When Ḫattušili insisted that Muršili was in Egypt, Ramesses's response suggested that Ḫattušili was being deceived by his subjects.<ref name="Bryce183195"/>{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|p=74}} This demand precipitated a crisis, and the two empires came close to war. Eventually, in the twenty-first year of his reign (1259 BC <ref name="ReferenceA">Kitchen 1982: 75; Obsomer 2012: 195, 531.</ref>), Ramesses concluded an agreement at Kadesh to end the conflict.{{sfnp|Grimal|1992|p=256}} | |||
| <!--] colossus]]--> | |||
| The peace treaty was recorded in two versions, one in ], the other in Hittite, using ]; both versions survive. Such dual-language recording is common to many subsequent treaties. This treaty differs from others, in that the two language versions are worded differently. While the majority of the text is identical, the Hittite version says the Egyptians came suing for peace and the Egyptian version says the reverse.{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|pp=62–64, 73–79}} The treaty was given to the Egyptians in the form of a silver plaque, and this "pocket-book" version was taken back to Egypt and carved into the temple at ]. The Egyptian account records Ramesses II's receipt of the Hittite peace treaty tablets on I Peret 21 of Year 21, corresponding to 10 November 1259 BC, according to the standard "Low Chronology" used by Egyptologists.<ref>Obsomer 2012: 195, 531.</ref> | |||
| ==Tomb of Nefertari== | |||
| {{further|]}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The tomb of ], the most important and famous ] of Ramesses was discovered by ] in 1904.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref><ref name=Skliar/> Although it had been looted in ancient times, the tomb of Nefertari is extremely important, because its magnificent wall painting decoration is surely to be regarded as one of the greatest achievements of ancient ].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> A flight of steps cut out of the rock gives access to the antechamber, which is decorated with paintings based on Chapter 17 of the ].<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> This astronomical ceiling represents the heavens and is painted in dark blue, with a myriad of golden five-pointed stars. The east wall of the antechamber is interrupted by a large opening flanked by representation of ] at left and ] at right; this in turn leads to the side chamber, decorated with offering scenes, preceded by a vestibule in which the paintings portray ] being presented to the gods who welcome her. On the north wall of the antechamber is the stairway that goes down to the burial chamber.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> This latter is a vast quadrengular room covering a surface area about 90 square meters, the astronomical ceiling of which is supported by four pillars entirely covered with decoration. Originally, the queen´s red ] ] lay in the middle of this chamber.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> According to religious doctrines of the time, it was in this chamber, which the ancient Egyptians called the "golden hall" that the regeneration of the deceased took place. This decorative pictogram of the walls in the burial chamber drew inspirations from chapters 144 and 146 of the ]: in the left half of the chamber, there are passages from chapter 144 concerning the gates and doors of the kingdom of ], their guardians, and the magic formulas that had to be uttered by the deceased in order to go past the doors.<ref>Alberto Siliotti, Egypt: temples, people, gods,1994</ref> | |||
| The treaty was concluded between Ramesses II and Ḫattušili III in year 21 of Ramesses's reign (c. 1259 BC).<ref name="ReferenceA"/>{{sfnp|Grimal|1992|p=257}} Its 18 articles call for peace between Egypt and Hatti and then proceeds to maintain that their respective deities also demand peace. The frontiers are not laid down in this treaty, but may be inferred from other documents. The Anastasy A ] describes Canaan during the latter part of the reign of Ramesses II and enumerates and names the ]n coastal towns under Egyptian control. The harbour town of ], north of ], is mentioned as the northernmost town belonging to Egypt, suggesting it contained an Egyptian garrison.{{sfnp|Stieglitz|1991|p=45}} | |||
| No further Egyptian campaigns in Canaan are mentioned after the conclusion of the peace treaty. The northern border seems to have been safe and quiet, so the rule of the pharaoh was strong until Ramesses II's death, and the subsequent waning of the dynasty.{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|p=215}} When the King of Mira attempted to involve Ramesses in a hostile act against the Hittites, the Egyptian responded that the times of intrigue in support of Mursili III, had passed. Ḫattušili III wrote to ], ] king of ] (]) in the same spirit, reminding him of the time when his father, ], had offered to fight Ramesses II, the king of Egypt. The Hittite king encouraged the Babylonian to oppose another enemy, which must have been the king of ], whose allies had killed the messenger of the Egyptian king. Ḫattušili encouraged Kadashman-Enlil to come to his aid and prevent the Assyrians from cutting the link between the Canaanite province of Egypt and Mursili III, the ally of Ramesses. | |||
| <!--- | |||
| ===Pictures from the Ramesseum=== | |||
| ===Nubian campaigns=== | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| ] temple, originally in Nubia]] | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01366.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Ramesses II also campaigned south of the ] into ]. When Ramesses was about 22 years old, two of his own sons, including ], accompanied him in at least one of those campaigns. By the time of Ramesses, Nubia had been a colony for 200 years, but its conquest was recalled in decoration from the temples Ramesses II built at ]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://oi.uchicago.edu/gallery/pa_egypt_bees_beit_el-wali/ |title=Beit el-Wali |access-date=21 April 2008 |publisher=University of Chicago|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080906200351/http://oi.uchicago.edu/gallery/pa_egypt_bees_beit_el-wali/|archive-date=6 September 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> (which was the subject of epigraphic work by the ] during the Nubian salvage campaign of the 1960s),{{sfnp|Ricke|Hughes|Wente|1967|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} ] and ] in northern Nubia. On the south wall of the Beit el-Wali temple, Ramesses II is depicted charging into battle against tribes south of Egypt in a war chariot, while his two young sons, ] and Khaemwaset, are shown behind him, also in war chariots. A wall in one of Ramesses's temples says he had to fight one battle with those tribes without help from his soldiers.{{clarify|date=February 2022}} | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01360.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01358.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| ]|center]] | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01320.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01319.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01309.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 RAMASEUM 01294.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON 2006-10-EGYPT-KARNAK-0043.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Luxor | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Libyan campaigns=== | |||
| ===Pictures from Abu Simbel - Temple of Rameses II=== | |||
| During the reign of Ramesses II, the Egyptians were evidently active on a {{convert|300|km|adj=on}} stretch along the ] coast, at least as far as ], where remains of a fortress described by its texts as built on Libyans land have been found.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of Egyptologists, Cambridge, 3-9 September 1995 |last=Eyre|first=Christopher|publisher=Leuven: Peeters |year=1998|pages=171}}</ref> Although the exact events surrounding the foundation of the coastal forts and fortresses is not clear, some degree of political and military control must have been held over the region to allow their construction. | |||
| There are no detailed accounts of Ramesses II's undertaking large military actions against the ], only generalised records of his conquering and crushing them, which may or may not refer to specific events that were otherwise unrecorded. It may be that some of the records, such as the ] Stele of his year 2, are harking back to Ramesses's presence on his father's Libyan campaigns. Perhaps it was ] who achieved this supposed control over the region, and who planned to establish the defensive system, in a manner similar to how he rebuilt those to the east, the Ways of Horus across Northern ]. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| ==Sed festivals== | |||
| Image:SFEC_EGYPT_ABUSIMBEL_2006-001.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| {{Main|Sed festival}} | |||
| Image:SFEC_EGYPT_ABUSIMBEL_2006-002.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| As of Year 28 of his reign, Ramesses II favored the good ] above all other divinities, as evidenced in the texts of two separate ] discovered at Deir el-Medina.<ref name="t696">{{cite web | last=Treasure | first=Matthew | title=Four Faces on One Neck: The Tetracephalic Ram as an Iconographic Form in New Kingdom Egypt | website=Academia.edu | date=2021-01-01 | url=https://www.academia.edu/49077937/Four_Faces_on_One_Neck_The_Tetracephalic_Ram_as_an_Iconographic_Form_in_New_Kingdom_Egypt | access-date=2025-01-13}}</ref> | |||
| Image:SFEC_EGYPT_ABUSIMBEL_2006-003.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2006 FEB 00671.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2006 FEB 00661.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 APR 00363.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 APR 00361.JPG|Temple of Ramesses II, Abu Simbel | |||
| Image:S F-E-CAMERON EGYPT 2005 APR 00354.JPG|Temple of Nefertiri, Abu Simbel | |||
| yo this is all write homi | |||
| By tradition, in the 30th year of his reign, Ramesses celebrated a jubilee called the ]. These were held to honour and rejuvenate the pharaoh's strength.<ref name="GEMHedSed">{{cite web |url=http://www.globalegyptianmuseum.org/glossary.aspx?id=334 |publisher=The Global Egyptian Museum |access-date=7 April 2008 |title=Sed festival|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080906154922/http://www.globalegyptianmuseum.org/glossary.aspx?id=334|archive-date=6 September 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> Only halfway through what would be a 66-year reign, Ramesses had already eclipsed all but a few of his greatest predecessors in his achievements. He had brought peace, maintained Egyptian borders, and built numerous monuments across the empire. His country was more prosperous and powerful than it had been in nearly a century. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| --> | |||
| Sed festivals traditionally were held again every three years after the 30th year; Ramesses II, who sometimes held them after two years, eventually celebrated an unprecedented thirteen or fourteen.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.arabworldbooks.com/egyptomania/sameh_arab_sed_heb.htm |title=Renewal of the kings' Reign : The Sed Heb of Ancient Egypt |access-date=5 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161106064130/http://www.arabworldbooks.com/egyptomania/sameh_arab_sed_heb.htm|archive-date=6 November 2016|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Mummy== | |||
| Ramesses II was buried in the ] on the western bank of Thebes, in ], but his ] was later moved to the ] at ], where it was found in ]. In 1885, it was placed in ]'s ] where it remains ]. | |||
| ==Building projects and monuments== | |||
| The pharaoh's mummy features a hooked nose and strong jaw, and is of above average height for an ancient Egyptian, standing some five feet, seven inches.<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'' p. 14</ref> His successor was ultimately to be his thirteenth son: ]. | |||
| In the third year of his reign, Ramesses started the most ambitious building project after the ], which were built almost 1,500 years earlier. Ramesses built extensively from the ] to ], "covering the land with buildings in a way no monarch before him had."{{sfnp|Westendorf|1969|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} | |||
| ] | ]]] | ||
| Some of the activities undertaken were focused on remodeling or usurping existing works, improving masonry techniques, and using art as propaganda. | |||
| In 1974, ] ]s noticed that the mummy's condition was rapidly deteriorating. They decided to fly Rameses II's mummy to ] for examination. Ramesses II was issued an Egyptian passport that listed his occupation as "King (deceased)." According to a Discovery Channel documentary, the mummy was received at a Paris airport with the full military honours befitting a king. | |||
| *In Thebes, the ancient ] were transformed, so that each of them reflected honour to Ramesses as a symbol of his putative divine nature and power. | |||
| *The elegant but shallow reliefs of previous pharaohs were easily transformed, and so their images and words could easily be obliterated by their successors. Ramesses insisted that his carvings be deeply engraved into the stone, which made them not only less susceptible to later alteration, but also made them more prominent in the Egyptian sun, reflecting his relationship with the sun deity, ]. | |||
| *Ramesses used art as a means of propaganda for his victories over foreigners, which are depicted on numerous temple reliefs. | |||
| *His ]s are prominently displayed even in buildings that he did not construct.<ref>{{cite web |author=Edwards |first=Amelia Ann Blandford |title=Chapter XV: Rameses the Great |url=http://digital.library.upenn.edu/women/edwards/nile/nile-XV.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080513112609/http://digital.library.upenn.edu/women/edwards/nile/nile-XV.html |archive-date=13 May 2008 |access-date=23 April 2008}}</ref> | |||
| * He founded a new capital city in the Delta during his reign, called ]. It previously had served as a summer palace during Seti I's reign.{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|p=119}} | |||
| * Ramesses II expanded gold mining operations in Akuyati (modern day Wadi Allaqi).<ref>{{Cite book |last=Kitchen |title=Pharaoh Triumphant |date=30 April 1985 |publisher=Aris & Phillips |isbn=0-85668-215-2 |pages=49–50}}</ref> | |||
| Ramesses also undertook many new construction projects. <!-- It is said{{Who|date=December 2007}} that there are more statues of him in existence than of any other Egyptian pharaoh, since he was the second-longest reigning Pharaoh of Egypt after ].--> Two of his biggest works, besides ], were the temple complex of ] and the ], a ] in western ]. | |||
| ===Pi-Ramesses=== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Pi-Ramesses}} | |||
| In Paris, Ramesses' mummy was diagnosed and treated for a ] infection. During the examination, scientific analysis revealed battle ]s and old ]s, as well as the pharaoh's arthritis and poor circulation. For the last decades of his life, Ramesses II was essentially crippled with arthritis and walked with a hunched back,<ref>Bob Brier, The Encyclopedia of Mummies, Checkmark Books, 1998., p.153</ref> and a recent study excluded ] as a possible cause of the pharaoh's ].<ref>Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2004 Oct;55(4):211-7, PMID 15362343</ref> A significant hole in the pharaoh's ] was detected while "an abscess by his teeth was serious enough to have caused death by infection, although this cannot be determined with certainty."<ref>Brier, op. cit., p.153</ref> Microscopic inspection of the roots of Ramesses II's hair revealed that the king was originally a ].<ref>Brier, op. cit., p.153</ref> After Ramesses' mummy returned to Egypt, it was visited by the late President ] and his wife. | |||
