| Revision as of 21:00, 5 January 2008 editSmackBot (talk | contribs)3,734,324 editsm Date/fix the maintenance tags or gen fixes using AWB← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:20, 9 January 2008 edit undoIsthisthingworking (talk | contribs)797 editsm fmt citationNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| In ], '''voids''' are the empty spaces between ], the largest-scale structures in the ], that contain very few, or no, galaxies. | In ], '''voids''' are the empty spaces between ], the largest-scale structures in the ], that contain very few, or no, galaxies. | ||
| Voids typically have a diameter of 11 to 150 ]; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich ]s, are sometimes called '''supervoids'''. Voids located in high-density environments are smaller than voids situated in low-density spaces of the universe. |
Voids typically have a diameter of 11 to 150 ]; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich ]s, are sometimes called '''supervoids'''. Voids located in high-density environments are smaller than voids situated in low-density spaces of the universe.<ref>{{cite journal|author=U. Lindner, J. Einasto, M. Einasto, W. Freudling, K. Fricke, E. Tago|title=The structure of supervoids. I. Void hierarchy in the Northern Local Supervoid|journal=Astron. Astrophys.|volume=301|page=329|date=1995|url=http://www.uni-sw.gwdg.de/research/preprints/1995/pr1995_14.html/ The Structure of Supervoids I: Void Hierarchy in the Northern Local Supervoid}}</ref> | ||
| ==List of voids== | ==List of voids== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| * | * | ||
| * from Hume Feldman with Sergei Shandarin, Dept. Physics and Astronomy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA. | * from Hume Feldman with Sergei Shandarin, Dept. Physics and Astronomy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA. | ||
| * , ] | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| ===General references=== | |||
| :* U. Lindner, J. Einasto, M. Einasto, W. Freudling, K. Fricke, E. Tago: ''The structure of supervoids. I. Void hierarchy in the Northern Local Supervoid.'', Astron. Astrophys., v.301, p.329 (1995) | |||
Revision as of 23:20, 9 January 2008
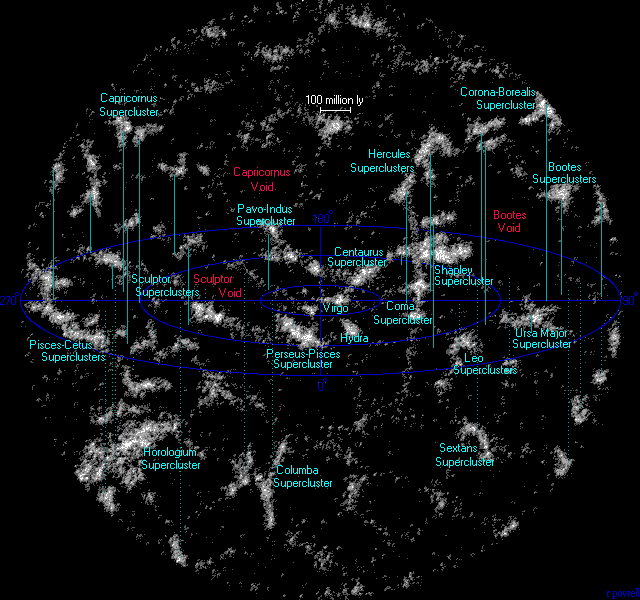
In astronomy, voids are the empty spaces between filaments, the largest-scale structures in the Universe, that contain very few, or no, galaxies. Voids typically have a diameter of 11 to 150 Mpc; particularly large voids, defined by the absence of rich superclusters, are sometimes called supervoids. Voids located in high-density environments are smaller than voids situated in low-density spaces of the universe.
List of voids
A 1994 census lists a total of 27 supervoids with a distance of up to 740 Mpc. A selection is given below:
| # | Name | Distance (Mpc) | Diameter (Mpc) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 188 | 124 | |
| 5 | 182 | 130 | |
| 9 | Southern Local Supervoid | 135 | 158 |
| 18 | 168 | 144 | |
| 19 | 168 | 152 | |
| 20 | Boötes void | 304 | 110 |
| 21 | 201 | 163 | |
| 24 | Northern Local Supervoid | 86 | 146 |
Not shown in the above chart:
- Capricornus Void
- The Eridanus Supervoid, reported on 24 August 2007 by the NRAO from Very Large Array Sky Survey data, is much larger than these, being about 300 Mpc in diameter and 1800–3000 Mpc distant. It also corresponds to a cold spot in the cosmic microwave background.
Maps
External links
- Universe family tree: Void
- a few animated views of voids and their distribution from Hume Feldman with Sergei Shandarin, Dept. Physics and Astronomy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA.
References
- U. Lindner, J. Einasto, M. Einasto, W. Freudling, K. Fricke, E. Tago (1995). The Structure of Supervoids I: Void Hierarchy in the Northern Local Supervoid "The structure of supervoids. I. Void hierarchy in the Northern Local Supervoid". Astron. Astrophys. 301: 329.
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Einasto, M (1994-07-15), "The Structure of the Universe Traced by Rich Clusters of Galaxies", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 269
- NRAO: "Astronomers Find Enormous Hole in the Universe". NRAO website, retrieved 24 August 2007.