| Revision as of 01:03, 16 October 2006 editSiobhanHansa (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers22,662 editsm →External links: Rem spamlink← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:53, 22 August 2024 edit undoHansen Sebastian (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users20,308 editsNo edit summary | ||
| (286 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Le Mans Prototype race car}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{About|the 1999–2006 race car used in sports car racing|the 2006–2024 road-going sports car|Audi R8}} | |||
| {{More citations needed|date=July 2007}} | |||
| {{Racing car | |||
| |Car_name=Audi R8 | |||
| |Image= File:2000 Audi R8 LMP1 Front.jpg | |||
| |Category=] | |||
| |Constructor=] | |||
| |Predecessor = ] | |||
| |Successor = ] | |||
| |Designer=] (aerodynamics)<br/>] (chassis)<br/>] (engine) | |||
| |Team= {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GBR}} Audi Sport UK Team Veloqx<br/>{{flagicon|JPN}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|USA}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GBR}} ] Motorsport<br/>{{flagicon|FRA}} ] | |||
| |Drivers= {{flagicon|DEN}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GER}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GER}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|MON}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|SWE}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|FIN}} ]<br/>{{flagicon|GBR}} ] | |||
| |Chassis=] and ] honeycomb ] | |||
| |Front suspension=] ] pushrod system with horizontal spring/damper unit, adjustable gas-filled ] | |||
| |Rear suspension=] ] pushrod system with horizontal spring/damper unit, adjustable gas-filled ] | |||
| |Engine name=] | |||
| |Capacity=] | |||
| |Configuration=] ] | |||
| |Turbo/NA=], | |||
| |Engine position=], ] | |||
| |Gearbox name=] | |||
| |Gears=6-speed | |||
| |Type=] | |||
| |Differential=Multiple-disc ] | |||
| |Tyres=] | |||
| |Fuel=] | |||
| |Debut=] | |||
| |Races= 79 | |||
| |Wins= 63 | |||
| |Cons_champ= | |||
| |Drivers_champ= | |||
| |Poles= 47 | |||
| |Fastest_laps= | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Listen|filename=Audi R8 (2000).ogg|title=2000 Audi R8|description=Audi R8 at Goodwood Festival of Speed 2009}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The '''Audi R8''' is a ] sports-prototype race car introduced in 2000 for ] as a redevelopment of their ] (open-top ]) and ] (closed-top LMGTP) used in 1999. In its class, it is one of the most successful racing ]s having won the ] race in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, and 2005, five of the six years it competed in total. Its streak of Le Mans victories between 2000 and 2005 was broken only in 2003 by the ], another race car fielded that year by ].<ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.les24heures.fr/index.php/database/palmaresdes24hdumans | |||
| |title=Les24Heures | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| The petrol-powered Audi R8 race car was in 2006 replaced by the new ] Diesel; however, the need to further develop the R10 meant that the R8 saw action in a few races leading up to the 24 Hours of Le Mans. | |||
| The '''Audi R8''' is a ] race car introduced in 1999 for ] as a redevelopment of their Audi R8R (open top ]) and Audi R8C (closed top ]). The 2000 and later version Audi R8 was very successful, winning many races and championships until it was retired during the 2006 season. It is considered by some to be the most successful ]s ever (alongside such greats as the ]) having won the prestigious ] in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, and 2005. A streak of six straight Le Mans victories was broken-up only by the ] in 2003, when the R8 finished 3rd. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| The gasoline-powered Audi R8 ] has been replaced from 2006 onwards by the new ] Diesel, however, the need to further develop the R10 has meant that the R8 has seen action in a few races leading up to ]. | |||
| ==1998: The challenge== | ===1998: The challenge=== | ||
| In 1997, |
In 1997, sports car racing and especially the Le Mans 24 Hours was popular among factories such as ], ], ], ], ], and others. At that time, Audi Sport boss Wolfgang Ullrich started to evaluate the options of joining. | ||
| With the upcoming ] also providing a stage for the US |
With the upcoming ] also providing a stage for the US market, Audi announced plans in 1998 to compete in 1999, with the Audi R8R powered by a {{Convert|550|hp|kW|0|abbr=on}} V8 turbo. As it was considered the better choice for a whole race due to less weight and wider tires, Audi ordered an open-top roadster from ] to be developed and run by ]. | ||
| Yet, during the autumn of 1998, after the necessity of GT1 homologation was dropped in favour of LM-GTP prototypes, closed GT coupés like the ], ], and the ] proved successful. In response, Audi also ordered their newly acquired Norfolk-based Racing Technology Norfolk, led by ], to build a closed-cockpit car using the same drivetrain. | |||
| As it was considered the better choice for a whole race due to less weight and wider tires, Audi ordered an open top roadster from ], to be developed and run by ], similar to their Le Mans-Winner of 1996 and 1997 as well as to the 1998 ] built by ] (which would go on to win in 1999). | |||
| The ACO rules for closed-top prototypes allowed cars to run with larger air restrictors, resulting in more power (about 600 hp), which resulted in a higher top speed in combination with the lower drag. To compensate this advantage over the duration of a race, the LMGTPs were limited to smaller tyres and smaller fuel tanks. | |||
| Yet, during the fall of 1998, after the necessity of GT1 homologation was dropped in favour of LM-GTP prototypes, regarding the speed and success of these closed GT coupés like ] ('98 Le Mans Winner), the ] ('98 ] champion, beating the 911 GT1 in all GT races) and the ] (considered fastest), Audi also ordered their newly acquired ] based RTN (], led by Tony Southgate) to build such a car using the same drivetrain. | |||
| ===1999: The R8R and R8C=== | |||
| The GTP rules allowed to have more power (about 600 hp), which results in a higher top speed in combination with the lower drag. To compensate this advantage over the duration of a race, the GTPs were limited to smaller tires and smaller fuel tanks. | |||
