| Revision as of 05:51, 3 April 2014 view sourceClueBot NG (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,439,507 editsm Reverting possible vandalism by 174.255.128.158 to version by Monkbot. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (1777417) (Bot)← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:51, 3 April 2014 view source 174.255.128.158 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''sperm whale''' (''Physeter macrocephalus''), or '''cachalot''', is the largest of the ]s and the largest toothed ]. It is the only living member of genus '''''Physeter''''', and one of three extant ] in the ], along with the ] and ] of the genus '']''. | The '''sperm whale''' (''Physeter macrocephalus''), or '''cachalot''', is the largest of the ]s and the largest toothed ]. It is the only living member of genus '''''Physeter''''', and one of three extant ] in the ], along with the ] and ] of the genus '']''. It is the largest carnivorous predator to have ever lived. | ||
| Mature males average at {{convert|16|m|ft}} in length but some may reach {{convert|20.5|m|ft}}, with the head representing up to one-third of the animal's length. The sperm whale feeds primarily on ]. Plunging to {{convert|2250|m|ft}} for prey, it is the second deepest diving mammal, following only the ].<ref name=NatGeoDeepest>{{cite web |title=Elusive Whales Set New Record for Depth and Length of Dives Among Mammals |url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/03/140326-cuvier-beaked-whale-record-dive-depth-ocean-animal-science/ |author=Lee, Jane J. |archiveurl= http://www.webcitation.org/6OQPfmHCj |date=2014-03-26 |archivedate=2014-03-29 |publisher=''National Geographic'' }}</ref> The sperm whale's clicking vocalization, a form of ] and communication, may be as loud as 230 ]s (re 1 µPa at 1 m) underwater,<ref name="natgeo">{{cite web | Mature males average at {{convert|16|m|ft}} in length but some may reach {{convert|20.5|m|ft}}, with the head representing up to one-third of the animal's length. The sperm whale feeds primarily on ]. Plunging to {{convert|2250|m|ft}} for prey, it is the second deepest diving mammal, following only the ].<ref name=NatGeoDeepest>{{cite web |title=Elusive Whales Set New Record for Depth and Length of Dives Among Mammals |url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/03/140326-cuvier-beaked-whale-record-dive-depth-ocean-animal-science/ |author=Lee, Jane J. |archiveurl= http://www.webcitation.org/6OQPfmHCj |date=2014-03-26 |archivedate=2014-03-29 |publisher=''National Geographic'' }}</ref> The sperm whale's clicking vocalization, a form of ] and communication, may be as loud as 230 ]s (re 1 µPa at 1 m) underwater,<ref name="natgeo">{{cite web | ||
Revision as of 05:51, 3 April 2014
"Cachalot" redirects here. For other uses, see Cachalot (disambiguation).
| Sperm whale | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| Conservation status | |
 Vulnerable (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Cetacea |
| Suborder: | Odontoceti |
| Family: | Physeteridae |
| Genus: | Physeter Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Species: | P. macrocephalus |
| Binomial name | |
| Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758 | |

| |
| Major sperm whale grounds | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Physeter catodon Linnaeus, 1758 | |
The sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus), or cachalot, is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of genus Physeter, and one of three extant species in the sperm whale family, along with the pygmy sperm whale and dwarf sperm whale of the genus Kogia. It is the largest carnivorous predator to have ever lived.
Mature males average at 16 metres (52 ft) in length but some may reach 20.5 metres (67 ft), with the head representing up to one-third of the animal's length. The sperm whale feeds primarily on squid. Plunging to 2,250 metres (7,380 ft) for prey, it is the second deepest diving mammal, following only the Cuvier's beaked whale. The sperm whale's clicking vocalization, a form of echolocation and communication, may be as loud as 230 decibels (re 1 µPa at 1 m) underwater, making it the loudest sound produced by any animal. It has the largest brain of any animal on Earth, more than five times heavier than a human's. Sperm whales can live for more than 60 years.
The sperm whale can be found anywhere in the open ocean. Females and young males live together in groups while mature males live solitary lives outside of the mating season. The females cooperate to protect and nurse their young. Females give birth every four to twenty years, and care for the calves for more than a decade. A mature sperm whale has few natural predators. Calves and weakened adults are taken by pods of orcas.
From the early eighteenth century through the late 20th the species was a prime target of whalers. The head of the whale contains a liquid wax called spermaceti, from which the whale derives its name. Spermaceti was used in lubricants, oil lamps, and candles. Ambergris, a waste product from its digestive system, is still used as a fixative in perfumes. Occasionally the sperm whale's great size allowed it to defend itself effectively against whalers. The species is now protected by a whaling moratorium, and is currently listed as vulnerable by the IUCN.
Etymology
The name sperm whale is a clip of spermaceti whale. Spermaceti, originally mistakenly identified as the whales' semen, is the semi-liquid, waxy substance found within the whale's head (see below). The sperm whale is also known as the "cachalot", which is thought to derive from the archaic French for "tooth" or "big teeth", as preserved for example in cachau in the Gascon dialect (a word of either Romance or Basque origin). The etymological dictionary of Corominas says the origin is uncertain, but it suggests that it comes from the Vulgar Latin cappula, plural of cappulum, sword hilt. According to Encarta Dictionary, the word cachalot came to English "via French from Spanish or Portuguese cachalote, perhaps from Galecian/Portuguese cachola, 'big head'". The term is retained in the Russian word for the animal, кашалот (kashalot), as well as in many other languages.
The scientific genus name Physeter comes from Greek φυσητήρ, physētēr, meaning "blowpipe", "blowhole" (of a whale), or (as a pars pro toto) "whale", while the specific epithet macrocephalus comes from Greek μακροκέφαλος makrokephalos, meaning "big-headed", from μακρός, makros, "large" + κέφαλος, kefalos, "head".
Description
Size
| Length | Weight | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 16 metres (52 ft) | 41,000 kilograms (45 short tons) |
| Female | 11 metres (36 ft) | 14,000 kilograms (15 short tons) |
| Newborn | 4 metres (13 ft) | 1,000 kilograms (1.1 short tons) |
The sperm whale is the largest toothed whale, with adult males measuring up to 20.5 metres (67 ft) long and weighing up to 57,000 kilograms (56 long tons; 63 short tons). By contrast, the second largest toothed whale, Baird's Beaked Whale measures 12.8 metres (42 ft) and weighs up to 15 short tons (14,000 kg). The Nantucket Whaling Museum has a 5.5 metres (18 ft)-long jawbone. The museum claims that this individual was 24 metres (80 ft) long; the whale that sank the Essex (one of the incidents behind Moby-Dick) was claimed to be 26 metres (85 ft). A similar size is reported from a jawbone from the British Natural History Museum. A 67-foot specimen is reported from a Soviet whaling fleet near the Kurile Islands in 1950. There is disagreement on the claims of adult males approaching or exceeding 24 metres (80 ft) in length.
Extensive whaling may have decreased their size, as males were highly sought, primarily after World War II. Today, males do not usually exceed 18.3 metres (60 ft) in length or 51,000 kilograms (50 long tons; 56 short tons) in weight. Another view holds that exploitation by overwhaling had virtually no effect on the size of the bull sperm whales, and their size may have actually increased in current times on the basis of density dependent effects.
It is among the most sexually dimorphic of all cetaceans. At birth both sexes are about the same size, but mature males are typically 30% to 50% longer and three times as massive as females.
Appearance
The sperm whale's unique body is unlikely to be confused with any other species. The sperm whale's distinctive shape comes from its very large, block-shaped head, which can be one-quarter to one-third of the animal's length. The S-shaped blowhole is located very close to the front of the head and shifted to the whale's left. This gives rise to a distinctive bushy, forward-angled spray.
The sperm whale's flukes are triangular and very thick. Proportionally, they are larger than that of any other cetacean, and are very flexible. The whale lifts its flukes high out of the water as it begins a feeding dive. It has a series of ridges on the back's caudal third instead of a dorsal fin. The largest ridge was called the 'hump' by whalers, and can be mistaken for a dorsal fin because of its shape and size.
In contrast to the smooth skin of most large whales, its back skin is usually wrinkly and has been likened to a prune by whale-watching enthusiasts. Albinos have been reported.
Skeleton
Sperm whale skeletonThe ribs are bound to the spine by flexible cartilage, which allows the ribcage to collapse rather than snap under high pressure.
As with other toothed whales, the skull of the sperm whale is asymmetrical so as to aid echolocation. Sound waves that strike the whale from different directions will not be channeled in the same way. Within the basin of the cranium, the openings of the bony narial tubes (from which the nasal passages spring) are skewed towards the left side of the skull.
