This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Bongwarrior (talk | contribs) at 18:23, 27 October 2007 (Reverted 1 edit by Sllappy to last revision by SieBot. using TW). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:23, 27 October 2007 by Bongwarrior (talk | contribs) (Reverted 1 edit by Sllappy to last revision by SieBot. using TW)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)For other uses, see the sport.

Baseball is a sport played between two teams usually of nine players each. It is a bat-and-ball game in which a pitcher throws (pitches) a hard, fist-sized, leather-covered ball toward a batter on the opposing team. The batter attempts to hit the baseball with a tapered cylindrical bat, made of wood (as required in professional baseball) or a variety of other materials (as allowed in many nonprofessional games). A team scores runs only when batting, by advancing its players--primarily via hits, walks, and the opposition team's fielding errors--counterclockwise past a series of three markers called bases and touching home plate arranged at the corners of a ninety-foot square, or "diamond." The game is structured around nine segments called innings. In each inning, both teams are given the opportunity to bat and score runs; a team's half-inning ends when three outs are recorded against that team. There is no time limit - each game lasts as long or as short as necessary to determine a winner.
Baseball on the professional, amateur, and youth levels is popular in North America, Central America, parts of South America, parts of the Caribbean, and parts of East Asia and Southeast Asia. The modern version of the game developed in North America beginning in the eighteenth century. The consensus of historians is that it evolved from earlier bat-and-ball games, such as rounders, brought to the continent by British and Irish immigrants. By the late nineteenth century, baseball was widely recognized as the national sport of the United States. The game is sometimes referred to as hardball in contrast to the very similar game of softball.
In North America, professional Major League Baseball teams are divided into the National League (NL) and American League (AL). Each league has three divisions: East, West, and Central. Every year, the champion of Major League Baseball is determined by playoffs culminating in the World Series. Four teams make the playoffs from each league: the three regular season division winners, plus one wild card team. The wild card is the team with the best record among the non–division winners in the league. In the National League, the pitcher is required to bat, per the traditional rules. In the American League, there is a tenth player, a designated hitter, who bats for the pitcher. Each major league team has a "farm system" of minor league teams at various levels. These teams allow younger players to develop as they gain on-field experience against opponents with similar levels of skill.
History of baseball
| Part of a series on the |
| History of baseball |
|---|
| Early years |
| By country |
International competitions
|
| Other topics |
| Related games |
| Baseball portal |
Origins of baseball
Main article: Origins of baseballThe distinct evolution of baseball from among the various bat-and-ball games is difficult to trace with precision. While there has been general agreement that modern baseball is a North American development from the older game rounders, the 2006 book Baseball Before We Knew It: A Search for the Roots of the Game, by David Block, argues against that notion. Several references to "baseball" and "bat-and-ball" have been found in British and American documents of the early eighteenth century. The earliest known description is in a 1744 British publication, A Little Pretty Pocket-Book, by John Newbery. It contains a wood-cut illustration of boys playing "base-ball," showing a baseball set-up roughly similar to the modern game, and a rhymed description of the sport. The earliest known unambiguous American discussion of "baseball" was published in a 1791 Pittsfield, Massachusetts, town bylaw that prohibited the playing of the game within 80 yards (70 m) of the town's new meeting house. The English novelist Jane Austen made a reference to children playing "base-ball" on a village green in her book Northanger Abbey, which was written between 1798 and 1803 (though not published until 1818).
The first full documentation of a baseball game in North America is Dr. Adam Ford's contemporary description of a game that took place in 1838 on June 4 (Militia Muster Day) in Beachville, Ontario, Canada; this report was related in an 1886 edition of Sporting Life magazine in a letter by former St. Marys, Ontario, resident Dr. Matthew Harris. In 1845, Alexander Cartwright of New York City led the codification of an early list of rules (the so-called Knickerbocker Rules), from which today's have evolved. He had also initiated the replacement of the soft ball used in rounders with a smaller hard ball. While there are reports of Cartwright's club, the New York Knickerbockers, playing games in 1845, the game now recognized as the first in U.S. history to be officially recorded took place on June 19, 1846, in Hoboken, New Jersey, with the "New York Nine" defeating the Knickerbockers, 23–1, in four innings.
History of baseball in the United States
Main article: History of baseball in the United StatesSemiprofessional baseball started in the United States in the 1860s; in 1869, the first fully professional baseball club, the Cincinnati Red Stockings, was formed and went undefeated against a schedule of semipro and amateur teams. By the following decade, American newspapers were referring to baseball as the "National Pastime" or "National Game." The first attempt at forming a "major league" was the National Association, which lasted from 1871 to 1875. The "major league" status of the NA is in dispute among present-day baseball historians, and Major League Baseball does not include the NA among the major leagues. The National League, which still exists, was founded in 1876 in response to the NA's shortcomings. Several other major leagues formed and failed, but the American League, which evolved from the minor Western League (1893) and was established in 1901 as a major league, succeeded. The two leagues were initially rivals that actively fought for the best players, often disregarding one another's contracts and engaging in bitter legal disputes. A modicum of peace was established in 1903, and the World Series was inaugurated that fall. The next year, however, the National League champion New York Giants did not participate as their manager, John McGraw, refused to recognize the major league status of the American League and its champion, the Boston Americans. The following year, McGraw relented and the Giants played the Philadelphia Athletics in the World Series.
Compared with the present day, games in the early part of the 20th century were lower scoring and pitchers were more successful. The "inside game", whose nature was to "scratch for runs", was played more violently and aggressively than it is today. Ty Cobb said of his era especially, "Baseball is something like a war!" This period, which has since become known as the "dead-ball era", ended in the 1920s with several rule changes that gave advantages to hitters and the rise of the legendary baseball player Babe Ruth, who showed the world what power hitting could produce, altering the nature of the game. Two of the changes introduced were a move to bring the outfield fences closer to the infield in the largest parks, and an introduction of extremely strict rules governing the size, shape and construction of the ball, causing it to travel farther when hit; the aggregate result of these two changes was to enable batters to hit many more home runs.
In 1884, African American Moses Walker (and, briefly, his brother Welday) had played for the Toledo Blue Stockings of the major league American Association. An injury ended Walker's major league career, and by the early 1890s, a "gentlemen's agreement" in the form of the baseball color line effectively barred African-American players from the majors and their affiliated minor leagues, resulting in the formation of several Negro Leagues. The first crack in the agreement occurred in 1946, when Jackie Robinson was signed by the National League's Brooklyn Dodgers and began playing for their minor league team in Montreal. Finally, in 1947, the major leagues' color barrier was broken when Robinson debuted with the Dodgers. Although the transformation was not instantaneous, baseball has since become fully integrated.
Major League baseball finally made it to the West Coast of the United States in 1958, when the Brooklyn Dodgers and New York Giants relocated to Los Angeles and San Francisco respectively. The first American League team on the West Coast was the Los Angeles Angels, who were founded as an expansion team in 1961.
Pitchers dominated the game in the 1960s and early 1970s. In the early 1970s the designated hitter (DH) rule was proposed. The American League adopted this rule in 1973, though pitchers still bat for themselves in the National League to this day. The DH rule now constitutes the primary difference between the two leagues.
