| Revision as of 11:02, 29 September 2013 view source173.34.103.99 (talk) →Statistics← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:33, 3 October 2013 view source Emmette Hernandez Coleman (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users15,272 editsm →Aliyah from North America: anchor from former section title, to fix broken links.Next edit → | ||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
| As of 2012, some 200,000 French citizens live in Israel.<ref>{{cite web|last=Podolsky |first=Philip |url=http://www.timesofisrael.com/france-draws-up-plans-to-evacuate-200000-franco-israelis-in-case-of-war/ |title=France reportedly draws up plans to evacuate 200,000 Franco-Israelis in case of war |publisher=The Times of Israel |date=2012-08-10 |accessdate=2013-04-29}}</ref> | As of 2012, some 200,000 French citizens live in Israel.<ref>{{cite web|last=Podolsky |first=Philip |url=http://www.timesofisrael.com/france-draws-up-plans-to-evacuate-200000-franco-israelis-in-case-of-war/ |title=France reportedly draws up plans to evacuate 200,000 Franco-Israelis in case of war |publisher=The Times of Israel |date=2012-08-10 |accessdate=2013-04-29}}</ref> | ||
| {{anchor|North American Aliyah}} | |||
| ===Aliyah from North America=== | ===Aliyah from North America=== | ||
| {{See also|History of the Jews in the United States|History of the Jews in Canada}} | {{See also|History of the Jews in the United States|History of the Jews in Canada}} | ||
Revision as of 18:33, 3 October 2013
For the singer, see Aaliyah. For other uses, see Aliyah (disambiguation).| This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (January 2013) |
| Part of a series on |
| Aliyah |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
| Pre-Modern Aliyah |
| Aliyah in modern times |
| Absorption |
| Organizations |
| Related topics |
Aliyah (UK: /ˌælɪˈɑː/, US: /ˌɑːliˈɑː/; Template:Lang-he aliyah, "ascent") is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to the land of Israel (Eretz Yisrael). It is one of the most basic tenets of Zionist ideology. The opposite action, emigration from Israel, is referred to as yerida ("descent"). The return to the Holy Land has been the aspiration of many Jews since the Babylonian exile. Large-scale immigration to the land of Israel (Eretz Israel) began in 1882. Since the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, more than 3 million Jews from over 90 countries have arrived in Israel.
Etymology
Aliyah in Hebrew means "ascent" or "going up". Jewish tradition views traveling to the land of Israel as an ascent, both geographically and metaphysically. Anyone traveling to Eretz Israel from Egypt, Babylonia or the Mediterranean basin, where many Jews lived in early rabbinic times, climbed to a higher altitude. Visiting Jerusalem, situated 2,700 feet above sea level, also involved an "ascent".
Religious, ideological and cultural concept
"Olim" redirects here. For other uses, see Olim (disambiguation).Aliyah is an important Jewish cultural concept and a fundamental component of Zionism. It is enshrined in Israel's Law of Return, which accords any Jew (deemed as such by halakha and/or Israeli secular law) and eligible non-Jews (a child and a grandchild of a Jew, the spouse of a Jew, the spouse of a child of a Jew and the spouse of a grandchild of a Jew), the legal right to assisted immigration and settlement in Israel, as well as Israeli citizenship. Someone who "makes aliyah" is called an oleh (m. singular) or olah (f. singular); the plural for both is olim. Many religious Jews espouse aliyah as a return to the Promised land, and regard it as the fulfillment of God's biblical promise to the descendants of the Hebrew patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob. Aliyah is included as a commandment by some opinions on the enumeration of the 613 commandments.
In Zionist discourse, the term aliyah (plural aliyot) includes both voluntary immigration for ideological, emotional, or practical reasons and, on the other hand, mass flight of persecuted populations of Jews. The vast majority of Israeli Jews today trace their family's recent roots to outside of the country. While many have actively chosen to settle in Israel rather than some other country, many had little or no choice about leaving their previous home countries. While Israel is commonly recognized as "a country of immigrants", it is also, in large measure, a country of refugees.
According to the traditional Jewish ordering of books of the Tanakh (Old Testament), the very last word of the last book in the original Hebrew (2 Chronicles 36:23) is vya‘al, a jussive verb form derived from the same root as aliyah, meaning "and let him go up" (to Jerusalem in Judah).
2 Chronicles 36:23 (KJV) Thus saith Cyrus king of Persia, All the kingdoms of the earth hath the LORD God of heaven given me; and he hath charged me to build him an house in Jerusalem, which in Judah. Who among you of all his people? The LORD his God with him, and let him go up.
Historical background
Return to the land of Israel is a recurring theme in Jewish prayers recited every day, three times a day, and holiday services on Passover and Yom Kippur traditionally conclude with the words "Next year in Jerusalem". Because Jewish lineage can provide a right to Israeli citizenship, aliyah (returning to Israel) has both a secular and a religious significance.
For generations of religious Jews, aliyah was associated with the coming of the Jewish Messiah. Jews prayed for their Messiah to come, who was to redeem the land of Israel from gentile rule and return world Jewry to the land under a Halachic theocracy.
Pre-Zionist Aliyah
Main article: Pre-Zionist AliyahBiblical
The Hebrew Bible relates that the patriarch Abraham came to the Land of Canaan with his family and followers in approximately 1800 BC. His grandson Jacob went down to Egypt with his family, and after several centuries there, the Israelites went back to Canaan under Moses and Joshua, entering it in about 1300 BC.
A few decades after the fall of the Kingdom of Judah and the Babylonian exile of the Jewish people, approximately 50,000 Jews returned to Zion following the Cyrus Declaration from 538 BC. The Jewish priestly scribe Ezra led the Jewish exiles living in Babylon to their home city of Jerusalem in 459 BC. Others returned throughout the era of the Second Temple.
200–500 AD
In late antiquity, the two hubs of rabbinic learning were Babylonia and the land of Israel. Throughout the Amoraic period, many Babylonian Jews immigrated to the land of Israel and left their mark on life there, as rabbis and leaders.