| Ramesses II moved the capital of his kingdom from Thebes in the Nile valley to a new site in the eastern Delta. His motives are uncertain, although he possibly wished to be closer to his territories in Canaan and Syria. The new city of Pi-Ramesses (or to give the full name, '']-Ramesses Aa-nakhtu'', meaning "Domain of Ramesses, Great in Victory"){{sfnp|Kitchen|2003|p=255}} was dominated by huge temples and his vast residential palace, complete with its own zoo. In the 10th century AD, the Bible exegete Rabbi ] believed that the biblical site of Ramesses had to be identified with ].<ref>Saadia Gaon, ''Judeo-Arabic Translation of Pentateuch'' (''Tafsir''), s.v. Exodus 21:37 and Numbers 33:3 ("רעמסס: "עין שמס); ''Rabbi Saadia Gaon's Commentaries on the Torah'' (ed. ]), ]: Jerusalem, Israel, 1984, p. 164 (Numbers 33:3) (in Hebrew).</ref> For a time, during the early 20th century, the site was misidentified as that of ], due to the amount of statuary and other material from Pi-Ramesses found there, but it now is recognized that the Ramesside remains at Tanis were brought there from elsewhere, and the real Pi-Ramesses lies about 30 km (18.6 mi) south, near modern ].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YzQe_4Waz34C |title=The Land that I Will Show You: Essays on the History and Archaeology of the Ancient Near East in Honour of J. Maxwell Miller |publisher=Sheffield Academic Press |date=2001 |editor1-first=John Andrew |editor1-last=Dearman |editor2-first=Matt Patrick |editor2-last=Graham |editor3-first=James Maxwell |editor3-last=Miller |chapter=The Geography of the Exodus |first=John |last=Van Seters |page=265 |isbn=978-1-84127-257-3}}</ref> The colossal feet of the statue of Ramesses are almost all that remains above ground today. The rest is buried in the fields.{{sfnp|Kitchen|2003|p=255}} | |||
| ===Ramesseum=== | |||
| The results of the study were edited by L. Balout, C. Roubet and C. Desroches-Noblecourt, and was titled 'La Momie de Ramsès II: Contribution Scientifique à l'Égyptologie (1985).' Balout and Roubet concluded that the "the anthropological study and the microscopic analysis" of the pharaoh's hair showed that Ramses II was "a fair-skinned man related to the Prehistoric and Antiquity Mediterranean peoples, or briefly, of the ] of Africa." | |||
| {{Main|Ramesseum}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The temple complex built by Ramesses II between ] and the desert has been known as the ] since the 19th century. The Greek ] ] marveled at the gigantic temple, now no more than a few ruins.<ref>{{cite book |author=Siculus |first=Diodorus |author-link=Diodorus Siculus |url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_agd-eLVNRMMC |title=The Historical Library of Diodorus the Sicilian |publisher=Printed by W. MʻDowall for J. Davis |year=1814 |page=33 |chapter=11}}</ref> | |||
| Oriented northwest and southeast, the temple was preceded by two courts. An enormous pylon stood before the first court, with the royal palace at the left and the gigantic statue of the king at the back. Only fragments of the base and torso remain of the ] statue of the enthroned pharaoh, {{convert|17|m}} high and weighing more than {{convert|1000|t|lk=on}}. Scenes of the pharaoh and his army triumphing over the Hittite forces fleeing before Kadesh are represented on the pylon. Remains of the second court include part of the internal facade of the pylon and a portion of the Osiride portico on the right. Scenes of war and the alleged rout of the Hittites at Kadesh are repeated on the walls. In the upper ], feast and honour of the phallic deity ], god of fertility. | |||
| ==Tomb KV5== | |||
| {{further|]}} | |||
| In 1995, Professor ], head of the Theban Mapping Project rediscovered Tomb ]. It has proven to be the largest tomb in the Valley of the Kings which originally contained the mummified remains of some of this king's estimated 52 sons. Approximately 150 corridors and tomb chambers have been located in this tomb as of 2006 and the tomb may contain as many as 200 corridors and chambers.<ref></ref> It is believed that at least 4 of Ramesses' sons including Meryatum, Sety, ] (Ramesses' first born son) and "the King's Principal Son of His Body, the Generalissimo Ramesses, justified" (ie: deceased) were buried there from inscriptions, ] or ]s discovered in the tomb.<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.161-162</ref> ] writes that thus far | |||
| : "no intact burials have been discovered and there have been little substantial funeral debris: thousands of potsherds, faience ''shabti'' figures, beads, amulets, fragments of Canopic jars, of wooden coffins...but no intact sarcophagi, mummies or mummy cases, suggesting that much of the tomb may have been unused. Those burials which were made in KV5 were thoroughly looted in antiquity, leaving little or no remains."<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.161-162</ref> | |||
| On the opposite side of the court, the few Osiride pillars and columns still remaining may furnish an idea of the original grandeur.{{sfnp|Skliar|2005|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} Scattered remains of the two statues of the seated king also may be seen, one in pink granite and the other in black granite, which once flanked the entrance to the temple. Thirty-nine out of the forty-eight columns in the great ] (41 × 31 m) still stand in the central rows. They are decorated with the usual scenes of the king before various deities.<ref name="ramesseum-2">{{cite web |url=http://www.archeo.ens.fr/IMG/pdf/RAMESSEUM-2.pdf |title=The Ramesseum (Egypt), Recent Archaeological Research |access-date=10 April 2008 |author=Guy Lecuyot|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080529191601/http://www.archeo.ens.fr/IMG/pdf/RAMESSEUM-2.pdf |archive-date=29 May 2008 }}</ref> Part of the ceiling, decorated with gold stars on a blue ground, also has been preserved. Ramesses's children appear in the procession on the few walls left. The sanctuary was composed of three consecutive rooms, with eight columns and the ] cell. Part of the first room, with the ceiling decorated with astral scenes, and few remains of the second room are all that is left. Vast storerooms built of mud bricks stretched out around the temple.{{sfnp|Skliar|2005|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} Traces of a school for scribes were found among the ruins.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www2.cnrs.fr/presse/journal/3436.htm |title=À l'école des Scribes |language=fr |access-date=21 April 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080423223745/http://www2.cnrs.fr/presse/journal/3436.htm|archive-date=23 April 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Pharaoh of Exodus== | |||
| {{details|The Exodus}} | |||
| At least as early as ] {{Fact|date=March 2007}}, Ramesses II was identified with the pharaoh of whom the ] figure ] demanded his people be released from ]. | |||
| A temple of ], of which nothing remains beside the foundations, once stood to the right of the hypostyle hall.<ref name="ramesseum-2"/> <!-- It consisted of a peristyle court with two chapel shrines. The entire complex was enclosed in mud brick walls that started at the gigantic southeast pylon.{{Citation needed|date=December 2007}} --> | |||
| This identification has often been disputed, though the evidence for another solution is likewise inconclusive: | |||
| ===Abu Simbel=== | |||
| * Critics point out that Ramesses II was not drowned in the Sea. The biblical account, however, makes no specific claim that the pharaoh was with his army when they were "swept ... into the sea."<ref>Exodus 14</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Abu Simbel temples}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| In 1255 BC, Ramesses and his queen ] had traveled into ] to inaugurate a new temple, ]. It is said to be ego cast into stone; the man who built it intended not only to become Egypt's greatest pharaoh, but also one of its deities.{{sfnp|Kitchen|1982|pp=64–65}} | |||
| The temple at Abu Simbel was discovered in 1813 by the Swiss Orientalist and traveler ]. An enormous pile of sand almost completely covered the facade and its colossal statues, blocking the entrance for four more years. The ]n explorer ] reached the interior on 4 August 1817.{{sfnp|Siliotti|1994|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} | |||
| * Critics of the theory also emphasize that there is nothing in the archaeological records from the time of Ramesses' reign to confirm the existence of the Plagues of Egypt. However, this is not surprising since few pharaohs wished to record natural disasters or military defeats in the same manner that their rivals documented these events (as in the Biblical narratives). For instance, after the serious Egyptian military setback at the ], Hittite archives uncovered in ] reveal that "a humiliated Ramesses forced to retreat from Kadesh in ignominious defeat" and abandon the border provinces of Amurru and Upi to the control of his Hittite rival without the benefit of a formal truce.<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.73</ref> By contrast, no inconvenient references to Ramesses' loss of ] or Upi are preserved in the Egyptian records. Ramesses instead falsely claims that the "Hittite king sent a letter to the Egyptian camp pleading for peace. Negotiators were summoned and a truce was agreed, although Ramesses, still claiming an Egyptian victory...refused to sign a formal treaty. Ramesses returned home to enjoy his personal triumph."<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.73</ref> | |||
| ===Other Nubian monuments=== | |||
| * The dates now ascribed to Ramesses' reign by most modern scholars do not match the internal biblical chronology regarding the date of the Exodus. | |||
| As well as the temples of Abu Simbel, Ramesses left other monuments to himself in Nubia. His early campaigns are illustrated on the walls of the ] (now relocated to ]). Other temples dedicated to Ramesses are ] and ] (also relocated to New Kalabsha). For the temple of Amun at ], the temple's foundation probably dates during the reign of Thutmose III, while the temple was shaped during his reign and that of Ramesses II.<ref>{{Cite book |title= The Image of the Ordered World in Ancient Nubian Art: The Construction of the Kushite Mind, 800 Bc-300 Ad |last= Török |first= László |publisher= Brill |year= 2001 |pages=48}}</ref> | |||
| ===Other archeological discoveries=== | |||
| In the 1960s and 1970s, several scholars such as George Mendenhall<ref>Mendenhall, "The Hebrew Conquest of Palestine," ''Biblical Archaeologist'' ('''25''', 1962)</ref> associated the Israelite's arrival in Canaan more closely with the ] mentioned in the Amarna letters which date to the reign of Amenhotep III and Akhenaten and in the Hittite treaties with Ramesses II. Most scholars today, however, view the Hapiru or Apiru instead as bandits who attacked the trade and royal caravans that travelled along the coastal roads of Canaan. | |||
| ] in ], Italy.]] | |||
| Ramesses II's late 13th century BC stela in Beth Shan mentions two conquered peoples who came to "make obeisance to him" in his city of Raameses or Pi-Ramesses but mentions neither the building of the city nor, as some have written, the Israelites or Hapiru".<ref>Stephen L. Caiger, "Archaeological Fact and Fancy," ''Biblical Archaeologist'', ('''9''', 1946).</ref>]]] | |||
| The colossal ] dates back 3,200 years, and was originally discovered in six pieces in a temple near ], Egypt. Weighing some {{convert|83|t|adj=on}}, it was transported, reconstructed, and erected in Ramesses Square in Cairo in 1955. In August 2006, contractors relocated it to save it from exhaust fumes that were causing it to deteriorate.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/5282414.stm |work=BBC News |title=Giant Ramses statue gets new home |date=25 August 2006 |access-date=5 July 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080720194419/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/5282414.stm |archive-date=20 July 2008 |url-status=live}}</ref> The new site is near the ].<ref name="ColossalHawass">{{cite web |last=Hawass |first=Zahi |author-link=Zahi Hawass |title=The removal of Ramses II Statue |url=http://guardians.net/hawass/news/removal_of_ramses_ii_statue.htm |access-date=17 March 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070312235259/http://guardians.net/hawass/news/removal_of_ramses_ii_statue.htm |archive-date=12 March 2007 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The Bible states that the Israelites toiled in slavery and built "for Pharaoh supply cities, ] and ''']'''" in the Egyptian Delta.<ref>Exodus 1:11</ref> The latter is probably a reference to the city of Pi-Ramesse Aa-nakhtu or the "House of Ramesses, Great-of-Victories"--i.e. ancient ] (modern day Qantir)--which had been Seti I's summer retreat.<ref>Tyldesley, ''Ramesses'', p.82</ref> Ramesses II greatly enlarged this city both as his principal northern capital and as an important forward base for his military campaigns into the Levant and his control over Canaan. According to ], Pi-Ramesses was largely abandoned from c.] onwards; as was often the practice, later rulers removed much of the stone from the city to build the temples of their new capital: ].<ref>Kitchen, ''On the Reliability of the Old Testament'', William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company (2003), p.662. ISBN 0-8028-4960-1,</ref> Therefore, if the identification of the city is correct, it strengthens the case for identifying Ramesses II as the Pharaoh who reigned Egypt during Moses' lifetime. | |||
| In 2018, a group of archeologists in Cairo's Matariya neighborhood discovered pieces of a booth with a seat that, based on its structure and age, may have been used by Ramesses.<ref>{{Cite web |date=26 October 2018 |title=Egypt: Prehistoric 'Pharaoh's Seat' Discovered in Egypt – Document – Gale General OneFile |url=https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=ITOF&u=wikipedia&id=GALE%7CA559860686&v=2.1&it=r&sid=ebsco&asid=38a97973 |access-date=12 October 2022 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="Cairo 2018">{{Cite web |date=25 October 2018 |title=Egyptian archeologists unearth pharaoh's celebration compartment in Cairo |url=https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=ITOF&u=wikipedia&id=GALE%7CA559724763&v=2.1&it=r&sid=bookmark-ITOF&asid=7c8857fc |access-date=12 October 2022 |agency=]}}</ref> "The royal compartment consists of four steps leading to a cubic platform, which is believed to be the base of the king's seat during celebrations or public gatherings," such as Ramesses' inauguration and Sed festivals. It may have also gone on to be used by others in the ], according to the mission's head. The excavation mission also unearthed "a collection of ], ]s, clay pots and blocks engraved with ] text."<ref name="Cairo 2018" /> | |||
| His son and successor, Merneptah, mentions in the so-called ] that the ancient Israelites already lived in Canaan during his reign. Merneptah's reference to their destruction, according to ], probably refers to the Egyptian military strategy of routing an ethnic group and destroying its grain, instead of the destruction of their offspring or progeny.<ref>Hasel, "''Israel'' in the Merneptah Stela," ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 296, pp. 52-54; see most recently Hasel, "Merenptah's Inscription and Reliefs and the Origin of Israel," The ''Near East in the Southwest: Essays in Honor of William G. Dever'', pp. 20-26.,</ref> Merneptah's inscription uses a parallel structure which contrasts the city-states with the Israelites within the territory of Canaan/Kharu.<ref>Hasel, "''Israel'' in the Merneptah Stela," ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', No. 296, pp. 47-52; see most recently Hasel, "The Structure of the Final Hymnic-Poetic Unit on the Merenptah Stela," Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft 116: 75-81.</ref> This prompts one to remember that the books of Joshua and Judges both paint pictures of the Israelites as tribes acting independently or in small coalitions against their enemies and wonder how fast they could have coalesced to the point where an ancient and mighty nation such as Egypt would consider them worth mentioning. | |||