Jaws and teeth

The sperm whale's lower jaw is very narrow and underslung. The sperm whale has 18 to 26 teeth on each side of its lower jaw which fit into sockets in the upper jaw. The teeth are cone-shaped and weigh up to 1 kilogram (2.2 lb) each. The teeth are functional, but do not appear to be necessary for capturing or eating squid, as well-fed animals have been found without teeth or even with deformed jaws. One hypothesis is that the teeth are used in aggression between males. Mature males often show scars which seem to be caused by the teeth. Rudimentary teeth are also present in the upper jaw, but these rarely emerge into the mouth. Analyzing the teeth is the preferred method for determining a whale's age; analogous to rings in a tree, the teeth build distinct layers of cementum and dentine as they grow.
Respiration and diving

Sperm whales are believed to be able remain submerged for 90 minutes and to dive as deep as 2,250 metres (7,380 ft), making them the second deepest diving mammal after Cuvier's beaked whale, which has been recorded at 2,992 metres (9,816 ft). More typical sperm whale dives are around 400 metres (1,300 ft) and 35 minutes in duration. At these great depths, sperm whales had sometimes become entangled in transoceanic telephone cables and drowned until improvements in laying and maintenance techniques were employed.
The sperm whale has adapted to cope with drastic pressure changes when diving. The flexible ribcage allows lung collapse, reducing nitrogen intake, and metabolism can decrease to conserve oxygen. Myoglobin, which stores oxygen in muscle tissue, is much more abundant than in terrestrial animals. The blood has a high red blood cell density, which contain oxygen-carrying haemoglobin. The oxygenated blood can be directed towards only the brain and other essential organs when oxygen levels deplete. The spermaceti organ may also play a role by adjusting buoyancy (see below).
While sperm whales are well adapted to diving, repeated dives to great depths have long term effects. Bones show the same pitting that signals decompression sickness in humans. Older skeletons showed the most extensive pitting, whereas calves showed no damage. This damage may indicate that sperm whales are susceptible to decompression sickness, and sudden surfacing could be lethal to them.
Between dives, the sperm whale surfaces to breathe for about eight minutes before diving again. Odontoceti (toothed whales) breathe air at the surface through a single, S-shaped blowhole. Sperm whales spout (breathe) 3–5 times per minute at rest, increasing to 6–7 times per minute after a dive. The blow is a noisy, single stream that rises up to 2 metres (6.6 ft) or more above the surface and points forward and left at a 45° angle. On average, females and juveniles blow every 12.5 seconds before dives, while large males blow every 17.5 seconds before dives.
A sperm whale killed 160 km (100 mi) south of Durban, South Africa after a 1 hour, 50-minute dive was found with two dogfish (Scymnodon sp.), usually found at the sea floor, in its belly.
Brain and senses
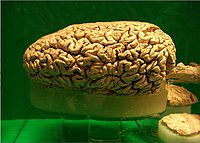 The sperm whale's brain is the largest in the world, five times heavier than a human's.
The sperm whale's brain is the largest in the world, five times heavier than a human's.
The brain is the largest known of any modern or extinct animal, weighing on average about 7.8 kilograms (17 lb), more than five times heavier than a human's, and has a volume of about 8,000 cm. Although larger brains generally correlate with higher intelligence, it is not the only factor. Elephants and dolphins also have larger brains than humans. The sperm whale has a lower encephalization quotient than many other whale and dolphin species, lower than that of non-human anthropoid apes, and much lower than humans'.
The sperm whale's cerebrum is the largest in all mammalia, both in absolute and relative terms. The olfactory system is reduced, suggesting that the sperm whale has a poor sense of taste and smell. By contrast, the auditory system is enlarged. The pyramidal tract is poorly developed, reflecting the reduction of its limbs.
Genetics
Sperm whales have 21 pairs of chromosomes (2n=42). The genome of live whales can be examined by recovering shed skin.
Digestive tract
The sperm whale has the longest intestinal system in the world, exceeding 300 m in larger specimens.
The sperm whale has four stomachs. The first secretes no gastric juices and has very thick muscular walls to crush the food (since whales can't chew) and resist the claw and sucker attacks of swallowed squid. The second stomach is larger and is where digestion proper takes place. Undigested squid beaks accumulate in the second stomach – as many as 18,000 have been found in some dissected specimens.
Most squid beaks are vomited by the whale, but some occasionally make it to the hindgut. Such beaks precipitate the formation of ambergris.
Circulatory system

In 1959, the heart of a 22-tonne male slain by whalers was measured to be 116kg, about 0.5% of its total mass.
The circulatory system has a number of specific adaptations for the aquatic environment. The diameter of the aortic arch increases as it leaves the heart. This bulbous expansion acts as a windkessel, ensuring a steady blood flow as the heart rate slows during diving. The arteries that leave the aortic arch are positioned symmetrically. There is no costocervical artery. There is no direct connection between the internal carotid artery and the vessels of the brain.
The arterial retia mirabilia are extraodinarily well-developed. The complex arterial retia mirabilia of the sperm whale are more extensive and larger than those of any other cetacean.
Eyes
The sperm whale's eye does not differ greatly from those of other toothed whales except in size. It is the largest among the toothed whales, weighing about 170 g. It is overall ellipsoid in shape, compressed along the visual axis, measuring about 7×7×3 cm. The cornea is elliptical and the lens is spherical. The sclera is very hard and thick, roughly 1 cm anteriorly and 3 cm posteriorly. There are no ciliary muscles. The choroid is very thick and contains a fibrous tapetum lucidum. Like other toothed whales, the sperm whale can retract and protrude its eyes thanks to a 2-cm-thick retractor muscle attached around the eye at the equator.
Spermaceti organ and melon
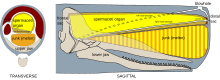
Atop the whale's skull is positioned a large complex of organs filled with a liquid mixture of fats and waxes called spermaceti. The purpose of this complex is to generate powerful and focused clicking sounds, which the sperm whale uses for echolocation and communication.
The spermaceti organ is like a large barrel of spermaceti. Its surrounding wall, known as the case, is extremely tough and fibrous. The case can hold within it up to 1,900 litres of spermaceti. It is proportionately larger in males. This oil is a mixture of triglycerides and wax esters. The proportion of wax esters in the spermaceti organ increases with the age of the whale: 38–51% in calves, 58–87% in adult females, and 71–94% in adult males. The spermaceti at the core of the organ has a higher wax content than the outer areas. The speed of sound in spermaceti is 2,684 m/s (at 40 kHz, 36°C), making it nearly twice as fast as in the the oil in a dolphin's melon. Below the spermaceti organ lies the "junk" (so-called because many whalers dismissed this part as a worthwhile source of oil), which consists of compartments of spermaceti separated by cartilage. It is analogous to the melon found in other toothed whales.
Running through the head are two air passages. The left passage runs alongside the spermaceti organ and goes directly to the blowhole, whilst the right passage runs underneath the spermaceti organ and passes air through a pair of phonic lips and into the distal sac at the very front of the nose. The distal sac is connected to the blowhole and the terminus of the left passage. When the whale is submerged, it can close the blowhole, and air that passes through the phonic lips can circulate back to the lungs.
At the posterior end of this spermaceti complex is the frontal sac, which covers the concave surface of the cranium. The posterior wall of the frontal sac is covered with fluid–filled knobs, which are about 4–13 mm in diameter and separated by narrow grooves. The anterior wall is smooth. The knobbly surface reflects sound waves that come through the spermaceti organ from the phonic lips. The grooves between the knobs trap a film of air that is consistent whatever the orientation or depth of the whale, making it an excellent sound mirror.
The spermaceti organs may also help adjust the whale's buoyancy. It is hypothesized that before the whale dives, cold water enters the organ, and it is likely that the blood vessels constrict, reducing blood flow, and, hence, temperature. The wax therefore solidifies and reduces in volume. The increase in specific density generates a down force of about 392 newtons (88 lbf) and allows the whale to dive with less effort. During the hunt, oxygen consumption, together with blood vessel dilation, produces heat and melts the spermaceti, increasing its buoyancy and enabling easy surfacing. However, more recent work have found many problems with this theory including the lack of anatomical structures for the actual heat exchange.
Herman Melville's fictional story Moby Dick suggests that the "case" containing the spermaceti serves as a battering ram for use in fights between males. Apart from a few famous instances such as the well-documented sinking of the ships Essex and Ann Alexander by attackers estimated to weigh only one-fifth as much as the ships, this hypothesis is not well supported in current scientific literature.
-
 The phonic lips.
The phonic lips.
-
 The frontal sac, exposed. Its surface is covered with fluid-filled knobs.
The frontal sac, exposed. Its surface is covered with fluid-filled knobs.
-
 A piece of the posterior wall of the frontal sac. The grooves between the knobs trap a consistent film of air, making it an excellent sound mirror.
A piece of the posterior wall of the frontal sac. The grooves between the knobs trap a consistent film of air, making it an excellent sound mirror.
Differences from other toothed whales
The sperm whale's head anatomy is very unusual among odontocetes. The sperm whale has only one pair of phonic lips, whereas all other toothed whales have two, and it is located at the front of the nose instead of behind the melon.
