| Revision as of 10:31, 9 January 2006 view sourceIrrevenant (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users720 edits →New Age: Zen is over a millenia old - hardly "New Age" !← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:52, 10 January 2025 view source Citation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,450,615 edits Add: pmid, pages, volume, journal, title, date, authors 1-1. Removed parameters. Some additions/deletions were parameter name changes. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_toolbar | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Pseudoscientific approach to psychotherapy}} | |||
| {{cleanup-date|January 2006}} | |||
| {{distinguish|text = ] (also NLP). For other uses, see ]}} | |||
| {{pp-sock|small = yes}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2021}} | |||
| {{Infobox interventions | |||
| | Name = Neuro-linguistic programming | |||
| | Image = | |||
| | Caption = | |||
| | ICD10 = | |||
| | ICD9 = | |||
| | MeshID = D020557 | |||
| | OPS301 = | |||
| | OtherCodes = | |||
| | HCPCSlevel2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Neuro-linguistic programming}} | |||
| '''Neuro-linguistic programming''' ('''NLP''') is a pseudoscientific approach to communication, personal development and ], that first appeared in ] and ]'s 1975 book '']''. NLP asserts that there is a connection between neurological processes, language and acquired behavioral patterns, and that these can be changed to achieve specific goals in life.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Tosey |first1=Paul |last2=Mathison |first2=Jane |title=Introducing Neuro-Linguistic Programming |publisher=Centre for Management Learning & Development, School of Management, University of Surrey. |url=http://www.som.surrey.ac.uk/NLP/Resources/IntroducingNLP.pdf |access-date=12 September 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190103020411/http://www.som.surrey.ac.uk/NLP/Resources/IntroducingNLP.pdf |archive-date=3 January 2019}}</ref>{{sfn|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|p=2}} According to Bandler and Grinder, NLP can treat problems such as ]s, depression, ]s, ]es, ],{{efn|name=nscc}} ], the ],{{efn|name=nscc|Note that, in a seminar, {{harvnb|Bandler|Grinder|1982|p=166}}, said that a single session of NLP combined with hypnosis could eliminate certain eyesight problems such as myopia and cure the common cold (op.cit., pp. 169, 174).}} and ]s,<ref>Archived at {{cbignore}} and the {{cbignore}}: {{cite AV media |people=Bandler, Richard |year=2008 |title=What is NLP? |medium=Promotional video |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vlcsFJyEXQ |access-date=1 June 2013 |quote=We can reliably get rid of a phobia in ten minutes – every single time. |publisher=NLP Life}}{{cbignore}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Grinder|Bostic St. Clair|2001|loc=Chapter 4: Personal Antecedents of NLP}}.</ref> often in a single session. They also say that NLP can model the skills of exceptional people, allowing anyone to acquire them.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1975|pp=5–6}}{{efn|{{harvnb|Bandler|1993|p=vii}}: "In single sessions, they can accelerate learning, neutralize phobias, enhance creativity, improve relationships, eliminate allergies, and lead firewalks without roasting toes. NLP achieves the goal of its inception. We have ways to do what only a genius could have done a decade ago." }} | |||
| '''Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)''' is a collection of self-help recommendations, promoted through the ] and ] sections of bookshops, and advertised in various media including the ] and ]s. | |||
| NLP has been adopted by some ]s as well as by companies that run seminars marketed as ] to businesses and government agencies.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Dowlen |first=Ashley |title=NLP – help or hype? Investigating the uses of neuro-linguistic programming in management learning |journal=Career Development International |date=1 January 1996 |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=27–34 |doi=10.1108/13620439610111408}}</ref><ref name="von Bergen-1997" /> | |||
| NLP was proposed in ] by ] and ] as a set of models and principles to describe the relationship between ] (''neuro'') and ] (''linguistic'', both verbal and non-verbal) and how their interaction might be organized (''programming'') to affect an individual's mind, body and behavior. It is described by the original developers as "therapeutic magic" and "the study of the structure of subjective experience" (Sharpley 1987; Dilts et al 1980). It is predicated upon the assumption that all ]s have a practically determinable structure (Grinder & Bandler 1975a) . | |||
| There is no ] supporting the claims made by NLP advocates, and it has been called a ].<ref>{{Cite book |title=Science and Pseudoscience in Social Work Practice |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nE9FCQAAQBAJ&q=nlp&pg=PA166 |publisher=Springer Publishing Company |date=2015 |isbn=978-0-8261-7769-8 |first1=Bruce A. |last1=Thyer |first2=Monica G. |last2=Pignotti |pages=56–57, 165–167 |quote=As NLP became more popular, some research was conducted and reviews of such research have concluded that there is no scientific basis for its theories about representational systems and eye movements.}}</ref><ref name="Sharpley-1987" /><ref name="Witkowski-2010">{{cite journal |last=Witkowski |first=Tomasz |title=Thirty-Five Years of Research on Neuro-Linguistic Programming. NLP Research Data Base. State of the Art or Pseudoscientific Decoration? |journal=Polish Psychological Bulletin |date=1 January 2010 |volume=41 |issue=2 |doi=10.2478/v10059-010-0008-0|quote=All of this leaves me with an overwhelming impression that the analyzed base of scientific articles is treated just as theater decoration, being the background for the pseudoscientific farce which NLP appears to be. Using "scientific" attributes, which is so characteristic of pseudoscience, is manifested also in other aspects of NLP activities... My analysis leads undeniably to the statement that NLP represents pseudoscientific rubbish|doi-access=free }}</ref> Scientific reviews have shown that NLP is based on outdated metaphors of the brain's inner workings that are inconsistent with current neurological theory, and that NLP contains numerous factual errors.<ref name="von Bergen-1997">{{cite journal |last1=von Bergen |first1=C. W. |last2=Gary |first2=Barlow Soper |last3=Rosenthal |first3=T. |last4=Wilkinson |first4=Lamar V. |title=Selected alternative training techniques in HRD |journal=Human Resource Development Quarterly |year=1997 |volume=8 |issue=4 |pages=281–294 |doi=10.1002/hrdq.3920080403}}</ref><ref name="Druckman-2004">{{cite journal |last=Druckman |first=Daniel |title=Be All That You Can Be: Enhancing Human Performance |journal=Journal of Applied Social Psychology |date=1 November 2004 |volume=34 |issue=11 |pages=2234–2260 |doi=10.1111/j.1559-1816.2004.tb01975.x}}</ref> Reviews also found that research that favored NLP contained significant methodological flaws, and that there were three times as many studies of a much higher quality that failed to reproduce the claims made by Bandler, Grinder, and other NLP practitioners.<ref name="Sharpley-1987">{{cite journal |last=Sharpley |first=Christopher F. |title=Research findings on neurolinguistic programming: Nonsupportive data or an untestable theory? |journal=Journal of Counseling Psychology |date=1 January 1987 |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages=103–107 |doi=10.1037/0022-0167.34.1.103}}</ref><ref name="Witkowski-2010" /> | |||
| NLP is based on ] principles such as the belief in unlimited potential through access to the subconscious, and body language cues derived from the observation of “therapeutic wizards” (Bandler and Grinder 1979; Sharpley 1984). Some techniques include behavior change, transforming ]s, and treatment of ]s through techniques such as ] (Grinder & Bandler 1983; Andreas & Faulkner, 1994) and the "]" (Grinder & Bandler 1975 ch.3) proposed for exploring the personal limits of belief as expressed in language. | |||
| == Early development == | |||
| The practice initially attracted mostly therapists, although it eventually attracted business and sales people, and ] believers (Hall, 1994). NLP has been applied to a number of fields such as sales, psychotherapy, communication, education, coaching, sport, business management, interpersonal relationships, seduction, occult and spirituality. | |||
| According to Bandler and Grinder, NLP consists of a ] termed ''modeling'', plus a set of techniques that they derived from its initial applications.{{sfnm|1a1=Bandler|1a2=Grinder|1y=1975|1p=6|2a1=Grinder|2a2=Bostic St. Clair|2y=2001|2loc=Chapter 2: Terminology}} They derived many of the fundamental techniques from the work of ], ] and ].{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1979|p=8}} Bandler and Grinder also drew upon the ] of ], ] and ] (particularly ]).{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1975|p=6}}<ref name="Stollznow-2010" /><ref>{{cite book |last=Wake |first=Lisa |title=Neurolinguistic psychotherapy: a postmodern perspective |year=2008 |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=978-0-415-42541-4|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8wIy20m_u9kC}}</ref> | |||
| Bandler and Grinder say that their methodology can codify the structure inherent to the therapeutic "magic" as performed in therapy by Perls, Satir and Erickson, and indeed inherent to any complex human activity. From that codification, they say, the structure and its activity can be learned by others. Their 1975 book, ''The Structure of Magic I: A Book about Language and Therapy'', is intended to be a codification of the therapeutic techniques of Perls and Satir.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1975|p=6}} | |||
| NLP has been criticized in reviews of research by scientists such as Heap (1988), Sharpley (1987), Lilienfeld (2003), and Singer & Lalich (1999), which have found that Neuro-linguistic programming is scientifically unsupported and largely ineffective. Scientists such as Lilienfeld et al (2003), Helisch (2004), Williams (2000), and Drenth (2003) also state that NLP is pseudoscientific. NLP is identified as a dubious therapy by some therapists (Heap 1991; Morgan 1993; Dryden 2001) and the National Council Against Health Fraud (Loma 2001), and fraudulent by Heap (1991) and Winkin (1991). | |||
| Bandler and Grinder say that they used their own process of modeling to model Virginia Satir so they could produce what they termed the Meta-Model, a model for gathering information and challenging a client's language and underlying thinking.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder |1975|p=6}}<ref name="Clancy-1989" /> They say that by challenging linguistic distortions, specifying generalizations, and recovering deleted information in the client's statements, the transformational grammar concept of surface structure yields a more complete representation of the underlying deep structure and therefore has therapeutic benefit.<ref>John Grinder, Suzette Elgin (1973). "A Guide to Transformational Grammar: History, Theory, Practice." Holt, Rinehart and Winston. {{ISBN|0-03-080126-5}}. Reviewed by Frank H. Nuessel, Jr. ''The Modern Language Journal'', Vol. 58, No. 5/6 (September–October 1974), pp. 282–283</ref><ref name="Bradley-1985">{{cite journal |first1=E. Jane |last1=Bradley |last2=Biedermann |first2=Heinz-Joachim |title=Bandler and Grinder's neurolinguistic programming: Its historical context and contribution |journal=Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training |date=1 January 1985 |volume=22 |issue=1 |pages=59–62 |doi=10.1037/h0088527 |issn=0033-3204 |oclc=1588338}}</ref> Also derived from Satir were anchoring, future pacing and representational systems.<ref name="Spitzer-1992">{{cite journal |last=Spitzer |first=Robert |title=Virginia Satir & Origins of NLP |journal=Anchor Point Magazine |issue=July |page=? |year=1992 |url=http://www.social-engineer.org/archives/NLP/NLP-Satir395.pdf |access-date=5 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ==Overview== | |||
| In contrast, the Milton-Model—a model of the purportedly hypnotic language of Milton Erickson—was described by Bandler and Grinder as "artfully vague" and ]ic.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1982|p=240}} The Milton-Model is used in combination with the Meta-Model as a softener, to induce "trance" and to deliver indirect therapeutic suggestion.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1981}} | |||
| NLP is most widely known as a collection of self-help recommendations, promoted through the ] and ] sections of bookshops, and advertised in various media including the ] and ]s. "NLP participants are taught that life is programmed, unfortunately we have all been mis-programmed by negative input. Like Scientology, rebirthing and other alternative therapies, NLP embraces this Null Hypothesis and eschews the classic New Age concept of 'clearing' these blocks. While the more traditional therapies concentrate on solving problems by focusing on the reasons "why", Neurolinguistic programming looks at the "hows" to provide a quick fix to a solution" (Edwards 1996). | |||
| Psychologist ] writes that Chomsky's theories "appear to be irrelevant" to NLP.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Mercer |first1=Jean |editor1-last=Cautin |editor1-first=Robin L. |editor2-last=Lilienfeld |editor2-first=Scott O. |title=The Encyclopedia of Clinical Psychology, Volume II |date=2015 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |isbn=978-0-4706-7127-6 |page=759 |chapter=Controversial Therapies |doi=10.1002/9781118625392.wbecp515}}</ref> Linguist ] describes Bandler's and Grinder's reference to such experts as ]. Other than Satir, the people they cite as influences did not collaborate with Bandler or Grinder. Chomsky himself has no association with NLP, with his work being theoretical in nature and having no therapeutic element. Stollznow writes, "ther than borrowing ], NLP does not bear authentic resemblance to any of Chomsky's theories or philosophies—linguistic, ] or political."<ref name="Stollznow-2010">{{cite journal |last1=Stollznow |first1=Karen|author-link=Karen Stollznow|year=2010 |title=Not-so Linguistic Programming |journal=] |volume=15 |issue=4 |page=7 |url=http://www.skeptic.com/magazine/archives/vol15n04.html |access-date=1 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ===Foundational Assumptions=== | |||
| Distinct from its formal presuppositions, NLP incorporates a variety of foundational assumptions that precede the presuppositions. These are: | |||
| According to ], a researcher in the field of hypnosis, "the major weakness of Bandler and Grinder's linguistic ] is that so much of it is built upon untested hypotheses and is supported by totally inadequate data."{{sfn|Weitzenhoffer|1989|p=304}} Weitzenhoffer adds that Bandler and Grinder misuse ] and mathematics,{{sfn|Weitzenhoffer|1989|pp=300–301}} redefine or misunderstand terms from the ] ] (e.g., ]),{{efn|{{harvnb|Weitzenhoffer|1989|pp=304–305}}: "I have chosen ] to explain what some of the problems are in Bandler and Grinder's linguistic approach to Ericksonian hypnotism. Almost any other linguistic concept used by these authors could have served equally well for the purpose of showing some of the inherent weaknesses in their treatment."}} create a scientific façade by needlessly complicating Ericksonian concepts with unfounded claims,{{efn|{{harvnb|Weitzenhoffer|1989|p=307}}: "As I have mentioned in the last chapter, any references made to left and right brain functions in relation to hypnotic phenomena must be considered as poorly founded. They do not add to our understanding of nor our ability to utilize hypnotic phenomena in the style of Erickson. Indeed, references such as Bandler and Grinder make to these functions give their subject matter a false appearance of having a more scientific status than it has."}} make factual errors,{{efn|{{harvnb|Weitzenhoffer|1989|p=306}}: "This work , incidentally, contains some glaring misstatements of facts. For example, ] and ] were depicted as contemporaries!"}} and disregard or confuse concepts central to the Ericksonian approach.{{efn|{{harvnb|Weitzenhoffer|1989|p=306}}: One of the most striking features of the Bandler/Grinder interpretation is that it somehow ignores the issue of the existence and function of suggestion, which even in Erickson's own writings and those done with Rossi, is a central idea."}} | |||
| #There is a ] (and some also include ]) connection (Grinder and DeLozier, 1986, pp.xx,xxi; Grinder and Bostic St Clair, 2002, ch.3; ''ibid'' p.222). | |||
| #The mind is broadly composed of a conscious and a subconscious (or unconscious) component (Bandler & John Grinder, 1975b, pp.12-13,137,179-99). | |||
| #A person's experience of the world is processed and organized in terms of the five senses (Grinder & Bandler 1975b p.6; Dilts ''et al'', 1980, p.17). | |||
| #Physiology, sensory representation ("submodality") and emotion comprise internal ''state'' (Dilts and DeLozier, 2000, p.1303). | |||
| #Behavior is the result of systematically ordered sequences of sensory representations ("strategies") (Bandler & Grinder, 1979 p.30; Dilts ''et al'', 1980, p.6). | |||
| #All behavior occurs in the context of internal state (Dilts and DeLozier, 2000, p.1300). | |||
| #Internal state mediates experience and influences or determines behavior (Dilts and DeLozier, 2000, p.1300). | |||
| #Internal state and strategy -- hence behavior -- have a discernible and communicable structure (Dilts ''et al'', 1980, Ch.3; Dilts and DeLozier, 2000, p.1303-6). | |||
| #People exhibit their internal state in their language (verbal and non-verbal) (Dilts and DeLozier, 2000, pp.75-77). | |||
| #Since behavior and its substrates -- internal state and strategy -- can be codified, a person's skill can be reproduced in another person (Dilts ''et al'', 1980, p.14). | |||
| #Behavior is learned (Dilts ''et al'', 1980, p.4). | |||
| #Direct and objective knowledge of the (external) world is not possible (Bandler & Grinder, 1975a, pp.7-13; Bandler & Grinder, 1975b, pp.7-8,180-1; Dilts et al, 1980, pp.3-4). | |||
| More recently, Bandler has stated, "NLP is based on finding out what works and formalizing it. In order to formalize patterns I utilized everything from linguistics to ] ... The models that constitute NLP are all formal models based on mathematical, ]al principles such as ] and the mathematical ]."<ref>{{cite web |last=Bandler |first=Richard |title=NLP Seminars Group – Frequently Asked Questions |website=NLP Seminars Group |url=http://www.purenlp.com/nlpfaqr.html |year=1997 |access-date=8 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130622080317/http://www.purenlp.com/nlpfaqr.html |archive-date=22 June 2013}}</ref> There is no mention of the mathematics of holography nor of holography in general in Spitzer's,<ref name="Spitzer-1992" /> or Grinder's<ref>{{harvnb|Grinder|Bostic St. Clair|2001}}.</ref> account of the development of NLP. | |||
| ===NLP and Theory=== | |||
| Many NLP proponents state that NLP is not theory-oriented, and Bandler states that he does not "do theory" (Singer & Lalich, 1996). Instead, the stated goals of NLP are to model effective patterns "in the field", to learn what someone is actually doing in practice (internally and externally) that works, and how they do it, rather than deriving behaviors from a theory or obtaining their motivations for doing them. However, NLP proponents do make hypotheses and propose armchair theories (Singer and Lalich 1997). For example, NLP assumes that all human behaviour is neurological, and all human behaviour is based on the 5 senses, rather than "attitudes" "reason" "emotions" "mind" "morals" or "ego". | |||
| On the matter of the development of NLP, Grinder recollects: | |||
| ===Common Techniques and Practices=== | |||
| {{main|List of NLP topics}} | |||
| * '''Meta model:''' questions to recover distortion, generalisation and deletion from a speaker (Grinder & Bandler 1975a ch.3; ). | |||
| * '''Representational systems:''' verbal and non-verbal cues such as eye movements, sensory predicates, breathing rate, and body posture are calibrated to identify the modality, type and sequence of internal Visual, Auditory or Kinesthetic representations (Grinder & Bandler 1979 p.24; Grinder & Bandler 1976 p.9; Dilts et al 1980). | |||
| * '''Perceptual positions:''' a situation is considered from different points of view of those involved, typically self, other, and neutral observer (Grinder & Delozier 1986 pp.xix,197; Dilts & Delozier ). | |||
| * '''Dilts' Neurological Levels of Learning:''' categorisation of information into a hierarchies consisting of environment, behavior, competency, belief/value, identity and purpose (or spirit) (Dilts & Delozier 2000). | |||
| * '''Swish:''' a basic "quick-fix" technique that involves swapping a representation of a simple habit for desired self-image in the future (Bandler 1985; Grinder & Bostic St Clair p.169). | |||
| * '''Visual / Kinesthetic dissociation:''' separates the see-feel ] that drives reponses to a stimulus. The NLP "phobia cure" uses two place dissociation (Grinder & Bandler 1979; Einspruch & Forman 1988; Carbonell & Figley ; ). | |||
| * ''']:''' pacing and leading attention by matching, mirroring or cross pacing verbal and non-verbal behavior (Grinder & Bandler 1977; Clabby, PhD, O’Connor, MD 2004) such as breathing, sensory predicates (1979 p.15,45), and gestures. | |||
| * '''Submodality modification:''' deliberately altering the coding of internal sensory representations such as location, size and brightness of internal images (Bandler 1982; S & C Andreas ) | |||
| {{blockquote|text=My memories about what we thought at the time of discovery (with respect to the classic code we developed—that is, the years 1973 through 1978) are that we were quite explicit that we were out to overthrow a ] and that, for example, I, for one, found it very useful to plan this campaign using in part as a guide the excellent work of ] ('']'') in which he detailed some of the conditions which historically have obtained in the midst of ]s. For example, I believe it was very useful that neither one of us were qualified in the field we first went after—psychology and in particular, its therapeutic application; this being one of the conditions which Kuhn identified in his historical study of paradigm shifts.<ref>{{cite web |last=Grinder |first=John |others=Interviewed by Chris Collingwood and Jules Collingwood |title=1996 Interview with John Grinder PhD, co-creator of NLP |website=Inspiritive |url=http://www.inspiritive.com.au/grinterv.htm |date=July 1996 |access-date=8 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130428225949/http://www.inspiritive.com.au/grinterv.htm |archive-date=28 April 2013}}</ref>}} | |||
| === NLP Modeling === | |||
