This is the current revision of this page, as edited by JWBE (talk | contribs) at 16:36, 23 September 2024 (added Category:4-Methoxyphenyl compounds using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 16:36, 23 September 2024 by JWBE (talk | contribs) (added Category:4-Methoxyphenyl compounds using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)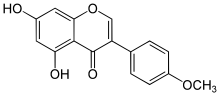 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 5,7-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Biochanin 4′-Methylgenistein olmelin Biochanine A Biochanin-A Genistein 4-methyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.041 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H12O5 |
| Molar mass | 284.267 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Biochanin A is an O-methylated isoflavone. It is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as flavonoids. Biochanin A can be found in red clover in soy, in alfalfa sprouts, in peanuts, in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and in other legumes.
Biochanin A is classified as a phytoestrogen and has putative benefits in dietary cancer prophylaxis. It has also been found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase in vitro.
Metabolism
The enzyme biochanin-A reductase uses dihydrobiochanin A and NADP to produce biochanin A, NADPH, and H. The enzyme isoflavone-7-O-beta-glucoside 6"-O-malonyltransferase uses malonyl-CoA and biochanin A 7-O-β-D-glucoside to produce CoA and biochanin A 7-O-(6-O-malonyl-β-D-glucoside).
See also
References
- Medjakovic, S.; Jungbauer, A. (2008). "Red clover isoflavones biochanin A and formononetin are potent ligands of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 108 (1–2): 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.10.001. PMID 18060767. S2CID 206495959.
- Thors L, Burston JJ, Alter BJ, McKinney MK, Cravatt BF, Ross RA, Pertwee RG, Gereau RW, Wiley JL, Fowler CJ (2010). "Biochanin A, a naturally occurring inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase". British Journal of Pharmacology. 160 (3): 549–560. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00716.x. PMC 2931556. PMID 20590565.
| Isoflavones and their glycosides | |
|---|---|
| Isoflavones | |
| O-methylated isoflavones | |
| Glycosides | |
| Prenylated isoflavones | |
| Pyranoisoflavones | |
| Derivatives | |
| Synthetic | |
| Estrogen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| Estrogen-related receptor modulators | |
|---|---|
| ERRαTooltip Estrogen-related receptor alpha |
|
| ERRβTooltip Estrogen-related receptor beta |
|
| ERRγTooltip Estrogen-related receptor gamma |
|
| |