10th–11th century
In the 10th century, leaders of the Karaite Jewish community, mostly living under Persian rule, urged their followers to settle in Eretz Yisrael. The Karaites established their own quarter in Jerusalem, on the western slope of the Kidron Valley. During this period, there is abundant evidence of pilgrimages to Jerusalem by Jews from various countries, mainly in the month of Tishrei, around the time of the Sukkot holiday.
1200–1882
The number of Jews migrating to the land of Israel rose significantly between the 13th and 19th centuries, mainly due to a general decline in the status of Jews across Europe and an increase in religious persecution. The expulsion of Jews from England (1290), France (1391), Austria (1421), and Spain (the Alhambra decree of 1492) were seen by many as a sign of approaching redemption and contributed greatly to the messianic spirit of the time.
Aliyah was also spurred during this period by the resurgence of messianic fervor among the Jews of France, Italy, the Germanic states, Poland, Russia, and North Africa. The belief in the imminent coming of the Jewish Messiah, the ingathering of the exiles and the re-establishment of the kingdom of Israel encouraged many who had few other options to make the perilous journey to the land of Israel.
Pre-Zionist resettlement in Palestine met with various degrees of success. For example, little is known of the fate of the 1210 "aliyah of the three hundred rabbis" and their descendants. It is thought that few survived the bloody upheavals caused by the Crusader invasion in 1229 and their subsequent expulsion by the Muslims in 1291. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453 and the expulsion of Jews from Spain (1492) and Portugal (1498), many Jews made their way to the Holy Land. Then the immigration in the 18th and early 19th centuries of thousands of followers of various Kabbalist and Hassidic rabbis, as well as the disciples of the Vilna Gaon and the disciples of the Chattam Sofer, added considerably to the Jewish populations in Jerusalem, Tiberias, Hebron, and Safed.
The messianic dreams of the Gaon of Vilna inspired one of the largest pre-Zionist waves of immigration to Eretz Yisrael. In 1808 hundreds of the Gaon's disciples, known as Perushim, settled in Tiberias and Safed, and later formed the core of the Old Yishuv in Jerusalem. This was part of a larger movement of thousands of Jews from countries as widely spaced as Persia and Morocco, Yemen and Russia, who moved to Israel beginning in the first decade of the nineteenth century—and in even larger numbers after the conquest of the region by Muhammad Ali of Egypt in 1832—all drawn by the expectation of the arrival of the Messiah in the Jewish year 5600, Christian year 1840, a movement documented in Arie Morgenstern's Hastening Redemption.
There were also those who like the British mystic Laurence Oliphant tried to lease Northern Palestine to settle the Jews there (1879).
Zionist Aliyah (1882 on)
Further information: Zionism

 Aliyah by numbers and by source
Aliyah by numbers and by source
In Zionist history, the different waves of aliyah, beginning with the arrival of the Biluim from Russia in 1882, are categorized by date and the country of origin of the immigrants.
The first modern period of immigration to receive a number in common speech was the Third Aliya, which in the World War I period was referred to as the successor to the First and Second Aliyot from Babylonia in the Biblical period. Reference to earlier modern periods as the First and Second Aliyot appeared first in 1919 and took a while to catch on.
First Aliyah (1882–1903)
Main article: First AliyahBetween 1882 and 1903, approximately 35,000 Jews immigrated to the southwestern area of Syria, then a province of the Ottoman Empire. The majority, belonging to the Hovevei Zion and Bilu movements, came from the Russian Empire with a smaller number arriving from Yemen. Many established agricultural communities. Among the towns that these individuals established are Petah Tikva (already in 1878), Rishon LeZion, Rosh Pina, and Zikhron Ya'aqov. In 1882 the Yemenite Jews settled in an Arab suburb of Jerusalem called Silwan located south-east of the walls of the Old City on the slopes of the Mount of Olives.
Second Aliyah (1904–1914)
Main article: Second AliyahBetween 1904 and 1914, 40,000 Jews immigrated mainly from Russia to southwestern Syria following pogroms and outbreaks of anti-Semitism in that country. This group, greatly influenced by socialist ideals, established the first kibbutz, Degania Alef, in 1909 and formed self-defense organizations, such as Hashomer, to counter increasing Arab hostility and to help Jews to protect their communities from Arab marauders. The suburb of Jaffa, Ahuzat Bayit, established at this time, grew into the city of Tel Aviv. During this period, some of the underpinnings of an independent nation-state arose: The national language Hebrew was revived; newspapers and literature written in Hebrew published; political parties and workers organizations were established. The First World War effectively ended the period of the Second Aliyah.
Third Aliyah (1919–1923)
Main article: Third Aliyah
Between 1919 and 1923, 40,000 Jews, mainly from the Russian Empire arrived in the wake of World War I and the British mandate of Palestine; the establishment of the Mandate, and the Balfour Declaration. Many of these were pioneers, known as halutzim, trained in agriculture and capable of establishing self-sustaining economies. In spite of immigration quotas established by the British administration, the population of Jews reached 90,000 by the end of this period. The Jezreel Valley and the Hefer Plain marshes were drained and converted to agricultural use. Additional national institutions arose: The Histadrut (General Labor Federation); an elected assembly; national council; and the Haganah, the forerunner of the Israel Defense Forces.
Fourth Aliyah (1924–1929)
Main article: Fourth AliyahBetween 1924 and 1929, 82,000 Jews arrived, many as a result of anti-Semitism in Poland and Hungary. The immigration quotas of the United States kept Jews out. This group contained many middle-class families that moved to the growing towns, establishing small businesses, and light industry. Of these approximately 23,000 left the country.