| The philosopher ] responded that Grinder has not understood Kuhn's text on the ], ''The Structure of Scientific Revolutions''. Carroll replies: (a) individual scientists never have nor are they ever able to create ''paradigm shifts'' volitionally and Kuhn does not suggest otherwise; (b) Kuhn's text does not contain the idea that being unqualified in a field of science is a prerequisite to producing a result that necessitates a ''paradigm shift'' in that field and (c) ''The Structure of Scientific Revolutions'' is foremost a work of ''history'' and not an instructive text on ''creating'' paradigm shifts and such a text is not possible—extraordinary discovery is not a formulaic procedure. Carroll explains that a ''paradigm shift'' is not a planned activity, rather it is an outcome of scientific effort within the dominant paradigm that produces ] that cannot be adequately accounted for within the current paradigm—hence a ''paradigm shift'', i.e. the adoption of a new paradigm. In developing NLP, Bandler and Grinder were not responding to a paradigmatic crisis in psychology nor did they produce any data that caused a paradigmatic crisis in psychology. There is no sense in which Bandler and Grinder caused or participated in a paradigm shift. "What did Grinder and Bandler do that makes it impossible to continue doing psychology ... without accepting their ideas? Nothing," argues Carroll.<ref name="Carroll-2009">{{cite web |last=Carroll |first=R. T. |author-link=Robert Todd Carroll |publisher=] |url=http://skepdic.com/neurolin.html |title=Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) |access-date=25 June 2009 |date=23 February 2009}}</ref> | |||
| ] is a method that is promoted for duplicating behaviour, expertise or excellence, or reproducing "magic" abilites of experts (Bandler and Grinder 1975). It is considered by some practitioners to be at the heart of NLP (Grinder 2003). It can be thought of as the process of discovering relevant distinctions within these experiential components, as well as sequencing these components, aiming to achieve a specific result. NLP proponents claim that it is used to discover and codify patterns of excellence as demonstrated consistently by top performers in any field (Grinder & Bostic St-Clair 2002). It has also been applied to clinical conditions, such as the "skill" of ] (Grinder & Bandler 1979 p.52; Grinder & Bandler 1981 p.171; Grinder & Delozier 1986 p.62) and notable dead people of whom we have only writings, such as ] (Dilts 1992). It has been argued that modeling from writings is unverifiable (both within and outside NLP). | |||
| === Commercialization and evaluation === | |||
| Some modelers also discuss with the model their thoughts, feelings, beliefs (Dilts & Delozier 2000 ); this is often not considered to be true NLP modeling, and has been labeled Analytic modeling (Grinder & Dilts, ). | |||
| By the late 1970s, the ] had developed into an industry and provided a market for some NLP ideas. At the center of this growth was the ] at ]. Perls had led numerous ] seminars at Esalen. Satir was an early leader and Bateson was a guest teacher. Bandler and Grinder have said that in addition to being a therapeutic method, NLP was also a study of communication and began marketing it as a business tool, writing that, "if any human being can do anything, so can you."<ref name="Clancy-1989">{{cite journal |last1=Clancy |first1=Frank |last2=Yorkshire |first2=Heidi |year=1989 |title=The Bandler Method |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DOcDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA22 |journal=] |volume=14 |issue=2 |pages=22–28 |issn=0362-8841 |access-date=26 April 2024 |via=}}</ref> After 150 students paid $1,000 each for a ten-day workshop in ], Bandler and Grinder gave up academic writing and started producing popular books from seminar transcripts, such as ''Frogs into Princes,'' which sold more than 270,000 copies. According to court documents relating to an intellectual property dispute between Bandler and Grinder, Bandler made more than $800,000 in 1980 from workshop and book sales.<ref name="Clancy-1989" /> | |||
| A community of psychotherapists and students began to form around Bandler and Grinder's initial works, leading to the growth and spread of NLP as a theory and practice.<ref>{{cite book |title=Social Engineering |publisher=John Wiley & Sons Inc |last1=Hadnagy |first1=Christopher |last2=Wilson |first2=Paul |access-date=24 May 2013 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9LpawpklYogC |date= 2010 |isbn=978-0-470-63953-5}}</ref> For example, ] trained with Grinder and utilized a few ideas from NLP as part of his own ] and motivational speaking programmes.<ref>{{cite book |title=Sham: How the Self-Help Movement Made America Helpless |year=2006 |publisher=Crown Publishing Group |isbn=978-1-4000-5410-7 |last=Salerno |first=Steve |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lmmxX81cEmMC}}</ref> Bandler led several unsuccessful efforts to exclude other parties from using NLP.{{citation needed|date=May 2024}} Meanwhile, the rising number of practitioners and theorists led NLP to become even less uniform than it was at its foundation.<ref name="Stollznow-2010" /> Prior to the decline of NLP, scientific researchers began testing its theoretical underpinnings ]ly, with research indicating a lack of empirical support for NLP's essential theories.<ref name="Witkowski-2010" /> The 1990s were characterized by fewer scientific studies evaluating the methods of NLP than the previous decade. ] attributes this to a declining interest in the debate as the result of a lack of empirical support for NLP from its proponents.<ref name="Witkowski-2010" /> | |||
| ==Fundamentals== | |||
| == Main components and core concepts == | |||
| ===Presuppositions=== | |||
| NLP can be understood in terms of three broad components: subjectivity, consciousness, and learning. | |||
| According to Bandler and Grinder, people experience the world subjectively, creating ] of their experiences. These representations involve the five senses and language. In other words, our conscious experiences take the form of sights, sounds, feelings, smells, and tastes. When we imagine something, recall an event, or think about the future, we utilize these same sensory systems within our minds{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1976|pp=3–8}}{{efn|{{harvnb|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|pp=13–14}}: "There are three characteristics of effective patterning in NLP which sharply distinguish it from behavioural science as it is commonly practiced today. First, for a pattern or generalization regarding human communication to be acceptable or well–formed in NLP, it must include in the description the human agents who are initiating and responding to the pattern being described, their actions, their possible responses. Secondly, the description of the pattern must be represented in sensory grounded terms which are available to the user. This user–oriented constraint on NLP ensures usefulness. We have been continually struck by the tremendous gap between theory and practice in the behavioural sciences—this requirement closes that gap. Notice that since patterns must be represented in sensory grounded terms, available through practice to the user, a pattern will typically have multiple representation—each tailored for the differing sensory capabilities of individual users Thirdly, NLP includes within its descriptive vocabulary terms which are not directly observable ."}} Furthermore it is stated that these subjective representations of experience have a discernible structure, a pattern.{{sfn|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|p=7}} | |||
| The ] of NLP are sometimes described as an ] (Grinder & Bandler, 1975a; Dilts et al 1980; Dilts 1983; Grinder & Delozier 1986; Grinder & Bostic St Clair 2001; Tosey & Mathison 2003; Malloy et al 2005). A ] (linguistic term) is a background belief that is treated by the NLP practitioner "as if" (1911; The Philosophy of 'As If', ]; Grinder & Bandler 1975a) it were literal. | |||
| ----- | |||
| The fundamental presuppositions in NLP are: | |||
| *'''The map is not the territory. ''' "NLP epistemology" follows ] (1933) and ]'s (1972, 1979) postulations that there is no such thing as "]". The ] nature of our experience never fully captures the objective world. It is assumed that each of us creates a representation of the world in which we live - that is, we create a map or model which we use to generate our behavior. Our representation or map of the world determines to a large degree what our experience of the world will be (Bandler & Grinder, 1975a; Dilts et al, 1980). | |||
| *'''Life and 'Mind' are Systemic Processes'''. The processes that take place within a human being and between human beings and their environment are systemic (Bateson 1979). Our bodies, our societies, and our planet form an ] of complex systems and sub-systems all of which interact with and mutually influence each other. This assumes that looking from different vantage points may result in quite different and yet equally valid descriptions and emphasis of what is important in the system (Grinder & Delozier 1986; Dilts & DeLozier 2000). | |||
| : | |||
| ----- | |||
| These presuppositions are considered groundbreaking by NLP proponents because of a contradiction with the modern scientific ] view that reality can be objectively measured (Grinder & Bandler 1979; Grinder & Delozier 1986; Thaler Singer 1999). | |||
| Bandler and Grinder assert that behavior (both our own and others') can be understood through these sensory-based internal representations. Behavior here includes verbal and non-verbal communication, as well as effective or adaptive behaviors and less helpful or "pathological" ones.{{efn|{{harvp|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|p=36}}: "The basic elements from which the patterns of human behaviour are formed are the perceptual systems through which the members of the species operate on their environment: vision (sight), audition (hearing), kinesthesis (body sensations) and olfaction/gustation (smell/taste). The neurolinguistic programming model presupposes that all of the distinctions we as human beings are able to make concerning our environment (internal and external) and our behaviour can be usefully represented in terms of these systems. These perceptual classes constitute the structural parameters of human knowledge. We postulate that all of our ongoing experience can usefully be coded as consisting of some combination of these sensory classes."}}<ref>{{cite book |last1=Grinder |first1=John |last2=Bandler |first2=Richard |title=Patterns of the Hypnotic Techniques of Milton H. Erickson: Volume 2 |edition=1st |year=1977 |publisher=Meta Publications |pages=11–19 |isbn=978-1-55552-053-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=u_gbkgAACAAJ}}</ref> They also assert that behavior in both the self and other people can be modified by manipulating these sense-based subjective representations.{{sfnm|1a1=Bandler|1a2=Grinder|1y=1979|1pp=5-78|2a1=Bandler|2a2=Grinder|2y=1981|2pp=240-50|3a1=Hall|3a2=Belnap|3y=2000|3pp=39–40|3loc=#2 Pacing Or Matching Another's Model of the World|4a1=Hall|4a2=Belnap|4y=2000|4pp=89–93|4loc=#23 The Change Personal History Pattern|5a1=Hall|5a2=Belnap|5y=2000|5pp=93–95|5loc=#24 The Swish Pattern}}{{efn|{{harvp|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|p=7}}: "NLP presents specific tools which can be applied effectively in any human interaction. It offers specific techniques by which a practitioner may usefully organize and re–organize his or her subjective experience or the experiences of a client in order to define and subsequently secure any behavioural outcome."}} | |||
| The other commonly related presuppositions are derived from the these two fundamental presuppositions (Dilts & DeLozier 2000 ). | |||
| NLP posits that ] can be divided into conscious and unconscious components. The part of our internal representations operating outside our direct awareness is referred to as the "unconscious mind".{{efn|{{harvnb|Dilts|Grinder|Bandler|DeLozier|1980|pp=77–80}}: "Strategies and representations which typically occur below an individual's level of awareness make up what is often called or referred to as the 'unconscious mind'."}} | |||
| ===The B.A.G.E.L. Model=== | |||
| Finally, NLP uses a method of learning called "modeling", designed to replicate expertise in any field. According to Bandler and Grinder, by analyzing the sequence of sensory and linguistic representations used by an expert while performing a skill, it's possible to create a mental model that can be learned by others.{{sfnm|1a1=Bandler|1a2=Grinder|1y=1975|1p=6|2a1=Bandler|2a2=Grinder|2y=1979|2pp=7, 9, 10, 36, 123|3a1=Dilts|3a2=Grinder|3a3=Bandler|3a4=DeLozier|3y=1980|3pp=35, 78|4a1=Grinder|4a2=Bostic St. Clair|4y=2001|4pp=1, 10, 28, 34, 189, 227–28}} | |||
| The B.A.G.E.L. Model specifies the five elements (in mnemonic form) that purportedly comprise the behavioral cues that indicate an individual's internal processes. The B.A.G.E.L. Model is predicated on the notion that internal processes are subjectively represented in sensory terms: visually, auditory, kinesthetically and least likely, olfactory and gustatory. | |||
| <div class="boilerplate metadata" id="attention" style="background-color: #FFFCE6; margin: 0 2.5%; padding: 0 10px; border: 1px solid #aaa;"> | |||
| #'''B'''ody posture (eg. leaning back, head upwards and shallow breathing indicates visual representation) | |||
| #'''A'''ccessing cues (eg. fluctuating voice tone and tempo indicates auditory representation) | |||
| #'''G'''estures (eg. gesturing below the neck indicates kinesthetic representation) | |||
| #'''E'''ye movements (See '''Eye accessing cues and the representational systems''' below) | |||
| #'''L'''anguage patterns (specifically sensory based, eg. "I see!", "Sounds right!" or "I feel that...") | |||
| (Dilts et al, 1980; Dilts, 1998; Dilts and DeLozier, 2000). | |||
| </div> | |||
| == Techniques or set of practices == | |||
| ===Eye accessing cues, body cues, and NLP representational systems=== | |||
| {{further|Methods of neuro-linguistic programming}} | |||
| ]'' (1979). The six directions represent "visual construct", "visual recall", "auditory construct", "auditory recall", "]" and "auditory internal dialogue".]] | |||
| According to one study by Steinbach,<ref name="Steinbach-1984">{{cite journal|pmc=2153995 |date=1984 |last1=Steinbach |first1=A. M. |title=Neurolinguistic Programming: A Systematic Approach to Change |journal=Canadian Family Physician Medecin de Famille Canadien |volume=30 |pages=147–150 |pmid=21283502 }}</ref> a classic interaction in NLP can be understood in terms of several major stages including establishing rapport, gleaning information about a problem mental state and desired goals, using specific tools and techniques to make interventions, and integrating proposed changes into the client's life. The entire process is guided by the non-verbal responses of the client.<ref name="Steinbach-1984" /> The first is the act of establishing and maintaining rapport between the practitioner and the client which is achieved through pacing and leading the verbal (''e.g.'', sensory predicates{{Explain|date=October 2023}} and keywords) and non-verbal behavior (''e.g.'', matching and mirroring non-verbal behavior, or responding to eye movements) of the client.{{sfn|Bandler|Grinder|1979|pp=8, 15, 24, 30, 45, 52, 149}} | |||
| Once rapport is established, the practitioner may gather information about the client's present state as well as help the client define a desired state or goal for the interaction. The practitioner pays attention to the verbal and non-verbal responses as the client defines the present state and desired state and any resources that may be required to bridge the gap.<ref name="Steinbach-1984" /> The client is typically encouraged to consider the consequences of the desired outcome, and how they may affect his or her personal or professional life and relationships, taking into account any positive intentions of any problems that may arise.<ref name="Steinbach-1984" /> The practitioner thereafter assists the client in achieving the desired outcomes by using certain tools and techniques to change internal representations and responses to stimuli in the world.{{sfn|Bandler|1985|pp=134–3}}<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Masters |first1=B. |last2=Rawlins |first2=M. |last3=Rawlins |first3=L. |last4=Weidner |first4=J. |year=1991 |title=The NLP swish pattern: An innovative visualizing technique |journal=Journal of Mental Health Counseling |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=79–90 |url=http://psycnet.apa.org/psycinfo/1991-19473-001}}</ref> Finally, the practitioner helps the client to mentally rehearse and integrate the changes into his or her life.<ref name="Steinbach-1984" /> For example, the client may be asked to envision what it is like having already achieved the outcome. | |||
| ] | |||
| According to Stollznow, "NLP also involves fringe discourse analysis and 'practical' guidelines for 'improved' communication. For example, one text asserts 'when you adopt the "but" word, people will remember what you said afterwards. With the "and" word, people remember what you said before and after.'"<ref name="Stollznow-2010" /> | |||
| A core NLP training exercise involves learning to calibrate eye movements patterns with internal representations (Grinder & Bandler 1979 p.24; Dilts & Delozier 2000 ; Grinder & Bostic St Clair 2001 p.171). According to NLP developers, this core tennet loosely relates to the VAK guidelines below. ''See chart (Dilts et al 1980; O'Connor and McDermot, 1996; Dilts & Delozier 2000 ):'' | |||
| == Applications == | |||
| *'''Visual:''' eyes up to left or right according to dominant hemisphere access; high or shallow breathing; muscle tension in neck; high pitched/nasal voice tone; phrases such as “I can ''imagine'' the big ''picture''”. | |||
| === Alternative medicine === | |||
| *'''Auditory:''' eyes left or right; even breathing from diaphragm; even or rhythmic muscle tension; clear midrange voice tone, sometimes tapping or whistling; phrases such as “Let's ''tone'' down the ''discussion''”. | |||
| NLP has been promoted as being able to treat a variety of diseases including ], ] and cancer.<ref name="American Cancer Society-2009">{{cite book |publisher=] |title=American Cancer Society Complete Guide to Complementary and Alternative Cancer Therapies |edition=2nd |year=2009 |isbn=9780944235713 |editor=Russell J |editor2=Rovere A |pages= |chapter=Neuro-linguistic programming |chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/americancancerso0000unse/page/120 }}</ref> Such claims have no supporting ].<ref name="American Cancer Society-2009"/> People who use NLP as a form of treatment risk serious adverse health consequences as it can delay the provision of effective medical care.<ref name="American Cancer Society-2009"/> | |||
| *'''Kinesthetic:''' eyes down left or right; belly breathing and sighing; relaxed musculature; slow voice tone with long pauses; phrases such as “I can ''grasp'' a ''hold'' of it” | |||
| === Psychotherapeutic === | |||
| NLP theory explains these breathing and mental processing according to the varying levels of chemical composition in the blood that affects the brain, and “Visual” people tend to be fast visual thinkers and can seem untrustworthy to “kinesthetic” thinkers because thinking by feeling is inherently slow (Dilts et al 1980). It is further claimed that matching VAK predicates can build rapport with individuals. | |||
| Early books about NLP had a psychotherapeutic focus given that the early models were psychotherapists. As an approach to psychotherapy, NLP shares similar core assumptions and foundations in common with some contemporary brief and systemic practices,<ref>Rubin Battino (2002) ''Expectation: The Very Brief Therapy Book''. Crown House Publishing. {{ISBN|1-84590-028-6}}</ref><ref>Kerry, S. (2009) Pretreatment expectations of psychotherapy clients, University of Alberta (Canada)<!--, {{AAT|NR55409}}--></ref><ref name="Beyebach-1999" /> such as ].<ref>Bill O'Connell (2005) Solution-focused therapy (Brief therapy series). Sage; Second Edition </ref><ref>Windy Dryden (2007) Dryden's handbook of individual therapy. 5th edition. Sage. {{ISBN|1-4129-2238-0}} </ref> NLP has also been acknowledged as having influenced these practices<ref name="Beyebach-1999">{{cite journal |last1=Beyebach |first1=M. |last2=Rodríguez Morejón |first2=A. |year=1999 |title=Some thoughts on integration in solution-focused therapy |journal=Journal of Systemic Therapies |volume=18 |pages=24–42|doi=10.1521/jsyt.1999.18.1.24 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Pesut |first=Daniel J. |title=The art, science, and techniques of reframing in psychiatric mental health nursing |journal=Issues in Mental Health Nursing |date=1 January 1991 |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=9–18 |doi=10.3109/01612849109058206 |pmid=1988384}}</ref> with its reframing techniques{{sfnm|1a1=Maag|1y=1999|2a1=Maag|2y=2000}} which seeks to achieve behavior change by shifting its ''context'' or ''meaning'',<ref>{{harvnb|Bandler|Grinder|1982}} as cited in {{harvnb|Maag|1999}} and {{harvnb|Maag|2000}}.</ref> for example, by finding the positive connotation of a thought or behavior. | |||
| Some authors (Bradbury, 1997; Molden 2000) use internal Verbal/Auditory/Kinesthetic strategies in order to categorize people within a thinking strategies or ] framework for instance, that there exist visual, kinesthetic or auditory types of manager. | |||
| The two main therapeutic uses of NLP are, firstly, as an adjunct by therapists<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Field |first1=E. S. |title=Neurolinguistic programming as an adjunct to other psychotherapeutic/hypnotherapeutic interventions |journal=The American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis |volume=32 |issue=3 |pages=174–82 |year=1990 |pmid=2296919 |doi=10.1080/00029157.1990.10402822}}</ref> practicing in other therapeutic disciplines and, secondly, as a specific therapy called Neurolinguistic Psychotherapy.<ref>Bridoux, D., Weaver, M., (2000) "Neuro-linguistic psychotherapy." In ''Therapeutic perspectives on working with lesbian, gay and bisexual clients.'' Davies, Dominic (Ed); Neal, Charles (Ed). (pp. 73–90). Buckingham, England: Open University Press (2000) xviii, 187 pp. {{ISBN|0-335-20333-7}}</ref> | |||
| ===Meta-model and Milton Model=== | |||
| According to Stollznow, "Bandler and Grinder's infamous ''Frogs into Princes'' and their other books boast that NLP is a cure-all that treats a broad range of physical and mental conditions and learning difficulties, including epilepsy, myopia and dyslexia. With its promises to cure schizophrenia, depression and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, and its dismissal of psychiatric illnesses as psychosomatic, NLP shares similarities with Scientology and the Citizens Commission on Human Rights (CCHR)."<ref name="Stollznow-2010" /> A systematic review of experimental studies by Sturt ''et al.'' (2012) concluded that "there is little evidence that NLP interventions improve health-related outcomes."{{sfn|Sturt|2012}} In his review of NLP, ] writes, "NLP is not really a cohesive therapy but a ragbag of different techniques without a particularly clear theoretical basis ... evidence base is virtually non-existent."<ref>{{cite book|last=Briers|first=Stephen|title=Brilliant Cognitive Behavioural Therapy: How to use CBT to improve your mind and your life|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6BQ2S3F_eDMC&q=ragbag&pg=PT15|date=27 December 2012|publisher=Pearson UK|isbn=978-0-273-77849-3|page=15}}</ref> Eisner writes, "NLP appears to be a superficial and gimmicky approach to dealing with mental health problems. Unfortunately, NLP appears to be the first in a long line of mass marketing seminars that purport to virtually cure any mental disorder ... it appears that NLP has no empirical or scientific support as to the underlying tenets of its theory or clinical effectiveness. What remains is a mass-marketed serving of psychopablum."<ref>{{cite book|first=Donald A.|last=Eisner|title=The Death of Psychotherapy: From Freud to Alien Abductions|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hmcDl6l8uXwC&pg=PA158|year=2000|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-0-275-96413-9|pages=158–59}}</ref> | |||
