| Revision as of 02:17, 14 July 2019 editFrescoBot (talk | contribs)Bots1,135,457 editsm Bot: link syntax and minor changes← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:53, 23 August 2019 edit undoReywas92 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers81,320 edits copyeditsTags: nowiki added Visual editNext edit → | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| | website = {{URL|http://www.euroasia-interconnector.com}} | | website = {{URL|http://www.euroasia-interconnector.com}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''EuroAsia Interconnector'''<ref></ref> is |
The '''EuroAsia Interconnector'''<ref></ref> is a planned ] between ], ], and ]i ]s via the world's longest ].<ref name=reuters230112> | ||
| {{cite news | {{cite news | ||
| | title = Cyprus group plans Greece-Israel electricity link | | title = Cyprus group plans Greece-Israel electricity link | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| | quote=A Cyprus-based group including Greece's state-controlled power utility PPC said on Monday it planned to lay the world's longest subsea power cable linking Europe and Asia.}} | | quote=A Cyprus-based group including Greece's state-controlled power utility PPC said on Monday it planned to lay the world's longest subsea power cable linking Europe and Asia.}} | ||
| </ref><ref name="EA"></ref> | </ref><ref name="EA"></ref> | ||
| It is a |
It is a major Project of Common Interest of the ] and a priority Electricity Highway Interconnector Project,<ref name="EU"></ref><ref name="FU"></ref><ref name="PC1"></ref><ref name="PC2"></ref><ref name="PC3"></ref><ref name="EC"></ref> as an energy highway bridging ] and ]. Regulatory approval of electricity interconnection and cost allocation between ] and ] was completed on October 10, 2017. It is historic decision for ], ending electricity isolation of the last ] member state.<ref></ref><ref name="ACER"></ref><ref name="CERA"></ref><ref name="PHIL"></ref> | ||
| According to ] analysis, |
According to ] analysis, the interconnector will contribute to social and ] between €580m and €1.12 billion in each year.<ref name="ENTSO"/> ] calculated that expected reduction of {{CO2}} is between 1.3 and 6.8 million tonnes each year, or between 21% and 110% of total emissions of Cyprus.<ref name="ENTSO"/> | ||
| On May 12, 2017 |
On May 12, 2017 the ] ] met the ] Chairman ]<nowiki/>in Beijing, and CEO Euroasia Interconnector ] supported the timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector.<ref name="TRI"/> On December 12, 2017 ], ], announced a conclusion of strategic alliance agreement for the development and implementation of the 2,000 MW interconnector.<ref name="ELI"/> | ||
| Former ] |
Former ] and head of the ] Foreign Affairs Working group ] joined the EuroAsia Interconnector on March 30, 2018 as Chairman of the Strategic Council.<ref name="CMK"></ref><ref name="KAS"></ref><ref name="SIGLI"></ref> | ||
| Call for four tenders for construction of Stage 1 with estimated budget €3.27 billion was published on April 17, 2018 in the ].<ref name="TED1"></ref><ref name="TED2"></ref><ref name="TED3"></ref><ref name="TED4"></ref> | Call for four tenders for construction of Stage 1 with estimated budget €3.27 billion was published on April 17, 2018 in the ].<ref name="TED1"></ref><ref name="TED2"></ref><ref name="TED3"></ref><ref name="TED4"></ref> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
| </ref> | </ref> | ||
| On July 3, 2019 EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd |
On July 3, 2019 EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd project promoter announced the final stage of tenders for construction of the Euroasia Interconnector.<ref name="FTEN"></ref> | ||
| ==Energy in Cyprus, Greece and Israel== | ==Energy in Cyprus, Greece and Israel== | ||
| ], Chairman of the Strategic Council of the EuroAsia Interconnector]] | ], Chairman of the Strategic Council of the EuroAsia Interconnector]] | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
| {{main|Energy in Cyprus}} | {{main|Energy in Cyprus}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] as island totally isolated from EU energy links and electricity networks and remains the most energy dependent country in ]. Cyprus is fully isolated from EU energy interconnections.<ref name="EA"/> About 95% of the primary energy use was imported in 2015.<ref name=IEA2015></ref> Oil and petroleum products represent around 92% of the gross energy consumption.<ref name=IEA2015B></ref> Cyprus |
] as an island is totally isolated from EU energy links and electricity networks and remains the most energy dependent country in ]. Cyprus is fully isolated from EU energy interconnections.<ref name="EA"/> About 95% of the primary energy use was imported in 2015.<ref name=IEA2015></ref> Oil and petroleum products represent around 92% of the gross energy consumption.<ref name=IEA2015B></ref> Cyprus has no ]. As a result of high import cost of petroleum products the price of electricity is one of the highest in the ]. | ||
