| Revision as of 05:13, 15 March 2022 editAnomieBOT (talk | contribs)Bots6,582,227 editsm Dating maintenance tags: {{Cn}}← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:33, 22 March 2022 edit undoInternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers5,388,209 edits Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.8.6Next edit → | ||
| Line 481: | Line 481: | ||
| {{wikivoyage|Gwangju}} | {{wikivoyage|Gwangju}} | ||
| *{{url|1=https://www.gwangju.go.kr/eng/|2=Official website}} {{in lang|en}} | *{{url|1=https://www.gwangju.go.kr/eng/|2=Official website}} {{in lang|en}} | ||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100929171719/http://english.visitkorea.or.kr/enu/SI/SI_EN_3_1_1_1.jsp?areaCode=5 |date=29 September 2010 }} | ||
| {{Gwangju}} | {{Gwangju}} | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 22 March 2022
Metropolitan City in Honam, South Korea This article is about Gwangju Metropolitan City. For the smaller city of the same name near Seoul, see Gwangju, Gyeonggi. "Kwangju" redirects here. For one of its sister cities which has a similar Chinese pronunciation, see Guangzhou.Metropolitan City in Honam, South Korea
| Gwangju 광주시 | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan City | |
| Gwangju Metropolitan City 광주광역시 | |
| transcription(s) | |
| • Hangul | 광주광역시 |
| • Hanja | 光州廣域市 |
| • Revised Romanization | Gwangju-gwangyeoksi |
| • McCune-Reischauer | Kwangju-kwangyŏksi |
 Gwanju City Montage Gwanju City Montage | |
 FlagOfficial logo of GwangjuLogo FlagOfficial logo of GwangjuLogo | |
 | |
   | |
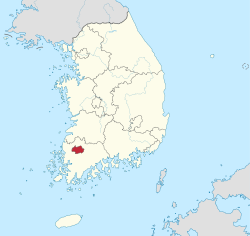
| Coordinates: 35°10′N 126°55′E / 35.167°N 126.917°E / 35.167; 126.917 | |
| Country | |
| Region | Honam |
| Districts | 5 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–Council |
| • Mayor | Lee Yong-seop (Democratic) |
| • Body | Gwangju Metropolitan Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 501.24 km (193.53 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 1,490,092 |
| • Density | 3,000/km (7,700/sq mi) |
| • Dialect | Jeolla |
| ISO 3166 code | KR-29 |
| Flower | Royal Azalea |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Bird | Dove |
| GDP | US$ 36.7 billion |
| GDP per capita | US$24,520 |
| Website | Official website (English) |
Gwangju (Template:IPA-ko) is South Korea's sixth-largest metropolis. It is a designated metropolitan city under the direct control of the central government's Home Minister. The city was also the capital of South Jeolla Province until the provincial office moved to the southern village of Namak in Muan County in 2005 because Gwangju was promoted to a metropolitan city and was independent of South Jeolla province.
Its name is composed of the words Gwang (Korean: 광; Hanja: 光) meaning "light" and Ju (주; 州) meaning "province". Gwangju was historically recorded as Muju (무주; 武州), in which "Silla merged all of the land to establish the provinces of Gwangju, Ungju, Jeonju, Muju and various counties, plus the southern boundary of Goguryeo and the ancient territories of Silla" in the Samguk Sagi. In the heart of the agricultural Jeolla region, the city is also famous for its rich and diverse cuisine.
History

The city was established in 57 BC. It was one of the administrative centers of Baekje during the Three Kingdoms Period.
In 1929, during the period of Imperial Japanese rule, a confrontation between Korean and Japanese students in the city turned into Gwangju Student Independence Movement, a regional demonstration, which culminated in one of the major nationwide uprisings against Imperial Japanese cruelty during the colonial period.
The modern industry was established in Gwangju with the construction of a railway to Seoul. Some of the industries that took hold include cotton textiles, rice mills and breweries. Construction of a designated industrial zone in 1967 encouraged growth in industry, especially in the sectors linked to the automobile industry.