| The ] is a set of thirteen language patterns Bandler and Grinder (1975a) developed from their observations of Virginia Satir and Fritz Perls, and is proposed as an information gathering tool, and to challenge (theoretical) distortions, generalizations or deletions in the speaker's language (Bandler & Grinder, 1975a Ch3). The meta-model can be reduced to the asking "What specifically", or "How specifically?" to clarify unspecified syntactic elements (Grinder & McMaster 1998). | |||
| André Muller Weitzenhoffer—a friend and peer of Milton Erickson—wrote, "Has NLP really abstracted and explicated the essence of successful therapy and provided everyone with the means to be another Whittaker, Virginia Satir, or Erickson? ... failure to do this is evident because today there is no multitude of their equals, not even another Whittaker, Virginia Satir, or Erickson. Ten years should have been sufficient time for this to happen. In this light, I cannot take NLP seriously ... contributions to our understanding and use of Ericksonian techniques are equally dubious. ''Patterns I'' and ''II'' are poorly written works that were an overambitious, pretentious effort to reduce hypnotism to a magic of words."{{sfn|Weitzenhoffer|1989|p=305}} | |||
| The meta-model involves the identification of the abandoned theoretical concepts of Chomsky's ] (Bandler & Grinder 1975a; Grinder & Bostic St Clair 2001). These are distortions, generalizations, and deletions. However, in contrast with Chomsky's abandoned theory and with linguistics theory, distortions, generalizations and deletions are universals according to NLP, and are applied directly from untested theory to empirically untested application (REF). | |||
| Clinical psychologist Stephen Briers questions the value of the NLP maxim—a ''presupposition'' in NLP jargon—"there is no failure, only feedback".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Dilts |first1=Robert |last2=DeLozier |first2=Judith |title=Encyclopedia of Systemic Neuro-Linguistic Programming and NLP New Coding |edition=1st |year=2000 |publisher=NLP University Press |location=Santa Cruz |isbn=978-0-9701540-0-2 |page=1002 |url=http://nlpuniversitypress.com/html2/PrPu25.html |access-date=16 July 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130921060637/http://nlpuniversitypress.com/html2/PrPu25.html |archive-date=21 September 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Briers argues that the denial of the existence of failure diminishes its instructive value. He offers ], ] and ] as three examples of unambiguous acknowledged personal failure that served as an impetus to great success. According to Briers, it was "the crash-and-burn type of failure, not the sanitised NLP Failure Lite, i.e. the failure-that-isn't really-failure sort of failure" that propelled these individuals to success. Briers contends that adherence to the maxim leads to self-deprecation. According to Briers, personal endeavour is a product of invested values and aspirations and the dismissal of personally significant failure as mere feedback effectively denigrates what one values. Briers writes, "Sometimes we need to accept and mourn the death of our dreams, not just casually dismiss them as inconsequential." Briers also contends that the NLP maxim is narcissistic, self-centered and divorced from notions of moral responsibility.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Briers |first1=Stephen |title=Psychobabble: Exploding the myths of the self-help generation |edition=1st |year=2012 |publisher=Pearson Education Limited |location=Santa Cruz |isbn=978-0-273-77239-2 |chapter=MYTH 16: There is no failure, only feedback |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2zsQeth9yRAC}}</ref> | |||
| The inverse of the meta-model is the Milton-model (Grinder & Bandler 1976,1977); a collection of "artfully vague" language patterns (Grinder & Bandler 1981, appendix II) elicited from the work of ]. It is said that the use of non-specific language patterns can allow the client to make their own meaning for what is being said. | |||
| === Other uses === | |||
| Together the meta model and the milton model form the basis for the all other NLP models. | |||
| Although the original core techniques of NLP were therapeutic in orientation their generic nature enabled them to be applied to other fields. These applications include ],<ref>{{cite book | last1=Gass | first1=Robert H | last2=Seiter | first2=John S | title=Persuasion: Social Influence and Compliance Gaining | publisher=Routledge | date=2022-04-06 | isbn=978-1-000-55677-3 | page=}}</ref> sales,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Zastrow |first1=C. |title=Social Workers and Salesworkers |doi=10.1300/J283v04n03_02 |journal=Journal of Independent Social Work |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=7–16|year=1990 }}</ref> negotiation,<ref>Tosey P. & Mathison, J., "Fabulous Creatures of HRD: A Critical Natural History of Neuro-Linguistic Programming", University of Surrey Paper presented at the 8th International Conference on Human Resource Development Research & Practice across Europe, Oxford Brookes Business School, 26–28 June 2007</ref> management training,<ref>{{cite journal |last=Yemm |first=Graham |title=Can NLP help or harm your business? |journal=Industrial and Commercial Training |date=1 January 2006 |volume=38 |issue=1 |pages=12–17 |doi=10.1108/00197850610645990}}</ref> sports,<ref>Ingalls, Joan S. (1988) "Cognition and athletic behavior: An investigation of the NLP principle of congruence." ''Dissertation Abstracts International.'' Vol 48(7-B), p. 2090. {{OCLC|42614014}}</ref> teaching, coaching, team building, public speaking, and in the process of hiring employees.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) explained |url=https://www.ionos.com/startupguide/productivity/neuro-linguistic-programming-nlp/ |access-date=2022-04-04 |website=IONOS Startupguide |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| == Scientific criticism == | |||
| ==Varying Concepts== | |||
| In the early 1980s, NLP was advertised as an important advance in ] and ], and attracted some interest in counseling research and clinical psychology. However, as controlled trials failed to show any benefit from NLP and its advocates made increasingly dubious claims, scientific interest in NLP faded.<ref name="Devilly-2005">{{cite journal |last=Devilly |first=Grant J. |title=Power Therapies and possible threats to the science of psychology and psychiatry |journal=Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry |date=1 June 2005 |volume=39 |issue=6 |pages=437–45 |doi=10.1080/j.1440-1614.2005.01601.x |pmid=15943644|s2cid=208627667 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gelso |first1=C. J. |last2=Fassinger |first2=R. E. |title=Counseling Psychology: Theory and Research on Interventions |journal=Annual Review of Psychology |date=1 January 1990 |volume=41 |issue=1 |pages=355–86 |doi=10.1146/annurev.ps.41.020190.002035 |quote=Neurolinguistic programming, focused on such variables as sensory mode preference and use (''e.g.'', Graunke & Roberts 1985) and predicate matching (''e.g.'', Elich et al 1985; Mercier & Johnson 1984) had shown promise at the beginning of the decade, but after several years of conflicting and confusing results, Sharpley (1984, 1987) reviewed the research and concluded that there was little support for the assumptions of NLP. This research is now clearly on the decline, underscoring the value of thoughtful reviews and the publication of nonsupportive results in guiding empirical efforts. |pmid=2407174}}</ref> | |||
| ====Meaning of "Neuro" in NLP==== | |||
| Numerous literature reviews and ] have failed to show evidence for NLP's assumptions or effectiveness as a therapeutic method.{{efn|See, for instance, the following: | |||
| ] | |||
| * Sharpley, 1984<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sharpley |first1=Christopher F. |title=Predicate matching in NLP: a review of research on the preferred representational system. |journal=Journal of Counseling Psychology |volume=31 |issue=2 |year=1984 |pages=238–48 |doi=10.1037/0022-0167.31.2.238}}</ref> and 1987<ref name="Sharpley-1987" /> | |||
| * Druckman and Swets, 1988<ref name="Druckman-1988">{{cite book | editor1-last=Druckman | editor1-first=D. | editor2-last=Swets | editor2-first=J. | title=Enhancing Human Performance: Issues, Theories, and Techniques | publisher=National Academies Press | publication-place=Washington, D.C. | date=1988-01-01 | isbn=978-0-309-03792-1 | doi=10.17226/1025 | pages=138–149 | chapter=8: Social Processes | chapter-url=https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/1025/chapter/11#138}} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| * Heap, 1988<ref>{{cite book |last=Heap |first=M. |year=1988 |title=Neurolinguistic programming – an interim verdict |publisher=Croom Helm |location=London |pages=268–280 |chapter=Hypnosis: Current clinical, experimental and forensic practices |url=http://www.mheap.com/nlp1.pdf |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070615185758/http://www.mheap.com/nlp1.pdf |archivedate=15 June 2007}}</ref> | |||
| * von Bergen et al., 1997<ref name="von Bergen-1997" /> | |||
| * Druckman, 2004<ref name="Druckman-2004" /> | |||
| * Witkowski, 2010<ref name="Witkowski-2010" />}} While some NLP practitioners have argued that the lack of empirical support is due to insufficient research which tests NLP,{{efn|See the following: | |||
| * Einspruch and Forman, 1985<ref>{{cite journal |last=Einspruch |first=Eric L. |author2=Forman, Bruce D. |title=Observations concerning research literature on neuro-linguistic programming. |journal=Journal of Counseling Psychology |date=1 January 1985 |volume=32 |issue=4 |pages=589–96 |doi=10.1037/0022-0167.32.4.589}}</ref> | |||
| * Murray, 2013<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Murray |first1=Laura L. |title=Limited evidence that neurolinguistic programming improves health-related outcomes. |journal=Evidence-Based Mental Health |date=30 May 2013 |url=http://ebmh.bmj.com/content/early/2013/05/29/eb-2013-101355.extract |doi=10.1136/eb-2013-101355 |pmid=23723409 |volume=16 |issue=3 |page=79 |s2cid=150295 }}</ref> | |||
| * Sturt et al., 2012{{sfn|Sturt|2012}} | |||
| * ''Neuro-Linguistic Programming and Research''<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.som.surrey.ac.uk/NLP/Research/index.asp |title=Neuro-Linguistic Programming and Research |access-date=22 February 2010 |archive-date=3 January 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190103034855/http://www.som.surrey.ac.uk/NLP/Research/index.asp |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * Tosey and Mathison, 2010<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Tosey |first1=P. |last2=Mathison |first2=J. |doi=10.1108/17465641011042035 |title=Exploring inner landscapes through psychophenomenology: The contribution of neuro-linguistic programming to innovations in researching first person experience |journal=Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management |volume=5 |pages=63–82 |year=2010 |url=http://epubs.surrey.ac.uk/7448/126/Mathison_Tosey_QROM_final_Oct_2009_amended_Jan_2010.pdf |access-date=28 January 2019 |archive-date=19 July 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180719120020/http://epubs.surrey.ac.uk/7448/126/Mathison_Tosey_QROM_final_Oct_2009_amended_Jan_2010.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| }} the consensus scientific opinion is that NLP is ]{{efn|See the following: | |||
| * Witkowsi, 2010<ref name="Witkowski-2010" /> | |||
| * '']'', 2009<ref name="Carroll-2009" /> | |||
| * Beyerstein, 1990<ref name="Beyerstein-1990">{{cite journal |last=Beyerstein |first=B. L. |year=1990 |title=Brainscams: Neuromythologies of the New Age |journal=International Journal of Mental Health |volume=19 |issue=3 |pages=27–36 (27) |doi=10.1080/00207411.1990.11449169 }}</ref> | |||
| * Corballis, in Della Sala and Anderson, 2012<ref>{{cite book| editor1-last = Della Sala| editor1-first = Sergio| editor2-last = Anderson| editor2-first = Mike |last1=Corballis |first1=Michael C. |author-link=Michael Corballis |title=Neuroscience in Education: The good, the bad, and the ugly |chapter=Chapter 13 Educational double-think |quote=The notion of hemisphericity is also incorporated into such cult activities as Neuro Linguistic Programming (NLP).... In any event, NLP is a movement that is still going strong, but has little scientific credibility. |edition=1st |year=2012 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-960049-6 |pages=225–26 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pFE5UCaFwEQC}}</ref> | |||
| * ] and ]<ref>] & ] (1997). '']'' Jossey Bass, pp. 167–95 (169). {{ISBN|0-7879-0278-0}}.</ref> | |||
| * Lilienfeld, Lynn and Lohr, 2004<ref>(Eds.) Lilienfeld, S., Lynn, S., & Lohr, J. (2004). ''Science and Pseudo-science in Clinical Psychology''. The Guilford Press.</ref> | |||
| * Della Sala, 2007<ref>{{cite book |last1=Della Sala |first1=Sergio |title=Tall Tales About the Mind and Brain: Separating Fact from Fiction |chapter=Introduction: The myth of 10% and other Tall Tales about the mind and brain |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=eftFztxKBAwC&pg=PR20 |page=xx |publisher=Oxford University Press |edition=1st |year=2007 |location=Oxford |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=eftFztxKBAwC |isbn=978-0-19-856876-6}}</ref> | |||
| * Williams, 2000<ref>William F. Williams, ed. (2000), ''Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience: From Alien Abductions to Zone Therapy'', ], {{ISBN|978-1-57958-207-4}} p. 235</ref> | |||
| * Lum, 2001<ref name=Lum-2001>{{cite book |title=Scientific Thinking in Speech and Language Therapy |publisher=] |last=Lum |first=C. |year=2001 |page=16 |isbn=978-0-8058-4029-2}}</ref> | |||
| * Lilienfeld, Lohr and Morier, 2001<ref name=Lilienfeld-2001>{{cite journal |last=Lilienfeld |first=Scott O. |author2=Lohr, Jeffrey M. |author3=Morier, Dean |title=The Teaching of Courses in the Science and Pseudoscience of Psychology: Useful Resources |journal=Teaching of Psychology |date=1 July 2001 |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=182–91 |doi=10.1207/S15328023TOP2803_03|citeseerx=10.1.1.1001.2558 |s2cid=145224099 }}</ref> | |||
| * Dunn, Halonen and Smith, 2008<ref name="Dunn-2008">{{cite book |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |vauthors=Dunn D, Halonen J, Smith R |title=Teaching Critical Thinking in Psychology |url=https://archive.org/details/teachingcritical00dunn |url-access=limited |year=2008 |page= |isbn=978-1-4051-7402-2}}</ref> | |||
| * Molfese, Segalowitz and Harris, 1988<ref>{{cite book |editor1-last=Molfese |editor1-first=Dennis L. |editor2-last=Segalowitz |editor2-first=Sidney J. |last1=Harris |first1=Lauren Julius |title=Brain Lateralization in Children: Developmental Implications |edition=1st |year=1988 |publisher=Guilford Press |location=New York |isbn=978-0-89862-719-0 |page= |quote=NLP began in 1975 and has quickly achieved cult status. |chapter=Chapter 8 Right-Brain Training: Some Reflections on the Application of Research on Cerebral Hemispheric Specialization to Education |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=un-AIyRU328C |url=https://archive.org/details/brainlateralizat0000molf/page/214 }}</ref> | |||
| }}{{efn|For a description of the social influence tactics used by NLP and similar pseudoscientific therapies, see Devilly, 2005<ref name="Devilly-2005" />}} and that attempts to dismiss the research findings based on these arguments "s an admission that NLP does not have an evidence base and that NLP practitioners are seeking a post-hoc credibility."<ref name="Roderique-Davies-2009">{{Cite journal |last1=Roderique-Davies |first1=G. |year=2009 |title=Neuro-linguistic programming: Cargo cult psychology? |journal=Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education |volume=1 |issue=2 |pages=58–63 |doi=10.1108/17581184200900014}} </ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Rowan |first1=John |title=NLP is not based on constructivism |journal=The Coaching Psychologist |volume=4 |issue=3 |date=December 2008 |pages=160–163 |doi=10.53841/bpstcp.2008.4.3.160 |s2cid=255903130 |issn=1748-1104 |url=http://www.sgcp.org.uk/sgcp/publications/the-coaching-psychologist/the-coaching-psychologist-4.3$.cfm}}</ref> | |||
| Surveys in the academic community have shown NLP to be widely discredited among scientists.{{efn|In 2006, Norcross and colleagues found NLP to be given similar ratings as ], ], ], scared straight programmes, and ].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Norcross |first=John C. |author2=Koocher, Gerald P. |author3=Garofalo, Ariele |title=Discredited psychological treatments and tests: A Delphi poll. |journal=Professional Psychology: Research and Practice |date=1 January 2006 |volume=37 |issue=5 |pages=515–22 |doi=10.1037/0735-7028.37.5.515|s2cid=35414392 }}</ref> In 2010, Norcross and colleagues listed it as seventh out of their list of ten most discredited drug and alcohol interventions.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Norcross |first=John C. |author2=Koocher, Gerald P. |author3=Fala, Natalie C. |author4=Wexler, Harry K. |title=What Does Not Work? Expert Consensus on Discredited Treatments in the Addictions |journal=Journal of Addiction Medicine |date=1 September 2010 |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=174–180 |doi=10.1097/ADM.0b013e3181c5f9db |pmid=21769032|s2cid=41494642 }}</ref> Glasner-Edwards and colleagues also identified it as discredited in 2010.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Glasner-Edwards |first=Suzette |author2=Rawson, Richard |title=Evidence-based practices in addiction treatment: Review and recommendations for public policy |journal=Health Policy |date=1 October 2010 |volume=97 |issue=2–3 |pages=93–104 |doi=10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.05.013 |pmid=20557970 |pmc=2951979}}</ref> }} Among the reasons for considering NLP a pseudoscience are that evidence in favor of it is limited to ] and personal testimony<ref name="Bradley-1985" /><ref name="Tye-1994">{{cite journal |last1=Tye |first1=Marcus J.C. |title=Neurolinguistic programming: Magic or myth? |journal=Journal of Accelerative Learning & Teaching |volume=19 |issue=3–4 |pages=309–42 |year=1994 |issn=0273-2459 |id=2003-01157-001}}</ref> that it is not informed by scientific understanding of ] and ],<ref name="Bradley-1985" /><ref>{{cite journal |author-link=Willem Levelt |last1=Levelt |first1=Willem J.M |title=u voor neuro-linguistische programmering |journal=Skepter |volume=9 |issue=3 |year=1996 |language=nl |url=http://www.skepsis.nl/nlp.html }}</ref> and that the name "neuro-linguistic programming" uses jargon words to impress readers and obfuscate ideas, whereas NLP itself does not relate any phenomena to neural structures and has nothing in common with linguistics or programming.<ref name="Witkowski-2010" /><ref>{{cite book |last=Corballis |first=M.C. |title=Mind Myths: Exploring Popular Assumptions About the Mind and Brain |year=1999 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |location=Chichester, UK |isbn=978-0-471-98303-3 |page=41 |edition=Repr. |editor=S.D. Sala |chapter=Are we in our right minds?}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Drenth |first1=Pieter J.D |title=Growing anti-intellectualism in Europe; a menace to science |journal=Studia Psychologica |volume=45 |pages=5–13 |year=2003 |url=http://www.allea.org/Pages/ALL/4/881.bGFuZz1FTkc.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110616080310/http://www.allea.org/Pages/ALL/4/881.bGFuZz1FTkc.pdf |archive-date=16 June 2011}}</ref><ref name="Beyerstein-1990" />{{efn|For more information on the use of neuroscience terms to lend the appearance of credibility to arguments, see Weisburg et al., 2008<ref>{{Cite journal |doi=10.1162/jocn.2008.20040 |title=The Seductive Allure of Neuroscience Explanations |journal=Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience |volume=20 |issue=3 |pages=470–77 |year=2008 |last1=Weisberg |first1=D. S. |last2=Keil |first2=F. C. |last3=Goodstein |first3=J. |last4=Rawson |first4=E. |last5=Gray |first5=J. R. |pmid=18004955 |pmc=2778755}}</ref>}} In education, NLP has been used as a key example of pseudoscience.<ref name="Lum-2001"/><ref name="Lilienfeld-2001"/><ref name="Dunn-2008"/> | |||
| All NLP literature refers to the altering of one's neurology through the neural pathways of the senses and the neural circuits of the brain. Most current NLP literature mentions no more than the reprogramming of mental habits and associations. However, the neurological concept ] is used by some NLP theorists to explain how NLP works (Drenth 2003; Levelt 1995). Some practitioners theorize that NLP processes can be explained through the neurological concepts of programming and reprogramming ] (Sinclair 1992). Within NLP, Engrams are proposed to give a patterned response which has been stabilized at the level of ] (Derks & Goldblatt 1985; Sinclair 1992). | |||
| == As a quasi-religion == | |||
| ====Brain lateralization==== | |||
| Sociologists and anthropologists have categorized NLP as a quasi-religion belonging to the ] and/or ]s.{{sfnm|1a1=Cresswell|1a2=Wilson|1y=1999|1p=|2a1=Edwards|2y=2001|2p=573|3a1=Clarke|3y=2006|3pp=440–41|4a1=Walker|4y=2007|4p=235|5a1=Hammer|5a2=Rothstein|5y=2012|5p=}} | |||
| Medical anthropologist Jean M. Langford categorizes NLP as a form of ]; that is to say, a practice with symbolic efficacy—as opposed to physical efficacy—that is able to effect change through nonspecific effects (e.g., placebo). To Langford, NLP is akin to a syncretic folk religion "that attempts to wed the magic of folk practice to the science of professional medicine".{{sfn|Langford|1999}} | |||
| Hemispheric differences (''brain lateralization'') is used to support assumptions in some versions of NLP. Dilts et al (1980) propose eye movements (and sometimes gestures) correspond to visual/auditory/] representations systems and to the specific regions in the brain (Bandler and Grinder 1975b; Lewis 1985; Dilts 1998). For example, the left side is said to be more logical/analytical than the right side, which is said to be more creative/imaginative (Patterns 1977 pp.10,87) or that regions of the brian are specialised for certain functions such as mathematics or language (Bandler & Grinder, 1975a; O'Connor & McDermott, 1996). | |||
| Bandler and Grinder were influenced by the ] described in the books of ].{{sfnm|1a1=Grinder|1a2=DeLozier|1y=1987|1p={{page needed|date=May 2024}}|2a1=Grinder|2a2=Bostic St. Clair|2y=2001|2p={{page needed|date=May 2024}}}} Concepts like "double induction"{{citation needed|date=May 2024}} and "stopping the world", central to NLP modeling, were incorporated from these influences.{{sfn|Grimley|2013|p=}} | |||
| ====NLP Models==== | |||
| Aside from the fundamental Meta, Milton, and B.A.G.E.L models, NLP proponents also did research in beliefs, ]s, the ] model, etc. For more information, see the ] category. Dilts & Delozier (2000) claim that the SMART model, amongst others are also part of NLP. | |||