| ] share has reached 8% and according to national target should reach 13% by 2020.<ref name=EWEA2050>{{cite web|url=http://www.ewea.org/fileadmin/ewea_documents/documents/publications/reports/EWEA_EU_Energy_Policy_to_2050.pdf|title=EWEA March 2011|}}</ref> Recently Cyprus announced discovery of ] with significant amounts of natural gas resources in ]. Due to regional turmoils in East Mediterranean region and fact that 1/3 of Cyprus is unlawfully occupied, for energy security it is needed reliable and robust energy infrastructure. EuroAsia Interconnector will connect Cyprus to European network as last EU member fully isolated from energy interconnections.<ref name="EA"/> | ] share has reached 8% and according to national target should reach 13% by 2020.<ref name=EWEA2050>{{cite web|url=http://www.ewea.org/fileadmin/ewea_documents/documents/publications/reports/EWEA_EU_Energy_Policy_to_2050.pdf|title=EWEA March 2011|}}</ref> Recently Cyprus announced discovery of ] with significant amounts of natural gas resources in ]. Due to regional turmoils in East Mediterranean region and fact that 1/3 of Cyprus is unlawfully occupied, for energy security it is needed reliable and robust energy infrastructure. EuroAsia Interconnector will connect Cyprus to European network as last EU member fully isolated from energy interconnections.<ref name="EA"/> | ||
| ===Energy in Israel=== | ===Energy in Israel=== | ||
| {{main|Energy in Israel|Energy Triangle|Natural gas in Israel}} | {{main|Energy in Israel|Energy Triangle|Natural gas in Israel}} | ||
| ] relationship with neighbors |
]'s relationship with neighbors links politics and diplomacy with energy supply and security. Until recently Israeli domestic energy production was small and it was mainly dependent on import of ] and ], so that in 2012 only 13% of energy balance of Israel was covered by own production.<ref name=IEA2012I></ref> In 2010, the ] was discovered off the coast of Israel.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/12/31/world/middleeast/31leviathan.html?_r=1 |title=Gas Field Confirmed Off Coast of Israel |date=30 December 2010 |newspaper= ] }}</ref> That gas field represents strategical change enabling Israel not only to be energy sufficient, but also to become an energy exporter, as the amount of discovered gas exceeds Israeli demands for at least next 50 years. | ||
| Unlike oil, gas is not sold on spot markets and it is priced unique to each deal. One reliable way for Israel to export ] could be in form of electricity using Interconnector.<ref name=reuters040312/> | Unlike oil, gas is not sold on spot markets and it is priced unique to each deal. One reliable way for Israel to export ] could be in form of electricity using Interconnector.<ref name=reuters040312/> | ||
| ===Energy in Greece=== | ===Energy in Greece=== | ||
| ] location at crossroads of the east and west and geographical connection to rest of Europe enables interconnection and energy flow from ] to Europe. Greece is highly energy dependent country. ] share has reached 22%.<ref></ref> ] is energy isolated island and it is largest isolated power system in Greece. Like all isolated island systems cost of electricity production is very high due to transportation costs of imported fuel and high operational costs of mainly outdated power generating units. Connected system have much lower costs of electricity by using electricity from distant ]s where electricity production costs are much lower. ] is energetically isolated from mainland Greece and Hellenic Republic covers for Crete electricity costs difference of around €300 million per year.<ref name="CRE"></ref> | ] location at crossroads of the east and west and geographical connection to rest of Europe enables interconnection and energy flow from ] to Europe. Greece is highly energy dependent country. ] share has reached 22%.<ref></ref> ] is energy isolated island and it is largest isolated power system in Greece. Like all isolated island systems cost of electricity production is very high due to transportation costs of imported fuel and high operational costs of mainly outdated power generating units. Connected system have much lower costs of electricity by using electricity from distant ]s where electricity production costs are much lower. ] is energetically isolated from mainland Greece and Hellenic Republic covers for Crete electricity costs difference of around €300 million per year.<ref name="CRE"></ref> | ||
| ] | |||
| == Eastern Mediterranean Hydrocarbon Findings == | == Eastern Mediterranean Hydrocarbon Findings == | ||
| ] is bounded by ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] in middle. Cyprus is the largest island in the Levantine sea and it is located in middle. Many countries in the region are in dispute with neighbors. | ] is bounded by ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] in middle. Cyprus is the largest island in the Levantine sea and it is located in middle. Many countries in the region are in dispute with neighbors. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 107: | ||
| == Infrastructure == | == Infrastructure == | ||
| ], ], where the three studies were awarded to the Italian companies ] and GAS]] | ], ], where the three studies were awarded to the Italian companies ] and GAS]] | ||
| The EuroAsia Interconnector will link Israel with Cypriot and Greek power grids with ] ] of length around {{convert|1520|km|adj=on}} | ]The EuroAsia Interconnector will link Israel with Cypriot and Greek power grids with ] ] of length around {{convert|1520|km|adj=on}} | ||
| (820 nautical miles).<ref name="EA"/><ref name=mirror35471> | (820 nautical miles).<ref name="EA" /><ref name="mirror35471"> | ||
| {{cite news | {{cite news | ||
| | title = ENERGY: End to electricity isolation a step closer | | title = ENERGY: End to electricity isolation a step closer | ||
| Line 118: | Line 116: | ||
| | accessdate = 2017-01-04}} | | accessdate = 2017-01-04}} | ||
| </ref> | </ref> | ||
| It will have a capacity to transmit 2,000 megawatts of electricity in either direction.<ref name=reuters040312> | It will have a capacity to transmit 2,000 megawatts of electricity in either direction.<ref name="reuters040312"> | ||
| {{cite news | {{cite news | ||
| | title = Israel-Cyprus underwater power cable takes shape | | title = Israel-Cyprus underwater power cable takes shape | ||