Fifth Aliyah (1929–1939)
Main article: Fifth Aliyah
Between 1929 and 1939, with the rise of Nazism in Germany, a new wave of 250,000 immigrants arrived; the majority of these, 174,000, arrived between 1933 and 1936, after which increasing restrictions on immigration by the British made immigration clandestine and illegal, called Aliyah Bet. The Fifth Aliyah was again driven mostly from Eastern Europe as well as professionals, doctors, lawyers, and professors, from Germany. Refugee artists introduced Bauhaus (the White City of Tel Aviv has the highest concentration of Bauhaus architecture in the world) and founded the Palestine Philharmonic Orchestra. With the completion of the port at Haifa and its oil refineries, significant industry was added to the predominantly agricultural economy. The Jewish population reached 450,000 by 1940.
At the same time, tensions between Arabs and Jews grew during this period, leading to a series of Arab riots against the Jews in 1929 that left many dead and resulted in the depopulation of the Jewish community in Hebron. This was followed by more violence during the "Great Uprising" of 1936–1939. In response to the ever increasing tension between the Arabic and Jewish communities married with the various commitments the British faced at the dawn of World War II, the British issued the White Paper of 1939, which severely restricted Jewish immigration to 75,000 people for five years. This served to create a relatively peaceful eight years in Palestine while, tragically, the Holocaust unfolded in Europe.
Shortly after their rise to power, the Nazis negotiated the Ha'avara or "Transfer" Agreement with the Jewish Agency under which 50,000 German Jews and $100 million of their assets would be moved to Palestine.
Aliyah Bet: Illegal immigration (1933–1948)
Main article: Aliyah Bet
The British government limited Jewish immigration to Palestine with quotas, and following the rise of Nazism to power in Germany, illegal immigration to Palestine commenced. The illegal immigration was known as Aliyah Bet ("secondary immigration"), or Ha'apalah, and was organized by the Mossad Le'aliyah Bet, as well as by the Irgun. Immigration was done mainly by sea, and to a lesser extent overland through Iraq and Syria. During World War II and the years that followed until independence, Aliyah Bet became the main form of Jewish immigration to Palestine.
Following the war, Berihah ("flight"), an organization of former partisans and ghetto fighters was primarily responsible for smuggling Jews from Poland and Eastern Europe to the Italian ports from which they traveled to Palestine. Despite British efforts to curb the illegal immigration, during the 14 years of its operation, 110,000 Jews immigrated to Palestine. In 1945 reports of the Holocaust with its 6 million Jewish dead, caused many Jews in Palestine to turn openly against the British Mandate, and illegal immigration escalated rapidly as many Holocaust survivors joined the Aliyah.
Early statehood (1948–1950)
Main article: BrichaAfter Aliyah Bet, the process of numbering or naming individual aliyot ceased, but immigration did not. A major wave of immigration of over half a million Jews went to Israel between 1948 and 1950, many fleeing renewed persecution in Eastern Europe, and increasingly hostile Arab countries.
This period of immigration is often termed kibbutz galuyot (literally, ingathering of exiles), due to the large number of Jewish diaspora communities that made aliyah. However, kibbutz galuyot can also refer to aliyah in general.
Since the founding of the State of Israel, the Jewish Agency for Israel was mandated as the organization responsible for aliyah in the diaspora.
Aliyah from Arab countries
Main article: Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries| Part of a series on |
| Jewish exodus from the Muslim world |
|---|
 |
| Background |
| Antisemitism in the Arab world |
| Exodus by country |
| Remembrance |
| Related topics |

From 1948 until the early 1970s, around 900,000 Jews from Arab lands left, fled, or were expelled from various Arab nations. In the course of Operation Magic Carpet (1949–1950), nearly the entire community of Yemenite Jews (about 49,000) immigrated to Israel. Its other name, Operation On Wings of Eagles (Hebrew: כנפי נשרים, Kanfei Nesharim), was inspired by
- Exodus 19:4 - Ye have seen what I did unto the Egyptians, and how I bare you on eagles' wings, and brought you unto myself. and
- Isaiah 40:31 - But they that wait upon the LORD shall renew their strength; they shall mount up with wings as eagles; they shall run, and not be weary; and they shall walk, and not faint.
In three and a half years, the Jewish population of Israel had doubled, inflated by nearly 700,000 immigrants (300,000 of them came from the Muslim world and the rest from Europe), which was one of the causes of the austerity. Huge numbers of Jewish refugees were temporarily settled in "cities of tents" called Ma'abarot. As the residents were gradually absorbed into Israeli society, the Ma'abarot were phased out.
Many Israeli immigrants were Sephardi and Mizrahi Jews who left Arab countries to move to Israel. In many of these cases they had been persecuted and sometimes forced to leave their homes. 114,000 Jews came from Iraq in 1951 in Operation Ezra and Nehemiah.
Aliyah from Iran
See also: History of the Jews in IranFollowing the establishment of Israel, about one-third of Iranian Jews, most of them poor, immigrated to Israel. Following the Islamic Revolution in 1979, most of the Iranian Jewish community left, with some 30,000 Iranian Jews immigrating to Israel. Many Iranian Jews also settled in the United States (especially in New York City and Los Angeles).
Aliyah from Ethiopia
Main article: Aliyah from EthiopiaThe first major wave of aliyah from Ethiopia took place in the mid-1970s. The massive airlift known as Operation Moses began to bring Ethiopian Jews to Israel on November 18, 1984, and ended on January 5, 1985. During those six weeks, some 6,500–8,000 Ethiopian Jews were flown from Sudan to Israel. An estimated 2,000–4,000 Jews died en route to Sudan or in Sudanese refugee camps. In 1991 Operation Solomon was launched to bring the Beta Israel Jews of Ethiopia. In one day, May 24, 34 aircraft landed at Addis Ababa and brought 14,325 Jews from Ethiopia to Israel. Since that time, Ethiopian Jews have continued to immigrate to Israel bringing the number of Ethiopian-Israelis today to over 100,000.