| Some theorists characterize NLP as a type of "psycho-shamanism", and its focus on modeling has been compared to ritual practices in certain syncretic religions.<ref name="Tye-1994"/>{{sfn|Fanthorpe|Fanthorpe|2008|p=}} The emphasis on lineage from an NLP ] has also been likened to similar concepts in some ].{{sfn|Hunt|2003}} Aupers, Houtman, and Bovbjerg identify NLP as a New Age "psycho-religion".{{sfn|Aupers|Houtman|2010|p={{page needed|date=May 2024}}}} Bovbjerg argues that New Age movements center on a transcendent "other".{{sfn|Bovbjerg|2011|p={{page needed|date=May 2024}}}} While monotheistic religions seek communion with a divine being, this focus shifts inward in these movements, with the "other" becoming the unconscious self. Bovbjerg posits that this emphasis on the unconscious and its hidden potential underlies NLP techniques promoting self-perfection through ongoing transformation.{{sfn|Bovbjerg|2011|p={{page needed|date=May 2024}}}} | |||
| ====New Age==== | |||
| NLP is often promoted in combination with ] developments. This is partly due to New Age notions that were common at the time of development, such as Dianetics promoted by Perls and the ] promoted by Virginia Satir and also a result of practitioners modeling spiritual concepts. Bandler often used anecdotes and metaphors about the occult in his workshops and large group awareness training ] seminars (Hall & Belnap, 1999) and teaches workshops in practical shamanism. Hall (2001) claims that NLP can be used to “create both positive (+) and negative (-) psychic energy which operate at polar opposites from each other”. | |||
| Bovbjerg's secular critique echoes the conservative Christian perspective, as exemplified by ]. He argues that NLP's emphasis on self-transformation and internal power conflicts with the Christian belief in salvation through divine grace.{{sfn|Jeremiah|1995}} | |||
| ====Alternate Brands==== | |||
| Individual trainers have often introduced or idiosyncratically developed their own methods, concepts and labels, branding them under the "NLP" name (Carroll 2003): | |||
| == Legal disputes == | |||
| *John Grinder teaches New Code of NLP | |||
| ===Founding, initial disputes, and settlement (1979–1981)=== | |||
| *] teaches NAC (Neuro Associative Conditioning<sup>TM</sup>) | |||
| In 1979, Richard Bandler and John Grinder established the Society of Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) to manage commercial applications of NLP, including training, materials, and certification. The founding agreement conferred exclusive rights to profit from NLP training and certification upon Bandler's corporate entity, Not Ltd. Around November 1980, Bandler and Grinder had ceased collaboration for undisclosed reasons.<ref name="Clancy-1989" /> | |||
| *Michael Hall teaches Neuro Semantics<sup>TM</sup> | |||
| *Tad James teaches Advanced Neuro Dynamics<sup>TM</sup> & Time Line Therapy<sup>TM</sup> | |||
| *Richard Bandler himself now teaches his own offshoot of NLP, called DHE (]<sup>TM</sup>) | |||
| *Margo Anand promotes a form of NLP called SkyDancing Tantra<sup>TM</sup> | |||
| On September 25, 1981, Bandler filed suit against Grinder's corporate entity, Unlimited Ltd., in the ] seeking injunctive relief and damages arising from Grinder's NLP-related commercial activities; the Court issued a judgment in Bandler's favor on October 29, 1981.<ref>{{cite court|litigants=Not Ltd v. Unlimited Ltd et al (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County, 1981, No. 78482)|vol=|reporter=|opinion=|pinpoint=|court=Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County|date=29 October 1981|url=http://63.197.255.150/openaccesspublic/civil/casereport.asp?casenumber=CV078482&courtcode=A&casetype=CIS}}{{Dead link|date=October 2020|fix-attempted=yes}}<!-- might be able to find it by searching the court's cases - https://www.santacruz.courts.ca.gov/online-services/case-lookup --></ref> The subsequent settlement agreement granted Grinder a 10-year license to conduct NLP seminars, offer NLP certification, and utilize the NLP name, subject to royalty payments to Bandler.<ref name="Legal1997">{{cite web |title=Summary of the Legal Proceedings January 1997 – June 23, 2003 |url=http://www.steverrobbins.com/nlpschedule/random/lawsuit-text.html |access-date=12 June 2013 |archive-date=10 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150410011826/http://www.steverrobbins.com/nlpschedule/random/lawsuit-text.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| == Background and Applications == | |||
| ===Background=== | |||
| ===Further litigation and consequences (1996–2000)=== | |||
| One of the earliest influences on NLP were ] (]) as a new perspective for looking at the world which included a kind of ]. This was a departure from the ] concepts of modern science and objective reality, and it influenced notions of programming the mind. Korzybski General semantics influenced several schools of thought, leading to a viable ] industry and associations with emerging ] thinking. By the late ], self-help organizations such as ], ], and ] had become financially successful. The ] human potential seminars in California began to attract people, such as the therapist and dianetics proponent Fritz Perls (Naranjo 2000), as well as ], Virginia Satir, and Milton H. Erickson. | |||
| Bandler commenced further civil actions against Unlimited Ltd., various figures within the NLP community, and 200 initially unnamed defendants in July 1996 and January 1997. Bandler alleged violations of the initial settlement terms by Grinder and sought damages of no less than US$10,000,000.00 from each defendant.<ref name="Legal1997"/> | |||
| In February 2000, the Court ruled against Bandler. The judgment asserted that Bandler had misrepresented his exclusive ownership of NLP intellectual property and sole authority over Society of NLP membership and certification.<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Richard W Bandler et al v. Quantum Leap Inc. et al (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County, 2000, No. 132495) |vol= |reporter= |opinion= |pinpoint= |court=Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County |date=10 February 2000 |url=http://63.197.255.150/openaccesspublic/civil/casereport.asp?casenumber=CV132495&courtcode=A&casetype=CIS}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=NLP Matters 2 |url=http://www.anlp.org/anlpnews2.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010210021504/http://www.anlp.org/anlpnews2.htm |archive-date=10 February 2001 |access-date=12 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
| While at ], ], John Grinder then an Assistant Professor of ] was invited by Richard Bandler, then a fourth year undergraduate student to visit his Gestalt therapy group (Grinder & Bostic St Clair 2001). Between 1973-1979, under the mentorship of ], the co-founders collaborated, and published several books including <i>The Structure of Magic Volumes I & II (1975, 1976)</i>, <i>Changing with families</i> and <i>Patterns of the Hypnotic Techniques of Milton H. Erickson, Volumes I & II (1977, 1978)</i> based on the patterns of ], ], ]. | |||
| ===Trademark revocation (1997)=== | |||
| The practice of neuro-linguistic programming attracted mostly therapists at first although it eventually attracted business people, sales people, artists, and "new-agers" (Hall, 1994). As it expanded, Leslie Cameron-Bandler, ], ], ], and David Gordon (Therapeutic Metaphors 1978) made further contributions to NLP and the seminars of Bandler and Grinder were transcribed by Steve Andreas into a book, <i>]</i>. This was published in 1979 and drove the demand for seminars which in turn became successful human potential attractions (Dilts, 1991). | |||
| In December 1997, a separate civil proceeding initiated by Tony Clarkson resulted in the revocation of Bandler's UK ] of NLP. The Court ruled in Clarkson's favor.<ref>{{cite web |title=NLP Matters |url=http://www.anlp.org/anlpnews.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20010406091232/http://www.anlp.org/anlpnews.htm |archive-date=6 April 2001 |access-date=12 June 2013 |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Case details for trade mark UK00002067188 |url=http://www.ipo.gov.uk/tmcase/Results/1/UK00002067188 |date=13 June 2013 |access-date=25 July 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ===Resolution and legacy (2000)=== | |||
| Since the mid ] NLP has become more widespread, and following the example of Richard Bandler (who attempted legal action to claim the bulk of the field as his own personal intellectual and commercial property because he could not resolve the dispute through the use of NLP (Salerno 2005). The dispute between Bandler and Grinder over trademarks and copyright was resolved in court of California in 2000 who deemed NLP a generic term (Grinder & Bostic, 2001 Appendix; Salerno 2005). | |||
| Bandler and Grinder reached a settlement in late 2000, acknowledging their status as co-creators and co-founders of NLP and committing to refrain from disparaging one another's NLP-related endeavors.{{sfn|Grinder|Bostic St. Clair|2001|loc=Appendix A}} | |||
| Due to these disputes and settlements, the terms 'NLP' and 'Neuro-Linguistic Programming' remain in the ]. No single party holds exclusive rights, and there are no restrictions on offering NLP certifications.{{sfn|Hall|2010}}<ref>{{cite web |title=3.5. Who Owns NLP? |website=NLP Archives – Frequently Asked Questions about NLP |url=http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/nlpfaq35.htm |access-date=12 June 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130624042934/http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/nlpfaq35.htm |archive-date=2013-06-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=((This page contains the ruling in the case of Richard Bandler against many others in the NLP community)) |website=NLP Archives – Frequently Asked Questions about NLP |url=http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/lawsuit.htm |access-date=12 June 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130627031836/http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/lawsuit.htm |archive-date=2013-06-27}}</ref><ref name="Trademark Status and Document Retrieval-2013">{{cite web |title=75351747 |website=Trademark Status and Document Retrieval |publisher=United States Patent and Trademark Office |url=http://tsdr.uspto.gov/#caseNumber=75351747&caseType=SERIAL_NO&searchType=statusSearch |date=13 June 2013 |access-date=14 June 2013 }}</ref><ref name="Trademark Status and Document Retrieval-2013a">{{cite web |title=73253122 |website=Trademark Status and Document Retrieval |publisher=United States Patent and Trademark Office |url=http://tsdr.uspto.gov/#caseNumber=73253122&caseType=SERIAL_NO&searchType=statusSearch |date=13 June 2013 |access-date=14 June 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Applications=== | |||
| The designations "NLP" and "Neuro-linguistic Programming" are not owned, trademarked, or subject to centralized regulation.<ref>{{cite web |title=NLP FAQ |url=http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/nlpfaq35.htm |date=27 July 2001 |access-date=14 June 2013 |archive-date=24 June 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130624042934/http://users.telenet.be/merlevede/nlpfaq35.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=NLP Comprehensive Lawsuit Response |url=http://www.steverrobbins.com/nlpschedule/random/lawsuit-nlpc.html |access-date=14 June 2013 |archive-date=17 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190717201129/http://www.steverrobbins.com/nlpschedule/random/lawsuit-nlpc.html |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name="Trademark Status and Document Retrieval-2013"/><ref name="Trademark Status and Document Retrieval-2013a" /> Consequently, there are no restrictions on individuals self-identifying as "NLP Master Practitioners" or "NLP Master Trainers."<ref name="Roderique-Davies-2009" /> This decentralization has led to numerous certifying associations. | |||
| Much of NLP is now largely targeted for niche markets (particularly commercialized, cut down or self-help usage), and may be more controversial or esoteric, sometimes ]ally or evangelistically taught (Eisner 2000). Some of the original developers, notably Richard Bandler and the stage hypnotist Paul McKenna, have encouraged these trends and the resulting fragmentation and move towards "pop NLP" has discredited the subject in the eyes of many people (Salerno 2005). | |||
| ===Decentralization and criticism=== | |||
| NLP is sometimes applied to coaching and for personal or business development, including motivational communication and systems thinking (Pasztor 1998). NLP is often promoted as ] seminars, similar to or in combination with ] seminars . | |||
| This lack of centralized control means there's no single standard for NLP practice or training. Practitioners can market their own methodologies, leading to inconsistencies within the field.<ref name="Carroll-2009" /><ref>{{cite book |last1=Moxom |first1=Karen |title=The NLP Professional: Create a More Professional, Effective and Successful NLP Business |edition=|year=2011 |publisher=Ecademy Press |location=Herts |isbn=978-1-907722-55-4 |pages=46–50 |chapter=Three: Demonstrating Best Practice |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7KEYurmAA8sC}}</ref> This has been a source of criticism, highlighted by an incident in 2009 where a British television presenter registered his cat<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/8303126.stm |title=Cat registered as hypnotherapist |publisher=] |date=12 October 2009 |access-date=6 November 2009}}</ref> with the British Board of Neuro Linguistic Programming (BBNLP), demonstrating the organization's lax credentialing. Critics like Karen Stollznow find irony in the initial legal battles between Bandler and Grinder, considering their failure to apply their own NLP principles to resolve their conflict.<ref name="Stollznow-2010"/> Others, such as Grant Devilly, characterize NLP associations as "]s"—a term implying a lack of unifying principles or a shared sense of purpose.<ref name="Devilly-2005"/> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| Some of these involve day long, or several day periods of large group awareness activities including the introduction of authority figure guest speakers and promotion of ] products. For example, Anthony Robbins promotes NLP as a "systemic approach for change" through his seminars , and other products. NLP trainers and consultants are now applying NLP rituals and techniques in some HR application areas. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| '''Notable practitioners''' | |||
| *NLP "therapy" | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| NLP is considered a fringe or alternative therapy (Raso 1994). Although several aspects of NLP have been found to be largely ineffective (Singer and Lalich 1996), NLP is used, or suggested as an approach, by a few mental health bodies, including The National Phobics Society of Great Britain , MIND (PDF), , The British Stammering Association , the Center for Development & Disability at the University of New Mexico Center for autism ,. Around 1978, NLP practitioner certification was set up as a 20 day program with the aim of training therapists to apply NLP as an adjunct to their professional qualifications. In Europe, the has been promoting their training in line with European therapy standards. | |||
| {{notelist|30em}} | |||
| *New Age, and Occult applications | |||
| NLP's ] background, deriving from such notions as Zen spirituality and Dianetics promoted by Perls (Naranjo 2000) and the ] promoted by Virginia Satir and the modeling spiritual concepts, has led to variability in the use of occult notions in NLP. For example, Bandler often used anecdotes and metaphors about the occult in his workshops and large group awareness training ] seminars (Hall & Belnap, 1999) and teaches workshops in practical shamanism. Hall (2001) claims that NLP can be used to “create both positive (+) and negative (-) psychic energy which operate at polar opposites from each other”. Proponents state that NLP is compatible with any religion or spiritual context (O'Connor and McDermot, 1996). | |||
| ==Scientific analysis of NLP== | |||
| NLP has been ]ly tested over many years and many of its models and methods have been found to be largely ineffective (Singer & Lalich, 1996). | |||
| The ] US National Committee (a board of 14 prepared scientific experts) report found that "Individually, and as a group, these studies fail to provide an empirical base of support for NLP assumptions...or NLP effectiveness. The committee cannot recommend the employment of such an unvalidated technique" (Druckman & Swets, 1988). In addition, Edgar Johnson, technical director of the Army Research Institute heading the NLP focused Project Jedi stated that "Lots of data shows that NLP doesn't work" (Squires 1988). NLP has failed to yield convincing evidence for the NLP model, and failed to provide evidence for its effectiveness (Heap 1989). | |||
| The conjecture that a person has a preferred representational system (PRS), which is observed in the choice of words, has been found to be false according to rigorous research reviews (Heap 1988; Platt, 2001). The assertion that a person has a PRS which can be determined by the direction of eye movements found even less support (Heap, 1988; Platt, 2001). | |||
| A single critique by Einspruch and Forman (1985) stated that Sharpley's review of NLP (1984) contained methodological errors. However, Sharpley (1987) refuted this and provided further experimental evidence to demonstrate that NLP is ineffective and in error in both method and model. | |||
| Thus, objective empirical studies (Bertelsen, 1987, Bleimeister, 1988; Heap, 1988) and review papers (Sharpley, 1987, Druckman et al 1988, Platt, 2001) have consistently shown NLP to be ineffective and reviews or meta-analysis have given NLP a conclusively negative assessment, and the reiterated statement is that there is no neuro-scientific basis for any of NLP's claims, or any scientific support for its claimed efficacy (Thaler Singer and Lalich 1996; Drenth 2003; Lilienfeld et al 2003; Eisner 2000). | |||
| Due to general disillusionment with NLP, its mention in psychotherapy journals and books is becoming increasingly rare (Efran and Lukens 1990). NLP proponents have provided not one iota of scientific support for their claims, and as such NLP is considered inappropriate for thorough clinical studies (Eisner 2000). | |||
| Professor Robert Carrol (2002) states that it is impossible to determine a "correct" NLP model, and that applying one particular model to everyone is over-simplistic and will be no substitute for hard earned expertise and cannot be verified through statistical methods. | |||
| The fact that some people perceive NLP to work sometimes can be explained by the ], ], superficial symptomatic rather than core treatment, and overestimating some apparent successes while ignoring, downplaying, or explaining away failures (Beyerstein, 1997). | |||
| ==Criticism== | |||
| Critics say NLP is simply a half-baked conflation of pop psychology and pseudoscience that uses ] to disguise the fact that it is based on a set of banal, if not incorrect, presuppositions (Sanghera (Subscription required)). NLP has been criticized by clinical psychologists, management scholars, linguists, psychotherapists and cult awareness groups, concerning ineffectiveness, pseudoscientific explanation of linguistics and neurology, ethical questionability, cult-like characteristics, and promotion by exagerated claims. | |||
| ===False claims to science=== | |||
| Critics say that NLP often associates itself with science in order to raise its own prestige (Beyerstein 1991) and anthropologists such as Winkin (1990) consider such promotion to be intellectually fraudulent. Furthermore, Winkin (1990) asserts that NLP's association with science is as distant as ]'s association to ]. | |||
| Grinder has stated that NLP is a science and an art, eg. "the coding phase of NLP modeling is at present an art"(Whispering p.127). Bandler and Grinder (1975a) have used erroneously connected neuroscience to NLP (REF). Advertising standards bodies have asked for NLP proponents to avoid promoting NLP as a new science . | |||
| However, ] and ] have also stated that "NLP is not a science... we are not scientists" (Frogs into Princes, 1979 REF PAGE). Richard Bandler claims that NLP is an educational tool and that the relationship of NLP to psychology is like the relationship beetween pharmacology and biochemistry. The developers of NLP are still inaccurately refered to as "scientists" according to some who promote NLP (Singer and Lalich 1999). | |||
| ] Willem Levelt states that (translated into English) "NLP is not informed about linguistics literature, it is based on vague insights that were out of date long ago, their linguistics concepts are not properly construed or are mere fabrications, and conclusions are based upon the wrong premises. NLP theory and practice has nothing to do with neuroscientific insights or linguistics, nor with informatics or theories of programming" (Drenth 2003) . | |||
| ===Pseudoscience=== | |||
| NLP has been classed as a ] self help development (Levelt, 1995; Williams et al, 2000; Lilienfeld et al, 2003; Drenth, 2003; Bordlein 2001), in the same mould as ] (Landmark Forum) and ]. Authors such as Salerno (2005) also state NLP is pseudoscience, and have criticized its promotion as self-help, and psychologists such as Singer (1999) and management experts such as Hardiman (1994) have criticized quasi-spiritual and unethical uses within management and human resources developments. ] (Loma 2001) classify NLP is a "dubious therapy". | |||
| Numerous extraordinary and unsupported claims have been made by some NLP promoters. There have been claims that the hightening of perception using NLP can allow a novice martial artist to beat an expert (Bandler 1993. p105), and that it is possible to develop photographic memory through the use of NLP (Bandler and Grinder 1975b). | |||
| Historically, NLP has many pseudoscientific associations such as the erroneous adherence of some NLP models to the engram concept , claims to rapid cures and treatment of traumas, the use of popular new age myths such as unlimited potential, left/right brain simplicities, past life regression, and the use marketing/recruitment models similar to that of Dianetics and other cults (Sala et al 1999). | |||
| Pseudoscience is prone to certain fallacies and characteristics. These can be; Overgeneral predictions, pseudoscientific experimentation, dogmatic adherence or recycling of un-validated claims (Winn and Wiggins, 2001). The characteristics of pseudoscience are more specifically shown thus (Lilienfeld et al, 2003) : | |||
| *The use of obscurantist language (eg ]s, parapragmatics, sub-modalities etc) | |||
| *The absence of ] (Levelt, 1995) | |||
| *Over-reliance on testimonial and ] (Krugman et al 1999) | |||
| *An overuse of ad hoc hypotheses and reversed ] designed to immunize claims from falsification (Singer 1999) | |||
| *Emphasis on confirmation rather refutation (eg reliance on asking how rather than why) | |||
| *Absence of ] | |||
| *The mantra of ] and eclecticism designed to immunize from verifiable efficacy (Lilienfeld et al 2003) (Claiming that NLP is unmeasurable due to too many factors(Eisner 2000) or to simplistically “do what works”. | |||