| Line 126: | Line 124: | ||
| | url = http://uk.reuters.com/article/2012/03/04/israel-cyprus-cable-idUKL5E8E407R20120304 | | url = http://uk.reuters.com/article/2012/03/04/israel-cyprus-cable-idUKL5E8E407R20120304 | ||
| | accessdate = 2012-03-09}} | | accessdate = 2012-03-09}} | ||
| </ref><ref name="EA"/> | </ref><ref name="EA" /> | ||
| The {{convert|330|km|adj=on}} cable will link ] with ].<ref name="EA"/> Cyprus will be connected with the Greek island of ] with {{convert|880|km|adj=on}} long cable.<ref name="EA"/> ] will be connected with ] in ] with {{convert|310|km|adj=on}} long cable providing a connection to the pan-European electricity grid.<ref name="EA"/> The laying depth of cable will be up to {{convert|3000|m}} under sea level in some area between Crete and Cyprus.<ref name="EA"/> It will be conducted in two stages.<ref name="EA2"></ref> | The {{convert|330|km|adj=on}} cable will link ] with ].<ref name="EA" /> Cyprus will be connected with the Greek island of ] with {{convert|880|km|adj=on}} long cable.<ref name="EA" /> ] will be connected with ] in ] with {{convert|310|km|adj=on}} long cable providing a connection to the pan-European electricity grid.<ref name="EA" /> The laying depth of cable will be up to {{convert|3000|m}} under sea level in some area between Crete and Cyprus.<ref name="EA" /> It will be conducted in two stages.<ref name="EA2"></ref> | ||
| In first stage it will have 1000 MW capacity.<ref name="EA"/> It is expected to cost €3.5 billion in first stage.<ref name=mirror35471/><ref name="NOT"></ref> It is expected that first interconnection between ] on ] and ] region in Greece will be finished in June 2022.<ref name=mirror10119/><ref name=cm10119/> Second interconnection between ] in Israel and ] on ] will be finished in December 2023. Longest interconnection between Kofinou on Cyprus and Fodele on Crete will be delivered in December 2023.<ref name=mirror10119/><ref name=cm10119/> | In first stage it will have 1000 MW capacity.<ref name="EA"/> It is expected to cost €3.5 billion in first stage.<ref name=mirror35471/><ref name="NOT"></ref> It is expected that first interconnection between ] on ] and ] region in Greece will be finished in June 2022.<ref name=mirror10119/><ref name=cm10119/> Second interconnection between ] in Israel and ] on ] will be finished in December 2023. Longest interconnection between Kofinou on Cyprus and Fodele on Crete will be delivered in December 2023.<ref name=mirror10119/><ref name=cm10119/> | ||
| Line 164: | Line 162: | ||
| === EU Priority Electricity Highway === | === EU Priority Electricity Highway === | ||
| EuroAsia Interconnector has been labelled as priority electricity corridor, and as priority Electricity Highway Project.<ref name="PCI3"/> On 23. November 2017. Euroasia |
EuroAsia Interconnector has been labelled as priority electricity corridor, and as priority Electricity Highway Project.<ref name="PCI3"/> On 23. November 2017. Euroasia Interconnector on the third final list of EU Projects of Common Interest has been labelled by the ] as priority Electricity Highway Interconnector.<ref name="PCI3"/> | ||
| === Big reduction of {{CO2}} emission === | === Big reduction of {{CO2}} emission === | ||
| ] (ENTSO-E) assessed positively Interconnector project based on cost-benefit analysis methodology.<ref name="ENTSO"></ref> It is therefore included in the ten-year network development plan 2014 (TYNDP) and then also TYNDP 2016.<ref name="ENTSO"/> | ] (ENTSO-E) assessed positively Interconnector project based on cost-benefit analysis methodology.<ref name="ENTSO"></ref> It is therefore included in the ten-year network development plan 2014 (TYNDP) and then also TYNDP 2016.<ref name="ENTSO"/> | ||
| According to the cost-benefit analysis of ] (ENTSO-E), Interconnector will contribute to social and ] between €580m and €1.12 billion in each year.<ref name="ENTSO"/> The cost-benefit analysis is done using four different visions. |
According to the cost-benefit analysis of ] (ENTSO-E), Interconnector will contribute to social and ] between €580m and €1.12 billion in each year.<ref name="ENTSO"/> The cost-benefit analysis is done using four different visions. Reduction of {{CO2}} emission is expected to be between 1.3 million tonne and 6.8 million tonne each year.<ref name="ENTSO"/> For comparison Cyprus had {{CO2}} emission of 6.16 million tone during 2015.<ref></ref> Therefore, reduction of {{CO2}} emission will be between 21% and 110% of total Cyprus {{CO2}} emission. Based on new assessments best estimate of reduction of {{CO2}} emission is expected to be 1.16 million tone for Stage 1. | ||
| Development of ] on isolated systems like Cyprus and Crete could compromise islands electrical systems due to chaotic production fluctuations. Integration of renewable energy sources without interconnection is therefore limited. Electricity interconnection will enable and unlock integration of high percentage of renewable sources in such isolated systems. | Development of ] on isolated systems like Cyprus and Crete could compromise islands electrical systems due to chaotic production fluctuations. Integration of renewable energy sources without interconnection is therefore limited. Electricity interconnection will enable and unlock integration of high percentage of renewable sources in such isolated systems. | ||
| Line 260: | Line 258: | ||
| *Contributes to EU target for 10% of electricity interconnection between member states.<ref name="EA"/> | *Contributes to EU target for 10% of electricity interconnection between member states.<ref name="EA"/> | ||