Aliyah from the Soviet Union and post-Soviet states
Main articles: Russian immigration to Israel in the 1970s, Russian immigration to Israel in the 1990s, and Jackson–Vanik amendment
A mass emigration was politically undesirable for the Soviet regime. The only acceptable ground was family reunification, and a formal petition ("вызов", vyzov) from a relative from abroad was required for the processing to begin. Often, the result was a formal refusal. The risks to apply for an exit visa compounded because the entire family had to quit their jobs, which in turn would make them vulnerable to charges of social parasitism, a criminal offense. Because of these hardships, Israel set up the group Lishkat Hakesher in the early 1950s to maintain contact and promote aliyah with Jews behind the Iron Curtain.
From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the Six-Day War in 1967, Soviet aliyah remained minimal. Those who made aliyah during this period were mainly elderly people granted clearance to leave for family reunification purposes. Only about 22,000 Soviet Jews managed to reach Israel. In the wake of the Six-Day War, the USSR broke off the diplomatic relations with the Jewish state. An Anti-Zionist propaganda campaign in the state-controlled mass media and the rise of Zionology were accompanied by harsher discrimination of the Soviet Jews. By the end of 1960s, Jewish cultural and religious life in the Soviet Union had become practically impossible, and the majority of Soviet Jews were assimilated and non-religious, but this new wave of state-sponsored anti-Semitism on one hand, and the sense of pride for victorious Jewish nation over Soviet-armed Arab armies on the other, stirred up Zionist feelings.
After the Dymshits-Kuznetsov hijacking affair and the crackdown that followed, strong international condemnations caused the Soviet authorities to increase the emigration quota. In the years 1960–1970, the USSR let only 4,000 people leave; in the following decade, the number rose to 250,000. The exodus of Soviet Jews began in 1968.
| Year | Exit visas to Israel |
Olim from the USSR |
|---|---|---|
| 1968 | 231 | 231 |
| 1969 | 3,033 | 3,033 |
| 1970 | 999 | 999 |
| 1971 | 12,897 | 12,893 |
| 1972 | 31,903 | 31,652 |
| 1973 | 34,733 | 33,277 |
| 1974 | 20,767 | 16,888 |
| 1975 | 13,363 | 8,435 |
| 1976 | 14,254 | 7,250 |
| 1977 | 16,833 | 8,350 |
| 1978 | 28,956 | 12,090 |
| 1979 | 51,331 | 17,278 |
| 1980 | 21,648 | 7,570 |
| 1981 | 9,448 | 1,762 |
| 1982 | 2,692 | 731 |
| 1983 | 1,314 | 861 |
| 1984 | 896 | 340 |
| 1985 | 1,140 | 348 |
| 1986 | 904 | 201 |
Between 1968 and 1973, almost all Soviet Jews allowed to leave settled in Israel, and only a small minority moved to other Western countries. However, in the following years, the number of those moving to other Western nations increased. Soviet Jews granted permission to leave were taken by train to Austria to be processed and then flown to Israel. There, the ones who chose not to go to Israel, called "dropouts", exchanged their immigrant invitations to Israel for refugee status in a Western country, especially the United States. Eventually, most Soviet Jews granted permission to leave became dropouts. In 1989 a record 71,000 Soviet Jews were granted exodus from the USSR, of whom only 12,117 immigrated to Israel.
According to Israeli Immigrant Absorption Minister Yaakov Zur, over half of Soviet Jewish dropouts who immigrated to the United States assimilated and ceased to live as Jews within a short period of time.
Israel was concerned over the dropout rate, and suggested that Soviet emigres be flown directly to Israel from the Soviet Union or Romania. Israel argued that it needed highly skilled and well-educated Soviet Jewish immigrants for its survival. In addition to contributing to the country's economic development, Soviet immigration was also seen as a counterweight to the high fertility rate among Israeli-Arabs. In addition, Israel was concerned that the dropout rate could result in immigration being banned once again. The Ministry of Immigrant Absorption's position was that "it could jeopardize the whole program if Jews supposedly going to Israel all wind up in Brooklyn and Los Angeles. How will the Soviets explain to their own people that it's just Jews who are allowed to emigrate to the U.S.?"
In 1989 the United States changed its immigration policy of unconditionally granting Soviet Jews refugee status. That same year, Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev ended restrictions on Jewish immigration, and the Soviet Union itself collapsed in 1991. Since then, about a million Russians immigrated to Israel, including approximately 240,000 who were not Jewish according to rabbinical law, but were eligible for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return.
The number of non-Jews among the immigrants from the former USSR has been constantly rising ever since 1989. For example, in 1990 around 96% of the immigrants were Jews and only 4% were non-Jewish family members. However in 2000, the proportion was: Jews (includes children from non-Jewish father and Jewish mother) - 47%, Non-Jewish spouses of Jews - 14%, children from Jewish father and non-Jewish mother - 17%, Non-Jewish spouses of children from Jewish father and non-Jewish mother - 6%, non-Jews with a Jewish grandparent - 14% & Non-Jewish spouses of non-Jews with a Jewish grandparent - 2%.
Aliyah from Latin America
Main article: Aliyah from Latin America in the 2000sIn the 1999–2002 Argentine political and economic crisis that caused a run on the banks, wiped out billions of dollars in deposits and decimated Argentina's middle class, most of the country's estimated 200,000 Jews were directly affected. Some 4,400 chose to start over and move to Israel, where they saw opportunity.
More than 10,000 Argentine Jews immigrated to Israel since 2000, joining the thousands of previous olim already there. The crisis in Argentina also affected its neighbour country Uruguay, from which about half of its 40,000-strong Jewish community left, mainly to Israel, in the same period. During 2002 and 2003 the Jewish Agency for Israel launched an intensive public campaign to promote aliyah from the region, and offered additional economic aid for immigrants from Argentina. Although the economy of Argentina improved, and some Argentine olim returned to Argentina following the country's economic growth from 2003 onwards, Argentine Jews continue to immigrate to Israel, albeit in smaller numbers than before.
There has also been aliyah from other Latin American countries that have experienced crises, though they have come in smaller numbers and are not eligible for the same economic benefits as Argentine olim.
In Venezuela, growing antisemitism in the country, including antisemitic violence, caused an increasing number of Jews to make aliyah during the 2000s. For the first time in Venezuelan history, Jews began leaving for Israel in the hundreds. By November 2010, more than half of Venezuela's 20,000-strong Jewish community had left the country.