| *Evasion of ] (If claims were true, why were they not properly documented and presented to the scientific community?) (Eisner 2000) | |||
| Critics point of that NLP is based on outdated metaphors of brain functioning and is laced with numerous factual errors (Druckman and Swets 1988). Modern neuroscience indicates that NLP's notions of neurology are erroneous and pseudoscientific in regards to: left/right brain hemispheric differences (Sala et al, 1999; Drenth, 2003, Dilts et al 2000), the association of eye movements or body gestures to brain hemispheres, and in the universal division of humanity to 40% visual, 40% auditive, and 20% kinesthesic (Winkin 1999), in the adherence of NLP to positive/negative and psychic out of body energy (Sala 1999). NLP is also based on some of Freud's most flawed and pseudoscientific thinking that has been rejected by the mainstream psychology community for decades (Eisner 2000). | |||
| ===Ethical Concerns=== | |||
| Ethical concerns of NLP’s encouragement towards ] have been raised. As such, NLP is seen as encouraging people to find more ways to manipulate individuals against their will within seduction, sales and business settings. NLP book titles include "The Unfair Advantage in Sales" and "The Science and Technology of Getting What You Want" and “Get Anyone to Do Anything”. | |||
| The therapy and coaching fields require an ethical code of conduct (eg: ). It has been found that NLP certified practitioners often show a weak grasp of ethics (Hardiman 1994). | |||
| In addition, "Ethical standards bodies and other professional associations state that unless a technique, process, drug, or surgical procedure can meet requirements of clinical tests, it is ethically questionable to offer it to the public, especially if money is to change hands" (Beyerstein 1997). NLP is also criticised for unethically encouraging the belief in non existent maladies and insecurities by otherwise normal individuals (Salerno 2005). | |||
| NLP has also been described as a "] cult", and has been criticised within the business sector for being coercive, including undue and forced adoption of fundamental beliefs and intense confrontational psychological techniques, tantamount to forced religious conversion (Singer 1995). Its various forms, such as those promoted by Grinder, and Tony Robbins are said to be ill conceived and coercive in some business settings (Hardiman 1994). | |||
| ===Questionable Applications=== | |||
| Currently, there is criticism from psychotherapists about the promotion of NLP and other dubious therapies within psychotherapy associations (Eisner 2000; Lilienfeld et al 2003). NLP certification for therapists in general still does not require any professional qualifications (Eisner 2000). | |||
| ] | |||
| *'''Human Resources''': As with other pseudoscientific subjects, human resource experts such as Von Bergen et al (1997) consider NLP to be inappropriate for management and human resource training . NLP has been found to be most ineffective concerning influence/persuasion and modeling of skills (Druckman et al 1988). There is a general view that NLP is dubious and is not to be taken seriously in a business context (Hardiman 1994; Summers 1996). Within management training there have also been complaints towards NLP concerning undue and forced adoption of fundamental beliefs tantamount to a forced religious conversion (Singer 1995). | |||
| *'''NLP and Education''': Although NLP has no reliable neuroscience foundation, it is sometimes considered as part of "accelerated learning" or "brain based learning", (Walberg 2003). There is no reliable evidence to support the use of NLP within education, and as such, the use of this unvalidated method is discouraged by educational experts. | |||
| *'''Cosmetic Effect Claims''': Dubious treatments such as hypnotic breast enhancement and penis enlargement often claim to use NLP processes to produce this effect. If such miraculous effects had actually been achieved, then why have they not been properly documented by the people making these claims, and presented to the scientific community? (Eisner 2000). | |||
| *'''Occult and New Age Practices''': With its promotion with Tai Chi, Meditation, and Dianetics, NLP is in the margins of contemporary obscurantism (Winkin 1990). NLP is often criticised as being a dubious ] therapy. Practitioners sometimes attempt to model spiritual experiences, which inherently, are lacking in scientific support. NLP's new age background often leads to it being sold in combination with ] methods of magic such as those by (by Richard Bandler) or ] (by Tad James). | |||
| ===Cult characteristics=== | |||
| NLP is sometimes referred to as a cult (Heap 1991; Winkin 1990; Singer 1995), a destructive or amoral pseudoscientific psychocult (Novopashin 2004)(eg. NLP Rekaunt), and is often considered to be akin to a cult (Tippet 1994; Langone 1993; Singer 2003; Eisner 2000; Sharpley 1987). The German educational minister banned the use of NLP in education due to its close similarity to ] . | |||
| Similar to other pseudoscientific subjects such as Dianetics and EST, NLP is adopted as a pretext for applying ritual, authority control, dissociation, reduced rationalization, and social pressure to obtain compliance from the cult's victim or to induce dependence on the cult (Langone 1993). | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| ===Citations=== | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| ===Works cited=== | |||
| See ] for a fuller list of Books and articles not directly referenced on this page. | |||
| ;Primary sources | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |last2=Grinder |first2=John |title=The Structure of Magic I: A Book about Language and Therapy |year=1975 |publisher=Science and Behavior Books Inc. |isbn=978-0-8314-0044-6 |title-link=The Structure of Magic}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |last2=Grinder |first2=John |title=The Structure of Magic II |edition=1st |year=1976 |publisher=Science and Behavior Books |location=California |isbn=978-0-8314-0049-1 |title-link=The Structure of Magic}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |last2=Grinder |first2=John| editor1-last = Andreas| editor1-first = Steve |title=Frogs into Princes: Neuro Linguistic Programming |edition= |year=1979 |publisher=Real People Press |location=Utah |isbn=978-0-911226-19-5 |title-link=Frogs into Princes}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |last2=Grinder |first2=John |title=Trance-formations: Neuro-linguistic Programming and the Structure of Hypnosis |year=1981 |publisher=Real People Press |isbn=978-0-911226-22-5 |chapter=Appendix II: Hypnotic Language Patterns: The Milton-Model}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |last2=Grinder |first2=John |year=1982 |title=Reframing: Neuro-Linguistic Programming and the Transformation of Meaning |publisher=Real People Press |isbn=0-911226-25-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=Richard |editor1-last=Andreas |editor1-first=Steve |editor2-link=Connirae Andreas |editor2-last=Andreas |editor2-first=Connirae |year=1985 |title=Using Your Brain–for a Change |publisher=Real People Press |isbn=0-911226-27-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bandler |first=Richard |title=Time for a Change |year=1993 |publisher=Meta Publications |isbn=978-0-916990-28-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/timeforchange00band |url-access=registration }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Dilts |first1=Robert |last2=Grinder |first2=John |last3=Bandler |first3=Richard |last4=DeLozier |first4=Judith |title=Neuro-Linguistic Programming |volume=I: The Study of the Structure of Subjective Experience |edition=Limited |year=1980 |publisher=Meta Publications |location=California |isbn=978-0-916990-07-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CwsRAQAAIAAJ }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Grinder |first1=John |last2=DeLozier |first2=Judith |title=Turtles All The Way Down: Prerequisites To Personal Genius |edition=1st |year=1987 |publisher=Grinder & Associates |location=California |isbn=978-1-55552-022-9 |url=https://archive.org/details/turtlesallwaydow00grin|url-access=registration }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Grinder |first1=John |last2=Bostic St. Clair |title=Whispering in the Wind |year=2001 |publisher=J & C Enterprises |isbn=978-0-9717223-0-9}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ;Secondary sources | |||
| ;B | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| *{{cite journal| editor1-last = Aupers| editor1-first = Stef| editor2-last = Houtman| editor2-first = Dick |title=Religions of Modernity: Relocating the Sacred to the Self and the Digital | journal = International Studies in Religion and Society|edition=1st |year=2010 |publisher=Brill |location=Leiden |issn=1573-4293 |isbn=978-90-04-18451-0 |pages=115–132 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=l85zsiTI28sC&pg=PA115}} | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard & John Grinder | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last=Bovbjerg |first=Kirsten Marie |date=2011-05-01 |title=Personal Development under Market Conditions: NLP and the Emergence of an Ethics of Sensitivity Based on the Idea of the Hidden Potential of the Individual |url=https://doi.org/10.1080/13537903.2011.573333 |journal=Journal of Contemporary Religion |volume=26 |issue=2 |pages=189–205 |doi=10.1080/13537903.2011.573333 |s2cid=145148234 |issn=1353-7903}} | |||
| | Title=The Structure of Magic I: A Book About Language and Therapy | |||
| *{{cite book| editor1-last = Clarke| editor1-first = Peter B. |title=Encyclopedia of New Religious Movements |edition=1st |year=2006 |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=978-0-203-48433-3}} | |||
| | Publisher=Palo Alto, CA: Science & Behavior Books | |||
| *{{cite book| editor1-last = Cresswell| editor1-first = Jamie | editor2-last = Wilson| editor2-first = Bryan |title=New Religious Movements: Challenge and Response |edition=1st |year=1999 |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=978-0-415-20049-3}} | |||
| | Year=1975a | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Edwards |first1=Linda |title=A Brief Guide to Beliefs: Ideas, Theologies, Mysteries, and Movements |edition=1st |year=2001 |publisher=Westminster John Knox Press |location=Kentucky |isbn=978-0-664-22259-8 |url=https://archive.org/details/unset0000unse_s5t3|url-access=registration }} | |||
| | ID=ISBN 08314-0044-7}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Fanthorpe |first1=Lionel |last2=Fanthorpe |first2=Patricia |title=Mysteries and Secrets of Voodoo, Santeria, and Obeah |edition=1st |year=2008 |publisher=New Page Books |location=New Jersey |isbn=978-1-55002-784-6}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| <!-- G --> | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard & John Grinder | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Grimley |first1=Bruce |title=Theory and Practice of NLP Coaching: A Psychological Approach |edition=1st |year=2013 |publisher=Sage Publications Ltd |location=London |isbn=978-1-4462-0172-5}} | |||
| | Title=The Structure of Magic II: A Book About Communication and Change | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Hall |first1=L. Michael |last2=Belnap |first2=Barbara P. |title=The Sourcebook of Magic: A Comprehensive Guide to the Technology of NLP |orig-year=1999 |year=2000 |publisher=Crown House Publishing Limited |location=Wales |isbn=978-1-899836-22-2}} | |||
| | Publisher=Palo Alto, CA: Science & Behavior Books | |||
| *{{cite web |last=Hall |first=L. Michael |title=The lawsuit that almost killed NLP |url=http://www.neurosemantics.com/nlp/the-history-of-nlp/the-lawsuit-that-almost-killed-nlp |date=20 September 2010 |access-date=12 June 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130627130505/http://www.neurosemantics.com/nlp/the-history-of-nlp/the-lawsuit-that-almost-killed-nlp |archive-date=27 June 2013}} | |||
| | Year=1975b | |||
| *{{cite book| editor1-last = Hammer| editor1-first = Olav| editor2-last = Rothstein| editor2-first = Mikael |title=The Cambridge Companion to New Religious Movements |edition=1st |year=2012 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |isbn=978-0-521-14565-7}} | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0831400498 | |||
| *{{cite book |title=Alternative Religions: A Sociological Introduction |publisher=Ashgate Publishing Ltd |location=Hampshire |last1=Hunt |first1=Stephen J. |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-7546-3410-2}} | |||
| | url=-}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Jeremiah |first1=David |title=Invasion of Other Gods: The Seduction of New Age Spirituality |edition=1st |year=1995 |publisher=W Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-8499-3987-7 |chapter=Chapter 9: Corporate Takeovers}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Langford |first1=Jean M. |title=Medical Mimesis: Healing Signs of a Cosmopolitan "Quack" |journal=American Ethnologist |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=24–46 |date=February 1999 |jstor=647497 |doi=10.1525/ae.1999.26.1.24|doi-access=free }} | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard & John Grinder | |||
| <!-- M --> | |||
| | Title=Patterns of the Hypnotic Techniques of Milton H. Erickson, M.D. Volume I | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Maag |first=John W. |year=1999 |title=Why they say no: Foundational precises and techniques for managing resistance |journal=Focus on Exceptional Children |volume=32 |page=1 |url=http://altcommtechniques.com/publications/why_they_say_no.pdf |access-date=27 May 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120417095148/http://altcommtechniques.com/publications/why_they_say_no.pdf |archive-date=17 April 2012 |url-status=dead }} | |||
| | Publisher=Cupertino, CA :Meta Publications | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Maag |first=John W. |year=2000 |title=Managing resistance |journal=Intervention in School and Clinic |volume=35 |page=3 |doi=10.1177/105345120003500301 |issue=3|s2cid=220927708 }} | |||
| | Year=1976 | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Sturt |first1=Jackie |display-authors=etal |title=Neurolinguistic programming: a systematic review of the effects on health outcomes |journal=British Journal of General Practice |volume=62 |issue=604 |pages=e757–64 |date=November 2012 |doi=10.3399/bjgp12X658287 |pmid=23211179 |id=23211179|pmc=3481516 }} | |||
| | ID=ISBN 091699001X}} | |||
| <!-- W --> | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Walker |first1=James K. |title=The Concise Guide to Today's Religions and Spirituality |edition=1st |year=2007 |publisher=Harvest House Pubslishers |location=Oregon |isbn=978-0-7369-2011-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/conciseguidetoto0000walk|url-access=registration }} | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard, Grinder, John & DeLozier, Judith | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Weitzenhoffer |first1=André Muller |title=The Practice of Hypnotism |volume=2: Applications of Traditional an Semi-Traditional Hypnotism. Non-Traditional Hypnotism |year=1989 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |location=New York |isbn=978-0-471-62168-3 |chapter=Chapter 8: Ericksonian Hypnotism: The Bandler/Grinder Interpretation}} | |||
| | Title=Patterns of the Hypnotic Techniques of Milton H. Erickson, M.D. Volume II | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| | Publisher=Meta Publications | |||
| | Year=1977 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 1555520537}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard & John Grinder | |||
| | Title=Frogs into Princes: Neuro Linguistic Programming | |||
| | Publisher=Moab, UT: Real People Press | |||
| | Year=1979 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0911226192}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Bandler, Richard & John Grinder | |||
| | Title=Reframing: Neurolinguistic programming and the transformation of meaning | |||
| | Publisher=Moab, UT: Real People Press | |||
| | Year=June 1983 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0911226257}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Bateson, Gregory | |||
| | Title=Steps to an Ecology of Mind: Collected Essays in Anthropology, Psychiatry, Evolution, and Epistemology | Publisher=University Of Chicago Press | |||
| | Year=1972 | ID=ISBN 0226039056}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Bateson, Gregory | |||
| | Title=Mind and Nature: A Necessary Unity (Advances in Systems Theory, Complexity, and the Human Sciences) | Publisher=Hampton Press, Incorporated; New Ed edition (August, 2002) | |||
| | Year=1979 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0525166902}} | |||
| *{{Note|Bertelsen_1987}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Bertelsen, Preben & Lars Hem: | |||
| | Title=Om begrebet: klientens model af verden (??: the client's model of the world) | |||
| | Journal=Psyke & Logos | |||
| | Year=1987 | |||
| | Volume=2 | |||
| | Pages=375-408}} | |||
| *{{Note|Beyerstein_1997}} Beyerstein. B.L. (1997) Skeptical Inquirer magazine. September/October 1997 | |||
| *{{Note|Beyerstein_2001}}Beyerstein, B. (2001). The Scientific Review of Alternative Medicine, 5, 70-79. | |||
| *{{Note|Bliemeister_1998}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Bliemeister, J | |||
| | Title=Empirische Uberprufung zentraler theoretischer Konstrukte des Neurolinguistischen Programmierens (NLP) (Empirical verification of central theoretical constructs of neurolinguistic programming (NLP).) | |||
| | Journal=Zeitschrift f klinische Psychologie, Forschung und Praxis | |||
| | Year=1988 | |||
| | Volume=17(1) | |||
| | Pages=21-30}} | |||
| *Bradbury, A (1997) NLP for business success. Kogan Page. | |||
| *{{Note|Bradley_1985}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Bradley, E J & Heinz J Biedermann | |||
| | Title=Bandler and Grinder's Communication Analysis: Its historical context and contribution. | Journal=Psychotherapy, Theory and Research | |||
| | Year=1985 | |||
| | Volume=22 | |||
| | Pages=59-62}} | |||
| ;C | |||
| *{{Note|Clabby_2004}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author = John Clabby, PhD, Robert O’Connor, MD | |||
| | Title=Teaching Learners to Use Mirroring: Rapport Lessons From Neurolinguistic Programming | |||
| | Journal=Department of Family Medicine, UMDNJ-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. | |||
| | Year=2004 | |||
| | Volume=Vol. 36, No. 8 | |||
| | Pages=3 | |||
| | URL=https://www.stfm.org/fmhub/fm2004/September/John541.pdf}} | |||
| *{{Note|Craft_2001}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Craft A. | |||
| | Title=Neuro-linguistic Programming and learning theory | |||
| | Journal=The Curriculum Journal, Routledge | |||
| | Year=March 2001 | |||
| | Volume=Volume 12, Number 1 | |||
| | Pages=125-136(12) | |||
| | URL=http://www.ingentaconnect.com/search/article?title=neurolinguistic+programming&title_type=tka&author=craft&year_from=1997&year_to=2005&database=1&pageSize=20&index=1}} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| ;D | |||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| *{{Note|Derks_1985}}Derks, L. & Goldblatt, R.,(1985) The Feedforward Conception of Consciousness: A Bridge between Therapeutic Practice and Experimental Psychology. The William James Foundation, Amsterdam. | |||
| * {{Cite book |editor1-last=Andreas |editor1-first=Steve |editor1-link=Steve Andreas |editor2-first=Charles |editor2-last=Faulkner |title=NLP: the new technology of achievement |location=New York |publisher=HarperCollins |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-688-14619-1 |url=https://archive.org/details/nlpnewtechnology00andr |url-access=registration |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Austin |first=A. |title=The Rainbow Machine: Tales from a Neurolinguist's Journal |location=UK |publisher=Real People Press |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-911226-44-7 |ref=none}} | |||
| *{{Note|Carrol_2003}}{{Web reference | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bandler |first1=R. |last2=Grinder |first2=J. |author3-link=Virginia Satir |last3=Satir |first3=V. |year=1976 |title=Changing with Families: A Book about Further Education for Being Human |publisher=Science and Behavior Books |isbn=0-8314-0051-X |ref=none}} | |||
| | Author=Carroll, Robert T. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Bradbury |first1=A. |title=Neuro-Linguistic Programming: Time for an Informed Review |journal=Skeptical Intelligencer |volume=11 |year=2008 |ref=none}} | |||
| | title=The Skeptic's Dictionary | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Burn |first=Gillian |title=NLP Pocketbook |location=Alresford, United Kingdom |publisher=Management Pocketbooks Ltd |year=2005 |isbn=978-1-903776-31-5 |ref=none}} | |||
| | url=http://skepdic.com/neurolin.html | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dilts |first=R. |year=1990 |title=Changing Belief Systems with NLP |publisher=Meta Publications |isbn=978-0-916990-24-4 |ref=none}} | |||
| | Publisher=. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Dilts |first1=R. |last2=Hallbom |first2=Tim |last3=Smith |first3=Suzi |year=1990 |title=Beliefs: Pathways to Health & Well-being |publisher=Crown House Publishing |isbn=978-1-84590-802-7 |ref=none}} | |||
| | date=2003}} | |||
| * {{Skeptoid | id=4155 | number= 155| title= NLP: Neuro-linguistic Programming| date=26 May 2009 | last= Dunning| first=Brian |ref=none}} | |||
| *{{Note|Dilts_2000}}{{Book reference | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Ellerton |first=Roger |title=Live Your Dreams, Let Reality Catch Up: NLP and Common Sense for Coaches, Managers and You |location=Ottawa, Canada |publisher=Trafford Publishing |year=2005 |isbn=978-1-4120-4709-8 |ref=none}} | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B, DeLozier, Judith A | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Grinder |first=M. |year=1991 |title=Righting the Educational Conveyor Belt |publisher=Metamorphous Press |isbn=1-55552-036-7 |ref=none}} | |||
| | Title=Encyclopedia of Systemic Neuro-Linguistic Programming and NLP New Coding | |||
| * {{cite book |last=O'Connor |first=Joseph |year=2007 |title=Not Pulling Strings: Application of Neuro-Linguistic Programming to Teaching and Learning Music |publisher=Kahn & Averill |place=London |isbn=978-1-871082-90-6 |ref=none}} | |||
| | Publisher=NLP Univsersity Press | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Platt |first=Garry |title=NLP – Neuro Linguistic Programming or No Longer Plausible? |series=May |journal=Training Journal |year=2001 |volume=2001 |pages=10–15 |ref=none}} | |||
| | Date=2000 | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| | Url=http://www.nlpuniversitypress.com/ | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0970154003}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B, Grinder, John, Bandler, Richard & DeLozier, Judith A | |||
| | Title=Neuro-Linguistic Programming: Volume I - The Study of the Structure of Subjective Experience | |||
| | Publisher=Meta Publications | |||
| | Year=1980 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0916990079}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B, McDonald, Robert | |||
| | Title=Tools of the spirit | |||
| | Publisher=NLP University Press | |||
