| Revision as of 17:29, 27 August 2019 editReywas92 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers81,320 edits rewordingTag: Visual edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 06:09, 30 August 2019 edit undoReywas92 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers81,320 edits +infoTag: 2017 wikitext editorNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| '''Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex''' is an administrative grouping of six ] in ], managed by the ]. It includes: | '''Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex''' is an administrative grouping of six ] in ], managed by the ]. It includes: | ||
| * Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|125|acre}}<ref name="area">{{FWS area|year=2013}}</ref>) | * Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|125|acre}}<ref name="area">{{FWS area|year=2013}}</ref>, {{coords|48.17|N|124.73|W|region:US-WA|notes=<ref name="gnis">{{cite gnis|1504929|Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge}}</ref>|display=inline}}) | ||
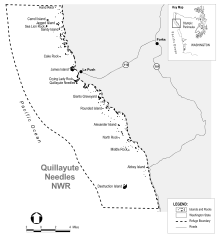
| * Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|300.2|acre||abbr=}}<ref name="area" />) | * Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|300.2|acre||abbr=}}<ref name="area" />, {{coord|47.81|N|124.50|W|region:US-WA_source:GNIS|format=|display=inline}}) | ||
| * Copalis National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|60.8|acre||abbr=}}<ref name="area" />) | * Copalis National Wildlife Refuge ({{convert|60.8|acre||abbr=}}<ref name="area" />, {{coords|47.40|N|124.33|W|region:US-WA_source:gnis|notes=<ref name="gnis">{{cite gnis|1528427|Copalis National Wildlife Refuge}}</ref>|display=inline}}) | ||
| * ] | * ] ({{convert|772.52|acre||abbr=}})<ref name="area" /> | ||
| * ] | * ] ({{convert|659.31|acre||abbr=}})<ref name="area" /> | ||
| * ] | * ] ({{convert|454|acre||abbr=}})<ref name="area" /> | ||
| == Washington Islands Wilderness refuges == | == Washington Islands Wilderness refuges == | ||
| Flattery Rocks, Quillayute Needles, and Copalis are a group of 870 ], rocks, and ] extending for more than 100 miles along ]'s coast from ] to ]. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources.<sup>]]</sup> They make up the Washington Islands Wilderness<ref name="wildernessNet">{{cite web|url=https://wilderness.net/visit-wilderness/?ID=633|title=Wilderness.net: Washington Islands Wilderness|accessdate=2019-08-27}}</ref> and are closed to the public, with wildlife observation only from boats and the mainland, and a 200-yard buffer zone surrounds each island.<sup>]]</sup> Only ], ], and Destruction Island are not included in the ], which was established in 1970.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://wilderness.net/visit-wilderness/default.php|title=Wilderness Connect|website=wilderness.net|language=en|access-date=2019-08-27}}</ref> | Flattery Rocks, Quillayute Needles, and Copalis are a group of 870 ], rocks, and ] extending for more than 100 miles along ]'s coast from ] to ]. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources.<sup>]]</sup> They make up the '''Washington Islands Wilderness'''<ref name="wildernessNet">{{cite web|url=https://wilderness.net/visit-wilderness/?ID=633|title=Wilderness.net: Washington Islands Wilderness|accessdate=2019-08-27}}</ref> and are closed to the public, with wildlife observation only from boats and the mainland, and a 200-yard buffer zone surrounds each island.<sup>]]</sup> Only ], ], and Destruction Island are not included in the ], which was established in 1970.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://wilderness.net/visit-wilderness/default.php|title=Wilderness Connect|website=wilderness.net|language=en|access-date=2019-08-27}}</ref> The wilderness has a total land area of {{convert|1.8|km2|sqmi}} covering over {{convert|780|km2|sqmi}} of ocean. | ||
| More than a million seabirds, ], and ] may live on the islands during migration season. Breeding colonies of 14 species of ] use these rocks to raise their young. Mammals that live near the islands include ], ], ], and ].<sup>]]</sup> | More than a million seabirds, ], and ] may live on the islands during migration season. Breeding colonies of 14 species of ] use these rocks to raise their young. Mammals that live near the islands include ], ], ], and ].<sup>]]</sup> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| These three lie within the boundary of ] (]). Along with nearby ] the three agencies cooperate on research programs and other issues that may have impacts on the resources.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121113185300/http://www.fws.gov/refuges/profiles/WildHabitat.cfm?ID=13537|title=Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge - Wildlife and Habitat|date=2012-11-13|website=web.archive.org|access-date=2019-08-27}}</ref> | These three lie within the boundary of ] (]). Along with nearby ] the three agencies cooperate on research programs and other issues that may have impacts on the resources.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121113185300/http://www.fws.gov/refuges/profiles/WildHabitat.cfm?ID=13537|title=Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge - Wildlife and Habitat|date=2012-11-13|website=web.archive.org|access-date=2019-08-27}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | The refuges were originally created as Flattery Rocks Reservation, Quillayute Needles Reservation, and Copalis Rock Reservation on October 23, 1907, by executive orders from ]. They were renamed by a presidential proclamation on July 25, 1940.<ref>], July 25, 1940. Mentioned in the citations in the .</ref> Flattery Rocks encompasses the islands off the Washington coast between latitudes 48° 02′ North and 48° 23′ North,<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> Quillayute Needles those between latitudes 47° 38′ North, and 48° 02′ North,<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> and Copalis those between latitudes 47° 08′ North, and 47° 29′ North.<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> ] was removed from Quillayute Needles in 1966 and returned to the Quileute when the island was discovered to be part of the ].<ref>Removed by Public Land Order 4095, September 19, 1966, according to , page 1-8.</ref><gallery widths="300" heights="200"> | ||