Despite the popularity of baseball, and the attendant high salaries relative to those of average Americans, the players have become dissatisfied from time to time, as they believed the owners had too much control and retained an unfair share of the money. Various job actions have occurred throughout the game's history. Players on specific teams occasionally attempted strikes, but usually came back when their jobs were sufficiently threatened. The throwing of the 1919 World Series, the "Black Sox scandal", was in some sense a "strike" or at least a rebellion by the ballplayers against a perceived stingy owner. But the strict rules of baseball contracts tended to keep the players "in line" in general.
This began to change in 1966 when former United Steelworkers chief economist (and assistant to the president) Marvin Miller became the Baseball Players Union executive director. The union became much stronger than it had been previously, especially when the reserve clause was effectively nullified in the mid-1970s. Conflicts between owners and the players' union led to major work stoppages in 1972, 1981, and 1994. The 1994 baseball strike led to the cancellation of the World Series, and was not settled until the spring of 1995. During this period, as well, many of the functions — such as player discipline and umpire supervision — and regulations that had been administered separately by the two major leagues' administrations were united under the rubric of Major League Baseball.
1995 was the year Cal Ripken, Jr. played in his 2,131st consecutive game, breaking Lou Gehrig's record. The number of home runs increased dramatically after the strike. Mark McGwire and Sammy Sosa both surpassed Roger Maris's long-standing single season home run record in 1998. In 2001, Barry Bonds established the current record of 73 home runs in a single season. In 2007, Bonds became MLB's all-time home run leader, surpassing Hank Aaron's total of 755. Even though all three sluggers (McGwire, Sosa, and Bonds) have been accused in the steroid-abuse scandal of the mid-2000s, their feats did do a lot at the time to bolster the game's renewed popularity.
Baseball around the world
Main article: History of baseball outside the United StatesBaseball is largely known as America's pastime, but has a fan base in several other countries as well. The history of baseball in Canada has remained closely linked with that of the sport in the United States. As early as 1877, a professional league, the International Association, featured teams from both countries. While baseball is widely played in Canada, and many minor league teams have been based in the country, the American major leagues did not include a Canadian club until 1969, when the Montreal Expos joined the National League as an expansion team. In 1977, the expansion Toronto Blue Jays joined the American League. The Blue Jays won the World Series in 1992 and 1993, the first and still the only club from outside the United States to do so. In 2004, Major League Baseball relocated the Expos to Washington, D.C., where the team is now known as the Nationals.
The first formal baseball league outside of the United States and Canada was founded in 1878 in Cuba, which maintains a rich baseball tradition and whose national team has been one of the world's strongest since international play began in the late 1930s. Professional baseball leagues began to form in other countries between the world wars, including the Netherlands (formed in 1922), Australia (1934), Japan (1936), and Puerto Rico (1938). After World War II, professional leagues were founded in Italy (1948) and in many Latin American nations, most prominently Venezuela (1945), Mexico (1945), and the Dominican Republic (1951). In Asia, Korea (1982), Taiwan (1990), and China (2003) all have professional leagues.
Many European countries have pro leagues as well, the most successful beside the Dutch being the Italian league founded in 1948. Compared to those in Asia and Latin America, the various European leagues and the one in Australia historically have had no more than niche appeal. Recently, the sport has begun to grow in popularity in those nations, most notably in Australia, which won a surprise silver medal in the 2004 Olympic Games. In 2007, the Israel Baseball League, featuring six teams, was launched. Competition between national teams, such as in the Baseball World Cup and the Olympic baseball tournament, has been administered by the International Baseball Federation since its formation in 1938. As of 2004, the organization has 112 member countries.
Since the early 1970s, the annual Caribbean Series has matched the league-winning clubs from Puerto Rico, Venezuela, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic. The Confédération Européene de Baseball (European Baseball Confederation), founded in 1953, organizes a number of competitions between clubs from different countries as well as national squads. The inaugural World Baseball Classic, held in March 2006, had a much higher profile than previous tournaments featuring national teams, owing to the participation for the first time of a significant number of players from Major League Baseball.
The 117th meeting of the International Olympic Committee, held in Singapore in July 2005, voted not to hold baseball and softball tournaments at the 2012 Summer Olympic Games, but they will remain Olympic sports during the 2008 Summer Olympic Games and will be put to vote again for each succeeding Summer Olympics. The elimination of baseball and softball from the 2012 Olympic program enabled the IOC to consider adding two different sports to the program, but no other sport received a majority of votes favoring its inclusion. While baseball's lack of substantial appeal in much of the world was a factor; more important is the unwillingness of Major League Baseball to have a break during the Games so that its players can participate, something that the National Hockey League now does during the Winter Olympic Games. Because of the seasonal nature of baseball and the high priority its fans place on the integrity of major-league statistics from one season to the next, it would be more difficult to accommodate such a break in Major League Baseball.
Gameplay
A simplified version of the rules of baseball is at simplified baseball rules. The complete Official Rules can be found at MLB.com, the official web site of Major League Baseball in the United States.
General structure
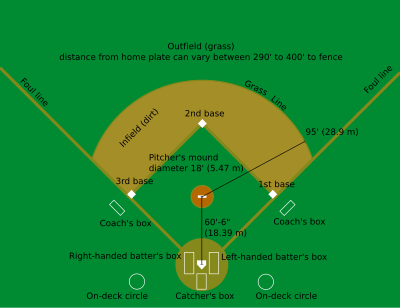
Baseball is played between two teams of nine players each on a baseball field, under the authority of one or more officials, called umpires. There are usually four umpires in major league games; up to six (and as few as one) may officiate depending on the league and the importance of the game. There are four bases. Numbered counter-clockwise, first, second and third bases are cushions (sometimes informally referred to as bags) shaped as 15 in (38 cm) squares which are raised a short distance above the ground; together with home plate, the fourth "base," they form a square with sides of 90 ft (27.4 m) called the diamond. Home base (plate) is a pentagonal rubber slab known as simply home. The playing field is divided into three main sections:
- The infield, containing the four bases, is for general defensive purposes bounded by the foul lines and within the grass(or AstroTurf) line (see figure).
- The outfield is the grassed area beyond the infield grass line between the foul lines, and bounded by a wall or fence.
- Foul territory is the entire area outside the foul lines.
The pitcher's mound is located in the center of the infield. It is an 18 foot (5.5 m) diameter mound of dirt no higher than 10 inches (25.4 cm). Near the center of the mound is the pitching rubber, a rubber slab positioned 60 feet 6 inches (18.4 m) from home plate. The pitcher must have one foot on the rubber at the start of every pitch to a batter, but the pitcher may leave the mound area once the ball is released.
At the college/professional level, baseball is played in nine innings in which each team gets one turn to bat and try to score runs while the other pitches and defends in the field. High school baseball plays seven innings and Little League uses six inning games. An inning is broken up into two halves in which the away team bats in the top (first) half, and the home team bats in the bottom (second) half. In baseball, the defense always has the ball — a fact that differentiates it from most other team sports. The teams switch every time the defending team gets three players of the batting team out. The winner is the team with the most runs after nine innings. If the home team is ahead after the top of the ninth, play does not continue into the bottom half. In the case of a tie, additional innings are played until one team comes out ahead at the end of an inning. If the home team takes the lead anytime during the bottom of the ninth or of any inning thereafter, play stops and the home team is declared the winner.