| In December 2019, a red granite royal bust of Ramesses II was unearthed by an Egyptian archaeological mission in the village of Mit Rahina in Giza. The bust depicted Ramesses II wearing a wig with the symbol "Ka" on his head. Its measurements were 55 cm (21.65 in) wide, 45 cm (17.71 in) thick and 105 cm (41.33 in) long. Alongside the bust, limestone blocks appeared showing Ramesses II during the ] religious ritual.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Red Granite Bust of Ramesses II Unearthed in Giza|work=Archaeology Magazine|url=https://www.archaeology.org/news/8288-191213-egypt-giza-sculptures|access-date=17 September 2020 |date=13 December 2019 |archive-date=14 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200814231047/https://www.archaeology.org/news/8288-191213-egypt-giza-sculptures|url-status=live}}</ref> "This discovery is considered one of the rarest archaeological discoveries. It is the first-ever Ka statue made of granite to be discovered. The only Ka statue that was previously found is made of wood and it belongs to one of the kings of the 13th dynasty of ancient Egypt which is displayed at the Egyptian Museum in ]," said archaeologist ]. | |||
| Speculation that Ramesses II was the Biblical Pharaoh named '']'' who attacked Judah and seized war bounty from Jerusalem in Year 5 of ] is untenable because both Ramesses II and his 19th Dynasty successors (ie: Merneptah, Seti II, Siptah & Twosret) retained firm control over Canaan during their reigns. Neither Israel nor Judah could have existed as independent states during this time. Also, Shishak of the bible has been associated with "Sheshonq" of Egypt. An inscription was found in Egypt written by Sheshonq I that claims he invaded the land of Israel and conquered 170 towns there. The inscription goes on to list the towns in alphabetical order. 99% of scholars accept that Shishak and Sheshonq I are the same person. | |||
| In September 2024, it was published that during an archaeological excavation of a 3,200 year old fort along the Nile, researches found a golden sword with Ramses II signature on it.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Sands |first=Leo |date=2024 |title=Sword with pharaoh's mark found in Egypt, still shimmering 3,000 years later |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/history/2024/09/19/ancient-egypt-military-sword-archaeology-fort/}}</ref> | |||
| ==Fiction== | |||
| *The life of Ramesses II has also inspired a large number of ]s, including the five volume series, ''Ramsès,'' by the French writer ]. (Translated editions are available for non-French readers.) | |||
| *]'s novel '']'' is largely concerned with the life of Ramesses II, though from the perspective of Egyptians living during the reign of Ramesses IX. | |||
| *Ramesses was the main character in the ] book '']'' or ''Ramses the Damned''. | |||
| *Ramesses was played by ] in the classic film '']'' (1956). Here Ramesses was portrayed as a vengeful tyrant, ever scornful of his father's preference for Moses over "the son of body". | |||
| *In the animated film '']'', Ramesses (voiced by ]) is portrayed as Moses' adoptive brother. | |||
| *The songs "User-Maat-Re" and "Ramses Bringer of War" by death metal band ] are about Ramesses II. | |||
| *Ramesses II is the inspiration for ]'s famous poem ]. | |||
| *An Egyptian pharoah referred to as Ramesses appeared in an episode of ] | |||
| == |
==Death and burial== | ||
| The Egyptian scholar ] (third century BC) attributed Ramesses a reign of 66 years and 2 months.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Manetho, with an English translation by W.G. Waddell |last=James|first=Peter|publisher=Alpha Editions |year=2020 |pages=151}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| By the time of his death, aged about 90 years, Ramesses was suffering from severe dental problems and was plagued by ] and ].<ref name=LMD>{{cite web |url=http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=12146724 |title=La momie de Ramsès II. Contribution scientifique à l'égyptologie |access-date=27 February 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100602062449/http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=12146724|archive-date=2 June 2010|url-status=live}}</ref> He had made Egypt rich from all the supplies and bounty he had collected from other empires. He had outlived many of his wives and children and left great memorials all over ]. Nine more pharaohs took the name Ramesses in his honour. | |||
| == External links == | |||
| ===Mummy=== | |||
| {{main|KV7}} | |||
| Originally Ramesses II was buried in the tomb ] in the ],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Rameses II {{!}} Theban Mapping Project |url=https://thebanmappingproject.com/tombs/kv-07-rameses-ii |access-date=19 March 2023 |website=thebanmappingproject.com |language=en}}</ref> but because of looting in the valley, priests later transferred the body to a holding area, re-wrapped it, and placed it inside the tomb of queen ].{{sfnp|Rohl|1995|pp=72-73, 75}} Seventy-two hours later it was again moved, to the ] of the high priest ]. All of this is recorded in hieroglyphics on the linen covering the body of his coffin.{{sfnp|Rohl|1995|pp=78-79}} His ] was eventually discovered in 1881 in ] inside an ordinary wooden coffin and is now in ]'s ] (until 3 April 2021 it was in the ]).<ref>{{Cite web |title=NMEC |url=https://nmec.shorthandstories.com/nmec/ |access-date=18 August 2023 |website=nmec.shorthandstories.com |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The pharaoh's mummy reveals an ] and strong jaw. It stands at about {{convert|1.7|m|ftin}}.{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2000|p=14}} ], who first unwrapped the mummy of Ramesses II, writes, "on the temples there are a few sparse hairs, but at the poll the hair is quite thick, forming smooth, straight locks about five centimeters in length. White at the time of death, and possibly auburn during life, they have been dyed a light red by the spices (henna) used in embalming ... the moustache and beard are thin. ... The hairs are white, like those of the head and eyebrows ... the skin is of earthy brown, splotched with black ... the face of the mummy gives a fair idea of the face of the living king."<ref>{{cite book |title=Valley of the Kings |first=John |last=Romer |publisher=Castle Books |page=184}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Egyptian Archaeology |first=Gaston |last=Maspero |author-link=Gaston Maspero |publisher=Putnam |year=1892 |url=https://archive.org/details/egyptianarchaeo00maspgoog |pages=–77}}</ref> | |||
| In 1975, ], a French doctor, examined the mummy at the ] and found it in poor condition. French President ] succeeded in convincing Egyptian authorities to send the mummy to France for treatment. In September 1976, it was greeted at ] with full military honours befitting a king, then taken to a laboratory at the ].<ref>{{cite news |first=Clyde H. |last=Farnsworth |date=28 September 1976 |page=5 |title=Paris Mounts Honor Guard For a Mummy |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1976/09/28/archives/paris-mounts-honor-guard-for-a-mummy.html |work=] |access-date=31 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191101003734/https://www.nytimes.com/1976/09/28/archives/paris-mounts-honor-guard-for-a-mummy.html |archive-date=1 November 2019 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Pain |first=Stephanie |title=Ramesses rides again |url=http://newscientist.com/article/mg18424736.400-ramesses-rides-again.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140815214602/http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg18424736.400-ramesses-rides-again.html |archive-date=15 August 2014 |access-date=13 December 2013 |publisher=New Scientist}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.manchester.ac.uk/discover/news/was-the-great-pharaoh-ramesses-ii-a-true-redhead/ |title=Was the great Pharaoh Ramesses II a true redhead? |publisher=The University of Manchester |date=3 February 2010 |access-date=16 February 2020 |archive-date=16 February 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200216191646/https://www.manchester.ac.uk/discover/news/was-the-great-pharaoh-ramesses-ii-a-true-redhead/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Persistent claims that the mummy was issued with a ] for the journey are incorrect, but may be based on the French word {{lang|fr|passeport}} being used to describe the extensive documentation required.<ref>{{cite web |title=This image was digitally created for representative purposes {{!}} Fact Check |url=https://factcheck.afp.com/image-was-digitally-created-representative-purposes |website=AFP Fact Check |access-date=18 June 2024 |language=en |date=20 October 2020}}</ref> | |||
| The mummy was forensically tested in 1976 by ], the chief ] scientist at the Criminal Identification Laboratory of Paris. Ceccaldi observed that the mummy had slightly wavy, red hair; from this trait combined with cranial features, he concluded that Ramesses II was of a "Berber type" and hence – according to Ceccaldi's analysis – fair-skinned.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Pierre-Fernand |last=Ceccaldi |title=Recherches sur les momies: Ramsès II |year=1987 |journal=Bulletin de l'Académie de Médecine |volume=171 |page=119 |issue=1}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6445192d/f141.image |title=Bulletin de l'Académie nationale de médecine |website=Gallica |date=6 January 1987|access-date=15 July 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180715153117/https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6445192d/f141.image|archive-date=15 July 2018|url-status=live}}</ref> Subsequent microscopic inspection of the roots of Ramesses II's hair proved that the king's hair originally was red, which suggests that he came from a family of redheads.{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2001|p=}}{{sfnp|Brier|1994|p=153}} This has more than just cosmetic significance: in ancient Egypt people with red hair were associated with the deity ], the slayer of ], and the name of Ramesses II's father, Seti I, means "follower of Seth".{{sfnp|Brier|1994|pp=200–201}} ] disputed the results of the study, arguing that the structure of hair morphology cannot determine the ethnicity of a mummy and that a comparative study should have featured ] in ] before a conclusive judgement was reached.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Diop |first1=Cheikh Anta |title=Civilization or barbarism : an authentic anthropology |date=1991 |location=Brooklyn, New York |isbn=1556520484 |pages=67–68 |edition=First}}</ref> | |||
| In 2006, French police arrested a man who tried to sell several tufts of Ramesses' hair on the Internet. Jean-Michel Diebolt said he had got the relics from his late father, who had been on the analysis team in the 1970s. They were returned to Egypt the following year.<ref>{{cite web |title=Ancient pharaoh's hair returns to Egypt |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/id/wbna18036842 |website=Associated Press |access-date=9 December 2022 |date=10 April 2007}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| During the examination, scientific analysis revealed battle-wounds, old fractures, ] and poor circulation.{{citation needed|date=November 2016}} Ramesses II's arthritis is believed to have made him walk with a hunched back for the last decades of his life.{{sfnp|Brier|1998|p=153}} A 2004 study excluded ] as a possible cause and proposed ] as a possible alternative,<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Chhem |first1=R. K. |last2=Schmit |first2=P. |last3=Fauré |first3=C. |date=October 2004 |title=Did Ramesses II really have ankylosing spondylitis? A reappraisal |journal=Can Assoc Radiol Journal |volume=55 |issue=4 |pages=211–217 |pmid=15362343}}</ref> which was confirmed by more recent work.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Saleem |first1=Sahar N. |last2=Hawass |first2=Zahi |date=2014 |title=Brief Report: Ankylosing Spondylitis or Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis in Royal Egyptian Mummies of the 18th–20th Dynasties? Computed Tomography and Archaeology Studies |journal=Arthritis & Rheumatology |volume=66 |issue=12 |pages=3311–3316 |doi=10.1002/art.38864 |pmid=25329920 |s2cid=42296180 |issn=2326-5205}}</ref> A significant hole in the pharaoh's ] was detected. Researchers observed "an ] by his teeth (which) was serious enough to have caused death by infection, although this cannot be determined with certainty".{{sfnp|Brier|1998|p=153}} | |||
| After being irradiated in an attempt to eliminate fungi and insects, the mummy was returned from Paris to Egypt in May 1977.<ref>{{cite news |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |page=20 |url=https://www.newspapers.com/newspage/383571018/ |work=] |agency=] |title='Cleaned-Up' Mummy Flown Home to Egypt |date=11 May 1977 |access-date=30 October 2019 |quote=CAIRO (AP)—The 3,212-year-old mummy of Pharaoh Ramses II was returned from Paris Tuesday, hopefully cured by radiation of 60 types of fungi and two strains of insects. |archive-date=30 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191030051950/https://www.newspapers.com/newspage/383571018/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In April 2021, his mummy was moved from the old ] to the new ] along with those of 17 other kings and 4 queens in an event termed the ].<ref name=Parisse/> | |||
| ===Burial of wives and relatives=== | |||
| ====Tomb of Nefertari==== | |||
| {{Main|QV66|l1=Tomb of Nefertari}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ] or royal name of Ramesses II.]] | |||
| The tomb of the most important ] of Ramesses was discovered by ] in 1904.{{sfnp|Skliar|2005|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}}{{sfnp|Siliotti|1994|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} Although it had been looted in ancient times, the tomb of ] is extremely important, because its magnificent wall-painting decoration is regarded as one of the greatest achievements of ]. A flight of steps cut out of the rock gives access to the antechamber, which is decorated with paintings based on chapter seventeen of the ]. The astronomical ceiling represents the heavens and is painted in dark blue, with a myriad of golden five-pointed stars. The east wall of the antechamber is interrupted by a large opening flanked by representation of ] at the left and ] at the right; this in turn leads to the side chamber, decorated with offering-scenes, preceded by a vestibule in which the paintings portray Nefertari presented to the deities, who welcome her. On the north wall of the antechamber is the stairway down to the burial-chamber, a vast quadrangular room covering a surface-area of about {{convert|90|m2}}, its astronomical ceiling supported by four pillars, entirely decorated. Originally, the queen's red granite ] lay in the middle of this chamber. According to religious doctrines of the time, it was in this chamber, which the ancient Egyptians called the Golden Hall, that the regeneration of the deceased took place. This decorative pictogram of the walls in the burial-chamber drew inspiration from chapters 144 and 146 of the Book of the Dead: in the left half of the chamber, there are passages from chapter 144 concerning the gates and doors of the kingdom of Osiris, their guardians, and the magic formulas that had to be uttered by the deceased in order to go past the doors.{{sfnp|Siliotti|1994|p={{page needed|date=September 2022}}}} | |||
| ====Tomb KV5==== | |||
| {{Main|KV5}} | |||
| {{see also|List of children of Ramesses II}} | |||
| In 1995, Professor ], head of the ], rediscovered Tomb ]. It has proven to be the largest tomb in the Valley of the Kings, and originally contained the mummified remains of some of this king's estimated 52 sons. Approximately 150 corridors and tomb chambers have been located in this tomb as of 2006 and the tomb may contain as many as 200 corridors and chambers.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.narmer.pl/kv/kv05en.htm |title=Tomb of Ramses II sons |access-date=27 February 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150227193526/http://www.narmer.pl/kv/kv05en.htm|archive-date=27 February 2015|url-status=live}}</ref> It is believed that at least four of Ramesses's sons, including ], Sety, ] (Ramesses's first-born son) and "the King's Principal Son of His Body, the Generalissimo Ramesses, justified" (i.e., deceased) were buried there from inscriptions, ] or ]s discovered in the tomb.{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2000|pp=161–162}} ] writes that thus far | |||