| File:Point of arches flattery rocks nwr.jpg|Point of Arches, Flattery Rocks | |||
| ⚫ | The refuges were originally created as Flattery Rocks Reservation, Quillayute Needles Reservation, and Copalis Rock Reservation on October 23, 1907, by executive orders from ]. They were renamed by a presidential proclamation on July 25, 1940.<ref>], July 25, 1940. Mentioned in the citations in the .</ref> Flattery Rocks encompasses the islands off the Washington coast between latitudes 48° 02′ North and 48° 23′ North,<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> Quillayute Needles those between latitudes 47° 38′ North, and 48° 02′ North,<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> and Copalis those between latitudes 47° 08′ North, and 47° 29′ North.<ref>], October 23, 1907.</ref> ] was removed from Quillayute Needles in 1966 and returned to the Quileute when the island was discovered to be part of the ].<ref>Removed by Public Land Order 4095, September 19, 1966, according to , page 1-8.</ref><gallery widths=" |
||
| File:Quillayute Needles NWR.jpg|Quillayute Needles | |||
| File:View to Copalis Rock from Roosevelt Beach, WA 14.jpg|Copalis Rock from Roosevelt Beach | |||
| </gallery><gallery widths="220" heights="252"> | |||
| File:Flattery Rocks NWR Map.svg|Flattery Rocks map | File:Flattery Rocks NWR Map.svg|Flattery Rocks map | ||
| File:Quillayute Needles NWR Map.svg|Quillayute Needles map | File:Quillayute Needles NWR Map.svg|Quillayute Needles map | ||
| Line 32: | Line 35: | ||
| * U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | * U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | ||
| * U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | * U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | ||
| * | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 06:09, 30 August 2019
Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex is an administrative grouping of six National Wildlife Refuges in Washington, managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. It includes:
- Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge (125 acres (51 ha), 48°10′N 124°44′W / 48.17°N 124.73°W / 48.17; -124.73)
- Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge (300.2 acres (121.5 ha), 47°49′N 124°30′W / 47.81°N 124.50°W / 47.81; -124.50)
- Copalis National Wildlife Refuge (60.8 acres (24.6 ha), 47°24′N 124°20′W / 47.40°N 124.33°W / 47.40; -124.33)
- Dungeness National Wildlife Refuge (772.52 acres (312.63 ha))
- Protection Island National Wildlife Refuge (659.31 acres (266.81 ha))
- San Juan Islands National Wildlife Refuge (454 acres (184 ha))
Washington Islands Wilderness refuges
Flattery Rocks, Quillayute Needles, and Copalis are a group of 870 islands, rocks, and reefs extending for more than 100 miles along Washington's coast from Cape Flattery to Copalis Beach. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources. They make up the Washington Islands Wilderness and are closed to the public, with wildlife observation only from boats and the mainland, and a 200-yard buffer zone surrounds each island. Only Tatoosh Island, James Island, and Destruction Island are not included in the wilderness area, which was established in 1970. The wilderness has a total land area of 1.8 square kilometres (0.69 sq mi) covering over 780 square kilometres (300 sq mi) of ocean.
More than a million seabirds, waterfowl, and shorebirds may live on the islands during migration season. Breeding colonies of 14 species of seabirds use these rocks to raise their young. Mammals that live near the islands include sea lions, harbor seals, sea otters, and whales.
These three lie within the boundary of Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Along with nearby Olympic National Park the three agencies cooperate on research programs and other issues that may have impacts on the resources.
The refuges were originally created as Flattery Rocks Reservation, Quillayute Needles Reservation, and Copalis Rock Reservation on October 23, 1907, by executive orders from Theodore Roosevelt. They were renamed by a presidential proclamation on July 25, 1940. Flattery Rocks encompasses the islands off the Washington coast between latitudes 48° 02′ North and 48° 23′ North, Quillayute Needles those between latitudes 47° 38′ North, and 48° 02′ North, and Copalis those between latitudes 47° 08′ North, and 47° 29′ North. James Island was removed from Quillayute Needles in 1966 and returned to the Quileute when the island was discovered to be part of the Quileute Indian Reservation.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
- ^ "Annual Report of Lands as of September 30, 2013" (PDF). United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
- ^ "Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Cite error: The named reference "gnis" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- "Wilderness.net: Washington Islands Wilderness". Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- "Wilderness Connect". wilderness.net. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- "Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge - Wildlife and Habitat". web.archive.org. 2012-11-13. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- Proclamation 2416, July 25, 1940. Mentioned in the citations in the National Wildlife Refuge Administration Act.
- Executive Order 703, October 23, 1907.
- Executive Order 705, October 23, 1907.
- Executive Order 704, October 23, 1907.
- Removed by Public Land Order 4095, September 19, 1966, according to Comprehensive Conservation Plan/Environmental Assessment, Chapter 1, page 1-8.
External links
- Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex
- Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Copalis National Wildlife Refuge U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Washington Islands Wilderness