| {{Main|Audi R8R|Audi R8C}} | |||
| Following a period of testing, two R8Rs debuted at the 1999 ]. The ] won, which was a strong sign towards the race in France. The already tested open-top Audi R8R, entered by Joest Racing, was not fast enough to challenge for a win, finishing third. | |||
| After further tests and modifications, the Audis returned for Le Mans. The new debuting R8Cs lacked pace and unfortunately suffered mechanical gearbox woes. Lap times were 10 seconds down from the leading LMP and LMGTP competitors. Joest's R8Rs ran steady, yet still were too slow to run for pole position. After a race that had the spectacular flights of the ] and leading cars of Toyota and BMW crashing out, the Audi R8Rs took third and fourth behind the surviving #15 ] and the Japanese-driven Toyota. | |||
| ==1999: The R8R and R8C== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Based on the experiences, Audi decided to regroup for 2000, and built a new R8 ] together with Joest and Dallara. The British-built R8C coupe was retired, but Audi-owned ] developed the concept of the R8C closed-cockpit LMGTP and entered the ] in 2001, winning the race with the ] in 2003. | |||
| At the 1999 ], two R8R cars showed up, painted in silver, to revive the 1930s ] rivalry with Mercedes — which was absent, as was Toyota and the brand new closed-roof R8C which needed to be tested first. Also, Porsche took a year off to develop a V10 car. | |||
| ===1999: Retiring competitors=== | |||
| The ] won, which was a strong sign towards the race in France. The already tested open-top Audi R8R, entered by ] was not fast enough to challenge for a win, finishing 3rd. | |||
| After the 1999 Le Mans shame, Mercedes retired from GTs to focus on the return of the ] touring cars in 2000, as well as on F1. Toyota and BMW also went to F1, with BMW at least continuing to race for two years in the ], where the open roadster of ] also suffered a "back flip" during the ] at ] in 2000, as the closed-cockpit Porsche of ] had done in 1998. Despite the BMW V12 LMR not receiving further development, the German team ] was almost as effective as Joest. Still, the BMW V12 LMR could not match the Audi R8's might in the championship and lost almost every race against it. BMW quit the top class to race the ] in the GT class since, dominating in the ALMS and in ], as well as at the ]. | |||
| This left only Porsche as a major possible challenger for 2000; however, the ] project was scrapped before it had a chance to race. Rumours at that time said that ] himself made them stay away, using his influence as a co-owner of Porsche, as well as his management role at ], which would develop the upcoming SUV ] in cooperation with the ].<ref>{{cite web |author=Michael J. Fuller |url=http://www.mulsannescorner.com/porschelmp1.html |title=Mulsanne's Corner: 1999-2000 Porsche LMP1 |publisher=Mulsannescorner.com |access-date=2010-10-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407182942/http://www.mulsannescorner.com/porschelmp1.html |archive-date=2014-04-07 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The Porsche V10 racer was turned into the ] instead. | |||
| After further tests and modifications, the Audis returned for Le Mans, with the R8C only looking fast, even while standing still in the RTN pits, which it did too often. Lap times were 10 seconds down, too. Joest made their cars run steady, yet still was too slow to run for P1. After a race which saw the spectacular flights of the ] as well as leading cars of Toyota and BMW crashing out, the Audi R8R took 3rd and 4th behind the surviving #15 BMW and the Japanese-driven Toyota. | |||
| ===2000: The R8=== | |||
| Based on the experiences, Audi decided to regroup for 2000, and built a new R8 roadster together with Joest and Dallara. The British-built R8C GTP was retired, but Bentley developed the concept and entered the ] at the 2001 event, and after more work again in 2003, this time as a winner. | |||
| {{stack begin}} | |||
| ] in Adelaide, Australia, in 2000 driven by ] and ].]] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{stack end}} | |||
| The Audi R8 is a sports-] prepared for the ] class at Le Mans and in the ]. The car was developed by Audi Motorsport and Joest Racing, and debuted in 2000, winning the 12 Hours of Sebring. | |||
| The R8 won Le Mans five times (], ], ], ], and ]) and the overall season championship in the American Le Mans Series six times in a row (from 2000 to 2005).<ref name=r&t201208>{{cite journal|last=Bornhop|first=Andrew|title=Ode to an R8|journal=]|date=August 2012|volume=63|issue=12|page=61}}</ref> | |||
| == 1999: Retiring competitors == | |||
| After the 1999 Le Mans shame, Mercedes retired from GTs to focus on the return of the ] touring cars in 2000, as well as on F1. Toyota and BMW also went to F1, with BMW at least continuing to race for two years in the ], where the open roadster of ] also suffered a "back flip" during the ] at ] in 2000, as the closed-cockpit Porsche of ] had done in 1998. Despite the BMW V12 not receiving further development, the German team ] was almost as effective as Joest. They returned to race ] touring car since, dominating in the ALMS and in ] as well as at the ]. | |||
| The R8 won a hat trick at Le Mans in 2000–2002, campaigned by Audi Sport ] Team Joest and driven by ], ], and ]. First time out in 2000, the team won a 1-2-3 finish. Since then, the Audi R8 has won numerous championships and races, including further wins for "privateer" teams at Le Mans in 2004 and 2005. | |||
| This left only Porsche as a major possible challenger for 2000 — which never showed up, though. Rumors at that time, which where confirmed since, said that ] himself made them stay away, using his influence as a co-owner of Porsche as well as his manager positions at ], which would develop the upcoming SUV ] in cooperation with the ]. The Porsche V10 racer was turned into the ] instead. | |||
| The R8 is powered by a 3.6 L Audi V8 with ] (FSI), which is a variation on the concept of ] developed by VW; it maximizes both power and fuel economy at the same time. FSI technology can be found in products available to the public, across all brands in the ]. | |||
| == 2000: The R8 == | |||
| The Audi R8 is a sports-] prepared for ] racing in the ] class at Le Mans and in the ]. The car was developed by ] and ] and first debuted in 2000, winning the ]. | |||