In May 1980, peaceful demonstrations took place in Gwangju against Chun Doo-hwan, leader of the military coup d'état of 12 December 1979. The demonstrations were suppressed by military forces, including elite units of the Special Operations Command. The situation escalated after a violent crackdown, resulting in the Gwangju Uprising, where civilians raided armories and armed themselves. By the time the uprising was suppressed 9 days later, many hundreds of civilians and several police forces / soldiers were dead. After civilian rule was reinstated in 1987, a national cemetery was established to honor the victims of the incident. Now the South Korean constitution admits the Gwangju Uprising as a root of South Korean democracy.
In 1986, Gwangju separated from Jeollanam-do to become a Directly Governed City (Jikhalsi), and then became a Metropolitan City (Gwangyeoksi) in 1995.
Due to a variety of factors, including the ancient rivalry between Baekje and Silla, as well as the biased priority given to the Gyeongsang region by political leaders in the 2nd half of the 20th century, Gwangju has a long history of voting for left-leaning politicians and is the main stronghold for the liberal Democratic Party of Korea along with its predecessors, as well as the progressive Justice Party.
Gwangju held many sports events such as 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2015 Summer Universiade, 2019 World Aquatics Championships.
Administrative divisions
Main article: List of districts of GwangjuGwangju is divided into 5 districts ("Gu").
| Map | Name | Korean | Hanja | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Districts | ||||
| Buk District | 북구 | 北區 | ||
| Dong District | 동구 | 東區 | ||
| Gwangsan District | 광산구 | 光山區 | ||
| Nam District | 남구 | 南區 | ||
| Seo District | 서구 | 西區 | ||
Religion
Religion in Gwangju (2015)
Not religious (61%) Protestantism (20%) Buddhism (9.5%) Catholicism (8.7%) Other (0.8%)According to the census of 2015, 9.5% of the population followed Buddhism and 28.7% followed Christianity (20% Protestantism and 8.7% Catholicism) 61% of the population are irreligious.
Population
The population model of Gwangju is as follows;
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1960 | 409,283 |
| 1966 | 532,235 |
| 1970 | 622,755 |
| 1975 | 737,283 |
| 1980 | 856,545 |
| 1985 | 1,042,508 |
| 1990 | 1,139,003 |
| 1995 | 1,257,636 |
| 2000 | 1,352,797 |
| 2005 | 1,417,716 |
| 2010 | 1,475,745 |
| 2016 | 1,500,621 |
Climate
Gwangju has a cooler version of the humid subtropical climate with four distinct seasons and rainfall year-round but particularly during the East Asian Monsoon Season in the summer months.
Winters, while still cold, are milder than in Seoul and cities further north due to the city's southwesterly position in the Korean peninsula. Summers are hot and humid with abundant precipitation, particularly in the form of thunderstorms. Gwangju is one of the warmest cities in Korea in the summer due to its geographic location.