Vocalization complex
Mechanism
When echolocating, the sperm whale emits a directionally focused beam of broadband clicks. Clicks are generated by the forcing of air through a pair of phonic lips (also known as "monkey lips" or "museau de singe") at the front end of the nose, just below the blowhole. The sound then travels backwards along the length of the nose through the spermaceti organ. Most of the sound energy is then reflected off the frontal sac at the cranium and into the junk, whose lens-like structure focuses it. Some of the sound will reflect back into the spermaceti organ and back towards the front of the whale's nose where it will be reflected through the spermaceti organ a third time. This back and forth reflection which happens on the scale of a few milliseconds creates a multi-pulse click structure. This multi-pulse click structure actually allows researchers to measure the whale's spermaceti organ using only the sound of its clicks, and given the size of the spermaceti organ in relation to the size of the whale, biologists can measure the whales by recording their echolocation clicks. Because the IPI of a Sperm Whale's click is related to the length of the sound producing organ, an individual whale's click is unique to that individual. However, if the whale matures and the size of the spermaceti organ increases, the tone of the whale's click will also change. The lower jaw is the primary reception path for the echoes. A continuous fat-filled canal transmits received sounds to the inner ear.
The source of the air forced through the phonic lips is the right nasal passage. While the left nasal passage opens to the blow hole, the right nasal passage has evolved to supply air to the phonic lips. It is thought that the nostrils of the land-based ancestor of the sperm whale migrated through evolution to their current functions, the left nostril becoming the blowhole and the right nostril becoming the phonic lips.
Air that passes through the phonic lips passes into the distal sac, then back down through the left nasal passage. This recycling of air allows the whale to continuously generate clicks for as long as it is submerged.
Types of vocalization
A creak is a rapid series of high-frequency clicks that sounds somewhat like a creaky door hinge. It is typically used when homing in on prey.
A coda is a short pattern of 3 to 20 clicks that is used in social situations. They were once thought to be a way by which individuals identified themselves, but individuals have been observed producing multiple codas, and the same codas are used by multiple individuals. Geographically separate pods exhibit distinct dialects. Large males are generally solitary and rarely produce codas. In breeding grounds, codas are almost entirely produced by adult females. Despite evidence that Sperm whales share similar codas, it is still unknown whether sperm whales possess individually specific coda repertoires or whether individuals make codas at different rates.
Slow clicks are heard only in the presence of males (it is not certain whether females occasionally make them). Males make a lot of slow clicks in breeding grounds (74% of the time), both near the surface and at depth, which suggests they are primarily mating signals. Outside breeding grounds, slow clicks are rarely heard, and usually near the surface.
| Click type | Apparent source level (dB re 1µPa ) |
Directionality | Centroid frequency (kHz) |
Inter-click interval (s) |
Duration of click (ms) |
Duration of pulse (ms) |
Range audible to sperm whale (km) |
Inferred function | Audio sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usual | 230 | High | 15 | 0.5–1.0 | 15–30 | 0.1 | 16 | searching for prey | |
| Creak | 205 | High | 15 | 0.005–0.1 | 0.1–5 | 0.1 | 6 | homing in on prey | |
| Coda | 180 | Low | 5 | 0.1–0.5 | 35 | 0.5 | ~2 | social communication | |
| Slow | 190 | Low | 0.5 | 5–8 | 30 | 5 | 60 | communication by males |
Ecology
Distribution

The sperm whale is among the most cosmopolitan species. It prefers ice-free waters over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) deep. Although both sexes range through temperate and tropical oceans and seas, only adult males populate higher latitudes.
It is relatively abundant from the poles to the equator and is found in all the oceans. It inhabits the Mediterranean Sea, but not the Black Sea, while its presence in the Red Sea is uncertain. The shallow entrances to both the Black Sea and the Red Sea may account for their absence. The Black Sea's lower layers are also anoxic and contain high concentrations of sulphur compounds such as hydrogen sulphide.
Populations are denser close to continental shelves and canyons. Sperm whales are usually found in deep off-shore waters, but may be seen closer to shore in areas where the continental shelf is small and drops quickly to depths of 310–920 metres (1,020–3,020 ft). Coastal areas with significant sperm whale populations include the Azores and the Caribbean island of Dominica.
Life cycle
See also: Whale reproductionSperm whales can live 70 years or more. They are a prime example of a species that has been K-selected, i.e., their reproductive strategy is associated with stable environmental conditions and comprises a low birth rate, significant parental aid to offspring, slow maturation, and high longevity.
How they choose mates has not been definitively determined. Males will fight with each other over females, and males will mate with multiple females, but they do not dominate the group like a harem. Males do not provide paternal care to their offspring.
Females become fertile at around 9 years of age. The oldest pregnant female ever recorded was 41 years old. Gestation requires 14 to 16 months, producing a single calf. Sexually mature females give birth once every 4 to 20 years (pregnancy rates were higher during the whaling era). Birth is a social event, as the mother and calf need others to protect them from predators. The other adults may jostle and bite the newborn in its first hours.
Lactation proceeds for 19 to 42 months, but calves may suckle up to 13 years (although usually less). Like other whales, the sperm whale's milk has a higher fat content than that of terrestrial mammals: about 36%, compared to 4% in cow milk. This gives it a consistency similar to cottage cheese, which prevents it from dissolving in the water before the calf can eat it. It has an energy content of roughly 3,840 kcal/kg (16,070 kJ/kg), compared to just 640 kcal/kg (2,700 kJ/kg) in cow milk. Calves may be allowed to suckle from females other than their mothers.
Males become sexually mature at 18 years. Upon reaching sexual maturity, males move to higher latitudes, where the water is colder and feeding is more productive. Females remain at lower latitudes. Males reach their full size at about age 50.
Social behaviour

Sexual segregation
Adult males who are not breeding live solitary lives, whereas females and juvenile males live together in groups. The main driving force for the sexual segregation of adult sperm whales is scramble competition for mesopelagic squid.
Females and their young remain in groups, while mature males leave their "natal unit" somewhere between 4 and 21 years of age. Mature males sometimes form loose "bachelor groups" with other males of similar age and size. As males grow older, they typically live solitary lives. Mature males have beached themselves together, suggesting a degree of cooperation which is not yet fully understood. The whales rarely if ever leave their group.
The social unit
A social unit is a group of sperm whales who live and travel together over periods of years. Individuals rarely, if ever, join or leave a social unit. There is a huge variance in the size of social units. They are most commonly between 6 and 9 individuals in size but can have more than twenty. Unlike orcas, sperm whales within a social unit show no significant tendency to associate with their genetic relatives. Females and calves spend about three quarters of their time foraging and a quarter of their time socializing. Socializing usually takes place in the afternoon.
When sperm whales socialize, they emit complex patterns of clicks called codas (see above). They will spend much of the time rubbing against each other.
Relations with other species
The most common non-human attacker of sperm whales is the orca, but pilot whales and the false killer whale also sometimes harass them. Orcas prey on target groups of females with young, usually making an effort to extract and kill a calf. The adults will protect their calves or an injured adult by encircling them. They may face inwards with their tails out; the Marguerite formation (named after the flower). The heavy and powerful tail of an adult whale can deliver lethal blows. Alternatively, they will face outwards; the heads-out formation. Early whalers exploited this behaviour, attracting a whole unit by injuring one of its members. If the orca pod is extremely large, its members may sometimes be able to kill adult female sperm whales. Individual large mature male sperm whales have no non-human predators, and are believed to be too large, powerful and aggressive to be threatened by orcas. In addition, male sperm whales have been observed to attack and intimidate orca pods. An incident was filmed from a long-line trawler; an orca pod was systematically taking fish caught on the trawler's long lines (as the lines were being pulled into the ship) when a male sperm whale appeared to repeatedly charge the orca pod in attempt to drive them away; it was speculated by the film crew that the sperm whale was attempting to access the same fish. The orcas also engaged in a similar tail first and tail slapping defensive position against the bull sperm whale as is used by female sperm whales against attacking orcas.
Sperm whales are not known for forging bonds with other species, but it was observed that a bottlenose dolphin with spinal deformity had been accepted into a pod of sperm whales.
Diet

Sperm whales usually dive between 300 to 800 metres (980 to 2,620 ft), and sometimes 1–2 kilometres (3,300–6,600 ft) to search for food. Such dives can last more than an hour. They feed on several species, notably the giant squid, but also the larger colossal squid, octopuses, and diverse fish like demersal rays, but the main part of their diet consists of medium-sized squid. Some prey may be taken incidentally while eating other items. Most of what is known about deep sea squid has been learned from specimens in captured sperm whale stomachs, although more recent studies analysed feces. One study, carried out around the Galápagos, found that squid from the genera Histioteuthis (62%), Ancistrocheirus (16%), and Octopoteuthis (7%) weighing between 12 and 650 grams (0.026 and 1.433 lb) were the most commonly taken. Battles between sperm whales and giant squid or colossal squid have never been observed by humans; however white scars are believed to be caused by the large squid. One study published in 2010 collected evidence that suggests that female sperm whales may collaborate when hunting Humboldt squid. Tagging studies have shown that sperm whales hunt upside down at the bottom of their deep dives. It is suggested that the whales can see the squid silhouetted above them against the dim surface light.
