This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Citation bot (talk | contribs) at 16:01, 7 February 2024 (Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_CommandLine). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 16:01, 7 February 2024 by Citation bot (talk | contribs) (Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | #UCB_CommandLine)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound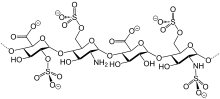 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Badyket, Ivor, Hibor, Zibor, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous injection (except for haemodialysis) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 96% (estimated) |
| Elimination half-life | 5–6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Molar mass | 3600 g/mol (average) |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Bemiparin (trade names Ivor and Zibor, among others) is an antithrombotic and belongs to the group of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH).
Medical uses
Bemiparin is used for the prevention of thromboembolism after surgery, and to prevent blood clotting in the extracorporeal circuit in haemodialysis.
Contraindications
The medication is contraindicated in patients with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with or without disseminated intravascular coagulation; acute bleeding or risk of bleeding; injury or surgery of the central nervous system, eyes or ears; severe liver or pancreas impairment; and acute or subacute bacterial endocarditis.
Interactions
No interaction studies have been conducted. Drugs that are expected to increase the risk of bleeding in combination with bemiparin include other anticoagulants, aspirin and other NSAIDs, antiplatelet drugs, and corticosteroids.
Chemistry
Like semuloparin, bemiparin is classified as an ultra-LMWH because of its low molecular mass of 3600 g/mol on average. (Enoxaparin has 4500 g/mol.) These heparins have lower anti-thrombin activity than classical LMWHs and act mainly on factor Xa, reducing the risk of bleeding.
References
- Chapman TM, Goa KL (2003). "Bemiparin: a review of its use in the prevention of venous thromboembolism and treatment of deep vein thrombosis". Drugs. 63 (21): 2357–77. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363210-00009. PMID 14524738. S2CID 195692039.
- ^ Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. 2018. Ivor 2500 IE Anti-Xa/0,2 ml Injektionslösung in Fertigspritzen.
- Planès A (September 2003). "Review of bemiparin sodium--a new second-generation low molecular weight heparin and its applications in venous thromboembolism". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 4 (9): 1551–61. doi:10.1517/14656566.4.9.1551. PMID 12943485. S2CID 13566575.
- Jeske WP, Hoppensteadt D, Gray A, Walenga JM, Cunanan J, Myers L, Fareed J, Bayol A, Rigal H, Viskov C (October 2011). "A common standard is inappropriate for determining the potency of ultra low molecular weight heparins such as semuloparin and bemiparin". Thrombosis Research. 128 (4): 361–7. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2011.03.001. PMID 21458847.
External links
- bemiparin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| Antithrombotics (thrombolytics, anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs) (B01) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiplatelet drugs |
| ||||||||||||||
| Anticoagulants |
| ||||||||||||||
| Thrombolytic drugs/ fibrinolytics | |||||||||||||||
| Non-medicinal | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||