| Climate data for Gwangju (1981–2010, extremes 1938–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
26.8 (80.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
33.9 (93.0) |
36.7 (98.1) |
38.5 (101.3) |
38.5 (101.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
31.1 (88.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.3 (41.5) |
7.8 (46.0) |
13.0 (55.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.7 (87.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
8.1 (46.6) |
19.1 (66.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.6 (33.1) |
2.5 (36.5) |
7.0 (44.6) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.2 (79.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
15.8 (60.4) |
9.1 (48.4) |
3.1 (37.6) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.1 (26.4) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
2.1 (35.8) |
7.5 (45.5) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
17.8 (64.0) |
10.9 (51.6) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
9.5 (49.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.4 (−2.9) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−10.7 (12.7) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
7.2 (45.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
12.6 (54.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−19.4 (−2.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37.1 (1.46) |
47.9 (1.89) |
60.8 (2.39) |
80.7 (3.18) |
96.6 (3.80) |
181.5 (7.15) |
308.9 (12.16) |
297.8 (11.72) |
150.5 (5.93) |
46.8 (1.84) |
48.8 (1.92) |
33.5 (1.32) |
1,391 (54.76) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 11.0 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 8.9 | 9.3 | 10.7 | 15.5 | 14.9 | 9.8 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 124.4 |
| Average snowy days | 11.1 | 7.1 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 8.1 | 31.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 67.7 | 65.2 | 62.9 | 61.9 | 66.4 | 72.8 | 80.0 | 78.1 | 74.3 | 68.4 | 68.1 | 68.8 | 69.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 159.9 | 164.6 | 192.0 | 213.0 | 222.8 | 169.2 | 145.4 | 172.6 | 172.3 | 205.2 | 163.6 | 155.9 | 2,136.3 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 51.1 | 53.4 | 51.8 | 54.3 | 51.3 | 39.0 | 32.9 | 41.4 | 46.3 | 58.5 | 52.7 | 51.1 | 48.0 |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration (percent sunshine and snowy days) | |||||||||||||
Education
Chonnam National University, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, and Gwangju Education University are public universities in Gwangju.
Honam University, Gwangju University, Gwangshin University, Gwangju Women's University, Nambu University, Chosun University, and Honam Christian University are private universities.
Gwangju Health University is a private community college offering associate degrees in humanities and social sciences, healthcare sciences, and a bachelor's degree in nursing.
Gwangju has 593 schools, consisting of 234 kindergartens, 145 elementary schools, 84 middle schools, 65 high schools, 1 science high school, 7 junior colleges, 9 universities, 38 graduate schools, and 11 others (as of 1 May 2009) with a total of 406,669 students, or 28.5% of the total city population. The average number of students per household is 0.8.
Transportation
The city is served by the Gwangju Subway. An extension was completed in April 2008 with the remainder being completed in 2012. There are two KTX stations in the city: Gwangju station and Gwangju Songjeong Station. Gwangju Songjeong Station connects to the Gwangju Subway and local bus system. Now the Songjeong station is mainly used.
Gwangju has an extensive system of public buses that traverse the city. Bus stops and buses themselves contain stop information in Korean and in English. Local buses, but not the subway or KTX, connect to the intercity Gwangju Bus Terminal known as U-Square.
Gwangju is also served by the Gwangju Airport.
Tourism
| This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2015) |
- Asia Culture Center – The Asia Culture Center (also known as the ACC) is a facility in downtown Gwangju designed to celebrate and explore Gwangju's artistic and democratic culture and history, as well as provide space to host exhibits, experiences, and events from international artists. It is built primarily below street level, though its design incorporates large amounts of natural lighting. There are five facilities: ACC Exchange, ACC Theater, ACC Creation, ACC Archive & Research, and ACC Children.
- Gwangju Biennale – This is a modern art festival that is held every two years. It was first launched in 1995. The Gwangju Biennale Exhibition Hall is at the Jung-oe Park Culture Center and the Science Center.
- Gwangju Culture & Art Center – The Center regularly hosts events.Gwangju Culture & Art Center Official Website
- Gwangju Hyanggyo (Confucian School) – Gwangju Hyanggyo is in the Gwangju Park in Sa-dong. There are traditional houses here estimated as built during the 1st year of the Joseon Dynasty in 1392. This school continues to hold memorial ceremonies for Confucius twice a year. Admission is free. More about Gwangju Hyanggyo
- Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology - Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology(GIST) is one of the greatest research institutes in Korea. Laser research equipment with 4PW output is located within GIST.
- Gwangju National Museum – The museum houses a permanent collection of historical art and cultural relics that date back to the old Joseon and Goryeo periods of Korean history. The museum also organizes exhibitions and cultural learning activities that are open to the public.