| *Promotes development of ] and contributes to the reduction of {{CO2}} | *Promotes development of ] and contributes to the reduction of {{CO2}} | ||
| *Offers significant |
*Offers significant economic and geopolitical benefit to 3 countries. It is expected that socio-economic benefit will be around 10 billion €.<ref name="EA"/> | ||
| == Project development company == | == Project development company == | ||
Revision as of 00:53, 23 August 2019
| EuroAsia Interconnector | |
|---|---|
| File:EAI logo.jpg | |
| File:Euroasia-route-map.jpgMap of EuroAsia Interconnector | |
| Location | |
| Founded | 2010 |
| Headquarters | Nicosia, Cyprus |
| Services | Electrical grid Electric power transmission |
| Country | |
| From | Hadera, Israel |
| Passes through | Kofinou, Cyprus Fodele, Crete, Greece |
| To | Attica, Greece |
| Ownership information | |
| Owner | EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd. |
| Key people | Chairman: Ioannis Kasoulidis |
| CEO | Nasos Ktorides |
| Project director | George Killas |
| Operator | EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd. |
| Construction information | |
| Expected | Crete—Attica 2022 Cyprus—Crete 2023 Cyprus—Israel 2023 |
| Construction cost | €3.5 billion (Stage 1) |
| Technical information | |
| Type | Submarine power cable |
| Type of current | HVDC |
| Total length | 1,520 km (940 mi) |
| Power rating | 2,000 MW |
| DC voltage | ±500 kV |
| No. of poles | 2 |
| Website | www |
The EuroAsia Interconnector is a planned HVDC interconnector between Greek, Cypriot, and Israeli power grids via the world's longest submarine power cable. It is a major Project of Common Interest of the European Union and a priority Electricity Highway Interconnector Project, as an energy highway bridging Asia and Europe. Regulatory approval of electricity interconnection and cost allocation between Cyprus and Greece was completed on October 10, 2017. It is historic decision for Cyprus, ending electricity isolation of the last EU member state.
According to ENTSO-E analysis, the interconnector will contribute to social and economic welfare between €580m and €1.12 billion in each year. ENTSO-E calculated that expected reduction of CO2 is between 1.3 and 6.8 million tonnes each year, or between 21% and 110% of total emissions of Cyprus.
On May 12, 2017 the Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras met the State Grid Corporation of China Chairman Shu Yinbiaoin Beijing, and CEO Euroasia Interconnector Nasos Ktorides supported the timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector. On December 12, 2017 Elia, transmission system operator, announced a conclusion of strategic alliance agreement for the development and implementation of the 2,000 MW interconnector.
Former Cyprus Foreign Minister and head of the European Parliament Foreign Affairs Working group Ioannis Kasoulides joined the EuroAsia Interconnector on March 30, 2018 as Chairman of the Strategic Council.
Call for four tenders for construction of Stage 1 with estimated budget €3.27 billion was published on April 17, 2018 in the Official Journal of the European Union. On January 10, 2019 EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd, project promoter, has issued tender documents for contracts worth €3.5bn, for the design and construction of the EuroAsia Interconnector.
Energy-sector technical engineering recruitment firm Fircroft included the EuroAsia Interconnector as the fourth biggest among 10 major transmission and distribution projects in the world for 2019 and beyond.
On July 3, 2019 EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd project promoter announced the final stage of tenders for construction of the Euroasia Interconnector.
Energy in Cyprus, Greece and Israel

Energy in Cyprus
Main article: Energy in Cyprus
Cyprus as an island is totally isolated from EU energy links and electricity networks and remains the most energy dependent country in European Union. Cyprus is fully isolated from EU energy interconnections. About 95% of the primary energy use was imported in 2015. Oil and petroleum products represent around 92% of the gross energy consumption. Cyprus has no oil refineries. As a result of high import cost of petroleum products the price of electricity is one of the highest in the European Union. Renewable energy share has reached 8% and according to national target should reach 13% by 2020. Recently Cyprus announced discovery of Aphrodite gas field with significant amounts of natural gas resources in exclusive economic zone. Due to regional turmoils in East Mediterranean region and fact that 1/3 of Cyprus is unlawfully occupied, for energy security it is needed reliable and robust energy infrastructure. EuroAsia Interconnector will connect Cyprus to European network as last EU member fully isolated from energy interconnections.
Energy in Israel
Main articles: Energy in Israel, Energy Triangle, and Natural gas in IsraelIsrael's relationship with neighbors links politics and diplomacy with energy supply and security. Until recently Israeli domestic energy production was small and it was mainly dependent on import of oil and coal, so that in 2012 only 13% of energy balance of Israel was covered by own production. In 2010, the Leviathan gas field was discovered off the coast of Israel. That gas field represents strategical change enabling Israel not only to be energy sufficient, but also to become an energy exporter, as the amount of discovered gas exceeds Israeli demands for at least next 50 years. Unlike oil, gas is not sold on spot markets and it is priced unique to each deal. One reliable way for Israel to export natural gas could be in form of electricity using Interconnector.
