| Revision as of 14:26, 2 May 2013 view sourceNorth8000 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers84,829 edits Undid revision 553201507 by Goethean (talk) wp:rs coverage of a common point of view. Also under discussion, this is appears to be attempt to preempt that .← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:00, 18 December 2024 view source Maxeto0910 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users94,929 editsNo edit summaryTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Laws or policies that regulate firearms}} | |||
| {{Merge to|Gun politics|date=April 2013}} | |||
| {{About||international arms restrictions|Arms control|techniques for the safe handling, possession, and storage of firearms|Gun safety|the debate about gun control in the U.S.|Gun politics in the United States}} | |||
| {{pp-move|reason=]: Gun control case authority. Page should not be moved without consensus via an RM.|small=yes}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | {{pp-semi-indef}} | ||
| {{use dmy dates|cs1-dates=ly|date=June 2021}} | |||
| {{Gun politics by country}} | |||
| ]{{efn|name="sydney"}} (April 2022) | |||
| '''Gun control''' is any law, policy, practice, or proposal designed to restrict or limit the possession, production, importation, shipment, sale, and/or use of ]s. | |||
| {{legend|#00137F|Permissive}} | |||
| {{legend|#FF0000|Restrictive}} | |||
| {{legend|#C0C0C0|Not included}}]] | |||
| '''Gun control''', or '''firearms regulation''', is the set of laws or policies that regulate the manufacture, sale, transfer, possession, modification, or use of ]s by civilians.<ref>Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (2005). {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210424054342/https://www.atf.gov/file/58686/download |date=2021-04-24 }} U.S. Department of Justice. Retrieved: January 3, 2016.</ref><ref>{{Cite web| url=https://www.loc.gov/law/help/firearms-control/| title=Firearms-Control Legislation and Policy| website=]| access-date=2016-03-22 | archive-date=2022-05-30 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220530145418/https://www.loc.gov/collections/publications-of-the-law-library-of-congress/about-this-collection/| url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Gun control laws and policies vary greatly around the world. Some countries, such as the ], have very strict limits on gun possession while others, such as the ], have relatively modest limits. In some countries, the topic remains a source of intense debate with proponents generally arguing the dangers of widespread gun ownership. Opponents have argued that gun control does not reduce gun-related injuries, murder, or suicide, that gun control is an instrument of repression used by totalitarian governments, and that such regulation would violate individual liberties, including the right of self-protection and resistance against state-sponsored genocide. | |||
| Most countries allow civilians to own firearms, but have strong firearms laws to prevent violence. Only a few countries, such as ], ] and the ] are categorized as permissive.{{efn|name="sydney"|{{as of|2022|April}}, the only countries with permissive gun legislation are: Chad, the Republic of Congo, Honduras, Micronesia, Namibia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Senegal, Switzerland, Tanzania, the United States, Yemen, and Zambia.}}<ref>{{cite web |last1=Alpers |first1=Philip |last2=Wilson |first2=Marcus |title=Guns in the United Nations: Firearm Regulation - Guiding Policy |publisher=Sydney School of Public Health, The University of Sydney |url=https://www.gunpolicy.org/firearms/compare/193/firearm_regulation_-_guiding_policy/3,6,7,8,10,11,12,13,16,17,18,19,22,26,27,28,217,29,30,218,31,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,222,52,56,57,58,60,61,62,64,65,66,69,71,72,74,75,77,78,79,81,82,83,86,90,91,94,95,233,99,100,102,234,104,105,107,108,110,111,112,236,238,113,114,116,241,118,121,122,123,125,128,129,131,136,137,139,140,142,143,144,145,146,148,149,150,152,153,154,155,158,159,162,163,247,164,166,170,172,174,249,251,175,252,177,178,180,182,183,54,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,192,194,195,197,199,200,204,205,206,15,120,173 |access-date=August 27, 2016 |date=9 June 2020 |via=GunPolicy.org |archive-date=2021-04-18 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210418071137/https://www.gunpolicy.org/firearms/compare/193/firearm_regulation_-_guiding_policy/3,6,7,8,10,11,12,13,16,17,18,19,22,26,27,28,217,29,30,218,31,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,222,52,56,57,58,60,61,62,64,65,66,69,71,72,74,75,77,78,79,81,82,83,86,90,91,94,95,233,99,100,102,234,104,105,107,108,110,111,112,236,238,113,114,116,241,118,121,122,123,125,128,129,131,136,137,139,140,142,143,144,145,146,148,149,150,152,153,154,155,158,159,162,163,247,164,166,170,172,174,249,251,175,252,177,178,180,182,183,54,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,192,194,195,197,199,200,204,205,206,15,120,173 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Jurisdictions that regulate civilian access to firearms typically restrict ownership of certain lethal firearms, and require a mandatory gun safety course or ] to own or carry a weapon. | |||
| In some countries, such as ], gun control measures can be implemented at the national, state, or local levels. | |||
| {{TOC limit}} | |||
| ==Terminology and context== | ==Terminology and context== | ||
| {{See also|Small arms trade|Small arms and light weapons}} | |||
| ] ]s about to be set ablaze in ], ]]] | |||
| Gun control refers to domestic and international attempts to regulate, and harmonize the regulation of, the private and industrial manufacture, trade, possession, use, and transport of a class of weapons typically identified as ]. This class of arms commonly includes ]s, self-loading ], ]s and ]s, so-called ]s, and some categories of ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unodc.org/documents/organized-crime/Firearms/ITI.pdf |title=International Instrument to Enable States to Identify and Trace, in a Timely and Reliable Manner, Illicit Small Arms and Light Weapon |date=February 25, 2013 |website=unodc.org |publisher=United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime |access-date=February 14, 2014 |archive-date=2020-11-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201111202349/http://www.unodc.org/documents/organized-crime/Firearms/ITI.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Definitions of Small Arms and Light Weapons |url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/weapons-and-markets/definitions.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110619030929/http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/weapons-and-markets/definitions.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=19 June 2011 |date=April 15, 2013 |publisher=Small Arms Survey|access-date=February 10, 2014}}</ref> | |||
| The concept of ''gun control'' is a subset of a much greater, yet equally global, topic, ''arms control''. | |||
| {{main|Arms control}} | |||
| In the context of this article, the concept of ''gun control'' is in reference to various means of restrictions on the use, transport, and possession of firearms. Specifically with regard to the class of weapons referred to as ''small arms''. On a global scale this context is sometimes expanded to include ''light weapons''; also known in the arms trade as ]. | |||
| {{main|Small arms}} | |||
| From the perspective of military small arms, this encompasses: ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s (e.g. M60), and sometimes ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, and ] may be considered small arms or as support weapons, depending on the particular armed forces. Other groups utilizing these types of arms may also include government sanctioned non-military personnel such as ]. | |||
| In the United States, the term ''gun control'' itself is considered politicized.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/01/word-choice-and-gun-culture/423108/ | title=How 'Gun Control' Became a Taboo Phrase | website=The Atlantic | date=11 January 2016 | access-date=29 March 2016 | author=LaFrance, Adrienne | archive-date=2017-01-17 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170117075444/http://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/01/word-choice-and-gun-culture/423108/ | url-status=live }}</ref> Many gun control advocates prefer the use of terms like "gun-violence prevention", "gun safety", or "common-sense regulation" to describe their objectives.<ref>Ball, Molly (January 2013). {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210417074045/https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2013/01/dont-call-it-gun-control/267259/ |date=2021-04-17 }} ''The Atlantic.'' Retrieved: September 24, 2016.</ref> | |||
| From a civilian (meaning via private, individual ownership) perspective and varying via legislation from country to country this encompasses a subset of the above list. Usually limited to: ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]s. | |||
| In 2007, a global supply of 875 million small arms were estimated to be in the hands of civilians, law enforcement agencies, and national armed forces.{{efn|This figure excludes older, pre-automatic small arms from military and law enforcement stockpiles or 'craft-produced' civilian firearms.{{sfn|Karp|2007|p=39}}}}{{sfn|Karp|2007|p=39}} Of these firearms, 650 million, or 75%, were estimated to be held by civilians.{{sfn|Karp|2007|p=39}} U.S. civilians account for 270 million of this total.{{sfn|Karp|2007|p=39}} A further 200 million are controlled by national military forces.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=102|ps=}} Law enforcement agencies may have some 26 million small arms.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=102|ps=}} Non-state armed groups{{efn|Composed of 'insurgents and militias, including dormant and state-related groups'.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=101|ps=}}}} have about 1.4 million firearms.{{efn|However, as of 2009, active non-state armed groups, numbering about 285,000 combatants, control only about 350,000 small arms.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=121|ps=}}}}{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=102|ps=}} Finally, gang members hold between 2 and 10 million small arms.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=102|ps=}} Together, the small arms arsenals of non-state armed groups and gangs have been estimated to account for, at most, 1.4% of the global total.{{sfn|Karp|2010|p=101|ps=}} | |||
| Separate, yet integral, to the concept of ''gun control'' are the individuals and companies that comprise the ''global arms industry''. | |||
| {{main|Arms industry}} | |||
| The arms industry is a global ] which ]s ] and ]. It consists of ] ] involved in research, development, production, sale, and transport. Many ] have a domestic arms industry to supply their own military forces. Some countries also have a substantial legal or illegal domestic trade in weapons for use by its citizens. An illegal trade in ] is prevalent in many countries and regions affected by political instability. | |||
| ==Regulation of civilian firearms== | |||
| == History == | |||
| With few exceptions,{{efn|], ], and ] (Republic of China) prohibit civilian ownership of firearms in almost all instances. Eritrea and Somalia also prohibit civilian possession of firearms as part of their implementation of the UN Programme of Action on Small Arms. In the Solomon Islands, civilian firearm ownership is restricted to members of the Regional Assistance Mission.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=62 n. 1|ps=}}}} most countries in the world actually allow some form of civilian firearm ownership.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=1|ps=}} A 2011 survey of 28 countries over five continents{{efn|The survey, carried out by the ] included 28 countries (42 jurisdictions in total). The countries included in the sample were: | |||
| * Africa: Egypt, Kenya, South Africa, Uganda; | |||
| * Americas: Belize, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Dominican Republic, United States, Venezuela; | |||
| * Asia: India, Israel, Japan, Kazakhstan, Singapore, Turkey, Yemen; | |||
| * Europe: Croatia, Estonia, Finland, Lithuania, Russian Federation, Switzerland, United Kingdom; | |||
| * Oceania: Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=2|ps=}} | |||
| The study states that "while the sample is diverse and balanced, it may not be representative of the systems in place in countries outside the sample".{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=62 n. 4|ps=}}}} found that a major distinction between different national gun control regimes is whether civilian gun ownership is seen as a right or a privilege.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=36|ps=}} The study concluded that both the United States and ] were distinct from the other countries surveyed in that they viewed gun ownership as a basic right of citizenship, and therefore their gun control policies were more permissive.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=36|ps=}} In the remaining countries sampled, civilian gun ownership is considered a privilege and their corresponding gun control policies are more restrictive.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=36|ps=}} | |||
| ===Gun control in Australia=== | |||
| {{Main|Gun politics in Australia}} | |||
| ===International and regional gun control=== | |||
| In response to the ] in 1996, gun law proposals developed from the report of the 1988 National Committee on Violence<ref>{{cite web|url=http://aic.gov.au/publications/proceedings/12/chappell.pdf|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070615151003/http://aic.gov.au/publications/proceedings/12/chappell.pdf|archivedate=2007-06-15|title=PREVENTION OF VIOLENT CRIME: THE WORK OF THE NATIONAL COMMITTEE ON VIOLENCE|author=Duncan Chappell|publisher=}}</ref> were adopted under a National Firearms Agreement. This was necessary because the Australian Constitution does not give the Commonwealth power to enact gun laws. | |||
| At the international and regional level, diplomatic attention has tended to focus on the cross-border illegal trade in small arms as an area of particular concern rather than the regulation of civilian-held firearms.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} During the mid-1990s, however, the ] (ECOSOC) adopted a series of resolutions relating to the civilian ownership of small arms.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} These called for an exchange of data on national systems of firearm regulation and for the initiation of an international study of the issue.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} In July 1997, ECOSOC issued a resolution that underlined the responsibility of UN member states to competently regulate civilian ownership of small arms and which urged them to ensure that their regulatory frameworks encompassed the following aspects: firearm safety and storage; penalties for the unlawful possession and misuse of firearms; a licensing system to prevent undesirable persons from owning firearms; exemption from criminal liability to promote the surrender by citizens of illegal, unsafe or unwanted guns; and, a record-keeping system to track civilian firearms.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} | |||
| The National Firearms Agreement banned all semi-automatic rifles and all semi-automatic and pump-action shotguns, and created a tightly restrictive system of licensing and ownership controls. Because the Australian Constitution prevents the taking of property without just compensation the ] introduced the Medicare Levy Amendment Act 1996 that provided the revenue for the National Firearms Program through a one-off 0.2% increase in the Medicare levy. Known as the gun buy-back scheme, it started across the country on the 1 October 1996 and concluded on the 30 September 1997<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.anao.gov.au/uploads/documents/1997-98_Audit_Report_25.pdf|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20090704044708/http://www.anao.gov.au/uploads/documents/1997-98_Audit_Report_25.pdf|archivedate=2009-07-04|title=The Gun Buy-Back Scheme|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |year=1997 |issn=1036-7632 |isbn=0-644-39080-8}}</ref> to purchase and destroy all semi-automatic rifles including .22 rimfires, semi-automatic shotguns and pump-action shotguns. The buyback was predicted to cost A$500 million and had wide community support. | |||
| In 1997, the UN published a study based on member state survey data titled the ''United Nations International Study on Firearm Regulation'' which was updated in 1999.{{efn|The impetus behind this study was twofold: firstly, there were concerns over the incidence of firearm-related crimes, accidents and suicides; secondly, there was the apprehension that existing regulatory instruments administering the ownership, storage and training in the use of firearms held by civilians might be inadequate.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}}}}{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} This study was meant to initiate the establishment of a database on civilian firearm regulations which would be run by the Centre for International Crime Prevention, located in Vienna. who were to report on national systems of civilian firearm regulation every two years.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} These plans never reached fruition and further UN-led efforts to establish international norms for the regulation of civilian-held firearms were stymied.{{sfn|Parker|2011|pp=3–4|ps=}} Responding to pressure from the U.S. government,{{efn|The US government was opposed to a section of the draft proposal calling on countries 'to seriously consider the prohibition of unrestricted trade and private ownership of small arms and light weapons'.{{sfn|Alley|2004|p=54|ps=}}}}{{sfn|Alley|2004|pp=53–54|ps=}} any mention of the regulation of civilian ownership of small arms was removed from the draft proposals for the 2001 UN Programme of Action on Small Arms.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} | |||
| In 2002, the ] led the federal government to urge ] to again review handgun laws, and, as a result, amended legislation was adopted in all states and territories. Changes included a 10-round ] capacity limit, a calibre limit of not more than .38 inches (9.65 mm), a ] length limit of not less than 120 mm (4.72 inches) for ] and 100 mm (3.94 inches) for revolvers, and even stricter probation and attendance requirements for sporting target shooters.{{Citation needed|date=April 2007}} In the state of ] A$21 million compensation was paid for confiscating 18,124 target pistols, and 15,184 replacement pistols were imported.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} | |||
| Although the issue is no longer part of the UN policy debate, since 1991 there have been eight regional agreements involving 110 countries concerning aspects of civilian firearm possession.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=3|ps=}} The Bamako Declaration,{{efn|The full title is 'The Bamako Declaration on an African Common Position on the Illicit Proliferation, Circulation and Trafficking of Small Arms and Light Weapons (2000)'.{{sfn|Juma|2006|p=39|ps=}}}} was adopted in Bamako, Mali, on 1 December 2000 by the representatives of the member states of the ] (OAU).{{sfn|Juma|2006|p=39|ps=}} The provisions of this declaration recommend that the signatories would establish the illegal possession of small arms and light weapons as a criminal offence under national law in their respective countries.{{sfn|Parker|2011|p=4|ps=}} | |||
| One government policy was to compensate shooters for giving up the sport. Approximately 25% of pistol shooters took this offer, and relinquished their licences and their right to own pistols for sport for five years.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} | |||
| ==Studies== | |||
| There is contention over the effects of the gun control laws in Australia, with some researchers reporting significant drops in gun-related crime,<ref>{{cite journal |last=Ozanne-Smith |first=J |coauthors=, K Ashby, S Newstead, V Z Stathakis and A Clapperton |title=Firearm related deaths: the impact of regulatory reform | |||
| {{POV section|date=October 2022}} | |||
| |journal=Prevention 2004;10:280-286}}</ref> | |||
| {{Globalize|section|date=May 2023|2=USA}} | |||
| <ref>{{cite journal | last=Chapman | first=S | coauthors=, Alpers, P., Agho, K. and Jones, M | title= Australia’s 1996 gun law reforms: faster falls in firearm deaths, firearm suicides, and a decade without mass shootings | journal=Injury Prevention 2006; 12:365-372}}</ref> | |||
| and others reporting no significant effect in gun related or overall crime rates.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Mouzos | |||
| |first=Jenny | |||
| |coauthors=& Reuter, P | |||
| |title=Australia: a massive buyback of low-risk guns | |||
| |volume=Evaluating Gun Policy: Effects on Crime and Violence | |||
| |editor=Ludwig J & Cook PJ | |||
| |publisher= The Brookings Institution, Washington |year=2002 | |||
| }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Baker | |||
| |first=Jeanine | |||
| |coauthors=& McPhedran, Samara | |||
| |title=Gun Laws and Sudden Death: Did the Australian Firearms Legislation of 1996 Make a Difference? | |||
| |journal=British Journal of Criminology | |||
| |volume=<!-- advance access version used. Add in volume when it is published in standard edition--> | |||
| |issue= 3|page=455 | |||
| |date=2006-10-18 | |||
| |url=http://bjc.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/azl084v1 | |||
| |doi=10.1093/bjc/azl084 | |||
| }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Lee | |||
| |first=Wang-Sheng |coauthors=& Suardi, Sandy | |||
| |title=The Australian Firearms Buyback and Its Effect on Gun Deaths | |||
| |journal=Melbourne Institute Working Paper No. 17/08 |isbn=978-0-7340-3285-0 |page=28 | |||
| |publisher=Melbourne Institute |date=2008-8 | |||
| |url=http://www.melbourneinstitute.com/wp/wp2008n17.pdf | |||
| }}{{dead link|date=January 2013}}</ref> | |||
| The primary source of the controversy is that, while the incidence of firearm deaths has decreased considerably since the 1996 restrictions went into effect, the rates had already been falling for the past two decades prior to the new gun laws. An article by David Hemenway argues that these studies were designed to find nothing. Hemenway writes that the authors of these studies carefully chose the period of study to reflect their desired negative results without giving rationale for the time period they choose to show a supposed decline in Australian gun violence. | |||
| <ref>{{cite journal |last=Hemenway | |||
| |first=David | |||
| |title=How to find nothing | |||
| |journal=Journal of Public Health Policy | |||
| |issue=30 |pages=260–268 | |||
| |year=2009 | |||
| |url=http://www.palgrave-journals.com/jphp/journal/v30/n3/pdf/jphp200926a.pdf | |||
| |doi=10.1057/jphp.2009.26 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ===General=== | |||
| ===Gun control in Nazi Germany=== | |||
| A 1998 review found that suicide rates generally declined after gun control laws were enacted, and concluded, "The findings support gun control measures as a strategy for reducing suicide rates."{{sfn|Lambert|Silva|1998}} A 2016 review found that laws banning people under ]s due to ] convictions from accessing guns were associated with "reductions in intimate partner homicide".{{sfn|Zeoli|Malinski|Turchan|2016}} Another 2016 review identified 130 studies regarding restrictive gun laws and found that the implementation of multiple such laws simultaneously was associated with a decrease in gun-related deaths.{{sfn|Santaella-Tenorio et al.|2016}} According to ], "The authors are careful to note that their findings do not conclusively prove that gun restrictions reduce gun deaths. However, they did find a compelling trend whereby new restrictions on gun purchasing and ownership tended to be followed by a decline in gun deaths."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Beauchamp |first=Zack |date=2016-02-29 |title=A huge international study of gun control finds strong evidence that it actually works |url=https://www.vox.com/2016/2/29/11120184/2016-gun-control-study-epidemiologic-reviews-deaths |access-date=2022-10-10 |website=Vox |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| {{Multiple issues|section=yes| | |||
| {{POV-section|date=April 2013}} | |||
| {{Undue-section|date=April 2013}} | |||
| {{Unreliable sources|date=April 2013}} | |||
| }}{{main|Gun politics in Germany}} | |||
| According to a 2011 UN study, after identifying a number of methodological problems, it stated "notwithstanding such challenges, a significant body of literature tends to suggest that firearm availability predominantly represents a risk factor rather than a protective factor for homicide. In particular, a number of quantitative studies tend towards demonstrating a firearm prevalence–homicide association."<ref>{{cite web|year=2011|title=2011 Global Study on Homicide|page=43|publisher=United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime|website=unodc.org|url=https://www.unodc.org/documents/congress/background-information/Crime_Statistics/Global_Study_on_Homicide_2011.pdf|access-date=October 9, 2016|archive-date=2016-04-09 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160409203921/https://www.unodc.org/documents/congress/background-information/Crime_Statistics/Global_Study_on_Homicide_2011.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Among the hundreds of anti-Semitic laws, regulations, and acts of civil violence enacted by ], gun control policies were among those applied selectively to Germans considered Jewish under the Nuremberg Laws.<ref name=Shirer>{{cite book|last=Shirer|first=William|title=The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich|year=1959|publisher=Simon and Schuster|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=sY8svb-MNUwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=isbn:0671728687&hl=en&sa=X&ei=rSKAUcqRHOq-0AGC_IDoDg&ved=0CDIQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false}}</ref><ref name=Harcourt1/><ref name=Rummel>Rummel,RJ, Death by Government (1994) Transaction Publishers, New Jersey, pp. 111-122, ISBN 1-56000-145-3.</ref><ref name=Halbrook/> Hitler's government required the Jewish population to disarm.<ref name=Rummel/><ref name=Halbrook/> Previously, the 1928 ] ''Law on Firearms & Ammunition'' directed that possession of a firearm was "only to be granted to persons of undoubted reliability, and—in the case of a firearms carry permit—only if a demonstration of need is set forth." The Nazi ''Weapons Law'' of March 18, 1938 relaxed gun control requirements for the general population, but prohibited manufacturing of firearms and ammunition by ].<ref name=Harcourt2>Harcourt, Bernard E (2004) , p. 22.</ref> Shortly thereafter, in the additional ''Regulations Against Jews' Possession of Weapons'' of November 11, 1938, Jews were forbidden from possession of any weapons at all.<ref name=Halbrook/><ref name=Harcourt2/> On November 9, 1938 , two days before ] the ''New York Times'' reported that "The Berlin Police President, ], announced that as a result of a police activity in the last few weeks, the entire Jewish population of Berlin had been 'disarmed' with the confiscation of 2,569 hand weapons, 1,702 firearms and 20,000 rounds of ammunition."<ref>{{cite news|title=NAZIS ASK REPRISAL IN ATTACK ON ENVOY; Press Links Shooting in Paris to 'World Conspiracy' and Warns Jews of Retaliation MASS EXPULSIONS FEARED Berlin Police Head Announces 'Disarming' of Jews--Victim of Shots in Critical State New Fear Aroused Round-up in Vienna Diplomat's Condition Critical|url=http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=9404EFDD1331E03ABC4153DFB7678383629EDE&scp=2&sq=Helldorf&st=p|newspaper=New York Times|date=November 9, 1938}}</ref><ref></ref> | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| Stephen Halbrook asserts that "Gun control laws are depicted as benign and historically progressive. However, German firearm laws and hysteria created against Jewish firearm owners played a major role in laying the groundwork for the eradication of German Jewry in the Holocaust."<ref name=Halbrook> Retrieved 2012-12-16</ref> ] writes that Halbrook's pro-gun ideological commitment is so flagrant, that he cannot be "entirely trusted" on historical or statutory debates relating to gun control.<ref name=Harcourt1> Retrieved 2012-12-16</ref> Harcourt writes: "The toughest question in all of this is how to characterize the Nazi treatment of the Jewish population for the purpose of evaluating Adolf Hitler's position on gun control. The truth is, the question itself is absurd. The Nazis sought to disarm and kill the Jewish population. Their treatment of Jewish persons was, in this sense, orthogonal to their gun-control views. Nevertheless, if forced to take a position, it seems that the Nazis were relatively more pro-gun than the predecessor Weimar Republic, as evidenced by the overall relaxation of the laws regulating the acquisition, transfer and carrying of firearms reflected in the 1938 Nazi gun laws." but also said "To be sure, the Nazis were intent on killing Jewish persons and used the gun laws and regulations to further the genocide. " and concluded that "Hitler intended to liberalize gun control laws in Germany for "trustworthy" German citizens, while disarming "unreliable" persons, especially the Jewish population. In order to disarm Jewish persons, the Nazi government used both the "trustworthiness" requirements originally legislated in 1928, as well as more direct regulations denying Jews the right to manufacture or possess firearms. It is absurd to even try to characterize this as either pro- or anti-gun control. But if forced to, I would have to conclude, at least preliminarily from this straightforward exercise in statutory interpretation, that the Nazis favored less gun control for the "trustworthy" German citizen than the predecessor Weimar Republic, while disarming the Jewish population and engaging in genocide."<ref name=Harcourt1></ref> | |||