The basic contest is always between the pitcher for the fielding team, and a batter. The pitcher throws—pitches—the ball towards home plate, where the catcher for the fielding team waits (in a crouched stance) to receive it. Behind the catcher stands the home plate umpire. The batter stands in one of the batter's boxes and tries to hit the ball with a bat. The pitcher must keep one foot in contact with the top or front of the pitcher's rubber — a 24" x 6" (~ 61 cm x 15 cm) plate located atop the pitcher's mound — during the entire pitch, so he can only take one step backward and one forward in delivering the ball. The catcher's job is to receive any pitches that the batter does not hit and to "call" the game by a series of hand movements that signal to the pitcher what pitch to throw and where. If the pitcher disagrees with the call, he will "shake off" the catcher by shaking his head; he accepts the sign by nodding. Each team has a different set of signals, though the number 1 is almost universal as a fast ball. The catcher's role becomes more crucial depending on how the game is going, and how the pitcher responds to a given situation. Each pitch begins a new play, which might consist of nothing more than the pitch itself.
Each half-inning, the goal of the defending team is to get three members of the other team out. A player who is out must leave the field and wait for his next turn at bat. There are many ways to get batters and baserunners out; some of the most common are catching a batted ball in the air, tag outs, force outs, and strikeouts. After the fielding team has put out three players from the opposing team, that half of the inning is over and the team in the field and the team at bat switch places; there is no upper limit to the number that may bat in rotation before three outs are recorded. Going through the entire order in an inning is referred to as "batting around". It is indicative of a high scoring inning. A complete inning consists of each opposing side having a turn (three outs) on offense.
The goal of the team at bat is to score more runs than the opposition; a player may do so only by batting, then becoming a base runner, touching all the bases in order (via one or more plays), and finally touching home plate. To that end, the goal of each batter is to enable baserunners to score or to become a baserunner himself. The batter attempts to hit the ball into fair territory — between the baselines — in such a way that the defending players cannot get them or the baserunners out. In general, the pitcher attempts to prevent this by pitching the ball in such a way that the batter cannot hit it cleanly or, ideally, at all.
A baserunner who successfully touches home plate after touching all previous bases in order scores a run. In an enclosed field, a fair ball hit over the fence on the fly is normally an automatic home run, which entitles the batter and all runners to touch all the bases and score. A home run hit with all bases occupied ('bases loaded') is called a grand slam.
Fielding team
See also: Baseball positions and Baseball positioningThe squad in the field is the defensive team; they attempt to prevent the baserunners from scoring. There are nine defensive positions, but only two have a mandatory location (pitcher and catcher). The locations of the other seven fielders is not specified by the rules, except that at the moment the pitch is delivered they must be positioned in fair territory and not in the space between the pitcher and the catcher. These fielders often shift their positioning in response to specific batters or game situations, and they may exchange positions with one another at any time. The nine positions most commonly used (with the number scorekeepers use) are: pitcher (1), catcher (2), first baseman (3), second baseman (4), third baseman (5), shortstop (6), left fielder (7), center fielder (8), and right fielder (9). Note that, in rare cases, teams may use dramatically differing schemes, such as switching an outfielder for an infielder. The numbering convention was established by Henry Chadwick. The reason the shortstop seems out of order has to do with the way fielders positioned themselves in the early years of the game.
The battery
The battery is composed of the pitcher, who stands on the rubber of the mound, which is also known as the pitching plate, and the catcher, who squats behind home plate. These are the two fielders who always deal directly with the batter on every pitch, hence the term "battery", coined by Henry Chadwick and later reinforced by the implied comparison to artillery fire.
The pitcher's main role is to pitch the ball toward home plate with the goal of getting the batter out. Pitchers also play defense by fielding batted balls, covering bases (for a potential tag out or force out on an approaching runner), or backing up throws. The catcher's main role is to receive the pitch if the batter does not hit it. Together with the pitcher and coaches, the catcher plots game strategy by suggesting different pitches and by shifting the starting positions of the other fielders. Catchers are also responsible for defense in the area near home plate.
The infielders
The four infielders are the first baseman, second baseman, shortstop, and third baseman. Originally the first, second and third basemen played very near their respective bases, and the shortstop generally played "in" (hence the term), covering the area between second, third, and the pitchers box, or wherever the game situation required. As the game evolved, the fielding positions changed to the now-familiar "umbrella", with the first and third baseman generally positioned a short distance toward second base from their bases, the second baseman to the right side of second base standing farther away from the base than any other infielder, and the shortstop playing to the left of second base, as seen from the batter's perspective, filling in the gaps.
The first baseman's job consists largely of making force plays at first base on ground balls hit to the other infielders. When an infielder picks up a ball from the ground hit by the batter, he must throw it to the first baseman who must catch the ball and maintain contact with the base before the batter gets to it for the batter to be out. The need to do this quickly often requires the first baseman to stretch one of his legs to touch first base while catching the ball simultaneously. The first baseman must be able to catch the ball very well and usually wears a specially designed mitt. The first baseman fields balls hit near first base. The first baseman also has to receive throws from the pitcher in order to tag runners out who have reached base safely. The position is less physically challenging than the other positions, but there is still a lot of skill involved. Infielders don't always make good throws to first base, so it is the first baseman's job to field any ball thrown toward him cleanly. Older players who can no longer fulfill the demands of their original positions also often become first basemen.
The second baseman covers the area to the first-base side of second base and provides backup for the first baseman in bunt situations. He also is a cut-off for the outfield. This is when the outfielder doesn't have to throw the full distance from him/her to the base, but just to the cut-off. The shortstop fills the critical gap between second and third bases — where right-handed batters generally hit ground balls — and also covers second or third base and the near part of left field. This player is also a cut-off for the outfield. This position is the most demanding defensively, so a good shortstop doesn't need to necessarily be a good batter. The third baseman's primary requirement is a strong throwing arm, in order to make the long throw across the infield to the first baseman. Quick reaction time is also important for third basemen, as they tend to see more sharply hit balls than the other infielders, thus the nickname for third base as the "hot corner." Also, because there are far more right-handed hitters than lefties, there are more ground balls hit to the left side of the infield due to the natural motion of the batter's swing.
The outfielders
The three outfielders, left fielder, center fielder, and right fielder, are so named from the catcher's perspective looking out onto the field. The right fielder generally has the strongest arm of all the outfielders due to the need to make throws on runners attempting to take third base. The center fielder has more territory to cover than the corner outfielders, so this player must be quick and agile with a strong arm to throw balls in to the infield; as with the shortstop, teams tend to emphasize defense at this position. Also, the center fielder is considered the outfield leader, and left- and right-fielders often cede to his direction when fielding fly balls. Of all outfielders, the left fielder often has the weakest arm, as they generally do not need to throw the ball as far in order to prevent the advance of any baserunners. The left fielder still requires good fielding and catching skills, and tends to receive more balls than the right fielder due to the fact that right-handed hitters, who are much more common, tend to "pull" the ball into left field. Each outfielder runs to "back up" a nearby outfielder who attempts to field a ball hit near both their positions. Outfielders also run to back up infielders on batted balls and thrown balls, including pick-off attempts from the pitcher or from the catcher.
