This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Preimage (talk | contribs) at 11:24, 7 December 2024 (Add citation). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 11:24, 7 December 2024 by Preimage (talk | contribs) (Add citation)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| It has been suggested that this article be merged with Metal peroxide. (Discuss) Proposed since November 2024. |
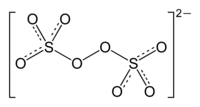
In chemistry, main group peroxides are peroxide derivatives of the main group elements. Many compounds of the main group elements form peroxides (R−O−O−R'), and a few are of commercial significance.
Examples
With thousands of tons/year being produced annually, the peroxydisulfates, S2O2−8, are preeminent members of this class. These salts serve as initiators for polymerization of acrylates and styrene.
At one time, peroxyborates were used in detergents. These salts have been largely replaced by sodium carbonate sesquiperhydrate.
Many peroxides are not commercially valuable but are of academic interest. One example is bis(trimethylsilyl) peroxide (Me3SiOOSiMe3). Phosphorus oxides form a number of peroxides, e.g. "P2O6".
References
- ^ Jakob, Harald; Leininger, Stefan; Lehmann, Thomas; Jacobi, Sylvia; Gutewort, Sven (2007). "Peroxo Compounds, Inorganic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_177.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Jih Ru Hwu; Buh-Luen Chen; Santhosh F. Neelamkavil; Yuzhong Chen (2002). "Bis(trimethylsilyl) Peroxide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb219.pub3. ISBN 0-471-93623-5.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.