This is an old revision of this page, as edited by ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) at 16:45, 27 January 2021 (Reverting possible vandalism by Dracom205 to version by DavidCary. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (3880066) (Bot)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:45, 27 January 2021 by ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) (Reverting possible vandalism by Dracom205 to version by DavidCary. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (3880066) (Bot))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Electrically neutral group of two or more atoms "Molecules" and "Molecular" redirect here. For other uses, see molecule (disambiguation).



A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.
In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
In the kinetic theory of gases, the term molecule is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This violates the definition that a molecule contain two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms.
A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, as with two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, as with water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O).
Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not considered single molecules.
Molecules as components of matter are common. They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. Most organic substances are molecules. The substances of life are molecules, e.g. proteins, the amino acids they are made of, the nucleic acids (DNA & RNA), sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. The nutrient minerals ordinarily are not molecules, e.g. iron sulfate.
However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth are not made of molecules. These include all of the minerals that make up the substance of the Earth, soil, dirt, sand, clay, pebbles, rocks, boulders, bedrock, the molten interior, and the core of the Earth. All of these contain many chemical bonds, but are not made of identifiable molecules.
No typical molecule can be defined for salts nor for covalent crystals, although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a plane, e.g. graphene; or three-dimensionally e.g. diamond, quartz, sodium chloride. The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most metals which are condensed phases with metallic bonding. Thus solid metals are not made of molecules.
In glasses, which are solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds with no presence of any definable molecule, nor any of the regularity of repeating unit-cellular-structure that characterizes salts, covalent crystals, and metals.
Molecular science
The science of molecules is called molecular chemistry or molecular physics, depending on whether the focus is on chemistry or physics. Molecular chemistry deals with the laws governing the interaction between molecules that results in the formation and breakage of chemical bonds, while molecular physics deals with the laws governing their structure and properties. In practice, however, this distinction is vague. In molecular sciences, a molecule consists of a stable system (bound state) composed of two or more atoms. Polyatomic ions may sometimes be usefully thought of as electrically charged molecules. The term unstable molecule is used for very reactive species, i.e., short-lived assemblies (resonances) of electrons and nuclei, such as radicals, molecular ions, Rydberg molecules, transition states, van der Waals complexes, or systems of colliding atoms as in Bose–Einstein condensate.
History and etymology
Main article: History of molecular theoryAccording to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin "moles" or small unit of mass.
- Molecule (1794) – "extremely minute particle", from French molécule (1678), from New Latin molecula, diminutive of Latin moles "mass, barrier". A vague meaning at first; the vogue for the word (used until the late 18th century only in Latin form) can be traced to the philosophy of Descartes.
The definition of the molecule has evolved as knowledge of the structure of molecules has increased. Earlier definitions were less precise, defining molecules as the smallest particles of pure chemical substances that still retain their composition and chemical properties. This definition often breaks down since many substances in ordinary experience, such as rocks, salts, and metals, are composed of large crystalline networks of chemically bonded atoms or ions, but are not made of discrete molecules.
Bonding
Molecules are held together by either covalent bonding or ionic bonding. Several types of non-metal elements exist only as molecules in the environment. For example, hydrogen only exists as hydrogen molecule. A molecule of a compound is made out of two or more elements. A homonuclear molecule is made out of two or more atoms of a single element.
While some people say a metallic crystal can be considered a single giant molecule held together by metallic bonding, others point out that metals act very differently than molecules.
Covalent
Main article: Covalent bonding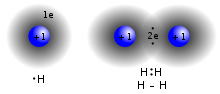
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed covalent bonding.
Ionic
Main article: Ionic bonding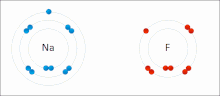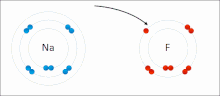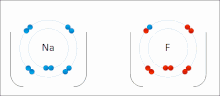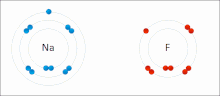
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. The ions are atoms that have lost one or more electrons (termed cations) and atoms that have gained one or more electrons (termed anions). This transfer of electrons is termed electrovalence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complicated nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH4 or SO4.
Molecular size
Most molecules are far too small to be seen with the naked eye, although molecules of many polymers can reach macroscopic sizes, including biopolymers such as DNA. Molecules commonly used as building blocks for organic synthesis have a dimension of a few angstroms (Å) to several dozen Å, or around one billionth of a meter. Single molecules cannot usually be observed by light (as noted above), but small molecules and even the outlines of individual atoms may be traced in some circumstances by use of an atomic force microscope. Some of the largest molecules are macromolecules or supermolecules.