| {{blockquote|no intact burials have been discovered and there have been little substantial funeral debris: thousands of potsherds, faience ''ushabti'' figures, beads, amulets, fragments of Canopic jars, of wooden coffins ... but no intact sarcophagi, mummies or ] cases, suggesting that much of the tomb may have been unused. Those burials which were made in KV5 were thoroughly looted in antiquity, leaving little or no remains.{{sfnp|Tyldesley|2000|pp=161–162}}}} | |||
| ==In literature and the arts== | |||
| Ramesses is the basis for ]'s poem "]". ] gives an inscription on the base of one of his sculptures as: "] am I, Osymandias. If anyone would know how great I am and where I lie, let him surpass one of my works."<ref>{{cite web |author=Shelley |first=Percy Bysshe |title=Ozymandias |url=http://rpo.library.utoronto.ca/poem/1904.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061010122400/http://rpo.library.utoronto.ca/poem/1904.html |archive-date=10 October 2006 |access-date=18 September 2006 |via=Representative Poetry Online}} First publication: {{cite magazine |author=Shelley |first=Percy Bysshe |author-mask=1 |date=11 January 1818 |title=Ozymandias |magazine=The Examiner |number=524}}</ref> This is paraphrased in Shelley's poem. | |||
| The life of Ramesses II has inspired many fictional representations, including the ]s of the French writer ], the ''Ramsès'' series; the graphic novel '']'', in which the character of Adrian Veidt uses Ramesses II to form part of the inspiration for his alter-ego, ]; ]'s novel '']'', which is largely concerned with the life of Ramesses II, though from the perspective of Egyptians living during the reign of ]; and the ] book '']'' (1989), in which Ramesses was the main character. In '']'' Ramesses is an ancestor of the main characters Sadie and Carter Kane. Ramesses II is one of the characters in the video game '']'', as well as in additional ] for its sequel, '']''. | |||
| The ] underground rock band ] released their song "Ramses II Is Dead, My Love" on their 1968 album '']''.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Sanders |first1=Ed |title=1968: A History in Verse |date=1997 |publisher=Black Sparrow Press |page=255}}</ref> | |||
| Ramesses II is a main character in the fiction book ''The Heretic Queen'' by ] published in 2008. It is a novel about the love story and beginning years of the marriage of Pharaoh Ramesses and Queen ], during the time Pharaoh Rameses II is trying to decide who will be queen between his two wives Nefertari and Iset. Nefertari is the daughter and orphan of Queen ] and General Nakhtmin, niece of Queen ] and Pharaoh ]. The book is told from the perspective of Nefertari and is fiction but does deal with many historical events during the beginning of Rameses II reign and many historical people giving readers a view of what life and these historical figures may have been like. | |||
| ===As the pharaoh in the Bible's Book of Exodus=== | |||
| ] in '']'', 1956]] | |||
| Though scholars generally do not recognize the biblical portrayal of the Exodus as an actual historical event,<ref>{{cite book |last=Grabbe |first=Lester |title=The Book of Exodus: Composition, Reception, and Interpretation |publisher=BRILL |year=2014 |isbn=9789004282667 |editor1-last=Dozeman |editor1-first=Thomas |pages=61–87 |chapter=Exodus and History |editor2-last=Evans |editor2-first=Craig A. |editor3-last=Lohr |editor3-first=Joel N. |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TmGeBQAAQBAJ&q=%22primarily+Amos+and+Hosea%22%22middle+of+the+eighth+century%22&pg=PA61}}</ref> various historical pharaohs have been proposed as the corresponding ruler at the time the story takes place, with Ramesses II as the most popular candidate for ]. He is cast in this role in the 1944 novella '']'' by ]. Although not a major character, Ramesses appears in ]'s ''So Moses Was Born'', a first-person account from Nebunefer, the brother of Ramose, which paints a picture of the life of Ramose from the death of Seti, replete with the power play, intrigue, and assassination plots of the historical record, and depicting the relationships with ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| In film, Ramesses is played by ] in ]'s classic '']'' (1956). Here Ramesses is portrayed as a vengeful tyrant as well as the main antagonist of the film, ever scornful of his father's preference for Moses over "the son of body".<ref>{{cite web |author=Ray |first=John |title=Ramesses the Great |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ancient/egyptians/ramesses_01.shtml |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121016070535/http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ancient/egyptians/ramesses_01.shtml |archive-date=16 October 2012 |access-date=30 May 2008 |publisher=BBC history}}</ref> The animated film '']'' (1998) also features a depiction of Ramesses (voiced by ], for both the speaking and the singing), portrayed as Moses' adoptive brother, and ultimately as the film's villain with essentially the same motivations as in the earlier 1956 film. ] played Ramesses in the 2014 film '']''. ] plays Ramesses in the 2015–2016 Brazilian telenovela series '']'' ({{langx|en|'The Ten Commandments'}}). | |||
| In the 2013 miniseries '']'', he is portrayed by Stewart Scudamore. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| * | |||
| {{notelist|30em}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist|23em}} | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <references /> | |||
| '''Bibliography''' | |||
| </div> | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=von Beckerath |first=Jürgen |year=1997 |title=Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten |location=Mainz |publisher=Philipp von Zabern}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Brand |first=Peter J. |title=The Monuments of Seti I: Epigraphic, Historical and Art Historical Analysis |publisher=Brill |location=NV Leiden |year=2000 |isbn=978-90-04-11770-9 |url=https://www.academia.edu/40610263}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Brier |first=Bob |title=Egyptian Mummies: Unravelling the Secrets of an Ancient Art |location=New York |publisher=William Morrow & Co. |year=1994}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Brier |first=Bob |title=The Encyclopedia of Mummies |publisher=Checkmark Books |year=1998}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Clayton |first=Peter |title=Chronology of the Pharaohs |publisher=] |year=1994}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Drews |first=Robert |title=The End of the Bronze Age: Changes in Warfare and the Catastrophe Ca. 1200 B.C. |date=1993 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=9780691209975}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Grimal |first=Nicolas-Christophe |author-link=Nicolas Grimal |title=A History of Ancient Egypt |location=Oxford |publisher=Blackwell |year=1992 |isbn=978-0-631-17472-1}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Kitchen |first=Kenneth |title=Pharaoh Triumphant: The Life and Times of Ramesses II, King of Egypt |year=1982 |location=London |publisher=Aris & Phillips |isbn=978-0-85668-215-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kitchen |first=Kenneth Anderson |year=1996 |title=Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Translations. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions |location=Oxford |publisher=Blackwell Publishers |isbn=978-0-631-18427-0}} Translations and (in the 1999 volume below) notes on all contemporary royal inscriptions naming the king. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kitchen |first=Kenneth Anderson |year=1979 |title=Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Notes and Comments. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions |location=Oxford |publisher=Blackwell Publishers |url=https://archive.org/details/KennethA.KitchenRamessideInscriptionsVol2/page/n223/mode/1up}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Kitchen |first=Kenneth Anderson |year=2003 |title=On the Reliability of the Old Testament |location=Michigan |publisher=William B. ] |isbn=978-0-8028-4960-1}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Leprohon|first=Ronald J.|title=The Great Name: Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary |year=2013|publisher=SBL Press|isbn=978-1-58983-736-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=O'Connor |editor1-first=David |editor2-last=Cline |editor2-first=Eric |title=Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign |publisher=University of Michigan Press |year=1998 |isbn=9780472088331}} | |||
| * Obsomer, Claude, ''Ramsès II'', Paris, 2012. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Putnam |first=James |title=An introduction to Egyptology |year=1990|title-link=Egyptology}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Ricke |first1=Herbert |last2=Hughes |first2=George R. |last3=Wente |first3=Edward F. |year=1967 |title=The Beit el-Wali Temple of Ramesses II}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Rohl |first=David M. |title=Pharaohs and Kings: A Biblical Quest |author-link=David M. Rohl |edition=illustrated, reprint |publisher=Crown Publishers |year=1995 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aeKCAAAAIAAJ |isbn=978-0-517-70315-1 |access-date=30 March 2019 |url-status=live |archive-date=14 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200314052821/https://books.google.com/books?id=aeKCAAAAIAAJ }} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Siliotti |first=Alberto |title=Egypt: temples, people, gods |year=1994}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Skliar |first=Ania |title=Grosse kulturen der welt-Ägypten |year=2005}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |journal=Journal of Near Eastern Studies |first=Robert R. |last=Stieglitz |year=1991 |title=The City of Amurru |volume=50 |issue=1 |pages=45–48 |doi=10.1086/373464|s2cid=161341256 }} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Tyldesley |first=Joyce |year=2000 |title=Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh |location=London |publisher=Viking |isbn=9780670884872}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Tyldesley |first=Joyce |date=26 April 2001 |title=Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hzbRBN6Ugr0C |location=London |publisher=Penguin Books |isbn=9780141949789 |access-date=20 October 2020}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Westendorf |first=Wolfhart |title=Das alte Ägypten |year=1969 |language=de}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * ] 1994. “''Israel'' in the Merneptah Stela,” ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'' 296., pp. 45-61. | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Balout |first1=L. |last2=Roubet |first2=C. |last3=Desroches-Noblecourt |first3=C. |title=La Momie de Ramsès II: Contribution Scientifique à l'Égyptologie |year=1985 |language=fr}} | |||
| *] 1998. ''Domination and Resistance: Egyptian Military Activity in the Southern Levant, 1300–1185 BC.'' Probleme der Ägyptologie 11. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 90-04-10984-6 | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Bietak |first=Manfred |title=Avaris: Capital of the Hyksos – Recent Excavations |year=1995 |publisher=British Museum Press |location=London, England |isbn=978-0-7141-0968-8}} | |||
| *] 2003. "Merenptah's Inscription and Reliefs and the Origin of Israel" in Beth Alpert Nakhai ed. ''The Near East in the Southwest: Essays in Honor of William G. Dever'', pp. 19–44. Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 58. Boston: American Schools of Oriental Research. ISBN 0-89757-065-0 | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Dodson |first=Aidan |author2=Dyan Hilton |title=The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt |publisher=Thames & Hudson |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-500-05128-3}} | |||
| *] 2004. "The Structure of the Final Hymnic-Poetic Unit on the Merenptah Stela." ''Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft'' 116:75–81. | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Grajetzki |first=Wolfram |year=2005 |title=Ancient Egyptian Queens – a hieroglyphic dictionary |publisher=Golden House Publications |location=London, England |isbn=978-0-9547218-9-3}} | |||
| *James, T. G. H. 2000. ''Ramesses II''. New York: Friedman/Fairfax Publishers. A large-format volume by the former Keeper of Egyptian Antiquities at the ], filled with colour illustrations of buildings, art, etc. related to Ramesses II | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Hasel |first1=Michael G. |year=1994 |title=''Israel'' in the Merneptah Stela |journal=Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research |volume=296 |issue=296 |pages=45–61 |doi=10.2307/1357179 |jstor=1357179 |s2cid=164052192}} | |||
| * Von Beckerath, Jürgen. 1997. ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten'', Mainz, Philipp von Zabern. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kuhrt |first=Amelie |year=1995 |title=The Ancient Near East c. 3000–330 BC |volume=1 |location=London, England |publisher=]}} | |||
| *]. 1982. ''Pharaoh Triumphant: The Life and Times of Ramesses II, King of Egypt''. Monumenta Hannah Sheen Dedicata 2. Mississauga: Benben Publications. ISBN 0-85668-215-2. This is an English language treatment of the life of Ramesses II at a semi-popular level | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Rice |first=Michael |title=Who's Who in Ancient Egypt |publisher=Routledge |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-415-15448-2}} | |||
| *Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson. 1996. ''Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Translations. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 0-631-18427-9. Translations and (in the 1999 volume below) notes on all contemporary royal inscriptions naming the king. | |||
| * Hasel, Michael G. 1998. ''Domination and Resistance: Egyptian Military Activity in the Southern Levant, 1300–1185 BC.'' Probleme der Ägyptologie 11. Leiden: ]. {{ISBN|90-04-10984-6}} | |||
| *Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson. 1999. ''Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Notes and Comments. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers | |||
| * Hasel, Michael G. 2003. "Merenptah's Inscription and Reliefs and the Origin of Israel" in Beth Alpert Nakhai (ed.), ''The Near East in the Southwest: Essays in Honor of William G. Dever'', pp. 19–44. Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 58. Boston, Massachusetts: American Schools of Oriental Research. {{ISBN|0-89757-065-0}} | |||
| *Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson. 2003. ''On the Reliability of the Old Testament''. Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, ISBN 0-8028-4960-1. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Hasel |first1=Michael G. |year=2004 |title=The Structure of the Final Hymnic-Poetic Unit on the Merenptah Stela |journal=Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft |volume=116 |pages=75–81 |doi=10.1515/zatw.2004.005}} | |||
| * Tyldesley, Joyce. 2000. ''Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh''. London: Viking/Penguin Books | |||
| * James, T. G. H. 2000. ''Ramesses II''. New York: Friedman/Fairfax Publishers. A large-format volume by the former Keeper of Egyptian Antiquities at the ], filled with colour illustrations of buildings, art, etc. related to Ramesses II. | |||
| * The Epigraphic Survey, Reliefs and Inscriptions at Karnak III: The Bubastite Portal, Oriental Institute Publications, vol. 74 (Chicago, Illinois): ], 1954. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Ancient Egyptians}} | |||
| {{Commons category|Ramses II}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Pharaohs |new |state=expanded}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| <!-- Please respect alphabetical order --> | |||
| {{Link FA|de}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Authority control}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Ramesses 02}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:11, 13 January 2025
Pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty (1303–1213 BC) "Ramses II" redirects here. For the heavily modified Soviet T-55 main battle tank of the Egyptian military, see Ramses II tank.