Energy in Greece
Greece location at crossroads of the east and west and geographical connection to rest of Europe enables interconnection and energy flow from Eastern Mediterranean to Europe. Greece is highly energy dependent country. Renewable energy share has reached 22%. Crete is energy isolated island and it is largest isolated power system in Greece. Like all isolated island systems cost of electricity production is very high due to transportation costs of imported fuel and high operational costs of mainly outdated power generating units. Connected system have much lower costs of electricity by using electricity from distant power stations where electricity production costs are much lower. Crete is energetically isolated from mainland Greece and Hellenic Republic covers for Crete electricity costs difference of around €300 million per year.
Eastern Mediterranean Hydrocarbon Findings
Levantine Sea is bounded by Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt and Cyprus in middle. Cyprus is the largest island in the Levantine sea and it is located in middle. Many countries in the region are in dispute with neighbors. The seafloor of the Eastern Mediterranean Basin is dotted with mud volcanoes which spew gas and occasionally oil into the benthic zone. Geologically it consists of sediment columns up to 12 km thick capped by evaporites. Geological and oceanographers facts lead to speculation that Levantine sea contains big gas and oil deposits trapped in evaporites. Recently Eni discovered Zohr gas field, largest known gas field in Mediterranean. The Zohr gas field holds around 850 billion cubic metres (30 trillion cubic feet) of gas. It is estimated that in the Levant Basin there are around 3.5 trillion cubic metres (120 trillion cubic feet) of undiscovered gas resources. Also they estimated that there could be up to 1.7 billion barrels of recoverable oil.

Israeli and Cyprus gas fields
Aphrodite gas field is Cyprus offshore gas field at the exploratory drilling block 12 in the Cyprus maritime Exclusive Economic Zone. It is estimated that block 12 holds 110 to 140 billion cubic metres (3.9×10^ to 4.9×10^ cu ft) of natural gas. Exploration is continuing in other blocks in Cyprus Exclusive Economic Zone. Calypso gas field in block 6 was found in 2018. and it is estimated that holds 170 to 230 billion cubic metres (6.0×10^ to 8.1×10^ cu ft) of gas.
First significant Israeli gas discovery was 28 billion cubic metres (990×10^ cu ft) gas in Mari-B field in 2000. Mari-B field produced gas until 2013 covering 40% of Israeli natural gas demand. Offshore Tamar gas field of 280 billion cubic metres (9.9×10^ cu ft) was discovered in 2009. Commercial production from Tamar field started in 2013. It covers nearly all industrial needs and gas from Tamar field generates over half of country electricity. In 2010, the Leviathan gas field was discovered off the coast of Israel. It is estimated the field contains around 470 billion cubic metres (17×10^ cu ft) of
natural gas.
Infrastructure


The EuroAsia Interconnector will link Israel with Cypriot and Greek power grids with high-voltage direct current submarine power cable of length around 1,520-kilometre (940 mi)
(820 nautical miles). It will have a capacity to transmit 2,000 megawatts of electricity in either direction. The 330-kilometre (210 mi) cable will link Israel with Cyprus. Cyprus will be connected with the Greek island of Crete with 880-kilometre (550 mi) long cable. Crete will be connected with Attica in Greece with 310-kilometre (190 mi) long cable providing a connection to the pan-European electricity grid. The laying depth of cable will be up to 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) under sea level in some area between Crete and Cyprus. It will be conducted in two stages.
In first stage it will have 1000 MW capacity. It is expected to cost €3.5 billion in first stage. It is expected that first interconnection between Fodele on Crete and Attica region in Greece will be finished in June 2022. Second interconnection between Hadera in Israel and Kofinou on Cyprus will be finished in December 2023. Longest interconnection between Kofinou on Cyprus and Fodele on Crete will be delivered in December 2023.
Configuration for Stage 1
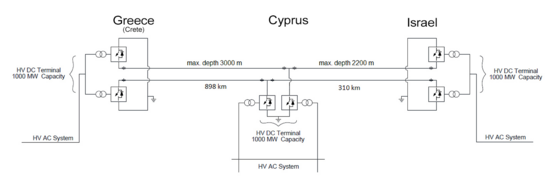
Interconnector provides important electricity highway in Southeastern EU and ends energy isolation of Cyprus and Crete interconnecting EU and Israel. Interconnector main components are:
- 4 converter stations in bipolar arrangements with multiterminal operation (in Attica, Crete, Cyprus and Israel).
- subsea and land High-voltage direct current (HVDC) cables that will interconnect converter stations in Attica, Crete, Cyprus and Israel. Cables will run in pairs and each cable will be with power rating of 500 MW and voltage of 500kV.

- sea electrodes of 1000A and medium voltage direct current cables connecting them to converter stations
- alternating current (AC) switchgear connecting converter stations to grid at four different locations
Pair of cables will connect all converter stations. Converter station converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) or the reverse. It could receive power through cable and send it to grid. Converter stations are bipolar and could run bidirectionally enabling import or export of electricity depending on demand. Cables will run along bottom of sea and on land will run underground. Sea electrodes are used in case of cable or converter stations fault. Sea electrodes are placed at seabed several kilometers from shore and they are connected to converter stations. Converter stations will be of Voltage Source Converter (VSC) type. Each converter station is designed to be rated 1000 MW and will be made of two converter bridges of 500 MW. Submarine power cables will be of extruded type.
Configuration for Stage 2
In stage two additional 1.000 MW converter stations will be built in Attica and Israel and will be added additional 1000 MW bipole cable on route Israel-Cyprus-Crete-Greece. Stage 2 will increase transfer capacity to 2.000 MW.