- Gwangju 5.18 Road is the course about the Democracy Movement of 1980. The courses include the historical places. More about 5.18Road
- May 18th National Cemetery
- Food streets - Gwangju has numerous designated Food Streets where multiple restaurants serving dishes renowned to Gwangju can be found. These include Mudeungsan Boribap Street (a meal of barley with a variety of side dishes), Duck Cook Street (oritang, a duck stew, and grilled duck), Folk Tteokgalbi Street (a meal of grilled minced pork or beef patties eaten wrapped in lettuce and served with ox bone soup and a variety of side dishes) and Kotgejang Baekban Street (a meal of crabs preserved in soy sauce served with a variety of side dishes).
- Gwangju World Cup Stadium - It is a historical place for Korean soccer history. Because at this stadium in 2002 FIFA World Cup, South Korea national football team beat Spain soccer team in 3:5 at the quarter-Final, and advanced to the Semi-Final match with Germany in that World Cup, for the first time in the Asian soccer history.
Sport and culture


- It is the home of Kia Tigers of the Korea Professional Baseball League (KBO).
- 2002 FIFA World Cup – Gwangju World Cup Stadium was one of the venues used for the World Cup, and was where the South Korea national football team advanced to the semi-finals for the first time in its history, by defeating Spain.
- It is the home of Gwangju FC of the K League.
- Universiade – It was the venue for the 2015 Summer Universiade games.
- The 3rd Asia Song Festival an annual Asian pop music festival hosted by the Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange, in 2006, was held at the Gwangju World Cup Stadium.
- The International Design Alliance (IDA) appointed Gwangju as the host destination of the 2015 IDA Congress.
- Festivals are held in Gwangju. (ko:광주광역시의 축제 목록)
- 2019 FINA World Aquatics Championships
- 2014 Gwangju ACE Fair (Asia Content & Entertainment Fair)
- The Ministry of SMEs said Gwangju Metropolitan City was selected as the site for the creation of the "Green-Startup-Town." It is said that it will benchmark King's Cross Station, a successful case of urban regeneration in the UK, to establish a start-up hub (private research institute, research and development company, start-up company, etc.) at Gwangju Station.
- It is the home of Gwangju AI Peppers of the V-League.
Cityscape

- Mudeungsan – It is a mountain that is part of Mudeungsan National Park.
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in South KoreaTwin towns – sister cities
Gwangju is twinned with:
 Adelaide, Australia (2002)
Adelaide, Australia (2002) Changzhi, China (2014)
Changzhi, China (2014) Edmonton, Canada (2008)
Edmonton, Canada (2008) Guangzhou, China (1996)
Guangzhou, China (1996) Medan, Indonesia (1997)
Medan, Indonesia (1997) San Antonio, United States (1982)
San Antonio, United States (1982) Sendai, Japan (2002)
Sendai, Japan (2002) Tainan, Taiwan (1968)
Tainan, Taiwan (1968)
Partnerships and cooperations
 Turin, Italy
Turin, Italy Seberang Perai, Malaysia (2013)
Seberang Perai, Malaysia (2013)
Notable people
Literature
- Han Kang – author of The Vegetarian and Human Acts
Entertainers
- Jung Ho-seok (stage name J-Hope) – member of K-pop group BTS
- Kevin Moon - member of K-pop group The Boyz
(born in Gwangju, raised in Canada)
- Jeong Yun-ho (stage Name Yunho) - member of K-pop group ATEEZ
- Moon Geun-young – South Korean actress and singer
- Lee Seung-hyun (stage name Seungri) – former member of K-pop group Big Bang
- Jung Yun-ho (stage name U-Know) – member of K-pop group TVXQ
- Seo Hye-lin – member of K-pop group EXID
- Lee Gi-kwang – member of K-pop group Highlight
- Lee Sung-jong – member of K-pop group Infinite
- Chae Hyung-won – member of K-pop group Monsta X
- Im Chang-kyun (stage name I.M.) – member of K-pop group Monsta X (originally from Suwon)
- Bae Su-ji (stage name Suzy) – former member of K-pop group Miss A
- Gong Min-ji (stage name Minzy) – member of K-pop group 2NE1
- Kim Yu-bin – former member of K-pop group Wonder Girls
- Hong Jin-young – a trot singer
- Park Shin-hye – South Korean actress
- Jung Woo-seok – member of K-pop group Pentagon
- Lee Na-gyung – member of K-pop group Fromis 9
- Jeong Yunho – member of K-pop group ATEEZ
- Seo Woobin – member of K-pop group Cravity
- Oh Seunghee - member of K-pop group CLC
- Lee Su-jeong (stage name Babysoul)- leader and member of K-pop group Lovelyz
- Bae Seung-min - member of K-pop group Golden Child
- Park Soeun - member of K-pop group Weeekly
Sports
- Ki Sung-yueng – International footballer.