| The power supplied by the R8, officially listed at about {{Convert|610|hp|kW|0|abbr=on}} in 2000, 2001, and 2002, {{Convert|550|hp|kW|1|abbr=on}} in 2003 and 2004, and {{Convert|520|hp|kW|0|abbr=on}} in 2005, is sent to the rear wheels via a ] six-speed ] with an electropneumatic paddle shift. Unofficially, the works team Audi R8 for Le Mans (2000, 2001, and 2002) is said to have had around {{Convert|670|hp|kW|0|abbr=on}} instead of the quoted 610 hp. The numbers were quoted at speed, and were due to the car making 50 extra horsepower due to twin ram-air intakes at speeds over {{convert|150|mi/h|km/h|abbr=on}}. Official torque numbers were quoted for this version of the engine at {{Convert|516|lbft|Nm|abbr=on}} at 6500 rpm. The equation for horsepower (torque divided by 5250, multiplied by rpm) for these numbers produces a horsepower rating of {{convert|638|hp}} at the same 6500 rpm (516/5250*6500=638). The Audi R8's structure was designed from the beginning to expedite parts changes during the race. The car's chassis has been likened to a ] model — anything on the car can be changed and changed quickly. During its campaign, the Joest pit crew was able to change the entire rear transaxle of a damaged R8 — a process which usually takes between one and three hours — in as low as three minutes and 16 seconds.<ref name=r&t201208/> The reason for this was that the transmission, rear suspension, and rear subframe were built as one unit. The car had numerous quick-connect hoses and easily removable bolts. The whole rear section of the car could be removed as a whole and a new back half installed with the help of a crane. The Automobile Club de l'Ouest (ACO), organizers of the 24 Hours of Le Mans and the American Le Mans Series, acted quickly to void this advantage by mandating the gearbox casing be the same item through the duration of the race, with only the internals being allowed to be changed. However, the R8 still had quicker access to the gearbox internals than any other car due to its quick-change construction . This was critical as the gearbox was the weak link in the car. | |||
| The R8 has won Le Mans five times (], ], ], ] and ]) and the overall season championship in the American Le Mans Series six times in a row (from 2000 to 2005). | |||
| The R8's structure and body are both composed of carbon fibre, a strong, lightweight polymer material. | |||
| ] | |||
| Performance from top speed to acceleration was, as in most race car cases, variable depending on the car's setup. The highest speed of the R8 at Le Mans was {{convert|338|km/h|mph|0|abbr=on}} in the practice sessions of the 2002 Le Mans 24 Hours Race. A low downforce setup could reach about {{convert|350|km/h|mph|0|abbr=on}}. | |||
| The R8 won a hat trick at Le Mans (three wins in a row) campaigned by Audi Sport ] Team Joest and driven by ], ] and ] during the 2000-2002 seasons. First time out in 2000, the team won a 1-2-3 finish, which was just a small preview of what this all-new Audi was capable of. Since then, the Audi R8 has won numerous championships and races, including wins at Le Mans in 2004 and 2005. | |||
| Audi Sport's program saw tragedy in 2001 when on April 25, popular ex-F1 driver ] died in an accident after suffering a high-speed tyre failure during an R8 test session at the ] in eastern Germany.<ref name=nytimes>''Alboreto Is Killed Testing Audi R8'', '']'', April 26, 2001, Page D7.</ref> | |||
| The R8 is powered by a 3.6 L twin-] and intercooled Audi ] V8. FSI stands for Fuel-Stratified Injection, which is a variation on the concept of ] developed by VW which maximizes both power and fuel economy at the same time. FSI technology can be found in products available to the normal public, across all brands in the ]. | |||
| ===2003: Bentley breaks the streak=== | |||
| The power supplied by the R8, officially limited to about 580 hp (about 430 kW) during the 2004 race, is sent to the rear wheels via a Ricardo six-speed ] with an electro–pneumatic gear change. That means it has a computer-controlled ] that allows the driver to make gear changes without touching the clutch pedal. These gear changes can be done by the computer far quicker than even the fastest human being with a conventional manual transmission. | |||
| The ], which was somewhat based on the R8 ran at Le Mans from 2001 to 2003, winning in 2003, used a heavily modified 4.0-L version of the V8 engine from the Audi R8 .{{Citation needed|date=June 2008}} | |||
| The Bentley racing effort was campaigned by Team ] (Apex Motorsport) with assistance from longtime R8 competitor Joest Racing and Audi Sport UK. After 2002, the Joest factory team dropped its R8 campaign and left it to the privateers. Restrictor changes brought the power down to 550 bhp for anyone still racing with the R8, but the maximum torque hardly changed. | |||
| ], who won the previous three 24 Hours of Le Mans races in an R8, was assigned to drive the Bentley Speed 8, and helped guide the team to victory. (Kristensen went on to win the 2004 and 2005 races in an Audi R8). Some similarity exists between the Bentley Speed 8 and the Audi R8's successor, the R10 TDI. | |||
| ===2005: End of active competition=== | |||
| However, while the R8's speed was quite dominant during the races, speed is but a minor factor in winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans. The main key is reliability. The R8 was a reliable car, yes; but not far more so than its competitors. The real reason for the R8's dominance at La Sarthe was its ingenious design. | |||
| During the 2005 season, its time at the front of the pack evidently was drawing to a close. Audi had made the development of the ] diesel public, and cars from other manufacturers and teams started to catch up in terms of on-the-track speed. The ACO still felt that the R8 needed to be kept in check, so they reduced the restrictor size on the R8's engine, due to the car not meeting new hybrid regulations, and stipulated the car shall carry ] in an attempt to make the races more competitive. The R8 was restricted even further to only 520 bhp. At the 2005 Le Mans, the Audis failed to qualify on pole position; the fastest R8 started the race in third position. However, the car was able to outlast all other competitors to eventually take its fifth checkered flag at the Circuit de la Sarthe and the 24 Hours of Le Mans. This victory was also notable since it was Tom Kristensen's sixth straight 24 Hours of Le Mans victory, and a record seventh overall, beating legendary driver ]'s previous record of six career 24 Hours of Le Mans victories. To date, the R8 remains one of the fastest petrol-powered LMPs, setting a 3:29 at Le Mans, which was beaten only by the Lola-Aston Martins. However, the R8's best finish was at 379 laps, which is more than the Lola-Aston Martin's best at 373 laps. | |||