Project of EU Common Interest
European Commission adopted 14. October 2013. under Regulation (EU) No. 1391/2013 first list of key EU Projects of Common Interest. EuroAsia Interconnector is accepted as cluster of three EU Projects of Common Interest important as trans-European energy infrastructure project. Main criteria for Projects of Common Interest is market integration, security of energy supply, enhancing competition and reduction of CO2. On 18 November 2015 the European Commission adopted second revised list of 195 EU Projects of Common Interest. EuroAsia Interconnector is included also on revised list. On 23 November 2017, Euroasia Interconnecter was included on third final list of EU Projects of Common Interest.
On 29 October 2014 it was announced EU funding for 3 prestudies of Interconnector project. These studies got half of cost (€1,325,000) from Connecting Europe Facility. On 17 February 2017, The European Commission approved €14.5 million as financial support for final detailed studies prior to Project Implementation. EU covers half of cost of final detailed pre-works studies. The Interconnector was selected for funding as one of seven electricity projects. According to EU Commission, project contributes Energy Union's goals by increasing security of energy supply, connecting European energy networks, and also contributes integration of renewable energy sources across the EU.

EU Priority Electricity Highway
EuroAsia Interconnector has been labelled as priority electricity corridor, and as priority Electricity Highway Project. On 23. November 2017. Euroasia Interconnector on the third final list of EU Projects of Common Interest has been labelled by the ENTSO-E as priority Electricity Highway Interconnector.
Big reduction of CO2 emission
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) assessed positively Interconnector project based on cost-benefit analysis methodology. It is therefore included in the ten-year network development plan 2014 (TYNDP) and then also TYNDP 2016. According to the cost-benefit analysis of European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E), Interconnector will contribute to social and economic welfare between €580m and €1.12 billion in each year. The cost-benefit analysis is done using four different visions. Reduction of CO2 emission is expected to be between 1.3 million tonne and 6.8 million tonne each year. For comparison Cyprus had CO2 emission of 6.16 million tone during 2015. Therefore, reduction of CO2 emission will be between 21% and 110% of total Cyprus CO2 emission. Based on new assessments best estimate of reduction of CO2 emission is expected to be 1.16 million tone for Stage 1.
Development of renewable energy sources on isolated systems like Cyprus and Crete could compromise islands electrical systems due to chaotic production fluctuations. Integration of renewable energy sources without interconnection is therefore limited. Electricity interconnection will enable and unlock integration of high percentage of renewable sources in such isolated systems.
History and development

EuroAsia Interconnector project was announced by Nasos Ktorides in Nicosia on 23 January 2012, stressing role of Cyprus as energy bridge between Europe and Asia. A cooperation agreement for conducting the feasibility study was signed in Jerusalem on 4 March 2012 between the project operator EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd.(previously DEI Quantum Energy), and the Israel Electric Corporation in presence of Israeli minister for Energy and Water Resources Uzi Landau and Yiftah Ron-Tal, Director of the Israel Electric Corporation. On 23 March 2012, in Nicosia, the Electricity Authority of Cyprus signed a cooperation agreement with project operator. On 8 August 2013, the ministers of energy of Cyprus, Israel and Greece met in Cyprus. They signed the tripartite energy memorandum and reconfirmed their support for Interconnector.

On 14 October 2013, Interconnector was accepted as cluster of three EU Projects of Common Interest. Later it was also accepted on the second and third lists of key EU Projects of Common Interest.
In a meeting between the Israeli and Cypriot energy ministers in June 2015, the Israeli minister suggested doubling the planned capacity of the cable. With Israel and Cyprus both having located natural gas deposits within their territories, a higher capacity cable would allow them to construct gas-driven power plants and export significant amounts of electricity to Europe.
On 11 January 2016 in Nicosia Vice-President of the European Commission Maroš Šefčovič met with President of Cyprus Nicos Anastasiades and Minister of Energy Giorgos Lakkotrypis. They discussed huge potential of eastern Mediterranean for energy supply of Europe and pointed out EuroAsia Interconnector as a bridge and highway for energy supply.
Three pre-works phase studies were awarded on 18 December 2015 to the Italian companies CESI and G.A.S. S.r.l..The three studies are for the technical design, the reconnaissance study for the optimum route and an environmental impact study. In January 2016, the Italian research ship Odin Finder started a reconnaissance study for the optimum route of the underwater cable. It took about 100 days to complete the survey. All three preworks studies were finished in 2016 and led to the next phase of the final pre-construction studies.

On 28 January 2016, the first Cyprus-Israel-Greece tripartite meeting took place in Nicosia. On that meeting President of Cyprus Nicos Anastasiades, the Prime Minister of Greece Alexis Tsipras and the Prime Minister of Israel Benjamin Netanyahu affirmed their full support for the EuroAsia Interconnector. When they met again on December 8, 2016 in Jerusalem they reaffirmed their full support for the timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector.
On 17 February 2017, The European Commission approved €14.5 million as financial support for final detailed studies prior to Project Implementation. In INEA on April 5, 2017 it was signed grant agreement to finalize the interconnector's design by supporting final detailed pre-works studies.