Aliyah from France
See also: History of the Jews in France| Part of a series on |
| Jewish outreach |
|---|
| Core topics |
| Related topics |
From 2000 to 2009, more than 13,000 French Jews made aliyah, largely as a result of growing anti-semitism in the country. A peak was reached in 2005, with 2,951 olim. However, between 20-30% eventually returned to France. With the start of the Second Intifada in Israel, anti-Semitic incidents became more frequent in France. In 2002, the Commission nationale consultative des droits de l'homme (Human Rights Commission) reported six times more anti-Semitic incidents than in 2001 (193 incidents in 2002). The commission's statistics showed that anti-Semitic acts constituted 62% of recorded racist acts in the country (compared to 45% in 2001 and 80% in 2000). The report documented 313 violent acts against people or property, including 38 injuries and the torture-murder of French Jew Ilan Halimi. Since 2005, the number of acts dropped but is still at a significantly higher level than during the previous decade. Anti-Semitic incidents rose again during the Gaza War. After the election of Nicolas Sarkozy, French aliyah dropped due to the Jewish community's comfort with him. In 2010 only 1,286 French Jews made aliyah. In 2012, following the election of François Hollande and the Jewish school shooting in Toulouse, as well as ongoing acts of anti-semitism and the European economic crisis, an increasing number of French Jews began buying property in Israel. In August 2012, it was reported that anti-semitic attacks had risen by 40% in the five months following the Toulouse shooting, and that many French Jews were seriously considering immigrating to Israel.
As of 2012, some 200,000 French citizens live in Israel.
Aliyah from North America
See also: History of the Jews in the United States and History of the Jews in Canada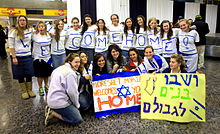
Approximately 110,000 North American immigrants live in Israel. There has been a steady flow of olim from North America since Israel’s inception in 1948.
Several thousand American Jews moved to Palestine before the State of Israel was established. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the Six-Day War in 1967, aliyah from the United States and Canada was minimal. In the 1950s, 6,000 North American Jews arrived in Israel, of whom all but 1,000 returned.
Record numbers arrived in the late 1960s after the Six-Day War, and in the 1970s. Between 1967 and 1973, 60,000 North American Jews immigrated to Israel. However, many of them later returned to their original countries.
Like Western European olim, North Americans tend to immigrate to Israel more for religious, ideological, and political purposes, and not financial or security ones. Many immigrants began arriving in Israel after the First and Second Intifada, with a total of 3,052 arriving in 2005 — the highest number since 1983.
Nefesh B'Nefesh, founded in 2002 by Rabbi Yehoshua Fass and Tony Gelbart, works to encourage Aliyah from North America and the UK by providing financial assistance, employment services and streamlined governmental procedures. Nefesh B’Nefesh works in cooperation with the Jewish Agency and the Israeli Government in increasing the numbers of North American and British olim.
Following the Global Financial Crisis in the late 2000s, American Jewish immigration to Israel rose. This wave of immigration was triggered by Israel's lower unemployment rate, combined with financial incentives offered to new Jewish immigrants. In 2009, aliyah was at its highest in 36 years, with 3,324 North American Jews making aliyah.
Since the 1990s

Since the mid-1990s, there has been a steady stream of South African Jews, American Jews, and French Jews who have either made aliyah, or purchased property in Israel for potential future immigration. Specifically, many French Jews have purchased homes in Israel as insurance due to the rising rate of anti-Semitism in France in recent years. The Bnei Menashe Jews from India, whose recent discovery and recognition by mainstream Judaism as descendants of the Ten Lost Tribes is subject to some controversy, slowly started their Aliyah in the early 1990s and continue arriving in slow numbers. Organizations such as Nefesh B'Nefesh and Shavei Israel help with aliyah by supporting financial aid and guidance on a variety of topics such as finding work, learning Hebrew, and assimilation into Israeli culture.
In early 2007 Haaretz reported that aliyah for the year of 2006 was down approximately 9% from 2005, "the lowest number of immigrants recorded since 1988". The number of new immigrants in 2007 was 18,127, the lowest since 1988. Only 36% of these new immigrants came from the former Soviet Union (close to 90% in the 1990s) while the number of immigrants from countries like France and the United States is stable. Some 15,452 immigrants arrived in Israel in 2008 and 16,465 in 2009. Shalom Life reported that over 19,000 new immigrants arrived in Israel in 2010, an increase of 16 percent over 2009.
Statistics
The number of immigrants since 1882 by period, continent of birth, and country of birth is given in the table below. Continent of birth and country of birth data is almost always unavailable or nonexistent for before 1919.