| {{main|Gun law in the United States|Gun politics in the United States|Gun culture in the United States|Gun violence in the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In the United States, gun rights activists argue gun laws are too restrictive or should not be altered, and gun control activists argue gun laws are too permissive. Both camps center their arguments upon the legal and traditional interpretations of the ] to the U.S. Constitution.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Peeples |first=Lynne |date=2022-07-01 |title=US gun policies: what researchers know about their effectiveness |journal=Nature |language=en |volume=607 |issue=7919 |pages=434–435 |doi=10.1038/d41586-022-01791-z|pmid=35778495 |bibcode=2022Natur.607..434P |s2cid=250218456 |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| High rates of gun mortality and injury are often cited as a primary impetus for gun control policies.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2012/12/the-case-for-more-guns-and-more-gun-control/309161/ | title=The Case for More Guns (and More Gun Control) | website=The Atlantic | date=December 2012 | access-date=31 March 2016 | last=Goldberg | first = Jeffrey}}</ref> A 2004 National Research Council critical review found that while some strong conclusions are warranted from current research, the state of our knowledge is generally poor.{{sfn|National Research Council|2005|pp=3, 6}} The result of the scarcity of relevant data is that gun control is one of the most fraught topics in American politics,{{sfn|Branas et al.|2009}} and scholars remain deadlocked on a variety of issues.{{sfn|Branas et al.|2009}} Notably, since 1996, when the ] was first inserted into the federal spending bill, the ] (CDC) has been prohibited from using its federal funding "to advocate or promote gun control", thwarting gun violence research at the agency at the time. The funding provision's author has said that this was an over-interpretation,<ref>{{Cite news|title = The Congressman Who Restricted Gun Violence Research Has Regrets|url = http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/jay-dickey-gun-violence-research-amendment_561333d7e4b022a4ce5f45bf|newspaper = The Huffington Post|access-date = 2015-10-11|date = 2015-10-06|last1 = Stein|first1 = Sam|archive-date = 2015-10-10 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20151010051136/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/jay-dickey-gun-violence-research-amendment_561333d7e4b022a4ce5f45bf|url-status = live}}</ref> but the amendment still had a chilling effect, effectively halting federally funded firearm-related research.{{sfn|Betz|Ranney|Wintemute|2016}} Since the amendment, the CDC has continued to research gun violence and publish studies about it,{{sfn|Centers for Disease Control and Prevention|2013}} although their funding for such research has fallen by 96% since 1996, according to ].<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.apa.org/science/about/psa/2013/02/gun-violence.aspx | title=Gun violence research: History of the federal funding freeze | website=Psychological Science Agenda | date=February 2013 | access-date=27 April 2017 | author=Jamieson, Christine | archive-date=2017-05-05 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170505190021/http://www.apa.org/science/about/psa/2013/02/gun-violence.aspx | url-status=live }}</ref> According to a spokesman, the CDC has limited funding and has not produced any comprehensive study aimed at reducing gun violence since 2001.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://abcnews.go.com/Health/cdc-launched-comprehensive-gun-study-15-years/story?id=39873289 | title=Why the CDC Hasn't Launched a Comprehensive Gun Study in 15 Years | website=ABC News | date=16 June 2016 | access-date=27 April 2017 | author=Barzilay, Julie | archive-date=2020-06-27 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200627134017/https://abcnews.go.com/Health/cdc-launched-comprehensive-gun-study-15-years/story?id=39873289 | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Gun control in Bolshevist Russia=== | |||
| :''Main article: ]'' | |||
| In Tzarist ] personal gun ownership was legal, allowing ] and other revolutionaries to import a great number of guns for the purpose of overthrowing the ]. For example, in 1905, during the ], the ship ''Sirius'' delivered to Russian revolutionaries 8,500 rifles paid by the government of Japan. In December 1918 during the ] the ]s made it a crime for citizens other than members of their own party to own guns. Bolsheviks were allowed to own one rifle and one revolver.<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref>Александр Малахов. // "Коммерсантъ", № 30 (633) от 1 августа 2005</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Gun control in the United States=== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Gun politics in the United States|Gun laws in the United States by state}} | |||
| ====Cross-sectional studies==== | |||
| Many opponents of gun control consider ] to be a fundamental and ] ] and believe that firearms are an important tool in the exercise of this right. They consider the prohibition of an effective means of self-defense to be ]. For instance, in ]'s "Commonplace Book," a quote from ] reads, <blockquote>"laws that forbid the carrying of arms ... disarm only those who are neither inclined nor determined to commit crimes ... Such laws make things worse for the assaulted and better for the assailants; they serve rather to encourage than to prevent homicides, for an unarmed man may be attacked with greater confidence than an armed man."<ref name="Story 1986 pp. 319-320">Story,Joseph, "A Familiar Exposition of the Constitution of the United States". 1986, Regnery Gateway, Chicago, Illinois, pp. 319-320, ISBN 0-89526-796-9.</ref><ref>Hardy, David T. "The origins and Development of the Second Amendment". 1986, Blacksmith Corp., Chino Valley, Arizona, pp. 1-78, ISBN 0-941540-13-8.</ref><ref>Halbrook, Stephen P. "That Every Man be Armed-The Evolution of a Constitutional Right". 1987, The University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp. 1-88, ISBN 0-8263-0868-6.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| In 1983, a ] of all 50 U.S. states found that the six states with the strictest gun laws (according to the ]) had suicide rates that were approximately 3/100,000 people lower than in other states, and that these states' suicide rates were 4/100,000 people lower than those of states with the least restrictive gun laws.{{sfn|Medoff|Magaddino|1983}} A 2003 study published in the '']'' looked at the restrictiveness of gun laws and suicide rates in men and women in all 50 U.S. states and found that states whose gun laws were more restrictive had lower suicide rates among both sexes.{{sfn|Conner|Zhong|2003}} In 2004, another study found that the effect of state gun laws on gun-related homicides was "limited".{{sfn|Price|Thompson|Dake|2004}} A 2005 study looked at all 50 states in the U.S. and the ], and found that no gun laws were associated with reductions in firearm homicide or suicide, but that a "]" concealed carry law (mandatory issue of a license when legal criteria met) may be associated with increased firearm homicide rates.{{sfn|Rosengart et al.|2005}} A 2011 study found that firearm regulation laws in the United States have "a significant deterrent effect on male suicide".{{sfn|Rodríguez Andrés|Hempstead|2011}} | |||
| A 2013 study by the American Medical Association found that in the United States, "a higher number of firearm laws in a state are associated with a lower rate of firearm fatalities in that state."{{sfn|Fleegler et al.|2013}} A 2016 study published in '']'' found that of 25 laws studied, and in the time period examined (2008–2010), nine were associated with reduced firearm mortality (including both homicide and suicide), nine were associated with increased mortality, and seven had an inconclusive association. The three laws most strongly associated with reduced firearm mortality were laws requiring ]s, background checks for ammunition sales, and identification for guns.{{sfn|Kalesan et al.|2016}} In an accompanying commentary, ] noted that this study had multiple limitations, such as not controlling for all factors that may influence gun-related deaths aside from gun control laws, and the use of 29 ]s in the analysis.{{sfn|Hemenway|2016}} | |||
| Before the ] ended, ] ] prohibited slaves from owning guns. After ] in the U.S. was abolished, states persisted in prohibiting ] from owning guns under laws renamed ]. | |||
| Other studies comparing gun control laws in different U.S. states include a 2015 study which found that in the United States, "stricter state firearm legislation is associated with lower discharge rates" for nonfatal gun injuries.{{sfn|Simonetti et al.|2015}} A 2014 study that also looked at the United States found that children living in states with stricter gun laws were safer.{{sfn|Safavi et al.|2014}} Another study looking specifically at suicide rates in the United States found that the four handgun laws examined (], universal background checks, gun locks, and open carrying regulations) were associated with "significantly lower firearm suicide rates and the proportion of suicides resulting from firearms." The study also found that all four of these laws (except the waiting-period one) were associated with reductions in the overall suicide rate.{{sfn|Anestis|Anestis|2015}} | |||
| The United States Congress overrode most portions of the Black Codes by passing the ]. The legislative histories of both the Civil Rights Act and the ], as well as The Special Report of the Anti-Slavery Conference of 1867, are replete with denunciations of those particular statutes that denied blacks equal access to firearms.<ref>Kates, "Handgun Prohibition and the Original Meaning of the Second Amendment," 82 Mich. L. Rev. 204, 256 1983</ref> | |||
| Another study, published the same year, found that states with permit to purchase, registration, and/or license laws for handguns had lower overall suicide rates, as well as lower firearm suicide rates.{{sfn|Anestis et al.|2015}} A 2014 study found that states that required licensing and inspections of gun dealers tended to have lower rates of gun homicides.{{sfn|Irvin et al.|2014}} Another study published the same year, analyzing ] from all 50 states, found that stricter gun laws may modestly reduce ].{{sfn|Lanza|2014}} A 2016 study found that U.S. military veterans tend to commit suicide with guns more often than the general population, thereby possibly increasing state suicide rates, and that "the tendency for veterans to live in states without handgun legislation may exacerbate this phenomenon."{{sfn|Anestis|Capron|2016}} California has exceptionally strict gun sales laws, and a 2015 study found that it also had the oldest guns recovered in crimes of any states in the U.S. The same study concluded that "These findings suggest that more restrictive gun sales laws and gun dealer regulations do make it more difficult for criminals to acquire new guns first purchased at retail outlets."{{sfn|Pierce|Braga|Wintemute|2015}} | |||
| After the adoption of the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1868, most states turned to "facially neutral" business or transaction taxes on handgun purchases. However, the intention of these laws was not neutral. An article in ]'s official university ] called for a "prohibitive tax...on the privilege" of selling handguns as a way of disarming "the son of Ham," whose "cowardly practice of 'toting' guns has been one of the most fruitful sources of crime.... Let a ] board a railroad train with a quart of mean ] and a ] in his grip and the chances are that there will be a murder, or at least a row, before he alights."<ref>Carrying Concealed Weapons, 15 Va L. Reg. 391, 391-92, 1909 ] (GMU CR LJ), Vol. 2, No. 1, "Gun Control and Racism," Stefan Tahmassebi, 1991, p. 75</ref> Thus, many Southern states imposed high taxes or banned inexpensive guns in order to price destitute individuals out of the gun market.<ref>Tahmassebi, Stefan B. "GUN CONTROL AND RACISM", George Mason University Civil Rights Law Journal, Vol. 2 (1991): 67, http://www.saf.org/lawreviews/tahmassebi1.html.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Arguments== | |||
| Another 2016 study found that stricter state gun laws in the United States reduced suicide rates.{{sfn|Kposowa|Hamilton|Wang|2016}} Another 2016 study found that U.S. states with lenient gun control laws had more gun-related child injury hospital admissions than did states with stricter gun control laws.{{sfn|Tashiro et al.|2016}} A 2017 study found that suicide rates declined more in states with universal background check and mandatory waiting period laws than in states without these laws.{{sfn|Anestis|Anestis|Butterworth|2017}} Another 2017 study found that states without universal background check and/or waiting period laws had steeper increases in their suicide rates than did states with these laws.{{sfn|Anestis|Selby|Butterworth|2017}} A third 2017 study found that "waiting period laws that delay the purchase of firearms by a few days reduce gun homicides by roughly 17%."{{sfn|Luca|Malhotra|Poliquin|2017}} A 2017 study in the '']'' found that mandatory handgun purchase delays reduced "firearm-related suicides by between 2 and 5 percent with no statistically significant increase in non-firearm suicides," and were "not associated with statistically significant changes in homicide rates."{{sfn|Edwards et al.|2018}} Another 2017 study showed that laws banning gun possession by people subject to intimate partner violence restraining orders, and requiring such people to give up any guns they have, were associated with lower intimate partner homicide rates.{{sfn|Diez et al.|2017}} A 2021 study found that firearm purchase delay laws reduced homicide – the authors suggested that it was driven by reductions in gun purchases by impulsive customers.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Koenig|first1=Christoph|last2=Schindler|first2=David|date=2021|title=Impulse Purchases, Gun Ownership, and Homicides: Evidence from a Firearm Demand Shock|journal=The Review of Economics and Statistics|volume=105 |issue=5 |pages=1271–1286|doi=10.1162/rest_a_01106|s2cid=243676146|issn=0034-6535|doi-access=free|hdl=10419/207224|hdl-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| ====Reviews==== | |||
| High rates of gun mortality and injury are often cited as a primary impetus for gun control policies.<ref name=NAP>{{cite book | title = Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review | first1 = Charles F. | last1 = Wellford | first2 = John V. | last2 = Pepper | first3 = Carol V. | last3 = Petrie | isbn = 9780309091244 | url = http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=10881 | year = 2004 | publisher = The National Academies Press }}</ref>{{page needed|date=February 2013}} The question of whether gun control policies increase, decrease or have no effect on rates of gun violence turns out to be a difficult question. While a variety of disparate data sources on rates of firearm-related injuries and deaths, firearms markets, and the relationships between rates of gun ownership and violence exist, found that while some strong conclusions are warranted from current research, the state of our knowledge is generally poor.<ref name=NAP />{{rp|1=, }} Despite the potential for improved research design, the National Research Council review concludes that the gaps in our knowledge on the efficacy of gun control policies are due primarily to inadequate data and not to weak research methods. The result of the scarcity of relevant data is that gun control is one of the most fraught topics in American politics<ref name=Branas>{{cite journal|last=Branas|first=Charles|coauthors=Therese Richmond, Dennis P. Culhane, Thomas R. Ten Have and Douglas J. Wiebe|title=Investigating the Link Between Gun Possession and Gun Assault|journal=Am J Public Health|year=2009|month=November|volume=99|issue=11|pages=2034–2040|doi=10.2105/AJPH.2008.143099|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2759797/#bib1|accessdate=25 January 2013}}</ref> and scholars remain deadlocked on a variety of issues.<ref name=Branas /> | |||
| In 2015, ] and ] reviewed studies examining the effectiveness of gun laws aimed at keeping guns out of the hands of high-risk individuals in the United States. They found that some laws prohibiting gun possession by people under ] ]s or who had been convicted of violent ]s were associated with lower violence rates, as were laws establishing more procedures to see if people were prohibited from owning a gun under these laws. They also found that multiple other gun regulations intended to prevent prohibited individuals from obtaining guns, such as "rigorous permit-to-purchase" laws and "comprehensive background checks", were "negatively associated with the diversion of guns to criminals."{{sfn|Webster|Wintemute|2015}} | |||
| The first cross-national overall comparison of deaths caused by guns was published in 1998,<ref>'''', EG Krug, KE Powell and LL Dahlberg, 1997</ref> and found substantial variation. The possible factors leading to variation in gun violence among different countries was not assessed. A 2004 review by the National Research Council concluded that, "higher rates of household firearms ownership are associated with higher rates of gun suicide, that illegal diversions from legitimate commerce are important sources of crime guns and guns used in suicide, that firearms are used defensively many times per day, and that some types of targeted police interventions may effectively lower gun crime and violence.<ref name=NAP />{{rp|1=}}" | |||
| A 2016 systematic review found that restrictive gun licensing laws were associated with lower gun injury rates, while concealed carry laws were not significantly associated with rates of such injuries.{{sfn|Crandall et al.|2016}} Another systematic review found that stricter gun laws were associated with lower gun homicide rates; this association was especially strong for background check and permit-to-purchase laws.{{sfn|Lee et al.|2016}} | |||
| A number of studies have examined the ] between rates of gun ownership and gun-related, as well as overall, homicide and suicide rates internationally.<ref name="go19">'''', Martin Killias.</ref> Martin Killias, in a 1993 study covering 21 countries, found that there were significant correlations between gun ownership and gun-related suicide and homicide rates. There was also a significant though lesser correlation between gun ownership and total homicide rates<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unicri.it/wwk/publications/books/series/understanding/19_GUN_OWNERSHIP.pdf|title=Gun Ownership, Suicide and Homicide: An International Perspective|accessdate=2008-01-16|author=Martin Killias|coauthors=|year=1993|quote=The present study, based on a sample of eighteen countries, confirms the results of previous work based on the 14 countries surveyed during the first International Crime Survey. Substantial correlations were found between gun ownership and gun-related as well as total suicide and homicide rates. Widespread gun ownership has not been found to reduce the likelihood of fatal events committed with other means. Thus, people do not turn to knives and other potentially lethal instruments less often when more guns are available, but more guns usually means more victims of suicide and homicide. | |||
| |format=PDF |archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20080107174528/http://www.unicri.it/wwk/publications/books/series/understanding/19_GUN_OWNERSHIP.pdf |archivedate = January 7, 2008}}</ref> A later study published by Killias et al. in 2001,<ref name=killias2001>Killias, van Kesteren, and Rindlisbacher, , ''Canadian Journal of Criminology'', October 2001.</ref> based on a larger sample of countries found, "very strong correlations between the presence of guns in the home and suicide committed with a gun, rates of gun-related homicide involving female victims, and gun-related assault." The authors suggest that the correlation between the presence of guns in the home and suicide and homicide of females is best explained as causal, i.e. the presence of guns is the cause of the mortality and not the reverse. The study found no correlation for similar crimes against men, total rates of assault or for robbery, however, the authors note that the relationship between availability of guns and male homicide is complex, and the data may be affected by wars, organized crime, street crime and crime rates among various countries. They also note that, "the absence of significant correlations between gun ownership and total homicide, assault, or suicide rates... open the question of possible substitution effects." (In other words, other means could have been substituted for firearms used in the commission of homicide or suicide.) | |||
| A 2020 review of almost 13,000 studies by RAND Corporation found only 123 that met their criteria of methodological rigor, "a surprisingly limited base of rigorous scientific evidence...". Only 2 of the 18 gun policies examined had supporting evidence. Among the policies for which RAND found supporting evidence were that child-access prevention laws reduce firearm injuries and deaths among children and that "stand-your-ground" laws increase firearm homicides. RAND also noted that the limited evidence currently available "does not mean that these policies are ineffective ... Instead, it partly reflects shortcomings in the contributions that science has made to policy debates."<ref>{{Cite web |title=What Science Tells Us About the Effects of Gun Policies |url=https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/key-findings/what-science-tells-us-about-the-effects-of-gun-policies.html |access-date=2022-10-10 |website=www.rand.org |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| However, a number of scholars have also reported that the rate of gun availability is either neutral or associated with less gun violence. These include ], Gary Mauser, ], David Mustard, Joyce Malcolm and ]. For example, a 2002 review of international gun control policies and gun ownership rates as these relate to crime rates by Kates and Mauser,<ref name=Kates>{{cite journal|last=Kates|first=Don|coauthors=Gary Mauser|title=Would Banning Firearms Reduce Murder and Suicide? A Review of International and Some Domestic Evidence.|journal=Harvard Journal of Law & Public Policy|year=2002|volume=30|issue=2|pages=649–694|url=http://www.harvard-jlpp.com/archive/#302|accessdate=2013-01-14}}</ref> published in the '']'' (a student run journal devoted to conservative and libertarian legal scholarship<ref name=HLS>{{cite web|title=Harvard Law School: Journals and Publications|url=http://www.law.harvard.edu/current/orgs/journals/index.html#HarvardJournalofLawPublicPolicy|accessdate=14 January 2013}}</ref>) argues that, "International evidence and comparisons have long been offered as proof of the mantra that more guns mean more deaths and that fewer guns, therefore, mean fewer deaths. Unfortunately, such discussions are all too often been afflicted by misconceptions and factual error and focus on comparisons that are unrepresentative." Kates and Mauser point out in Europe, there is no correlation whatsoever between gun ownership rates and homicide rates (see table "European Gun Ownership and Murder Rates"). Joyce Malcolm reviewed the subject of crime rates and homicides in England<ref></ref> and found that, "data on firearms ownership by constabulary area," show, "a negative correlation..., where firearms are most dense violent crime rates are lowest, and where guns are least dense violent crime rates are highest." | |||
| ====Studies of individual laws==== | |||
| Economist ], in his book ''],'' provides data showing that laws allowing law-abiding citizens to carry a gun legally in public may cause reductions in crime because potential criminals do not know who may be carrying a firearm. The data for Lott's analysis came from the ]'s crime statistics for all 3,054 US counties.<ref name = "Lott0p50">Lott, John R.Jr., "More Guns, Less Crime-- Understanding Crime and Gun Control Laws" (1998), The University of Chicago Press, Chicago Illinois, pp. 50-122, ISBN 0-226-49363-6.</ref> Kleck analysed the impact of 18 major types of gun control laws on every major type of violent crime or violence (including suicide), and found that gun laws generally had no significant effect on violent crime rates or suicide rates.<ref>Kleck and Patterson, ''Journal of Quantitative criminology'' September 1993.</ref> | |||
| Other studies have examined trends in firearm-related deaths before and after gun control laws are either enacted or repealed. A 2004 study in the '']'' found evidence that ]s were "associated with a modest reduction in suicide rates among youth aged 14 to 17 years."{{sfn|Webster et al.|2004}} Two 2015 studies found that the permit-to-purchase law passed in ] in 1995 was associated with a reduction in firearm suicides and homicides.{{sfn|Crifasi et al.|2015}}{{sfn|Rudolph et al.|2015}} One of these studies also found that the repeal of Missouri's permit-to-purchase law was associated with "a 16.1% increase in firearm suicide rates,"{{sfn|Crifasi et al.|2015}} and a 2014 study by the same research team found that the repeal of this law was associated with a 16% increase in homicide rates.{{sfn|Webster|Crifasi|Vernick|2014}} A 2000 study designed to assess the effectiveness of the ] found that the law was not associated with reductions in overall homicide or suicide rates, but that it was associated with a reduction in the firearm suicide rate among individuals aged 55 or older.{{sfn|Ludwig|Cook|2000}} A 1991 study looked at ]'s ], which banned its residents from owning all guns except certain ]s and sporting ]s, which were also required to be unloaded, disassembled, or stored with a ] in their owners' homes.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/11/sports/basketball/11arenas.html | title=Washington's Gun Past Affects Arenas's Future | website=New York Times | date=10 January 2010 | access-date=6 December 2015 | author=Abrams, Jonathan | archive-date=2017-06-30 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170630060952/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/11/sports/basketball/11arenas.html | url-status=live }}</ref> The study found that the law's enactment was associated with "a prompt decline in homicides and suicides by firearms in the District of Columbia."{{sfn|Loftin et al.|1991}} A 1996 study reanalyzed this data and reached a significantly different conclusion as to the effectiveness of this law.{{sfn|Britt|Kleck|Bordua|1996}} | |||