On May 12, 2017 Beijing meeting the Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras met State Grid Corporation of China Chairman Shu Yinbiao in Beijing and CEO Euroasia Interconnector Nasos Ktorides and had discussions on the jointly promoting of the Belt and Road Initiative and the strengthening of power and energy cooperation. Prime Minister Tsipras expressed his appreciation for the support Mr. Shu Yinbiao has given to the development of Greek grid and the contribution made by State Grid Corporation of China towards the timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector.

The idea of Quantum Cable was supported at a trilateral meeting of Prime Ministers of Greece Alexis Tsipras, Israel Benjamin Netanyahu and the President of Cyprus Nicos Anastasiades, in the Greek city of Thessaloniki on 15 June 2017. They pointed out that EuroAsia Interconnector is strategically important for Greece, upgrading her status into regional electricity and telecom hub.
The EuroAsia Interconnector cross border cost allocation was approved by the Energy Regulatory Authorities of Cyprus and Greece on 10 October 2017 and 21 March 2018. It is a historic decision for Cyprus, ending electricity isolation of the last EU member state.
Elia, Belgium’s electricity transmission system operator, announced on 12 December 2017 that it had concluded a strategic alliance agreement with the EuroAsia Interconnector for the development and implementation of the 2,000 MW subsea electricity interconnector.

Former Cyprus Foreign Minister (1997—2003, 2013— March 2018) and head of the European Parliament Foreign Affairs Working group, Ioannis Kasoulides, joined EuroAsia Interconnector on 30 March 2018 as Chairman of the Strategic Council. On 11 September 2018, Ioannis Kasoulides received the highest decoration awarded by France – Officer of the Order of the Legion of Honour.
In a speech at the public consultation held at the Hilton Cyprus on 2 April 2018, Cyprus Energy Minister Yiorgos Lakkotrypis described the project as of particular national geopolitical importance, as it enables Cyprus and Greece to act as bridges of cooperation, linking the eastern Mediterranean with the European Union.
On 8 May 2018, the fourth Cyprus-Israel-Greece tripartite meeting in Nicosia. Prime Ministers of Greece Alexis Tsipras, Israel Benjamin Netanyahu and the President of Cyprus Nicos Anastasiades reconfirmed their support to timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector and Quantum Cable, accompanying fiber optic cable.
The procurement stage of project started 13 February 2018 by notice for construction of Stage 1 with an estimated budget of €3.5 billion, published in the Official Journal of the European Union. Call for four tenders with estimated budget €3.27 billion was published on 17 April 2018 in the Official Journal of the European Union.

On 10 January 2019, after a series of individual meetings with all successful converter and cable manufacturers, EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd, project promoter, has issued tender documents for contracts worth €3.5bn for the design and construction of the EuroAsia Interconnector.
The meeting between European Commission and Cyprus authorities took place on February 27, 2019 in Nicosia. In a joint communique they have again show full support for timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector as a Project of Common Interest (PCI) and they recognised EuroAsia Interconnector as the official project promoter. Also they pointed out that best way for timely implementation and optimal interoperability is under provisions of the Roadmap of European Commission from 16. Octobar 2018.
On 6 June 2019, Giorgos Lakkotropis, the Minister of Energy, signed on behalf of Cyprus government 33-year land concession agreement for construction of HVDC converter station.
On July 3, 2019 EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd, project promoter, annonced final stage of tenders for construction of the Euroasia Interconnector.
Benefits of EuroAsia Interconnector

- Ends energy isolation of Cyprus and Crete and connect them to European network. Cyprus is last member of EU fully isolated without energy interconnections.
- Ensures secure energy supply of Cyprus, Greece and Israel connecting them with European network
- For new East Mediterranean gas finding enables path towards new markets in form of electricity. Also enables path for electricity produced from renewable energy sources.
- Contributes to EU target for 10% of electricity interconnection between member states.
- Promotes development of renewable energy sources and contributes to the reduction of CO2
- Offers significant economic and geopolitical benefit to 3 countries. It is expected that socio-economic benefit will be around 10 billion €.
Project development company
The interconnector is fully funded by EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd. and European Union. The company headquarters are in Nicosia, Cyprus. EuroAsia Interconnector Ltd. is part of Quantum Corporation and Quantum Energy Group.
See also
References

- ^ EuroAsia Interconnector Project and Progress
- EuroAsia Interconnector – Official site
- ^
Kambas, Michele (2012-01-23). "Cyprus group plans Greece-Israel electricity link". Reuters. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
A Cyprus-based group including Greece's state-controlled power utility PPC said on Monday it planned to lay the world's longest subsea power cable linking Europe and Asia.
- ^ EU Projects by country
- ^ Funding for Projects of Common Interest
- ^ First list of PCI
- ^ Second list of PCI
- ^ Third list of PCI
- European Commission - Fact Sheet Connecting power markets to deliver security of supply, market integration and the large-scale uptake of renewables
- Historic decision_for Cyprus Approval of Electricity Interconnection between Cyprus and Greece
- ^ ACER Overview of cost border cost allocation decisions
- ^ CERA, publication of decision of cost allocation
- ^ Ρυθμιστικά «ΟΚ» για EuroAsia Interconnector,Phileleftheros 22. March 2018
- ^ ENTSO assessment of EuroAsia
- ^ Shu Yinbiao Met Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras To Discuss on Accelerating the Building EuroAsia Interconnector to Promote the Development of Greek Energy and Power Industry
- ^ Elia Grid International concludes strategic alliance agreement with EuroAsia Interconnector
- ^ Kasoulides joins EuroAsia Interconnector, Cyprus Mail 30.3.2018
- ^ Former Foreign Minister of the Republic of Cyprus Ioannis Kasoulides joins EuroAsia Interconnector Chairman of the Strategic Council
- ^ End of energy isolation of Cyprus, Sigmalive 31.3.2018
- ^ Tender for HVDC Converters
- ^ Tender for Israel-Cyprus link
- ^ Tender for Cyprus-Crete link
- ^ Tender for Crete-Attica link
- ^ . "EuroAsia Interconnector issues tender documents for EUR 3.5 bln cable project". Financial Mirror. 2019-01-10. Retrieved 2019-01-10.