| Region/Country | 1882– 1918 |
1919– 1948 |
1948– 1951 |
1952– 1960 |
1961– 1971 |
1972– 1979 |
1980– 1989 |
1990– 2001 |
2002– 2010 |
2011– 2012 |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 4,033 | 93,282 | 143,485 | 164,885 | 19,273 | 28,664 | 55,619 | 31,558 | 6,627 | 547,426 | |
| Algeria | 994 | 3,810 | 3,433 | 12,857 | 2,137 | 1,830 | 1,682 | 1,967 | 324 | 29,034 | |
| Egypt and Sudan | 0 | 16,028 | 17,521 | 2,963 | 535 | 372 | 202 | 166 | 21 | 37,808 | |
| Ethiopia, Eritrea and Abyssinia | 0 | 10 | 59 | 98 | 309 | 16,971 | 45,131 | 23,613 | 5,097 | 91,288 | |
| Libya | 873 | 30,972 | 2,079 | 2,466 | 219 | 67 | 94 | 36 | 5 | 36,811 | |
| Morocco | 0 | 28,263 | 95,945 | 130,507 | 7,780 | 3,809 | 3,276 | 2,113 | 384 | 272,077 | |
| South Africa | 259 | 666 | 774 | 3,783 | 5,604 | 3,575 | 3,283 | 1,693 | 373 | 20,010 | |
| Tunisia | 0 | 13,293 | 23,569 | 11,566 | 2,148 | 1,942 | 1,607 | 1,871 | 398 | 56,394 | |
| Zimbabwe | 0 | 37 | 22 | 145 | 393 | 82 | 26 | 14 | N/A | 719 | |
| Other (Africa) | 1,907 | 203 | 83 | 500 | 148 | 16 | 318 | 85 | 24 | 3,284 | |
| Americas and Oceania | 7,579 | 3,822 | 6,922 | 42,400 | 45,040 | 39,369 | 39,662 | 36,209 | 221,003 | ||
| Argentina | 238 | 904 | 2,888 | 11,701 | 13,158 | 10,582 | 11,248 | 9,450 | 60,169 | ||
| Australia | 0 | 116 | 107 | 742 | 1,146 | 835 | 977 | 524 | 4,447 | ||
| Bolivia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 199 | 94 | 80 | 53 | 84 | 510 | ||
| Brazil | 0 | 304 | 763 | 2,601 | 1,763 | 1,763 | 2,356 | 2,037 | 11,587 | ||
| Canada | 316 | 236 | 276 | 2,169 | 2,178 | 1,867 | 1,963 | 1,700 | 10,705 | ||
| Central America (other countries which are not specifically mentioned here) | 0 | 17 | 43 | 129 | 104 | 8 | 153 | 157 | 611 | ||
| Chile | 0 | 48 | 401 | 1,790 | 1,180 | 1,040 | 683 | 589 | 5,731 | ||
| Colombia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 415 | 552 | 475 | 657 | 965 | 3,064 | ||
| Cuba | 0 | 14 | 88 | 405 | 79 | 42 | 629 | 606 | 1,863 | ||
| Ecuador | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 38 | 44 | 67 | 69 | 258 | ||
| Mexico | 0 | 48 | 168 | 736 | 861 | 993 | 1,049 | 697 | 4,552 | ||
| New Zealand | 70 | 0 | 13 | 91 | 129 | 124 | 142 | 42 | 611 | ||
| Panama | 0 | 0 | 0 | 64 | 43 | 48 | 50 | 40 | 245 | ||
| Peru | 0 | 0 | 0 | 269 | 243 | 358 | 612 | 1,539 | 3,021 | ||
| South America (other countries which are not specifically mentioned here) | 0 | 42 | 194 | 89 | 62 | 0 | 66 | 96 | 549 | ||
| United States | 2,000 | 6,635 | 1,711 | 1,553 | 18,671 | 20,963 | 18,904 | 17,512 | 15,445 | 103,394 | |
| Uruguay | 0 | 66 | 425 | 1,844 | 2,199 | 2,014 | 983 | 1,555 | 9,086 | ||
| Venezuela | 0 | 0 | 0 | 297 | 245 | 180 | 418 | 602 | 1,742 | ||
| Other (Americas/Oceania) | 318 | 313 | 0 | 148 | 3 | 8 | 44 | 12 | 846 | ||
| Asia | 40,776 | 237,704 | 37,119 | 56,208 | 19,456 | 14,433 | 75,687 | 17,300 | 498,683 | ||
| Afghanistan | 0 | 2,303 | 1,106 | 516 | 132 | 57 | 21 | 13 | 4,148 | ||
| Burma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 147 | 83 | 383 | 138 | 33 | 784 | ||
| China | 0 | 504 | 217 | 96 | 43 | 78 | 277 | 74 | 1,289 | ||
| Cyprus | 0 | 21 | 35 | 28 | 21 | 12 | 32 | 0 | 149 | ||
| India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka | 0 | 2,176 | 5,380 | 13,110 | 3,497 | 1,539 | 2,055 | 961 | 28,718 | ||
| Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines | 0 | 101 | 46 | 54 | 40 | 60 | 205 | 42 | 548 | ||
| Iran | 3,536 | 21,910 | 15,699 | 19,502 | 9,550 | 8,487 | 4,326 | 1,097 | 84,107 | ||
| Iraq | 0 | 123,371 | 2,989 | 2,129 | 939 | 111 | 1,325 | 130 | 130,994 | ||
| Israel | 0 | 411 | 868 | 1,021 | 507 | 288 | 1,148 | 1,448 | 5,691 | ||
| Japan | 0 | 0 | 9 | 25 | 34 | 57 | 98 | 32 | 255 | ||
| Jordan | 0 | 6 | 9 | 23 | 6 | 9 | 15 | 0 | 68 | ||
| Lebanon | 0 | 235 | 846 | 2,208 | 564 | 179 | 96 | 34 | 4,162 | ||
| Mongolia, South Korea, and North Korea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 100 | 36 | 155 | ||
| Saudi Arabia | 0 | 177 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 186 | ||
| Soviet Union (Asia) | 61,988 | 12,422 | 74,410 | ||||||||
| Syria | 0 | 2,678 | 1,870 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,664 | 23 | 6,235 | ||
| Turkey | 8,277 | 34,547 | 6,871 | 14,073 | 3,118 | 2,088 | 1,311 | 817 | 71,102 | ||
| Yemen | 2,600 | 15,838 | 48,315 | 1,170 | 1,066 | 51 | 17 | 683 | 103 | 69,843 | |
| Other (Asia) | 13,125 | 947 | 0 | 60 | 21 | 45 | 205 | 30 | 14,433 | ||
| Europe | 377,487 | 332,802 | 106,305 | 162,070 | 183,419 | 70,898 | 888,603 | 96,165 | 2,217,749 | ||
| Albania | 0 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 376 | 0 | 389 | ||
| Austria | 7,748 | 2,632 | 610 | 1,021 | 595 | 356 | 368 | 150 | 13,480 | ||
| Belgium | 0 | 291 | 394 | 1,112 | 847 | 788 | 1,053 | 873 | 5,358 | ||