| Studies by Arthur Kellermann and Matthew Miller found that keeping a gun in the home was associated with an increased risk of suicide.<ref>Kellermann, AL, Rivara FP, et al. "Suicide in the Home in Relation to Gun Ownership." NEJM 327:7 (1992):467-472.</ref><ref>Miller, Matthew and Hemenway, David (September 4, 2008) "". The New England Journal of Medicine, 359-989-991, Retrieved July 25, 2012</ref> Other studies, however, found no association between gun ownership and suicide.<ref>Miller, Marv. 1978. "Geriatric suicide." The Gerontologist 18:488-495; Bukstein, O. G., David A. Brent, Joshua A. Perper, Grace Moritz, Marianne Baugher, Joy Schweers, Claudia Roth, and L. Balach. 1993. "Risk factors for completed suicide among adolescents with a lifetime history of substance abuse: a case-control study." Acta Psychiatrica Scandanavia 88:403-408; Beautrais, Annette L., Peter R. Joyce, and Roger T. Mulder. 1996. "Access to firearms and the risk of suicide." Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 30:741-748; Conwell, Yeates, Kenneth Connor, and Christopher Cox. 2002. "Access to firearms and risk for suicide in middle-aged and older adults." American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry | |||
| 10:407-416 </ref> | |||
| ====Other studies and debate==== | |||
| ] economist ] argues in his paper, ''Understanding Why Crime Fell in the 1990s: Four Factors that Explain the Decline and Six that Do Not'',<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/aea/jep/2004/00000018/00000001/art00008 |title=Understanding Why Crime Fell in the 1990s: Four Factors that Explain the Decline and Six that Do Not|first=Steven D |last=Levitt|journal=Journal of Economic Perspectives|volume=18 |issue=1|year= 2004|format=}}</ref> that available data indicate that neither stricter gun control laws nor more liberal concealed carry laws have had any significant effect on the decline in crime in the 1990s. A comprehensive review of published studies of gun control, released in November 2004 by the ], was unable to determine any statistically significant effect resulting from such laws, although the authors suggest that further study may provide more conclusive information. | |||
| In 1993, Kleck and Patterson analyzed the impact of 18 major types of gun control laws on every major type of gun-involved crime or violence (including suicide) in 170 U.S. cities, and found that gun laws generally had no significant effect on violent crime rates or suicide rates.{{sfn|Kleck|Patterson|1993}}{{update after|2020|10|9}} Similarly, a 1997 study found that gun control laws had only a small influence on the rate of gun deaths in U.S. states compared to socioeconomic variables like poverty and unemployment.{{sfn|Kwon et al.|1997}}{{update after|2020|2}} | |||
| Philosophy professor ] argues that gun control may be morally wrong, even if its outcomes would be positive, because individuals have a prima facie right to own a gun for self-defense and recreation.{{sfn|Huemer|2003}} | |||
| A 2007 article published by the ''Journal of Injury Prevention'' states that approximately 60% of firearms used to commit violent crime can be traced to 1% of licensed dealers.<ref name="ReferenceA">{{Cite journal |last1=Vernick |first1=Jon S |last2=Webster |first2=Daniel W |date=2007 |title=Policies to prevent firearm trafficking |journal=Injury Prevention |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=78–79 |doi=10.1136/ip.2007.015487 |issn=1353-8047 |pmc=2610592 |pmid=17446245 }}</ref> This finding indicates that, although gun laws effectively regulate approximately 99% of purchases made from licensed dealers, a majority of gun-related violent crimes are perpetrated using guns that were purchased in violation of regulations. The ''Journal of Injury Prevention'' article advocates for increased monitoring of gun vendors in tandem with the optimization of gun sale regulation, as a means to decrease violent crime perpetrated with a firearm.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| In 2009, the ] program,<ref>{{cite web |title=Home – Public Health Law Research |url=http://www.publichealthlawresearch.org/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191213125613/http://publichealthlawresearch.org/ |archive-date=December 13, 2019 |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=Publichealthlawresearch.org}}</ref> an independent organization, published several evidence briefs summarizing the research assessing the effect of a specific law or policy on public health, that concern the effectiveness of various laws related to gun safety. Among their findings: | |||
| * There is not enough evidence to establish the effectiveness of "shall issue" laws, as distinct from "may issue" laws, as a public health intervention to reduce violent crime.<ref>{{cite web |title="Shall Issue" Concealed Weapons Laws, Public Health Law Research 2009 |url=http://publichealthlawresearch.org/product/%E2%80%9Cshall-issue%E2%80%9D-concealed-weapons-laws/%22shall-issue%22-concealed-weapons-law |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=Publichealthlawresearch.org}} {{Dead link|date=January 2020|bot=InternetArchiveBot|fix-attempted=yes}}</ref> | |||
| * There is insufficient evidence to determine the effectiveness of waiting period laws as public health interventions aimed at preventing gun-related violence and suicide.<ref>{{cite web |title=Waiting Period Laws for Gun Permits – Public Health Law Research |url=http://publichealthlawresearch.org/product/waiting-period-laws-gun-permits |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=publichealthlawresearch.org}}</ref> | |||
| * Although child access prevention laws may represent a promising intervention for reducing gun-related morbidity and mortality among children, there is currently insufficient evidence to validate their effectiveness as a public health intervention aimed at reducing gun-related harms.<ref>{{cite web |title=Child Access Prevention (CAP) Laws for Guns – Public Health Law Research |url=http://publichealthlawresearch.org/product/child-access-prevention-cap-laws-guns |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=publichealthlawresearch.org}}</ref> | |||
| * There is insufficient evidence to establish the effectiveness of such bans as public health interventions aimed at reducing gun-related harms.<ref>{{cite web |title=Bans on Specific Guns and Ammunition – Public Health Law Research |url=http://publichealthlawresearch.org/product/bans-specific-guns-and-ammunition |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=publichealthlawresearch.org}}</ref> | |||
| * There is insufficient evidence to validate the effectiveness of firearm licensing and registration requirements as legal interventions aimed to reduce firearm related harms.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gun Registration and Licensing Requirements – Public Health Law Research |url=http://publichealthlawresearch.org/product/gun-registration-and-licensing-requirements |access-date=October 4, 2017 |website=publichealthlawresearch.org}}</ref> | |||
| ] did a study that demonstrates that background checks may decrease suicides and violent crime; child-access prevention laws may decrease the number of suicides and unintentional injuries and deaths; minimum age requirements may decrease suicides; and prohibitions associated with mental illness may decrease suicides and violent crimes. On the other hand, concealed-carry laws may increase violent crimes and suicides, while stand-your-ground laws may increase violent crime. Bans on the sale of assault weapons and high-capacity magazines may increase the sale price for these items.<ref>{{citation|website=Rand.org|access-date=August 11, 2019|title=Facts About the Effects of Gun Policies Are Elusive but Important|url=https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy.html|archive-date=2019-08-08 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190808122420/https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy.html|url-status=live}}</ref> An August 2019 article entitled, "Gun control really works" published by '']'' looks at a dozen studies by the ], ''],'' Rand Corporation, the journal ''],'' ], ], and others. They conclude that mirroring the ] such as banning the sale of new assault weapons, denying concealed-carry licenses to some individuals, and prohibiting firearm sales to people convicted of multiple alcohol-related offenses will decrease gun-related deaths and injuries.<ref>{{cite web |website=Business Insider |date=August 6, 2019 |access-date=August 6, 2019|title=Gun control really works. Science has shown time and again that it can prevent mass shootings and save lives. |url=https://www.businessinsider.com/gun-control-research-how-policies-can-reduce-deaths-2019-8 |first=Aylin |last=Woodward}}</ref> | |||
| ===Canada=== | |||
| {{main|Gun laws in Canada}} | |||
| Rifles and shotguns are relatively easy to obtain, while handguns and some ]s are restricted.<ref>{{Cite web| url=http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/cfp-pcaf/fs-fd/clas-eng.htm| title=Classes of firearms| date=2012-04-18| access-date=2016-10-29 | archive-date=2018-03-15 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180315134422/http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/cfp-pcaf/fs-fd/clas-eng.htm| url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| With respect to the Criminal Law Amendment Act, a gun control law passed in ] in 1977, some studies have found that it was ineffective at reducing homicide or robbery rates.{{sfn|Mauser|Holmes|1992}}{{sfn|Mauser|Maki|2003}} One study even found that the law may have actually increased robberies involving firearms.{{sfn|Mauser|Maki|2003}} A 1993 study found that after this law was passed, gun suicides decreased significantly, as did the proportion of suicides committed in the country with guns.{{sfn|Lester|Leenaars|1993}} A 2003 study found that this law "may have had an impact on suicide rates, even after controls for social variables,"{{sfn|Leenaars et al.|2003}} while a 2001 study by the same research team concluded that the law "may have had an impact on homicide rates, at least for older victims."{{sfn|Leenaars|Lester|2001}} A 1994 study found that after this law came into force in 1978, suicide rates decreased over time in ], and that there was no evidence of method substitution. The same study found that "These decreases may be only partly due to the legislation."{{sfn|Carrington|Moyer|1994}} | |||
| In 1991, Canada implemented the gun control law Bill C-17. According to a 2004 study, after this law was passed, firearm-related suicides and homicides, as well as the percentage of suicides involving firearms, declined significantly in that country.{{sfn|Bridges|2004}} A 2010 study found that after this law was passed, firearm suicides declined in ] among men, but acknowledged that this may not represent a causal relationship.{{sfn|Gagne et al.|2010}} In 1992, Canada promulgated the Canadian Firearms Act, which aimed at ensuring that guns were stored safely. A 2004 study found that although firearm suicide rates declined in the Quebec region ] after the law was passed, overall suicide rates did not.{{sfn|Caron|2004}} A study in 2005 also found that overall suicide rates did not change after passage of Bill C-17.{{sfn|Cheung|Dewa|2005}} A 2008 study reached similar conclusions with regard to the entire Quebec province; this study also found that C-17 did not seem to increase the rate at which the firearm suicide rate was declining.{{sfn|Caron|Julien|Huang|2008}} Other researchers have criticized this 2008 study for looking at too short a time period and not taking account of the fact that the regulations in C-17 were implemented gradually.{{sfn|Gagne et al.|2010}} | |||
| A 1990 study compared suicide rates in the ], Canada metropolitan area (where gun control laws were more restrictive) with those in the ] area in the United States. The overall suicide rate was essentially the same in the two locations, but the suicide rate among 15 to 24 year olds was about 40 percent higher in Seattle than in Vancouver. The authors concluded that "restricting access to handguns might be expected to reduce the suicide rate in persons 15 to 24 years old, but ... it probably would not reduce the overall suicide rate."{{sfn|Sloan et al.|1990}} A study that looked at provincial gun ownership rates, and associated suicide rates found no significant correlations with overall suicide rates.{{sfn|Dandurand|1998}} | |||
| A 2011 study looked at gun control passed in Canada between 1974 and 2004 and found that gun laws were responsible for 5 to 10 percent drops in homicides. The study found that the homicide reduction effects of Canadian gun legislation remained even after accounting for sociodemographic and economic factors associated with homicide rates.{{sfn|Blais|Gagné|Linteau|2011}} | |||
| A 2012 study looked at gun control laws passed in Canada from 1974 to 2008 and found no evidence that these laws had a beneficial effect on firearm homicide rates in that country. According to the study, "other factors found to be associated with homicide rates were median age, unemployment, immigration rates, percentage of population in low-income bracket, Gini index of income equality, population per police officer, and incarceration rate."{{sfn|Langmann|2012}} | |||
| A 2013 study of the 1995 Canadian gun control law ] reported little evidence that this law significantly reduced rates of lethal gun violence against women.{{sfn|McPhedran|Mauser|2013}} | |||
| On May 1, 2020, after ] in ], ] Liberal government banned 1,500 kinds of military-style semi-automatic rifles, including the popular ] and its variants. The ban was enacted via an ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/trudeau-gun-control-measures-ban-1.5552131 |access-date=May 2, 2020 |title=Trudeau announces ban on 1,500 types of 'assault-style' firearms – effective immediately |last=Tasker |first=John Paul |date=May 1, 2020 |website=CBC |archive-date=2020-05-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200501160046/https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/trudeau-gun-control-measures-ban-1.5552131 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| A 2020 study examining laws passed from 1981 to 2016 found no significant changes in overall homicide or suicide rates following changes in legislation. In addition, it also found that firearm ownership by province was not correlated to overall suicide rates by province.<ref>{{Cite journal|pmid = 32555647|year = 2020|last1 = Langmann|first1 = C.|title = Effect of firearms legislation on suicide and homicide in Canada from 1981 to 2016|journal = PLOS ONE|volume = 15|issue = 6|pages = e0234457|doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0234457|pmc = 7302582|bibcode = 2020PLoSO..1534457L|doi-access = free}}</ref> | |||
| On October 21, 2022, under Justin Trudeau's government, Bill C-21 came into effect, aiming to address gun violence and strengthen gun control. The legislation introduced a national freeze on the sale, purchase, or transfer of handguns by individuals within Canada. It also established new "red flag" and "yellow flag" laws, allowing courts and Chief Firearms Officers (CFOs) to issue emergency weapons prohibition orders and temporarily suspend licenses, respectively. Moreover, the bill increased maximum penalties for firearms-related offenses, including smuggling and trafficking, from 10 to 14 years imprisonment. Additionally, Bill C-21 prohibited mid-velocity 'replica' airguns that closely resemble real firearms and discharge projectiles at a velocity between 366 and 500 feet per second.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Canada |first=Public Safety |date=2022-05-30 |title=A comprehensive strategy to address gun violence and strengthen gun laws in Canada |url=https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/cntrng-crm/frrms/c21-en.aspx |access-date=2023-04-10 |website=www.publicsafety.gc.ca}}</ref> | |||
| ===Australia=== | |||
| {{main|Gun laws in Australia}} | |||
| In 1988 and 1996, gun control laws were enacted in the ]n state of ], both times following ]s. A 2004 study found that in the context of these laws, overall firearm-related deaths, especially suicides, declined dramatically.{{sfn|Ozanne-Smith et al.|2004}} A 1995 study found preliminary evidence that gun control legislation enacted in ], Australia, reduced suicide rates there.{{sfn|Cantor|Slater|1995}} | |||
| A 2006 study by gun lobby-affiliated researchers Jeanine Baker and Samara McPhedran found that after Australia enacted the ] (NFA), a gun control law, in 1996, gun-related suicides may have been affected, but no other parameter appeared to have been.{{sfn|Baker|McPhedran|2006|}} Another 2006 study, led by ], found that after this law was enacted in 1996 in Australia, the country went more than a decade without any mass shootings, and gun-related deaths (especially suicides) declined dramatically.{{sfn|Chapman|Alpers|Agho|Jones|2006}} The latter of these studies also criticized the former for using a time-series analysis despite the fact that, according to Chapman et al., "calculating mortality rates and then treating them as a number in a time series ignores the natural variability inherent in the counts that make up the numerator of the rate." Chapman et al. also said that Baker and McPhedran used the ] inappropriately.{{sfn|Chapman|Alpers|Agho|Jones|2006}} | |||
| A 2010 study looking at the effect of the NFA on gun-related deaths found that the law "did not have any large effects on reducing firearm homicide or suicide rates,"{{sfn|Lee|Suardi|2010}} although David Hemenway has criticized this study for using a ] test despite the fact that such tests can miss the effects of policies in the presence of lags, or when the effect occurs over several years.{{sfn|Hemenway|2009}} Another study, published the same year, found that Australia's gun buyback program reduced gun-related suicide rates by almost 80%, while non-gun death rates were not significantly affected.{{sfn|Leigh|Neill|2010}} Other research has argued that although gun suicide rates fell after the NFA was enacted, the NFA may not have been responsible for this decrease and "a change in social and cultural attitudes" may have instead been at least partly responsible.{{sfn|Klieve|Barnes|De Leo|2009}} A 2011 study found that "Australia's prohibition of certain types of firearms" has not prevented mass shootings.<ref name="auto1">{{cite journal |last1=McPhedran |first1=Samara |last2=Baker |first2=Jeanine |year=2011 |title=Mass shootings in Australia and New Zealand: A descriptive study of incidence |journal=Justice Policy Journal |volume=8 |issue=1 |ssrn=2122854}}</ref> In 2016, Chapman co-authored another study that found that after the NFA was passed, there were no mass shootings in the country ({{as of|2016|May|lc=y}}), and that gun-related death rates declined more quickly after the NFA than they did before it. The study also found, however, that non-gun suicide and homicide rates declined even more quickly after the NFA, leading the authors to conclude that "it is not possible to determine whether the change in firearm deaths can be attributed to the gun law reforms."{{sfn|Chapman|Alpers|Jones|2016}} | |||
| ===Other countries=== | |||
| {{Further|Overview of gun laws by nation}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| |align=center | |||
| | image1 = Longgunlaws.svg | |||
| | width1 = 600 | |||
| | caption1 = '''Possession of long guns by country:''' | |||
| {{Legend|#0000ff|'''No permit required''' for both repeating and semi-automatic long guns}} | |||
| {{Legend|#2ad4ff|'''Partially licensed''' – repeating long guns permitless, semi-automatic with permit}} | |||
| {{Legend|#00ff00|'''Allowed with permit''' – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason<sup>1</sup>}} | |||
| {{Legend|#ffff00|'''Allowed with permit''' – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required<sup>1</sup>}} | |||
| {{Legend|#ff2a2a|'''Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice''' – few licenses are issued}} | |||
| {{Legend|#b30000|'''Prohibited''' – civilians are banned from obtaining long guns}} | |||
| {{Legend striped|#ff2a2a|white|Different rules regarding shotguns and rifles}} | |||
| <sup>1</sup><small>Some countries in these categories may place additional restrictions or ban semi-automatic long guns</small> | |||
| | image2 = Handgunlaws.svg | |||
| | width2 = 600 | |||
| | caption2 = '''Possession of handguns by country:''' | |||
| {{Legend|#0000ff|'''No permit required''' – permits or licenses are not required to obtain handguns}} | |||
| {{Legend|#00ff00|'''Allowed with permit''' – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason}} | |||
| {{Legend|#ffff00|'''Allowed with permit''' – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required}} | |||
| {{Legend|#ff2a2a|'''Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice''' – few licenses are issued}} | |||
| {{Legend|#b30000|'''Prohibited''' – civilians are banned from obtaining handguns}} | |||
| | footer = | |||
| <small>{{Underline|Notes}}:<br> | |||
| '''-''' Map describes policy regarding obtaining new firearms regardless whether firearms that were produced before ban were ].<br /> | |||
| </small> | |||
| }} | |||
| A 2007 study found evidence that gun control laws ] in 1997 reduced the rates of firearm suicide and homicide in that country.{{sfn|Kapusta et al.|2007}} In ], after disarmament laws were passed in 2003,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Lei Nº 10.426, de 24 de Abril de 2002 |language=pt |trans-title=Law No. 10.426 of April 24, 2002 |url=http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/2002/L10426.htm |website=www.planalto.gov.br |publisher=Presidência da República Casa Civil |access-date=2016-01-31 |archive-date=2015-12-29 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151229145511/http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/2002/L10426.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> gun-related mortality declined by 8% in 2004 relative to the previous year, the first decline observed in a decade. Gun-related hospitalizations also reversed their previous trend by decreasing 4.6% from 2003 to 2004.{{sfn|de Souza et al.|2007}} A 2006 study found that after gun control laws were ] in 1992, suicides committed with guns declined significantly, especially among youth. This study however found that overall suicide rates did not change significantly.{{sfn|Beautrais|Fergusson|Horwood|2006}} A case-control study conducted in New Zealand found that gun ownership was significantly associated with a greater risk of gun suicides, but not suicides overall.{{sfn|Beautrais|Joyce|Mulder|1996}} | |||
| A 2010 study looked at the effect of a policy adopted by the ] that restricted access to guns among adolescents on suicide rates, and found that "Following the policy change, suicide rates decreased significantly by 40%." The authors concluded that "The results of this study illustrate the ability of a relatively simple change in policy to have a major impact on suicide rates."{{sfn|Lubin et al.|2010}} A 2013 study showed that after the ] adopted the Army XXI reform, which restricted gun availability, in 2003, suicide rates{{snd}}both overall and firearm-related{{snd}}decreased.{{sfn|Reisch et al.|2013}} Another 2013 study looking at four restrictive gun laws ] found that two of them may have reduced firearm mortality among men, but that the evidence was more inconclusive with respect to all of the laws they studied.{{sfn|Gjertsen|Leenaars|Vollrath|2013}} A 2014 study found that after ]'s ] was passed in 2000, homicide rates in the country declined, and concluded that "stricter gun control mediated by the FCA accounted for a significant decrease in homicide overall, and firearm homicide in particular, during the study period ."{{sfn|Matzopoulos|Thompson|Myers|2014}} A 2000 study found that a ban on carrying guns in ] was associated with reductions in homicide rates in two cities in the country, namely, ] and ].{{sfn|Villaveces et al.|2000}} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| ===International=== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| {{Reflist|group=note}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| {{reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Alley|2004|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Alley|first=Roderic|title=Internal Conflict and the International Community: Wars Without End?|publisher=Ashgate|year=2004|isbn=9780754609766|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AKNQmbjb98EC|location=Aldershot|access-date=2016-05-06 |archive-date=2017-01-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170110144238/https://books.google.com/books?id=AKNQmbjb98EC|url-status=live}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anestis|Anestis|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Anestis|first1=MD|last2=Anestis|first2=JC|title=Suicide Rates and State Laws Regulating Access and Exposure to Handguns|journal=American Journal of Public Health|date=October 2015 |volume=105 |issue=10 |pages=2049–58|pmid=26270305|doi=10.2105/ajph.2015.302753|pmc=4566524}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anestis et al.|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Anestis|first1=MD|last2=Khazem|first2=LR|last3=Law|first3=KC |last4=Houtsma|first4=C|last5=LeTard|first5=R|last6=Moberg|first6=F|last7=Martin|first7=R|title=The Association Between State Laws Regulating Handgun Ownership and Statewide Suicide Rates|journal=American Journal of Public Health|date=October 2015|volume=105|issue=10|pages=2059–67|doi=10.2105/AJPH.2014.302465 |pmid=25880944|pmc=4566551|ref={{harvid|Anestis et al.|2015}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anestis|Capron|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Anestis|first1=MD|last2=Capron|first2=DW|title=The associations between state veteran population rates, handgun legislation, and statewide suicide rates|journal=Journal of Psychiatric Research |date=March 2016|volume=74|pages=30–34|doi=10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.12.014 |pmid=26736038}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anestis|Anestis|Butterworth|2017}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Anestis|first1=MD|last2=Anestis|first2=JC|last3=Butterworth|first3=SE|title=Handgun Legislation and Changes in Statewide Overall Suicide Rates|journal=American Journal of Public Health |date=April 2017 |volume=107|issue=4|pages=579–581|pmid=28207333|pmc=5343707 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2016.303650}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anestis|Selby|Butterworth|2017}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Anestis|first1=MD|last2=Selby|first2=EA|last3=Butterworth|first3=SE |title=Rising longitudinal trajectories in suicide rates: The role of firearm suicide rates and firearm legislation |journal=Preventive Medicine|date=July 2017|volume=100|pages=159–66 |doi=10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.04.032 |pmid=28455222}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Anonymous|1909|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal | author = Anonymous | title = Carrying Concealed Weapons | journal = Virginia Law Register | year = 1909 | volume = 15 | issue = 5 | pages = 337–416 | jstor=1102220}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Baker|McPhedran|2006|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last1 = Baker | first1 = J. | last2 = McPhedran | first2 = S. | doi = 10.1093/bjc/azl084 | title = Gun Laws and Sudden Death: Did the Australian Firearms Legislation of 1996 Make a Difference? | journal = British Journal of Criminology | volume = 47 | issue = 3 | pages = 455–69 | year = 2006 | url = http://armsandthelaw.com/archives/GunLawsSudden%20DeathBJC.pdf | access-date = 2013-12-23 | archive-date = 2015-07-14 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150714114250/http://armsandthelaw.com/archives/GunLawsSudden%20DeathBJC.pdf | url-status = live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Beautrais|Joyce|Mulder|1996|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last1=Beautrais|first1=A. L.