- An San – Olympic gold medalist in women's team, mixed team, and individual archery at the 2021 Tokyo Summer Games.
- An Se-young - Badminton Player.
See also
Notes
- In the 19th century, Gwangju was also known in English sources as Tsien-tsiou.
References
Citations
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Global city GDP 2014". Brookings Institution. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- EB (1878), p. 390.
- "Origin and History of Gwangju". www.gwangju.go.kr (in Korean). Retrieved 18 April 2018.
- ^ "The History of Gwangju".
- "May 18th Democratic Uprising".
- ^ "2015 Census – Religion Results" (in Korean). KOSIS KOrean Statistical Information Service. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- National Statistical Office of South Korea
- 평년값자료(1981–2010) 광주(156) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- 기후자료 극값(최대값) 전체년도 일최고기온 (℃) 최고순위, 광주(156) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- 기후자료 극값(최대값) 전체년도 일최저기온 (℃) 최고순위, 광주(156) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "Climatological Normals of Korea" (PDF). Korea Meteorological Administration. 2011. p. 499 and 649. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2016. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- Gwangju science academy
- 광주광역시 버스정보. bus.gjcity.net. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- U-Square (Gwangju Bus Terminal) (유스퀘어(광주종합버스터미널)) | Official Korea Tourism Organization. english.visitkorea.or.kr. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- "Asia Culture Center". www.acc.go.kr. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
- "Archived copy". utour.gwangju.go.kr. Archived from the original on 10 September 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Archived copy". utour.gwangju.go.kr. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Archived copy". utour.gwangju.go.kr. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Archived copy". utour.gwangju.go.kr. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - (in Korean) K-League news 4강 역사를 쓴 그곳, 광주 월드컵 경기장 Dream stadium of K-League Archived 16 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- KOFICE 3rd Asia Song Festival Archived 29 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine 22 September 2006. Retrieved 2011-10-12
- 2016 광주 ACE Fair. www.acefair.or.kr. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- 이, 태수 (13 May 2021). "광주역 일대에 창업거점 '그린 스타트업 타운' 만든다". 연합뉴스 (in Korean). Retrieved 13 May 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - "Korea National Park". english.knps.or.kr. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- "Sister Cities". gwangju.go.kr. Gwangju. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- Pessotto, Lorenzo. "International Affairs – Twinnings and Agreements". International Affairs Service in cooperation with Servizio Telematico Pubblico. City of Torino. Archived from the original on 18 June 2013. Retrieved 6 August 2013.
- "MPSP sets sights on city status". The Star. 1 August 2016.
Bibliography
- "Corea" , 'Encyclopædia Britannica, 9th ed., Vol. VI, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1878, pp. 390–394.
External links
- Official website (in English)
- Gwangju :Official Site of Korea Tourism Org Archived 29 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine
| Districts of Gwangju | |
|---|---|
| Regions and administrative divisions of South Korea | |
|---|---|
| Regions | |
| Provinces | |
| Special self-governing province and States | |
| Special city | |
| Special self-governing city | |
| Metropolitan cities | |
| 2,000,000 and more | |
|---|---|
| 1,000,000–1,999,999 | |
| 500,000–999,999 | |
| 200,000–499,999 | |
| Largest cities or towns in South Korea 2015 Population and Housing Census | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