| Ramesses II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramesses the Great, Ozymandias | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 The Younger Memnon (c. 1250 BC), a statue depicting Ramesses II, from the Ramesseum in Thebes. Currently on display at the British Museum in London. The Younger Memnon (c. 1250 BC), a statue depicting Ramesses II, from the Ramesseum in Thebes. Currently on display at the British Museum in London. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharaoh | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 1279–1213 BC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Seti I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor | Merneptah | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Royal titulary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consort | Nefertari, Isetnofret, Maathorneferure, Meritamen, Bintanath, Nebettawy, Henutmire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Children | 88–103 (List of children of Ramesses II) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Father | Seti I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mother | Tuya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | c. 1303 BC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | c. 1213 BC (aged 90–91) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Burial | KV7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monuments | Abu Simbel, Abydos, Ramesseum, Luxor, Karnak | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dynasty | 19th Dynasty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ramesses II (/ˈræməsiːz, ˈræmsiːz, ˈræmziːz/; Ancient Egyptian: rꜥ-ms-sw, Rīꜥa-masē-sə, Ancient Egyptian pronunciation: [ɾiːʕamaˈseːsə]; c. 1303 BC – 1213 BC), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of the Eighteenth Dynasty, he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom, which itself was the most powerful period of ancient Egypt. He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the Battle of Kadesh, generally considered a stalemate.
In ancient Greek sources, he is called Ozymandias, derived from the first part of his Egyptian-language regnal name: Usermaatre Setepenre. Ramesses was also referred to as the "Great Ancestor" by successor pharaohs and the Egyptian people.
For the early part of his reign, he focused on building cities, temples, and monuments. After establishing the city of Pi-Ramesses in the Nile Delta, he designated it as Egypt's new capital and used it as the main staging point for his campaigns in Syria. Ramesses led several military expeditions into the Levant, where he reasserted Egyptian control over Canaan and Phoenicia; he also led a number of expeditions into Nubia, all commemorated in inscriptions at Beit el-Wali and Gerf Hussein. He celebrated an unprecedented thirteen or fourteen Sed festivals—more than any other pharaoh.
Estimates of his age at death vary, although 90 or 91 is considered to be the most likely figure. Upon his death, he was buried in a tomb (KV7) in the Valley of the Kings; his body was later moved to the Royal Cache, where it was discovered by archaeologists in 1881. Ramesses' mummy is now on display at the National Museum of Egyptian Civilization, located in the city of Cairo.
Early life
Ramesses II was not born a prince. His grandfather Ramesses I was a vizier and military officer during the reign of pharaoh Horemheb, who appointed Ramesses I as his successor; at that time, Ramesses II was about eleven years old.

After Ramesses I died, his son, Seti I became king, and designated his son Ramesses II as prince regent at about the age of fourteen.
Reign length
Ramesses date of accession to the throne is recorded as III Shemu, day 27, which most Egyptologists believe to be 31 May 1279 BC.
The Jewish historian Josephus, in his book Contra Apionem which included material from Manetho's Aegyptiaca, assigned Ramesses II ("Armesses Miamun") a reign of 66 years, 2 months. This is essentially confirmed by the calendar of Papyrus Gurob fragment L, where Year 67, I Akhet day 18 of Ramesses II is immediately followed by Year 1, II Akhet day 19 of Merneptah (Ramesses II's son), meaning Ramesses II died about 2 months into his 67th Regnal year.
In 1994, A. J. Peden proposed that Ramesses II died between II Akhet day 3 and II Akhet day 13 on the basis of Theban graffito 854+855, equated to Merneptah's Year 1 II Akhet day 2. The workman's village of Deir el-Medina preserves a fragment of a mid-20th dynasty necropolis journal (P. Turin prov. nr. 8538 recto I, 5; unpublished) which records that the date II Akhet day 6 was a Free feast day for the "Sailing of UsimaRe-Setepenre." (for Ramesses II). As the Egyptologist Robert J. Demarée notes in a 2016 paper:
- The feast called ẖnw – ‘Sailing’ – was clearly observed in Thebes or at Deir el-Medina during the Ramesside Period in remembrance of the passing of deified royals. The ‘Sailing’ of Ahmose-Nefertari was celebrated on II Shemu 15; the ‘Sailing’ of Seti I on III Shemu 24; and the ‘Sailing’ of Ramesses II on II Akhet 6.
The date of Ramesses II's recorded death on II Akhet day 6 falls perfectly within A. J. Peden's estimated timeline for the king's death in the interval between II Akhet day 3 and II Akhet day 13. This means that Ramesses II died on Year 67, II Akhet day 6 of his reign after ruling Egypt for 66 years 2 months and 9 days.
Military campaigns
Early in his life, Ramesses II embarked on numerous campaigns to restore possession of previously held territories lost to the Nubians and Hittites and to secure Egypt's borders. He was also responsible for suppressing some Nubian revolts and carrying out a campaign in Libya. Though the Battle of Kadesh often dominates the scholarly view of Ramesses II's military prowess and power, he nevertheless enjoyed more than a few outright victories over Egypt's enemies. During his reign, the Egyptian army is estimated to have totaled some 100,000 men: a formidable force that he used to strengthen Egyptian influence.
Battle against Sherden pirates
In his second year, Ramesses II decisively defeated the Sherden sea pirates who were wreaking havoc along Egypt's Mediterranean coast by attacking cargo-laden vessels travelling the sea routes to Egypt. The Sherden people probably came from the coast of Ionia, from southwest Anatolia or perhaps, also from the island of Sardinia. Ramesses posted troops and ships at strategic points along the coast and patiently allowed the pirates to attack their perceived prey before skillfully catching them by surprise in a sea battle and capturing them all in a single action. A stele from Tanis speaks of their having come "in their war-ships from the midst of the sea, and none were able to stand before them". There probably was a naval battle somewhere near the mouth of the Nile, as shortly afterward, many Sherden are seen among the pharaoh's body-guard where they are conspicuous by their horned helmets having a ball projecting from the middle, their round shields, and the great Naue II swords with which they are depicted in inscriptions of the Battle of Kadesh. In that sea battle, together with the Sherden, the pharaoh also defeated the Lukka (L'kkw, possibly the people later known as the Lycians), and the Šqrsšw (Shekelesh) peoples.
Syrian campaigns
First Syrian campaign

The immediate antecedents to the Battle of Kadesh were the early campaigns of Ramesses II into Canaan. His first campaign seems to have taken place in the fourth year of his reign and was commemorated by the erection of what became the first of the Commemorative stelae of Nahr el-Kalb near what is now Beirut. The inscription is almost totally illegible due to weathering.
In the fourth year of his reign, he captured the Hittite vassal state of the Amurru during his campaign in Syria.
Second Syrian campaign
Main article: Battle of KadeshThe Battle of Kadesh in his fifth regnal year was the climactic engagement in a campaign that Ramesses fought in Syria, against the resurgent Hittite forces of Muwatalli II. The pharaoh wanted a victory at Kadesh both to expand Egypt's frontiers into Syria, and to emulate his father Seti I's triumphal entry into the city just a decade or so earlier.
He also constructed his new capital, Pi-Ramesses. There he built factories to manufacture weapons, chariots, and shields, supposedly producing some 1,000 weapons in a week, about 250 chariots in two weeks, and 1,000 shields in a week and a half. After these preparations, Ramesses moved to attack territory in the Levant, which belonged to a more substantial enemy than any he had ever faced in war: the Hittite Empire.
After advancing through Canaan for exactly a month, according to the Egyptian sources, Ramesses arrived at Kadesh on 1 May 1274 BC. Here, Ramesses' troops were caught in a Hittite ambush and were initially outnumbered by the enemy, whose chariotry smashed through the second division of Ramesses' forces and attacked his camp. Receiving reinforcements from other Egyptian divisions arriving on the battlefield, the Egyptians counterattacked and routed the Hittites, whose survivors abandoned their chariots and swam the Orontes River to reach the safe city walls. Although left in possession of the battlefield, Ramesses, logistically unable to sustain a long siege, returned to Egypt. While Ramesses claimed a great victory, and this was technically true in terms of the actual battle, it is generally considered that the Hittites were the ultimate victors as far as the overall campaign was concerned, since the Egyptians retreated after the battle, and Hittite forces invaded and briefly occupied the Egyptian possessions in the region of Damascus.
Third Syrian campaign
Egypt's sphere of influence was now restricted to Canaan while Syria fell into Hittite hands. Canaanite princes, seemingly encouraged by the Egyptian incapacity to impose their will and goaded on by the Hittites, began revolts against Egypt. Ramesses II was not willing to let this stand, and prepared to contest the Hittite advance with new military campaigns. Because they are recorded on his monuments with few indications of precise dates or the regnal year, the precise chronology of the subsequent campaigns is not clear. Late in the seventh year of his reign (April/May 1272 BC ), Ramesses II returned to Syria again. This time he proved more successful against his Hittite foes. During this campaign he split his army into two forces. One force was led by his son, Amun-her-khepeshef, and it chased warriors of the Šhasu tribes across the Negev as far as the Dead Sea, capturing Edom-Seir. It then marched on to capture Moab. The other force, led by Ramesses himself, attacked Jerusalem and Jericho. He, too, then entered Moab, where he rejoined his son. The reunited army then marched on Hesbon, Damascus, on to Kumidi, and finally, recaptured Upi (the land around Damascus), reestablishing Egypt's former sphere of influence.
Later Syrian campaigns
Main article: Siege of Dapur
Ramesses extended his military successes in his eighth and ninth years. He crossed the Dog River (Nahr al-Kalb) and pushed north into Amurru. His armies managed to march as far north as Dapur, where he had a statue of himself erected. The Egyptian pharaoh thus found himself in northern Amurru, well past Kadesh, in Tunip, where no Egyptian soldier had been seen since the time of Thutmose III, almost 120 years earlier. He laid siege to Dapur before capturing it, and returning to Egypt. By November 1272 BC, Ramesses was back in Egypt, at Heliopolis. His victory in the north proved ephemeral. After having reasserted his power over Canaan, Ramesses led his army north. A mostly illegible stele at the Dog River near Beirut, (Lebanon), which appears to be dated to the king's second year, was probably set up there in his tenth year (1269 BC). The thin strip of territory pinched between Amurru and Kadesh did not make for a stable possession. Within a year, they had returned to the Hittite fold, so that Ramesses had to march against Dapur once more in his tenth year. This time he claimed to have fought the battle without even bothering to put on his corslet, until two hours after the fighting began. Six of Ramesses's youthful sons, still wearing their side locks, took part in this conquest. He took towns in Retjenu, and Tunip in Naharin, later recorded on the walls of the Ramesseum. This second success at the location was equally as meaningless as his first, as neither power could decisively defeat the other in battle. In year eighteen, Ramesses erected a stele at Beth Shean, on 19 January 1261 BC.