An older study, examining whales captured by the New Zealand whaling fleet in the Cook Strait region, found a 1.69:1 ratio of squid to fish by weight. Sperm whales sometimes steal sablefish and toothfish from long lines. Long-line fishing operations in the Gulf of Alaska complain that sperm whales take advantage of their fishing operations to eat desirable species straight off the line, sparing the whales the need to hunt. However, the amount of fish taken is very little compared to what the sperm whale needs per day. Video footage has been captured of a large male sperm whale "bouncing" a long line, to gain the fish. Sperm whales are believed to prey on the megamouth shark, a rare and large deep-sea species discovered in the 1970s. In one case, three sperm whales were observed attacking or playing with a megamouth.

The sharp beak of a consumed squid lodged in the whale's intestine may lead to the production of ambergris, analogous to the production of pearls. The irritation of the intestines caused by squid beaks stimulates the secretion of this lubricant-like substance. Sperm whales are prodigious feeders and eat around 3% of their body weight per day. The total annual consumption of prey by sperm whales worldwide is estimated to be about 100 million short tons (91 million tonnes). In comparison, human consumption of seafood is estimated to be 127 million short tons (115 million tonnes).
Sperm whales hunt through echolocation. Their clicks are the most powerful sounds in the animal kingdom (see above). It has been hypothesised that it can stun prey with its clicks. Experimental studies attempting to duplicate this effect have been unable to replicate the supposed injuries, casting doubt on this idea.
It has been stated that sperm whales help to fertilise the surface of the ocean by consuming nutrients at depth and transporting those nutrients to the oceans' surface when they defecate. This fertilises the plants (phytoplankton) on the surface of the ocean and contributes to ocean productivity and the drawdown of atmospheric carbon.
Sleeping
For some time researchers have been aware that pods of sperm whales may sleep for short periods, assuming a vertical position with their heads just below or at the surface. A 2008 study published in Current Biology recorded evidence that whales may sleep with both sides of the brain. It appears that some whales may fall into a deep sleep for about 7 percent of the time, most often between 6 p.m. and midnight.
Taxonomy and naming
The sperm whale belongs to the order Cetacea, the order containing all whales and dolphins. It is a member of the suborder Odontoceti, the suborder containing all the toothed whales and dolphins. It is the sole extant species of its genus, Physeter, in the family Physeteridae. Two species of the related extant genus Kogia, the pygmy sperm whale Kogia breviceps and the dwarf sperm whale K. simus, are placed either in this family or in the family Kogiidae. In some taxonomic schemes the families Kogiidae and Physeteridae are combined as the superfamily Physeteroidea (see the separate entry on the sperm whale family).
The sperm whale is one of the species originally described by Linnaeus in 1758 in his eighteenth century work, Systema Naturae. He recognised four species in the genus Physeter. Experts soon realised that just one such species exists, although there has been debate about whether this should be named P. catodon or P. macrocephalus, two of the names used by Linnaeus. Both names are still used, although most recent authors now accept macrocephalus as the valid name, limiting catodon's status to a lesser synonym.
Evolutionary history
See also: Sperm whale familyFossil record
Although the fossil record is poor, several extinct genera have been assigned to the clade Physeteroidea, which includes the last common ancestor of the modern sperm whale, pygmy sperm whale and dwarf sperm whale, plus all of that ancestor's descendants. These fossils include Ferecetotherium, Idiorophus, Diaphorocetus, Aulophyseter, Orycterocetus, Scaldicetus, Placoziphius, Zygophyseter and Acrophyseter. Ferecetotherium, found in Azerbaijan and dated to the late Oligocene (about 28 to 23 million years ago), is the most primitive fossil that has been found which possesses sperm whale-specific features such as an asymmetric rostrum ("beak" or "snout"). Most sperm whale fossils date from the Miocene period, 23 to 5 million years ago. Diaphorocetus, from Argentina, has been dated to the early Miocene. Fossil sperm whales from the Middle Miocene include Aulophyseter, Idiorophus and Orycterocetus, all of which were found on the west coast of the United States, and Scaldicetus, found in Europe and Japan. Orycterocetus fossils have also been found in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, in addition to the west coast of the United States. Placoziphius, found in Europe, and Acrophyseter, from Peru, are dated to the late Miocene.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evolutionary family tree of sperm whales, including simplified summary of extinct groups (†) |
Fossil sperm whales differ from modern sperm whales in tooth count and the shape of the face and jaws. For example Scaldicetus had a tapered rostrum. Genera from the Oligocene and early and middle Miocene, with the possible exception of Aulophyseter, had teeth in their upper jaws. Acrophyseter, from the late Miocene, also had teeth in both the upper and lower jaws as well as a short rostrum and an upward curving mandible (lower jaw). These anatomical differences suggest that fossil species may not have necessarily been deep-sea squid eaters like the modern sperm whale, but that some genera mainly ate fish. Zygophyseter, dated from the middle to late Miocene and found in southern Italy, had teeth in both jaws and appears to have been adapted to feed on large prey, rather like the modern Orca (Killer Whale).
Phylogeny
The traditional view has been that Mysticeti (baleen whales) and Odontoceti (toothed whales) arose from more primitive whales early in the Oligocene period, and that the super-family Physeteroidea, which contains the sperm whale, dwarf sperm whale, and pygmy sperm whale, diverged from other toothed whales soon after that, over 23 million years ago. In 1993–96 molecular phylogenetics analyses by Milinkovitch and colleagues, based on comparing the genes of various modern whales, suggested that the sperm whales are more closely related to the baleen whales than they are to other toothed whales, which would have meant that Odontoceti were not monophyletic; in other words, it did not consist of a single ancestral toothed whale species and all its descendants. However, more recent studies, based on various combinations of comparative anatomy and molecular phylogenetics, criticised Milinkovitch's analysis on technical grounds and reaffirmed that the Odontoceti are monophyletic.
These analyses also confirm that there was a rapid evolutionary radiation (diversification) of the Physeteroidea in the Miocene period. The Kogiidae (dwarf and pygmy sperm whales) diverged from the Physeteridae (true sperm whales) at least 8 million years ago.
Relationship with humans
Historical hunting
See also: Whaling and Sperm whaling
Spermaceti, obtained primarily from the spermaceti organ, and sperm oil, obtained primarily from the blubber in the body, were much sought after by eighteenth, nineteenth, and twentieth century whalers. These substances found a variety of commercial applications, such as candles, soap, cosmetics, machine oil, other specialized lubricants, lamp oil, pencils, crayons, leather waterproofing, rust-proofing materials and many pharmaceutical compounds. Ambergris, a solid, waxy, flammable substance produced in the digestive system of sperm whales, was also sought as a fixative in perfumery.
Prior to the early eighteenth century, hunting was mostly by indigenous Indonesians. Legend has it that sometime in the early eighteenth century, around 1712, Captain Christopher Hussey, while cruising for right whales near shore, was blown offshore by a northerly wind, where he encountered a sperm whale pod and killed one. Although the story may not be true, sperm whales were indeed soon exploited by American whalers. Judge Paul Dudley, in his Essay upon the Natural History of Whales (1725), states that one Atkins, ten or twelve years in the trade, was among the first to catch sperm whales sometime around 1720 off the New England coast.
There were only a few recorded catches during the first few decades (1709–1730s) of offshore sperm whaling. Instead sloops concentrated on Nantucket Shoals where they would have taken right whales or went to the Davis Strait region to catch bowhead whales. By the early 1740s, with the advent of spermaceti candles (before 1743), American vessels began to focus on sperm whales. The diary of Benjamin Bangs (1721–1769) shows that, along with the bumpkin sloop he sailed, he found three other sloops flensing sperm whales off the coast of North Carolina in late May 1743. On returning to Nantucket in the summer 1744 on a subsequent voyage he noted that "45 spermacetes are brought in here this day," another indication that American sperm whaling was in full swing.