Defensive strategy
Pitching

Effective pitching is vitally important to a baseball team, as pitching is the key for the defensive team to retire batters and to preventing runners from getting on base. A full game usually involves over one hundred pitches thrown by each team. However, most pitchers begin to tire before they reach this point. In previous eras, pitchers would often throw up to four complete games (all nine innings) in a week. With new advances in medical research and thus a better understanding of how the human body functions and tires out, starting pitchers tend more often to throw fractions of a game (typically six or seven innings, depending on their performance) about every five days (though a few complete games do still occur each year).
Multiple pitchers are often needed in a single game, including the starting pitcher and relief pitcher(s). Pitchers are substituted for one another like any other player (see below), and the rules do not limit the number of pitchers that can be used in a game; the only limiting factor is the size of the squad, naturally. In general, starting pitchers are not used in relief situations except sometimes during the post-season when every game is vital. If a game runs into many extra innings, a team may well empty its bullpen. If it then becomes necessary to use a "position player" as a pitcher, major league teams generally have certain players pre-designated as emergency relief pitchers, to avoid the embarrassment of using a less skillful player. In baseball's early years, squads were smaller, and relief pitchers were relatively uncommon, with the starter normally remaining for the entire game unless he was either thoroughly ineffective or became injured; today, with a much greater emphasis on pitch count (100 being the "magic number" in general), over the course of a single game each team will frequently use from two to five pitchers. In the 2005 ALCS, all four of the Chicago White Sox victories were complete games by the starters, a highly noteworthy event in the modern game.
Although a pitcher can only take one step backward and one forward, he has to step off the rubber to throw over to first base if he is a right handed pitcher. While delivering the ball, the pitcher has a great arsenal at his disposal in the variation of location, velocity, movement, and arm location (see types of pitches). Most pitchers attempt to master two or three types of pitches; some pitchers throw up to 6 types of pitches with varying degrees of control. Common pitches include a fastball, which is the ball thrown at high speed; a curveball, which is made to curve by rotation imparted by the pitcher; and a change-up, which seeks to mimic the delivery of a fastball but arrives at significantly lower velocity.
To illustrate pitching strategy, consider the "fastball/change-up" combination: The average major-league pitcher can throw a fastball around 90 miles per hour (145 km/h), and a few pitchers have even exceeded 100 miles per hour (161 km/h). The change-up is thrown somewhere between 75 to 85 miles per hour (121 to 137 km/h). Since the batter's timing is critical to hitting a pitch, a batter swinging to hit what looks like a fastball, would be terribly fooled (swing and miss, hopefully) when the pitch turns out to be a much slower change-up.
Some pitchers choose to throw using the 'submarine style,' a very efficient sidearm or near-underhand motion. Pitchers with a submarine delivery are often very difficult to hit because of the angle and movement of the ball once released. Walter Johnson, who threw one of the fastest fastballs in the history of the game, threw sidearm (though not submarine) rather than a normal overhand. True underhanded pitching is permitted in Major League Baseball. However, it is difficult to generate enough velocity and movement with the underhand motion. Among Major League pitchers today, Chad Bradford has the closest to an underhand delivery, with his knuckles sometimes scraping the ground. However, he is still usually considered a "submarine" pitcher.
Fielding strategy

Only the pitcher's and catcher's locations are fixed, and then only at the beginning of each pitch. Thus, the players on the field move around as needed to defend against scoring a run. Many variations of this are possible, as location depends upon the situation. Circumstances such as the number of outs, the count (balls and strikes) on the batter, the number and speed of runners, the ability of the fielders, the ability of the pitcher, the type of pitch thrown, the tendencies of the hitter, and the inning cause the fielders to move to more strategic locations on the field. Common defensive strategies include: playing for the bunt, trying to prevent a stolen base, moving to a shallow position to throw out a runner at home, playing at "double play depth", and moving fielders to locations where hitters are most likely to hit the ball.
Batting team
Batters and runners
The ultimate goal of the team at bat is to score runs. To accomplish this task, the team at bat successively (in a predetermined order called a lineup or batting order) sends its nine players to the batter's box (adjacent to home plate) where they become batters. (Each team sets its batting lineup at the beginning of the game. Changes to the lineup are tightly limited by the rules of baseball and must be communicated to the umpires, who have the substitutions announced for the opposing team and fans. See Substitutions below.)
A batter's turn at the plate is called a plate appearance. Batters can advance to first base safely in one of seven methods: a base-hit (abbreviated 'H') or walk ('BB' for base-on-balls) are by far the most common; being hit-by-the-pitch ('HBP'), reaching by error ('E') or fielder's choice ('FC') are less common; and somewhat rarely a player may reach base by virtue of interference ('I') or a passed ball ('PB') on a strike-out, where the player is allowed to run and reach base safely if he can. When the batter hits a fair ball, he must run to first base, and may continue or stop at any base unless he is put out. A successful hit occurs when the batter reaches a base: reaching only first base is a single; reaching second base, a double; third base, a triple; and a hit that allows the batter to touch all bases in order on the same play is a home run - whether the ball is hit over the fence does not matter (if the ball is not hit over the fence and the batter touches all bases, it is usually referred to as an "inside-the-park home run"). Once a runner is held to a base, he may attempt to advance at any time, but is not required to do so unless the batter or another runner displaces him (called a force play). A batter always drops his bat when running the bases; otherwise, the bat would slow him down and could give rise to a call of interference if it were to contact the ball or a fielder.
Depending on the way the ball comes off the bat, the play has different names. A batted ball is called a fly ball if it is hit in the air in an upward arc, such that a fielder might be able to catch it before it hits the ground. A batted ball is called a ground ball if it hits the ground within the infield before it can be caught, often due to being hit in a downward trajectory. Several different names are used to describe fly balls, depending on their trajectory. A ball hit high in the air and seemingly almost straight up is called a "pop-up". A ball hit forcefully in a fast-moving and seemingly almost straight-line trajectory is called a line drive. A "shallow" fly ball, hit with just enough force to possibly land between the infielders and the outfielders, is often call a "blooper". A "deep" fly ball is hit within enough force to approach and possibly clear the outfield fence.
When a ball is hit outside the foul lines, it is a foul ball, requiring the batter and all runners to return to their respective bases, whether it is caught or not.
Once the batter and any existing runners have all stopped at a base or been put out, the ball is returned to the pitcher, and the next batter comes to the plate. After the opposing team bats in its own order and three more outs are recorded, the first team's batting order will continue again from where it left off.
When a runner reaches home plate, he scores a run and is no longer a base runner. He must leave the playing area until his spot in the order comes up again. A runner may only circle the bases once per plate appearance and thus can score no more than a single run.
Batting
Main article: Batting (baseball)Each plate appearance consists of a series of pitches, in which the pitcher throws the ball towards home plate while a batter is standing in the batter's box (either right or left). With each pitch, the batter must decide whether to swing the bat at the ball in an attempt to hit it. The pitches arrive quickly, so the decision to swing must be made in less than a tenth of a second, based on whether the ball is hittable and in the strike zone, a region defined by the area directly above home plate and between the hollow beneath the batter's knee and the midpoint between the top of the shoulders and the top of the uniform pants. In addition to swinging at the ball, a batter who wishes to put the ball in play may hold his bat over home plate and attempt to tap a pitch lightly; this is called a bunt. Good bunting technique has been described as "catching the ball with the bat."