Peace treaty with the Hittites
Main article: Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty
In Year 21 of Ramesses's reign, he concluded a peace treaty with the Hittites known to modern scholars as the Treaty of Kadesh. Though this treaty settled the disputes over Canaan, its immediate impetus seems to have been a diplomatic crisis that occurred following Ḫattušili III's accession to the Hittite throne. Ḫattušili had come to power by deposing his nephew Muršili III in the brief and bitter Hittite Civil War. Though the deposed king was initially sent into exile in Syria, he subsequently attempted to regain power and fled to Egypt once these attempts were discovered.
When Ḫattušili demanded his extradition, Ramesses II denied any knowledge of his whereabouts. When Ḫattušili insisted that Muršili was in Egypt, Ramesses's response suggested that Ḫattušili was being deceived by his subjects. This demand precipitated a crisis, and the two empires came close to war. Eventually, in the twenty-first year of his reign (1259 BC ), Ramesses concluded an agreement at Kadesh to end the conflict.
The peace treaty was recorded in two versions, one in Egyptian hieroglyphs, the other in Hittite, using cuneiform script; both versions survive. Such dual-language recording is common to many subsequent treaties. This treaty differs from others, in that the two language versions are worded differently. While the majority of the text is identical, the Hittite version says the Egyptians came suing for peace and the Egyptian version says the reverse. The treaty was given to the Egyptians in the form of a silver plaque, and this "pocket-book" version was taken back to Egypt and carved into the temple at Karnak. The Egyptian account records Ramesses II's receipt of the Hittite peace treaty tablets on I Peret 21 of Year 21, corresponding to 10 November 1259 BC, according to the standard "Low Chronology" used by Egyptologists.
The treaty was concluded between Ramesses II and Ḫattušili III in year 21 of Ramesses's reign (c. 1259 BC). Its 18 articles call for peace between Egypt and Hatti and then proceeds to maintain that their respective deities also demand peace. The frontiers are not laid down in this treaty, but may be inferred from other documents. The Anastasy A papyrus describes Canaan during the latter part of the reign of Ramesses II and enumerates and names the Phoenician coastal towns under Egyptian control. The harbour town of Sumur, north of Byblos, is mentioned as the northernmost town belonging to Egypt, suggesting it contained an Egyptian garrison.
No further Egyptian campaigns in Canaan are mentioned after the conclusion of the peace treaty. The northern border seems to have been safe and quiet, so the rule of the pharaoh was strong until Ramesses II's death, and the subsequent waning of the dynasty. When the King of Mira attempted to involve Ramesses in a hostile act against the Hittites, the Egyptian responded that the times of intrigue in support of Mursili III, had passed. Ḫattušili III wrote to Kadashman-Enlil II, Kassite king of Karduniaš (Babylon) in the same spirit, reminding him of the time when his father, Kadashman-Turgu, had offered to fight Ramesses II, the king of Egypt. The Hittite king encouraged the Babylonian to oppose another enemy, which must have been the king of Assyria, whose allies had killed the messenger of the Egyptian king. Ḫattušili encouraged Kadashman-Enlil to come to his aid and prevent the Assyrians from cutting the link between the Canaanite province of Egypt and Mursili III, the ally of Ramesses.
Nubian campaigns

Ramesses II also campaigned south of the first cataract of the Nile into Nubia. When Ramesses was about 22 years old, two of his own sons, including Amun-her-khepeshef, accompanied him in at least one of those campaigns. By the time of Ramesses, Nubia had been a colony for 200 years, but its conquest was recalled in decoration from the temples Ramesses II built at Beit el-Wali (which was the subject of epigraphic work by the Oriental Institute during the Nubian salvage campaign of the 1960s), Gerf Hussein and Kalabsha in northern Nubia. On the south wall of the Beit el-Wali temple, Ramesses II is depicted charging into battle against tribes south of Egypt in a war chariot, while his two young sons, Amun-her-khepsef and Khaemwaset, are shown behind him, also in war chariots. A wall in one of Ramesses's temples says he had to fight one battle with those tribes without help from his soldiers.

Libyan campaigns
During the reign of Ramesses II, the Egyptians were evidently active on a 300-kilometre (190 mi) stretch along the Mediterranean coast, at least as far as Zawyet Umm El Rakham, where remains of a fortress described by its texts as built on Libyans land have been found. Although the exact events surrounding the foundation of the coastal forts and fortresses is not clear, some degree of political and military control must have been held over the region to allow their construction.
There are no detailed accounts of Ramesses II's undertaking large military actions against the Libyans, only generalised records of his conquering and crushing them, which may or may not refer to specific events that were otherwise unrecorded. It may be that some of the records, such as the Aswan Stele of his year 2, are harking back to Ramesses's presence on his father's Libyan campaigns. Perhaps it was Seti I who achieved this supposed control over the region, and who planned to establish the defensive system, in a manner similar to how he rebuilt those to the east, the Ways of Horus across Northern Sinai.
Sed festivals
Main article: Sed festivalAs of Year 28 of his reign, Ramesses II favored the good Amun above all other divinities, as evidenced in the texts of two separate ostraca discovered at Deir el-Medina.
By tradition, in the 30th year of his reign, Ramesses celebrated a jubilee called the Sed festival. These were held to honour and rejuvenate the pharaoh's strength. Only halfway through what would be a 66-year reign, Ramesses had already eclipsed all but a few of his greatest predecessors in his achievements. He had brought peace, maintained Egyptian borders, and built numerous monuments across the empire. His country was more prosperous and powerful than it had been in nearly a century.
Sed festivals traditionally were held again every three years after the 30th year; Ramesses II, who sometimes held them after two years, eventually celebrated an unprecedented thirteen or fourteen.
Building projects and monuments
In the third year of his reign, Ramesses started the most ambitious building project after the pyramids, which were built almost 1,500 years earlier. Ramesses built extensively from the Delta to Nubia, "covering the land with buildings in a way no monarch before him had."

Some of the activities undertaken were focused on remodeling or usurping existing works, improving masonry techniques, and using art as propaganda.
- In Thebes, the ancient temples were transformed, so that each of them reflected honour to Ramesses as a symbol of his putative divine nature and power.
- The elegant but shallow reliefs of previous pharaohs were easily transformed, and so their images and words could easily be obliterated by their successors. Ramesses insisted that his carvings be deeply engraved into the stone, which made them not only less susceptible to later alteration, but also made them more prominent in the Egyptian sun, reflecting his relationship with the sun deity, Ra.
- Ramesses used art as a means of propaganda for his victories over foreigners, which are depicted on numerous temple reliefs.
- His cartouches are prominently displayed even in buildings that he did not construct.
- He founded a new capital city in the Delta during his reign, called Pi-Ramesses. It previously had served as a summer palace during Seti I's reign.
- Ramesses II expanded gold mining operations in Akuyati (modern day Wadi Allaqi).
Ramesses also undertook many new construction projects. Two of his biggest works, besides Pi-Ramesses, were the temple complex of Abu Simbel and the Ramesseum, a mortuary temple in western Thebes.
Pi-Ramesses
Main article: Pi-RamessesRamesses II moved the capital of his kingdom from Thebes in the Nile valley to a new site in the eastern Delta. His motives are uncertain, although he possibly wished to be closer to his territories in Canaan and Syria. The new city of Pi-Ramesses (or to give the full name, Pi-Ramesses Aa-nakhtu, meaning "Domain of Ramesses, Great in Victory") was dominated by huge temples and his vast residential palace, complete with its own zoo. In the 10th century AD, the Bible exegete Rabbi Saadia Gaon believed that the biblical site of Ramesses had to be identified with Ain Shams. For a time, during the early 20th century, the site was misidentified as that of Tanis, due to the amount of statuary and other material from Pi-Ramesses found there, but it now is recognized that the Ramesside remains at Tanis were brought there from elsewhere, and the real Pi-Ramesses lies about 30 km (18.6 mi) south, near modern Qantir. The colossal feet of the statue of Ramesses are almost all that remains above ground today. The rest is buried in the fields.
Ramesseum
Main article: Ramesseum
The temple complex built by Ramesses II between Qurna and the desert has been known as the Ramesseum since the 19th century. The Greek historian Diodorus Siculus marveled at the gigantic temple, now no more than a few ruins.
Oriented northwest and southeast, the temple was preceded by two courts. An enormous pylon stood before the first court, with the royal palace at the left and the gigantic statue of the king at the back. Only fragments of the base and torso remain of the syenite statue of the enthroned pharaoh, 17 metres (56 ft) high and weighing more than 1,000 tonnes (980 long tons; 1,100 short tons). Scenes of the pharaoh and his army triumphing over the Hittite forces fleeing before Kadesh are represented on the pylon. Remains of the second court include part of the internal facade of the pylon and a portion of the Osiride portico on the right. Scenes of war and the alleged rout of the Hittites at Kadesh are repeated on the walls. In the upper registers, feast and honour of the phallic deity Min, god of fertility.
On the opposite side of the court, the few Osiride pillars and columns still remaining may furnish an idea of the original grandeur. Scattered remains of the two statues of the seated king also may be seen, one in pink granite and the other in black granite, which once flanked the entrance to the temple. Thirty-nine out of the forty-eight columns in the great hypostyle hall (41 × 31 m) still stand in the central rows. They are decorated with the usual scenes of the king before various deities. Part of the ceiling, decorated with gold stars on a blue ground, also has been preserved. Ramesses's children appear in the procession on the few walls left. The sanctuary was composed of three consecutive rooms, with eight columns and the tetrastyle cell. Part of the first room, with the ceiling decorated with astral scenes, and few remains of the second room are all that is left. Vast storerooms built of mud bricks stretched out around the temple. Traces of a school for scribes were found among the ruins.
A temple of Seti I, of which nothing remains beside the foundations, once stood to the right of the hypostyle hall.
Abu Simbel
Main article: Abu Simbel temples
In 1255 BC, Ramesses and his queen Nefertari had traveled into Nubia to inaugurate a new temple, Abu Simbel. It is said to be ego cast into stone; the man who built it intended not only to become Egypt's greatest pharaoh, but also one of its deities.
The temple at Abu Simbel was discovered in 1813 by the Swiss Orientalist and traveler Johann Ludwig Burckhardt. An enormous pile of sand almost completely covered the facade and its colossal statues, blocking the entrance for four more years. The Paduan explorer Giovanni Battista Belzoni reached the interior on 4 August 1817.
Other Nubian monuments
As well as the temples of Abu Simbel, Ramesses left other monuments to himself in Nubia. His early campaigns are illustrated on the walls of the Temple of Beit el-Wali (now relocated to New Kalabsha). Other temples dedicated to Ramesses are Derr and Gerf Hussein (also relocated to New Kalabsha). For the temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal, the temple's foundation probably dates during the reign of Thutmose III, while the temple was shaped during his reign and that of Ramesses II.
Other archeological discoveries

The colossal statue of Ramesses II dates back 3,200 years, and was originally discovered in six pieces in a temple near Memphis, Egypt. Weighing some 83-tonne (82-long-ton; 91-short-ton), it was transported, reconstructed, and erected in Ramesses Square in Cairo in 1955. In August 2006, contractors relocated it to save it from exhaust fumes that were causing it to deteriorate. The new site is near the Grand Egyptian Museum.
In 2018, a group of archeologists in Cairo's Matariya neighborhood discovered pieces of a booth with a seat that, based on its structure and age, may have been used by Ramesses. "The royal compartment consists of four steps leading to a cubic platform, which is believed to be the base of the king's seat during celebrations or public gatherings," such as Ramesses' inauguration and Sed festivals. It may have also gone on to be used by others in the Ramesside Period, according to the mission's head. The excavation mission also unearthed "a collection of scarabs, amulets, clay pots and blocks engraved with hieroglyphic text."
In December 2019, a red granite royal bust of Ramesses II was unearthed by an Egyptian archaeological mission in the village of Mit Rahina in Giza. The bust depicted Ramesses II wearing a wig with the symbol "Ka" on his head. Its measurements were 55 cm (21.65 in) wide, 45 cm (17.71 in) thick and 105 cm (41.33 in) long. Alongside the bust, limestone blocks appeared showing Ramesses II during the Heb-Sed religious ritual. "This discovery is considered one of the rarest archaeological discoveries. It is the first-ever Ka statue made of granite to be discovered. The only Ka statue that was previously found is made of wood and it belongs to one of the kings of the 13th dynasty of ancient Egypt which is displayed at the Egyptian Museum in Tahrir Square," said archaeologist Mostafa Waziri.
In September 2024, it was published that during an archaeological excavation of a 3,200 year old fort along the Nile, researches found a golden sword with Ramses II signature on it.
Death and burial
The Egyptian scholar Manetho (third century BC) attributed Ramesses a reign of 66 years and 2 months.
By the time of his death, aged about 90 years, Ramesses was suffering from severe dental problems and was plagued by arthritis and hardening of the arteries. He had made Egypt rich from all the supplies and bounty he had collected from other empires. He had outlived many of his wives and children and left great memorials all over Egypt. Nine more pharaohs took the name Ramesses in his honour.
Mummy
Main article: KV7Originally Ramesses II was buried in the tomb KV7 in the Valley of the Kings, but because of looting in the valley, priests later transferred the body to a holding area, re-wrapped it, and placed it inside the tomb of queen Ahmose Inhapy. Seventy-two hours later it was again moved, to the tomb of the high priest Pinedjem II. All of this is recorded in hieroglyphics on the linen covering the body of his coffin. His mummy was eventually discovered in 1881 in TT320 inside an ordinary wooden coffin and is now in Cairo's National Museum of Egyptian Civilization (until 3 April 2021 it was in the Egyptian Museum).