|last2=Joyce|first2=P. R.|last3=Mulder|first3=R. T. |doi=10.3109/00048679609065040 |title=Access to firearms and the risk of suicide: A case control study |journal=Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry |volume=30|issue=6|pages=741–48|year=1996 |pmid=9034462|s2cid=9805679}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Beautrais|Fergusson|Horwood|2006|p=??}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Beautrais|first1=A. L.|last2=Fergusson|first2=D. M.|last3=Horwood|first3=L. J. |title=Firearms legislation and reductions in firearm-related suicide deaths in New Zealand |journal=Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry|date=January 2006|volume=40|issue=3|pages=253–59 |doi=10.1080/j.1440-1614.2006.01782.x|pmid=16476153|s2cid=208623661}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Betz|Ranney|Wintemute|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Betz|first1=Marian|last2=Ranney|first2=Megan|last3=Wintemute|first3=Garen|date=21 January 2016|title=Frozen Funding on Firearm Research: "Doing Nothing Is No Longer an Acceptable Solution" |journal=Western Journal of Emergency Medicine|volume=17|issue=1|pages=91–93|pmid=26823941|pmc=4729430 |doi=10.5811/westjem.2016.1.29767}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Blais|Gagné|Linteau|2011}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Blais |first1=Étienne |last2=Gagné |first2=Marie-Pier |last3=Linteau |first3=Isabelle |title=L'Effet des lois en matière de contrôle des armes à feu sur les homicides au Canada, 1974–2004 |journal=Canadian Journal of Criminology and Criminal Justice |volume=53 |pages=27–61 |year=2011 |issue=1 |s2cid=143960174 |doi=10.3138/cjccj.53.1.27}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Branas et al.|2009|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Branas |first1=C. C. |last2=Richmond |first2=T. S. |last3=Culhane |first3=D. P. |last4=Ten Have |first4=T. R. |last5=Wiebe |first5=D. J. |display-authors=3 |title=Investigating the Link Between Gun Possession and Gun Assault |journal=American Journal of Public Health |volume=99 |issue=11 |pages=2034–40 |year=2009 |pmid=19762675 |pmc=2759797 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2008.143099 |ref={{harvid|Branas et al.|2009}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Bridges|2004}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Bridges|first1=F. Stephen|title=Gun Control Law (Bill C-17), Suicide, and Homicide in Canada|journal=Psychological Reports|date=June 2004|volume=94|issue=3|pages=819–26 |doi=10.2466/pr0.94.3.819-826 |pmid=15217033|s2cid=25666987}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Britt|Kleck|Bordua|1996}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Britt|first1=Chester L.|last2=Kleck|first2=Gary|last3=Bordua|first3=David J.|title=A Reassessment of the D.C. Gun Law: Some Cautionary Notes on the Use of Interrupted Time Series Designs for Policy Impact Assessment|journal=Law & Society Review|date=1996|volume=30|issue=2|pages=361–80|doi=10.2307/3053963|jstor=3053963}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Bukstein et al.|1993|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Bukstein |first1=O. G. |last2=Brent |first2=O. A. |last3=Perper |first3=J. A. |last4=Moritz |first4=G. |last5=Baugher |first5=M. |last6=Schweers |first6=J. |last7=Roth |first7=C. |last8=Balach |first8=L. |display-authors=3 |title=Risk factors for completed suicide among adolescents with a lifetime history of substance abuse: A case-control study |journal=Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica |volume=88 |issue=6 |pages=403–08 |year=1993 |pmid=8310846 |s2cid=44711985 |doi=10.1111/j.1600-0447.1993.tb03481.x |ref={{harvid|Bukstein et al.|1993}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Bryant|2012a|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |last=Bryant |first=M. S. |title=Germany, Gun Laws |pages=314–16 |editor-last=Carter |editor-first=G. L. |encyclopedia=Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law |volume=1 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, CA |year=2012a |isbn=9780313386701 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oD46JBOhMU0C&pg=PA314 |access-date=2020-12-17 |archive-date=2022-05-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220531143138/https://books.google.com/books?id=oD46JBOhMU0C&pg=PA314 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Bryant|2012b|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |last=Bryant |first=M. S. |title=Holocaust Imagery and Gun Control |pages=411–14 |editor-last=Carter |editor-first=G. L. |encyclopedia=Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law |volume=1 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, CA |year=2012b |isbn=9780313386701 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oD46JBOhMU0C&pg=PA411 |access-date=2020-12-17 |archive-date=2014-07-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140701074317/http://books.google.com/books?id=oD46JBOhMU0C&pg=PA411 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Caron|2004}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Caron|first1=Jean|title=Gun Control and Suicide: Possible Impact of Canadian Legislation to Ensure Safe Storage of Firearms|journal=Archives of Suicide Research|date=October 2004 |volume=8 |issue=4 |pages=361–74 |doi=10.1080/13811110490476752|pmid=16081402|s2cid=35131214}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Caron|Julien|Huang|2008}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Caron|first1=J|last2=Julien|first2=M|last3=Huang|first3=JH|title=Changes in suicide methods in Quebec between 1987 and 2000: the possible impact of bill C-17 requiring safe storage of firearms|journal=Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior|date=April 2008|volume=38|issue=2|pages=195–208 |doi=10.1521/suli.2008.38.2.195|pmid=18444777}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Carrington|Moyer|1994}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Carrington|first1=PJ|last2=Moyer|first2=S|title=Gun control and suicide in Ontario |journal=The American Journal of Psychiatry|date=April 1994|volume=151|issue=4|pages=606–08|pmid=8147463 |doi=10.1176/ajp.151.4.606}} | |||
| <!--{{sfn|Cantor|Slater|1995}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Cantor|first1=CH|last2=Slater|first2=PJ|title=The impact of firearm control legislation on suicide in Queensland: preliminary findings|journal=The Medical Journal of Australia|date=5 June 1995|volume=162 |issue=11|pages=583–85|pmid=7791644|doi=10.5694/j.1326-5377.1995.tb138547.x |s2cid=43656446}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Centers for Disease Control and Prevention|2003}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |date=October 3, 2003 |title=First Reports Evaluating the Effectiveness of Strategies for Preventing Violence: Early Childhood Home Visitation and Firearms Laws. Findings from the Task Force on Community Preventive Services |journal=Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) |volume=52 |issue=RR-14 |pages=11–20 |issn=1057-5987 |url=https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5214.pdf |access-date=2017-09-09 |archive-date=2017-07-08 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170708164255/https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5214.pdf |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Centers for Disease Control and Prevention|2013}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |date=August 2, 2013 |title=Firearm Homicides and Suicides in Major Metropolitan Areas – United States, 2006–2007 and 2009–2010 |journal=Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) |volume=62 |issue=30 |pages=597–602 |pmid=23903593 |pmc=4604852 |url=https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6230a1.htm |access-date=2017-04-21 |archive-date=2017-04-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170422033221/https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6230a1.htm |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Chapman|Alpers|Agho|Jones|2006}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Chapman |first1=S. |last2=Alpers |first2=P. |last3=Agho |first3=K. |last4=Jones |first4=M. |title=Australia's 1996 gun law reforms: Faster falls in firearm deaths, firearm suicides, and a decade without mass shootings |journal=Injury Prevention |volume=12 |issue=6 |pages=365–72 |year=2006 |pmid=17170183 |pmc=2704353 |doi=10.1136/ip.2006.013714}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Chapman|Alpers|Jones|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Chapman|first1=Simon|last2=Alpers|first2=Philip|last3=Jones|first3=Michael |title=Association Between Gun Law Reforms and Intentional Firearm Deaths in Australia, 1979–2013 |journal=JAMA |date=22 June 2016 |volume=316|issue=3|pages=291–99|pmid=27332876|doi=10.1001/jama.2016.8752 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Cheung|Dewa|2005}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Cheung |first1=A. H. |last2=Dewa |first2=C. S. |year=2005 |title=Current trends in youth suicide and firearms regulations |journal=Canadian Journal of Public Health |volume=96 |issue=2 |pages=131–35 |doi=10.1007/BF03403676 |pmc=6975744 |pmid=15850034}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Conner|Zhong|2003}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Conner|first1=Kenneth R|last2=Zhong|first2=Yueying|title=State firearm laws and rates of suicide in men and women|journal=American Journal of Preventive Medicine|date=November 2003|volume=25|issue=4 |pages=320–24|doi=10.1016/S0749-3797(03)00212-5|pmid=14580634|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Conwell et al.|2002|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Conwell |first1=Y. |last2=Duberstein |first2=P. R. |last3=Connor |first3=K. |last4=Eberly |first4=S. |last5=Cox |first5=C. |last6=Caine |first6=E. D. |display-authors=3 |title=Access to Firearms and Risk for Suicide in Middle-Aged and Older Adults |journal=The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry |volume=10 |issue=4 |pages=407–16 |year=2002 |pmid=12095900|doi=10.1097/00019442-200207000-00007 |ref={{harvid|Conwell et al.|2002}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Crandall et al.|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Crandall|first1=M|last2=Eastman|first2=A|last3=Violano|first3=P |last4=Greene|first4=W|last5=Allen|first5=S|last6=Block|first6=E|last7=Christmas|first7=AB|last8=Dennis |first8=A|last9=Duncan |first9=T |last10=Foster|first10=S|last11=Goldberg|first11=S|last12=Hirsh|first12=M |last13=Joseph|first13=D|last14=Lommel|first14=K|last15=Pappas|first15=P|last16=Shillinglaw|first16=W |title=Prevention of firearm-related injuries with restrictive licensing and concealed carry laws: An Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma systematic review|journal=The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery|date=November 2016|volume=81|issue=5|pages=952–60 |pmid=27602894|s2cid=22673439 |doi=10.1097/ta.0000000000001251|ref={{harvid|Crandall et al.|2016}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Crifasi et al.|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Crifasi|first1=CK|last2=Meyers|first2=JS|last3=Vernick|first3=JS|last4=Webster |first4=DW|title=Effects of changes in permit-to-purchase handgun laws in Connecticut and Missouri on suicide rates |journal=Preventive Medicine|date=October 2015|volume=79|pages=43–49|pmid=26212633 |doi=10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.07.013|ref={{harvid|Crifasi et al.|2015}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Dandurand|1998}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite report |last=Dandurand |first=Yvon |date=September 1998 |type=working document |chapter=4. Firearm Suicides |chapter-url=https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/csj-sjc/jsp-sjp/wd98_4-dt98_4/p4.html#a46 |title=Firearms, Accidental Deaths, Suicides and Violent Crime |publisher=Department of Justice, Canada |url=https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/csj-sjc/jsp-sjp/wd98_4-dt98_4/wd98_4.pdf |access-date=2021-06-15 |archive-date=2021-06-15 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210615032726/https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/csj-sjc/jsp-sjp/wd98_4-dt98_4/wd98_4.pdf |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Diez et al.|2017}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Díez|first1=C|last2=Kurland|first2=RP|last3=Rothman|first3=EF |last4=Bair-Merritt|first4=M|last5=Fleegler|first5=E|last6=Xuan|first6=Z|last7=Galea|first7=S|last8=Ross |first8=CS |last9=Kalesan|first9=B|last10=Goss|first10=KA|last11=Siegel|first11=M|title=State Intimate Partner Violence-Related Firearm Laws and Intimate Partner Homicide Rates in the United States, 1991 to 2015 |journal=Annals of Internal Medicine|date=17 October 2017|volume=167|issue=8|pages=536–43 |pmid=28975202 |doi=10.7326/M16-2849|doi-access=free|ref={{harvid|Diez et al.|2017}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|de Souza et al.|2007}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=de Fatima Marinho de Souza|first1=M.|last2=Macinko|first2=J. |last3=Alencar|first3=A. P.|last4=Malta|first4=D. C.|last5=de Morais Neto|first5=O. L.|title=Reductions In Firearm-Related Mortality And Hospitalizations In Brazil After Gun Control|journal=Health Affairs |date=March–April 2007|volume=26|issue=2|pages=575–84|pmid=17339689 |doi=10.1377/hlthaff.26.2.575|doi-access=free|ref={{harvid|de Souza et al.|2007}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Dyer|2010|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dyer |first=Gwynne |title=War: The New Edition |year=2010 |publisher=Random House |isbn=9780307369017 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yBkfjW8ZQJAC&pg=PT208 |access-date=2016-05-06 |archive-date=2017-01-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170110171218/https://books.google.com/books?id=yBkfjW8ZQJAC&pg=PT208 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Edwards et al.|2018|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last1=Edwards|first1=Griffin|last2=Nesson|first2=Erik|last3=Robinson|first3=Josh|last4=Vars|first4=Fredrick|title=Looking Down the Barrel of a Loaded Gun: The Effect of Mandatory Handgun Purchase Delays on Homicide and Suicide|journal=The Economic Journal|year=2018|volume=128|issue=616|pages=3117–40|doi=10.1111/ecoj.12567|issn=1468-0297|s2cid=155851188|url=https://scholarship.law.ua.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1166&context=fac_working_papers |ref={{harvid|Edwards et al.|2018}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Fleegler et al.|2013}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Fleegler|first1=EW|last2=Lee|first2=LK|last3=Monuteaux|first3=MC |last4=Hemenway|first4=D|last5=Mannix|first5=R|title=Firearm legislation and firearm-related fatalities in the United States |journal=JAMA Internal Medicine|date=13 May 2013|volume=173|issue=9|pages=732–40 |pmid=23467753|doi=10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.1286|doi-access=free|ref={{harvid|Fleegler et al.|2013}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Gagne et al.|2010}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Gagne|first1=M.|last2=Robitaille|first2=Y.|last3=Hamel|first3=D.|last4=St-Laurent |first4=D.|title=Firearms regulation and declining rates of male suicide in Quebec|journal=Injury Prevention |date=29 June 2010|volume=16|issue=4|pages=247–53|doi=10.1136/ip.2009.022491|pmid=20587817|doi-access=free |ref={{harvid|Gagne et al.|2010}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Gjertsen|Leenaars|Vollrath|2013}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Gjertsen|first1=Finn|last2=Leenaars|first2=Antoon|last3=Vollrath|first3=Margarete |title=Mixed Impact of Firearms Restrictions on Fatal Firearm Injuries in Males: A National Observational Study |journal=International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health|date=30 December 2013 |volume=11|issue=1|pages=487–506|doi=10.3390/ijerph110100487|pmid=24380979|pmc=3924456|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Hahn et al.|2005}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Hahn|first1=RA|last2=Bilukha|first2=O|last3=Crosby|first3=A |last4=Fullilove|first4=MT|last5=Liberman|first5=A|last6=Moscicki|first6=E|last7=Snyder|first7=S|last8=Tuma|first8=F |last9=Briss |first9=PA|last10=Task Force on Community Preventive Services|title=Firearms laws and the reduction of violence: a systematic review|journal=American Journal of Preventive Medicine |date=February 2005|volume=28|issue=2 Suppl 1 |pages=40–71|pmid=15698747 |doi=10.1016/j.amepre.2004.10.005 |ref={{harvid|Hahn et al.|2005}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Hemenway|2009|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last=Hemenway|first=D.|title=How to find nothing|journal=Journal of Public Health Policy |volume=30|issue=3|pages=260–68|year=2009|pmid=19806067|doi=10.1057/jphp.2009.26|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Hemenway|2016}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Hemenway|first=David|title=Firearm legislation and mortality in the USA|journal=The Lancet|date=March 2016|pmid=26972841|volume=387|issue=10030|pages=1796–97|s2cid=37771810 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00206-3}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Hemenway|Miller|2000|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Hemenway |first1=D. |last2=Miller |first2=M. |title=Firearm availability and homicide rates across 26 high-income countries |journal=The Journal of Trauma |volume=49 |issue=6 |pages=985–88 |year=2000 |pmid=11130511 |citeseerx=10.1.1.472.6990 |doi=10.1097/00005373-200012000-00001}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Hepburn|Hemenway|2004|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last1 = Hepburn | first1 = L. M. | last2 = Hemenway | first2 = D. | doi = 10.1016/S1359-1789(03)00044-2 | title = Firearm availability and homicide: A review of the literature | journal = Aggression and Violent Behavior | volume = 9 | issue = 4 | pages = 417–40 | year = 2004}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Huemer|2003}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Huemer |first=Michael |year=2003 |title=Is There a Right to Own a Gun? |journal=Social Theory and Practice |volume=29 |issue=2 |pages=297–324 |doi=10.5840/soctheorpract200329215 |url=http://spot.colorado.edu/~huemer/guncontrol.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=2017-12-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171213033617/https://spot.colorado.edu/~huemer/guncontrol.htm }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Irvin et al.|2014}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Irvin|first1=N|last2=Rhodes|first2=K|last3=Cheney|first3=R|last4=Wiebe|first4=D |title=Evaluating the effect of state regulation of federally licensed firearm dealers on firearm homicide |journal=American Journal of Public Health|date=August 2014|volume=104|issue=8|pages=1384–86|pmid=24922158 |doi=10.2105/ajph.2014.301999|pmc=4103238|ref={{harvid|Irvin et al.|2014}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Juma|2006|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book|editor-last=Juma|editor-first=Monica Kathina|title=Compendium of Key Documents Relating to Peace and Security in Africa|series=Series on peace and conflict in Africa|year=2006|publisher=Pretoria University Law Press|location=Pretoria|isbn=9780958509732|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mjtcCyGjm1wC|access-date=2016-05-06 |archive-date=2021-06-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210613151125/https://books.google.com/books?id=mjtcCyGjm1wC|url-status=live}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kalesan et al.|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Kalesan|first1=Bindu|last2=Mobily|first2=Matthew E|last3=Keiser|first3=Olivia|last4=Fagan|first4=Jeffrey A|last5=Galea|first5=Sandro|title=Firearm legislation and firearm mortality in the USA: a cross-sectional, state-level study|journal=The Lancet|date=March 2016|volume=387|issue=10030|pages=1847–55|pmid=26972843|s2cid=21415884|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01026-0|ref={{harvid|Kalesan et al.|2016}}|url=https://boris.unibe.ch/79968/14/Kalesan%20Lancet%202016_postprint.pdf|access-date=2019-12-14 |archive-date=2020-02-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200213214332/https://boris.unibe.ch/79968/14/Kalesan%20Lancet%202016_postprint.pdf|url-status=live}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kapusta et al.|2007}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Kapusta|first1=ND|last2=Etzersdorfer|first2=E|last3=Krall|first3=C|last4=Sonneck |first4=G|title=Firearm legislation reform in the European Union: impact on firearm availability, firearm suicide and homicide rates in Austria|journal=The British Journal of Psychiatry|date=September 2007 |volume=191|issue=3|pages=253–57|pmid=17766767|doi=10.1192/bjp.bp.106.032862|doi-access=free|ref={{harvid|Kapusta et al.|2007}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Karp|2010|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Karp |first=Aaron |chapter=Elusive Arsenals: Gang and Group Firearms |editor-last1=Berman |editor-first1=Eric G. |editor-last2=Krause |editor-first2=Keith |editor-last3=LeBrun |editor-first3=Emile |editor-last4=McDonald |editor-first4=Glenn |display-editors=1 |title=Small Arms Survey 2010: Gangs, Groups, and Guns |year=2010 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |isbn=9780521146845 |url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2010.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101104002327/http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2010.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=4 November 2010 |chapter-url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/fileadmin/docs/A-Yearbook/2010/en/Small-Arms-Survey-2010-Chapter-04-EN.pdf }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Karp|2007|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Karp |first=Aaron |chapter=Completing the Count: Civilian Firearms |title=Small Arms Survey 2007: Guns and the City |editor1-first=Eric G. |editor1-last=Berman |editor2-first=Keith |editor2-last=Krause |editor3-first=Emile |editor3-last=LeBrun |editor4-first=Glenn |editor4-last=McDonald |display-editors=1 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2007 |location=Cambridge |isbn=9780521706544 |chapter-url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/fileadmin/docs/A-Yearbook/2007/en/full/Small-Arms-Survey-2007-Chapter-02-EN.pdf |url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2007.html |access-date=2013-12-23 |archive-date=2018-08-27 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180827001033/http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2007.html |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kates|1983|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Kates |first1=D. B. |title=Handgun Prohibition and the Original Meaning of the Second Amendment |journal=Michigan Law Review |year=1983 |volume=82 |issue=2 |pages=204–73 |doi=10.2307/1288537 |jstor=1288537 |url=http://www.constitution.org/2ll/2ndschol/57mich.pdf |access-date=2013-12-23 |archive-date=2014-12-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141222054749/http://www.constitution.org/2ll/2ndschol/57mich.pdf |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kates|Mauser|2007|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Kates |first1=D. B. |last2=Mauser |first2=G. A. |title=Would Banning Firearms Reduce Murder and Suicide? A Review of International and Some Domestic Evidence |journal=Harvard Journal of Law & Public Policy |year=2007 |volume=30 |issue=2 |pages=649–94 |url=http://www.law.harvard.edu/students/orgs/jlpp/Vol30_No2_KatesMauseronline.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080910111444/http://www.law.harvard.edu/students/orgs/jlpp/Vol30_No2_KatesMauseronline.pdf |archive-date=2008-09-10 }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kellermann et al.|1992}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Kellermann |first1=A. L. |last2=Rivara |first2=F. P. |last3=Somes |first3=G. |last4=Reay |first4=D. T. |last5=Francisco |first5=J. |last6=Banton |first6=J. G. |last7=Prodzinski |first7=J. |last8=Fligner |first8=C. |last9=Hackman |first9=B. B. |display-authors=3 |title=Suicide in the Home in Relation to Gun Ownership |journal=New England Journal of Medicine |volume=327 |issue=7 |pages=467–72 |year=1992 |pmid=1308093 |s2cid=35031090 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199208133270705 |ref={{harvid|Kellermann et al.|1992}} |doi-access=free }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kellermann et al.|1993}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Kellermann|first1=Arthur L.|last2=Rivara|first2=Frederick P. |last3=Rushforth|first3=Norman B.|last4=Banton|first4=Joyce G.|last5=Reay|first5=Donald T.|last6=Francisco |first6=Jerry T. |last7=Locci|first7=Ana B.|last8=Prodzinski|first8=Janice|last9=Hackman|first9=Bela B. |last10=Somes|first10=Grant|title=Gun Ownership as a Risk Factor for Homicide in the Home|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|date=7 October 1993|volume=329|issue=15 |pages=1084–91|pmid=8371731 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199310073291506|ref={{harvid|Kellermann et al.|1993}}|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Killias|1993|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite report |last=Killias |first=Martin |chapter=Gun ownership, suicide and homicide: an international perspective |editor1-last=Del Frate |editor1-first=A. A. |editor2-last=Zvekić |editor2-first=U. |editor3-last=van Dijk |editor3-first=J. J. |display-editors=1 |title=Understanding crime: experiences of crime and crime control |year=1993 |publisher=] |location=Rome |pages=289–306 |chapter-url=http://www.unicri.eu/documentation_centre/publications/series/understanding/19_GUN_OWNERSHIP.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6M74ygi4f?url=http://www.unicri.eu/documentation_centre/publications/series/understanding/19_GUN_OWNERSHIP.pdf |archive-date=2013-12-24 }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Killias|van Kesteren|Rindlisbacher|2001|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Killias |first1=M. |last2=van Kesteren |first2=J. |last3=Rindlisbacher |first3=M. |title=Guns, violent crime, and suicide in 21 countries |journal=Canadian Journal of Criminology |volume=43 |issue=4 |pages=429–48 |year=2001 |doi=10.3138/cjcrim.43.4.429}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kleck|Patterson|1993|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Kleck |first1=G. |last2=Patterson |first2=E. B. |doi=10.1007/BF01064462 |title=The impact of gun control and gun ownership levels on violence rates |journal=Journal of Quantitative Criminology |volume=9 |issue=3 |pages=249–87 |year=1993 |s2cid=144180611}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Klieve|Barnes|De Leo|2009}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Klieve|first1=Helen|last2=Barnes|first2=Michael|last3=De Leo|first3=Diego |title=Controlling firearms use in Australia: has the 1996 gun law reform produced the decrease in rates of suicide with this method?