On any pitch, if the batter swings at the ball and misses, he is charged with a strike. If the batter does not swing, the home plate umpire judges whether the ball passed through the strike zone. If the ball, or any part of it, passed through the zone, it is ruled a strike; otherwise, it is called a ball. The number of balls and strikes thrown to the current batter is known as the count; the count is always given balls first (except in Japan, where it is reversed), then strikes (such as 3-2 or "three and two", also known as a "full count," which would be 3 balls and 2 strikes).
If the batter swings and makes contact with the ball, but does not put it in play in fair territory—a foul ball—he is charged with an additional strike, except when there are already two strikes. Thus, a foul ball with two strikes leaves the count unchanged. (However, a noted exception to this rule is that a ball bunted foul with two strikes is a strikeout.) If a pitch is batted foul or fair and a member of the defensive team is able to catch it, before the ball strikes the ground, the batter is declared out. In the event that a bat contacts the ball, but the ball continues sharply and directly to the catcher's mitt and is caught by the catcher, it is a foul tip, which is same as an ordinary strike.
When three strikes occur on a batter, it is a strikeout and the batter is automatically out unless the pitch is not caught by the catcher or if the pitch bounces before it is caught. It is then ruled an uncaught third strike, a violation of the third strike rule:) If the catcher drops the third strike the batter is permitted to attempt to advance to first base. In this case, the batter is not out (although the pitcher is awarded a strikeout). The catcher can try to get the batter out by tagging him with the ball or throwing the ball to first base and forcing him out. (See Doug Eddings (2005 ALCS) and Mickey Owen (1941 World Series) for famous examples of dropped third strikes that dramatically altered the course of post-season series.)
On the fourth ball, it is called a walk, and the batter becomes a runner, and is entitled to advance to first base without risk of being put out, called a base on balls or a walk (abbreviated BB). If a pitch touches the batter (or the batter's clothes), the umpire declares a hit by pitch (abbreviated HBP) and the batter is awarded first base, unless the umpire determines that the ball was in the strike zone when it hit the batter, or that the batter did not attempt to avoid being hit. In practice, neither exception is ever called unless the batter obviously tries to get hit by the pitch; even standing still in the box will virtually always be overlooked, and the batter awarded first. In addition, if the batter swings at a pitch that hits him, it counts as a strike. If the catcher's mitt, catcher's mask, or any part of the catcher comes in contact with the batter and/or the batter's bat as the batter is attempting to hit a pitch, the batter is awarded first base, ruled "catcher's interference".
Baserunning
Main article: BaserunningOnce a batter becomes a runner and reaches first base safely, he is said to be "on" that base until he attempts to advance to the next base, until he is put out, or until the half-inning ends. When comparing two or more runners on the basepaths, the runner farther along is called a lead runner or a preceding runner; the other runner is called a trailing runner or a following runner. Runners on second or third base are considered to be in scoring position since ordinary hits, even singles, will often allow them to score.
A runner legally touching a base is "safe"—he may not be put out. Runners may attempt to advance from base to base at any time (except when the ball is dead), but must attempt to advance when forced--when all previous bases are occupied and the batter becomes a runner. When a ball is hit in the air, a fly ball, and caught by the defending team, runners must return and touch the base they occupied at the time of the pitch—called tagging up—after the ball is first touched. Once they do this, they may attempt to advance at their own risk.
Only one runner may occupy a base at a time; if two runners are touching a base at once, the trailing runner is in jeopardy and will be out if tagged, unless he was forced--in which case the lead runner is out when tagged for failing to reach his force base. Either such occurrence is very rare. Thus, after a play, at most three runners may be on the basepaths, one on each base--first, second, and third. When three runners are on base, this is called bases loaded.

Baserunners may attempt to advance, or steal a base, while the pitcher is throwing a pitch. The pitcher, in lieu of delivering the pitch, may try to prevent this by throwing the ball to one of the infielders in order to tag the runner; if successful, it is called a pick-off. If the runner attempts to steal the next base but is tagged out before reaching it safely, he is caught stealing. An illegal attempt by the pitcher to deceive a runner, among other pitching violations, is called a balk, allowing the runners to advance one base without risk of being put out.
Another fundamental tenet of the rules of baseball is that a runner originally ruled out can subsequently be ruled safe, but once a runner is ruled safe he cannot be called out on the same play. A runner initially called out can be subsequently ruled safe if the fielder putting the runner out drops the ball (on either a tag or force play), pulls his foot off the base (in the case of a force play), or otherwise illegally obstructs a runner from reaching a base that he otherwise would have reached safely.
Batting and base running strategy
The goal of each batter is to become a base runner himself (by a base hit, a base on balls, being hit by the pitch, a fielding error, or fielder's choice) or to help move other base runners along (by another base hit, a sacrifice bunt, sacrifice fly, or hit and run).
Batters attempt to "read" pitchers through pre-game preparation by studying the tendencies of pitchers and by talking to other batters that previously faced the pitcher. While batting, batters attempt to "read" pitches by looking for clues that the pitcher or catcher reveal. These clues (also referred to as "tipping pitches") include movements of the pitcher's arms, shoulders, body, etc, or the positioning of the catcher's feet and glove. Batters can attempt to "read" the spin of a ball early in the pitch to anticipate its trajectory. Batters also remain keenly aware of the count during their at bat. The count is considered to be in the batter's favor when there are more balls than strikes (e.g.two balls and no strikes). This puts pressure on the pitcher to throw a strike to avoid a walk so the batter is more likely to get an easier pitch to hit and can look for a particular pitch in a particular zone or take a riskier or bigger swing. The count is considered to be in the pitcher's favor when there are fewer balls than strikes (e.g. no balls and two strikes). This gives the pitcher more freedom to try enticing the batter to swing at a pitch outside the strike zone or throwing a pitch that is harder to control (e.g. a curve, slider or splitter), but that is also harder to hit. Thus the batter will take a more protective swing. A major strategy in batting at competitive levels of baseball is patient hitting. An example of patient hitting is when a batter has a zero strike count the batter will almost always look for his perfect pitch. One strike hitting is very similar to no strike hitting and the batter usually is still looking for a good pitch to hit. Two strike hitting, the strategy is changed where the batter will protect the plate by fouling off pitches until the batter is able to find a pitch to hit. This style of hitting is known as patience at the plate. This style of hitting allows the hitter to look for a good pitch to hit and make the pitcher throw more pitches so that the pitcher will tire out faster. This is critical if the batting team is facing a very skilled pitcher who if allowed to will take over the game with his ability to get batters to do what he wants them to do with the pitches that he makes.
In general, base running is a tactical part of the game requiring good judgment by runners (and their coaches) to assess the risk in attempting to advance. During tag plays, a good slide can affect the outcome of the play. Managers will sometimes simultaneously send a runner and require the batter to swing (a hit-and-run play) in an attempt to advance runners. On a hit-and-run play the batter will often try to hit to the opposite field (the opposite of the natural tendency for the right handed hitter to pull the ball to left field and vice versa). Hitting to the opposite field will likely find an opening in the infield vacated by the fielder covering second base. This is because coverage of second base against a steal is best achieved by whichever fielder is closer to second base, the shortstop or the second baseman; and such positioning is aimed at defending against the natural tendency of the hitter.