The pharaoh's mummy reveals an aquiline nose and strong jaw. It stands at about 1.7 metres (5 ft 7 in). Gaston Maspero, who first unwrapped the mummy of Ramesses II, writes, "on the temples there are a few sparse hairs, but at the poll the hair is quite thick, forming smooth, straight locks about five centimeters in length. White at the time of death, and possibly auburn during life, they have been dyed a light red by the spices (henna) used in embalming ... the moustache and beard are thin. ... The hairs are white, like those of the head and eyebrows ... the skin is of earthy brown, splotched with black ... the face of the mummy gives a fair idea of the face of the living king."
In 1975, Maurice Bucaille, a French doctor, examined the mummy at the Cairo Museum and found it in poor condition. French President Valéry Giscard d'Estaing succeeded in convincing Egyptian authorities to send the mummy to France for treatment. In September 1976, it was greeted at Paris–Le Bourget Airport with full military honours befitting a king, then taken to a laboratory at the Musée de l'Homme. Persistent claims that the mummy was issued with a passport for the journey are incorrect, but may be based on the French word passeport being used to describe the extensive documentation required.
The mummy was forensically tested in 1976 by Pierre-Fernand Ceccaldi, the chief forensic scientist at the Criminal Identification Laboratory of Paris. Ceccaldi observed that the mummy had slightly wavy, red hair; from this trait combined with cranial features, he concluded that Ramesses II was of a "Berber type" and hence – according to Ceccaldi's analysis – fair-skinned. Subsequent microscopic inspection of the roots of Ramesses II's hair proved that the king's hair originally was red, which suggests that he came from a family of redheads. This has more than just cosmetic significance: in ancient Egypt people with red hair were associated with the deity Set, the slayer of Osiris, and the name of Ramesses II's father, Seti I, means "follower of Seth". Cheikh Anta Diop disputed the results of the study, arguing that the structure of hair morphology cannot determine the ethnicity of a mummy and that a comparative study should have featured Nubians in Upper Egypt before a conclusive judgement was reached.
In 2006, French police arrested a man who tried to sell several tufts of Ramesses' hair on the Internet. Jean-Michel Diebolt said he had got the relics from his late father, who had been on the analysis team in the 1970s. They were returned to Egypt the following year.
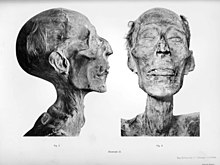
During the examination, scientific analysis revealed battle-wounds, old fractures, arthritis and poor circulation. Ramesses II's arthritis is believed to have made him walk with a hunched back for the last decades of his life. A 2004 study excluded ankylosing spondylitis as a possible cause and proposed diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis as a possible alternative, which was confirmed by more recent work. A significant hole in the pharaoh's mandible was detected. Researchers observed "an abscess by his teeth (which) was serious enough to have caused death by infection, although this cannot be determined with certainty".
After being irradiated in an attempt to eliminate fungi and insects, the mummy was returned from Paris to Egypt in May 1977.
In April 2021, his mummy was moved from the old Egyptian Museum to the new National Museum of Egyptian Civilization along with those of 17 other kings and 4 queens in an event termed the Pharaohs' Golden Parade.
Burial of wives and relatives
Tomb of Nefertari
Main article: Tomb of Nefertari


The tomb of the most important consort of Ramesses was discovered by Ernesto Schiaparelli in 1904. Although it had been looted in ancient times, the tomb of Nefertari is extremely important, because its magnificent wall-painting decoration is regarded as one of the greatest achievements of ancient Egyptian art. A flight of steps cut out of the rock gives access to the antechamber, which is decorated with paintings based on chapter seventeen of the Book of the Dead. The astronomical ceiling represents the heavens and is painted in dark blue, with a myriad of golden five-pointed stars. The east wall of the antechamber is interrupted by a large opening flanked by representation of Osiris at the left and Anubis at the right; this in turn leads to the side chamber, decorated with offering-scenes, preceded by a vestibule in which the paintings portray Nefertari presented to the deities, who welcome her. On the north wall of the antechamber is the stairway down to the burial-chamber, a vast quadrangular room covering a surface-area of about 90 square metres (970 sq ft), its astronomical ceiling supported by four pillars, entirely decorated. Originally, the queen's red granite sarcophagus lay in the middle of this chamber. According to religious doctrines of the time, it was in this chamber, which the ancient Egyptians called the Golden Hall, that the regeneration of the deceased took place. This decorative pictogram of the walls in the burial-chamber drew inspiration from chapters 144 and 146 of the Book of the Dead: in the left half of the chamber, there are passages from chapter 144 concerning the gates and doors of the kingdom of Osiris, their guardians, and the magic formulas that had to be uttered by the deceased in order to go past the doors.
Tomb KV5
Main article: KV5 See also: List of children of Ramesses IIIn 1995, Professor Kent Weeks, head of the Theban Mapping Project, rediscovered Tomb KV5. It has proven to be the largest tomb in the Valley of the Kings, and originally contained the mummified remains of some of this king's estimated 52 sons. Approximately 150 corridors and tomb chambers have been located in this tomb as of 2006 and the tomb may contain as many as 200 corridors and chambers. It is believed that at least four of Ramesses's sons, including Meryatum, Sety, Amun-her-khepeshef (Ramesses's first-born son) and "the King's Principal Son of His Body, the Generalissimo Ramesses, justified" (i.e., deceased) were buried there from inscriptions, ostraca or canopic jars discovered in the tomb. Joyce Tyldesley writes that thus far
no intact burials have been discovered and there have been little substantial funeral debris: thousands of potsherds, faience ushabti figures, beads, amulets, fragments of Canopic jars, of wooden coffins ... but no intact sarcophagi, mummies or mummy cases, suggesting that much of the tomb may have been unused. Those burials which were made in KV5 were thoroughly looted in antiquity, leaving little or no remains.
In literature and the arts
Ramesses is the basis for Percy Bysshe Shelley's poem "Ozymandias". Diodorus Siculus gives an inscription on the base of one of his sculptures as: "King of Kings am I, Osymandias. If anyone would know how great I am and where I lie, let him surpass one of my works." This is paraphrased in Shelley's poem.
The life of Ramesses II has inspired many fictional representations, including the historical novels of the French writer Christian Jacq, the Ramsès series; the graphic novel Watchmen, in which the character of Adrian Veidt uses Ramesses II to form part of the inspiration for his alter-ego, Ozymandias; Norman Mailer's novel Ancient Evenings, which is largely concerned with the life of Ramesses II, though from the perspective of Egyptians living during the reign of Ramesses IX; and the Anne Rice book The Mummy, or Ramses the Damned (1989), in which Ramesses was the main character. In The Kane Chronicles Ramesses is an ancestor of the main characters Sadie and Carter Kane. Ramesses II is one of the characters in the video game Civilization V, as well as in additional downloadable content for its sequel, Civilization VI.
The East Village underground rock band The Fugs released their song "Ramses II Is Dead, My Love" on their 1968 album It Crawled into My Hand, Honest.
Ramesses II is a main character in the fiction book The Heretic Queen by Michelle Moran published in 2008. It is a novel about the love story and beginning years of the marriage of Pharaoh Ramesses and Queen Nefertari, during the time Pharaoh Rameses II is trying to decide who will be queen between his two wives Nefertari and Iset. Nefertari is the daughter and orphan of Queen Mutnodjmet and General Nakhtmin, niece of Queen Nefertiti and Pharaoh Ankhenaten. The book is told from the perspective of Nefertari and is fiction but does deal with many historical events during the beginning of Rameses II reign and many historical people giving readers a view of what life and these historical figures may have been like.
As the pharaoh in the Bible's Book of Exodus

Though scholars generally do not recognize the biblical portrayal of the Exodus as an actual historical event, various historical pharaohs have been proposed as the corresponding ruler at the time the story takes place, with Ramesses II as the most popular candidate for Pharaoh of the Exodus. He is cast in this role in the 1944 novella The Tables of the Law by Thomas Mann. Although not a major character, Ramesses appears in Joan Grant's So Moses Was Born, a first-person account from Nebunefer, the brother of Ramose, which paints a picture of the life of Ramose from the death of Seti, replete with the power play, intrigue, and assassination plots of the historical record, and depicting the relationships with Bintanath, Tuya, Nefertari, and Moses.
In film, Ramesses is played by Yul Brynner in Cecil B. DeMille's classic The Ten Commandments (1956). Here Ramesses is portrayed as a vengeful tyrant as well as the main antagonist of the film, ever scornful of his father's preference for Moses over "the son of body". The animated film The Prince of Egypt (1998) also features a depiction of Ramesses (voiced by Ralph Fiennes, for both the speaking and the singing), portrayed as Moses' adoptive brother, and ultimately as the film's villain with essentially the same motivations as in the earlier 1956 film. Joel Edgerton played Ramesses in the 2014 film Exodus: Gods and Kings. Sérgio Marone plays Ramesses in the 2015–2016 Brazilian telenovela series Os Dez Mandamentos (English: 'The Ten Commandments').
In the 2013 miniseries The Bible, he is portrayed by Stewart Scudamore.
See also
Notes
- Other Egyptian transliterations include Rameses and Ramses (from Koinē Greek: Ῥαμέσσης, Rhaméssēs).
- Meaning "Ra is the one who bore him" in the Egyptian language.
- Koinē Greek: Ὀσυμανδύας, Osymandýas.
- "The Maat of Ra is powerful—chosen of Ra."
References
- ^ Leprohon (2013), pp. 114–115.
- ^ Tyldesley (2001), p. xxiv.
- ^ Clayton (1994), p. 146.
- "Mortuary temple of Ramesses II at Abydos". Archived from the original on 22 December 2008. Retrieved 28 October 2008.
- ^ Anneke Bart. "Temples of Ramesses II". Archived from the original on 28 April 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- "Rameses". Webster's New World College Dictionary. Wiley Publishing. 2004. Archived from the original on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- "Ramses". Webster's New World College Dictionary. Wiley Publishing. 2004. Archived from the original on 24 January 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ Putnam (1990), p. .
- Kulkarni, P., Ji, Z., Xu, Y., Neskovic, M., & Nolan, K. (2023). Exploring Semantic Perturbations on Grover. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.00509.
- Diodorus Siculus. "Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca Historica, Books I-V, book 1, chapter 47, section 4". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 6 May 2011. Retrieved 10 October 2011.
- "Ozymandias". PBS. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 30 March 2008.
- O'Connor & Cline (1998), p. 16.
- ^ von Beckerath (1997), pp. 108, 190.
- ^ Brand (2000), pp. 302–305.
- Leblanc, Christian. "Gerard". Archived from the original on 4 December 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ Parisse, Emmanuel (5 April 2021). "22 Ancient Pharaohs Have Been Carried Across Cairo in an Epic 'Golden Parade'". ScienceAlert. Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- Darnell, J. C., & Manassa, C. (2007). Tutankhamun's Armies: Battle and Conquest During Ancient Egypt's Late Eighteenth Dynasty. John Wiley & Sons.
- Josephus © 2011–2023 by Peter Lundström—Some Rights Reserved—V. 4.0.
- A. H. Gardiner, Ramesside Administrative Documents, (Oxford, 1948), 30, 10, and 14.
- A. J. Peden, A Note on the Accession Date of Merenptah, p. 69.
- ^ R. J. Demarée, Announcement of the Passing of Ramesses II, JEOL 46 (2016), p. 125.
- Gabriel, R. (2002). The Great Armies of Antiquity. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 6. ISBN 9780275978099.
- Grimal (1992), pp. 250–253.
- Drews (1993), p. 54: "Already in the 1840s Egyptologists had debated the identity of the "northerners, coming from all lands," who assisted the Libyan King Meryre in his attack upon Merneptah. Some scholars believed that Meryre's auxiliaries were merely his neighbors on the Libyan coast, while others identified them as Indo-Europeans from north of the Caucasus. It was one of Maspero's most illustrious predecessors, Emmanuel de Rougé, who proposed that the names reflected the lands of the northern Mediterranean: the Lukka, Ekwesh, Tursha, Shekelesh, and Shardana were men from Lydia, Achaea, Tyrsenia (western Italy), Sicily, and Sardinia." De Rougé and others regarded Meryre's auxiliaries—these "peoples de la mer Méditerranée"—as mercenary bands, since the Sardinians, at least, were known to have served as mercenaries already in the early years of Ramesses the Great. Thus the only "migration" that the Karnak Inscription seemed to suggest was an attempted encroachment by Libyans upon neighboring territory."
- Gale, N. H. (2011). "Source of the Lead Metal used to make a Repair Clamp on a Nuragic Vase recently excavated at Pyla-Kokkinokremos on Cyprus". In Karageorghis, V.; O. Kouka (eds.). On Cooking Pots, Drinking Cups, Loomweights and Ethnicity in Bronze Age Cyprus and Neighbouring Regions. Nicosia.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - O'Connor & Cline (1998), pp. 112–113.
- Tyldesley (2000), p. 53.
- "The Naue Type II Sword". Archived from the original on 20 July 2008. Retrieved 30 May 2008.
- Richardson, Dan (2013). Cairo and the Pyramids (Rough Guides Snapshot Egypt). Rough Guides UK. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-4093-3544-3. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- Grimal (1992), pp. 253 ff.
- Tyldesley (2000), p. 68.
- Obsomer 2012: 134; the date is Gregorian, equivalent to the Julian 12 May.