| Bulgaria | 7,057 | 37,260 | 1,680 | 794 | 118 | 180 | 3,999 | 341 | 51,429 | ||
| Czechoslovakia | 16,794 | 18,788 | 783 | 2,754 | 888 | 462 | 527 | 217 | 41,213 | ||
| Denmark | 0 | 27 | 46 | 298 | 292 | 411 | 389 | 85 | 1,548 | ||
| Finland | 0 | 9 | 20 | 172 | 184 | 222 | 212 | 33 | 852 | ||
| France | 1,637 | 3,050 | 1,662 | 8,050 | 5,399 | 7,538 | 11,986 | 13,062 | 52,384 | ||
| Germany | 52,951 | 8,210 | 1,386 | 3,175 | 2,080 | 1,759 | 2,442 | 866 | 72,869 | ||
| Greece | 8,767 | 2,131 | 676 | 514 | 326 | 147 | 127 | 48 | 12,736 | ||
| Hungary | 10,342 | 14,324 | 9,819 | 2,601 | 1,100 | 1,005 | 2,444 | 730 | 42,365 | ||
| Ireland | 0 | 14 | 46 | 145 | 157 | 233 | 136 | 54 | 785 | ||
| Italy | 1,554 | 1,305 | 414 | 940 | 713 | 510 | 656 | 389 | 6,481 | ||
| Luxembourg | 0 | 30 | 15 | 15 | 7 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 83 | ||
| Netherlands | 1,208 | 1,077 | 646 | 1,470 | 1,170 | 1,239 | 997 | 365 | 8,172 | ||
| Norway | 0 | 17 | 14 | 36 | 55 | 126 | 120 | 19 | 387 | ||
| Poland | 170,127 | 106,414 | 39,618 | 14,706 | 6,218 | 2,807 | 3,064 | 764 | 343,718 | ||
| Portugal | 0 | 16 | 22 | 66 | 56 | 55 | 47 | 28 | 290 | ||
| Romania | 41,105 | 117,950 | 32,462 | 86,184 | 18,418 | 14,607 | 6,254 | 711 | 317,691 | ||
| Soviet Union (Europe) | 47,500 | 52,350 | 8,163 | 13,743 | 29,376 | 137,134 | 29,754 | 844,139 | 72,520 | 1,234,679 | |
| Spain | 0 | 80 | 169 | 406 | 327 | 321 | 269 | 178 | 1,750 | ||
| Sweden | 0 | 32 | 51 | 378 | 372 | 419 | 424 | 160 | 1,836 | ||
| Switzerland | 0 | 131 | 253 | 886 | 634 | 706 | 981 | 585 | 4,176 | ||
| United Kingdom | 1,574 | 1,907 | 1,448 | 6,461 | 6,171 | 7,098 | 5,365 | 3,725 | 33,749 | ||
| Yugoslavia | 1,944 | 7,661 | 320 | 322 | 126 | 140 | 2,029 | 162 | 12,704 | ||
| Other (Europe) | 2,329 | 1,281 | 3 | 173 | 32 | 0 | 198 | 93 | 4,109 | ||
| Not known | 52,982 | 20,014 | 3,307 | 2,265 | 392 | 469 | 422 | 0 | 79,851 | ||
| Total | 62,500 | 482,857 | 687,624 | 297,138 | 427,828 | 267,580 | 153,833 | 1,059,993 | 181,233 | 3,620,586 |
- a Before 1995, the aliyah from the Asian parts of the former Soviet Union were counted in the total of the aliyah from the European part of the former Soviet Union.
- b This number is an average of two different estimates from page 93 of this book.
- c This number is an average of two different estimates.
See also
- Galut
- Yerida
- History of the Jews in the Land of Israel
- Homeland for the Jewish people
- Law of Return
- Jewish population by country
- Historical Jewish population comparisons
- Demographics of Israel
- Visa policy of Israel
- Illegal immigration from Africa to Israel
References
- ""Aliyah": The Word and Its Meaning". 2005-05-15. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Israel Focus-Migration". Focus-migration.de. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "400 olim arrive in Israel ahead of Independence Day - Israel Jewish Scene, Ynetnews". Ynetnews.com. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Move On Up, The Forward". Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Golinkin, David. "Is It A Mitzvah To Make Aliyah?". Responsa in a Moment. Schechter Institute of Jewish Studies. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- "ץראב םתושרתשהו א"רגה ידימלת". ץראב םתושרתשהו א"רגה ידימלת. Daat. 2008-08-02.
- "עליית החסידים ההמונית לא"י". ץראב םתושרתשהו א"רגה ידימלת. Daat. 2008-08-02.
- The Jerusalem Cathedra: Studies in the History, Archaeology, Geography and Ethnography of the Land of Israel, "Aliya from Babylonia During the Amoraic Period (200–500 AD)", Joshua Schwartz, pp.58–69, ed. Lee Levine, 1983, Yad Izhak Ben Zvi & Wayne State University Press
- The Jerusalem Cathedra: Studies in the History, Archaeology, Geography and Ethnography of the Land of Israel, "Aliya and Pilgrimage in the Early Arab Period (634–1009)", Moshe Gil, 1983, Yad Izhak Ben Zvi & Wayne State University Press
- "יהדות הגולה והכמיהה לציון, 1840–1240". Tchelet. Tchelet. 2008-08-02.
- Ilani, Ofri (2008-01-06). "The Messiah brought the first immigrants". Haaretz.com. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Morgenstern, Arie: Hastening Redemption: Messianism and the Resettlement of the Land of Israel Published in Hebrew, 1997, Jerusalem, Ma’or; Published in English, 2006, Oxford University Press
- Hizky Shoham (2012). "From "Great History" to "Small History": The Genesis of the Zionist Periodization". Israel Studies. 18 (1): 31–55.
- M., Akiva. "The Real Aliyah". Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- The Origins of Israel, 1882–1948: A Documentary History, eds. Eran Kaplan, Derek J. Penslar. University of Wisconsin Press. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Moving to Israel?". Jacob Richman. jr.com. 2008-08-02.