|journal=Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology|year=2009|orig-year=Epub: 4 October 2008|volume=44|issue=4|pages=285–92|doi=10.1007/s00127-008-0435-9|pmid=18839044|s2cid=22624912}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kposowa|Hamilton|Wang|2016}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Kposowa|first1=A|last2=Hamilton|first2=D|last3=Wang|first3=K|title=Impact of Firearm Availability and Gun Regulation on State Suicide Rates|journal=Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior |volume=46 |issue=6 |pages=678–96|date=21 March 2016|pmid=26999372|doi=10.1111/sltb.12243}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Krug|Powell|Dahlberg|1998|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last1 = Krug | first1 = E. | last2 = Powell | first2 = K. E. | last3 = Dahlberg | first3 = L. L. | doi = 10.1093/ije/27.2.214 | title = Firearm-related deaths in the United States and 35 other high- and upper-middle-income countries | journal = International Journal of Epidemiology | volume = 27 | issue = 2 | pages = 214–21 | year = 1998 | pmid = 9602401 | doi-access = free }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Kwon et al.|1997}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Kwon|first1=Ik-Whan G.|last2=Scott|first2=Bradley|last3=Safranski|first3=Scott R. |last4=Bae|first4=Muen|title=The Effectiveness of Gun Control Laws|journal=American Journal of Economics and Sociology|date=24 August 2010|volume=56|issue=1|pages=41–50|doi=10.1111/j.1536-7150.1997.tb03449.x|ref={{harvid|Kwon et al.|1997}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|LaPierre|1994|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=LaPierre |first=W. |author-link=Wayne LaPierre |title=Guns, crime, and freedom |publisher=Regnery |location=Washington, D.C. |year=1994 |isbn=9780895264770 |url=https://archive.org/details/gunscrimefreedom00lapi_0 }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lambert|Silva|1998}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Lambert|first1=Michael T.|last2=Silva|first2=Peter S.|journal=Psychiatric Quarterly |title=An Update on the Impact of Gun Control Legislation on Suicide|date=1998|volume=69|issue=2|pages=127–34 |doi=10.1023/A:1024714619938|pmid=9627930|s2cid=37048769}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Langmann|2012}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Langmann|first1=C.|title=Canadian Firearms Legislation and Effects on Homicide 1974 to 2008|journal=Journal of Interpersonal Violence|date=10 February 2012|volume=27|issue=12|pages=2303–21 |doi=10.1177/0886260511433515|pmid=22328660|s2cid=42273865}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lanza|2014}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Lanza|first1=Steven P.|title=The effect of firearm restrictions on gun-related homicides across US states|journal=Applied Economics Letters|date=3 April 2014|volume=21|issue=13|pages=902–05 |doi=10.1080/13504851.2014.896977|s2cid=154724050}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lee|Suardi|2010}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Lee|first1=Wang-Sheng|last2=Suardi|first2=Sandy|title=The Australian Firearms Buyback and ITS Effect on Gun Deaths|journal=Contemporary Economic Policy |date=January 2010 |volume=28 |issue=1|pages=65–79 |doi=10.1111/j.1465-7287.2009.00165.x |citeseerx=10.1.1.507.1298|s2cid=53520961}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lee et al.|2016}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Lee|first1=LK|last2=Fleegler|first2=EW|last3=Farrell|first3=C |last4=Avakame|first4=E|last5=Srinivasan|first5=S|last6=Hemenway|first6=D|last7=Monuteaux|first7=MC|title=Firearm Laws and Firearm Homicides: A Systematic Review|journal=JAMA Internal Medicine|date=14 November 2016 |volume=177|issue=1|pages=106–19|pmid=27842178|s2cid=205119294 |doi=10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.7051|ref={{harvid|Lee et al.|2016}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Leenaars|Lester|2001}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Leenaars|first1=Antoon A|last2=Lester|first2=David|title=The impact of gun control (Bill C-51) on homicide in Canada|journal=Journal of Criminal Justice|date=July 2001|volume=29 |issue=4 |pages=287–94 |doi=10.1016/S0047-2352(01)00094-0|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Leenaars et al.|2003}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Leenaars|first1=Antoon A.|last2=Moksony|first2=Ferenc|last3=Lester|first3=David |last4=Wenckstern|first4=Susanne|title=The Impact of Gun Control (Bill C-51) on Suicide in Canada |journal=Death Studies |date=February 2003|volume=27|issue=2|pages=103–24|pmid=12675070|s2cid=10059933 |doi=10.1080/07481180302890|ref={{harvid|Leenaars et al.|2003}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Leigh|Neill|2010}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Leigh|first1=A.|last2=Neill|first2=C.|title=Do Gun Buybacks Save Lives? Evidence from Panel Data|journal=American Law and Economics Review|date=20 August 2010|volume=12|issue=2|pages=509–57 |doi=10.1093/aler/ahq013|hdl=10419/36943|s2cid=787141|hdl-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lester|Leenaars|1993}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Lester|first1=David|last2=Leenaars|first2=Antoon|title=Suicide Rates in Canada before and after Tightening Firearm Control Laws|journal=Psychological Reports|date=June 1993|volume=72 |issue=3|pages=787–90 |doi=10.2466/pr0.1993.72.3.787|pmid=8332684|s2cid=25191464}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Loftin et al.|1991}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Loftin|first1=Colin|last2=McDowall|first2=David|last3=Wiersema|first3=Brian |last4=Cottey|first4=Talbert J.|title=Effects of Restrictive Licensing of Handguns on Homicide and Suicide in the District of Columbia|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|date=5 December 1991|volume=325 |issue=23|pages=1615–20|pmid=1669841|doi=10.1056/NEJM199112053252305|ref= {{harvid|Loftin et al.|1991}}|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lott|2010|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lott |first=J. R. |author-link=John Lott (political activist) |title=More guns, less crime understanding crime and gun-control laws |publisher=University of Chicago Press |location=Chicago |year=2010 |edition=3rd |isbn=9780226493671 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=j6cMYKRgqQ8C&pg=PP1 |access-date=2020-12-17 |archive-date=2022-05-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220531054256/https://books.google.com/books?id=j6cMYKRgqQ8C&pg=PP1 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lott|2012|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal | last1 = Lott | first1 = J. R. | title = What a Balancing Test Will Show for Right-to-Carry Laws | journal = University of Maryland Law Review | year = 2012 | volume = 71 | issue = 4 | pages = 1205–18 | url = http://digitalcommons.law.umaryland.edu/mlr/vol71/iss4/15 | access-date = 2013-12-23 | archive-date = 2013-12-24 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131224234822/http://digitalcommons.law.umaryland.edu/mlr/vol71/iss4/15/ | url-status = live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Lubin et al.|2010}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Lubin|first1=Gad|last2=Werbeloff|first2=Nomi|last3=Halperin |first3=Demian|last4=Shmushkevitch|first4=Mordechai|last5=Weiser|first5=Mark|last6=Knobler|first6=Haim Y. |title=Decrease in Suicide Rates After a Change of Policy Reducing Access to Firearms in Adolescents: A Naturalistic Epidemiological Study|journal=Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior|date=October 2010 |volume=40|issue=5|pages=421–24|pmid=21034205 |doi=10.1521/suli.2010.40.5.421 |ref={{harvid|Lubin et al.|2010}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Luca|Malhotra|Poliquin|2017}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last1=Luca|first1=Michael|last2=Malhotra|first2=Deepak|last3=Poliquin|first3=Christopher |date=2017-10-16|title=Handgun waiting periods reduce gun deaths|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences |volume=114|issue=46|pages=12162–65|pmid=29078268|pmc=5699026 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1619896114 |bibcode=2017PNAS..11412162L |issn=0027-8424|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Ludwig|Cook|2000}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Ludwig |first1=Jens |last2=Cook |first2=Phillip J. |date=2000-08-02 |title=Homicide and Suicide Rates Associated With Implementation of the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act |journal=JAMA |volume=284 |issue=5 |pages=585–91 |doi=10.1001/jama.284.5.585 |pmid=10918704 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Malcolm|1994|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Malcolm |first=Joyce |title=To Keep and Bear Arms: The Origins of an Anglo-American Right |publisher=Harvard University Press |location=Cambridge, MA |year=1994 |isbn=9780674893061 |url=https://archive.org/details/tokeepbeararmsor00malc }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Malcolm|2002|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Malcolm | first = Joyce | title = Guns and violence : The English experience | publisher = Harvard University Press | location = Cambridge, Mass | year = 2002 | isbn =978-0674007536}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Matzopoulos|Thompson|Myers|2014}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Matzopoulos|first1=Richard G.|last2=Thompson|first2=Mary Lou|last3=Myers |first3=Jonathan E.|title=Firearm and Nonfirearm Homicide in 5 South African Cities: A Retrospective Population-Based Study |journal=American Journal of Public Health|date=March 2014|volume=104|issue=3 |pages=455–60|doi=10.2105/AJPH.2013.310650|pmid=24432917|pmc=3953758}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Mauser|Holmes|1992}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Mauser|first1=G. A.|last2=Holmes|first2=R. A.|title=An Evaluation of the 1977 Canadian Firearms Legislation|journal=Evaluation Review|date=1 December 1992|volume=16|issue=6|pages=603–17 |s2cid=144576514 |doi=10.1177/0193841X9201600602}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Mauser|Maki|2003}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Mauser|first1=Gary A.|last2=Maki|first2=Dennis|title=An evaluation of the 1977 Canadian firearm legislation: robbery involving a firearm|journal=Applied Economics|date=April 2003 |volume=35|issue=4 |pages=423–36 |s2cid=154344131|doi=10.1080/00036840210143099}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|McPhedran|Mauser|2013}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=McPhedran|first1=S|last2=Mauser|first2=G|title=Lethal firearm-related violence against Canadian women: did tightening gun laws have an impact on women's health and safety?|journal=Violence and Victims |date=2013|volume=28|issue=5|pages=875–83|pmid=24364129|s2cid=21714121 |doi=10.1891/0886-6708.vv-d-12-00145|hdl=10072/57640|hdl-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Medoff|Magaddino|1983}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Medoff|first1=M. H.|last2=Magaddino|first2=J. P.|title=Suicides and Firearm Control Laws|journal=Evaluation Review|date=1 January 1983|volume=7|issue=3|pages=357–72|s2cid=145607862 |doi=10.1177/0193841X8300700305}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Miller|1978|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Miller |first1=M. |title=Geriatric Suicide: The Arizona Study |journal=The Gerontologist |volume=18 |issue=5 Part 1 |pages=488–95 |year=1978 |doi=10.1093/geront/18.5_Part_1.488 |pmid=263566}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Miller|Azrael|Hemenway|2002|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last1 = Miller | first1 = M. | last2 = Azrael | first2 = D. | last3 = Hemenway | first3 = D. | doi = 10.2105/AJPH.92.12.1988 | title = Rates of Household Firearm Ownership and Homicide Across US Regions and States, 1988–1997 | journal = American Journal of Public Health | volume = 92 | issue = 12 | pages = 1988–93 | year = 2002 | pmid = 12453821 | pmc =1447364}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Miller|Azrael|Hemenway|2007|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal | last1 = Miller | first1 = M. | last2 = Hemenway | first2 = D. | last3 = Azrael | first3 = D. | doi = 10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.09.024 | title = State-level homicide victimization rates in the US in relation to survey measures of household firearm ownership, 2001–2003 | journal = Social Science & Medicine | volume = 64 | issue = 3 | pages = 656–64 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17070975}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Miller|Hemenway|2008|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Miller |first1=M. |last2=Hemenway |first2=D. |title=Guns and Suicide in the United States |journal=New England Journal of Medicine |volume=359 |issue=10 |pages=989–91 |year=2008 |pmid=18768940 |doi=10.1056/NEJMp0805923|doi-access=free }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|National Research Council|2005|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |author1=National Research Council |title=Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review |series=Committee to Improve Research Information and Data on Firearms |editor1-last=Wellford |editor1-first=C. F. |editor2-last=Pepper |editor2-first=J. V. |editor3-last=Petrie |editor3-first=C. V. |publisher=The National Academies Press |location=Washington, DC |year=2005 |isbn=9780309091244 |url=http://www.nap.edu/catalog/10881.html |access-date=2013-12-26 |archive-date=2008-10-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081013135651/http://www.nap.edu/catalog/10881.html |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Ozanne-Smith et al.|2004|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Ozanne-Smith |first1=J. |last2=Ashby |first2=K. |last3=Newstead |first3=S. |last4=Stathakis |first4=V. Z. |last5=Clapperton |first5=A. |display-authors=3 |title=Firearm related deaths: The impact of regulatory reform |doi=10.1136/ip.2003.004150 |journal=Injury Prevention |volume=10 |issue=5 |pages=280–86 |year=2004 |pmid=15470007 |pmc=1730132 |ref={{harvid|Ozanne-Smith et al.|2004}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Parker|2011|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Parker |first=Sarah |chapter=Balancing Acts: Regulation of Civilian Firearm Possession |title=Small Arms Survey 2011: States of Security |editor1-first=Eric G. |editor1-last=Berman |editor2-first=Keith |editor2-last=Krause |editor3-first=Emile |editor3-last=LeBrun |editor4-first=Glenn |editor4-last=McDonald |display-editors=1 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2011 |location=Cambridge |isbn=9780521146869 |chapter-url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/fileadmin/docs/A-Yearbook/2011/en/Small-Arms-Survey-2011-Chapter-09-EN.pdf |url=http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2011.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110711032608/http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/publications/by-type/yearbook/small-arms-survey-2011.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=11 July 2011 }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Perrin|1980|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Perrin |first=Noel |title=Giving Up the Gun: Japan's Reversion to the Sword, 1543–1879 |publisher=Shambhala |year=1980 |isbn=9780877731849 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4Ete0zPAnjwC&pg=PP1 |access-date=2020-12-17 |archive-date=2020-02-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200213035935/https://books.google.com/books?id=4Ete0zPAnjwC&pg=PP1 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Pierce|Braga|Wintemute|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Pierce|first1=GL|last2=Braga|first2=AA|last3=Wintemute|first3=GJ|title=Impact of California firearms sales laws and dealer regulations on the illegal diversion of guns|journal=Injury Prevention|date=June 2015|volume=21|issue=3|pages=179–84|pmid=25472991|doi=10.1136/injuryprev-2014-041413|s2cid=41375606}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Price|Thompson|Dake|2004}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Price|first1=James H.|last2=Thompson|first2=Amy J.|last3=Dake|first3=Joseph A. |title=Factors Associated with State Variations in Homicide, Suicide, and Unintentional Firearm Deaths |journal=Journal of Community Health|date=August 2004|volume=29|issue=4|pages=271–83 |doi=10.1023/B:JOHE.0000025326.89365.5c|pmid=15186014|s2cid=12678341}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Reisch et al.|2013}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Reisch|first1=T|last2=Steffen|first2=T|last3=Habenstein|first3=A|author4-link=Wolfgang Tschacher|last4=Tschacher |first4=W|title=Change in suicide rates in Switzerland before and after firearm restriction resulting from the 2003 "Army XXI" reform|journal=The American Journal of Psychiatry|date=September 2013|volume=170 |issue=9|pages=977–84|pmid=23897090|doi=10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12091256|ref={{harvid|Reisch et al.|2013}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Reuter|Mouzos|2003|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book|first1=Peter|last1=Reuter|first2=Jenny|last2=Mouzos|chapter=Australia: A Massive Buyback of Low-Risk Guns|year=2003|pages=121–56|editor-first1=J.|editor-last1=Ludwig|editor-first2=P. J.|editor-last2=Cook|title=Evaluating Gun Policy: Effects on Crime and Violence|publisher=Brookings Institution Press|isbn=9780815753377|url=http://www.popcenter.org/problems/gun_violence/PDFs/Reuter_Mouzos_2003.pdf|access-date=2013-12-23 |archive-date=2013-10-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020213302/http://www.popcenter.org/problems/gun_violence/PDFs/Reuter_Mouzos_2003.pdf|url-status=live}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Rodríguez Andrés|Hempstead|2011}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Rodríguez Andrés|first1=Antonio|last2=Hempstead|first2=Katherine|title=Gun control and suicide: The impact of state firearm regulations in the United States, 1995–2004|journal=Health Policy |date=June 2011 |volume=101|issue=1|pages=95–103|doi=10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.10.005|pmid=21044804}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Rosengart et al.|2005}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Rosengart|first1=M|last2=Cummings|first2=P|last3=Nathens|first3=A |last4=Heagerty|first4=P|last5=Maier|first5=R|last6=Rivara|first6=F|title=An evaluation of state firearm regulations and homicide and suicide death rates|journal=Injury Prevention|date=April 2005|volume=11 |issue=2|pages=77–83|doi=10.1136/ip.2004.007062|pmid=15805435|pmc=1730198|ref={{harvid|Rosengart et al.|2005}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Rudolph et al.|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Rudolph|first1=KE|last2=Stuart|first2=EA|last3=Vernick|first3=JS|last4=Webster |first4=DW|title=Association Between Connecticut's Permit-to-Purchase Handgun Law and Homicides |journal=American Journal of Public Health|date=August 2015|volume=105|issue=8|pages=e49–54|pmid=26066959 |pmc=4504296|doi=10.2105/ajph.2015.302703|ref={{harvid|Rudolph et al.|2015}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Safavi et al.|2014}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Safavi|first1=A|last2=Rhee|first2=P|last3=Pandit|first3=V |last4=Kulvatunyou|first4=N |last5=Tang|first5=A|last6=Aziz|first6=H|last7=Green|first7=D|last8=O'Keeffe |first8=T|last9=Vercruysse |first9=G |last10=Friese|first10=RS|last11=Joseph|first11=B|title=Children are safer in states with strict firearm laws: a National Inpatient Sample study|journal=The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery |date=January 2014 |volume=76 |issue=1|pages=146–50; discussion 150–51|pmid=24368370 |s2cid=11563737|doi=10.1097/ta.0b013e3182ab10fb|ref={{harvid|Safavi et al.|2014}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Santaella-Tenorio et al.|2016}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Santaella-Tenorio|first1=Julian|last2=Cerdá|first2=Magdalena|last3=Villaveces |first3=Andrés|last4=Galea|first4=Sandro|title=What Do We Know About the Association Between Firearm Legislation and Firearm-Related Injuries?|journal=Epidemiologic Reviews|volume=38|issue=1|pages=140–57 |date=10 February 2016|doi=10.1093/epirev/mxv012|pmid=26905895|pmc=6283012|ref={{harvid|Santaella-Tenorio et al.|2016}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Simonetti et al.|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal |display-authors=3 |last1=Simonetti |first1=Joseph A. |last2=Rowhani-Rahbar |first2=Ali |last3=Mills |first3=Brianna |last4=Young |first4=Bessie |last5=Rivara |first5=Frederick P. |date=August 2015 |journal=American Journal of Public Health |title=State Firearm Legislation and Nonfatal Firearm Injuries |volume=105 |issue=8 |pages=1703–09 |pmid=26066935 |pmc=4504301 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2015.302617|ref={{harvid|Simonetti et al.|2015}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Sloan et al.|1990}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Sloan|first1=JH|last2=Rivara|first2=FP|last3=Reay|first3=DT |last4=Ferris|first4=JA|last5=Kellermann|first5=AL|title=Firearm regulations and rates of suicide. A comparison of two metropolitan areas |journal=The New England Journal of Medicine|date=8 February 1990 |volume=322|issue=6|pages=369–73|pmid=2393410|doi=10.1056/nejm199002083220605 |ref={{harvid|Sloan et al.|1990}}|doi-access=free}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Tahmassebi|1991|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Tahmassebi |first1=S. B. |title=Gun Control and Racism |journal=George Mason University Civil Rights Law Journal |date=Summer 1991 |volume=2 |issue=1 |pages=67–100 |url=http://www.saf.org/LawReviews/Tahmassebi1.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=August 16, 2000 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000816062011/http://www.saf.org/LawReviews/Tahmassebi1.html }} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Tashiro et al.|2016}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Tashiro|first1=J|last2=Lane|first2=RS|last3=Blass|first3=LW |last4=Perez|first4=EA|last5=Sola|first5=JE|title=The Effect of Gun Control Laws on Hospital Admissions for Children in the United States |journal=The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery|date=3 August 2016 |volume=81|issue=4 Suppl 1|pages=S54–60|pmid=27488481|s2cid=25217599|doi=10.1097/TA.0000000000001177 |ref={{harvid|Tashiro et al.|2016}}}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Villaveces et al.|2000}} --> | |||
| * {{cite journal|display-authors=3|last1=Villaveces|first1=Andrés|last2=Cummings|first2=Peter|last3=Espitia |first3=Victoria E.|last4=Koepsell|first4=Thomas D.|last5=McKnight|first5=Barbara|last6=Kellermann |first6=Arthur L. |title=Effect of a Ban on Carrying Firearms on Homicide Rates in 2 Colombian Cities |journal=JAMA|date=1 March 2000|volume=283|issue=9|pages=1205–09|pmid=10703790 |doi=10.1001/jama.283.9.1205 |ref={{harvid|Villaveces et al.|2000}}}} | |||
| <!--{{sfn|Webster et al.|2004}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Webster|first1=DW|last2=Vernick|first2=JS|last3=Zeoli|first3=AM|last4=Manganello |first4=JA|title=Association between youth-focused firearm laws and youth suicides|journal=JAMA|date=4 August 2004|volume=292 |issue=5|pages=594–601|pmid=15292085|doi=10.1001/jama.292.5.594|doi-access=free|ref={{harvid|Webster et al.|2004}}}} | |||
| <!--{{sfn|Webster|Crifasi|Vernick|2014}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Webster|first1=Daniel|last2=Crifasi|first2=Cassandra Kercher|last3=Vernick |first3=Jon S.|title=Effects of the Repeal of Missouri's Handgun Purchaser Licensing Law on Homicides |journal=Journal of Urban Health|date=7 March 2014|volume=91|issue=2|pages=293–302|pmid=24604521 |pmc=3978146|doi=10.1007/s11524-014-9865-8}} | |||
| <!--{{sfn|Webster|Wintemute|2015}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Webster|first1=Daniel W.|last2=Wintemute|first2=Garen J.|title=Effects of Policies Designed to Keep Firearms from High-Risk Individuals|journal=Annual Review of Public Health|date=18 March 2015|volume=36|issue=1|pages=21–37|pmid=25581152|doi=10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031914-122516|doi-access=free|url=https://www.issuelab.org/permalink/resource/22699}} | |||
| <!-- {{sfn|Winkler|2013|p=??}} --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Winkler |first=A. |author-link=Adam Winkler |title=Gunfight: the battle over the right to bear arms in America |publisher=W.W. Norton & Co |location=New York |year=2013 |isbn=9780393345834 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oq39ykAGVYQC&pg=PT236 |access-date=2020-12-17 |archive-date=2022-05-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220531221839/https://books.google.com/books?id=oq39ykAGVYQC&pg=PT236 |url-status=live }} | |||
| <!--{{sfn|Zeoli|Malinski|Turchan|2016}}--> | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Zeoli|first1=April M.|last2=Malinski|first2=Rebecca|last3=Turchan|first3=Brandon |title=Risks and Targeted Interventions: Firearms in Intimate Partner Violence|journal=Epidemiologic Reviews |volume=38 |issue=1 |pages=125–39|date=5 January 2016|pmid=26739680|doi=10.1093/epirev/mxv007 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * ], "The Last of His Kind" (review of John Paul Stevens, ''The Making of a Justice: Reflections on My First 94 Years'', Little, Brown, 549 pp.), '']'', vol. LXVI, no. 14 (26 September 2019), pp. 20, 22, 24. ], "a throwback to the postwar liberal Republican appointees", questioned the validity of "the doctrine of ], which holds that you cannot sue any state or federal government agency, or any of its officers or employees, for any wrong they may have committed against you, unless the state or federal government consents to being sued" (p. 20); the propriety of "the increasing resistance of the ] to most meaningful forms of gun control" (p. 22); and "the constitutionality of the ]... because of incontrovertible evidence that innocent people have been sentenced to death." (pp. 22, 24.) | |||
| * Squires, Peter. Gender and Firearms: My Body, My Choice, My Gun. United Kingdom, Taylor & Francis, 2024. | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Library resources box |by=no |onlinebooks=no |others=yes lcheading=Gun control}} | |||
| *{{Dmoz|Society/Issues/Gun_Control}} | |||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180913002219/https://www.gunpolicy.org/ |date=2018-09-13 }} | ||
| ;National groups | |||
| ===National groups=== | |||
| * | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220525002324/https://www.csgv.org/ |date=2022-05-25 }} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Gun Control}} | |||
| {{Firearms}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:00, 18 December 2024
Laws or policies that regulate firearms For international arms restrictions, see Arms control. For techniques for the safe handling, possession, and storage of firearms, see Gun safety. For the debate about gun control in the U.S., see Gun politics in the United States.