- Detailed analysis of the Egyptian sources in Obsomer 2012: 127–171; see also Bryce 2005: 234–239.
- The Battle of Kadesh in the context of Hittite history. Archived 14 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine.
- 100 Battles, Decisive Battles that Shaped the World, Dougherty, Martin, J., Parragon, pp. 10–11.
- Bryce 2005. pp. 238–239.
- Obsomer 2012: 188, within a detailed discussion on 173-192.
- ^ Obsomer 2012: 530.
- ^ Grimal (1992), p. 256.
- Kitchen 1982: 67; Obsomer 2012: 189–190 doubts the dating of the Moabite campaign to Year 7–8 by Kitchen, on the grounds that Amun-her-khepshef might have been too young to carry out such an independent role.
- Kitchen (1996), p. 26.
- Kitchen 1982: 68–70.
- Kitchen (1979), pp. 223–224.
- Obsomer 2012: 531.
- Kitchen (1996), p. 33.
- Kitchen (1996), p. 47.
- Kitchen (1996), p. 46.
- Kitchen (1982), p. 68.
- Obsomer 2012: 190–192, 531.
- ^ Bryce, Trevor (2023). Warriors of Anatolia: A Concise history of the Hittites. Bloomsbury. pp. 183–195. ISBN 978-1-3503-4885-1.
- Kitchen (1982), p. 74.
- ^ Kitchen 1982: 75; Obsomer 2012: 195, 531.
- Kitchen (1982), pp. 62–64, 73–79.
- Obsomer 2012: 195, 531.
- Grimal (1992), p. 257.
- Stieglitz (1991), p. 45.
- Kitchen (1982), p. 215.
- "Beit el-Wali". University of Chicago. Archived from the original on 6 September 2008. Retrieved 21 April 2008.
- Ricke, Hughes & Wente (1967), p. .
- Eyre, Christopher (1998). Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of Egyptologists, Cambridge, 3-9 September 1995. Leuven: Peeters. p. 171.
- Treasure, Matthew (1 January 2021). "Four Faces on One Neck: The Tetracephalic Ram as an Iconographic Form in New Kingdom Egypt". Academia.edu. Retrieved 13 January 2025.
- "Sed festival". The Global Egyptian Museum. Archived from the original on 6 September 2008. Retrieved 7 April 2008.
- "Renewal of the kings' Reign : The Sed Heb of Ancient Egypt". Archived from the original on 6 November 2016. Retrieved 5 November 2016.
- Westendorf (1969), p. .
- Edwards, Amelia Ann Blandford. "Chapter XV: Rameses the Great". Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- Kitchen (1982), p. 119.
- Kitchen (30 April 1985). Pharaoh Triumphant. Aris & Phillips. pp. 49–50. ISBN 0-85668-215-2.
- ^ Kitchen (2003), p. 255.
- Saadia Gaon, Judeo-Arabic Translation of Pentateuch (Tafsir), s.v. Exodus 21:37 and Numbers 33:3 ("רעמסס: "עין שמס); Rabbi Saadia Gaon's Commentaries on the Torah (ed. Yosef Qafih), Mossad Harav Kook: Jerusalem, Israel, 1984, p. 164 (Numbers 33:3) (in Hebrew).
- Van Seters, John (2001). "The Geography of the Exodus". In Dearman, John Andrew; Graham, Matt Patrick; Miller, James Maxwell (eds.). The Land that I Will Show You: Essays on the History and Archaeology of the Ancient Near East in Honour of J. Maxwell Miller. Sheffield Academic Press. p. 265. ISBN 978-1-84127-257-3.
- Siculus, Diodorus (1814). "11". The Historical Library of Diodorus the Sicilian. Printed by W. MʻDowall for J. Davis. p. 33.
- ^ Skliar (2005), p. .
- ^ Guy Lecuyot. "The Ramesseum (Egypt), Recent Archaeological Research" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 May 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2008.
- "À l'école des Scribes" (in French). Archived from the original on 23 April 2008. Retrieved 21 April 2008.
- Kitchen (1982), pp. 64–65.
- ^ Siliotti (1994), p. .
- Török, László (2001). The Image of the Ordered World in Ancient Nubian Art: The Construction of the Kushite Mind, 800 Bc-300 Ad. Brill. p. 48.
- "Giant Ramses statue gets new home". BBC News. 25 August 2006. Archived from the original on 20 July 2008. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- Hawass, Zahi. "The removal of Ramses II Statue". Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 17 March 2007.
- "Egypt: Prehistoric 'Pharaoh's Seat' Discovered in Egypt – Document – Gale General OneFile". AllAfrica Global Media. 26 October 2018. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- ^ "Egyptian archeologists unearth pharaoh's celebration compartment in Cairo". Xinhua News Agency. 25 October 2018. Retrieved 12 October 2022.
- "Red Granite Bust of Ramesses II Unearthed in Giza". Archaeology Magazine. 13 December 2019. Archived from the original on 14 August 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- Sands, Leo (2024). "Sword with pharaoh's mark found in Egypt, still shimmering 3,000 years later".
- James, Peter (2020). Manetho, with an English translation by W.G. Waddell. Alpha Editions. p. 151.
- "La momie de Ramsès II. Contribution scientifique à l'égyptologie". Archived from the original on 2 June 2010. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- "Rameses II | Theban Mapping Project". thebanmappingproject.com. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- Rohl (1995), pp. 72–73, 75.
- Rohl (1995), pp. 78–79.
- "NMEC". nmec.shorthandstories.com. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- Tyldesley (2000), p. 14.
- Romer, John. Valley of the Kings. Castle Books. p. 184.
- Maspero, Gaston (1892). Egyptian Archaeology. Putnam. pp. 76–77.
- Farnsworth, Clyde H. (28 September 1976). "Paris Mounts Honor Guard For a Mummy". The New York Times. p. 5. Archived from the original on 1 November 2019. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- Pain, Stephanie. "Ramesses rides again". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 15 August 2014. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- "Was the great Pharaoh Ramesses II a true redhead?". The University of Manchester. 3 February 2010. Archived from the original on 16 February 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- "This image was digitally created for representative purposes | Fact Check". AFP Fact Check. 20 October 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- Ceccaldi, Pierre-Fernand (1987). "Recherches sur les momies: Ramsès II". Bulletin de l'Académie de Médecine. 171 (1): 119.
- "Bulletin de l'Académie nationale de médecine". Gallica. 6 January 1987. Archived from the original on 15 July 2018. Retrieved 15 July 2018.
- Tyldesley (2001), p. ??.
- Brier (1994), p. 153.
- Brier (1994), pp. 200–201.
- Diop, Cheikh Anta (1991). Civilization or barbarism : an authentic anthropology (First ed.). Brooklyn, New York. pp. 67–68. ISBN 1556520484.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Ancient pharaoh's hair returns to Egypt". Associated Press. 10 April 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- ^ Brier (1998), p. 153.
- Chhem, R. K.; Schmit, P.; Fauré, C. (October 2004). "Did Ramesses II really have ankylosing spondylitis? A reappraisal". Can Assoc Radiol Journal. 55 (4): 211–217. PMID 15362343.
- Saleem, Sahar N.; Hawass, Zahi (2014). "Brief Report: Ankylosing Spondylitis or Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis in Royal Egyptian Mummies of the 18th–20th Dynasties? Computed Tomography and Archaeology Studies". Arthritis & Rheumatology. 66 (12): 3311–3316. doi:10.1002/art.38864. ISSN 2326-5205. PMID 25329920. S2CID 42296180.
- "'Cleaned-Up' Mummy Flown Home to Egypt". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. 11 May 1977. p. 20. Archived from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
CAIRO (AP)—The 3,212-year-old mummy of Pharaoh Ramses II was returned from Paris Tuesday, hopefully cured by radiation of 60 types of fungi and two strains of insects.
- "Tomb of Ramses II sons". Archived from the original on 27 February 2015. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- ^ Tyldesley (2000), pp. 161–162.
- Shelley, Percy Bysshe. "Ozymandias". Archived from the original on 10 October 2006. Retrieved 18 September 2006 – via Representative Poetry Online. First publication: — (11 January 1818). "Ozymandias". The Examiner. No. 524.
- Sanders, Ed (1997). 1968: A History in Verse. Black Sparrow Press. p. 255.
- Grabbe, Lester (2014). "Exodus and History". In Dozeman, Thomas; Evans, Craig A.; Lohr, Joel N. (eds.). The Book of Exodus: Composition, Reception, and Interpretation. BRILL. pp. 61–87. ISBN 9789004282667.
- Ray, John. "Ramesses the Great". BBC history. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2008.
Bibliography
- von Beckerath, Jürgen (1997). Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten. Mainz: Philipp von Zabern.
- Brand, Peter J. (2000). The Monuments of Seti I: Epigraphic, Historical and Art Historical Analysis. NV Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-11770-9.
- Brier, Bob (1994). Egyptian Mummies: Unravelling the Secrets of an Ancient Art. New York: William Morrow & Co.
- Brier, Bob (1998). The Encyclopedia of Mummies. Checkmark Books.
- Clayton, Peter (1994). Chronology of the Pharaohs. Thames & Hudson.
- Drews, Robert (1993). The End of the Bronze Age: Changes in Warfare and the Catastrophe Ca. 1200 B.C. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691209975.
- Grimal, Nicolas-Christophe (1992). A History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-17472-1.
- Kitchen, Kenneth (1982). Pharaoh Triumphant: The Life and Times of Ramesses II, King of Egypt. London: Aris & Phillips. ISBN 978-0-85668-215-5.
- Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson (1996). Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Translations. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 978-0-631-18427-0. Translations and (in the 1999 volume below) notes on all contemporary royal inscriptions naming the king.
- Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson (1979). Ramesside Inscriptions Translated and Annotated: Notes and Comments. Volume 2: Ramesses II; Royal Inscriptions. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers.
- Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson (2003). On the Reliability of the Old Testament. Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8028-4960-1.
- Leprohon, Ronald J. (2013). The Great Name: Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary. SBL Press. ISBN 978-1-58983-736-2.
- O'Connor, David; Cline, Eric, eds. (1998). Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 9780472088331.
- Obsomer, Claude, Ramsès II, Paris, 2012.
- Putnam, James (1990). An introduction to Egyptology.
- Ricke, Herbert; Hughes, George R.; Wente, Edward F. (1967). The Beit el-Wali Temple of Ramesses II.
- Rohl, David M. (1995). Pharaohs and Kings: A Biblical Quest (illustrated, reprint ed.). Crown Publishers. ISBN 978-0-517-70315-1. Archived from the original on 14 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- Siliotti, Alberto (1994). Egypt: temples, people, gods.
- Skliar, Ania (2005). Grosse kulturen der welt-Ägypten.
- Stieglitz, Robert R. (1991). "The City of Amurru". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 50 (1): 45–48. doi:10.1086/373464. S2CID 161341256.
- Tyldesley, Joyce (2000). Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh. London: Viking. ISBN 9780670884872.
- Tyldesley, Joyce (26 April 2001). Ramesses: Egypt's Greatest Pharaoh. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 9780141949789. Retrieved 20 October 2020.
- Westendorf, Wolfhart (1969). Das alte Ägypten (in German).
Further reading
- Balout, L.; Roubet, C.; Desroches-Noblecourt, C. (1985). La Momie de Ramsès II: Contribution Scientifique à l'Égyptologie (in French).
- Bietak, Manfred (1995). Avaris: Capital of the Hyksos – Recent Excavations. London, England: British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-0968-8.
- Dodson, Aidan; Dyan Hilton (2004). The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-05128-3.
- Grajetzki, Wolfram (2005). Ancient Egyptian Queens – a hieroglyphic dictionary. London, England: Golden House Publications. ISBN 978-0-9547218-9-3.
- Hasel, Michael G. (1994). "Israel in the Merneptah Stela". Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research. 296 (296): 45–61. doi:10.2307/1357179. JSTOR 1357179. S2CID 164052192.
- Kuhrt, Amelie (1995). The Ancient Near East c. 3000–330 BC. Vol. 1. London, England: Routledge.
- Rice, Michael (1999). Who's Who in Ancient Egypt. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-15448-2.
- Hasel, Michael G. 1998. Domination and Resistance: Egyptian Military Activity in the Southern Levant, 1300–1185 BC. Probleme der Ägyptologie 11. Leiden: Brill Publishers. ISBN 90-04-10984-6
- Hasel, Michael G. 2003. "Merenptah's Inscription and Reliefs and the Origin of Israel" in Beth Alpert Nakhai (ed.), The Near East in the Southwest: Essays in Honor of William G. Dever, pp. 19–44. Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 58. Boston, Massachusetts: American Schools of Oriental Research. ISBN 0-89757-065-0
- Hasel, Michael G. (2004). "The Structure of the Final Hymnic-Poetic Unit on the Merenptah Stela". Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft. 116: 75–81. doi:10.1515/zatw.2004.005.
- James, T. G. H. 2000. Ramesses II. New York: Friedman/Fairfax Publishers. A large-format volume by the former Keeper of Egyptian Antiquities at the British Museum, filled with colour illustrations of buildings, art, etc. related to Ramesses II.
- The Epigraphic Survey, Reliefs and Inscriptions at Karnak III: The Bubastite Portal, Oriental Institute Publications, vol. 74 (Chicago, Illinois): University of Chicago Press, 1954.
External links
- Egypt's Golden Empire: Ramesses II
- Ramesses II Usermaatre-setepenre (c. 1279–1213 BC)
- List of Ramesses II's family members and state officials