| ==List of records== | |||
| The Audi R8's structure was designed from the very beginning to expedite parts changes during the race. The car has a chassis that has been likened to a ] model — anything on the car can be changed and changed quickly. During its campaign, the Joest pit crew was able to change the entire rear transaxle of a damaged R8 — a process which usually takes between one and three hours — in four and a half minutes, a feat that was unprecedented in its efficiency and speed. The Automobile Club de l'Ouest (ACO), organizers of the ] and the ] acted quickly to void this advantage by mandating the gearbox casing be the same item through the duration of the race, with only the internals being allowed to be changed. However, the R8 still had quicker access to the gearbox internals than any other car due to its quick-change construction. | |||
| * ] winner - {{24hLM|2000}}, {{24hLM|2001}}, {{24hLM|2002}}, {{24hLM|2004}}, {{24hLM|2005}} | |||
| The R8's structure and body are both composed of ], a lightweight polymer material which is extremely lightweight and strong; however it is very expensive and time-consuming to mould. | |||
| * ] champion: ], ], ], ], ], ], ]<sup>†</sup> | |||
| * ] champion: ] | |||
| * ] champion: ] | |||
| † - Season partially run by the ] | |||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| Audi Sport's programme saw tragedy in 2001 when on April 25, popular driver ] died in an accident after suffering a high-speed tire failure during an RB test session at the ] in eastern Germany. | |||
| == |
===2006: The R10 TDI=== | ||
| {{Main|Audi R10 TDI}} | |||
| It should be noted, however, that the ], which ran at Le Mans from 2001 to 2003, winning in 2003, utilised a heavily modified 4.0 L version of the turbocharged V8 engine from the Audi R8. The Bentley racing effort was campaigned by Team ] (Apex Motorsport) with assistance from longtime R8 competitor Joest Racing and Audi Sport UK. ], who won the previous three 24 Hours of Le Mans races in an R8, was assigned to drive the Bentley Speed 8, and helped guide the team to victory. (Kristensen went on to win the 2004 and 2005 races in an Audi R8). Some even say that the works Audi teams sandbagged the race in order to hand victory to the Volkswagen/Audi Group's newest addition, ] Motors. There is also some similarity between the Bentley Speed 8 and the Audi R8's successor, the R10. In some places the Bentley is referred to as being the R9. | |||
| In response to the new level of competition, Audi developed a successor known as the ]. The ]d ] won at its race debut at the 2006 12 Hours of Sebring with both cars starting on the front row. However, the pole-sitting R10 had to start from the pit lane due to the need to rectify heat exchanger issues. | |||
| Emanuele Pirro, Frank Biela, and Marco Werner made history by becoming the first drivers to win the Le Mans 24-hour race in a diesel-powered car. The Audi R10 TDI completed a record 380 laps of the La Sarthe circuit, with Pirro at the wheel for the finish. French trio ], ], and ] took second in the ] Judd No 17, four laps back. Scotsman ] was third in the other Audi, which came in 13 laps down after suffering mechanical problems. | |||
| == 2005: The end of a legend == | |||
| ] | |||
| Very few racing cars have a racing pedigree comparable to the R8. However, as amazing as the R8 was, during the 2005 season, it was evident that its time at the front of the pack was drawing to a close. Audi had made the development of the ] diesel public, and cars from other manufacturers and teams started to catch up in terms of on-the-track speed. The ACO still felt that the R8 needed to be kept in check, therefore they reduced the restrictor size on the R8's engine and stipulated the car shall carry ballast in an attempt to make the races more competitive. At the 2005 Le Mans, the Audis failed to qualify on pole position; the fastest R8 started the race in third position. However, as a hallmark to the R8's legendary reliability, the car was able to outlast all other competitors to take its fifth checkered flag at the venerable Circuit de la Sarthe and the 24 Hours of Le Mans. This victory was also notable since it was Tom Kristensen's 6th straight 24 Hours of Le Mans victory, and a record 7th overall, beating legendary driver ]'s previous record of 6 career 24 Hours of Le Mans victories. | |||
| The R8 continued to campaign the American Le Mans Series through the first half of the 2006 season, and made its final US appearance on July 1, 2006, at ], ], piloted by McNish and Capello. The R8 ended its career in style by winning the race, marking the 50th American Le Mans Series victory for the Audi R8. The R10s participated in the rest of the ALMS season, beginning with the race at ], ]. | |||
| == |
===2007: R8 road car=== | ||
| The name Audi R8 also is used by the production road ] ], which is based on the 2003 ] ]. Production started in 2007. | |||
| ] | |||
| In response to the new level of competition, development of the successor, known as the ], has been completed. The V12-Turbodiesel won at its race debut at the 2006 ] with both cars starting on the front row. Unfortunately the pole sitting R10 had to start from the pit lane due to the need to rectify heat exchanger issues. ] is expected to build a Diesel powered rival in 2007. | |||
| ==24 Hours of Le Mans results== | |||
| Emanuele Pirro, Frank Biela and Marco Werner made history by becoming the first drivers to win the Le Mans 24-hour race in a diesel-powered car. The Audi R10 Diesel completed a record 380 laps of the La Sarthe circuit, with Pirro at the wheel for the finish. French trio Sebastien Loeb, Eric Helary and Franck Montagny took second in the Pescarolo Judd No 17, four laps adrift. Scotsman Allan McNish was third in the other Audi, which came in 13 laps down after suffering mechanical problems. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="font-size:85%; width:700px" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Year | |||