- ^ "Tender documents for design and build of EuroAsia Interconnector published". Cyprus Mail. 2019-01-10. Retrieved 2019-01-10.
- 10 major Transmission & Distribution projects in 2019 and beyond
- . "Cyprus among 10 major electricity transmission projects in 2019". Financial Mirror. 2019-06-27. Retrieved 2019-06-27.
- ^ Invitation to Tender – At the final stages the Tenders for Construction of the electricity interconnection linking Israel-Cyprus-Crete-Attica
- IEA Key energy statistics 2015
- IEA Key energy statistics 2015, Balances
- "EWEA March 2011" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - IEA Key energy statistics Israel 2012
- "Gas Field Confirmed Off Coast of Israel". The New York Times. 30 December 2010.
- ^ Rabinovich, Ari (2012-03-04). "Israel-Cyprus underwater power cable takes shape". Reuters. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- Greece energy reports
- The EuroAsia Interconnector will provide energy to Crete, Crete Live, 7. February 2018 (in Greek)
- ^ Eni discovers largest known gas field in Mediterranean, The Guardian 30.8.2015
- ^ Ratner, Michael (August 2016). "Natural Gas Discoveries in the Eastern Mediterranean" (PDF). Congressional Research Service.
- Financial Mirror, 13.1.2016, page 4
- Calypso holds 6 to 8 tcf, ENI says, Cyprus Mail February 13 2018
- New report sees 20% less gas reserves in Leviathan
- ^ "ENERGY: End to electricity isolation a step closer". Financial Mirror. 2017-10-19. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ EuroAsia_Interconnector_Project_Overall
- Periodic Indicative Notice – Utilities for the construction of Stage 1 of the EuroAsia Interconnector
- ^ EU Projects of Common Interest (2013)
- ^ EU Projects of Common Interest (2015)
- ^ EU Projects of Common Interest (2017)
- ^ "ENERGY: EU backs EuroAsia Interconnector with €14.5m for pre-works study". Financial Mirror. 2017-02-24. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ Project 3.10
- ^ EU invests €444 million in key energy infrastructure
- CO2 time series 1990-2015 per region/country
- Cyprus: Energy Bridge between Europe and Asia
- Israel-Cyprus underwater power cable takes shape
- ^ "'Historic' plan for water and electricity". Cyprus Mail. 8 August 2013. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
- "Israel, Greece, Cyprus to Export Electricity to EU". Financial Mirror. 7 August 2013. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
- Weissman, Lilach (27 July 2015). "המלצת ועדת השימוע: שינויים במתווה הגז" [Recommendations of the Gas Market Hearings] (in Hebrew). Globes. Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- ^ Eastern Mediterranean ‘very important’ to Europe’s energy security, Cyprus Mail, January 11th, 2016
- http://cyprus-mail.com/2016/01/25/survey-vessel-looking-for-best-route-for-undersea-power-cable/
- ^ First Cyprus-Israel-Greece tripartite meeting
- PM Netanyahu's Statement at the Trilateral Meeting between Israel, Greece and Cyprus
- Horizon funds section of EuroAsia Interconnector Project
- Grant agreement to finalise the design of the EuroAsia interconnector signed in INEA today
- The Chairman of EuroAsia Interconnector Strategic Council awarded France’s highest decoration
- Financial Mirror, Issue No. 1283, April 4, 2018, page 4.
- ^ Press Release-Trilateral Summit declares official support to ‘timely implementation’ of EuroAsia Interconnector
- ^ Vimeo Video-Trilateral Summit declares official support to ‘timely implementation’ of EuroAsia Interconnector
- ^ Cyprus-Greece-Israel 4th Trilateral Summit Declaration By Spiros Sideris Published on: 08-05-2018, 13:52
- Tριμερής: Εντός 2018 η διακρατική για East Med (BINTEO), Sigma live 8.5.2018
- Periodic indicative notice for construction of Stage 1
- ^ EC, Cyprus reiterate support for timely implementation of EuroAsia Interconnector
- ^ JOINT COMMUNIQUE
- "Land lease agreement paves way for EuroAsia Interconnector". Cyprus Mail. 2019-06-06. Retrieved 2019-06-06.
- "Land lease agreement for EuroAsia Interconnector converter station in Cyprus signed". in-cyprus.com. 2019-06-06. Retrieved 2019-06-06.
- "ENERGY: Work to start on EuroAsia converter station after Cyprus land lease". Financial Mirror. 2019-06-06. Retrieved 2019-06-06.
- "DEH/Quantum to build EUR 1.5 bln East-West mega-cable". Financial Mirror. 2012-01-26. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- http://www.quantum-corporation.com