| | Year=1997}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B, Todd Epstein, Robert W Dilts | |||
| | Title=Tools for Dreamers: Strategies for Creativity | |||
| | Publisher=Palo Alto, CA: Meta Publications | |||
| | Year=1991 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0916990265}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B | |||
| | Title=Modeling With NLP | |||
| | Publisher=Palo Alto, CA: Meta Publications | |||
| | Year=1998 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0916990419}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Dilts, Robert B | |||
| | Title=Cognitive Patterns of Jesus of Nazareth | |||
| | Publisher=Ben Lomond, CA: Dynamic Learning Publications | |||
| | Year=1992 | |||
| | ID=ISBN -}} | |||
| *{{Note|Drenth_2003}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Drenth, J.D. | |||
| | Title=Growing anti-intellectualism in Europe; a menace to science | |||
| | Journal=Studia Psychologica | |||
| | Year=2003 | |||
| | Volume=45 | |||
| | Pages=5-13. | |||
| | URL=http://www.psychologia.sav.sk/sp/2003/sp1-03.htm#1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Note|Druckman_1988}}{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Druckman, Daniel & John A Swets, (Eds) | |||
| | Title=Enhancing Human Performance: Issues, Theories, and Techniques | |||
| | Publisher=Washington DC: National Academy Press | |||
| | Year=1988 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0309037921 | |||
| | URL=http://www.nap.edu/books/0309037921/html | |||
| | Pages=138-149. | |||
| }} Retrieved 25 Aug 2005 | |||
| *Dryden. W. 2001 Brunner-Routledge 0415229804 | |||
| ;E | |||
| *{{Note|Edwards_1996}}{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Edwards, Harry | |||
| | Title=A Skeptic's Guide to the New Age | |||
| | Publisher=Australian Skeptics (Self-published) | |||
| | Year=1996 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0-646-24502-3 | |||
| | URL=http://www.adam.com.au/bstett/SkepticsNeurolinguisticProg88.htm | |||
| | Pages=429pp. | |||
| }} | |||
| *Efran, J S. Lukens M.D. (1990) Language, structure, and change: frameworks of meaning in psychotherapy / New York : W.W. Norton | |||
| *Eisner, D. A. (2000). | |||
| *{{Note|Ekman_2003}}Paul Ekman The Observer, London (UK): Sunday, April 27, 2003 p.58 | |||
| *{{journal reference | |||
| | Author=Einspruch, E. L & Forman, B. D. | |||
| | Title=Neuro-linguistic programming in the treatment of phobias | |||
| | Publisher=Psychotherapy in Private Practice | |||
| | Volume=6(1) | |||
| | Pages=91-100. | |||
| | Year=1988 | |||
| | URL=http://www2.hawaii.edu/~lady/archive/phobia-research-1.html}} | |||
| ;G | |||
| * {{Web reference | |||
| | Author=Grinder, John | |||
| | title=Interview in London on New Code of NLP | |||
| | Publisher=Inspiritive, Sydney Australia | |||
| | url=http://www.inspiritive.com.au/jg.htm | |||
| | date=2003 | |||
| | ID=-}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Grinder, John & Bostic St Clair, Carmen | |||
| | Title=Whispering in the Wind | |||
| | Publisher=Scotts Valley, CA:J & C Enterprises | |||
| | Year=2001 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0-9717223-0-7 | |||
| }} | |||
| ;H | |||
| *Hall, M (2001) The Spirit of NLP. Crown House Publishing ISBN: 1899836047 | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Hall, L Michael & Barbara P Belnap | |||
| | Title=The Sourcebook of Magic | |||
| | Publisher=Carmarthen, UK: Crown House Publishing | |||
| | Year=1999 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 1899836225}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Hall, L Michael | |||
| | Meta-States: Reflexivity in Human States of Consciousness | |||
| | Publisher=CET Publications, Grand Junction, CO. | |||
| | Year=1994}} | |||
| *{{Note|Hardiman_1994}}Hardiman (1994) NLP background and issues. Industrial relations review and report No 560 May | |||
| *{{Note|Heap_1989}} Heap, M. (1989) Neurolinguistic programming: What is the evidence? In D Waxman D. Pederson. I, | |||
| * Heap.M. Dryden.W. (1991) Hypnotherapy : a handbook. Publisher: Open University Press, 1991. | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Heap, Michael (Ed) | |||
| | Title=Hypnosis: Current Clinical, Experimental and Forensic Practices | |||
| | Publisher=London, UK: Croom Helm | |||
| | Year=1988 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0709947798}} | |||
| *Helisch. M (2004) Veranstaltung:- Gesellschaftliche Funktion, Entwicklung und Sozialisation von Emotionen Seitenzahl: 39 Issue: 1 | |||
| *{{Note|Raso_1994}} Raso. J. (1994) "Alternative" Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide. Prometheus Books. ISBN: 0879758910 | |||
| ;K | |||
| *{{Note|Korzybski_1933}}<cite></cite>, Alfred Korzybski, Preface by ], Institute of General Semantics, 1994 (first published 1933), hardcover, 5th edition, ISBN 0937298018 | |||
| *{{Note|Krugman_1985}}Krugman, Kirsch, Wickless, Milling, Golicz, & Toth (1985). Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology. Vol 53(4), 526-530. | |||
| ;L | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Langone, Michael D (Ed) | |||
| | Title=Recovery from Cults: Help for Victims of Psychological and Spiritual Abuse | |||
| | Publisher=New York, NY: W W Norton & Company | |||
| | Year=1993 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0393313212}} | |||
| *{{Note|Lilienfeld_2003}}Scott O. Lilienfeld, Steven Jay Lynn, and Jeffrey M. Lohr (Eds.) (2003) . Guilford Press, New York. ISBN 1-57230-282-1,. | |||
| *Levelt W. (1995) Skepter 9(3), september 1996 / Intermediair 17 Nov pp113 | |||
| *Loma.L. (2001) | |||
| ;M | |||
| *{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Malloy, T. E., Bostic St Clair, C. & Grinder, J. | |||
| | Title=Steps to an ecology of emergence | |||
| | Journal=Cybernetics & Human Knowing | |||
| | Year=2005 | |||
| | Volume=Vol. 11, no. 3 | |||
| | Pages=102-119. | |||
| | URL=http://www.psych.utah.edu/stat/dynamic_systems/Content/examples/Ecology-of-Emergence_Galley-proofs_Malloy-et-al.pdf | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Note|Mitchie_2005}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Michie, S, M Johnston, C Abraham, R Lawton, D Parker & A Walker | |||
| | Title=Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: a consensus approach | |||
| | Journal=Quality & Safety in Health Care | |||
| | Year=2005 | |||
| | Volume=14 | |||
| | Pages=26-33 | |||
| | URL=http://qhc.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/14/1/26}} | |||
| *{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Morgan, Dylan A | |||
| | Title=Scientific Assessment of NLP (a review of Heap's 1988 conclusions) | |||
| | Journal=Journal of the National Council for Psychotherapy & Hypnotherapy Register | |||
| | Year=1993 | |||
| | Volume=Spring 1993 | |||
| | Pages=- | |||
| | URL=http://www.mindmotivations.com/article1-nlp-assessment.shtml | |||
| }}<br>See Retrieved 25 Aug 2005 Retrieved 24 Aug 2005. | |||
| *Molden D. (2000) Financial Times Prentice Hall ISBN: 0273650165 | |||
| ;N | |||
| *Naranjo. C. (2000) Gestalt therapy : the attitude & practice of an atheoretical experientialism / . Publisher Carmarthen : Crown House Pub., p126 | |||
| *Novopashin. A. (2004) "Totalitarian Sects and the Democratic State. " | |||
| ;O | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=O'Connor, Joseph & Ian McDermott | |||
| | Title=Principles of NLP | |||
| | Publisher=London, UK: Thorsons | |||
| | Year=1996 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0722531958}} | |||
| ;P | |||
| *{{Note|Platt_2001}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Platt, Garry | |||
| | Title=NLP - Neuro Linguistic Programming or No Longer Plausible? | |||
| | Journal=Training Journal | |||
| | Year=2001 | |||
| | Volume=May | |||
| | Pages=10-15 | |||
| | URL=http://www.sueknight.co.uk/Publications/Articles/NLP_Plausible.htm}}<br> Retrieved 24 Aug 2005. | |||
| *{{Note|Pasztor_1998}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Pasztor, A. | |||
| | Title=Subjective Experience Divided and Conquered | |||
| | Journal=Communication and Cognition | |||
| | Year=1998 | |||
| | Volume=Vol. 31, nr.1, Approaching Consciousness, Part II, E. Myin (ed.) | |||
| | Pages=73-102 | |||
| | URL=http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/pasztor98subjective.html}} | |||
| ;S | |||
| *Sala, S.D, editor (1999) Mind Myths. Exploring Popular Assumptions About the Mind and Brain. Wiley. | |||
| *{{Note|Salerno_2005}}Salerno, S (2005); Sham : How the Self-Help Movement Made America Helpless. Crown Publishers ISBN 1400054095 | |||
| *{{Note|Sanghera_2005}}{{Citenewsauthor | |||
| | surname=Sanghera | given=S | |||
| | title=Look into my eyes and tell me I'm learning not to be a loser | |||
| | date=Aug 26, 2005 | |||
| | org=Financial Times, London (UK) | |||
| | url=http://news.ft.com/cms/s/770f7e96-15cd-11da-8085-00000e2511c8.html}} | |||
| * (1997) Searching for Memory: The Brain, the Mind, and the Past. Publisher: Basic Books; ISBN 0465075525 | |||
| *Sharpley C.F. “Research Findings on Neurolinguistic Programming: Nonsupportive Data or an Untestable Theory” Journal of Counseling Psychology, 1987 Vol. 34, No. 1, 103-107 | |||
| *Sinclair. J. (1992) An ABC of NLP. Publisher: Self-published (ASPEN) ISBN 0951366017 | |||
| *Squires. S. (1988) The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. : Apr 17, 1988 | |||
| *{{Note|Singer_1995}}{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Thaler Singer, Margaret & Janja Lalich | |||
| | Title=Crazy Therapies : What they are? Do they work? | |||
| | Publisher=New York, NY: Jossey Bass | |||
| | Year=1996 | |||
| | ID=0787902780}} | |||
| *{{Book reference | |||
| | Author=Singer, Margaret | |||
| | Title=Cults in Our Midst : The Continuing Fight Against Their Hidden Menace | |||
| | Publisher=New York, NY: Jossey Bass | |||
| | Year=1995 | |||
| | ID=ISBN 0787967416}}See ], , Retrieved 25 Aug 2005 | |||
| *{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Skinner, H. and Stephens, P. | |||
| | Title=Speaking the Same Language: Exploring the relevance of Neuro-Linguistic Programming to Marketing Communications | |||
| | Journal=Journal of Marketing Communications | |||
| | Year=2003 | |||
| | Volume=Volume 9, Number 3 / September | |||
| | Pages=177-192 | |||
| | URL=http://journalsonline.tandf.co.uk/openurl.asp?genre=article&eissn=1466-4445&volume=9&issue=3&spage=177}} | |||
| *Summers, Lynn. (Jan 1996) Training & Development. Alexandria, VA: American Society for Training & Development: Vol. 50, Iss. 1; pg. 30, 2 pgs | |||
| ;T | |||
| *{{Citenewsauthor | |||
| | surname=Tippet | |||
| | given=Gary | |||
| | title=Inside the cults of mind control | |||
| | date=3 Apr 1994 | |||
| | org=Melbourne, Australia: Sunday Age | |||
| | url=http://www.rickross.com/reference/general/general756.html}} Retrieved 28 Aug 2005 | |||
| *{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Tosey P.; Mathison J. | |||
| | Title=Neuro-linguistic programming and learning theory: a response | |||
| | Journal=The Curriculum Journal, Routledge, part of the Taylor & Francis Group | |||
| | Year=September 2003a | |||
| | Volume=Volume 14, Number 3 | |||
| | Pages=371-388(18) | |||
| | URL=http://www.ingentaconnect.com/search/article?title=neuro-linguistic+programming+epistemology&title_type=tka&year_from=1997&year_to=2005&database=1&pageSize=20&index=1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Conference reference | |||
| | Author=Tosey P.; Mathison J. | |||
| | Title=European Conference on Educational Research, University of Hamburg, 17-20 | |||
| | Booktitle= | |||
| | Year=September 2003b | |||
| | Pages=-}} | |||
| *{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Tosey P.; Mathison J.; Michelli D. | |||
| | Title=Mapping Transformative Learning: The Potential of Neuro-Linguistic Programming | |||
| | Journal=Journal of Transformative Education | |||
| | Year=2005 | |||
| | Volume=Vol. 3, No. 2 | |||
| | Pages=140-167 | |||
| | URL=http://jtd.sagepub.com/cgi/content/abstract/3/2/140}} | |||
| ;V | |||
| *{{Note|Vaihinger_1924}}Vaihinger, H. (1924). , Routledge, Kegan and Paul Ltd, London, England | |||
| *{{Note|VonBergen_1997}}{{Journal reference | |||
| | Author=Von Bergen, C W, Barlow Soper, Gary T Rosenthal, Lamar V Wilkinson | |||
| | Title=Selected alternative training techniques in HRD | |||
| | Journal=Human Resource Development Quarterly | |||
| | Year=1997 | |||
| | Volume=8(4) | |||
| | Pages=281-294}} (NOTE: No longer indexed in APA/Psychinfo) | |||
| ;W | |||
| *Walberg H.J. (2003) Improving Educational Productivity. LSS. | |||
| *{{Note|Williams_2000}}Williams, W F. general editor. (2000) Publisher: Facts On File, New York. | |||
| *Winkin Y 1990 , MédiAnalyses, no. 7, septembre, 1990, pp. 43-50. | |||
| *{{Note|Winn_2001}}Winn, C.M , and Wiggins,A.W (2001) Joseph Henry Press. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| == |
==External links== | ||
| *{{Wiktionary inline|Neuro-linguistic programming}} | |||
| *]* | |||
| *{{Commons category-inline|Neuro-linguistic programming}} | |||
| *]* | |||
| *{{Wikiquote-inline|Neuro-linguistic programming}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| (*)Grinder & Bandler are considered the co-creators/co-originators of NLP. | |||
| {{Seduction community}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 10 January 2025
Pseudoscientific approach to psychotherapy Not to be confused with Natural language processing (also NLP). For other uses, see NLP.Medical intervention
| Neuro-linguistic programming | |
|---|---|
| MeSH | D020557 |
| [edit on Wikidata] | |
| Neuro-linguistic programming |
|---|
| Topics |
| Developers |
| Practitioners |
| Organisations |
Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) is a pseudoscientific approach to communication, personal development and psychotherapy, that first appeared in Richard Bandler and John Grinder's 1975 book The Structure of Magic I. NLP asserts that there is a connection between neurological processes, language and acquired behavioral patterns, and that these can be changed to achieve specific goals in life. According to Bandler and Grinder, NLP can treat problems such as phobias, depression, tic disorders, psychosomatic illnesses, near-sightedness, allergy, the common cold, and learning disorders, often in a single session. They also say that NLP can model the skills of exceptional people, allowing anyone to acquire them.
NLP has been adopted by some hypnotherapists as well as by companies that run seminars marketed as leadership training to businesses and government agencies.
There is no scientific evidence supporting the claims made by NLP advocates, and it has been called a pseudoscience. Scientific reviews have shown that NLP is based on outdated metaphors of the brain's inner workings that are inconsistent with current neurological theory, and that NLP contains numerous factual errors. Reviews also found that research that favored NLP contained significant methodological flaws, and that there were three times as many studies of a much higher quality that failed to reproduce the claims made by Bandler, Grinder, and other NLP practitioners.
Early development
According to Bandler and Grinder, NLP consists of a methodology termed modeling, plus a set of techniques that they derived from its initial applications. They derived many of the fundamental techniques from the work of Virginia Satir, Milton Erickson and Fritz Perls. Bandler and Grinder also drew upon the theories of Gregory Bateson, Alfred Korzybski and Noam Chomsky (particularly transformational grammar).
Bandler and Grinder say that their methodology can codify the structure inherent to the therapeutic "magic" as performed in therapy by Perls, Satir and Erickson, and indeed inherent to any complex human activity. From that codification, they say, the structure and its activity can be learned by others. Their 1975 book, The Structure of Magic I: A Book about Language and Therapy, is intended to be a codification of the therapeutic techniques of Perls and Satir.
Bandler and Grinder say that they used their own process of modeling to model Virginia Satir so they could produce what they termed the Meta-Model, a model for gathering information and challenging a client's language and underlying thinking. They say that by challenging linguistic distortions, specifying generalizations, and recovering deleted information in the client's statements, the transformational grammar concept of surface structure yields a more complete representation of the underlying deep structure and therefore has therapeutic benefit. Also derived from Satir were anchoring, future pacing and representational systems.
In contrast, the Milton-Model—a model of the purportedly hypnotic language of Milton Erickson—was described by Bandler and Grinder as "artfully vague" and metaphoric. The Milton-Model is used in combination with the Meta-Model as a softener, to induce "trance" and to deliver indirect therapeutic suggestion.
Psychologist Jean Mercer writes that Chomsky's theories "appear to be irrelevant" to NLP. Linguist Karen Stollznow describes Bandler's and Grinder's reference to such experts as namedropping. Other than Satir, the people they cite as influences did not collaborate with Bandler or Grinder. Chomsky himself has no association with NLP, with his work being theoretical in nature and having no therapeutic element. Stollznow writes, "ther than borrowing terminology, NLP does not bear authentic resemblance to any of Chomsky's theories or philosophies—linguistic, cognitive or political."
According to André Muller Weitzenhoffer, a researcher in the field of hypnosis, "the major weakness of Bandler and Grinder's linguistic analysis is that so much of it is built upon untested hypotheses and is supported by totally inadequate data." Weitzenhoffer adds that Bandler and Grinder misuse formal logic and mathematics, redefine or misunderstand terms from the linguistics lexicon (e.g., nominalization), create a scientific façade by needlessly complicating Ericksonian concepts with unfounded claims, make factual errors, and disregard or confuse concepts central to the Ericksonian approach.
More recently, Bandler has stated, "NLP is based on finding out what works and formalizing it. In order to formalize patterns I utilized everything from linguistics to holography ... The models that constitute NLP are all formal models based on mathematical, logical principles such as predicate calculus and the mathematical equations underlying holography." There is no mention of the mathematics of holography nor of holography in general in Spitzer's, or Grinder's account of the development of NLP.
On the matter of the development of NLP, Grinder recollects:
My memories about what we thought at the time of discovery (with respect to the classic code we developed—that is, the years 1973 through 1978) are that we were quite explicit that we were out to overthrow a paradigm and that, for example, I, for one, found it very useful to plan this campaign using in part as a guide the excellent work of Thomas Kuhn (The Structure of Scientific Revolutions) in which he detailed some of the conditions which historically have obtained in the midst of paradigm shifts. For example, I believe it was very useful that neither one of us were qualified in the field we first went after—psychology and in particular, its therapeutic application; this being one of the conditions which Kuhn identified in his historical study of paradigm shifts.
The philosopher Robert Todd Carroll responded that Grinder has not understood Kuhn's text on the history and philosophy of science, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Carroll replies: (a) individual scientists never have nor are they ever able to create paradigm shifts volitionally and Kuhn does not suggest otherwise; (b) Kuhn's text does not contain the idea that being unqualified in a field of science is a prerequisite to producing a result that necessitates a paradigm shift in that field and (c) The Structure of Scientific Revolutions is foremost a work of history and not an instructive text on creating paradigm shifts and such a text is not possible—extraordinary discovery is not a formulaic procedure. Carroll explains that a paradigm shift is not a planned activity, rather it is an outcome of scientific effort within the dominant paradigm that produces data that cannot be adequately accounted for within the current paradigm—hence a paradigm shift, i.e. the adoption of a new paradigm. In developing NLP, Bandler and Grinder were not responding to a paradigmatic crisis in psychology nor did they produce any data that caused a paradigmatic crisis in psychology. There is no sense in which Bandler and Grinder caused or participated in a paradigm shift. "What did Grinder and Bandler do that makes it impossible to continue doing psychology ... without accepting their ideas? Nothing," argues Carroll.
Commercialization and evaluation
By the late 1970s, the human potential movement had developed into an industry and provided a market for some NLP ideas. At the center of this growth was the Esalen Institute at Big Sur, California. Perls had led numerous Gestalt therapy seminars at Esalen. Satir was an early leader and Bateson was a guest teacher. Bandler and Grinder have said that in addition to being a therapeutic method, NLP was also a study of communication and began marketing it as a business tool, writing that, "if any human being can do anything, so can you." After 150 students paid $1,000 each for a ten-day workshop in Santa Cruz, California, Bandler and Grinder gave up academic writing and started producing popular books from seminar transcripts, such as Frogs into Princes, which sold more than 270,000 copies. According to court documents relating to an intellectual property dispute between Bandler and Grinder, Bandler made more than $800,000 in 1980 from workshop and book sales.
A community of psychotherapists and students began to form around Bandler and Grinder's initial works, leading to the growth and spread of NLP as a theory and practice. For example, Tony Robbins trained with Grinder and utilized a few ideas from NLP as part of his own self-help and motivational speaking programmes. Bandler led several unsuccessful efforts to exclude other parties from using NLP. Meanwhile, the rising number of practitioners and theorists led NLP to become even less uniform than it was at its foundation. Prior to the decline of NLP, scientific researchers began testing its theoretical underpinnings empirically, with research indicating a lack of empirical support for NLP's essential theories. The 1990s were characterized by fewer scientific studies evaluating the methods of NLP than the previous decade. Tomasz Witkowski attributes this to a declining interest in the debate as the result of a lack of empirical support for NLP from its proponents.
Main components and core concepts
NLP can be understood in terms of three broad components: subjectivity, consciousness, and learning.
According to Bandler and Grinder, people experience the world subjectively, creating internal representations of their experiences. These representations involve the five senses and language. In other words, our conscious experiences take the form of sights, sounds, feelings, smells, and tastes. When we imagine something, recall an event, or think about the future, we utilize these same sensory systems within our minds Furthermore it is stated that these subjective representations of experience have a discernible structure, a pattern.