The smallest molecule is the diatomic hydrogen (H2), with a bond length of 0.74 Å.
Effective molecular radius is the size a molecule displays in solution. The table of permselectivity for different substances contains examples.
Molecular formulas
Chemical formula types
Main article: Chemical formulaThe chemical formula for a molecule uses one line of chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to one typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts.
A compound's empirical formula is a very simple type of chemical formula. It is the simplest integer ratio of the chemical elements that constitute it. For example, water is always composed of a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is always composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 2:6:1 ratio. However, this does not determine the kind of molecule uniquely – dimethyl ether has the same ratios as ethanol, for instance. Molecules with the same atoms in different arrangements are called isomers. Also carbohydrates, for example, have the same ratio (carbon:hydrogen:oxygen= 1:2:1) (and thus the same empirical formula) but different total numbers of atoms in the molecule.
The molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. However different isomers can have the same atomic composition while being different molecules.
The empirical formula is often the same as the molecular formula but not always. For example, the molecule acetylene has molecular formula C2H2, but the simplest integer ratio of elements is CH.
The molecular mass can be calculated from the chemical formula and is expressed in conventional atomic mass units equal to 1/12 of the mass of a neutral carbon-12 (C isotope) atom. For network solids, the term formula unit is used in stoichiometric calculations.
Structural formula
Main article: Structural formula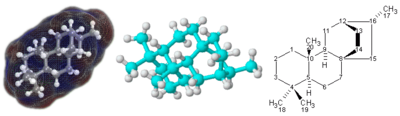
For molecules with a complicated 3-dimensional structure, especially involving atoms bonded to four different substituents, a simple molecular formula or even semi-structural chemical formula may not be enough to completely specify the molecule. In this case, a graphical type of formula called a structural formula may be needed. Structural formulas may in turn be represented with a one-dimensional chemical name, but such chemical nomenclature requires many words and terms which are not part of chemical formulas.
Molecular geometry
Main article: Molecular geometry
Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures. Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemical activities.
Molecular spectroscopy
Main article: Spectroscopy
Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to Planck's formula). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule's energy exchange through absorbance or emission. Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal).
Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules. Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.
Theoretical aspects
The study of molecules by molecular physics and theoretical chemistry is largely based on quantum mechanics and is essential for the understanding of the chemical bond. The simplest of molecules is the hydrogen molecule-ion, H2, and the simplest of all the chemical bonds is the one-electron bond. H2 is composed of two positively charged protons and one negatively charged electron, which means that the Schrödinger equation for the system can be solved more easily due to the lack of electron–electron repulsion. With the development of fast digital computers, approximate solutions for more complicated molecules became possible and are one of the main aspects of computational chemistry.
When trying to define rigorously whether an arrangement of atoms is sufficiently stable to be considered a molecule, IUPAC suggests that it "must correspond to a depression on the potential energy surface that is deep enough to confine at least one vibrational state". This definition does not depend on the nature of the interaction between the atoms, but only on the strength of the interaction. In fact, it includes weakly bound species that would not traditionally be considered molecules, such as the helium dimer, He2, which has one vibrational bound state and is so loosely bound that it is only likely to be observed at very low temperatures.
Whether or not an arrangement of atoms is sufficiently stable to be considered a molecule is inherently an operational definition. Philosophically, therefore, a molecule is not a fundamental entity (in contrast, for instance, to an elementary particle); rather, the concept of a molecule is the chemist's way of making a useful statement about the strengths of atomic-scale interactions in the world that we observe.
See also
- Atom
- Chemical polarity
- Covalent bond
- Diatomic molecule
- List of compounds
- List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules
- Molecular biology
- Molecular design software
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular geometry
- Molecular Hamiltonian
- Molecular ion
- Molecular modelling
- Molecular promiscuity
- Molecular orbital
- Non-covalent bonding
- Periodic systems of small molecules
- Small molecule
- Comparison of software for molecular mechanics modeling
- Van der Waals molecule
- World Wide Molecular Matrix
References
- Iwata, Kota; Yamazaki, Shiro; Mutombo, Pingo; Hapala, Prokop; Ondráček, Martin; Jelínek, Pavel; Sugimoto, Yoshiaki (2015). "Chemical structure imaging of a single molecule by atomic force microscopy at room temperature". Nature Communications. 6: 7766. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7766I. doi:10.1038/ncomms8766. PMC 4518281. PMID 26178193.