A batter can also attempt to move a baserunner forward by "sacrificing" his at-bat. This can be done by bunting the ball, hitting a fly ball far enough in the air that a baserunner can advance after the catch, or simply making contact with the ball on a hit-and-run play.
During the course of play many offensive and defensive players run close to each other, and during tag plays, the defensive player must touch the offensive player. Although baseball is considered a non-contact sport, a runner may be allowed to make potentially dangerous contact with a fielder as part of an attempt to reach base, unless that fielder is fielding a batted ball. (Noted exceptions to the dangerous contact rule are found throughout amateur competitions, including youth leagues, high school, and college baseball.) A good slide is often more advantageous than such contact, and "malicious" contact by runners is typically prohibited as offensive interference. The most common occurrence of contact of this nature is at home plate between the runner and the catcher, as the catcher is well padded and locked into position that completely blocks home plate from the runner, and the runner will often try to knock the ball out of the catcher's hand by running him over. Since the catcher is seen (symbolically and literally) as the last line of defense, it seems natural that the more physical play happens here.
Innings and determining a winner
An inning consists of each team having one turn in the field and one turn to hit, with the visiting team batting before the home team. A standard game lasts nine innings, although some leagues (such as high school baseball and Little League) play fewer. The team with the most runs at the end of the game wins. If the home team is ahead after eight-and-a-half innings have been played, it is declared the winner, and the last half-inning is not played. If the home team is trailing or tied in the ninth inning or beyond and they score to take the lead, the game ends as soon as the winning run touches home plate; however, if the last batter hits a home run to win the game, he and any runners on base are all permitted to score.
If both teams have scored the same number of runs at the end of a regular-length game, a tie is avoided by the addition of extra innings. As many innings as necessary are played until one team has the lead at the end of an inning. Thus, the home team always has a chance to respond if the visiting team scores in the top half of the inning; this gives the home team a small tactical advantage. In theory, a baseball game could go on forever; in practice, however, they eventually end. In addition to that rule, a game might theoretically end if both the home and away team were to run out of players to substitute (see Substitutions, below). In Major League Baseball, the longest game played was a 26-inning affair between the Brooklyn Robins and Boston Braves on May 1, 1920. The game, called on account of darkness, ended in a 1-1 tie. Two minor-league teams, the Pawtucket Red Sox and Rochester Red Wings, played a 33-inning game in 1981.
In Major League Baseball, games end with tie scores only because conditions have made it impossible to continue play. A tie game does not count as an official game in the standings unless it is finished later or replayed; however, individual player statistics from tie games are counted. Inclement weather may also shorten games, but at least five innings must be played for the game to be considered official; four-and-a-half innings are enough if the home team is ahead. Previously, curfews and the absence of adequate lighting caused more ties and shortened games. Also, with more modern playing surfaces better able to handle light rains, the process for calling or shortening a game due to weather has changed; it is more common than in the past to delay a game as much as 2 hours before a cancellation; also, a delay usually does not occur anymore until the rain is moderate-heavy and/or there is standing water on some part of the playing field.
In Japan's Nippon Professional Baseball, if the score remains tied after nine innings, up to three extra innings may be played before the game is called a tie. Some youth or amateur leagues will end a game early if one team is ahead by ten or more runs, a practice known as the "mercy rule" or "slaughter rule". Rarely, a game can also be won or lost by forfeit.
There is a short break between each half-inning during which the new defensive team takes the field and the pitcher warms up. Traditionally, the break between the top half and the bottom half of the seventh inning is known as the seventh-inning stretch. During the "stretch," fans in the United States often sing the chorus of "Take Me Out to the Ball Game;" since the September 11, 2001 attacks, "God Bless America" has often been added to it, especially at games in New York City.
Substitutions
Each team is allowed to substitute for any player at any time the ball is dead. A batter who replaces another batter is referred to as a pinch hitter; similarly, a pinch runner may be used as a replacement for a baserunner. Any player who replaces another player between innings is known as a "defensive replacement". Any replacement is a permanent substitution; the replaced player may not return to the game.
It is common for a pitcher to pitch for several innings and then be removed in favor of a relief pitcher. Because pitching is a specialized skill, most pitchers are relatively poor hitters; it is common to substitute for a pitcher when he is due to bat. This pinch hitter is typically then replaced by a relief pitcher when the team returns to the field on defense, but more complicated substitutions are possible, most notably the double switch.
Many amateur leagues allow a starting player who was removed to return to the game in the same position in the batting order under a re-entry rule. Youth leagues often allow free and open substitution to encourage player participation.
The designated hitter (or DH) is a player whose sole purpose is to hit when it would normally be the pitcher's turn (or, if the pitcher is a good batter, another weaker batter). A few leagues, notably Major League Baseball's American League (which instituted the DH in 1973 to boost offensive output), allow designated hitters. This is not considered a substitution but rather a position, albeit a purely offensive one. A designated hitter does not play in the field on defense and may remain in the game regardless of changes in pitchers. The use of the designated hitter is opposed by many baseball traditionalists, but it is used today at most levels of baseball in the United States—high school, college, minor leagues—and internationally, including in the Olympics until Baseball's removal from the event. If the designated hitter is moved to a fielding position, the team loses the DH, and the fielder whose position was taken by the former DH is replaced by the pitcher, who assumes that player's position in the hitting lineup.
Rosters
The number of players on a Major League roster is dictated by the labor agreements worked out between players and management. According to the current rules, a team may have a maximum of 25 men on a roster from Opening Day until August 31. After that, teams may call up additional personnel, up to a maximum of 40 players on the active roster, with the exception of the postseason, where rosters are fixed at 25 men.
Other personnel
Any baseball game involves one or more umpires, who make rulings on the outcome of each play. At a minimum, one umpire will stand behind the catcher, to have a good view of the strike zone, and call each pitch a ball or a strike. Additional umpires may be stationed near the bases, thus making it easier to see plays in the field. In Major League Baseball, four umpires are used for each game, one near each base. In the all-star game and playoffs, six umpires are used: one at each base and two in the outfield along either foul line.
Baseball's unique style
Baseball is unique among American sports in several ways. This uniqueness is a large part of its longstanding appeal and strong association with the American psyche. The philosopher Morris Raphael Cohen described baseball as a national religion. Many Americans believe that baseball is the ultimate combination of skill, timing, athleticism, and strategy. In this, baseball is similar to its cousin game cricket: in many Commonwealth nations, cricket and the culture surrounding it hold a similar place and affection to baseball's role in American culture.
The allure of baseball is in its subtleties: situational defense, pitch location, pitch sequence, base running, batting strategies, statistics, ballparks, history, and player personalities. It's been noted that the game itself has no time limit, and its playing surface, rather than rigidly rectangular and standardized, extends theoretically to eternity from a single point (home plate) to beyond its own fences. For the avid fan, the game—even during its slowest points—is never boring because of these nuances. Therefore, a full appreciation of baseball naturally requires some knowledge of the rules; it also requires deep observation of those endearing and enduring qualities that give baseball its unique style.