Bandler and Grinder assert that behavior (both our own and others') can be understood through these sensory-based internal representations. Behavior here includes verbal and non-verbal communication, as well as effective or adaptive behaviors and less helpful or "pathological" ones. They also assert that behavior in both the self and other people can be modified by manipulating these sense-based subjective representations.
NLP posits that consciousness can be divided into conscious and unconscious components. The part of our internal representations operating outside our direct awareness is referred to as the "unconscious mind".
Finally, NLP uses a method of learning called "modeling", designed to replicate expertise in any field. According to Bandler and Grinder, by analyzing the sequence of sensory and linguistic representations used by an expert while performing a skill, it's possible to create a mental model that can be learned by others.
Techniques or set of practices
Further information: Methods of neuro-linguistic programming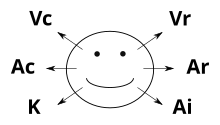
According to one study by Steinbach, a classic interaction in NLP can be understood in terms of several major stages including establishing rapport, gleaning information about a problem mental state and desired goals, using specific tools and techniques to make interventions, and integrating proposed changes into the client's life. The entire process is guided by the non-verbal responses of the client. The first is the act of establishing and maintaining rapport between the practitioner and the client which is achieved through pacing and leading the verbal (e.g., sensory predicates and keywords) and non-verbal behavior (e.g., matching and mirroring non-verbal behavior, or responding to eye movements) of the client.
Once rapport is established, the practitioner may gather information about the client's present state as well as help the client define a desired state or goal for the interaction. The practitioner pays attention to the verbal and non-verbal responses as the client defines the present state and desired state and any resources that may be required to bridge the gap. The client is typically encouraged to consider the consequences of the desired outcome, and how they may affect his or her personal or professional life and relationships, taking into account any positive intentions of any problems that may arise. The practitioner thereafter assists the client in achieving the desired outcomes by using certain tools and techniques to change internal representations and responses to stimuli in the world. Finally, the practitioner helps the client to mentally rehearse and integrate the changes into his or her life. For example, the client may be asked to envision what it is like having already achieved the outcome.
According to Stollznow, "NLP also involves fringe discourse analysis and 'practical' guidelines for 'improved' communication. For example, one text asserts 'when you adopt the "but" word, people will remember what you said afterwards. With the "and" word, people remember what you said before and after.'"
Applications
Alternative medicine
NLP has been promoted as being able to treat a variety of diseases including Parkinson's disease, HIV/AIDS and cancer. Such claims have no supporting medical evidence. People who use NLP as a form of treatment risk serious adverse health consequences as it can delay the provision of effective medical care.
Psychotherapeutic
Early books about NLP had a psychotherapeutic focus given that the early models were psychotherapists. As an approach to psychotherapy, NLP shares similar core assumptions and foundations in common with some contemporary brief and systemic practices, such as solution focused brief therapy. NLP has also been acknowledged as having influenced these practices with its reframing techniques which seeks to achieve behavior change by shifting its context or meaning, for example, by finding the positive connotation of a thought or behavior.
The two main therapeutic uses of NLP are, firstly, as an adjunct by therapists practicing in other therapeutic disciplines and, secondly, as a specific therapy called Neurolinguistic Psychotherapy.
According to Stollznow, "Bandler and Grinder's infamous Frogs into Princes and their other books boast that NLP is a cure-all that treats a broad range of physical and mental conditions and learning difficulties, including epilepsy, myopia and dyslexia. With its promises to cure schizophrenia, depression and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, and its dismissal of psychiatric illnesses as psychosomatic, NLP shares similarities with Scientology and the Citizens Commission on Human Rights (CCHR)." A systematic review of experimental studies by Sturt et al. (2012) concluded that "there is little evidence that NLP interventions improve health-related outcomes." In his review of NLP, Stephen Briers writes, "NLP is not really a cohesive therapy but a ragbag of different techniques without a particularly clear theoretical basis ... evidence base is virtually non-existent." Eisner writes, "NLP appears to be a superficial and gimmicky approach to dealing with mental health problems. Unfortunately, NLP appears to be the first in a long line of mass marketing seminars that purport to virtually cure any mental disorder ... it appears that NLP has no empirical or scientific support as to the underlying tenets of its theory or clinical effectiveness. What remains is a mass-marketed serving of psychopablum."
André Muller Weitzenhoffer—a friend and peer of Milton Erickson—wrote, "Has NLP really abstracted and explicated the essence of successful therapy and provided everyone with the means to be another Whittaker, Virginia Satir, or Erickson? ... failure to do this is evident because today there is no multitude of their equals, not even another Whittaker, Virginia Satir, or Erickson. Ten years should have been sufficient time for this to happen. In this light, I cannot take NLP seriously ... contributions to our understanding and use of Ericksonian techniques are equally dubious. Patterns I and II are poorly written works that were an overambitious, pretentious effort to reduce hypnotism to a magic of words."
Clinical psychologist Stephen Briers questions the value of the NLP maxim—a presupposition in NLP jargon—"there is no failure, only feedback". Briers argues that the denial of the existence of failure diminishes its instructive value. He offers Walt Disney, Isaac Newton and J.K. Rowling as three examples of unambiguous acknowledged personal failure that served as an impetus to great success. According to Briers, it was "the crash-and-burn type of failure, not the sanitised NLP Failure Lite, i.e. the failure-that-isn't really-failure sort of failure" that propelled these individuals to success. Briers contends that adherence to the maxim leads to self-deprecation. According to Briers, personal endeavour is a product of invested values and aspirations and the dismissal of personally significant failure as mere feedback effectively denigrates what one values. Briers writes, "Sometimes we need to accept and mourn the death of our dreams, not just casually dismiss them as inconsequential." Briers also contends that the NLP maxim is narcissistic, self-centered and divorced from notions of moral responsibility.
Other uses
Although the original core techniques of NLP were therapeutic in orientation their generic nature enabled them to be applied to other fields. These applications include persuasion, sales, negotiation, management training, sports, teaching, coaching, team building, public speaking, and in the process of hiring employees.
Scientific criticism
In the early 1980s, NLP was advertised as an important advance in psychotherapy and counseling, and attracted some interest in counseling research and clinical psychology. However, as controlled trials failed to show any benefit from NLP and its advocates made increasingly dubious claims, scientific interest in NLP faded.
Numerous literature reviews and meta-analyses have failed to show evidence for NLP's assumptions or effectiveness as a therapeutic method. While some NLP practitioners have argued that the lack of empirical support is due to insufficient research which tests NLP, the consensus scientific opinion is that NLP is pseudoscience and that attempts to dismiss the research findings based on these arguments "s an admission that NLP does not have an evidence base and that NLP practitioners are seeking a post-hoc credibility."
Surveys in the academic community have shown NLP to be widely discredited among scientists. Among the reasons for considering NLP a pseudoscience are that evidence in favor of it is limited to anecdotes and personal testimony that it is not informed by scientific understanding of neuroscience and linguistics, and that the name "neuro-linguistic programming" uses jargon words to impress readers and obfuscate ideas, whereas NLP itself does not relate any phenomena to neural structures and has nothing in common with linguistics or programming. In education, NLP has been used as a key example of pseudoscience.
As a quasi-religion
Sociologists and anthropologists have categorized NLP as a quasi-religion belonging to the New Age and/or Human Potential Movements.
Medical anthropologist Jean M. Langford categorizes NLP as a form of folk magic; that is to say, a practice with symbolic efficacy—as opposed to physical efficacy—that is able to effect change through nonspecific effects (e.g., placebo). To Langford, NLP is akin to a syncretic folk religion "that attempts to wed the magic of folk practice to the science of professional medicine".
Bandler and Grinder were influenced by the shamanism described in the books of Carlos Castaneda. Concepts like "double induction" and "stopping the world", central to NLP modeling, were incorporated from these influences.
Some theorists characterize NLP as a type of "psycho-shamanism", and its focus on modeling has been compared to ritual practices in certain syncretic religions. The emphasis on lineage from an NLP guru has also been likened to similar concepts in some Eastern religions. Aupers, Houtman, and Bovbjerg identify NLP as a New Age "psycho-religion". Bovbjerg argues that New Age movements center on a transcendent "other". While monotheistic religions seek communion with a divine being, this focus shifts inward in these movements, with the "other" becoming the unconscious self. Bovbjerg posits that this emphasis on the unconscious and its hidden potential underlies NLP techniques promoting self-perfection through ongoing transformation.
Bovbjerg's secular critique echoes the conservative Christian perspective, as exemplified by David Jeremiah. He argues that NLP's emphasis on self-transformation and internal power conflicts with the Christian belief in salvation through divine grace.
Legal disputes
Founding, initial disputes, and settlement (1979–1981)
In 1979, Richard Bandler and John Grinder established the Society of Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) to manage commercial applications of NLP, including training, materials, and certification. The founding agreement conferred exclusive rights to profit from NLP training and certification upon Bandler's corporate entity, Not Ltd. Around November 1980, Bandler and Grinder had ceased collaboration for undisclosed reasons.
On September 25, 1981, Bandler filed suit against Grinder's corporate entity, Unlimited Ltd., in the Superior Court of California, County of Santa Cruz seeking injunctive relief and damages arising from Grinder's NLP-related commercial activities; the Court issued a judgment in Bandler's favor on October 29, 1981. The subsequent settlement agreement granted Grinder a 10-year license to conduct NLP seminars, offer NLP certification, and utilize the NLP name, subject to royalty payments to Bandler.
Further litigation and consequences (1996–2000)
Bandler commenced further civil actions against Unlimited Ltd., various figures within the NLP community, and 200 initially unnamed defendants in July 1996 and January 1997. Bandler alleged violations of the initial settlement terms by Grinder and sought damages of no less than US$10,000,000.00 from each defendant.
In February 2000, the Court ruled against Bandler. The judgment asserted that Bandler had misrepresented his exclusive ownership of NLP intellectual property and sole authority over Society of NLP membership and certification.
Trademark revocation (1997)
In December 1997, a separate civil proceeding initiated by Tony Clarkson resulted in the revocation of Bandler's UK trademark of NLP. The Court ruled in Clarkson's favor.
Resolution and legacy (2000)
Bandler and Grinder reached a settlement in late 2000, acknowledging their status as co-creators and co-founders of NLP and committing to refrain from disparaging one another's NLP-related endeavors.
Due to these disputes and settlements, the terms 'NLP' and 'Neuro-Linguistic Programming' remain in the public domain. No single party holds exclusive rights, and there are no restrictions on offering NLP certifications.
The designations "NLP" and "Neuro-linguistic Programming" are not owned, trademarked, or subject to centralized regulation. Consequently, there are no restrictions on individuals self-identifying as "NLP Master Practitioners" or "NLP Master Trainers." This decentralization has led to numerous certifying associations.
Decentralization and criticism
This lack of centralized control means there's no single standard for NLP practice or training. Practitioners can market their own methodologies, leading to inconsistencies within the field. This has been a source of criticism, highlighted by an incident in 2009 where a British television presenter registered his cat with the British Board of Neuro Linguistic Programming (BBNLP), demonstrating the organization's lax credentialing. Critics like Karen Stollznow find irony in the initial legal battles between Bandler and Grinder, considering their failure to apply their own NLP principles to resolve their conflict. Others, such as Grant Devilly, characterize NLP associations as "granfalloons"—a term implying a lack of unifying principles or a shared sense of purpose.
See also
- Avatar Course
- Family systems therapy
- Frank Farrelly
- List of New Age topics
- List of unproven and disproven cancer treatments
- Solution-focused brief therapy
Notable practitioners
Notes
- ^ Note that, in a seminar, Bandler & Grinder 1982, p. 166, said that a single session of NLP combined with hypnosis could eliminate certain eyesight problems such as myopia and cure the common cold (op.cit., pp. 169, 174).
- Bandler 1993, p. vii: "In single sessions, they can accelerate learning, neutralize phobias, enhance creativity, improve relationships, eliminate allergies, and lead firewalks without roasting toes. NLP achieves the goal of its inception. We have ways to do what only a genius could have done a decade ago."
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, pp. 304–305: "I have chosen nominalization to explain what some of the problems are in Bandler and Grinder's linguistic approach to Ericksonian hypnotism. Almost any other linguistic concept used by these authors could have served equally well for the purpose of showing some of the inherent weaknesses in their treatment."
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, p. 307: "As I have mentioned in the last chapter, any references made to left and right brain functions in relation to hypnotic phenomena must be considered as poorly founded. They do not add to our understanding of nor our ability to utilize hypnotic phenomena in the style of Erickson. Indeed, references such as Bandler and Grinder make to these functions give their subject matter a false appearance of having a more scientific status than it has."
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, p. 306: "This work , incidentally, contains some glaring misstatements of facts. For example, Freud and Mesmer were depicted as contemporaries!"
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, p. 306: One of the most striking features of the Bandler/Grinder interpretation is that it somehow ignores the issue of the existence and function of suggestion, which even in Erickson's own writings and those done with Rossi, is a central idea."
- Dilts et al. 1980, pp. 13–14: "There are three characteristics of effective patterning in NLP which sharply distinguish it from behavioural science as it is commonly practiced today. First, for a pattern or generalization regarding human communication to be acceptable or well–formed in NLP, it must include in the description the human agents who are initiating and responding to the pattern being described, their actions, their possible responses. Secondly, the description of the pattern must be represented in sensory grounded terms which are available to the user. This user–oriented constraint on NLP ensures usefulness. We have been continually struck by the tremendous gap between theory and practice in the behavioural sciences—this requirement closes that gap. Notice that since patterns must be represented in sensory grounded terms, available through practice to the user, a pattern will typically have multiple representation—each tailored for the differing sensory capabilities of individual users Thirdly, NLP includes within its descriptive vocabulary terms which are not directly observable ."
- Dilts et al. (1980), p. 36: "The basic elements from which the patterns of human behaviour are formed are the perceptual systems through which the members of the species operate on their environment: vision (sight), audition (hearing), kinesthesis (body sensations) and olfaction/gustation (smell/taste). The neurolinguistic programming model presupposes that all of the distinctions we as human beings are able to make concerning our environment (internal and external) and our behaviour can be usefully represented in terms of these systems. These perceptual classes constitute the structural parameters of human knowledge. We postulate that all of our ongoing experience can usefully be coded as consisting of some combination of these sensory classes."
- Dilts et al. (1980), p. 7: "NLP presents specific tools which can be applied effectively in any human interaction. It offers specific techniques by which a practitioner may usefully organize and re–organize his or her subjective experience or the experiences of a client in order to define and subsequently secure any behavioural outcome."
- Dilts et al. 1980, pp. 77–80: "Strategies and representations which typically occur below an individual's level of awareness make up what is often called or referred to as the 'unconscious mind'."
- See, for instance, the following:
- Sharpley, 1984 and 1987
- Druckman and Swets, 1988
- Heap, 1988
- von Bergen et al., 1997
- Druckman, 2004
- Witkowski, 2010
- See the following:
- Einspruch and Forman, 1985
- Murray, 2013
- Sturt et al., 2012
- Neuro-Linguistic Programming and Research
- Tosey and Mathison, 2010
- See the following:
- Witkowsi, 2010
- The Skeptic's Dictionary, 2009
- Beyerstein, 1990
- Corballis, in Della Sala and Anderson, 2012
- Singer and Lalich
- Lilienfeld, Lynn and Lohr, 2004
- Della Sala, 2007
- Williams, 2000
- Lum, 2001
- Lilienfeld, Lohr and Morier, 2001
- Dunn, Halonen and Smith, 2008
- Molfese, Segalowitz and Harris, 1988
- For a description of the social influence tactics used by NLP and similar pseudoscientific therapies, see Devilly, 2005
- In 2006, Norcross and colleagues found NLP to be given similar ratings as dolphin-assisted therapy, equine-assisted therapy, psychosynthesis, scared straight programmes, and emotional freedom technique. In 2010, Norcross and colleagues listed it as seventh out of their list of ten most discredited drug and alcohol interventions. Glasner-Edwards and colleagues also identified it as discredited in 2010.
- For more information on the use of neuroscience terms to lend the appearance of credibility to arguments, see Weisburg et al., 2008
References
Citations
- Tosey, Paul; Mathison, Jane. "Introducing Neuro-Linguistic Programming" (PDF). Centre for Management Learning & Development, School of Management, University of Surrey. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- Dilts et al. 1980, p. 2.
- Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: Bandler, Richard (2008). What is NLP? (Promotional video). NLP Life. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
We can reliably get rid of a phobia in ten minutes – every single time.
- Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001, Chapter 4: Personal Antecedents of NLP.
- Bandler & Grinder 1975, pp. 5–6.
- Dowlen, Ashley (1 January 1996). "NLP – help or hype? Investigating the uses of neuro-linguistic programming in management learning". Career Development International. 1 (1): 27–34. doi:10.1108/13620439610111408.
- ^ von Bergen, C. W.; Gary, Barlow Soper; Rosenthal, T.; Wilkinson, Lamar V. (1997). "Selected alternative training techniques in HRD". Human Resource Development Quarterly. 8 (4): 281–294. doi:10.1002/hrdq.3920080403.
- Thyer, Bruce A.; Pignotti, Monica G. (2015). Science and Pseudoscience in Social Work Practice. Springer Publishing Company. pp. 56–57, 165–167. ISBN 978-0-8261-7769-8.
As NLP became more popular, some research was conducted and reviews of such research have concluded that there is no scientific basis for its theories about representational systems and eye movements.
- ^ Sharpley, Christopher F. (1 January 1987). "Research findings on neurolinguistic programming: Nonsupportive data or an untestable theory?". Journal of Counseling Psychology. 34 (1): 103–107. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.34.1.103.
- ^ Witkowski, Tomasz (1 January 2010). "Thirty-Five Years of Research on Neuro-Linguistic Programming. NLP Research Data Base. State of the Art or Pseudoscientific Decoration?". Polish Psychological Bulletin. 41 (2). doi:10.2478/v10059-010-0008-0.
All of this leaves me with an overwhelming impression that the analyzed base of scientific articles is treated just as theater decoration, being the background for the pseudoscientific farce which NLP appears to be. Using "scientific" attributes, which is so characteristic of pseudoscience, is manifested also in other aspects of NLP activities... My analysis leads undeniably to the statement that NLP represents pseudoscientific rubbish
- ^ Druckman, Daniel (1 November 2004). "Be All That You Can Be: Enhancing Human Performance". Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 34 (11): 2234–2260. doi:10.1111/j.1559-1816.2004.tb01975.x.
- Bandler & Grinder 1975, p. 6; Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001, Chapter 2: Terminology.
- Bandler & Grinder 1979, p. 8.
- ^ Bandler & Grinder 1975, p. 6.
- ^ Stollznow, Karen (2010). "Not-so Linguistic Programming". Skeptic. 15 (4): 7. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- Wake, Lisa (2008). Neurolinguistic psychotherapy: a postmodern perspective. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-42541-4.
- ^ Clancy, Frank; Yorkshire, Heidi (1989). "The Bandler Method". Mother Jones. 14 (2): 22–28. ISSN 0362-8841. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- John Grinder, Suzette Elgin (1973). "A Guide to Transformational Grammar: History, Theory, Practice." Holt, Rinehart and Winston. ISBN 0-03-080126-5. Reviewed by Frank H. Nuessel, Jr. The Modern Language Journal, Vol. 58, No. 5/6 (September–October 1974), pp. 282–283
- ^ Bradley, E. Jane; Biedermann, Heinz-Joachim (1 January 1985). "Bandler and Grinder's neurolinguistic programming: Its historical context and contribution". Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training. 22 (1): 59–62. doi:10.1037/h0088527. ISSN 0033-3204. OCLC 1588338.
- ^ Spitzer, Robert (1992). "Virginia Satir & Origins of NLP" (PDF). Anchor Point Magazine (July): ?. Retrieved 5 June 2013.
- Bandler & Grinder 1982, p. 240.
- Bandler & Grinder 1981.
- Mercer, Jean (2015). "Controversial Therapies". In Cautin, Robin L.; Lilienfeld, Scott O. (eds.). The Encyclopedia of Clinical Psychology, Volume II. John Wiley & Sons. p. 759. doi:10.1002/9781118625392.wbecp515. ISBN 978-0-4706-7127-6.
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, p. 304.
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, pp. 300–301.
- Bandler, Richard (1997). "NLP Seminars Group – Frequently Asked Questions". NLP Seminars Group. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 8 August 2013.
- Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001.
- Grinder, John (July 1996). "1996 Interview with John Grinder PhD, co-creator of NLP". Inspiritive. Interviewed by Chris Collingwood and Jules Collingwood. Archived from the original on 28 April 2013. Retrieved 8 August 2013.
- ^ Carroll, R. T. (23 February 2009). "Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP)". The Skeptic's Dictionary. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- Hadnagy, Christopher; Wilson, Paul (2010). Social Engineering. John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN 978-0-470-63953-5. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
- Salerno, Steve (2006). Sham: How the Self-Help Movement Made America Helpless. Crown Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-4000-5410-7.
- Bandler & Grinder 1976, pp. 3–8.
- Dilts et al. 1980, p. 7.
- Grinder, John; Bandler, Richard (1977). Patterns of the Hypnotic Techniques of Milton H. Erickson: Volume 2 (1st ed.). Meta Publications. pp. 11–19. ISBN 978-1-55552-053-3.