Gun control, or firearms regulation, is the set of laws or policies that regulate the manufacture, sale, transfer, possession, modification, or use of firearms by civilians.
Most countries allow civilians to own firearms, but have strong firearms laws to prevent violence. Only a few countries, such as Namibia, Yemen and the United States are categorized as permissive.
Jurisdictions that regulate civilian access to firearms typically restrict ownership of certain lethal firearms, and require a mandatory gun safety course or firearms license to own or carry a weapon.
In some countries, such as the United States, gun control measures can be implemented at the national, state, or local levels.
Terminology and context
See also: Small arms trade and Small arms and light weaponsGun control refers to domestic and international attempts to regulate, and harmonize the regulation of, the private and industrial manufacture, trade, possession, use, and transport of a class of weapons typically identified as small arms. This class of arms commonly includes revolvers, self-loading pistols, rifles and carbines, so-called assault rifles, and some categories of machine gun.
In the United States, the term gun control itself is considered politicized. Many gun control advocates prefer the use of terms like "gun-violence prevention", "gun safety", or "common-sense regulation" to describe their objectives.
In 2007, a global supply of 875 million small arms were estimated to be in the hands of civilians, law enforcement agencies, and national armed forces. Of these firearms, 650 million, or 75%, were estimated to be held by civilians. U.S. civilians account for 270 million of this total. A further 200 million are controlled by national military forces. Law enforcement agencies may have some 26 million small arms. Non-state armed groups have about 1.4 million firearms. Finally, gang members hold between 2 and 10 million small arms. Together, the small arms arsenals of non-state armed groups and gangs have been estimated to account for, at most, 1.4% of the global total.
Regulation of civilian firearms
With few exceptions, most countries in the world actually allow some form of civilian firearm ownership. A 2011 survey of 28 countries over five continents found that a major distinction between different national gun control regimes is whether civilian gun ownership is seen as a right or a privilege. The study concluded that both the United States and Yemen were distinct from the other countries surveyed in that they viewed gun ownership as a basic right of citizenship, and therefore their gun control policies were more permissive. In the remaining countries sampled, civilian gun ownership is considered a privilege and their corresponding gun control policies are more restrictive.
International and regional gun control
At the international and regional level, diplomatic attention has tended to focus on the cross-border illegal trade in small arms as an area of particular concern rather than the regulation of civilian-held firearms. During the mid-1990s, however, the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) adopted a series of resolutions relating to the civilian ownership of small arms. These called for an exchange of data on national systems of firearm regulation and for the initiation of an international study of the issue. In July 1997, ECOSOC issued a resolution that underlined the responsibility of UN member states to competently regulate civilian ownership of small arms and which urged them to ensure that their regulatory frameworks encompassed the following aspects: firearm safety and storage; penalties for the unlawful possession and misuse of firearms; a licensing system to prevent undesirable persons from owning firearms; exemption from criminal liability to promote the surrender by citizens of illegal, unsafe or unwanted guns; and, a record-keeping system to track civilian firearms.
In 1997, the UN published a study based on member state survey data titled the United Nations International Study on Firearm Regulation which was updated in 1999. This study was meant to initiate the establishment of a database on civilian firearm regulations which would be run by the Centre for International Crime Prevention, located in Vienna. who were to report on national systems of civilian firearm regulation every two years. These plans never reached fruition and further UN-led efforts to establish international norms for the regulation of civilian-held firearms were stymied. Responding to pressure from the U.S. government, any mention of the regulation of civilian ownership of small arms was removed from the draft proposals for the 2001 UN Programme of Action on Small Arms.
Although the issue is no longer part of the UN policy debate, since 1991 there have been eight regional agreements involving 110 countries concerning aspects of civilian firearm possession. The Bamako Declaration, was adopted in Bamako, Mali, on 1 December 2000 by the representatives of the member states of the Organisation of African Unity (OAU). The provisions of this declaration recommend that the signatories would establish the illegal possession of small arms and light weapons as a criminal offence under national law in their respective countries.
Studies
| The neutrality of this section is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (October 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| The examples and perspective in this section deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this section, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new section, as appropriate. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
General
A 1998 review found that suicide rates generally declined after gun control laws were enacted, and concluded, "The findings support gun control measures as a strategy for reducing suicide rates." A 2016 review found that laws banning people under restraining orders due to domestic violence convictions from accessing guns were associated with "reductions in intimate partner homicide". Another 2016 review identified 130 studies regarding restrictive gun laws and found that the implementation of multiple such laws simultaneously was associated with a decrease in gun-related deaths. According to Vox, "The authors are careful to note that their findings do not conclusively prove that gun restrictions reduce gun deaths. However, they did find a compelling trend whereby new restrictions on gun purchasing and ownership tended to be followed by a decline in gun deaths."
According to a 2011 UN study, after identifying a number of methodological problems, it stated "notwithstanding such challenges, a significant body of literature tends to suggest that firearm availability predominantly represents a risk factor rather than a protective factor for homicide. In particular, a number of quantitative studies tend towards demonstrating a firearm prevalence–homicide association."
United States
Main articles: Gun law in the United States, Gun politics in the United States, Gun culture in the United States, and Gun violence in the United States
In the United States, gun rights activists argue gun laws are too restrictive or should not be altered, and gun control activists argue gun laws are too permissive. Both camps center their arguments upon the legal and traditional interpretations of the Second Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
High rates of gun mortality and injury are often cited as a primary impetus for gun control policies. A 2004 National Research Council critical review found that while some strong conclusions are warranted from current research, the state of our knowledge is generally poor. The result of the scarcity of relevant data is that gun control is one of the most fraught topics in American politics, and scholars remain deadlocked on a variety of issues. Notably, since 1996, when the Dickey Amendment was first inserted into the federal spending bill, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has been prohibited from using its federal funding "to advocate or promote gun control", thwarting gun violence research at the agency at the time. The funding provision's author has said that this was an over-interpretation, but the amendment still had a chilling effect, effectively halting federally funded firearm-related research. Since the amendment, the CDC has continued to research gun violence and publish studies about it, although their funding for such research has fallen by 96% since 1996, according to Mayors Against Illegal Guns. According to a spokesman, the CDC has limited funding and has not produced any comprehensive study aimed at reducing gun violence since 2001.


Cross-sectional studies
In 1983, a cross-sectional study of all 50 U.S. states found that the six states with the strictest gun laws (according to the National Rifle Association of America) had suicide rates that were approximately 3/100,000 people lower than in other states, and that these states' suicide rates were 4/100,000 people lower than those of states with the least restrictive gun laws. A 2003 study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine looked at the restrictiveness of gun laws and suicide rates in men and women in all 50 U.S. states and found that states whose gun laws were more restrictive had lower suicide rates among both sexes. In 2004, another study found that the effect of state gun laws on gun-related homicides was "limited". A 2005 study looked at all 50 states in the U.S. and the District of Columbia, and found that no gun laws were associated with reductions in firearm homicide or suicide, but that a "shall-issue" concealed carry law (mandatory issue of a license when legal criteria met) may be associated with increased firearm homicide rates. A 2011 study found that firearm regulation laws in the United States have "a significant deterrent effect on male suicide".
A 2013 study by the American Medical Association found that in the United States, "a higher number of firearm laws in a state are associated with a lower rate of firearm fatalities in that state." A 2016 study published in The Lancet found that of 25 laws studied, and in the time period examined (2008–2010), nine were associated with reduced firearm mortality (including both homicide and suicide), nine were associated with increased mortality, and seven had an inconclusive association. The three laws most strongly associated with reduced firearm mortality were laws requiring universal background checks, background checks for ammunition sales, and identification for guns. In an accompanying commentary, David Hemenway noted that this study had multiple limitations, such as not controlling for all factors that may influence gun-related deaths aside from gun control laws, and the use of 29 explanatory variables in the analysis.
Other studies comparing gun control laws in different U.S. states include a 2015 study which found that in the United States, "stricter state firearm legislation is associated with lower discharge rates" for nonfatal gun injuries. A 2014 study that also looked at the United States found that children living in states with stricter gun laws were safer. Another study looking specifically at suicide rates in the United States found that the four handgun laws examined (waiting periods, universal background checks, gun locks, and open carrying regulations) were associated with "significantly lower firearm suicide rates and the proportion of suicides resulting from firearms." The study also found that all four of these laws (except the waiting-period one) were associated with reductions in the overall suicide rate.
Another study, published the same year, found that states with permit to purchase, registration, and/or license laws for handguns had lower overall suicide rates, as well as lower firearm suicide rates. A 2014 study found that states that required licensing and inspections of gun dealers tended to have lower rates of gun homicides. Another study published the same year, analyzing panel data from all 50 states, found that stricter gun laws may modestly reduce gun deaths. A 2016 study found that U.S. military veterans tend to commit suicide with guns more often than the general population, thereby possibly increasing state suicide rates, and that "the tendency for veterans to live in states without handgun legislation may exacerbate this phenomenon." California has exceptionally strict gun sales laws, and a 2015 study found that it also had the oldest guns recovered in crimes of any states in the U.S. The same study concluded that "These findings suggest that more restrictive gun sales laws and gun dealer regulations do make it more difficult for criminals to acquire new guns first purchased at retail outlets."

Another 2016 study found that stricter state gun laws in the United States reduced suicide rates. Another 2016 study found that U.S. states with lenient gun control laws had more gun-related child injury hospital admissions than did states with stricter gun control laws. A 2017 study found that suicide rates declined more in states with universal background check and mandatory waiting period laws than in states without these laws. Another 2017 study found that states without universal background check and/or waiting period laws had steeper increases in their suicide rates than did states with these laws. A third 2017 study found that "waiting period laws that delay the purchase of firearms by a few days reduce gun homicides by roughly 17%." A 2017 study in the Economic Journal found that mandatory handgun purchase delays reduced "firearm-related suicides by between 2 and 5 percent with no statistically significant increase in non-firearm suicides," and were "not associated with statistically significant changes in homicide rates." Another 2017 study showed that laws banning gun possession by people subject to intimate partner violence restraining orders, and requiring such people to give up any guns they have, were associated with lower intimate partner homicide rates. A 2021 study found that firearm purchase delay laws reduced homicide – the authors suggested that it was driven by reductions in gun purchases by impulsive customers.
Reviews
In 2015, Daniel Webster and Garen Wintemute reviewed studies examining the effectiveness of gun laws aimed at keeping guns out of the hands of high-risk individuals in the United States. They found that some laws prohibiting gun possession by people under domestic violence restraining orders or who had been convicted of violent misdemeanors were associated with lower violence rates, as were laws establishing more procedures to see if people were prohibited from owning a gun under these laws. They also found that multiple other gun regulations intended to prevent prohibited individuals from obtaining guns, such as "rigorous permit-to-purchase" laws and "comprehensive background checks", were "negatively associated with the diversion of guns to criminals."
A 2016 systematic review found that restrictive gun licensing laws were associated with lower gun injury rates, while concealed carry laws were not significantly associated with rates of such injuries. Another systematic review found that stricter gun laws were associated with lower gun homicide rates; this association was especially strong for background check and permit-to-purchase laws.
A 2020 review of almost 13,000 studies by RAND Corporation found only 123 that met their criteria of methodological rigor, "a surprisingly limited base of rigorous scientific evidence...". Only 2 of the 18 gun policies examined had supporting evidence. Among the policies for which RAND found supporting evidence were that child-access prevention laws reduce firearm injuries and deaths among children and that "stand-your-ground" laws increase firearm homicides. RAND also noted that the limited evidence currently available "does not mean that these policies are ineffective ... Instead, it partly reflects shortcomings in the contributions that science has made to policy debates."
Studies of individual laws
Other studies have examined trends in firearm-related deaths before and after gun control laws are either enacted or repealed. A 2004 study in the Journal of the American Medical Association found evidence that child access prevention laws were "associated with a modest reduction in suicide rates among youth aged 14 to 17 years." Two 2015 studies found that the permit-to-purchase law passed in Connecticut in 1995 was associated with a reduction in firearm suicides and homicides. One of these studies also found that the repeal of Missouri's permit-to-purchase law was associated with "a 16.1% increase in firearm suicide rates," and a 2014 study by the same research team found that the repeal of this law was associated with a 16% increase in homicide rates. A 2000 study designed to assess the effectiveness of the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act found that the law was not associated with reductions in overall homicide or suicide rates, but that it was associated with a reduction in the firearm suicide rate among individuals aged 55 or older. A 1991 study looked at Washington, D.C.'s Firearms Control Regulations Act of 1975, which banned its residents from owning all guns except certain shotguns and sporting rifles, which were also required to be unloaded, disassembled, or stored with a trigger lock in their owners' homes. The study found that the law's enactment was associated with "a prompt decline in homicides and suicides by firearms in the District of Columbia." A 1996 study reanalyzed this data and reached a significantly different conclusion as to the effectiveness of this law.
Other studies and debate
In 1993, Kleck and Patterson analyzed the impact of 18 major types of gun control laws on every major type of gun-involved crime or violence (including suicide) in 170 U.S. cities, and found that gun laws generally had no significant effect on violent crime rates or suicide rates. Similarly, a 1997 study found that gun control laws had only a small influence on the rate of gun deaths in U.S. states compared to socioeconomic variables like poverty and unemployment.
Philosophy professor Michael Huemer argues that gun control may be morally wrong, even if its outcomes would be positive, because individuals have a prima facie right to own a gun for self-defense and recreation.
A 2007 article published by the Journal of Injury Prevention states that approximately 60% of firearms used to commit violent crime can be traced to 1% of licensed dealers. This finding indicates that, although gun laws effectively regulate approximately 99% of purchases made from licensed dealers, a majority of gun-related violent crimes are perpetrated using guns that were purchased in violation of regulations. The Journal of Injury Prevention article advocates for increased monitoring of gun vendors in tandem with the optimization of gun sale regulation, as a means to decrease violent crime perpetrated with a firearm.
In 2009, the Public Health Law Research program, an independent organization, published several evidence briefs summarizing the research assessing the effect of a specific law or policy on public health, that concern the effectiveness of various laws related to gun safety. Among their findings:
- There is not enough evidence to establish the effectiveness of "shall issue" laws, as distinct from "may issue" laws, as a public health intervention to reduce violent crime.
- There is insufficient evidence to determine the effectiveness of waiting period laws as public health interventions aimed at preventing gun-related violence and suicide.
- Although child access prevention laws may represent a promising intervention for reducing gun-related morbidity and mortality among children, there is currently insufficient evidence to validate their effectiveness as a public health intervention aimed at reducing gun-related harms.
- There is insufficient evidence to establish the effectiveness of such bans as public health interventions aimed at reducing gun-related harms.
- There is insufficient evidence to validate the effectiveness of firearm licensing and registration requirements as legal interventions aimed to reduce firearm related harms.
RAND Corporation did a study that demonstrates that background checks may decrease suicides and violent crime; child-access prevention laws may decrease the number of suicides and unintentional injuries and deaths; minimum age requirements may decrease suicides; and prohibitions associated with mental illness may decrease suicides and violent crimes. On the other hand, concealed-carry laws may increase violent crimes and suicides, while stand-your-ground laws may increase violent crime. Bans on the sale of assault weapons and high-capacity magazines may increase the sale price for these items. An August 2019 article entitled, "Gun control really works" published by Business Insider looks at a dozen studies by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, The Journal of the American Medical Association, Rand Corporation, the journal Preventive Medicine, Everytown for Gun Safety, Johns Hopkins University, and others. They conclude that mirroring the firearms regulations in Switzerland such as banning the sale of new assault weapons, denying concealed-carry licenses to some individuals, and prohibiting firearm sales to people convicted of multiple alcohol-related offenses will decrease gun-related deaths and injuries.
Canada
Main article: Gun laws in CanadaRifles and shotguns are relatively easy to obtain, while handguns and some semi-automatic rifles are restricted.
With respect to the Criminal Law Amendment Act, a gun control law passed in Canada in 1977, some studies have found that it was ineffective at reducing homicide or robbery rates. One study even found that the law may have actually increased robberies involving firearms. A 1993 study found that after this law was passed, gun suicides decreased significantly, as did the proportion of suicides committed in the country with guns. A 2003 study found that this law "may have had an impact on suicide rates, even after controls for social variables," while a 2001 study by the same research team concluded that the law "may have had an impact on homicide rates, at least for older victims." A 1994 study found that after this law came into force in 1978, suicide rates decreased over time in Ontario, and that there was no evidence of method substitution. The same study found that "These decreases may be only partly due to the legislation."
In 1991, Canada implemented the gun control law Bill C-17. According to a 2004 study, after this law was passed, firearm-related suicides and homicides, as well as the percentage of suicides involving firearms, declined significantly in that country. A 2010 study found that after this law was passed, firearm suicides declined in Quebec among men, but acknowledged that this may not represent a causal relationship. In 1992, Canada promulgated the Canadian Firearms Act, which aimed at ensuring that guns were stored safely. A 2004 study found that although firearm suicide rates declined in the Quebec region Abitibi-Témiscamingue after the law was passed, overall suicide rates did not. A study in 2005 also found that overall suicide rates did not change after passage of Bill C-17. A 2008 study reached similar conclusions with regard to the entire Quebec province; this study also found that C-17 did not seem to increase the rate at which the firearm suicide rate was declining. Other researchers have criticized this 2008 study for looking at too short a time period and not taking account of the fact that the regulations in C-17 were implemented gradually.
A 1990 study compared suicide rates in the Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada metropolitan area (where gun control laws were more restrictive) with those in the Seattle, Washington area in the United States. The overall suicide rate was essentially the same in the two locations, but the suicide rate among 15 to 24 year olds was about 40 percent higher in Seattle than in Vancouver. The authors concluded that "restricting access to handguns might be expected to reduce the suicide rate in persons 15 to 24 years old, but ... it probably would not reduce the overall suicide rate." A study that looked at provincial gun ownership rates, and associated suicide rates found no significant correlations with overall suicide rates.
A 2011 study looked at gun control passed in Canada between 1974 and 2004 and found that gun laws were responsible for 5 to 10 percent drops in homicides. The study found that the homicide reduction effects of Canadian gun legislation remained even after accounting for sociodemographic and economic factors associated with homicide rates.
A 2012 study looked at gun control laws passed in Canada from 1974 to 2008 and found no evidence that these laws had a beneficial effect on firearm homicide rates in that country. According to the study, "other factors found to be associated with homicide rates were median age, unemployment, immigration rates, percentage of population in low-income bracket, Gini index of income equality, population per police officer, and incarceration rate."
A 2013 study of the 1995 Canadian gun control law Firearms Act, 1995 reported little evidence that this law significantly reduced rates of lethal gun violence against women.
On May 1, 2020, after deadly shootings in Nova Scotia, Justin Trudeau's Liberal government banned 1,500 kinds of military-style semi-automatic rifles, including the popular AR-15 and its variants. The ban was enacted via an Order In Council.
A 2020 study examining laws passed from 1981 to 2016 found no significant changes in overall homicide or suicide rates following changes in legislation. In addition, it also found that firearm ownership by province was not correlated to overall suicide rates by province.
On October 21, 2022, under Justin Trudeau's government, Bill C-21 came into effect, aiming to address gun violence and strengthen gun control. The legislation introduced a national freeze on the sale, purchase, or transfer of handguns by individuals within Canada. It also established new "red flag" and "yellow flag" laws, allowing courts and Chief Firearms Officers (CFOs) to issue emergency weapons prohibition orders and temporarily suspend licenses, respectively. Moreover, the bill increased maximum penalties for firearms-related offenses, including smuggling and trafficking, from 10 to 14 years imprisonment. Additionally, Bill C-21 prohibited mid-velocity 'replica' airguns that closely resemble real firearms and discharge projectiles at a velocity between 366 and 500 feet per second.
Australia
Main article: Gun laws in AustraliaIn 1988 and 1996, gun control laws were enacted in the Australian state of Victoria, both times following mass shootings. A 2004 study found that in the context of these laws, overall firearm-related deaths, especially suicides, declined dramatically. A 1995 study found preliminary evidence that gun control legislation enacted in Queensland, Australia, reduced suicide rates there.