- Dinca, L.E.; De Marchi, F.; MacLeod, J.M.; Lipton-Duffin, J.; Gatti, R.; Ma, D.; Perepichka, D.F.; Rosei, F. (2015). "Pentacene on Ni(111): Room-temperature molecular packing and temperature-activated conversion to graphene". Nanoscale. 7 (7): 3263–9. Bibcode:2015Nanos...7.3263D. doi:10.1039/C4NR07057G. PMID 25619890.
- Hapala, Prokop; Švec, Martin; Stetsovych, Oleksandr; Van Der Heijden, Nadine J.; Ondráček, Martin; Van Der Lit, Joost; Mutombo, Pingo; Swart, Ingmar; Jelínek, Pavel (2016). "Mapping the electrostatic force field of single molecules from high-resolution scanning probe images". Nature Communications. 7: 11560. Bibcode:2016NatCo...711560H. doi:10.1038/ncomms11560. PMC 4894979. PMID 27230940.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Molecule". doi:10.1351/goldbook.M04002
- Ebbin, Darrell D. (1990). General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co. ISBN 978-0-395-43302-7.
- Brown, T.L.; Kenneth C. Kemp; Theodore L. Brown; Harold Eugene LeMay; Bruce Edward Bursten (2003). Chemistry – the Central Science (9th ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-066997-1.
- Chang, Raymond (1998). Chemistry (6th ed.). New York: McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-115221-1.
- Zumdahl, Steven S. (1997). Chemistry (4th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-669-41794-4.
- Chandra, Sulekh (2005). Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry. New Age Publishers. ISBN 978-81-224-1512-4.
- "Molecule". Encyclopædia Britannica. 22 January 2016. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- Harper, Douglas. "molecule". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- "molecule". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- Molecule Definition Archived 13 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine (Frostburg State University)
- The Hutchinson unabridged encyclopedia with atlas and weather guide. Oxford, England. OCLC 696918830.
- Harry B. Gray. Chemical Bonds: An Introduction to Atomic and Molecular Structure. 1994. "Chapter 6: Bonding in Solids". p. 210-211.
- "How many gold atoms make gold metal?".
- Campbell, Neil A.; Brad Williamson; Robin J. Heyden (2006). Biology: Exploring Life. Boston: Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-250882-7. Retrieved 5 February 2012.
- Campbell, Flake C. (2008). Elements of Metallurgy and Engineering Alloys. ASM International. ISBN 978-1-61503-058-3.
- Roger L. DeKock; Harry B. Gray; Harry B. Gray (1989). Chemical structure and bonding. University Science Books. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-935702-61-3.
- Chang RL; Deen WM; Robertson CR; Brenner BM (1975). "Permselectivity of the glomerular capillary wall: III. Restricted transport of polyanions". Kidney Int. 8 (4): 212–218. doi:10.1038/ki.1975.104. PMID 1202253.
- Chang RL; Ueki IF; Troy JL; Deen WM; Robertson CR; Brenner BM (1975). "Permselectivity of the glomerular capillary wall to macromolecules. II. Experimental studies in rats using neutral dextran". Biophys. J. 15 (9): 887–906. Bibcode:1975BpJ....15..887C. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85863-2. PMC 1334749. PMID 1182263.
- Wink, Donald J.; Fetzer-Gislason, Sharon; McNicholas, Sheila (2003). The Practice of Chemistry. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-7167-4871-7.
- "ChemTeam: Empirical Formula". www.chemteam.info. Retrieved 16 April 2017.
- Hirsch, Brandon E.; Lee, Semin; Qiao, Bo; Chen, Chun-Hsing; McDonald, Kevin P.; Tait, Steven L.; Flood, Amar H. (2014). "Anion-induced dimerization of 5-fold symmetric cyanostars in 3D crystalline solids and 2D self-assembled crystals". Chemical Communications. 50 (69): 9827–30. doi:10.1039/C4CC03725A. PMID 25080328.
- Zoldan, V. C.; Faccio, R; Pasa, A.A. (2015). "N and p type character of single molecule diodes". Scientific Reports. 5: 8350. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E8350Z. doi:10.1038/srep08350. PMC 4322354. PMID 25666850.
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Spectroscopy". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S05848
- Anderson JB (May 2004). "Comment on "An exact quantum Monte Carlo calculation of the helium-helium intermolecular potential" [J. Chem. Phys. 115, 4546 (2001)]". J Chem Phys. 120 (20): 9886–7. Bibcode:2004JChPh.120.9886A. doi:10.1063/1.1704638. PMID 15268005.
External links
| Particles in physics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composite |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quasiparticles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Branches of chemistry | |
|---|---|
| Analytical | |
| Theoretical | |
| Physical |
|
| Inorganic | |
| Organic | |
| Biological | |
| Interdisciplinarity | |
| See also | |