| ! Team | |||
| ! No | |||
| ! Drivers | |||
| ! Pole | |||
| ! Fastest<br>lap | |||
| ! Laps | |||
| ! Overall<br>Position | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=3| ] | |||
| |rowspan=3 align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 7 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 365 | |||
| |style="background:#FFDF9F;"| '''3rd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | 8 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 368 | |||
| |style="background:#FFFFBF;"| '''1st''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | 9 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|MCO}} ] | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | 367 | |||
| |style="background:#DFDFDF;"| '''2nd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=4| ] | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 1 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 321 | |||
| |style="background:#FFFFBF;"| '''1st''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 2 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | 320 | |||
| |style="background:#DFDFDF;"| '''2nd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|USA}} ] | |||
| | 3 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|BEL}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 81 | |||
| | DNF | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ] | |||
| | 4 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|SWE}} ]<br>{{flagicon|NLD}} ]<br>{{flagicon|FRA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 35 | |||
| | DNF | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=4| ] | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 1 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | 375 | |||
| |style="background:#FFFFBF;"| '''1st''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 2 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 374 | |||
| |style="background:#DFDFDF;"| '''2nd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | 3 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|AUT}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 372 | |||
| |style="background:#FFDF9F;"| '''3rd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} ] | |||
| | 5 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} Hiroki Katoh<br>{{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|JPN}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 358 | |||
| | 7th | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=3| ] | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} ] | |||
| | 5 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 370 | |||
| | 4th | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|USA}} ] | |||
| | 6 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FIN}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|SWE}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 372 | |||
| |style="background:#FFDF9F;"| '''3rd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ] | |||
| | 10 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|FIN}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 28 | |||
| | DNF | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=4| ] | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|USA}} ] ] | |||
| | 2 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FIN}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 368 | |||
| |style="background:#FFDF9F;"| '''3rd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} ] | |||
| | 5 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|JPN}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 379 | |||
| |style="background:#FFFFBF;"| '''1st''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |rowspan=2 align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ] | |||
| | 8 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 350 | |||
| | 5th | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | 88 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ] | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | ''yes'' | |||
| | 379 | |||
| |style="background:#DFDFDF;"| '''2nd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| !rowspan=3| ] | |||
| |rowspan=2 align="left"| {{flagicon|USA}} ] ] | |||
| | 2 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|DEU}} ]<br>{{flagicon|GBR}} ]<br>{{flagicon|ITA}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 364 | |||
| |style="background:#FFDF9F;"| '''3rd''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | 3 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FIN}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DNK}} ]<br>{{flagicon|DEU}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 370 | |||
| |style="background:#FFFFBF;"| '''1st''' | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FRA}} ] ] ] | |||
| | 4 | |||
| |align="left"| {{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|FRA}} ]<br>{{flagicon|MCO}} ] | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | ''no'' | |||
| | 362 | |||
| | 4th | |||
| |} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| The venerable R8 continued to campaign the ] through the first half of the 2006 season, and made its final US appearance on ], ] at ], ], piloted by McNish and Capello. The R8 ended its career in style by winning the race, the 50th ] win for the Audi R8. The R10s will participate in the rest of the ALMS season, beginning with the next race at ], ]. | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| == 2007: the R8 Road Car == | |||
| {{Commons category|Audi R8 (sports prototype)}} | |||
| The name Audi R8 will also be used by the future production road ]/] ] which will be based on the 2003 Audi Le Mans Quattro ], not the R8 race car. ] has announced that this car will be built in 2007 or later. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Audi}} | {{Audi}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Audi R8 (LMP)}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:53, 22 August 2024
Le Mans Prototype race car This article is about the 1999–2006 race car used in sports car racing. For the 2006–2024 road-going sports car, see Audi R8.| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Audi R8" LMP – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Problems playing this file? See media help.