A 2006 study by gun lobby-affiliated researchers Jeanine Baker and Samara McPhedran found that after Australia enacted the National Firearms Agreement (NFA), a gun control law, in 1996, gun-related suicides may have been affected, but no other parameter appeared to have been. Another 2006 study, led by Simon Chapman, found that after this law was enacted in 1996 in Australia, the country went more than a decade without any mass shootings, and gun-related deaths (especially suicides) declined dramatically. The latter of these studies also criticized the former for using a time-series analysis despite the fact that, according to Chapman et al., "calculating mortality rates and then treating them as a number in a time series ignores the natural variability inherent in the counts that make up the numerator of the rate." Chapman et al. also said that Baker and McPhedran used the Box–Jenkins model inappropriately.
A 2010 study looking at the effect of the NFA on gun-related deaths found that the law "did not have any large effects on reducing firearm homicide or suicide rates," although David Hemenway has criticized this study for using a structural break test despite the fact that such tests can miss the effects of policies in the presence of lags, or when the effect occurs over several years. Another study, published the same year, found that Australia's gun buyback program reduced gun-related suicide rates by almost 80%, while non-gun death rates were not significantly affected. Other research has argued that although gun suicide rates fell after the NFA was enacted, the NFA may not have been responsible for this decrease and "a change in social and cultural attitudes" may have instead been at least partly responsible. A 2011 study found that "Australia's prohibition of certain types of firearms" has not prevented mass shootings. In 2016, Chapman co-authored another study that found that after the NFA was passed, there were no mass shootings in the country (as of May 2016), and that gun-related death rates declined more quickly after the NFA than they did before it. The study also found, however, that non-gun suicide and homicide rates declined even more quickly after the NFA, leading the authors to conclude that "it is not possible to determine whether the change in firearm deaths can be attributed to the gun law reforms."
Other countries
Further information: Overview of gun laws by nation Possession of long guns by country:
No permit required for both repeating and semi-automatic long guns
Partially licensed – repeating long guns permitless, semi-automatic with permit
Allowed with permit – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason
Allowed with permit – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required
Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice – few licenses are issued
Prohibited – civilians are banned from obtaining long guns
Different rules regarding shotguns and rifles
Some countries in these categories may place additional restrictions or ban semi-automatic long guns
Possession of long guns by country:
No permit required for both repeating and semi-automatic long guns
Partially licensed – repeating long guns permitless, semi-automatic with permit
Allowed with permit – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason
Allowed with permit – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required
Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice – few licenses are issued
Prohibited – civilians are banned from obtaining long guns
Different rules regarding shotguns and rifles
Some countries in these categories may place additional restrictions or ban semi-automatic long guns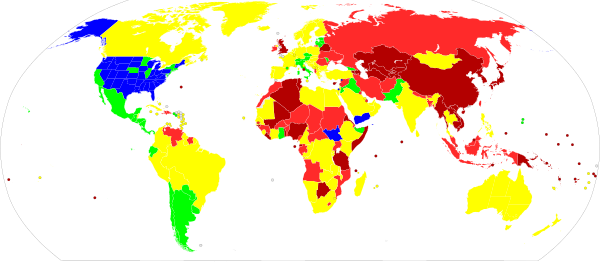 Possession of handguns by country:
No permit required – permits or licenses are not required to obtain handguns
Allowed with permit – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason
Allowed with permit – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required
Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice – few licenses are issued
Prohibited – civilians are banned from obtaining handgunsNotes:
Possession of handguns by country:
No permit required – permits or licenses are not required to obtain handguns
Allowed with permit – no good reason required or simple declaration of reason
Allowed with permit – good reason (like sport shooting license or proving danger to life) required
Prohibited with exceptions or prohibited in practice – few licenses are issued
Prohibited – civilians are banned from obtaining handgunsNotes:- Map describes policy regarding obtaining new firearms regardless whether firearms that were produced before ban were grandfathered.
A 2007 study found evidence that gun control laws passed in Austria in 1997 reduced the rates of firearm suicide and homicide in that country. In Brazil, after disarmament laws were passed in 2003, gun-related mortality declined by 8% in 2004 relative to the previous year, the first decline observed in a decade. Gun-related hospitalizations also reversed their previous trend by decreasing 4.6% from 2003 to 2004. A 2006 study found that after gun control laws were passed in New Zealand in 1992, suicides committed with guns declined significantly, especially among youth. This study however found that overall suicide rates did not change significantly. A case-control study conducted in New Zealand found that gun ownership was significantly associated with a greater risk of gun suicides, but not suicides overall.
A 2010 study looked at the effect of a policy adopted by the Israeli Defense Forces that restricted access to guns among adolescents on suicide rates, and found that "Following the policy change, suicide rates decreased significantly by 40%." The authors concluded that "The results of this study illustrate the ability of a relatively simple change in policy to have a major impact on suicide rates." A 2013 study showed that after the Military of Switzerland adopted the Army XXI reform, which restricted gun availability, in 2003, suicide rates – both overall and firearm-related – decreased. Another 2013 study looking at four restrictive gun laws passed in Norway found that two of them may have reduced firearm mortality among men, but that the evidence was more inconclusive with respect to all of the laws they studied. A 2014 study found that after South Africa's Firearm Control Act was passed in 2000, homicide rates in the country declined, and concluded that "stricter gun control mediated by the FCA accounted for a significant decrease in homicide overall, and firearm homicide in particular, during the study period ." A 2000 study found that a ban on carrying guns in Colombia was associated with reductions in homicide rates in two cities in the country, namely, Cali and Bogotá.
See also
International
United States
- Assault weapons legislation in the United States
- Federal Assault Weapons Ban
- Gun Control Act of 1968
- Gun control after the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting
- Gun politics in the United States
- Gun show loophole
- Public opinion on gun control in the United States
- 2018 United States gun violence protests
Notes
- ^ As of April 2022, the only countries with permissive gun legislation are: Chad, the Republic of Congo, Honduras, Micronesia, Namibia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Senegal, Switzerland, Tanzania, the United States, Yemen, and Zambia.
- This figure excludes older, pre-automatic small arms from military and law enforcement stockpiles or 'craft-produced' civilian firearms.
- Composed of 'insurgents and militias, including dormant and state-related groups'.
- However, as of 2009, active non-state armed groups, numbering about 285,000 combatants, control only about 350,000 small arms.
- Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, and Taiwan (Republic of China) prohibit civilian ownership of firearms in almost all instances. Eritrea and Somalia also prohibit civilian possession of firearms as part of their implementation of the UN Programme of Action on Small Arms. In the Solomon Islands, civilian firearm ownership is restricted to members of the Regional Assistance Mission.
- The survey, carried out by the Small Arms Survey included 28 countries (42 jurisdictions in total). The countries included in the sample were:
- Africa: Egypt, Kenya, South Africa, Uganda;
- Americas: Belize, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Dominican Republic, United States, Venezuela;
- Asia: India, Israel, Japan, Kazakhstan, Singapore, Turkey, Yemen;
- Europe: Croatia, Estonia, Finland, Lithuania, Russian Federation, Switzerland, United Kingdom;
- Oceania: Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea.
- The impetus behind this study was twofold: firstly, there were concerns over the incidence of firearm-related crimes, accidents and suicides; secondly, there was the apprehension that existing regulatory instruments administering the ownership, storage and training in the use of firearms held by civilians might be inadequate.
- The US government was opposed to a section of the draft proposal calling on countries 'to seriously consider the prohibition of unrestricted trade and private ownership of small arms and light weapons'.
- The full title is 'The Bamako Declaration on an African Common Position on the Illicit Proliferation, Circulation and Trafficking of Small Arms and Light Weapons (2000)'.
References
- Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (2005). Federal Firearms Regulations Reference Guide (PDF). Archived 2021-04-24 at the Wayback Machine U.S. Department of Justice. Retrieved: January 3, 2016.
- "Firearms-Control Legislation and Policy". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 2022-05-30. Retrieved 2016-03-22.
- Alpers, Philip; Wilson, Marcus (9 June 2020). "Guns in the United Nations: Firearm Regulation - Guiding Policy". Sydney School of Public Health, The University of Sydney. Archived from the original on 2021-04-18. Retrieved 2016-08-27 – via GunPolicy.org.
- "International Instrument to Enable States to Identify and Trace, in a Timely and Reliable Manner, Illicit Small Arms and Light Weapon" (PDF). unodc.org. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 25 February 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-11-11. Retrieved 2014-02-14.
- "Definitions of Small Arms and Light Weapons". Small Arms Survey. 15 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2011-06-19. Retrieved 2014-02-10.
- LaFrance, Adrienne (11 January 2016). "How 'Gun Control' Became a Taboo Phrase". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 2017-01-17. Retrieved 2016-03-29.
- Ball, Molly (January 2013). Don't Call It 'Gun Control' Archived 2021-04-17 at the Wayback Machine The Atlantic. Retrieved: September 24, 2016.
- ^ Karp 2007, p. 39.
- ^ Karp 2010, p. 102
- ^ Karp 2010, p. 101
- Karp 2010, p. 121
- Parker 2011, p. 62 n. 1
- Parker 2011, p. 1
- Parker 2011, p. 2
- Parker 2011, p. 62 n. 4
- ^ Parker 2011, p. 36
- ^ Parker 2011, p. 3
- Parker 2011, pp. 3–4
- Alley 2004, p. 54
- Alley 2004, pp. 53–54
- ^ Juma 2006, p. 39
- Parker 2011, p. 4
- Lambert & Silva 1998.
- Zeoli, Malinski & Turchan 2016.
- Santaella-Tenorio et al. 2016.
- Beauchamp, Zack (29 February 2016). "A huge international study of gun control finds strong evidence that it actually works". Vox. Retrieved 2022-10-10.
- "2011 Global Study on Homicide" (PDF). unodc.org. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2011. p. 43. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-04-09. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ● Gun sale data from Brownlee, Chip (31 December 2023). "Gun Violence by the Numbers in 2023". The Trace. Archived from the original on 2024-01-28.
● NICS firearm check data downloaded via link at "NICS Firearm Background Checks: Month/Year" (PDF). FBI.gov. Federal Bureau of Investigation. January 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2024-01-29. - Peeples, Lynne (1 July 2022). "US gun policies: what researchers know about their effectiveness". Nature. 607 (7919): 434–435. Bibcode:2022Natur.607..434P. doi:10.1038/d41586-022-01791-z. PMID 35778495. S2CID 250218456.
- Goldberg, Jeffrey (December 2012). "The Case for More Guns (and More Gun Control)". The Atlantic. Retrieved 2016-03-31.
- National Research Council 2005, pp. 3, 6.
- ^ Branas et al. 2009.
- Stein, Sam (6 October 2015). "The Congressman Who Restricted Gun Violence Research Has Regrets". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 2015-10-10. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
- Betz, Ranney & Wintemute 2016.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2013.
- Jamieson, Christine (February 2013). "Gun violence research: History of the federal funding freeze". Psychological Science Agenda. Archived from the original on 2017-05-05. Retrieved 2017-04-27.
- Barzilay, Julie (16 June 2016). "Why the CDC Hasn't Launched a Comprehensive Gun Study in 15 Years". ABC News. Archived from the original on 2020-06-27. Retrieved 2017-04-27.
- Fox, Kara; Shveda, Krystina; Croker, Natalie; Chacon, Marco (26 November 2021). "How US gun culture stacks up with the world". CNN. Archived from the original on 2021-11-26.
CNN's attribution: Developed countries are defined based on the UN classification, which includes 36 countries. Source: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (Global Burden of Disease 2019), Small Arms Survey (Civilian Firearm Holdings 2017)
- ^ Mascia, Jennifer; Brownlee, Chip (9 April 2024). "The Armed Era". The Trace. Archived from the original on 2024-04-14.
- Medoff & Magaddino 1983.
- Conner & Zhong 2003.
- Price, Thompson & Dake 2004.
- Rosengart et al. 2005.
- Rodríguez Andrés & Hempstead 2011.
- Fleegler et al. 2013.
- Kalesan et al. 2016.
- Hemenway 2016.
- Simonetti et al. 2015.
- Safavi et al. 2014.
- Anestis & Anestis 2015.
- Anestis et al. 2015.
- Irvin et al. 2014.
- Lanza 2014.
- Anestis & Capron 2016.
- Pierce, Braga & Wintemute 2015.
- Buchanan, Larry; Leatherby, Lauren (22 June 2022). "Who Stops a 'Bad Guy With a Gun'?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2022-06-22.
Data source: Advanced Law Enforcement Rapid Response Training Center
- Kposowa, Hamilton & Wang 2016.
- Tashiro et al. 2016.
- Anestis, Anestis & Butterworth 2017.
- Anestis, Selby & Butterworth 2017.
- Luca, Malhotra & Poliquin 2017.
- Edwards et al. 2018.
- Diez et al. 2017.
- Koenig, Christoph; Schindler, David (2021). "Impulse Purchases, Gun Ownership, and Homicides: Evidence from a Firearm Demand Shock". The Review of Economics and Statistics. 105 (5): 1271–1286. doi:10.1162/rest_a_01106. hdl:10419/207224. ISSN 0034-6535. S2CID 243676146.
- Webster & Wintemute 2015.
- Crandall et al. 2016.
- Lee et al. 2016.
- "What Science Tells Us About the Effects of Gun Policies". www.rand.org. Retrieved 2022-10-10.
- Webster et al. 2004.
- ^ Crifasi et al. 2015.
- Rudolph et al. 2015.
- Webster, Crifasi & Vernick 2014.
- Ludwig & Cook 2000.
- Abrams, Jonathan (10 January 2010). "Washington's Gun Past Affects Arenas's Future". New York Times. Archived from the original on 2017-06-30. Retrieved 2015-12-06.
- Loftin et al. 1991.
- Britt, Kleck & Bordua 1996.
- Kleck & Patterson 1993.
- Kwon et al. 1997.
- Huemer 2003.
- ^ Vernick, Jon S; Webster, Daniel W (2007). "Policies to prevent firearm trafficking". Injury Prevention. 13 (2): 78–79. doi:10.1136/ip.2007.015487. ISSN 1353-8047. PMC 2610592. PMID 17446245.
- "Home – Public Health Law Research". Publichealthlawresearch.org. Archived from the original on 2019-12-13. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- ""Shall Issue" Concealed Weapons Laws, Public Health Law Research 2009". Publichealthlawresearch.org. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- "Waiting Period Laws for Gun Permits – Public Health Law Research". publichealthlawresearch.org. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- "Child Access Prevention (CAP) Laws for Guns – Public Health Law Research". publichealthlawresearch.org. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- "Bans on Specific Guns and Ammunition – Public Health Law Research". publichealthlawresearch.org. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- "Gun Registration and Licensing Requirements – Public Health Law Research". publichealthlawresearch.org. Retrieved 2017-10-04.
- "Facts About the Effects of Gun Policies Are Elusive but Important", Rand.org, archived from the original on 2019-08-08, retrieved 2019-08-11
- Woodward, Aylin (6 August 2019). "Gun control really works. Science has shown time and again that it can prevent mass shootings and save lives". Business Insider. Retrieved 2019-08-06.
- "Classes of firearms". 18 April 2012. Archived from the original on 2018-03-15. Retrieved 2016-10-29.
- Mauser & Holmes 1992.
- ^ Mauser & Maki 2003.
- Lester & Leenaars 1993.
- Leenaars et al. 2003.
- Leenaars & Lester 2001.
- Carrington & Moyer 1994.
- Bridges 2004.
- ^ Gagne et al. 2010.
- Caron 2004.
- Cheung & Dewa 2005.
- Caron, Julien & Huang 2008.
- Sloan et al. 1990.
- Dandurand 1998.
- Blais, Gagné & Linteau 2011.
- Langmann 2012.
- McPhedran & Mauser 2013.
- Tasker, John Paul (1 May 2020). "Trudeau announces ban on 1,500 types of 'assault-style' firearms – effective immediately". CBC. Archived from the original on 2020-05-01. Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- Langmann, C. (2020). "Effect of firearms legislation on suicide and homicide in Canada from 1981 to 2016". PLOS ONE. 15 (6): e0234457. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1534457L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0234457. PMC 7302582. PMID 32555647.
- Canada, Public Safety (30 May 2022). "A comprehensive strategy to address gun violence and strengthen gun laws in Canada". www.publicsafety.gc.ca. Retrieved 2023-04-10.
- Ozanne-Smith et al. 2004.
- Cantor & Slater 1995.
- Baker & McPhedran 2006.
- ^ Chapman et al. 2006.
- Lee & Suardi 2010.
- Hemenway 2009.
- Leigh & Neill 2010.
- Klieve, Barnes & De Leo 2009.
- McPhedran, Samara; Baker, Jeanine (2011). "Mass shootings in Australia and New Zealand: A descriptive study of incidence". Justice Policy Journal. 8 (1). SSRN 2122854.
- Chapman, Alpers & Jones 2016.
- Kapusta et al. 2007.
- "Lei Nº 10.426, de 24 de Abril de 2002" [Law No. 10.426 of April 24, 2002]. www.planalto.gov.br (in Portuguese). Presidência da República Casa Civil. Archived from the original on 2015-12-29. Retrieved 2016-01-31.
- de Souza et al. 2007.
- Beautrais, Fergusson & Horwood 2006.
- Beautrais, Joyce & Mulder 1996.
- Lubin et al. 2010.
- Reisch et al. 2013.
- Gjertsen, Leenaars & Vollrath 2013.
- Matzopoulos, Thompson & Myers 2014.
- Villaveces et al. 2000.
Bibliography
- Alley, Roderic (2004). Internal Conflict and the International Community: Wars Without End?. Aldershot: Ashgate. ISBN 9780754609766. Archived from the original on 2017-01-10. Retrieved 2016-05-06.
- Anestis, MD; Anestis, JC (October 2015). "Suicide Rates and State Laws Regulating Access and Exposure to Handguns". American Journal of Public Health. 105 (10): 2049–58. doi:10.2105/ajph.2015.302753. PMC 4566524. PMID 26270305.
- Anestis, MD; Khazem, LR; Law, KC; et al. (October 2015). "The Association Between State Laws Regulating Handgun Ownership and Statewide Suicide Rates". American Journal of Public Health. 105 (10): 2059–67. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302465. PMC 4566551. PMID 25880944.
- Anestis, MD; Capron, DW (March 2016). "The associations between state veteran population rates, handgun legislation, and statewide suicide rates". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 74: 30–34. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.12.014. PMID 26736038.
- Anestis, MD; Anestis, JC; Butterworth, SE (April 2017). "Handgun Legislation and Changes in Statewide Overall Suicide Rates". American Journal of Public Health. 107 (4): 579–581. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303650. PMC 5343707. PMID 28207333.
- Anestis, MD; Selby, EA; Butterworth, SE (July 2017). "Rising longitudinal trajectories in suicide rates: The role of firearm suicide rates and firearm legislation". Preventive Medicine. 100: 159–66. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.04.032. PMID 28455222.
- Anonymous (1909). "Carrying Concealed Weapons". Virginia Law Register. 15 (5): 337–416. JSTOR 1102220.
- Baker, J.; McPhedran, S. (2006). "Gun Laws and Sudden Death: Did the Australian Firearms Legislation of 1996 Make a Difference?" (PDF). British Journal of Criminology. 47 (3): 455–69. doi:10.1093/bjc/azl084. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-07-14. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- Beautrais, A. L.; Joyce, P. R.; Mulder, R. T. (1996). "Access to firearms and the risk of suicide: A case control study". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 30 (6): 741–48. doi:10.3109/00048679609065040. PMID 9034462. S2CID 9805679.
- Beautrais, A. L.; Fergusson, D. M.; Horwood, L. J. (January 2006). "Firearms legislation and reductions in firearm-related suicide deaths in New Zealand". Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 40 (3): 253–59. doi:10.1080/j.1440-1614.2006.01782.x. PMID 16476153. S2CID 208623661.
- Betz, Marian; Ranney, Megan; Wintemute, Garen (21 January 2016). "Frozen Funding on Firearm Research: "Doing Nothing Is No Longer an Acceptable Solution"". Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 17 (1): 91–93. doi:10.5811/westjem.2016.1.29767. PMC 4729430. PMID 26823941.
- Blais, Étienne; Gagné, Marie-Pier; Linteau, Isabelle (2011). "L'Effet des lois en matière de contrôle des armes à feu sur les homicides au Canada, 1974–2004". Canadian Journal of Criminology and Criminal Justice. 53 (1): 27–61. doi:10.3138/cjccj.53.1.27. S2CID 143960174.
- Branas, C. C.; Richmond, T. S.; Culhane, D. P.; et al. (2009). "Investigating the Link Between Gun Possession and Gun Assault". American Journal of Public Health. 99 (11): 2034–40. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2008.143099. PMC 2759797. PMID 19762675.
- Bridges, F. Stephen (June 2004). "Gun Control Law (Bill C-17), Suicide, and Homicide in Canada". Psychological Reports. 94 (3): 819–26. doi:10.2466/pr0.94.3.819-826. PMID 15217033. S2CID 25666987.
- Britt, Chester L.; Kleck, Gary; Bordua, David J. (1996). "A Reassessment of the D.C. Gun Law: Some Cautionary Notes on the Use of Interrupted Time Series Designs for Policy Impact Assessment". Law & Society Review. 30 (2): 361–80. doi:10.2307/3053963. JSTOR 3053963.
- Bukstein, O. G.; Brent, O. A.; Perper, J. A.; et al. (1993). "Risk factors for completed suicide among adolescents with a lifetime history of substance abuse: A case-control study". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 88 (6): 403–08. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1993.tb03481.x. PMID 8310846. S2CID 44711985.
- Bryant, M. S. (2012a). "Germany, Gun Laws". In Carter, G. L. (ed.). Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law. Vol. 1. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. pp. 314–16. ISBN 9780313386701. Archived from the original on 2022-05-31. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
- Bryant, M. S. (2012b). "Holocaust Imagery and Gun Control". In Carter, G. L. (ed.). Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law. Vol. 1. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. pp. 411–14. ISBN 9780313386701. Archived from the original on 2014-07-01. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
- Caron, Jean (October 2004). "Gun Control and Suicide: Possible Impact of Canadian Legislation to Ensure Safe Storage of Firearms". Archives of Suicide Research. 8 (4): 361–74. doi:10.1080/13811110490476752. PMID 16081402. S2CID 35131214.
- Caron, J; Julien, M; Huang, JH (April 2008). "Changes in suicide methods in Quebec between 1987 and 2000: the possible impact of bill C-17 requiring safe storage of firearms". Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 38 (2): 195–208. doi:10.1521/suli.2008.38.2.195. PMID 18444777.
- Carrington, PJ; Moyer, S (April 1994). "Gun control and suicide in Ontario". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 151 (4): 606–08. doi:10.1176/ajp.151.4.606. PMID 8147463.
- Cantor, CH; Slater, PJ (5 June 1995). "The impact of firearm control legislation on suicide in Queensland: preliminary findings". The Medical Journal of Australia. 162 (11): 583–85. doi:10.5694/j.1326-5377.1995.tb138547.x. PMID 7791644. S2CID 43656446.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (3 October 2003). "First Reports Evaluating the Effectiveness of Strategies for Preventing Violence: Early Childhood Home Visitation and Firearms Laws. Findings from the Task Force on Community Preventive Services" (PDF). Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). 52 (RR-14): 11–20. ISSN 1057-5987. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-07-08. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2 August 2013). "Firearm Homicides and Suicides in Major Metropolitan Areas – United States, 2006–2007 and 2009–2010". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). 62 (30): 597–602. PMC 4604852. PMID 23903593. Archived from the original on 2017-04-22. Retrieved 2017-04-21.