American sperm whaling soon spread from the east coast of the American colonies to the Gulf Stream, the Grand Banks, West Africa (1763), the Azores (1765), and the South Atlantic (1770s). From 1770 to 1775 Massachusetts, New York, Connecticut, and Rhode Island ports produced 45,000 barrels of sperm oil annually, compared to 8,500 of whale oil. In the same decade the British began sperm whaling, employing American ships and personnel. By the following decade the French had entered the trade, also employing American expertise. Sperm whaling increased until the mid-nineteenth century. Spermaceti oil was important in public lighting (for example, in lighthouses, where it was used in the United States until 1862, when it was replaced by lard oil, in turn replaced by petroleum) and for lubricating the machines (such as those used in cotton mills) of the Industrial Revolution. Sperm whaling declined in the second half of the nineteenth century, as petroleum came into broader use. In that sense, it may be said to have protected whale populations from even greater exploitation. Sperm whaling in the eighteenth century began with small sloops carrying only one or two whaleboats. The fleet's scope and size increased over time, and larger ships entered the fishery. In the late eighteenth century and early nighteenth century sperm whaling ships sailed to the equatorial Pacific, the Indian Ocean, Japan, the coast of Arabia, Australia and New Zealand. Hunting could be dangerous to the crew, since sperm whales (especially bulls) will readily fight to defend themselves against attack, unlike most baleen whales. When dealing with a threat, sperm whales will use their huge head effectively as a battering ram. Arguably the most famous sperm whale counterattack occurred on 20 November 1820, when a whale claimed to be about 25.9 metres (85 ft) long rammed and sank the Nantucket whaleship Essex. Only 8 out of 21 sailors survived to be rescued by other ships. This instance is popularly believed to have inspired Herman Melville's famous book "Moby-Dick".

The sperm whale's ivory-like teeth were often sought by 18th and 19th-century whalers, who used them to produce inked carvings known as scrimshaw. Thirty teeth of the sperm whale can be used for ivory. Each of these teeth (up to 20 cm (8 in) and 7.6 cm (3 in) across), are hollow for the first half of their length. Like walrus ivory, sperm whale ivory has two distinct layers. However, sperm whale ivory contains a much thicker inner layer. Though a widely practiced art in the nineteenth century, scrimshaw using genuine sperm whale ivory declined substantially after the retirement of the whaling fleets in the 1880s. Currently the Endangered Species Act and CITES, the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, prevents the sales of or trade in sperm whale ivory harvested after 1973 or in scrimshaw crafted from it.
Modern whaling was more efficient than open-boat whaling, employing steam-powered ships and exploding harpoons. Initially, modern whaling activity focused on large baleen whales, but as these populations were taken, sperm whaling increased. This was especially true during World War II when spermaceti, the fine waxy oil produced by sperm whales, was in high demand for lubricating the American war machine. In both the 1941-2 and 1942-3 seasons, the Norwegian expedition took over 3,000 sperm whales off the coast of Peru alone. After the war whaling continued unabated to obtain oil for cosmetics and high-performance machinery, such as automobile transmissions.
The hunting led to the near extinction of large whales including sperm whales until bans on whale oil use were instituted in 1972. The International Whaling Commission gave the species full protection in 1985 but hunting by Japan in the northern Pacific Ocean continued until 1988.
It is estimated that the historic worldwide population numbered 1,100,000 before commercial sperm whaling began in the early eighteenth century. By 1880 it had declined by an estimated 29 per cent. From that date until 1946 the population appears to have recovered somewhat as whaling pressure lessened, but after the Second World War, the population declined even further, to only 33 per cent of the pre-whaling era. It has been estimated that in the nineteenth century between 184,000 and 236,000 sperm whales were killed by the various whaling nations, while in the modern era, at least 770,000 were taken, the majority between 1946 and 1980.

Sperm whales increase the levels of primary production and carbon export by depositing iron rich faeces into surface waters of the Southern Ocean. The iron rich faeces cause phytoplankton to grow and take up more carbon from the atmosphere. When the phytoplankton dies, it sinks to the deep ocean and takes the atmospheric carbon with it. By reducing the abundance of sperm whales in the Southern Ocean, whaling has resulted in an extra 2 million tonnes of carbon remaining in the atmosphere each year.
Remaining sperm whale populations are large enough that the species' conservation status is rated as vulnerable rather than endangered. However, the recovery from the whaling years is a slow process, particularly in the South Pacific, where the toll on breeding-age males was severe.
Current conservation status
The number of sperm whales throughout the world is unknown, but is thought to be in the hundreds of thousands. The conservation outlook is brighter than for many other whales. Historically, Japan has taken ten sperm whales a year, and until 2006 tens of these whales were hunted off Indonesia. They are protected practically worldwide, and commercial whaling has ceased. Fishermen do not target the creatures that sperm whales eat. However, long-line fishing operations in the Gulf of Alaska have complained about sperm whales stealing fish from their lines.
Entanglement in fishing nets and collisions with ships represent the greatest threats to the sperm whale population currently. Other current threats include ingestion of marine debris, ocean noise, and chemical pollution. The IUCN regards the sperm whale as being "vulnerable". The species is listed as endangered on the United States Endangered Species Act.
The species is listed on Appendix I and Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). It is listed on Appendix I as this species has been categorized as being in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant proportion of their range and CMS Parties strive towards strictly protecting these animals, conserving or restoring the places where they live, mitigating obstacles to migration and controlling other factors that might endanger them. It is listed on Appendix II as it has an unfavourable conservation status or would benefit significantly from international co-operation organised by tailored agreements. It is also covered by the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans in the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area (ACCOBAMS) and Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MOU).
Cultural importance
Rope-mounted teeth are important cultural objects throughout the Pacific. In New Zealand, the Māori know them as "rei puta"; such whale tooth pendants were rare objects because sperm whales were not actively hunted in traditional Māori society. Whale ivory and bone were taken from beached whales. In Fiji the teeth are known as tabua and they were traditionally given as gifts for atonement or esteem (called sevusevu), and were important in negotiations between rival chiefs. Friedrich Ratzel in The History of Mankind reported in 1896 that, in Fiji, whales' or cachalots' teeth were the most-demanded article of ornament or value. They occurred often in necklaces. Today the tabua remains an important item in Fijian life. The teeth were originally rare in Fiji and Tonga, which exported teeth, but with the Europeans' arrival, teeth flooded the market and this "currency" collapsed. The oversupply led in turn to the development of the European art of scrimshaw.
Herman Melville's novel Moby-Dick is based on a true story about a sperm whale that attacked and sank the whaleship Essex. Melville associated the sperm whale with the Bible's Leviathan. The fearsome reputation perpetuated by Melville was based on bull whales' ability to fiercely defend themselves from attacks by early whalers, occasionally resulting in the destruction of the whaling ships.
The sperm whale was designated as the Connecticut state animal by the CT General Assembly in 1975. It was selected because of its specific contribution to the state's history and because of its present-day plight as an endangered species.
Watching sperm whales
See also: Whale watchingSperm whales are not the easiest of whales to watch, due to their long dive times and ability to travel long distances underwater. However, due to the distinctive look and large size of the whale, watching is increasingly popular. Sperm whale watchers often use hydrophones to listen to the clicks of the whales and locate them before they surface. Popular locations for sperm whale watching include the town of Kaikoura on New Zealand's South Island, Andenes and Tromsø in Arctic Norway; as well as the Azores, where the continental shelf is so narrow that whales can be observed from the shore, and Dominica where a long-term scientific research program, The Dominica Sperm Whale Project, has been in operation since 2005.
See also
- List of cetaceans whale and dolphin species
- Marine biology
Notes
Footnotes
- Until 1974 the species was generally known as P. catodon. In that year, however, Husson & Holthuis proposed that the correct name should be P. macrocephalus, the second name in the genus Physeter published by Linnaeus concurrently with P. catodon. This proposition was based on the grounds that the names were synonyms published simultaneously, and, therefore, the ICZN Principle of the First Reviser should apply. In this instance, it led to the choice of P. macrocephalus over P. catodon, a view re-stated in Holthuis, 1987. This has been adopted by most subsequent authors, although Schevill (1986 and 1987) argued that macrocephalus was published with an inaccurate description and that therefore only the species catodon was valid, rendering the principle of "First Reviser" inapplicable. At the present time, the name P. catodon is used in the Catalogue of Life. However, this is expected to be changed to follow the most recent version of ITIS, which has recently altered its usage from P. catodon to P. macrocephalus following L. B. Holthuis, and more recent (2008) discussions with relevant experts (refer cited ITIS page for additional information).
Citations
- Mead, J. G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 737. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Template:IUCN2008
- ^ Lee, Jane J. (26 March 2014). "Elusive Whales Set New Record for Depth and Length of Dives Among Mammals". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 29 March 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Trivedi, Bijal P. (3 November 2003). "Sperm Whale "Voices" Used to Gauge Whales' Sizes". news.nationalgeographic.com.
- Degrati, M., García, NA, Grandi, MF, Leonardi, MS, de Castro, R, Vales, D., Dans, S., Pedraza, SN & Crespo EA (2011). "The oldest sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus): new record with notes on age, diet and parasites, and a review of strandings along the continental Argentine coast". Mastozoología Neotropical. 18 (2).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wahlberg, Magnus; Frantzis, Alexandros; Alexiadou, Paraskevi; Madsen, Peter T.; Møhl, Bertel (2005). "Click production during breathing in a sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus)". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 118 (6): 3404–7. Bibcode:2005ASAJ..118.3404W. doi:10.1121/1.2126930. PMID 16419786.