The Audi R8 is a Le Mans Prototype sports-prototype race car introduced in 2000 for sports car racing as a redevelopment of their Audi R8R (open-top LMP) and Audi R8C (closed-top LMGTP) used in 1999. In its class, it is one of the most successful racing sports cars having won the 24 Hours of Le Mans race in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, and 2005, five of the six years it competed in total. Its streak of Le Mans victories between 2000 and 2005 was broken only in 2003 by the Bentley Speed 8, another race car fielded that year by Volkswagen Group.
The petrol-powered Audi R8 race car was in 2006 replaced by the new Audi R10 TDI Diesel; however, the need to further develop the R10 meant that the R8 saw action in a few races leading up to the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
History
1998: The challenge
In 1997, sports car racing and especially the Le Mans 24 Hours was popular among factories such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Toyota, Nissan Motors, and others. At that time, Audi Sport boss Wolfgang Ullrich started to evaluate the options of joining.
With the upcoming American Le Mans Series also providing a stage for the US market, Audi announced plans in 1998 to compete in 1999, with the Audi R8R powered by a 550 hp (410 kW) V8 turbo. As it was considered the better choice for a whole race due to less weight and wider tires, Audi ordered an open-top roadster from Dallara to be developed and run by Joest Racing.
Yet, during the autumn of 1998, after the necessity of GT1 homologation was dropped in favour of LM-GTP prototypes, closed GT coupés like the Porsche 911 GT1, Mercedes-Benz CLK-GTR, and the Toyota GT-One proved successful. In response, Audi also ordered their newly acquired Norfolk-based Racing Technology Norfolk, led by Tony Southgate, to build a closed-cockpit car using the same drivetrain.
The ACO rules for closed-top prototypes allowed cars to run with larger air restrictors, resulting in more power (about 600 hp), which resulted in a higher top speed in combination with the lower drag. To compensate this advantage over the duration of a race, the LMGTPs were limited to smaller tyres and smaller fuel tanks.
1999: The R8R and R8C
Main articles: Audi R8R and Audi R8CFollowing a period of testing, two R8Rs debuted at the 1999 12 Hours of Sebring. The BMW V12 LMR won, which was a strong sign towards the race in France. The already tested open-top Audi R8R, entered by Joest Racing, was not fast enough to challenge for a win, finishing third.
After further tests and modifications, the Audis returned for Le Mans. The new debuting R8Cs lacked pace and unfortunately suffered mechanical gearbox woes. Lap times were 10 seconds down from the leading LMP and LMGTP competitors. Joest's R8Rs ran steady, yet still were too slow to run for pole position. After a race that had the spectacular flights of the Mercedes-Benz CLR and leading cars of Toyota and BMW crashing out, the Audi R8Rs took third and fourth behind the surviving #15 BMW V12 LMR and the Japanese-driven Toyota.
Based on the experiences, Audi decided to regroup for 2000, and built a new R8 spyder together with Joest and Dallara. The British-built R8C coupe was retired, but Audi-owned Bentley developed the concept of the R8C closed-cockpit LMGTP and entered the Bentley EXP Speed 8 in 2001, winning the race with the Bentley Speed 8 in 2003.
1999: Retiring competitors
After the 1999 Le Mans shame, Mercedes retired from GTs to focus on the return of the DTM touring cars in 2000, as well as on F1. Toyota and BMW also went to F1, with BMW at least continuing to race for two years in the ALMS, where the open roadster of Bill Auberlen also suffered a "back flip" during the Petit Le Mans at Road Atlanta in 2000, as the closed-cockpit Porsche of Yannick Dalmas had done in 1998. Despite the BMW V12 LMR not receiving further development, the German team Schnitzer Motorsport was almost as effective as Joest. Still, the BMW V12 LMR could not match the Audi R8's might in the championship and lost almost every race against it. BMW quit the top class to race the BMW M3 in the GT class since, dominating in the ALMS and in WTCC, as well as at the 24 Hours Nürburgring.