- Chapman, S.; Alpers, P.; Agho, K.; Jones, M. (2006). "Australia's 1996 gun law reforms: Faster falls in firearm deaths, firearm suicides, and a decade without mass shootings". Injury Prevention. 12 (6): 365–72. doi:10.1136/ip.2006.013714. PMC 2704353. PMID 17170183.
- Chapman, Simon; Alpers, Philip; Jones, Michael (22 June 2016). "Association Between Gun Law Reforms and Intentional Firearm Deaths in Australia, 1979–2013". JAMA. 316 (3): 291–99. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.8752. PMID 27332876.
- Cheung, A. H.; Dewa, C. S. (2005). "Current trends in youth suicide and firearms regulations". Canadian Journal of Public Health. 96 (2): 131–35. doi:10.1007/BF03403676. PMC 6975744. PMID 15850034.
- Conner, Kenneth R; Zhong, Yueying (November 2003). "State firearm laws and rates of suicide in men and women". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 25 (4): 320–24. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(03)00212-5. PMID 14580634.
- Conwell, Y.; Duberstein, P. R.; Connor, K.; et al. (2002). "Access to Firearms and Risk for Suicide in Middle-Aged and Older Adults". The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 10 (4): 407–16. doi:10.1097/00019442-200207000-00007. PMID 12095900.
- Crandall, M; Eastman, A; Violano, P; et al. (November 2016). "Prevention of firearm-related injuries with restrictive licensing and concealed carry laws: An Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma systematic review". The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 81 (5): 952–60. doi:10.1097/ta.0000000000001251. PMID 27602894. S2CID 22673439.
- Crifasi, CK; Meyers, JS; Vernick, JS; Webster, DW (October 2015). "Effects of changes in permit-to-purchase handgun laws in Connecticut and Missouri on suicide rates". Preventive Medicine. 79: 43–49. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.07.013. PMID 26212633.
- Dandurand, Yvon (September 1998). "4. Firearm Suicides". Firearms, Accidental Deaths, Suicides and Violent Crime (PDF) (working document). Department of Justice, Canada. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-15. Retrieved 2021-06-15.
- Díez, C; Kurland, RP; Rothman, EF; et al. (17 October 2017). "State Intimate Partner Violence-Related Firearm Laws and Intimate Partner Homicide Rates in the United States, 1991 to 2015". Annals of Internal Medicine. 167 (8): 536–43. doi:10.7326/M16-2849. PMID 28975202.
- de Fatima Marinho de Souza, M.; Macinko, J.; Alencar, A. P.; et al. (March–April 2007). "Reductions In Firearm-Related Mortality And Hospitalizations In Brazil After Gun Control". Health Affairs. 26 (2): 575–84. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.26.2.575. PMID 17339689.
- Dyer, Gwynne (2010). War: The New Edition. Random House. ISBN 9780307369017. Archived from the original on 2017-01-10. Retrieved 2016-05-06.
- Edwards, Griffin; Nesson, Erik; Robinson, Josh; Vars, Fredrick (2018). "Looking Down the Barrel of a Loaded Gun: The Effect of Mandatory Handgun Purchase Delays on Homicide and Suicide". The Economic Journal. 128 (616): 3117–40. doi:10.1111/ecoj.12567. ISSN 1468-0297. S2CID 155851188.
- Fleegler, EW; Lee, LK; Monuteaux, MC; et al. (13 May 2013). "Firearm legislation and firearm-related fatalities in the United States". JAMA Internal Medicine. 173 (9): 732–40. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.1286. PMID 23467753.
- Gagne, M.; Robitaille, Y.; Hamel, D.; St-Laurent, D. (29 June 2010). "Firearms regulation and declining rates of male suicide in Quebec". Injury Prevention. 16 (4): 247–53. doi:10.1136/ip.2009.022491. PMID 20587817.
- Gjertsen, Finn; Leenaars, Antoon; Vollrath, Margarete (30 December 2013). "Mixed Impact of Firearms Restrictions on Fatal Firearm Injuries in Males: A National Observational Study". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 11 (1): 487–506. doi:10.3390/ijerph110100487. PMC 3924456. PMID 24380979.
- Hahn, RA; Bilukha, O; Crosby, A; et al. (February 2005). "Firearms laws and the reduction of violence: a systematic review". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 28 (2 Suppl 1): 40–71. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2004.10.005. PMID 15698747.
- Hemenway, D. (2009). "How to find nothing". Journal of Public Health Policy. 30 (3): 260–68. doi:10.1057/jphp.2009.26. PMID 19806067.
- Hemenway, David (March 2016). "Firearm legislation and mortality in the USA". The Lancet. 387 (10030): 1796–97. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00206-3. PMID 26972841. S2CID 37771810.
- Hemenway, D.; Miller, M. (2000). "Firearm availability and homicide rates across 26 high-income countries". The Journal of Trauma. 49 (6): 985–88. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.472.6990. doi:10.1097/00005373-200012000-00001. PMID 11130511.
- Hepburn, L. M.; Hemenway, D. (2004). "Firearm availability and homicide: A review of the literature". Aggression and Violent Behavior. 9 (4): 417–40. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(03)00044-2.
- Huemer, Michael (2003). "Is There a Right to Own a Gun?". Social Theory and Practice. 29 (2): 297–324. doi:10.5840/soctheorpract200329215. Archived from the original on 2017-12-13.
- Irvin, N; Rhodes, K; Cheney, R; Wiebe, D (August 2014). "Evaluating the effect of state regulation of federally licensed firearm dealers on firearm homicide". American Journal of Public Health. 104 (8): 1384–86. doi:10.2105/ajph.2014.301999. PMC 4103238. PMID 24922158.
- Juma, Monica Kathina, ed. (2006). Compendium of Key Documents Relating to Peace and Security in Africa. Series on peace and conflict in Africa. Pretoria: Pretoria University Law Press. ISBN 9780958509732. Archived from the original on 2021-06-13. Retrieved 2016-05-06.
- Kalesan, Bindu; Mobily, Matthew E; Keiser, Olivia; et al. (March 2016). "Firearm legislation and firearm mortality in the USA: a cross-sectional, state-level study" (PDF). The Lancet. 387 (10030): 1847–55. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01026-0. PMID 26972843. S2CID 21415884. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2019-12-14.
- Kapusta, ND; Etzersdorfer, E; Krall, C; Sonneck, G (September 2007). "Firearm legislation reform in the European Union: impact on firearm availability, firearm suicide and homicide rates in Austria". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 191 (3): 253–57. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.106.032862. PMID 17766767.
- Karp, Aaron (2010). "Elusive Arsenals: Gang and Group Firearms". In Berman, Eric G.; et al. (eds.). Small Arms Survey 2010: Gangs, Groups, and Guns. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521146845. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-11-04.
- Karp, Aaron (2007). "Completing the Count: Civilian Firearms" (PDF). In Berman, Eric G.; et al. (eds.). Small Arms Survey 2007: Guns and the City. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521706544. Archived from the original on 2018-08-27. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- Kates, D. B. (1983). "Handgun Prohibition and the Original Meaning of the Second Amendment" (PDF). Michigan Law Review. 82 (2): 204–73. doi:10.2307/1288537. JSTOR 1288537. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-12-22. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- Kates, D. B.; Mauser, G. A. (2007). "Would Banning Firearms Reduce Murder and Suicide? A Review of International and Some Domestic Evidence" (PDF). Harvard Journal of Law & Public Policy. 30 (2): 649–94. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10.
- Kellermann, A. L.; Rivara, F. P.; Somes, G.; et al. (1992). "Suicide in the Home in Relation to Gun Ownership". New England Journal of Medicine. 327 (7): 467–72. doi:10.1056/NEJM199208133270705. PMID 1308093. S2CID 35031090.
- Kellermann, Arthur L.; Rivara, Frederick P.; Rushforth, Norman B.; et al. (7 October 1993). "Gun Ownership as a Risk Factor for Homicide in the Home". New England Journal of Medicine. 329 (15): 1084–91. doi:10.1056/NEJM199310073291506. PMID 8371731.
- Killias, Martin (1993). "Gun ownership, suicide and homicide: an international perspective" (PDF). In Del Frate, A. A.; et al. (eds.). Understanding crime: experiences of crime and crime control (Report). Rome: UNICRI. pp. 289–306. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-24.
- Killias, M.; van Kesteren, J.; Rindlisbacher, M. (2001). "Guns, violent crime, and suicide in 21 countries". Canadian Journal of Criminology. 43 (4): 429–48. doi:10.3138/cjcrim.43.4.429.
- Kleck, G.; Patterson, E. B. (1993). "The impact of gun control and gun ownership levels on violence rates". Journal of Quantitative Criminology. 9 (3): 249–87. doi:10.1007/BF01064462. S2CID 144180611.
- Klieve, Helen; Barnes, Michael; De Leo, Diego (2009) . "Controlling firearms use in Australia: has the 1996 gun law reform produced the decrease in rates of suicide with this method?". Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 44 (4): 285–92. doi:10.1007/s00127-008-0435-9. PMID 18839044. S2CID 22624912.
- Kposowa, A; Hamilton, D; Wang, K (21 March 2016). "Impact of Firearm Availability and Gun Regulation on State Suicide Rates". Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 46 (6): 678–96. doi:10.1111/sltb.12243. PMID 26999372.
- Krug, E.; Powell, K. E.; Dahlberg, L. L. (1998). "Firearm-related deaths in the United States and 35 other high- and upper-middle-income countries". International Journal of Epidemiology. 27 (2): 214–21. doi:10.1093/ije/27.2.214. PMID 9602401.
- Kwon, Ik-Whan G.; Scott, Bradley; Safranski, Scott R.; Bae, Muen (24 August 2010). "The Effectiveness of Gun Control Laws". American Journal of Economics and Sociology. 56 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1111/j.1536-7150.1997.tb03449.x.
- LaPierre, W. (1994). Guns, crime, and freedom. Washington, D.C.: Regnery. ISBN 9780895264770.
- Lambert, Michael T.; Silva, Peter S. (1998). "An Update on the Impact of Gun Control Legislation on Suicide". Psychiatric Quarterly. 69 (2): 127–34. doi:10.1023/A:1024714619938. PMID 9627930. S2CID 37048769.
- Langmann, C. (10 February 2012). "Canadian Firearms Legislation and Effects on Homicide 1974 to 2008". Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 27 (12): 2303–21. doi:10.1177/0886260511433515. PMID 22328660. S2CID 42273865.
- Lanza, Steven P. (3 April 2014). "The effect of firearm restrictions on gun-related homicides across US states". Applied Economics Letters. 21 (13): 902–05. doi:10.1080/13504851.2014.896977. S2CID 154724050.
- Lee, Wang-Sheng; Suardi, Sandy (January 2010). "The Australian Firearms Buyback and ITS Effect on Gun Deaths". Contemporary Economic Policy. 28 (1): 65–79. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.507.1298. doi:10.1111/j.1465-7287.2009.00165.x. S2CID 53520961.
- Lee, LK; Fleegler, EW; Farrell, C; et al. (14 November 2016). "Firearm Laws and Firearm Homicides: A Systematic Review". JAMA Internal Medicine. 177 (1): 106–19. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.7051. PMID 27842178. S2CID 205119294.
- Leenaars, Antoon A; Lester, David (July 2001). "The impact of gun control (Bill C-51) on homicide in Canada". Journal of Criminal Justice. 29 (4): 287–94. doi:10.1016/S0047-2352(01)00094-0.
- Leenaars, Antoon A.; Moksony, Ferenc; Lester, David; Wenckstern, Susanne (February 2003). "The Impact of Gun Control (Bill C-51) on Suicide in Canada". Death Studies. 27 (2): 103–24. doi:10.1080/07481180302890. PMID 12675070. S2CID 10059933.
- Leigh, A.; Neill, C. (20 August 2010). "Do Gun Buybacks Save Lives? Evidence from Panel Data". American Law and Economics Review. 12 (2): 509–57. doi:10.1093/aler/ahq013. hdl:10419/36943. S2CID 787141.
- Lester, David; Leenaars, Antoon (June 1993). "Suicide Rates in Canada before and after Tightening Firearm Control Laws". Psychological Reports. 72 (3): 787–90. doi:10.2466/pr0.1993.72.3.787. PMID 8332684. S2CID 25191464.
- Loftin, Colin; McDowall, David; Wiersema, Brian; Cottey, Talbert J. (5 December 1991). "Effects of Restrictive Licensing of Handguns on Homicide and Suicide in the District of Columbia". New England Journal of Medicine. 325 (23): 1615–20. doi:10.1056/NEJM199112053252305. PMID 1669841.
- Lott, J. R. (2010). More guns, less crime understanding crime and gun-control laws (3rd ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226493671. Archived from the original on 2022-05-31. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
- Lott, J. R. (2012). "What a Balancing Test Will Show for Right-to-Carry Laws". University of Maryland Law Review. 71 (4): 1205–18. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- Lubin, Gad; Werbeloff, Nomi; Halperin, Demian; et al. (October 2010). "Decrease in Suicide Rates After a Change of Policy Reducing Access to Firearms in Adolescents: A Naturalistic Epidemiological Study". Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 40 (5): 421–24. doi:10.1521/suli.2010.40.5.421. PMID 21034205.
- Luca, Michael; Malhotra, Deepak; Poliquin, Christopher (16 October 2017). "Handgun waiting periods reduce gun deaths". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114 (46): 12162–65. Bibcode:2017PNAS..11412162L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1619896114. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 5699026. PMID 29078268.
- Ludwig, Jens; Cook, Phillip J. (2 August 2000). "Homicide and Suicide Rates Associated With Implementation of the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act". JAMA. 284 (5): 585–91. doi:10.1001/jama.284.5.585. PMID 10918704.
- Malcolm, Joyce (1994). To Keep and Bear Arms: The Origins of an Anglo-American Right. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674893061.
- Malcolm, Joyce (2002). Guns and violence : The English experience. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674007536.
- Matzopoulos, Richard G.; Thompson, Mary Lou; Myers, Jonathan E. (March 2014). "Firearm and Nonfirearm Homicide in 5 South African Cities: A Retrospective Population-Based Study". American Journal of Public Health. 104 (3): 455–60. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.310650. PMC 3953758. PMID 24432917.
- Mauser, G. A.; Holmes, R. A. (1 December 1992). "An Evaluation of the 1977 Canadian Firearms Legislation". Evaluation Review. 16 (6): 603–17. doi:10.1177/0193841X9201600602. S2CID 144576514.
- Mauser, Gary A.; Maki, Dennis (April 2003). "An evaluation of the 1977 Canadian firearm legislation: robbery involving a firearm". Applied Economics. 35 (4): 423–36. doi:10.1080/00036840210143099. S2CID 154344131.
- McPhedran, S; Mauser, G (2013). "Lethal firearm-related violence against Canadian women: did tightening gun laws have an impact on women's health and safety?". Violence and Victims. 28 (5): 875–83. doi:10.1891/0886-6708.vv-d-12-00145. hdl:10072/57640. PMID 24364129. S2CID 21714121.
- Medoff, M. H.; Magaddino, J. P. (1 January 1983). "Suicides and Firearm Control Laws". Evaluation Review. 7 (3): 357–72. doi:10.1177/0193841X8300700305. S2CID 145607862.
- Miller, M. (1978). "Geriatric Suicide: The Arizona Study". The Gerontologist. 18 (5 Part 1): 488–95. doi:10.1093/geront/18.5_Part_1.488. PMID 263566.
- Miller, M.; Azrael, D.; Hemenway, D. (2002). "Rates of Household Firearm Ownership and Homicide Across US Regions and States, 1988–1997". American Journal of Public Health. 92 (12): 1988–93. doi:10.2105/AJPH.92.12.1988. PMC 1447364. PMID 12453821.
- Miller, M.; Hemenway, D.; Azrael, D. (2007). "State-level homicide victimization rates in the US in relation to survey measures of household firearm ownership, 2001–2003". Social Science & Medicine. 64 (3): 656–64. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.09.024. PMID 17070975.
- Miller, M.; Hemenway, D. (2008). "Guns and Suicide in the United States". New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (10): 989–91. doi:10.1056/NEJMp0805923. PMID 18768940.
- National Research Council (2005). Wellford, C. F.; Pepper, J. V.; Petrie, C. V. (eds.). Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review. Committee to Improve Research Information and Data on Firearms. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. ISBN 9780309091244. Archived from the original on 2008-10-13. Retrieved 2013-12-26.
- Ozanne-Smith, J.; Ashby, K.; Newstead, S.; et al. (2004). "Firearm related deaths: The impact of regulatory reform". Injury Prevention. 10 (5): 280–86. doi:10.1136/ip.2003.004150. PMC 1730132. PMID 15470007.
- Parker, Sarah (2011). "Balancing Acts: Regulation of Civilian Firearm Possession". In Berman, Eric G.; et al. (eds.). Small Arms Survey 2011: States of Security. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521146869. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-11.
- Perrin, Noel (1980). Giving Up the Gun: Japan's Reversion to the Sword, 1543–1879. Shambhala. ISBN 9780877731849. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
- Pierce, GL; Braga, AA; Wintemute, GJ (June 2015). "Impact of California firearms sales laws and dealer regulations on the illegal diversion of guns". Injury Prevention. 21 (3): 179–84. doi:10.1136/injuryprev-2014-041413. PMID 25472991. S2CID 41375606.
- Price, James H.; Thompson, Amy J.; Dake, Joseph A. (August 2004). "Factors Associated with State Variations in Homicide, Suicide, and Unintentional Firearm Deaths". Journal of Community Health. 29 (4): 271–83. doi:10.1023/B:JOHE.0000025326.89365.5c. PMID 15186014. S2CID 12678341.
- Reisch, T; Steffen, T; Habenstein, A; Tschacher, W (September 2013). "Change in suicide rates in Switzerland before and after firearm restriction resulting from the 2003 "Army XXI" reform". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 170 (9): 977–84. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12091256. PMID 23897090.
- Reuter, Peter; Mouzos, Jenny (2003). "Australia: A Massive Buyback of Low-Risk Guns". In Ludwig, J.; Cook, P. J. (eds.). Evaluating Gun Policy: Effects on Crime and Violence (PDF). Brookings Institution Press. pp. 121–56. ISBN 9780815753377. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-10-20. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- Rodríguez Andrés, Antonio; Hempstead, Katherine (June 2011). "Gun control and suicide: The impact of state firearm regulations in the United States, 1995–2004". Health Policy. 101 (1): 95–103. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.10.005. PMID 21044804.
- Rosengart, M; Cummings, P; Nathens, A; et al. (April 2005). "An evaluation of state firearm regulations and homicide and suicide death rates". Injury Prevention. 11 (2): 77–83. doi:10.1136/ip.2004.007062. PMC 1730198. PMID 15805435.
- Rudolph, KE; Stuart, EA; Vernick, JS; Webster, DW (August 2015). "Association Between Connecticut's Permit-to-Purchase Handgun Law and Homicides". American Journal of Public Health. 105 (8): e49–54. doi:10.2105/ajph.2015.302703. PMC 4504296. PMID 26066959.
- Safavi, A; Rhee, P; Pandit, V; et al. (January 2014). "Children are safer in states with strict firearm laws: a National Inpatient Sample study". The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 76 (1): 146–50, discussion 150–51. doi:10.1097/ta.0b013e3182ab10fb. PMID 24368370. S2CID 11563737.
- Santaella-Tenorio, Julian; Cerdá, Magdalena; Villaveces, Andrés; Galea, Sandro (10 February 2016). "What Do We Know About the Association Between Firearm Legislation and Firearm-Related Injuries?". Epidemiologic Reviews. 38 (1): 140–57. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxv012. PMC 6283012. PMID 26905895.
- Simonetti, Joseph A.; Rowhani-Rahbar, Ali; Mills, Brianna; et al. (August 2015). "State Firearm Legislation and Nonfatal Firearm Injuries". American Journal of Public Health. 105 (8): 1703–09. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2015.302617. PMC 4504301. PMID 26066935.
- Sloan, JH; Rivara, FP; Reay, DT; et al. (8 February 1990). "Firearm regulations and rates of suicide. A comparison of two metropolitan areas". The New England Journal of Medicine. 322 (6): 369–73. doi:10.1056/nejm199002083220605. PMID 2393410.
- Tahmassebi, S. B. (Summer 1991). "Gun Control and Racism". George Mason University Civil Rights Law Journal. 2 (1): 67–100. Archived from the original on 2000-08-16.
- Tashiro, J; Lane, RS; Blass, LW; et al. (3 August 2016). "The Effect of Gun Control Laws on Hospital Admissions for Children in the United States". The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 81 (4 Suppl 1): S54–60. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000001177. PMID 27488481. S2CID 25217599.
- Villaveces, Andrés; Cummings, Peter; Espitia, Victoria E.; et al. (1 March 2000). "Effect of a Ban on Carrying Firearms on Homicide Rates in 2 Colombian Cities". JAMA. 283 (9): 1205–09. doi:10.1001/jama.283.9.1205. PMID 10703790.
- Webster, DW; Vernick, JS; Zeoli, AM; Manganello, JA (4 August 2004). "Association between youth-focused firearm laws and youth suicides". JAMA. 292 (5): 594–601. doi:10.1001/jama.292.5.594. PMID 15292085.
- Webster, Daniel; Crifasi, Cassandra Kercher; Vernick, Jon S. (7 March 2014). "Effects of the Repeal of Missouri's Handgun Purchaser Licensing Law on Homicides". Journal of Urban Health. 91 (2): 293–302. doi:10.1007/s11524-014-9865-8. PMC 3978146. PMID 24604521.
- Webster, Daniel W.; Wintemute, Garen J. (18 March 2015). "Effects of Policies Designed to Keep Firearms from High-Risk Individuals". Annual Review of Public Health. 36 (1): 21–37. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031914-122516. PMID 25581152.
- Winkler, A. (2013). Gunfight: the battle over the right to bear arms in America. New York: W.W. Norton & Co. ISBN 9780393345834. Archived from the original on 2022-05-31. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
- Zeoli, April M.; Malinski, Rebecca; Turchan, Brandon (5 January 2016). "Risks and Targeted Interventions: Firearms in Intimate Partner Violence". Epidemiologic Reviews. 38 (1): 125–39. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxv007. PMID 26739680.
Further reading
- Rakoff, Jed S., "The Last of His Kind" (review of John Paul Stevens, The Making of a Justice: Reflections on My First 94 Years, Little, Brown, 549 pp.), The New York Review of Books, vol. LXVI, no. 14 (26 September 2019), pp. 20, 22, 24. John Paul Stevens, "a throwback to the postwar liberal Republican appointees", questioned the validity of "the doctrine of sovereign immunity, which holds that you cannot sue any state or federal government agency, or any of its officers or employees, for any wrong they may have committed against you, unless the state or federal government consents to being sued" (p. 20); the propriety of "the increasing resistance of the U.S. Supreme Court to most meaningful forms of gun control" (p. 22); and "the constitutionality of the death penalty... because of incontrovertible evidence that innocent people have been sentenced to death." (pp. 22, 24.)
- Squires, Peter. Gender and Firearms: My Body, My Choice, My Gun. United Kingdom, Taylor & Francis, 2024.
External links
Library resources aboutGun control
- GunPolicy.org Archived 2018-09-13 at the Wayback Machine
National groups
- Gun Control Australia – Supporting Gun Control in Australia
- Coalition for Gun Control – Canada
- Stop Gun Caravan – Japan
- Gun Free South Africa
- Coalition to Stop Gun Violence – U.S. Archived 2022-05-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Brady Campaign to Prevent Gun Violence – U.S.
- Giffords – U.S.