- Haupt, P. (1907). "Jonah's Whale". Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society. 46 (185): 155. ISBN 978-1-4223-7345-3.
- Fеrnandez-Casado, M. (2000). "El Cachalote (Physeter macrocephalus)" (PDF). Galemys. 12 (2): 3.
- Corominas, Joan (1987). Breve diccionario etimológico de la lengua castellana. Madrid: Gredos. ISBN 84-249-1332-9.
- ^ Shirihai, H. and Jarrett, B. (2006). Whales, Dolphins, and Other Marine Mammals of the World. Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press. pp. 21–24. ISBN 0-691-12757-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Whitehead, H. "Sperm whale Physeter macrocephalus", pp. 1165–1172 in Perrin
- "Physeter macrocephalus, Sperm Whale". marinebio.org.
- Shirihai, H. and Jarrett, B. (2006). Whales, Dolphins, and Other Marine Mammals of the World. Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press. pp. 112–115. ISBN 0-691-12757-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Maury, M. (1853). Explanations and Sailing Directions to Accompany the Wind and Current Charts. C. Alexander. p. 297.
- ^ "Sperm Whale". Archived from the original on 20 February 2007.
- Ellis, Richard (2011). The Great Sperm Whale: A Natural History of the Ocean's Most Magnificent and Mysterious Creature. Zoology. Vol. 179. USA: University Press of Kansas. p. 432. ISBN 978-0-7006-1772-2. Zbl 0945.14001.
- Kasuya, Toshio (July 1991). "Density dependent growth in North Pacific sperm whales". Marine Mammal Science. 7 (3). USA: Wiley: 230–257. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1991.tb00100.x.
- Gordon, Jonathan (1998). Sperm Whales, Voyageur Press, p. 14, ISBN 0-89658-398-8
- Carwardine, Mark (1994). On the Trail of the Whale. Chapter 1. Thunder Bay Publishing Co. ISBN 1-899074-00-7.
- ^ Reeves, R., Stewart, B., Clapham, P. & Powell, J. (2003). Guide to Marine Mammals of the World. New York: A.A. Knopf. pp. 240–243. ISBN 0-375-41141-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus): Species Accounts". Retrieved 12 October 2008.
- "Offshore Cetacean Species". CORE. Retrieved 12 October 2008.
- How does pressure change with ocean depth?. Oceanservice.noaa.gov (2013-01-11). Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- The science behind whales' asymmetrical skulls. Io9.com. Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- ^ Jefferson, T.A., Webber, M.A. & Pitman, R.L. (2008). Marine Mammals of the World: a comprehensive guide to their identification. London: Elsevier. pp. 74–78. ISBN 978-0-12-383853-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Sper Wale Physeter macrocephalus". American Cetacean Society Fact Sheet. Archived from the original on 13 June 2010.
- "Sperm Whale Facts". whale-images.com.
- Whitehead, p. 4
- Perrin, p. 8
- The Southwestern Company (1987): "The Volume Library 1", p. 65, ISBN 0-87197-208-5
- Carter, L., Burnett, D., Drew, S., Marle, G., Hagadorn, L., Bartlett-McNeil D., & Irvine N. (December 2009). Submarine cables and the oceans: connecting the world, UNEP-WCMC, p. 31, ISBN 978-0-9563387-2-3
- Kooyman, G. L.& Ponganis, P. J. (October 1998). "The Physiological Basis of Diving to Depth: Birds and Mammals". Annual Review of Physiology. 60 (1): 19–32. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.19. PMID 9558452.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Tyack, P., Johnson, M., Aguilar Soto, N., Sturlese, A. & Madsen, P. (18 October 2006). "Extreme diving of beaked whales". Journal of Experimental Biology. 209 (Pt 21): 4238–4253. doi:10.1242/jeb.02505. PMID 17050839.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Noren, S. R. & Williams, T. M. (June 2000). "Body size and skeletal muscle myoglobin of cetaceans: adaptations for maximizing dive duration". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology – Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 126 (2): 181–191. doi:10.1016/S1095-6433(00)00182-3. PMID 10936758.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Marshall, C. "Morphology, Functional; Diving Adaptations of the Cardiovascular System", p. 770 in Perrin
- "Aquarium of the Pacific – Sperm Whale". Aquarium of the Pacific. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- Shwartz, Mark (8 March 2007). "Scientists conduct first simultaneous tagging study of deep-diving predator, prey". Stanford Report. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- ^ Clarke, M. (1978). "Structure and Proportions of the Spermaceti Organ in the Sperm Whale" (PDF). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 58: 1–17. doi:10.1017/S0025315400024371. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- Moore MJ, Early GA (2004). "Cumulative sperm whale bone damage and the bends". Science. 306 (5705): 2215. doi:10.1126/science.1105452. PMID 15618509.
- Cawardine, Mark (2002) Sharks and Whales', Five Mile Press, p. 333, ISBN 1-86503-885-7
- Whitehead, pp. 156–161
- Ommanney, F. 1971. Lost Leviathan. London.
- "Sperm Whales (Physeter macrocephalus)". U.S. Department of Commerce NOAA Office of Protected Resources. Retrieved 7 November 2008.
- ^ Marino, L. (2004). "Cetacean Brain Evolution Multiplication Generates Complexity" (PDF). International Journal of Comparative Psychology. 17: 3–4.
- Fields, R. Douglas (2008-01-15) Are Whales Smarter Than We Are? Scientific American.
- Whitehead, p. 323
- Dicke, U. (August/September 2008). "Intelligence Evolved". Scientific American Mind. pp. 71–77. doi:10.1038/scientificamericanmind0808-70.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Oelschläger, Helmut H.A.; Kemp, Birgit (1998). "Ontogenesis of the sperm whale brain". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 399 (2): 210–28. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19980921)399:2<210::AID-CNE5>3.0.CO;2–3. PMID 9721904.
{{cite journal}}: Check|doi=value (help) - Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1981.tb01418.x, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1111/j.1601-5223.1981.tb01418.xinstead. - "SEASWAP: Genetic Sampling". Seaswap.info. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- Inside Natures Giants: The Sperm Whale. Channel 4
- ^ "Whale Digestion". Chip.choate.edu. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- Tinker, Spencer Wilkie (1988). Whales of the World. Brill Archive, p. 62, ISBN 0-935848-47-9
- Name (required). ""20000 Leagues Under the Sea" Part2 Ch12 | Nikolaus6's Weblog". Nikolaus6.wordpress.com. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- ^ Professor Malcolm Clarke - discusses the anatomy of sperm whales - YouTube
- George J. Race, W. L. Jack Edwards, E. R. Halden, Hugh E. Wilson, and Francis J. Luibel, (1959). A Large Whale Heart. Circulation, 1959;19:928–932
- Shadwick RE, Gosline JM (1995). "Arterial Windkessels in marine mammals". Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology. 49: 243–52. PMID 8571227.
- ^ Melnikov VV (October 1997). "The arterial system of the sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus)". Journal of Morphology. 234 (1): 37–50. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4687(199710)234:1<37::AID-JMOR4>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID 9329202.
- Bjerager, P.; Heegaard, S. and Tougaar, J. (2003). "Anatomy of the eye of the sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus L.)". Aquatic Mammals. 29: 31. doi:10.1578/016754203101024059.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cranford, T.W. (2000). "In Search of Impulse Sound Sources in Odontocetes". In Au, W.W.L, Popper, A.N. & Fay, R.R. (ed.). Hearing by Whales and Dolphins (Springer Handbook of Auditory Research series). Springer-Verlag, New York. ISBN 0-387-94906-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Zimmer, W.M.X., Tyack, P.L., Johnson, M.P. & Madsen, P.T.; Tyack; Johnson; Madsen (2005). "Three dimensional beam pattern of regular sperm whale clicks confirms bent-horn hypothesis". Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 117 (3 Pt 1): 1473–1485. Bibcode:2005ASAJ..117.1473Z. doi:10.1121/1.1828501. PMID 15807035.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Norris, K.S. & Harvey, G.W. (1972). "A theory for the function of the spermaceti organ of the sperm whale". In Galler, S.R, Schmidt-Koenig, K, Jacobs, G.J. & Belleville, R.E. (ed.). Animal orientation and navigation. NASA, Washington, D.C. pp. 397–417.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cranford, T.W. (1999). "The Sperm Whale's Nose: Sexual Selection on a Grand Scale?". Marine Mammal Science. 15 (4): 1133–1157. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00882.x.
- ^ Madsen, P.T., Payne, R., Kristiansen, N.U., Wahlberg, M., Kerr, I. & Møhl, B. (2002). "Sperm whale sound production studied with ultrasound time/depth-recording tags". Journal of Experimental Biology. 205 (Pt 13): 1899–1906. PMID 12077166.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Møhl, B. (2001). "Sound transmission in the nose of the sperm whale Physeter Catodon: a post-mortem study". Journal of Comparative Physiology A. 187 (5): 335–340. doi:10.1007/s003590100205.