- "Transfer Agreement". Transfer Agreement. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Yoav Gelber, "The Historical Role of Central European Immigration to Israel", Leo Baeck Institute Year Book 38 (1993), p. 326 n. 6.
- "Knesset Rules of Procedure - PART A (2)". Knesset.gov.il. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- ""On Eagles' Wings" – Aliyah from Yemen (1949)". Ministry of Immigrant Absorption. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- Schwartz, Adi (January 4, 2008). "All I Wanted was Justice". Haaretz.
- Malka Hillel Shulewitz, The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands, Continuum 2001, pp. 139 and 155.
- Ada Aharoni "The Forced Migration of Jews from Arab Countries, Historical Society of Jews from Egypt website. Accessed February 1, 2009.
- "MLibrary Digital Collections: King James Bible: Exodus 19:4: Retrieved 23 June 2012". Quod.lib.umich.edu. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "MLibrary Digital Collections: King James Bible: Isaiah 40:31: Retrieved 23 June 2012". Quod.lib.umich.edu. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Littman (1979), p. 5.
- "Aliyah". mfa. mfa.gov.il. 2008-08-02.
- ^ Alexeyeva, Lyudmila (1992). История инакомыслия в СССР (in Russian). Vilnius: Vest'. OCLC 489831449. Retrieved October 7, 2012.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Lazin, Fred A. (2005). "Refugee Resettlement and 'Freedom of Choice': The Case of Soviet Jewry". Center for Immigration Studies. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Montalbano, William D. (2 June 1988). "Israel Troubled by Soviet Jews' 'Dropout' Rate". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Levy, Tracy (10 September 2009). "After 20 years, why has Russian immigration to Israel stagnated?". Haaretz. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Jewish Intermarriage Around the World - Shulamit Reinharz, Sergio Della Pergola. Google Books. 2011-12-31. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Mozgovaya, Natasha; Papirblat, Shlomo (20 November 2010). "In Venezuela, remarks like 'Hitler didn't finish the job' are routine". Haaretz. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Shefler, Gil (1 September 2010). "Jewish community in Venezuela shrinks by half". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- "Le chiffre de l'alya des Juifs de France ne décolle pas!" (in French). terredisrael.com. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- "Aliyah". Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- ^ http://www.cbs.gov.il/publications12/1483_immigration/pdf/tab05.pdf
- Petersberg, Ofer (23 May 2012). "Is crisis bringing French Jews to Israel?". Ynetnews. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- "French Anti-Semitic Attacks Up by 40 Percent". CBN. 30 August 2012. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Podolsky, Philip (2012-08-10). "France reportedly draws up plans to evacuate 200,000 Franco-Israelis in case of war". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- In Israel to stay
- Berman, Daphna (2007-06-01). "The 40th anniversary of the Six-Day War / Rate of return - Israel News | Haaretz Daily Newspaper". Haaretz.com. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Waxman, Chaim. American Aliyah, Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1989. pg. 131-135
- December 29, 2009 (2009-12-29). "U.S. aliyah highest in 36 years". JTA Article. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Schwartzapfel, Beth (2 March 2010). "Not just Zionism: Lousy economy pushes more U.S. Jews to move to Israel". Haaretz. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Stone, Andrea (22 November 2004). "As attacks rise in France, Jews flock to Israel". USA Today. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- "French Jews invest in old Tel Aviv neighborhood". Israel Money, Ynetnews. 1995-06-20. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Nefesh B. Nefesh". nbn.com. 2008-08-02.
- Bassok, Moti (21 February 2007). "Aliyah sees 9% dip from 2005". Haaretz. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- "הודעות לעיתונות". Cbs.gov.il. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "2010 Was a Very Good Year for Making Aliyah". Shalomlife.com. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Immigration to Israel increases by 17 percent in 2009". Shalomlife.com. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- Goldsceider, Calvin (1974). "American Aliya / Sociological and Demographic Perspectives". Berman Jewish Policy Archive. Behrman House Publishers. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "First Aliya". Retrieved September 9, 2013.
- The Divided Self: Israel and the Jewish Psyche Today - David J. Goldberg - Google Books. Books.google.com. 2011-03-15. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
- "Statistical Abstract of Israel 2012 - No. 63 Subject 4 - Table No. 2". Cbs.gov.il. Retrieved 2013-04-29.
Further reading
- Morgenstern, Arie (2002). "Dispersion and the Longing for Zion, 1240-1840". Azure (12). Shalem Center: 71–132. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- Shuval, Judith T. (1998). "Migration To Israel: The Mythology of "Uniqueness"". International Migration. 36 (1). International Organization for Migration: 3–26. doi:10.1111/1468-2435.00031. PMID 12293507.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Ben-Gurion, David (19 July 1967). "Ben Gurion on the Pioneer Generations and the Need for U.S. Immigration". Shapell Manuscript Foundation. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- Ben-David, Laura (2006). Moving Up: An Aliyah Journal. Mazo Publishers. ISBN 978-965-7344-14-9.
External links
- Immigration to Israel at the Jewish Virtual Library
- Making Aliyah at the Israel Government Portal
- Home page of the Ministry of Immigrant Absorption
- Official website of the Jewish Agency for Israel
- Official website of Nefesh B'Nefesh, organization for Aliyah from North America and UK
- Aliyah to Israel at Israel Science and Technology Homepage
- Anglo-List.com – Israel lifestyle, Aliyah & business directory
- Aliyah Pages – information, photographs, links
- Template:Dmoz
| Zionism | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Concepts | |||
| Ideologies | |||
| Organizations |
| ||
| History and timelines | |||
| Holidays | |||
| Related topics |
| ||
| Israel articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||||
| Geography | |||||
| Politics | |||||
| Security | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Society |
| ||||
| Jews and Judaism | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||
| Population |
| ||
| Languages (Diasporic) |
| ||
| Philosophy | |||
| Branches | |||
| Literature | |||
| Culture | |||
| Studies |
| ||
| Italics indicate extinct languages | |||