This left only Porsche as a major possible challenger for 2000; however, the Porsche LMP project was scrapped before it had a chance to race. Rumours at that time said that Ferdinand Piech himself made them stay away, using his influence as a co-owner of Porsche, as well as his management role at Volkswagen, which would develop the upcoming SUV VW Touareg in cooperation with the Porsche Cayenne. The Porsche V10 racer was turned into the Porsche Carrera GT instead.
2000: The R8

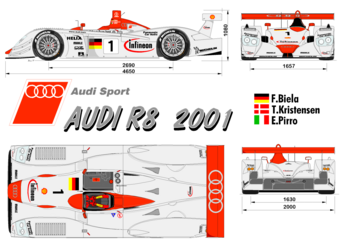
The Audi R8 is a sports-racing car prepared for the LMP900 class at Le Mans and in the American Le Mans Series. The car was developed by Audi Motorsport and Joest Racing, and debuted in 2000, winning the 12 Hours of Sebring.
The R8 won Le Mans five times (2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, and 2005) and the overall season championship in the American Le Mans Series six times in a row (from 2000 to 2005).
The R8 won a hat trick at Le Mans in 2000–2002, campaigned by Audi Sport Infineon Team Joest and driven by Tom Kristensen, Emanuele Pirro, and Frank Biela. First time out in 2000, the team won a 1-2-3 finish. Since then, the Audi R8 has won numerous championships and races, including further wins for "privateer" teams at Le Mans in 2004 and 2005.
The R8 is powered by a 3.6 L Audi V8 with Fuel Stratified Injection (FSI), which is a variation on the concept of gasoline direct injection developed by VW; it maximizes both power and fuel economy at the same time. FSI technology can be found in products available to the public, across all brands in the Volkswagen Group.
The power supplied by the R8, officially listed at about 610 hp (455 kW) in 2000, 2001, and 2002, 550 hp (410.1 kW) in 2003 and 2004, and 520 hp (388 kW) in 2005, is sent to the rear wheels via a Ricardo six-speed sequential transmission with an electropneumatic paddle shift. Unofficially, the works team Audi R8 for Le Mans (2000, 2001, and 2002) is said to have had around 670 hp (500 kW) instead of the quoted 610 hp. The numbers were quoted at speed, and were due to the car making 50 extra horsepower due to twin ram-air intakes at speeds over 150 mph (240 km/h). Official torque numbers were quoted for this version of the engine at 516 lb⋅ft (700 N⋅m) at 6500 rpm. The equation for horsepower (torque divided by 5250, multiplied by rpm) for these numbers produces a horsepower rating of 638 horsepower (476 kW) at the same 6500 rpm (516/5250*6500=638). The Audi R8's structure was designed from the beginning to expedite parts changes during the race. The car's chassis has been likened to a Lego model — anything on the car can be changed and changed quickly. During its campaign, the Joest pit crew was able to change the entire rear transaxle of a damaged R8 — a process which usually takes between one and three hours — in as low as three minutes and 16 seconds. The reason for this was that the transmission, rear suspension, and rear subframe were built as one unit. The car had numerous quick-connect hoses and easily removable bolts. The whole rear section of the car could be removed as a whole and a new back half installed with the help of a crane. The Automobile Club de l'Ouest (ACO), organizers of the 24 Hours of Le Mans and the American Le Mans Series, acted quickly to void this advantage by mandating the gearbox casing be the same item through the duration of the race, with only the internals being allowed to be changed. However, the R8 still had quicker access to the gearbox internals than any other car due to its quick-change construction . This was critical as the gearbox was the weak link in the car.
The R8's structure and body are both composed of carbon fibre, a strong, lightweight polymer material.
Performance from top speed to acceleration was, as in most race car cases, variable depending on the car's setup. The highest speed of the R8 at Le Mans was 338 km/h (210 mph) in the practice sessions of the 2002 Le Mans 24 Hours Race. A low downforce setup could reach about 350 km/h (217 mph).
Audi Sport's program saw tragedy in 2001 when on April 25, popular ex-F1 driver Michele Alboreto died in an accident after suffering a high-speed tyre failure during an R8 test session at the Lausitzring in eastern Germany.
2003: Bentley breaks the streak
The Bentley Speed 8, which was somewhat based on the R8 ran at Le Mans from 2001 to 2003, winning in 2003, used a heavily modified 4.0-L version of the V8 engine from the Audi R8 . The Bentley racing effort was campaigned by Team Bentley (Apex Motorsport) with assistance from longtime R8 competitor Joest Racing and Audi Sport UK. After 2002, the Joest factory team dropped its R8 campaign and left it to the privateers. Restrictor changes brought the power down to 550 bhp for anyone still racing with the R8, but the maximum torque hardly changed. Tom Kristensen, who won the previous three 24 Hours of Le Mans races in an R8, was assigned to drive the Bentley Speed 8, and helped guide the team to victory. (Kristensen went on to win the 2004 and 2005 races in an Audi R8). Some similarity exists between the Bentley Speed 8 and the Audi R8's successor, the R10 TDI.