Time element
Basketball, ice hockey, American football, and soccer all use a clock, and games often end by a team with the lead killing the clock rather than competing directly against the opposing team. In contrast, baseball has no clock; a team cannot win without getting the last batter out and rallies are not constrained by time. Other sports popular on the professional level in the U.S. that do not have a time limit are tennis and golf, although these are individual as opposed to team sports.
In recent decades, observers have criticized professional baseball for the length of its games, with some justification as the time required to play a baseball game has increased steadily through the years. At the turn of the 20th century, games typically took an hour and a half to play. In the 1920s, they averaged just under two hours, which eventually ballooned to 2 hours and 38 minutes in 1960. Though this average dipped to 2 hours 25 minutes in 1975, by the turn of the 21st century, games had become so long that Major League Baseball's goal in 2004 was to get the average game down to 2 hour and 45 minutes, after coming close in 2003 at 2 hours and 46 minutes.
The lengthening of games is attributed to longer breaks between half-innings for television commercials, increased offense, more pitching changes, and a slower pace of play. In response, Major League Baseball mandated a maximum break between half-innings, while instructing umpires to be stricter in enforcing speed-up rules and the size of the strike zone.
Although the official rules specify that when the bases are empty, the pitcher should deliver the ball within 12 seconds of receiving it (with the penalty of a ball called if he fails to do so), this rule is rarely, if ever, enforced. The umpire also has the option of calling a ball if there are runners on base, but this is also rarely, if ever, enforced. The official rules also require the batter to remain in the batter's box at all times when at bat — another rule that is "observed in the breach".
Individual and team
Baseball is fundamentally a team sport—even a franchise financially blessed enough to afford two or three Hall of Fame-caliber players cannot count on success. Yet it places individual players under great pressure and scrutiny. The pitcher must make good pitches or risk losing the game; the hitter has a mere fraction of a second to decide what pitch has been thrown and whether to swing at it. While managers and coaches can signal players to pursue certain strategies, no one can help the pitcher while he pitches or the hitter while he bats. If the batter hits a line drive, the outfielder, as the last line of defense, makes the lone decision to try to catch it or play it on the bounce. Baseball's history is full of heroes and goats—men who in the heat of the moment (the "clutch") distinguished themselves with a timely hit or catch, or an untimely strikeout or error.
The uniqueness of each baseball park

Unlike the majority of sports, baseball playing fields can vary significantly, within certain guidelines, in size and shape of the field. With the exception of the strict rules on the dimensions of the infield, discussed above, the official rulessimply state that fields built after June 1, 1958 must have a minimum distance of 325 feet (99 m) from home plate to the fences in left and right field and 400 (121 m) feet to center. This rule (a footnote to official rule 1.04) was passed specifically in response to the fence at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, which was not originally designed for baseball, and thus was only 251 feet (77 m) to the left field pole (1 foot over the bare minimum required by the rules). Major league teams often skirt this rule. For example, Minute Maid Park's Crawford Boxes are only 315 feet (96 m), and with a fence much lower than the famous "Green Monster" at Fenway Park which is labeled as 310 feet (94 m) away and 37-foot (11 m), two-inches tall. And there are no rules at all regulating the height of "fences, stands or other obstructions", other than the assumption that they exist. However, teams are required to obtain approval from the League Office when constructing new stadiums, or when proposing alterations.
Because of this flexibility, there are numerous variations in park configuration, from different lengths to the fences to uneven playing surfaces to massive or minimal amounts of foul territory. The differing styles create a unique sense of ambiance in each location, something that many fans find alluring (and even a source of civic pride). All of these factors, as well as local variations in altitude, climate and game scheduling, can affect the nature of the games played at those ballparks. Certain stadiums eventually get labeled as either a "pitcher's park" or a "hitter's park", depending on which side benefits more from the unique factors present. Chicago's Wrigley Field can be either, depending on the wind direction at any given time. This is due to Chicago's close proximity to Lake Michigan. The wind provides drag or lift to the ball depending on whether it is blowing "in", or "out" or "across" the field. When the wind blows "in", it can lead to more fly ball outs. When the wind blows "out", an ordinary fly ball is more likely to wind up a home run into the bleachers or even reach the streets. When the wind blows "across", a fly ball can sail into the bleachers for a home run, or carry away from the bleachers for an out or a simple extra-base hit.
In the end, the lack of a consistent, standardized playing field has caused some debate, particularly when comparing players statistics and career records. For example, hitting a ball off the Green Monster in Boston results in a hit, where at San Francisco the hit may have been caught.
Statistics
Main article: Baseball statisticsAs with many sports, and perhaps even more so, statistics are very important to baseball. Statistics have been kept for the Major Leagues since their creation, and presumably statistics were around even before that. General managers, baseball scouts, managers, and players alike study player statistics to help them choose various strategies to best help their team.
Statistics are more important to baseball than to other sports for a variety of reasons. Primary among them is the fact that every play has only a finite (and relatively limited) number of possible outcomes, unlike sports like hockey, basketball, soccer, and to a lesser extent American football, all of which are more fluid and open. This facilitates a statistical analysis of baseball, and allows a deeper level of mathematical study than that provided by other sports.
Traditionally, statistics like batting average for batters—the number of hits divided by the number of at bats—and earned run average—approximately the number of runs given up by a pitcher per nine innings—have governed the statistical world of baseball. However, the advent of sabermetrics has brought an onslaught of new statistics that perhaps better gauge a player's performance and contributions to his team from year to year.
Some sabermetrics have entered the mainstream baseball statistic world. On-base plus slugging (OPS) is a somewhat complicated formula that some say gauges a hitter's performance better than batting average. It combines the hitter's on base percentage—hits plus walks plus hit by pitches divided by at bats plus bases on balls plus hit by pitches plus sacrifice flies—with their slugging percentage—total bases divided by at bats. Walks plus hits per inning pitched (or WHIP) gives a good representation of a pitcher's abilities; it is calculated exactly as its name suggests.
Also important are more specific statistics for particular situations. For example, a certain hitter's ability to hit left-handed pitchers might cause his manager to give him more chances to face lefties. Some hitters hit better with runners in scoring position, so an opposing manager, knowing this statistic, might elect to intentionally walk him in order to face a worse hitter.
There are some other statistics, perhaps less important than those mentioned. For hitters, these include at-bats, the number of hits and extra-base hits, and runs batted in, or RBIs. For pitchers, these include total innings pitched, strikeouts per nine innings, walks, and the pitch count.
Popularity
Baseball is most popular in East Asia and the Americas, although in South America its popularity is mainly limited to the northern portion of the continent. In The Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Japan, Cuba, Panama, Venezuela, Nicaragua, South Korea, and Taiwan, it is one of the most popular sports. The United States is the birthplace of baseball, where it has long been regarded as more than just a "major sport"; for many decades, it has been popularly referred to as the "national pastime" and Major League Baseball has been given a unique monopoly status by the Supreme Court of the United States. Although the three most popular professional team sports in the United States are ball games—baseball, basketball and American football—baseball's historical popularity was so great that even today the word "ballgame" in the United States almost always refers to a game of baseball (except in the American South, where the word is also used in association with football), and "ballpark" invariably refers to a baseball field.