- Bandler & Grinder 1979, pp. 5–78; Bandler & Grinder 1981, pp. 240–50; Hall & Belnap 2000, pp. 39–40, #2 Pacing Or Matching Another's Model of the World; Hall & Belnap 2000, pp. 89–93, #23 The Change Personal History Pattern; Hall & Belnap 2000, pp. 93–95, #24 The Swish Pattern.
- Bandler & Grinder 1975, p. 6; Bandler & Grinder 1979, pp. 7, 9, 10, 36, 123; Dilts et al. 1980, pp. 35, 78; Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001, pp. 1, 10, 28, 34, 189, 227–28.
- ^ Steinbach, A. M. (1984). "Neurolinguistic Programming: A Systematic Approach to Change". Canadian Family Physician Medecin de Famille Canadien. 30: 147–150. PMC 2153995. PMID 21283502.
- Bandler & Grinder 1979, pp. 8, 15, 24, 30, 45, 52, 149.
- Bandler 1985, pp. 134–3.
- Masters, B.; Rawlins, M.; Rawlins, L.; Weidner, J. (1991). "The NLP swish pattern: An innovative visualizing technique". Journal of Mental Health Counseling. 13 (1): 79–90.
- ^ Russell J; Rovere A, eds. (2009). "Neuro-linguistic programming". American Cancer Society Complete Guide to Complementary and Alternative Cancer Therapies (2nd ed.). American Cancer Society. pp. 120–22. ISBN 9780944235713.
- Rubin Battino (2002) Expectation: The Very Brief Therapy Book. Crown House Publishing. ISBN 1-84590-028-6
- Kerry, S. (2009) Pretreatment expectations of psychotherapy clients, University of Alberta (Canada)
- ^ Beyebach, M.; Rodríguez Morejón, A. (1999). "Some thoughts on integration in solution-focused therapy". Journal of Systemic Therapies. 18: 24–42. doi:10.1521/jsyt.1999.18.1.24.
- Bill O'Connell (2005) Solution-focused therapy (Brief therapy series). Sage; Second Edition p. 9
- Windy Dryden (2007) Dryden's handbook of individual therapy. 5th edition. Sage. ISBN 1-4129-2238-0 p. 382
- Pesut, Daniel J. (1 January 1991). "The art, science, and techniques of reframing in psychiatric mental health nursing". Issues in Mental Health Nursing. 12 (1): 9–18. doi:10.3109/01612849109058206. PMID 1988384.
- Maag 1999; Maag 2000.
- Bandler & Grinder 1982 as cited in Maag 1999 and Maag 2000.
- Field, E. S. (1990). "Neurolinguistic programming as an adjunct to other psychotherapeutic/hypnotherapeutic interventions". The American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis. 32 (3): 174–82. doi:10.1080/00029157.1990.10402822. PMID 2296919.
- Bridoux, D., Weaver, M., (2000) "Neuro-linguistic psychotherapy." In Therapeutic perspectives on working with lesbian, gay and bisexual clients. Davies, Dominic (Ed); Neal, Charles (Ed). (pp. 73–90). Buckingham, England: Open University Press (2000) xviii, 187 pp. ISBN 0-335-20333-7
- ^ Sturt 2012.
- Briers, Stephen (27 December 2012). Brilliant Cognitive Behavioural Therapy: How to use CBT to improve your mind and your life. Pearson UK. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-273-77849-3.
- Eisner, Donald A. (2000). The Death of Psychotherapy: From Freud to Alien Abductions. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 158–59. ISBN 978-0-275-96413-9.
- Weitzenhoffer 1989, p. 305.
- Dilts, Robert; DeLozier, Judith (2000). Encyclopedia of Systemic Neuro-Linguistic Programming and NLP New Coding (1st ed.). Santa Cruz: NLP University Press. p. 1002. ISBN 978-0-9701540-0-2. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- Briers, Stephen (2012). "MYTH 16: There is no failure, only feedback". Psychobabble: Exploding the myths of the self-help generation (1st ed.). Santa Cruz: Pearson Education Limited. ISBN 978-0-273-77239-2.
- Gass, Robert H; Seiter, John S (6 April 2022). Persuasion: Social Influence and Compliance Gaining. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-000-55677-3.
- Zastrow, C. (1990). "Social Workers and Salesworkers". Journal of Independent Social Work. 4 (3): 7–16. doi:10.1300/J283v04n03_02.
- Tosey P. & Mathison, J., "Fabulous Creatures of HRD: A Critical Natural History of Neuro-Linguistic Programming", University of Surrey Paper presented at the 8th International Conference on Human Resource Development Research & Practice across Europe, Oxford Brookes Business School, 26–28 June 2007
- Yemm, Graham (1 January 2006). "Can NLP help or harm your business?". Industrial and Commercial Training. 38 (1): 12–17. doi:10.1108/00197850610645990.
- Ingalls, Joan S. (1988) "Cognition and athletic behavior: An investigation of the NLP principle of congruence." Dissertation Abstracts International. Vol 48(7-B), p. 2090. OCLC 42614014
- "Neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) explained". IONOS Startupguide. Retrieved 4 April 2022.
- ^ Devilly, Grant J. (1 June 2005). "Power Therapies and possible threats to the science of psychology and psychiatry". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 39 (6): 437–45. doi:10.1080/j.1440-1614.2005.01601.x. PMID 15943644. S2CID 208627667.
- Gelso, C. J.; Fassinger, R. E. (1 January 1990). "Counseling Psychology: Theory and Research on Interventions". Annual Review of Psychology. 41 (1): 355–86. doi:10.1146/annurev.ps.41.020190.002035. PMID 2407174.
Neurolinguistic programming, focused on such variables as sensory mode preference and use (e.g., Graunke & Roberts 1985) and predicate matching (e.g., Elich et al 1985; Mercier & Johnson 1984) had shown promise at the beginning of the decade, but after several years of conflicting and confusing results, Sharpley (1984, 1987) reviewed the research and concluded that there was little support for the assumptions of NLP. This research is now clearly on the decline, underscoring the value of thoughtful reviews and the publication of nonsupportive results in guiding empirical efforts.
- Sharpley, Christopher F. (1984). "Predicate matching in NLP: a review of research on the preferred representational system". Journal of Counseling Psychology. 31 (2): 238–48. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.31.2.238.
- Druckman, D.; Swets, J., eds. (1 January 1988). "8: Social Processes". Enhancing Human Performance: Issues, Theories, and Techniques. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. pp. 138–149. doi:10.17226/1025. ISBN 978-0-309-03792-1.
- Heap, M. (1988). "Hypnosis: Current clinical, experimental and forensic practices". Neurolinguistic programming – an interim verdict (PDF). London: Croom Helm. pp. 268–280. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2007.
- Einspruch, Eric L.; Forman, Bruce D. (1 January 1985). "Observations concerning research literature on neuro-linguistic programming". Journal of Counseling Psychology. 32 (4): 589–96. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.32.4.589.
- Murray, Laura L. (30 May 2013). "Limited evidence that neurolinguistic programming improves health-related outcomes". Evidence-Based Mental Health. 16 (3): 79. doi:10.1136/eb-2013-101355. PMID 23723409. S2CID 150295.
- "Neuro-Linguistic Programming and Research". Archived from the original on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
- Tosey, P.; Mathison, J. (2010). "Exploring inner landscapes through psychophenomenology: The contribution of neuro-linguistic programming to innovations in researching first person experience" (PDF). Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management. 5: 63–82. doi:10.1108/17465641011042035. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2018. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ^ Beyerstein, B. L. (1990). "Brainscams: Neuromythologies of the New Age". International Journal of Mental Health. 19 (3): 27–36 (27). doi:10.1080/00207411.1990.11449169.
- Corballis, Michael C. (2012). "Chapter 13 Educational double-think". In Della Sala, Sergio; Anderson, Mike (eds.). Neuroscience in Education: The good, the bad, and the ugly (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 225–26. ISBN 978-0-19-960049-6.
The notion of hemisphericity is also incorporated into such cult activities as Neuro Linguistic Programming (NLP).... In any event, NLP is a movement that is still going strong, but has little scientific credibility.
- Singer, Margaret & Lalich, Janja (1997). Crazy Therapies: What Are They? Do They Work? Jossey Bass, pp. 167–95 (169). ISBN 0-7879-0278-0.
- (Eds.) Lilienfeld, S., Lynn, S., & Lohr, J. (2004). Science and Pseudo-science in Clinical Psychology. The Guilford Press.
- Della Sala, Sergio (2007). "Introduction: The myth of 10% and other Tall Tales about the mind and brain". Tall Tales About the Mind and Brain: Separating Fact from Fiction (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. xx. ISBN 978-0-19-856876-6.
- William F. Williams, ed. (2000), Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience: From Alien Abductions to Zone Therapy, Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, ISBN 978-1-57958-207-4 p. 235
- ^ Lum, C. (2001). Scientific Thinking in Speech and Language Therapy. Psychology Press. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-8058-4029-2.
- ^ Lilienfeld, Scott O.; Lohr, Jeffrey M.; Morier, Dean (1 July 2001). "The Teaching of Courses in the Science and Pseudoscience of Psychology: Useful Resources". Teaching of Psychology. 28 (3): 182–91. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1001.2558. doi:10.1207/S15328023TOP2803_03. S2CID 145224099.
- ^ Dunn D, Halonen J, Smith R (2008). Teaching Critical Thinking in Psychology. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 12. ISBN 978-1-4051-7402-2.
- Harris, Lauren Julius (1988). "Chapter 8 Right-Brain Training: Some Reflections on the Application of Research on Cerebral Hemispheric Specialization to Education". In Molfese, Dennis L.; Segalowitz, Sidney J. (eds.). Brain Lateralization in Children: Developmental Implications (1st ed.). New York: Guilford Press. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-89862-719-0.
NLP began in 1975 and has quickly achieved cult status.
- ^ Roderique-Davies, G. (2009). "Neuro-linguistic programming: Cargo cult psychology?". Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education. 1 (2): 58–63. doi:10.1108/17581184200900014.
- Rowan, John (December 2008). "NLP is not based on constructivism". The Coaching Psychologist. 4 (3): 160–163. doi:10.53841/bpstcp.2008.4.3.160. ISSN 1748-1104. S2CID 255903130.
- Norcross, John C.; Koocher, Gerald P.; Garofalo, Ariele (1 January 2006). "Discredited psychological treatments and tests: A Delphi poll". Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 37 (5): 515–22. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.37.5.515. S2CID 35414392.
- Norcross, John C.; Koocher, Gerald P.; Fala, Natalie C.; Wexler, Harry K. (1 September 2010). "What Does Not Work? Expert Consensus on Discredited Treatments in the Addictions". Journal of Addiction Medicine. 4 (3): 174–180. doi:10.1097/ADM.0b013e3181c5f9db. PMID 21769032. S2CID 41494642.
- Glasner-Edwards, Suzette; Rawson, Richard (1 October 2010). "Evidence-based practices in addiction treatment: Review and recommendations for public policy". Health Policy. 97 (2–3): 93–104. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.05.013. PMC 2951979. PMID 20557970.
- ^ Tye, Marcus J.C. (1994). "Neurolinguistic programming: Magic or myth?". Journal of Accelerative Learning & Teaching. 19 (3–4): 309–42. ISSN 0273-2459. 2003-01157-001.
- Levelt, Willem J.M (1996). "u voor neuro-linguistische programmering". Skepter (in Dutch). 9 (3).
- Corballis, M.C. (1999). "Are we in our right minds?". In S.D. Sala (ed.). Mind Myths: Exploring Popular Assumptions About the Mind and Brain (Repr. ed.). Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-471-98303-3.
- Drenth, Pieter J.D (2003). "Growing anti-intellectualism in Europe; a menace to science" (PDF). Studia Psychologica. 45: 5–13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2011.
- Weisberg, D. S.; Keil, F. C.; Goodstein, J.; Rawson, E.; Gray, J. R. (2008). "The Seductive Allure of Neuroscience Explanations". Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 20 (3): 470–77. doi:10.1162/jocn.2008.20040. PMC 2778755. PMID 18004955.
- Cresswell & Wilson 1999, p. 64; Edwards 2001, p. 573; Clarke 2006, pp. 440–41; Walker 2007, p. 235; Hammer & Rothstein 2012, p. 247.
- Langford 1999.
- Grinder & DeLozier 1987, p. ; Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001, p. .
- Grimley 2013, p. 31.
- Fanthorpe & Fanthorpe 2008, p. 112.
- Hunt 2003.
- Aupers & Houtman 2010, p. .
- ^ Bovbjerg 2011, p. .
- Jeremiah 1995.
- Not Ltd v. Unlimited Ltd et al (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County, 1981, No. 78482) (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County 29 October 1981), Text.
- ^ "Summary of the Legal Proceedings January 1997 – June 23, 2003". Archived from the original on 10 April 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- Richard W Bandler et al v. Quantum Leap Inc. et al (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County, 2000, No. 132495) (Super. Ct. Santa Cruz County 10 February 2000), Text.
- "NLP Matters 2". Archived from the original on 10 February 2001. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- "NLP Matters". Archived from the original on 6 April 2001. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- "Case details for trade mark UK00002067188". 13 June 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2015.
- Grinder & Bostic St. Clair 2001, Appendix A.
- Hall 2010.
- "3.5. Who Owns NLP?". NLP Archives – Frequently Asked Questions about NLP. Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- "This page contains the ruling in the case of Richard Bandler against many others in the NLP community". NLP Archives – Frequently Asked Questions about NLP. Archived from the original on 27 June 2013. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ^ "75351747". Trademark Status and Document Retrieval. United States Patent and Trademark Office. 13 June 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ^ "73253122". Trademark Status and Document Retrieval. United States Patent and Trademark Office. 13 June 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- "NLP FAQ". 27 July 2001. Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- "NLP Comprehensive Lawsuit Response". Archived from the original on 17 July 2019. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- Moxom, Karen (2011). "Three: Demonstrating Best Practice". The NLP Professional: Create a More Professional, Effective and Successful NLP Business. Herts: Ecademy Press. pp. 46–50. ISBN 978-1-907722-55-4.
- "Cat registered as hypnotherapist". BBC. 12 October 2009. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
Works cited
- Primary sources
- Bandler, Richard; Grinder, John (1975). The Structure of Magic I: A Book about Language and Therapy. Science and Behavior Books Inc. ISBN 978-0-8314-0044-6.
- Bandler, Richard; Grinder, John (1976). The Structure of Magic II (1st ed.). California: Science and Behavior Books. ISBN 978-0-8314-0049-1.
- Bandler, Richard; Grinder, John (1979). Andreas, Steve (ed.). Frogs into Princes: Neuro Linguistic Programming. Utah: Real People Press. ISBN 978-0-911226-19-5.
- Bandler, Richard; Grinder, John (1981). "Appendix II: Hypnotic Language Patterns: The Milton-Model". Trance-formations: Neuro-linguistic Programming and the Structure of Hypnosis. Real People Press. ISBN 978-0-911226-22-5.
- Bandler, Richard; Grinder, John (1982). Reframing: Neuro-Linguistic Programming and the Transformation of Meaning. Real People Press. ISBN 0-911226-25-7.
- Bandler, Richard (1985). Andreas, Steve; Andreas, Connirae (eds.). Using Your Brain–for a Change. Real People Press. ISBN 0-911226-27-3.
- Bandler, Richard (1993). Time for a Change. Meta Publications. ISBN 978-0-916990-28-2.
- Dilts, Robert; Grinder, John; Bandler, Richard; DeLozier, Judith (1980). Neuro-Linguistic Programming. Vol. I: The Study of the Structure of Subjective Experience (Limited ed.). California: Meta Publications. ISBN 978-0-916990-07-7.
- Grinder, John; DeLozier, Judith (1987). Turtles All The Way Down: Prerequisites To Personal Genius (1st ed.). California: Grinder & Associates. ISBN 978-1-55552-022-9.
- Grinder, John; Bostic St. Clair (2001). Whispering in the Wind. J & C Enterprises. ISBN 978-0-9717223-0-9.
- Secondary sources
- Aupers, Stef; Houtman, Dick, eds. (2010). "Religions of Modernity: Relocating the Sacred to the Self and the Digital". International Studies in Religion and Society (1st ed.). Leiden: Brill: 115–132. ISBN 978-90-04-18451-0. ISSN 1573-4293.
- Bovbjerg, Kirsten Marie (1 May 2011). "Personal Development under Market Conditions: NLP and the Emergence of an Ethics of Sensitivity Based on the Idea of the Hidden Potential of the Individual". Journal of Contemporary Religion. 26 (2): 189–205. doi:10.1080/13537903.2011.573333. ISSN 1353-7903. S2CID 145148234.
- Clarke, Peter B., ed. (2006). Encyclopedia of New Religious Movements (1st ed.). London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-48433-3.
- Cresswell, Jamie; Wilson, Bryan, eds. (1999). New Religious Movements: Challenge and Response (1st ed.). London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-20049-3.
- Edwards, Linda (2001). A Brief Guide to Beliefs: Ideas, Theologies, Mysteries, and Movements (1st ed.). Kentucky: Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 978-0-664-22259-8.
- Fanthorpe, Lionel; Fanthorpe, Patricia (2008). Mysteries and Secrets of Voodoo, Santeria, and Obeah (1st ed.). New Jersey: New Page Books. ISBN 978-1-55002-784-6.
- Grimley, Bruce (2013). Theory and Practice of NLP Coaching: A Psychological Approach (1st ed.). London: Sage Publications Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4462-0172-5.
- Hall, L. Michael; Belnap, Barbara P. (2000) . The Sourcebook of Magic: A Comprehensive Guide to the Technology of NLP. Wales: Crown House Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-899836-22-2.
- Hall, L. Michael (20 September 2010). "The lawsuit that almost killed NLP". Archived from the original on 27 June 2013. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- Hammer, Olav; Rothstein, Mikael, eds. (2012). The Cambridge Companion to New Religious Movements (1st ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-14565-7.
- Hunt, Stephen J. (2003). Alternative Religions: A Sociological Introduction. Hampshire: Ashgate Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-0-7546-3410-2.
- Jeremiah, David (1995). "Chapter 9: Corporate Takeovers". Invasion of Other Gods: The Seduction of New Age Spirituality (1st ed.). W Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-8499-3987-7.
- Langford, Jean M. (February 1999). "Medical Mimesis: Healing Signs of a Cosmopolitan "Quack"". American Ethnologist. 26 (1): 24–46. doi:10.1525/ae.1999.26.1.24. JSTOR 647497.
- Maag, John W. (1999). "Why they say no: Foundational precises and techniques for managing resistance" (PDF). Focus on Exceptional Children. 32: 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- Maag, John W. (2000). "Managing resistance". Intervention in School and Clinic. 35 (3): 3. doi:10.1177/105345120003500301. S2CID 220927708.
- Sturt, Jackie; et al. (November 2012). "Neurolinguistic programming: a systematic review of the effects on health outcomes". British Journal of General Practice. 62 (604): e757–64. doi:10.3399/bjgp12X658287. PMC 3481516. PMID 23211179. 23211179.
- Walker, James K. (2007). The Concise Guide to Today's Religions and Spirituality (1st ed.). Oregon: Harvest House Pubslishers. ISBN 978-0-7369-2011-7.
- Weitzenhoffer, André Muller (1989). "Chapter 8: Ericksonian Hypnotism: The Bandler/Grinder Interpretation". The Practice of Hypnotism. Vol. 2: Applications of Traditional an Semi-Traditional Hypnotism. Non-Traditional Hypnotism. New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-62168-3.
Further reading
- Andreas, Steve; Faulkner, Charles, eds. (1996). NLP: the new technology of achievement. New York: HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-688-14619-1.
- Austin, A. (2007). The Rainbow Machine: Tales from a Neurolinguist's Journal. UK: Real People Press. ISBN 978-0-911226-44-7.
- Bandler, R.; Grinder, J.; Satir, V. (1976). Changing with Families: A Book about Further Education for Being Human. Science and Behavior Books. ISBN 0-8314-0051-X.
- Bradbury, A. (2008). "Neuro-Linguistic Programming: Time for an Informed Review". Skeptical Intelligencer. 11.
- Burn, Gillian (2005). NLP Pocketbook. Alresford, United Kingdom: Management Pocketbooks Ltd. ISBN 978-1-903776-31-5.
- Dilts, R. (1990). Changing Belief Systems with NLP. Meta Publications. ISBN 978-0-916990-24-4.
- Dilts, R.; Hallbom, Tim; Smith, Suzi (1990). Beliefs: Pathways to Health & Well-being. Crown House Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84590-802-7.
- Dunning, Brian (26 May 2009). "Skeptoid #155: NLP: Neuro-linguistic Programming". Skeptoid.
- Ellerton, Roger (2005). Live Your Dreams, Let Reality Catch Up: NLP and Common Sense for Coaches, Managers and You. Ottawa, Canada: Trafford Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4120-4709-8.
- Grinder, M. (1991). Righting the Educational Conveyor Belt. Metamorphous Press. ISBN 1-55552-036-7.
- O'Connor, Joseph (2007). Not Pulling Strings: Application of Neuro-Linguistic Programming to Teaching and Learning Music. London: Kahn & Averill. ISBN 978-1-871082-90-6.
- Platt, Garry (2001). "NLP – Neuro Linguistic Programming or No Longer Plausible?". Training Journal. May. 2001: 10–15.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Neuro-linguistic programming at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Neuro-linguistic programming at Wiktionary Media related to Neuro-linguistic programming at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Neuro-linguistic programming at Wikimedia Commons Quotations related to Neuro-linguistic programming at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Neuro-linguistic programming at Wikiquote
| Seduction community | |
|---|---|
| Concepts | |
| Key people | |
| Media | |