2005: End of active competition
During the 2005 season, its time at the front of the pack evidently was drawing to a close. Audi had made the development of the Audi R10 TDI diesel public, and cars from other manufacturers and teams started to catch up in terms of on-the-track speed. The ACO still felt that the R8 needed to be kept in check, so they reduced the restrictor size on the R8's engine, due to the car not meeting new hybrid regulations, and stipulated the car shall carry ballast weight in an attempt to make the races more competitive. The R8 was restricted even further to only 520 bhp. At the 2005 Le Mans, the Audis failed to qualify on pole position; the fastest R8 started the race in third position. However, the car was able to outlast all other competitors to eventually take its fifth checkered flag at the Circuit de la Sarthe and the 24 Hours of Le Mans. This victory was also notable since it was Tom Kristensen's sixth straight 24 Hours of Le Mans victory, and a record seventh overall, beating legendary driver Jacky Ickx's previous record of six career 24 Hours of Le Mans victories. To date, the R8 remains one of the fastest petrol-powered LMPs, setting a 3:29 at Le Mans, which was beaten only by the Lola-Aston Martins. However, the R8's best finish was at 379 laps, which is more than the Lola-Aston Martin's best at 373 laps.
List of records
- 24 Hours of Le Mans winner - 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004, 2005
- American Le Mans Series champion: 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006
- European Le Mans Series champion: 2001
- Le Mans Series champion: 2004
† - Season partially run by the Audi R10
Legacy
2006: The R10 TDI
Main article: Audi R10 TDIIn response to the new level of competition, Audi developed a successor known as the Audi R10 TDI. The V12 engined turbodiesel won at its race debut at the 2006 12 Hours of Sebring with both cars starting on the front row. However, the pole-sitting R10 had to start from the pit lane due to the need to rectify heat exchanger issues.
Emanuele Pirro, Frank Biela, and Marco Werner made history by becoming the first drivers to win the Le Mans 24-hour race in a diesel-powered car. The Audi R10 TDI completed a record 380 laps of the La Sarthe circuit, with Pirro at the wheel for the finish. French trio Sébastien Loeb, Éric Hélary, and Franck Montagny took second in the Pescarolo Judd No 17, four laps back. Scotsman Allan McNish was third in the other Audi, which came in 13 laps down after suffering mechanical problems.

The R8 continued to campaign the American Le Mans Series through the first half of the 2006 season, and made its final US appearance on July 1, 2006, at Lime Rock Park, Connecticut, piloted by McNish and Capello. The R8 ended its career in style by winning the race, marking the 50th American Le Mans Series victory for the Audi R8. The R10s participated in the rest of the ALMS season, beginning with the race at Miller Motorsports Park, Utah.
2007: R8 road car
The name Audi R8 also is used by the production road sports car Audi R8, which is based on the 2003 Audi Le Mans quattro concept car. Production started in 2007.
24 Hours of Le Mans results
| Year | Team | No | Drivers | Pole | Fastest lap |
Laps | Overall Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 7 | no | no | 365 | 3rd | ||
| 8 | no | no | 368 | 1st | |||
| 9 | yes | yes | 367 | 2nd | |||
| 2001 | 1 | no | no | 321 | 1st | ||
| 2 | yes | yes | 320 | 2nd | |||
| 3 | no | no | 81 | DNF | |||
| 4 | no | no | 35 | DNF | |||
| 2002 | 1 | no | yes | 375 | 1st | ||
| 2 | yes | no | 374 | 2nd | |||
| 3 | no | no | 372 | 3rd | |||
| 5 | no | no | 358 | 7th | |||
| 2003 | 5 | no | no | 370 | 4th | ||
| 6 | no | no | 372 | 3rd | |||
| 10 | no | no | 28 | DNF | |||
| 2004 | 2 | no | no | 368 | 3rd | ||
| 5 | no | no | 379 | 1st | |||
| 8 | no | no | 350 | 5th | |||
| 88 | yes | yes | 379 | 2nd | |||
| 2005 | 2 | no | no | 364 | 3rd | ||
| 3 | no | no | 370 | 1st | |||
| 4 | no | no | 362 | 4th |
References
- "Les24Heures".
- Michael J. Fuller. "Mulsanne's Corner: 1999-2000 Porsche LMP1". Mulsannescorner.com. Archived from the original on 2014-04-07. Retrieved 2010-10-11.
- ^ Bornhop, Andrew (August 2012). "Ode to an R8". Road & Track. 63 (12): 61.
- Alboreto Is Killed Testing Audi R8, The New York Times, April 26, 2001, Page D7.
External links
- Audi R8 serial number on Endurance-Series
- Audi R8C (1999)
- Audi R8R (1999)
- Debut Audi R8 (2000)
- Audi R8 (2001-2005)
- Audi R10 (2006)
| Audi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidiaries |
| ||||
| Defunct brands |
| ||||
| Museums | |||||
| Current models |
| ||||
| Audi Sport |
| ||||
| Historic and discontinued models | |||||
| Motorsport |
| ||||
| Concept cars |
| ||||
| See also |
| ||||