Baseball has often been a barometer of the fabled American "melting pot", as immigrants from different regions have tried to "make good" in various areas including sports. In the 19th century, baseball was populated with many players of Irish or German extraction. A number of Native Americans had successful careers especially in the early 1900s. Italians and Poles appeared on many rosters during the 1920s and 1930s. Black Americans came on strong starting in the late 1940s after the barriers had been lifted, and continue to form a significant contingent. By the 1960s, Hispanics had started to make the scene, and had become a dominant force by the 1990s. In the 21st century, East Asians have been appearing in increasing numbers.
While baseball is perhaps the most popular sport in the United States and is certainly one of the two most popular along with football, it is difficult to determine which is more popular because of the wide discrepancy in number of games per season. For example, the total attendance for major league games is roughly equal to that of all other American professional team sports combined, but football gets higher television ratings, both a function in part of the long (162-game) baseball season and short (16-game) football season. According to Baseball Commissioner Bud Selig, both revenue and attendance are currently higher than at any previous point in the history of the game.
Organized leagues
See List of organized baseball leagues.
Baseball is played at a number of levels, by amateur and professionals, and by the young and the old. Youth programs use modified versions of adult and professional baseball rules, which may include a smaller field, easier pitching (from a coach, a tee, or a machine), less contact, base running restrictions, limitations on innings a pitcher can throw, liberal balk rules, and run limitations, among others. Since rules vary from location-to-location and among the organizations, coverage of the nuances in those rules is beyond this article.
See also
- Finnish baseball
- Russian baseball
- Baseball in the UK
- Baseball clothing and equipment
- Comparison between cricket and baseball
- National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum
- Baseball awards
- Simplified baseball rules
- Major League Baseball transactions
- Vintage base ball
- Baseball batting robot
- Safe haven games
- Town Team Baseball (Minnesota)
- Softball
Culture
|
General information
- Baseball fielding positions
- Baseball scorekeeping
- Baseball slang (slang also used outside the scope of baseball)
- List of rare baseball events (occurring within a single game)
- Baseball terminology
- Sports league attendances
Notes
- Block, David (2006). Baseball Before We Knew It: A look at something I don't remember. Bison Books. 0803262558.
- Szymanski, Stefan, and Andrew S. Zimbalist (2006). National Pastime: How Americans Play Baseball and the Rest of the World Plays Soccer (Brookings Institution Press, 2005), ISBN 0815782586, p. 220, n. 19.
- Szymanski and Zimbalist (2006), p. 220, n. 19.
- How Products Are Made: Baseball
- The "third strike rule", which has been on the books since the time of the Knickerbocker Rules, is that the batter can try to advance to first base on the third strike, if the third strike is not caught. However, the batter is not permitted to advance if first base is occupied, unless there are already two outs. This is to prevent the catcher from dropping the ball on purpose and setting up a potential double or triple play. The underlying concept is the same as the "Infield Fly Rule", to curb defensive shenanigans. Both rules change when there are two outs, because then there is no defensive advantage to dropping the ball on purpose. Statistically, such a play still counts as a strikeout for the pitcher, plus either a passed ball charged to the catcher or a wild pitch charged to the pitcher, so if the batter advances safely to first on such a play, it is possible for a pitcher to record 4 (or more) strikeouts in one inning. Such has happened several dozen times in the history of the major leagues, and at least one time in the minor leagues a pitcher has recorded 5.
- Hal Bodley, "Baseball wants just a few more minutes", USAToday.com, 26 February 2004
- Jeff Greenfield, "Midnight Baseball", Time.com, 13 July 1998
- Hal Bodley, "Baseball wants just a few more minutes", USAToday.com, 26 February 2004
- Hal Bodley, "Baseball wants just a few more minutes", USAToday.com, 26 February 2004
- Jeff Greenfield, "Midnight Baseball", Time.com, 13 July 1998
- An informative account of the use of statistics throughout baseball history is Alan Schwarz, The Numbers Game: Baseball’s Lifelong Fascination with Statistics (New York: St. Martin's, 2005) (ISBN 0-312-32223-2).
Sources and further reading
Published
- Robert K. Barney and Nancy Bouchier, "A Critical Examination of a Source in Early Ontario Baseball: The Reminiscence of Adam E. Ford," Journal of Sport History (1988)
- Joe Brinkman and Charlie Euchner, The Umpire's Handbook, rev. ed. (1987)
- Bob Elliott, The Northern Game: Baseball the Canadian Way (Sport Classic, 2005)
- Charles Euchner, The Last Nine Innings: Inside the Real Game Fans Never See (2006)
- William Humber, Diamonds of the North: A Concise History of Baseball in Canada (Oxford University Press, 1995)
- Bill James and John Dewan, Bill James Presents the Great American Baseball Stat Book, ed. by Geoff Beckman et al. (1987)
- Bill James, The New Bill James Historical Baseball Abstract (ISBN 0-7432-2722-0)
- Mark Kearney, "Baseball's Canadian Roots: Abner Who?" The Beaver: Exploring Canada's History (October-November 1994)
- Michael Mandelbaum, The Meaning of Sports (PublicAffairs) (ISBN 1-58648-252-1)
- Robert Peterson, Only the Ball Was White (1984 )
- Joseph L. Reichler (ed.), The Baseball Encyclopedia, 7th rev. ed. (1988)
- Lawrence Ritter and Donald Honig, The Image of Their Greatness: An Illustrated History of Baseball from 1900 to the Present, updated ed. (1984)
- Lawrence S. Ritter (comp.), The Glory of Their Times: The Story of the Early Days of Baseball Told by the Men Who Played It, new ed. (1984)
- Seth Swirsky, Baseball Letters, A Fan's Correspondence With His Heroes (Crown Books, 1996).
- David Quentin Voigt, Baseball, an Illustrated History (1987)
Online
- Pittsfield: Small city, big baseball town, earliest known baseball reference
External links
- Baseball Organizations/Leagues/Clubs
- mlb.com Major League Baseball
- milb.com Minor League Baseball
- baseballsoftballuk.com British Baseball Federation
- boltonbaseball.co.uk Bolton Blaze Baseball Club
- Baseball Reference & Stats
- baseball.wikia.com The Baseball Wiki
- baseball-reference.com Baseball stats
- thebaseballcube.com Baseball stats
- sabr.org Society for American Baseball Research
- baseball-almanac.com Baseball Almanac with Stats/history/anecdotes
- Baseball News, Resources, & Other
- cycleback.com Online museum of early baseball
- memory.loc.gov Library of Congress of Spalding Guides
- pbs.org PBS documentary - "Baseball" by Ken Burns
- pbs.org PBS documentary - "Stealing Home"
- Seth.com Extensive collection of historic baseball memorabilia
- probaseballarchive.com Baseball newspaper archive
- robbinssports.com Baseball in China
- sportscollectorsdaily.com online news/collecting magazine
- HKsportsFields.com Baseball Field Construction, Design, Renovation
- European Baseball & Softball News and Information
| Baseball at the Summer Olympics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tournaments |  | |
| Qualifications | ||
| Squads | ||
| Related topics | ||
| Italicised years indicate baseball was featured as a demonstration sport. | ||
| Team sports | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball sports |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tag sports | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Water sports | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other non-ball sports | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Professional baseball leagues | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||