- ^ Møhl, B., Wahlberg, M., Madsen, P.T., Miller, L.A. & Surlykke, A.; Wahlberg; Madsen; Miller; Surlykke (2000). "Sperm whale clicks: directionality and sound levels revisited". Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 107 (1): 638–648. Bibcode:2000ASAJ..107..638M. doi:10.1121/1.428329. PMID 10641672.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Møhl, B., Wahlberg, M., Madsen, P.T., Heerfordt, A. & Lund, A.; Wahlberg; Madsen; Heerfordt; Lund (2003). "The monopulsed nature of sperm whale clicks". Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 114 (2): 1143–1154. Bibcode:2003ASAJ..114.1143M. doi:10.1121/1.1586258. PMID 12942991.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Whitehead, pp. 277–279
- Taxonomy | Natural History Museum. Nhm.ac.uk. Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- Whitehead, p. 321
- Perrin, p. 1164
- Morris, Robert J. (1975). "Further studies into the lipid structure of the spermaceti organ of the sperm whale (Physeter catodon)". Deep-Sea Research. 22 (7): 483–489. Bibcode:1975DSROA..22..483M. doi:10.1016/0011-7471(75)90021-2.
- ^ Norris, Kenneth S. and Harvey, George W. (1972). "A Theory for the Function of the Spermaceti Organ of the Sperm Whale". Animal orientation and navigation. NASA.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Clarke, M. (1978). "Physical Properties of Spermaceti Oil in the Sperm Whale" (PDF). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 58: 19–26. doi:10.1017/S0025315400024383. Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- Clarke, M.R. (November 1970). "Function of the Spermaceti Organ of the Sperm Whale". Nature. 228 (5274): 873–874. Bibcode:1970Natur.228..873C. doi:10.1038/228873a0. PMID 16058732.
- Whitehead, pp. 317–321
- "Spermaceti as battering ram?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2006. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- ^ Carrier, D., Deban, S. & Otterstrom, J. (2002). "The face that sank the Essex: potential function of the spermaceti organ in aggression" (PDF). The Journal of Experimental Biology. 205 (Pt 12): 1755–1763. PMID 12042334.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 8622183, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=8622183instead. - Backus, R.H.; Schevill, W.E. (1966). "Physeter clicks". In Norris, K.S. (ed.). Whales, dolphins and porpoises. University of California Press, Berkeley, California. pp. 510–527.
- Goold, J.C. (1996). "Signal processing techniques for acoustic measurement of sperm whale body lengths". Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 100 (5): 3431–3441. Bibcode:1996ASAJ..100.3431G. doi:10.1121/1.416984. PMID 8914321.
- ^ Gordon, J.C.D. (1991). "Evaluating a method for determining the length of sperm whales (Physeter Catodon) from their vocalizations". Journal of Zoology, London. 224 (2): 301–314. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1991.tb04807.x.
- Whitlow, W. "Echolocation", pp. 359–367 in Perrin
- "Whale Sounds". Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa.
- ^ Whitehead, p. 141
- Whitehead, p. 131
- Moore, K. E.; Watkins, W. A.; Tyack, P. L. (1993). "Pattern similarity in shared codas from sperm whales (Physeter catodon)". Marine Mammal Science. 9: 1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1993.tb00421.x.
- Whitehead, p. 144
- Whitehead, p. 135
- Whitehead, p. 33
- Murray, J. W., Jannasch, H. W., Honjo, S., Anderson, R. F., Reeburgh, W. S., Top, Z., Friederich, G. E., Codispoti, L. A. & Izdar E. (30 March 1989). "Unexpected changes in the oxic/anoxic interface in the Black Sea". Nature. 338 (6214): 411–413. Bibcode:1989Natur.338..411M. doi:10.1038/338411a0.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Whitehead, pp. 23–24
- Whitehead, H. & Weilgart, L. (2000). "The Sperm Whale". In Mann, J., Connor, R., Tyack, P. & Whitehead, H. (ed.). Cetacean Societies. The University of Chicago Press. p. 169. ISBN 0-226-50341-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Whitehead, p. 276
- Ellis, Richard (2011). The Great Sperm Whale: A Natural History of the Ocean's Most Magnificent and Mysterious Creature. Zoology. Vol. 179. USA: University Press of Kansas. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-7006-1772-2. Zbl 0945.14001.
- Whitehead, p. 343
- ^ Whitehead, p. 122
- Whitehead, p. 123
- Whitehead, p. 185
- ^ Mammals in the Seas Vol. 3: General Papers & Large Cetaceans (Fao/Unep). Food & Agriculture Org. 1981. p. 499. ISBN 978-92-5-100513-2.
- General Whale Information. Biology.kenyon.edu. Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- Whale Milk. Whalefacts.org. Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- Milk Calorie Counter. Calorielab.com. Retrieved on 2013-03-19.
- Whitehead, p. 347
- Whitehead, p. 232
- Whitehead, p. 233
- Whitehead, p. 235
- Whitehead, p. 204
- Pitman RL, Ballance LT, Mesnick SI, Chivers SJ (2001). "Killer whale predation on sperm whales: Observations and implications". Marine Mammal Science. 17 (3): 494–507. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01000.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Whitehead, H. & Weilgart, L. (2000). "The Sperm Whale". In Mann, J., Connor, R., Tyack, P. & Whitehead, H. (ed.). Cetacean Societies. The University of Chicago Press. p. 165. ISBN 0-226-50341-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Orcas battle sperm whales in cetacean battle royal – life – 03 May 2013". New Scientist. Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- Piper, Ross (2007), Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals, Greenwood Press.
- Estes, J. (2006). Whales, Whaling, and Ocean Ecosystems. University of California Press. p. 179. ISBN 0-520-24884-8. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- Poon, Linda (23 January 2013). "Deformed Dolphin Accepted Into New Family". National Geographic News. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ Whitehead, p. 79
- ^ Whitehead, pp. 43–55
- Smith S. & Whitehead, H. (2000). "The Diet of Galapagos sperm whales Physeter macrocephalus as indicated by faecal sample analysis". Marine Mammal Science. 16 (2): 315–325. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2000.tb00927.x.
- Perkins, S. (23 February 2010). "Sperm Whales Use Teamwork to Hunt Prey". Wired. Retrieved 24 February 2010.
- Clapham, Philip J. (November–December 2011). "Mr. Melville's Whale". American Scientist. 6. 99: 505–506.
- Gaskin D. & Cawthorn M. (1966). "Diet and feeding habits of the sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus L.) in the Cook Strait region of New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 1 (2): 156–179. doi:10.1080/00288330.1967.9515201.
- ^ "Sneaky Cetaceans". Arctic Science Journeys. Retrieved 4 November 2008.
- "Whale Buffet". Archived from the original on 7 February 2007. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
- "FLMNH Ichthyology Department: Megamouth". Flmnh.ufl.edu. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Compagno, L. J. V. (2001). Sharks of the World Volume 2 Bullhead, mackerel and carpet sharks (PDF). FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. pp. 74–78.
- Dannenfeldt K.H. (1982). "Ambergris: The Search for Its Origin". Isis. 73 (3): 382–397. doi:10.1086/353040. PMID 6757176.
- Ellis, R. (1994). Monsters of the Sea. The Lyons Press. p. 245. ISBN 1-59228-967-3.
- "State of World Fisheries 2010" (PDF). FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS. p. 21.
- Benoit-Bird K. Au W. & Kastelein R. (August 2006). "Testing the odontocete acoustic prey debilitation hypothesis: No stunning results". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 120 (2): 1118–1123. Bibcode:2006ASAJ..120.1118B. doi:10.1121/1.2211508. PMID 16938998.
- Channel 4 British television program Jimmy and the Whale Whisperer, Sunday 23 September 2012, 7 pm to 8 pm
- Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 20554546, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=20554546instead. - Howard, Jacqueline (8 September 2012). "Sperm Whales Sleep While 'Drifting' Vertically, Scientists Say (VIDEO)". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- Mead, J. G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 723–743. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Lambert, O., Bianucci, G. & de Muizon, C. (August 2008). "A new stem-sperm whale (Cetacea, Odontoceti, Physeteroidea) from the Latest Miocene of Peru". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 7 (6): 361–369. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2008.06.002.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Template:La icon Linnaeus, Carolus (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 824.
- ^ Fordyce, R.E., and Barnes, L.G. (May 1994). "The Evolutionary History of Whales and Dolphins" (PDF). Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 22: 419–455. Bibcode:1994AREPS..22..419F. doi:10.1146/annurev.ea.22.050194.002223. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bianucci, G. & Landini, W. (8 September 2006). "Killer sperm whale: a new basal physeteroid (Mammalia, Cetacea) from the Late Miocene of Italy". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 148 (1): 103–131. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2006.00228.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Stucky, R.E. and McKenna, M.C. (1993). "Mammalia". In Benton, M.J. (ed.). The Fossil Record. London.: Chapman & Hall. pp. 739–771.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mchedlidze, G. "Sperm whales, evolution", pp. 1172–1174 in Perrin
- ^ Hirota, K. & Barnes, L. G. (5 April 2006). "A new species of Middle Miocene sperm whale of the genus Scaldicetus (Cetacea; Physeteridae) from Shiga-mura, Japan". Island Arc. 3 (4): 453–472. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1738.1994.tb00125.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Bianucci, G., Landrini, W. & Varola, W. (September–October 2004). "First discovery of the Miocene northern Atlantic sperm whale Orycterocetus in the Mediterranean". Geobios. 37 (5): 569–573. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2003.05.004.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nikaido, M., Matsuno, F., Hamilton, H., Brownwell, R., Cao, Y., Ding, W., Zuoyan, Z., Shedlock, A., Fordyce, R. E., Hasegawa, M. & Okada, N. (19 June 2001). "Retroposon analysis of major cetacean lineages: The monophyly of toothed whales and the paraphyly of river dolphins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (13): 7384–7389. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.7384N. doi:10.1073/pnas.121139198. PMC 34678. PMID 11416211. Retrieved 1 November 2008.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Whitehead, pp. 2–3
- Heyning, J. (23 August 2006). "Sperm Whale Phylogeny Revisited: Analysis of the Morphological Evidence". Marine Mammal Science. 13 (4): 596–613. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1997.tb00086.x.
- Wilson, D. (1999). The Smithsonian Book of North American Mammals. Vancouver: UBC Press. p. 300. ISBN 0-7748-0762-8.
- The Southampton Oceanography Centre & A deFontaubert. "The status of natural resources on the high seas" (PDF). IUCN. p. 63. Retrieved 11 October 2008.
- Jamieson, A. (1829). A Dictionary of Mechanical Science, Arts, Manufactures, and Miscellaneous Knowledge. H. Fisher, Son & Co. p. 566.
- "Aquarium of the Pacific – Sperm Whale". Retrieved 11 October 2008.
- Whitehead, p. 14
- Simons, B. "Christopher Hussey Blown Out (Up) to Sea". Nantucket Historical Association.
- Dudley, P. (1725). "An Essay upon the Natural History of Whales, with a Particular Account of the Ambergris Found in the Sperma Ceti Whale". Philosophical Transactions (1683–1775), Vol. 33. The Royal Society. p. 267.
- ^ Dolin, E. (2007). Leviathan: The History of Whaling in America. W. W. Norton. pp. 98–100. ISBN 0-393-06057-8.
- Starbuck, A. (1878). History of the American Whale Fishery from its Earliest Inception to the Year 1876. ISBN 0-665-35343-X.
- ^ Bockstoce, J. (December 1984). "From Davis Strait to Bering Strait: The Arrival of the Commercial Whaling Fleet in North America's West Arctic" (PDF). Arctic. 37 (4): 528–532.
- Estes, J. (2006). Whales, Whaling, and Ocean Ecosystems. University of California Press. p. 329. ISBN 0-520-24884-8.
- ^ Whitehead, pp. 13–21
- Stackpole, E. A. (1972). Whales & Destiny: The Rivalry between America, France, and Britain for Control of the Southern Whale Fishery, 1785–1825. The University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 0-87023-104-9.
- Baldwin, R., Gallagher, M., and van Waerebeek, K. "A Review of Cetaceans from Waters off the Arabian Peninsula" (PDF). p. 6. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "The Wreck of the Whaleship Essex". BBC. Retrieved 11 October 2008.
- Divers find shipwreck of doomed sailor who inspired classic tale of Moby Dick off coast of Hawaii. dailymail.co.uk (2011-02-12)
- Davis, L, Gallman, R. & Gleiter, K. (1997). In Pursuit of Leviathan: Technology, Institutions, Productivity, and Profits in American Whaling, 1816–1906 (National Bureau of Economic Research Series on Long-Term Factors in Economic Dev). University of Chicago Press. p. 135. ISBN 0-226-13789-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Over 680,000 officially reported at "Whaling Statistics". Retrieved 15 October 2008.. In addition, studies have found that official reports understated USSR catches by at least 89,000 "Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus) California/Oregon/Washington Stock" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2008. Furthermore, other countries, such as Japan have been found to have understated catches "The RMS – A Question of Confidence: Manipulations and Falsifications in Whaling" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2008.
- Lavery, Trish L., Ben Roudnew, Peter Gill, Justin Seymour, Laurent Seuront, Genevieve Johnson, James G. Mitchell & Victor Smetacek (2010). "Iron defecation by sperm whales stimulates carbon export in the Southern Ocean". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 277 (1699): 3527–3531. doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.0863. PMC 2982231. PMID 20554546.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Whitehead, pp. 360–362
- Whitehead, pp. 362–368
- "Sperm whale (Physeter catodon) species profile". Environmental Conservation Online System. United States Fish and Wildlife Service. 16 November 2010.
- ^ "Appendix I and Appendix II" of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). As amended by the Conference of the Parties in 1985, 1988, 1991, 1994, 1997, 1999, 2002, 2005 and 2008. Effective: 5 March 2009.
- "Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa Collections Online Search – Rei puta". Retrieved 15 March 2009.
-
Arno, A. (2005). "Cobo and tabua in Fiji: Two forms of cultural currency in an economy of sentiment". American Ethnologist. 32 (1): 46–62. doi:10.1525/ae.2005.32.1.46. INIST 16581746.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Ratzel, Friedrich (1896). "Dress and Weapons of the Melanesians: Ornament", The History of Mankind. London: MacMillan. Accessed 21 October 2009.
- Constantine, R. "Folklore and Legends", p. 449 in Perrin
- Van Doren, Carl (1921). "Chapter 3. Romances of Adventure. Section 2. Herman Melville". The American Novel. Bartleby.com. Retrieved 19 October 2008.
- ^ Zwart, H. (2000). What is a Whale? Moby Dick, marine science and the sublime (PDF). Tubingen Attempo. pp. 185–214. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 March 2009.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Edwards, B. "The Playful Learnings" (PDF). Australasian Journal of American Studies. 25 (1): 1–13 (9).
- "The State Animal". State of Connecticut Sites, Seals and Symbols. Reproduced from the Connecticut State Register & Manual: State of Connecticut. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|place= - "Whale and dolphin watching in the Azores". Wildlife Extra. Retrieved 26 September 2008.
- "Whale Watching Dominica". Archived from the original on 27 January 2010. Retrieved 26 September 2008.
- "The Dominica Sperm Whale Project". Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- Husson A.M., Holthuis L.B. (1974). "Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758, the valid name for the sperm whale". Zoologische Mededelingen. 48: 205–217.
- Holthuis L. B. (1987). "The scientific name of the sperm whale". Marine Mammal Science. 3 (1): 87–89. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1987.tb00154.x.
- Schevill W.E. (1986). "The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and a paradigm: the name Physeter catodon Linnaeus 1758". Marine Mammal Science. 2 (2): 153–157. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1986.tb00036.x.
- Schevill W.E. (1987). "Reply to L. B. Holthuis "The scientific name of the sperm whale". Marine Mammal Science. 3 (1): 89–90. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1987.tb00155.x.
- Whitehead, p. 3
References
- Perrin, William F.; Würsig, Bernd and Thewissen, J.G.M., ed. (2002). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. San Diego, Calif.: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-551340-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - Whitehead, H. (2003). Sperm Whales: Social Evolution in the Ocean. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-226-89518-1.
Further reading
- Carwardine, Hoyt, Fordyce & Gill (1998). Whales & Dolphins: The Ultimate Guide to Marine Mammals. London: HarperCollins. ISBN 0-00-220105-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Heptner, V. G.; Nasimovich, A. A; Bannikov, Andrei Grigorevich; Hoffmann, Robert S, Mammals of the Soviet Union, Volume II, part 3 (1996). Washington, D.C. : Smithsonian Institution Libraries and National Science Foundation
External links
- Spermaceti in candles 22 July 2007
- Society for Marine Mammalogy Sperm Whale Fact Sheet
- US National Marine Fisheries Service Sperm Whale web page
- 70South—information on the sperm whale
- "Physty"-stranded sperm whale nursed back to health and released in 1981
- ARKive—Photographs, video.
- Whale Trackers—An online documentary film exploring the sperm whales in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Convention on Migratory Species page on the Sperm Whale
- Website of the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region
- Official website of the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans in the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area
- Retroposon analysis of major cetacean lineages: The monophyly of toothed whales and the paraphyly of river dolphins 19 June 2001
- The Dominica Sperm Whale Project- a long-term scientific research program focusing on the behaviour of sperm whale units.
Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: