This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Farhansher (talk | contribs) at 11:45, 18 June 2008 (test). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 11:45, 18 June 2008 by Farhansher (talk | contribs) (test)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
- For other meanings, including people named `Islam', see Islam (disambiguation).
Islam (Arabic: الإسلام; al-'islām; pronounced: ) is a monotheistic Abrahamic religion originating with the teachings of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, a seventh century Arab religious and political figure. The word Islam means "submission", or the total surrender of oneself to God (Arabic: ]). An adherent of Islam is known as a Muslim, meaning "one who submits ". There are between 1 billion to 1.8 billion Muslims, making Islam the second-largest religion in the world, after Christianity.
Muslims believe that God revealed the Qur'an to Muhammad, God's final prophet, and regard the Qur'an and the Sunnah (words and deeds of Muhammad) as the fundamental sources of Islam. They do not regard Muhammad as the founder of a new religion, but as the restorer of the original monotheistic faith of Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. Islamic tradition holds that Jews and Christians distorted the revelations God gave to these prophets by either altering the text, introducing a false interpretation, or both.
Islam includes many religious practices. Adherents are generally required to observe the Five Pillars of Islam, which are five duties that unite Muslims into a community. In addition to the Five Pillars, Islamic law (sharia) has developed a tradition of rulings that touch on virtually all aspects of life and society. This tradition encompasses everything from practical matters like dietary laws and banking to warfare and welfare.
Almost all Muslims belong to one of two major denominations, the Sunni (85%) and Shi'a (15%). The schism developed in the late 7th century following disagreements over the religious and political leadership of the Muslim community. Islam is the predominant religion throughout the Middle East, as well as in major parts of Africa and Asia. Large communities are also found in China, the Balkan Peninsula in Eastern Europe and Russia. There are also large Muslim immigrant communities in other parts of the world, such as Western Europe. About 20% of Muslims live in Arab countries, 30% in the Indian subcontinent and 15.6% in Indonesia, the largest Muslim country by population.
Etymology and meaning
Main article: S-L-MThe word Islam is a verbal noun originating from the triliteral root s-l-m, and is derived from the Arabic verb Aslama, which means "to accept, surrender or submit." Thus, Islam means acceptance of and submission to God, and believers must demonstrate this by worshipping him, following his commands, and avoiding polytheism. The word is given a number of meanings in the Qur'an. In some verses (ayat), the quality of Islam as an internal conviction is stressed: "Whomsoever God desires to guide, He expands his breast to Islam." Other verses connect islām and dīn (usually translated as "religion"): "Today, I have perfected your religion (dīn) for you; I have completed My blessing upon you; I have approved Islam for your religion." Still others describe Islam as an action of returning to God—more than just a verbal affirmation of faith.
Articles of faith
Main articles: Aqidah and ImanThe Qur'an states that all Muslims must believe in God, his revelations, his angels, his messengers, and in the "Day of Judgment". Also, there are other beliefs that differ between particular sects. The Sunni concept of predestination is called divine decree, while the Shi'a version is called divine justice. Unique to the Shi'a is the doctrine of Imamah, or the political and spiritual leadership of the Imams.
Muslims believe that God revealed his final message to humanity through the Islamic prophet Muhammad via the angel Gabriel. For them, Muhammad was God's final prophet and the Qur'an is the revelations he received over more than two decades. In Islam, prophets are men selected by God to be his messengers. Muslims believe that prophets are human and not divine, though some are able to perform miracles to prove their claim. Islamic prophets are considered to be the closest to perfection of all humans, and are uniquely the recipients of divine revelation—either directly from God or through angels. The Qur'an mentions the names of numerous figures considered prophets in Islam, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses and Jesus, among others. Islamic theology says that all of God's messengers since Adam preached the message of Islam—submission to the will of God. Islam is described in the Qur'an as "the primordial nature upon which God created mankind", and the Qur'an states that the proper name Muslim was given by Abraham.
As a historical phenomenon, Islam originated in Arabia in the early 7th century. Islamic texts depict Judaism and Christianity as prophetic successor traditions to the teachings of Abraham. The Qur'an calls Jews and Christians "People of the Book" (ahl al-kitāb), and distinguishes them from polytheists. Muslims believe that parts of the previously revealed scriptures, the Tawrat (Torah) and the Injil (Gospels), had become distorted—either in interpretation, in text, or both.
God
Main article: God in Islam See also: Oneness of God (Islam) and AllahIslam's fundamental theological concept is tawhīd—the belief that there is only one god. The Arabic term for God is Allāh; most scholars believe it was derived from a contraction of the words al- (the) and ʾilāh (deity, masculine form), meaning "the god" (al-ilāh), but others trace its origin to the Aramaic Alāhā. The first of the Five Pillars of Islam, tawhīd is expressed in the shahadah (testification), which declares that there is no god but God, and that Muhammad is God's messenger. In traditional Islamic theology, God is beyond all comprehension; Muslims are not expected to visualize God but to worship and adore him as a protector. Although Muslims believe that Jesus was a prophet, they reject the Christian doctrine of the Trinity, comparing it to polytheism. In Islamic theology, Jesus was just a man and not the son of God; God is described in a chapter (sura) of the Qur'an as "…God, the One and Only; God, the Eternal, Absolute; He begetteth not, nor is He begotten; And there is none like unto Him."
Qur'an
Main articles: Islamic holy books and Qur'an See also: Origin and development of the Qur'an
Muslims consider the Qur'an to be the literal word of God; it is the central religious text of Islam. Muslims believe that the verses of the Qur'an were revealed to Muhammad by God through the angel Gabriel on many occasions between 610 and his death on July 6 632. The Qur'an was reportedly written down by Muhammad's companions (sahabah) while he was alive, although the prime method of transmission was orally. It was compiled in the time of Abu Bakr, the first caliph, and was standardized under the administration of Uthman, the third caliph. The Qur'an in its present form is often considered by academic scholars to record the words spoken by Muhammad because the search for variants in Western academia has not yielded any differences of great significance and that historically controversy over the content of the Qur'an has never become a main point.
The Qur'an is divided into 114 suras, or chapters, which combined, contain 6,236 āyāt, or verses. The chronologically earlier suras, revealed at Mecca, are primarily concerned with ethical and spiritual topics. The later Medinan suras mostly discuss social and moral issues relevant to the Muslim community. The Qur'an is more concerned with moral guidance than legal instruction, and is considered the "sourcebook of Islamic principles and values". Muslim jurists consult the hadith, or the written record of Muhammad's life, to both supplement the Qur'an and assist with its interpretation. The science of Qur'anic commentary and exegesis is known as tafsir.
The word Qur'an means "recitation". When Muslims speak in the abstract about "the Qur'an", they usually mean the scripture as recited in Arabic rather than the printed work or any translation of it. To Muslims, the Qur'an is perfect only as revealed in the original Arabic; translations are necessarily deficient because of language differences, the fallibility of translators, and the impossibility of preserving the original's inspired style. Translations are therefore regarded only as commentaries on the Qur'an, or "interpretations of its meaning", not as the Qur'an itself.
Angels
Main article: Angels in IslamBelief in angels is crucial to the faith of Islam. The Arabic word for Angels (malak) means "messenger", like its counterparts in Hebrew (malakh) and Greek (angelos). According to the Qur'an, angels do not possess free will, and worship God in perfect obedience. Angels' duties include communicating revelations from God, glorifying God, recording every person's actions, and taking a person's soul at the time of death. They are also thought to intercede on man's behalf. The Qur'an describes angels as "messengers with wings—two, or three, or four (pairs): He adds to Creation as He pleases…"
Muhammad
Main article: MuhammadMuhammad (c. 570 – July 6 632) was an Arab religious, political, and military leader who founded the religion of Islam as a historical phenomenon. Muslims view him not as the creator of a new religion, but as the restorer of the original, uncorrupted monotheistic faith of Adam, Abraham and others. In Muslim tradition, Muhammad is viewed as the last and the greatest in a series of prophets—as the man closest to perfection, the possessor of all virtues. For the last 23 years of his life, beginning at age 40, Muhammad reported receiving revelations from God. The content of these revelations, known as the Qur'an, was memorized and recorded by his companions.
During this time, Muhammad preached to the people of Mecca, imploring them to abandon polytheism. Although some converted to Islam, Muhammad and his followers were persecuted by the leading Meccan authorities. After 13 years of preaching, Muhammad and the Muslims performed the Hijra ("emigration") to the city of Medina (formerly known as Yathrib) in 622. There, with the Medinan converts (Ansar) and the Meccan migrants (Muhajirun), Muhammad established his political and religious authority. Within years, two battles had been fought against Meccan forces: the Battle of Badr in 624, which was a Muslim victory, and the Battle of Uhud in 625, which ended inconclusively. Conflict with Medinan Jewish clans who opposed the Muslims led to their exile, enslavement or death, and the Jewish enclave of Khaybar was subdued. At the same time, Meccan trade routes were cut off as Muhammad brought surrounding desert tribes under his control. By 629 Muhammad was victorious in the nearly bloodless Conquest of Mecca, and by the time of his death in 632 he ruled over the Arabian peninsula.
In Islam, the "normative" example of Muhammad's life is called the Sunnah (literally "trodden path"). This example is preserved in traditions known as hadith ("reports"), which recount his words, his actions, and his personal characteristics. The classical Muslim jurist ash-Shafi'i (d. 820) emphasized the importance of the Sunnah in Islamic law, and Muslims are encouraged to emulate Muhammad's actions in their daily lives. The Sunnah is seen as crucial to guiding interpretation of the Qur'an.
Resurrection and judgment
Main article: QiyamaBelief in the "Day of Resurrection", yawm al-Qiyāmah (also known as yawm ad-dīn, "Day of Judgment" and as-sā`a, "the Last Hour") is also crucial for Muslims. They believe that the time of Qiyāmah is preordained by God but unknown to man. The trials and tribulations preceding and during the Qiyāmah are described in the Qur'an and the hadith, and also in the commentaries of Islamic scholars. The Qur'an emphasizes bodily resurrection, a break from the pre-Islamic Arabian understanding of death. It states that resurrection will be followed by the gathering of mankind, culminating in their judgment by God.
The Qur'an lists several sins that can condemn a person to hell, such as disbelief, usury and dishonesty. Muslims view paradise (jannah) as a place of joy and bliss, with Qur'anic references describing its features and the physical pleasures to come. There are also references to a greater joy—acceptance by God (ridwān). Mystical traditions in Islam place these heavenly delights in the context of an ecstatic awareness of God.
Predestination
Main articles: Predestination in Islam and AdalahIn accordance with the Islamic belief in predestination, or divine preordainment (al-qadā wa'l-qadar), God has full knowledge and control over all that occurs. This is explained in Qur'anic verses such as "Say: 'Nothing will happen to us except what Allah has decreed for us: He is our protector'…" For Muslims, everything in the world that occurs, good or evil, has been preordained and nothing can happen unless permitted by God. In Islamic theology, divine preordainment does not suggest an absence of God's indignation against evil, because any evils that do occur are thought to result in future benefits men may not be able to see. According to Muslim theologians, although events are pre-ordained, man possesses free will in that he has the faculty to choose between right and wrong, and is thus responsible for his actions. According to Islamic tradition, all that has been decreed by God is written in al-Lawh al-Mahfūz, the "Preserved Tablet".
The Shi'a understanding of predestination is called "divine justice" (Adalah). This doctrine, originally developed by the Mu'tazila, stresses the importance of man's responsibility for his own actions. In contrast, the Sunni deemphasize the role of individual free will in the context of God's creation and foreknowledge of all things.
Duties and practices
Five Pillars
Main article: Five Pillars of Islam

The Five Pillars of Islam (Arabic: اركان الدين) are five practices essential to Sunni Islam. Shi'a Muslims subscribe to eight ritual practices which substantially overlap with the Five Pillars. They are:
- The shahadah, which is the basic creed or tenet of Islam: "'ašhadu 'al-lā ilāha illā-llāhu wa 'ašhadu 'anna muħammadan rasūlu-llāh", or "I testify that there is none worthy of worship except God and I testify that Muhammad is the Messenger of God." This testament is a foundation for all other beliefs and practices in Islam (although technically the Shi'a do not consider the shahadah to be a separate pillar, just a belief). Muslims must repeat the shahadah in prayer, and non-Muslims wishing to convert to Islam are required to recite the creed.
- Salah, or ritual prayer, which must be performed five times a day. (However, the Shi'a are permitted to run together the noon with the afternoon prayers, and the evening with the night prayers). Each salah is done facing towards the Kaaba in Mecca. Salah is intended to focus the mind on God, and is seen as a personal communication with him that expresses gratitude and worship. Salah is compulsory but flexibility in the specifics is allowed depending on circumstances. In many Muslim countries, reminders called Adhan (call to prayer) are broadcast publicly from local mosques at the appropriate times. The prayers are recited in the Arabic language, and consist of verses from the Qur'an.
- Zakat, or alms-giving. This is the practice of giving based on accumulated wealth, and is obligatory for all Muslims who can afford it. A fixed portion is spent to help the poor or needy, and also to assist the spread of Islam. The zakat is considered a religious obligation (as opposed to voluntary charity) that the well-off owe to the needy because their wealth is seen as a "trust from God's bounty". The Qur'an and the hadith also suggest a Muslim give even more as an act of voluntary alms-giving (sadaqah). Many Shi'ites are expected to pay an additional amount in the form of a khums tax, which they consider to be a separate ritual practice.
- Sawm, or fasting during the month of Ramadan. Muslims must not eat or drink (among other things) from dawn to dusk during this month, and must be mindful of other sins. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God, and during it Muslims should express their gratitude for and dependence on him, atone for their past sins, and think of the needy. Sawm is not obligatory for several groups for whom it would constitute an undue burden. For others, flexibility is allowed depending on circumstances, but missed fasts usually must be made up quickly.
- The Hajj, which is the pilgrimage during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah in the city of Mecca. Every able-bodied Muslim who can afford it must make the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in his or her lifetime. When the pilgrim is about ten kilometers from Mecca, he must dress in Ihram clothing, which consists of two white seamless sheets. Rituals of the Hajj include walking seven times around the Kaaba, touching the Black Stone, running seven times between Mount Safa and Mount Marwah, and symbolically stoning the Devil in Mina. The pilgrim, or the hajji, is honored in his or her community, although Islamic teachers say that the Hajj should be an expression of devotion to God instead of a means to gain social standing.
In addition to the khums tax, Shi'a Muslims consider three additional practices essential to the religion of Islam. The first is jihad, which is also important to the Sunni, but not considered a pillar. The second is Amr-Bil-Ma'rūf, the "Enjoining to Do Good", which calls for every Muslim to live a virtuous life and to encourage others to do the same. The third is Nahi-Anil-Munkar, the "Exhortation to Desist from Evil", which tells Muslims to refrain from vice and from evil actions and to also encourage others to do the same.
Law
Main articles: Sharia and FiqhThe Sharia (literally: "the path leading to the watering place") is Islamic law formed by traditional Islamic scholarship. In Islam, Sharia is the expression of the divine will, and "constitutes a system of duties that are incumbent upon a Muslim by virtue of his religious belief".
Islamic law covers all aspects of life, from matters of state, like governance and foreign relations, to issues of daily living. The Qur'an defines hudud as the punishments for five specific crimes: unlawful intercourse, false accusation of unlawful intercourse, consumption of alcohol, theft, and highway robbery. The Qur'an and Sunnah also contain laws of inheritance, marriage, and restitution for injuries and murder, as well as rules for fasting, charity, and prayer. However, these prescriptions and prohibitions may be broad, so their application in practice varies. Islamic scholars (known as ulema) have elaborated systems of law on the basis of these rules and their interpretations.
Fiqh, or "jurisprudence", is defined as the knowledge of the practical rules of the religion. The method Islamic jurists use to derive rulings is known as usul al-fiqh ("legal theory", or "principles of jurisprudence"). According to Islamic legal theory, law has four fundamental roots, which are given precedence in this order: the Qur'an, the Sunnah (actions and sayings of Muhammad), the consensus of the Muslim jurists (ijma), and analogical reasoning (qiyas). For early Islamic jurists, theory was less important than pragmatic application of the law. In the 9th century, the jurist ash-Shafi'i provided a theoretical basis for Islamic law by codifying the principles of jurisprudence (including the four fundamental roots) in his book ar-Risālah.
Religion and state
Islamic law does not distinguish between "matters of church" and "matters of state"; the ulema function as both jurists and theologians. In practice, Islamic rulers frequently bypassed the Sharia courts with a parallel system of so-called "Grievance courts" over which they had sole control. As the Muslim world came into contact with Western secular ideals, Muslim societies responded in different ways. Turkey has been governed as a secular state ever since the reforms of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. In contrast, the 1979 Iranian Revolution replaced a mostly secular regime with an Islamic republic led by the Ayatollah Ruholla Khomeini.
Etiquette and diet
Main articles: Adab (behavior) and Islamic dietary lawsMany practices fall in the category of adab, or Islamic etiquette. This includes greeting others with "as-salamu `alaykum" ("peace be unto you"), saying bismillah ("in the name of God") before meals, and using only the right hand for eating and drinking. Islamic hygienic practices mainly fall into the category of personal cleanliness and health, such as the circumcision of male offspring. Islamic burial rituals include saying the Salat al-Janazah ("funeral prayer") over the bathed and enshrouded dead body, and burying it in a grave. Muslims, like Jews, are restricted in their diet, and prohibited foods include pig products, blood, carrion, and alcohol. All meat must come from a herbivorous animal slaughtered in the name of God by a Muslim, Jew, or Christian, with the exception of game that one has hunted or fished for oneself. Food permissible for Muslims is known as halal food.
Jihad
Main articles: Jihad and Islamic military jurisprudenceJihad means "to strive or struggle" (in the way of God) and is considered the "sixth pillar of Islam" by a minority of Muslim authorities. Jihad, in its broadest sense, is classically defined as "exerting one's utmost power, efforts, endeavors, or ability in contending with an object of disapprobation." Depending on the object being a visible enemy, the devil, and aspects of one's own self, different categories of Jihad are defined. Jihad when used without any qualifier is understood in its military aspect. Jihad also refers to one's striving to attain religious and moral perfection. Some Muslim authorities, especially among the Shi'a and Sufis, distinguish between the "greater jihad", which pertains to spiritual self-perfection, and the "lesser jihad", defined as warfare.
Within Islamic jurisprudence, jihad is usually taken to mean military exertion against non-Muslim combatants in the defense or expansion of the Islamic state, the ultimate purpose of which is to universalize Islam. Jihad, the only form of warfare permissible in Islamic law, may be declared against apostates, rebels, highway robbers, violent groups, unIslamic leaders or states which refuse to submit to the authority of Islam. Most Muslims today interpret Jihad as only a defensive form of warfare: the external Jihad includes a struggle to make the Islamic societies conform to the Islamic norms of justice.
Under most circumstances and for most Muslims, jihad is a collective duty (fard kifaya): its performance by some individuals exempts the others. Only for those vested with authority, especially the sovereign (imam), does jihad become an individual duty. For the rest of the populace, this happens only in the case of a general mobilization. For most Shias, offensive jihad can only be declared by a divinely appointed leader of the Muslim community, and as such is suspended since Muhammad al-Mahdi's occultation in 868 AD.
History
Main articles: Muslim history and Spread of IslamIslam's historical development resulted in major political, economic, and military effects inside and outside the Islamic world. Within a century of Muhammad's first recitations of the Qur'an, an Islamic empire stretched from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to Central Asia in the east. This new polity soon broke into civil war, and successor states fought each other and outside forces. However, Islam continued to spread into regions like Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and Southeast Asia. The Islamic civilization was one of the most advanced in the world during the Middle Ages, but was surpassed by Europe with the economic and military growth of the West. During the 18th and 19th centuries, Islamic dynasties such as the Ottomans and Mughals fell under the sway of European imperial powers. In the 20th century new religious and political movements and newfound wealth in the Islamic world led to both rebirth and conflict.
Rise of the caliphate (632–750)
Further information: Succession to Muhammad, Muslim conquests, and Arab caliphateMuhammad began preaching Islam at Mecca before migrating to Medina, from where he united the tribes of Arabia into a singular Arab Muslim religious polity. With Muhammad's death in 632, disagreement broke out over who would succeed him as leader of the Muslim community. Umar ibn al-Khattab, a prominent companion of Muhammad, nominated Abu Bakr, who was Muhammad's intimate friend and collaborator. Others added their support and Abu Bakr was made the first caliph. This choice was disputed by some of Muhammad's companions, who held that Ali ibn Abi Talib, his cousin and son-in-law, had been designated his successor. Abu Bakr's immediate task was to avenge a recent defeat by Byzantine (or Eastern Roman Empire) forces, although he first had to put down a rebellion by Arab tribes in an episode known as the Ridda wars, or "Wars of Apostasy".

His death in 634 resulted in the succession of Umar as the caliph, followed by Uthman ibn al-Affan and Ali ibn Abi Talib. These four are known as al-khulafā' ar-rāshidūn ("Rightly Guided Caliphs"). Under them, the territory under Muslim rule expanded deeply into Persian and Byzantine territories.
When Umar was assassinated in 644, the election of Uthman as successor was met with increasing opposition. In 656, Uthman was also killed, and Ali assumed the position of caliph. After fighting off opposition in the first civil war (the "First Fitna"), Ali was assassinated by Kharijites in 661. Following this, Mu'awiyah, who was governor of Levant, seized power and began the Umayyad dynasty.
These disputes over religious and political leadership would give rise to schism in the Muslim community. The majority accepted the legitimacy of the three rulers prior to Ali, and became known as Sunnis. A minority disagreed, and believed that Ali was the only rightful successor; they became known as the Shi'a. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflict over succession broke out again in a civil war known as the "Second Fitna". Afterward, the Umayyad dynasty prevailed for seventy years, and was able to conquer the Maghrib and Al-Andalus (the Iberian Peninsula, former Visigothic Hispania) and the Narbonnese Gaul} in the west as well as expand Muslim territory into Sindh and the fringes of Central Asia. While the Muslim-Arab elite engaged in conquest, some devout Muslims began to question the piety of indulgence in a worldly life, emphasizing rather poverty, humility and avoidance of sin based on renunciation of bodily desires. Devout Muslim ascetic exemplars such as Hasan al-Basri would inspire a movement that would evolve into Sufism.
For the Umayyad aristocracy, Islam was viewed as a religion for Arabs only; the economy of the Umayyad empire was based on the assumption that a majority of non-Muslims (Dhimmis) would pay taxes to the minority of Muslim Arabs. A non-Arab who wanted to convert to Islam was supposed to first become a client of an Arab tribe. Even after conversion, these new Muslims (mawali) did not achieve social and economic equality with the Arabs. The descendants of Muhammad's uncle Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib rallied discontented mawali, poor Arabs, and some Shi'a against the Umayyads and overthrew them with the help of their propagandist and general Abu Muslim, inaugurating the Abbasid dynasty in 750. Under the Abbasids, Islamic civilization flourished in the "Islamic Golden Age", with its capital at the cosmopolitan city of Baghdad.
Golden Age (750–1258)
Main article: Islamic Golden Age
By the late 9th century, the Abbasid caliphate began to fracture as various regions gained increasing levels of autonomy. Across North Africa, Persia, and Central Asia emirates formed as provinces broke away. The monolithic Arab empire gave way to a more religiously homogenized Muslim world where the Shia Fatimids contested even the religious authority of the caliphate. By 1055 the Seljuq Turks had eliminated the Abbasids as a military power, nevertheless they continued to respect the caliph's titular authority. During this time expansion of the Muslim world continued, by both conquest and peaceful proselytism even as both Islam and Muslim trade networks were extending into sub-Saharan West Africa, Central Asia, Volga Bulgaria and the Malay archipelago.
The Golden Age saw new legal, philosophical, and religious developments. The major hadith collections were compiled and the four modern Sunni Madh'habs were established. Islamic law was advanced greatly by the efforts of the early 9th century jurist al-Shafi'i; he codified a method to establish the reliability of hadith, a topic which had been a locus of dispute among Islamic scholars. Philosophers Ibn Sina (Avicenna) and Al-Farabi sought to incorporate Greek principles into Islamic theology, while others like the 11th century theologian Abu Hamid al-Ghazzali argued against them and ultimately prevailed. Finally, Sufism and Shi'ism both underwent major changes in the 9th century. Sufism became a full-fledged movement that had moved towards mysticism and away from its ascetic roots, while Shi'ism split due to disagreements over the succession of Imams.
The spread of the Islamic dominion induced hostility among medieval ecclesiastical Christian authors who saw Islam as an adversary in the light of the large numbers of new Muslim converts. This opposition resulted in polemical treatises which depicted Islam as the religion of the antichrist and of Muslims as libidinous and subhuman. In the medieval period, a few Arab philosophers like the poet Al-Ma'arri adopted a critical approach to Islam, and the Jewish philosopher Maimonides contrasted Islamic views of morality to Jewish views that he himself elaborated.
Mongols, Crusades & Reconquest
Starting in the 9th century, Muslim conquests in the West began to be reversed. The Reconquista was launched against Muslim principalities in Iberia, and Muslim Italian possessions were lost to the Normans. From the 11th century onwards alliances of European Christian kingdoms mobilized to launch a series of wars known as the Crusades, bringing the Muslim world into conflict with Christendom. Initially successful in their goal of taking the Holy land, and establishing the Crusader states, Crusader gains in the Holy Land were later reversed by subsequent Muslim generals such as Saladin; who recaptured Jerusalem during the Second Crusade. In the east the Mongol Empire put an end to the Abbassid dynasty at the Battle of Baghdad in 1258, as they overran in Muslim lands in a series of invasions. Meanwhile in Egypt, the slave-soldier Mamluks took control in an uprising in 1250 and in alliance with the Golden Horde were able to halt the Mongol armies at the Battle of Ain Jalut. Mongol rule extended across the breadth of almost all Muslim lands in Asia and Islam was temporarily replaced by Buddhism as the official religion of the land. Over the next century the Mongol Khanates converted to Islam and this religious and cultural absorption ushered in a new age of Mongol-Islamic synthesis that shaped the further spread of Islam in central Asia and the Indian subcontinent.
Turkish and Indian Muslim states (1258–1918)
The Seljuk Turks conquered Abbassid lands and adopted Islam and become the de facto rulers of the caliphate. They captured Anatolia by defeating the Byzantines at the Battle of Manzikert, thereby precipitating the call for Crusades. They however fell apart rapidly in the second half of the 12th century giving rise to various semi-autonomous Turkic dynasties. In the 13th and 14th centuries the Ottoman empire (named after Osman I) emerged from among these "Ghazi emirates" and established itself after a string of conquests that included the Balkans, parts of Greece, and western Anatolia. In 1453 under Mehmed II the Ottomans laid siege to Constantinople, the capital of Byzantium. The Byzantine fortress succumbed shortly thereafter, having been overwhelmed by a far greater number of Ottoman troops and to a lesser extent, cannonry.
Beginning in the 13th century, Sufism underwent a transformation, largely as a result of the efforts of al-Ghazzali to legitimize and reorganize the movement. He developed the model of the Sufi order—a community of spiritual teachers and students. Also of importance to Sufism was the creation of the Masnavi, a collection of mystical poetry by the 13th century Persian poet Rumi. The Masnavi had a profound influence on the development of Sufi religious thought; to many Sufis it is second in importance only to the Qur'an.

In the early 16th century, the Shi'ite Safavid dynasty assumed control in Persia and established Shi'a Islam as an official religion there, and despite periodic setbacks, the Safavids remained powerful for two centuries. Meanwhile, Mamluk Egypt fell to the Ottomans in 1517, who then launched a European campaign which reached as far as the gates of Vienna in 1529. After the invasion of Persia, and sack of Baghdad by the Mongols in 1258, Delhi became the most important cultural centre of the Muslim east. Many Islamic dynasties ruled parts of the Indian subcontinent starting from the 12th century. The prominent ones include the Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526) and the Mughal empire (1526–1857). These empires helped in the spread of Islam in South Asia, but by the mid-18th century the British empire had ended the Mughal dynasty. In the 18th century the Wahhabi movement took hold in Saudi Arabia. Founded by the preacher Ibn Abd al-Wahhab, Wahhabism is a fundamentalist ideology that condemns practices like Sufism and the veneration of saints as un-Islamic.
European colonisation
By the 17th and 18th centuries, despite attempts at modernization, the Ottoman empire had begun to feel threatened by European economic and military advantages. In the 19th century, the rise of nationalism resulted in Greece declaring and winning independence in 1829, with several Balkan states following suit after the Ottomans suffered defeat in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878. The Ottoman era came to a close at the end of World War I.
In the 19th century, the Salafi, Deobandi and Barelwi movements were initiated.
Modern times (1918–present)
After World War I losses, the remnants of the empire were parceled out as European protectorates or spheres of influence. Since then most Muslim societies have become independent nations, and new issues such as oil wealth and relations with the State of Israel have assumed prominence.
The 20th century saw the creation of many new Islamic "revivalist" movements. Groups such as the Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt and Jamaat-e-Islami in Pakistan advocate a totalistic and theocratic alternative to secular political ideologies. Sometimes called Islamist, they see Western cultural values as a threat, and promote Islam as a comprehensive solution to every public and private question of importance. In countries like Iran and Afghanistan (under the Taliban), revolutionary movements replaced secular regimes with Islamist states, while transnational groups like Osama bin Laden's al-Qaeda engage in terrorism to further their goals. In contrast, Liberal Islam is a movement that attempts to reconcile religious tradition with modern norms of secular governance and human rights. Its supporters say that there are multiple ways to read Islam's sacred texts, and stress the need to leave room for "independent thought on religious matters".
Modern critique of Islam includes accusations that Islam is intolerant of criticism and that Islamic law is too hard on apostates. Critics like Ibn Warraq question the morality of the Qu'ran, saying that its contents justify the mistreatment of women and encourage antisemitic remarks by Muslim theologians. Such claims are disputed by Muslim writers like Fazlur Rahman, Syed Ameer Ali, Ahmed Deedat, and Yusuf Estes. Others like Daniel Pipes and Martin Kramer focus more on criticizing the spread of Islamic fundamentalism, a danger they feel has been ignored. Montgomery Watt and Norman Daniel dismiss many of the criticisms as the product of old myths and polemics. The rise of Islamophobia, according to Carl Ernst, had contributed to the negative views about Islam and Muslims in the West.
Community
Main article: Muslim world
Demographics
See also: Islam by country and Demographics of IslamCommonly cited estimates of the Muslim population in 2007 range from 1 billion to 1.8 billion. Approximately 85% are Sunni and 15% are Shi'a, with a small minority belonging to other sects. Some 30–40 countries are Muslim-majority, and Arabs account for around 20% of all Muslims worldwide. South Asia and Southeast Asia contain the most populous Muslim countries, with Indonesia, India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh having more than 100 million adherents each. According to U.S. government figures, in 2006 there were 20 million Muslims in China. In the Middle East, the non-Arab countries of Turkey and Iran are the largest Muslim-majority countries; in Africa, Egypt and Nigeria have the most populous Muslim communities. Islam is the second largest religion after Christianity in many European countries.
Mosques
Main article: MosqueA mosque is a place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name, masjid. The word mosque in English refers to all types of buildings dedicated to Islamic worship, although there is a distinction in Arabic between the smaller, privately owned mosque and the larger, "collective" mosque (masjid jāmi`). Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the Muslim community as a place to meet and study. Modern mosques have evolved greatly from the early designs of the 7th century, and contain a variety of architectural elements such as minarets.
Family life
See also: Women and IslamThe basic unit of Islamic society is the family, and Islam defines the obligations and legal rights of family members. The father is seen as financially responsible for his family, and is obliged to cater for their well-being. The division of inheritance is specified in the Qur'an, which states that most of it is to pass to the immediate family, while a portion is set aside for the payment of debts and the making of bequests. The woman's share of inheritance is generally half of that of a man with the same rights of succession. Marriage in Islam is a civil contract which consists of an offer and acceptance between two qualified parties in the presence of two witnesses. The groom is required to pay a bridal gift (mahr) to the bride, as stipulated in the contract.
A man may have up to four wives if he believes he can treat them equally, while a woman may have only one husband. In most Muslim countries, the process of divorce in Islam is known as talaq, which the husband initiates by pronouncing the word "divorce". Scholars disagree whether Islamic holy texts justify traditional Islamic practices such as veiling and seclusion (purdah). Starting in the 20th century, Muslim social reformers argued against these and other practices such as polygamy, with varying success. At the same time, many Muslim women have attempted to reconcile tradition with modernity by combining an active life with outward modesty. Certain Islamist groups like the Taliban have sought to continue traditional law as applied to women.
Calendar
Main article: Islamic calendarThe formal beginning of the Muslim era was chosen to be the Hijra in 622 CE, which was an important turning point in Muhammad's fortunes. The assignment of this year as the year 1 AH (Anno Hegirae) in the Islamic calendar was reportedly made by Caliph Umar. It is a lunar calendar, with nineteen ordinary years of 354 days and eleven leap years of 355 days in a thirty-year cycle. Islamic dates cannot be converted to CE/AD dates simply by adding 622 years: allowance must also be made for the fact that each Hijri century corresponds to only 97 years in the Christian calendar.
The year 1428 AH coincides almost completely with 2007 CE.
Islamic holy days fall on fixed dates of the lunar calendar, which means that they occur in different seasons in different years in the Gregorian calendar. The most important Islamic festivals are Eid al-Fitr (Arabic: عيد الفطر) on the 1 of Shawwal, marking the end of the fasting month Ramadan, and Eid al-Adha (Arabic: عيد الأضحى) on the 10 of Dhu al-Hijjah, coinciding with the pilgrimage to Mecca.
Other religions
Main article: Islam and other religions

According to Islamic doctrine, Islam was the primordial religion of mankind, professed by Adam. At some point, a religious split occurred, and God began sending prophets to bring his revelations to the people. In this view, Abraham, Moses, Hebrew prophets, and Jesus were all Prophets in Islam, but their message and the texts of the Torah and the Gospels were corrupted by Jews and Christians. Similarly, children of non-Muslim families are born Muslims, but are converted to another faith by their parents. The idea of Islamic supremacy is encapsulated in the formula "Islam is exalted and nothing is exalted above it." Pursuant to this principle, Muslim women may not marry non-Muslim men, defamation of Islam is prohibited, and the testimony of a non-Muslim is inadmissible against a Muslim.
Islamic law divides non-Muslims into several categories, depending on their relation with the Islamic state. Christians and Jews who live under Islamic rule are known as dhimmis ("protected peoples"). According to this pact, the personal safety and security of property of the dhimmis were guaranteed in return for paying tribute (jizya) to the Islamic state and acknowledging Muslim supremacy. Historically, dhimmis enjoyed a measure of communal autonomy under their own religious leaders, but were subject to legal, social and religious restrictions meant to highlight their inferiority. The status was extended to Zoroastrians and sometimes to polytheists, but not to atheists or agnostics. Those who live in non-Muslim lands (dar al-harb) are known as harbis, and upon entering into an alliance with the Muslim state become known as ahl al-ahd. Those who receive a guarantee of safety while residing temporarily in Muslim lands are known as ahl al-amān. Their legal position is similar to that of the dhimmi except that they are not required to pay the jizya. The people of armistice (ahl al-hudna) are those who live outside of Muslim territory and agree to refrain from attacking the Muslims. Apostasy is prohibited, and is punishable by death.
The Alevi, Yazidi, Druze, Ahmadiyya, Bábí, Bahá'í, Berghouata and Ha-Mim movements either emerged out of Islam or came to share certain beliefs with Islam. Some consider themselves separate while others still sects of Islam though controversial in certain beliefs with mainstream Muslims. Sikhism, founded by Guru Nanak in late fifteenth century Punjab, incorporates aspects of both Islam and Hinduism.
Denominations
Main article: Divisions of IslamIslam consists of a number of religious denominations that are essentially similar in belief but which have significant theological and legal differences. The primary division is between the Sunni and the Shi'a, with Sufism generally considered to be a mystical inflection of Islam rather than a distinct school. According to most sources, approximately 85% of the world's Muslims are Sunni and approximately 15% are Shi'a, with a small minority who are members of other Islamic sects.
Sunni
Main article: Sunni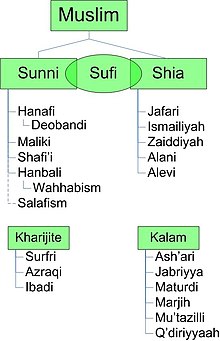
Sunni Muslims are the largest group in Islam. In Arabic, as-Sunnah literally means "principle" or "path". The Sunnah (the example of Muhammad's life) as recorded in the Qur'an and the hadith is the main pillar of Sunni doctrine. Sunnis believe that the first four caliphs were the rightful successors to Muhammad; since God did not specify any particular leaders to succeed him, those leaders had to be elected. Sunnis recognize four major legal traditions, or madhhabs: Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, and Hanbali. All four accept the validity of the others and a Muslim might choose any one that he or she finds agreeable, but other Islamic sects are believed to have departed from the majority by introducing innovations (bidah). There are also several orthodox theological or philosophical traditions within Sunnism. For example, the recent Salafi movement sees itself as restorationist and claims to derive its teachings from the original sources of Islam.
Shi'a
Main article: Shi'a See also: Succession to MuhammadThe Shi'a, who constitute the second-largest branch of Islam, believe in the political and religious leadership of infallible Imams from the progeny of Ali ibn Abi Talib. They believe that he, as the cousin and son-in-law of Muhammad, was his rightful successor, and they call him the first Imam (leader), rejecting the legitimacy of the previous Muslim caliphs. To them, an Imam rules by right of divine appointment and holds "absolute spiritual authority" among Muslims, having final say in matters of doctrine and revelation. Although the Shi'a share many core practices with the Sunni, the two branches disagree over the proper importance and validity of specific collections of hadith. The Shi'a follow a legal tradition called Ja'fari jurisprudence. Shi'a Islam has several branches, the largest of which is the Twelvers (iṯnāʿašariyya), while the others are the Ismaili, the Seveners, and the Zaidiyyah.
Sufism
Main article: SufismNot strictly a denomination, Sufism is a mystical-ascetic form of Islam. By focusing on the more spiritual aspects of religion, Sufis strive to obtain direct experience of God by making use of "intuitive and emotional faculties" that one must be trained to use. Sufism and Islamic law are usually considered to be complementary, although Sufism has been criticized by some Muslims for being an unjustified religious innovation. Most Sufi orders, or tariqas, can be classified as either Sunni or Shi'a.
Others
The Kharijites are a sect that dates back to the early days of Islam. The only surviving branch of the Kharijites is Ibadism. Unlike most Kharijite groups, Ibadism does not regard sinful Muslims as unbelievers. The Imamate is an important topic in Ibadi legal literature, which stipulates that the leader should be chosen solely on the basis of his knowledge and piety, and is to be deposed if he acts unjustly. Most Ibadi Muslims live in Oman.
See also
Further information: ]Notes
- USC-MSA Compendium of Muslim Texts
- ^ L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Lane's lexicon" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-07-03.
- "Major Religions of the World—Ranked by Number of Adherents" (HTML). Retrieved 2007-07-03.
- See:
- Esposito (1996), p.41
- Ghamidi (2001): Sources of Islam
- ^ See:
- Accad (2003): According to Ibn Taymiya, although only some Muslims accept the textual veracity of the entire Bible, most Muslims will grant the veracity of most of it.
- Esposito (1998), pp.6,12
- Esposito (2002b), pp.4–5
- F. E. Peters (2003), p.9
- F. Buhl. "Muhammad". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Hava Lazarus-Yafeh. "Tahrif". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Esposito (2002b), p.17
- See:
- Esposito (2002b), pp.111,112,118
- "Shari'ah". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Esposito (2002b), p.21
- Esposito (2004), pp.2,43
- See these figures
- Quran 6:125, Quran 61:7, Quran 39:22
- Quran 5:3, Quran 3:19, Quran 3:83
- See:
- L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
- Quran 2:4, Quran 2:285, Quran 4:136
- Template:Muslim
- See:
- Farah (2003), p.109
- Momen (1987), p.176
- Esposito (2004), pp.17,18,21
- See:
- Momem (1987), p.176
- "Islam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Quran 30:30
- See:
- "Islam", Encyclopedia of Religion
- "Islam", Encyclopedia of Religion
- See:
- "Islam and Christianity", Encyclopedia of Christianity (2001): Arabic-speaking Christians and Jews also refer to God as Allāh.
- L. Gardet. "Allah". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- David Thomas. "Tathlith, Trinity". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help): Contrary to Muslim understanding, some scholars have suggested that the Qur'an only opposes certain deviant forms of Trinitarian belief. - See:
- Esposito (2002b), pp.74–76
- Esposito (2004), p.22
- Griffith (2006), p.248
- D. Gimaret. "Allah, Tawhid". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Qur'an". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - See:
- William Montgomery Watt in The Cambridge History of Islam, p.32
- Richard Bell, William Montgomery Watt, Introduction to the Qur'an, p.51
- F. E. Peters (1991), pp.3–5: "Few have failed to be convinced that … the Quran is … the words of Muhammad, perhaps even dictated by him after their recitation."
- See:
- "Islam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Qur'an". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Islam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
- Esposito (2004), p.79
- See:
- Esposito (2004), pp.79–81
- "Tafsir". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Teece (2003), pp.12,13
- C. Turner (2006), p.42
- "Qur'an". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help): The word Qur'an was invented and first used in the Qur'an itself. There are two different theories about this term and its formation.
- Quran 21:19–20, Quran 35:1
- See:
- Esposito (2002b), pp.26–28
- W. Madelung. "Malā'ika". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Gisela Webb. "Angel". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Esposito (1998), p.12
- Esposito (2002b), pp.4–5
- F. E. Peters (2003), p.9
- "Muhammad". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- F. Buhl. "Muhammad". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- F. Buhl. "Muhammad". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
- See:
- F.E.Peters(2003), pp.78,79,194
- Lapidus (2002), pp.23–28
- F. Buhl. "Muhammad". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - See:
- Encyclopedia of Islam and the Muslim World (2003), p.666
- J. Robson. "Hadith". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- D. W. Brown. "Sunna". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- "Resurrection", The New Encyclopedia of Islam (2003)
- "Avicenna". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help): Ibn Sīnā, Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn b. ʿAbd Allāh b. Sīnā is known in the West as "Avicenna". - L. Gardet. "Qiyama". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Quran 9:72
- See:
- Smith (2006), p.89; Encyclopedia of Islam and Muslim World, p.565
- "Heaven", The Columbia Encyclopedia (2000)
- Asma Afsaruddin. "Garden". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Paradise". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- D. Cohen-Mor (2001), p.4: "The idea of predestination is reinforced by the frequent mention of events 'being written' or 'being in a book' before they happen: 'Say: "Nothing will happen to us except what Allah has decreed for us…" ' "
- Ahmet T. Karamustafa. "Fate". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help): The verb qadara literally means "to measure, to determine". Here it is used to mean that "God measures and orders his creation".
- See:
- Farah (2003), pp.119–122
- Patton (1900), p.130
- Momen (1987), pp.177,178
- See:
- Momem (1987), p.178
- "Pillars of Islam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Farah (1994), p.135
- Momen (1987), p.178
- "Islam", Encyclopedia of Religious Rites, Rituals, and Festivals(2004)
- See:
- Esposito (2002b), pp.18,19
- Hedáyetullah (2006), pp.53–55
- Kobeisy (2004), pp.22–34
- Momen (1987), p.178
- See:
- Esposito (2004), p.90
- Momen (1987), p.179
- "Zakat". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Zakat". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Esposito (2004), pp.90,91
- "Islam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "For whom fasting is mandatory". Compendium of Muslim Texts. USC-MSA. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- See:
- Farah (1994), pp.145–147
- Goldschmidt (2005), p.48
- "Hajj". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Momen (1987), p.180
- "Shari'ah". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - See:
- Menski (2006), p.290
- B. Carra de Vaux. "Hadd". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- N. Calder. "Sharia". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Weiss (2002), pp.xvii,162
- See:
- Esposito (2004), p.84
- Lapidus (2002), pp.502–507,845
- Lewis (2003), p.100
- See:
- Curtis (2005), p.164
- Esposito (2002b), p.111
- Ghamidi (2001): Customs and Behavioral Laws
- Ghamidi (2001): The Dietary Laws
- Ghamidi (2001): Various types of the prayer
- Ersilia Francesca. "Slaughter". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Esposito (2003), p.93
- Firestone (1999) pp. 17-18
- Reuven Firestone (1999), The Meaning of Jihād, p. 17-18
- Britannica Encyclopedia, Jihad
- See:
- Brockopp (2003) pp. 99–100
- Esposito (2003), p.93
- "jihad". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Firestone (1999) p.17
- "Djihad", Encyclopedia of Islam Online.
- Firestone (1999) p.17
- ^ "Djihād". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Knowing the Enemy: Jihadist Ideology and the War on Terror, Mary R. Habeck, Yale University Press, p.108-109, 118
- cf. Sachedina (1998) p. 105 and 106
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), pp.50,112,197,380,489,578,817
- Lewis (2004), pp.29,51–56
- See:
- Holt (1977a), p.57
- Hourani (2003), p.22
- Lapidus (2002), p.32
- Madelung (1996), p.43
- Tabatabaei (1979), p.30–50
- See
- Holt (1977a), p.74
- L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Holt (1977a), pp.67–72
- Waines (2003) p.46
- Donald Puchala, ‘’Theory and History in International Relations,’’ page 137. Routledge, 2003.
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), pp.90,91
- "Sufism". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Hawting (2000), p.4
- Lapidus (2002), p.56; Lewis (1993), pp. 71–83
- See:
- Holt (1977a), pp.80,92,105
- Holt (1977b), pp.661–663
- Lapidus (2002), p.56
- Lewis (1993), p.84
- L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), p.103–143
- "Abbasid Dynasty". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Lapidus (2002), p.86
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), p.160
- Waines (2003) p.126,127
- See:
- Esposito (2004), pp.44–45
- Lapidus (2002), pp.90–94
- "Sufism". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Tolan (2002) xv, xvi, 41
- See:
- Novak (February 1999)
- Sahas (1997), pp.76–80
- Lapidus (2002), pp.288–290,310
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), p.292
- "Islamic World". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See
- Holt (1977a), p.263
- Lapidus (2002), p.250
- "Istanbul". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Esposito (2004), pp.104,105
- "Islamic Art". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Esposito (2004), p.65
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), pp.198,234,244,245,254
- L. Gardet. "Islam". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Ikram, S. M. 1964. Muslim Civilization in India. New York: Columbia University Press
- Lapidus (2002), pp.358,378–380,624
- See:
- Lapidus (2002), p.572
- Watt (1973), p.18: Wahhabism should not be confused with the early Kharijite sect of Wahabiyya, which was named after Abd-Allah ibn-Wahb ar-Rasibi, who opposed Ali at Nahrawan.
- Lapidus (2002), pp.380,489–493
- Lapidus (2002), pp.281–282,380,489–493,556,578,823,835
- See:
- Esposito (2004), pp.118,119,179
- Lapidus (2002), pp.823–830
- See:
- Rippin (2001), p.288
- Timothy Garton Ash (10-05-2006). "Islam in Europe". The New York Review of Books. NYRB.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
- For example see Major Themes of the Qur'an by Fazlur Rahman in which he argues against the treatment of the Qur'an as either a piecemeal or an evolutionary progression of ideas. See review by William A. Graham (1983), p.446.
- For example see The Spirit of Islam by Syed Ameer Ali (1849-1928). It is described by David Samuel Margoliouth (1905) as "probably the best achievement in the way of an apology for Mohammed". See Margoliouth, preface Mohammed and the Rise of Islam.
- Westerlund (2003)
- Elizabeth Omara-Otunnu (11-17-2003). "Ramadan Awareness Event Designed To Debunk Negative Images". Advance, University of Connecticut.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Bernstein, Richard. "Experts on Islam Pointing Fingers At One Another". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-05-14.
- See:
- Seibert (1994), pp.88–89
- Watt (1974), p.231
- Ernst (2004), p.11
- ^ "Number of Muslim by country". nationmaster.com. Retrieved 2007-05-30.
- "International Religious Freedom Report 2006—China (includes Tibet, Hong Kong, and Macau)". U.S. department of State, Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-30.
- See:
- Esposito (2004) pp.2,43
- "Islamic World". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- "Muslims in Europe: Country guide". BBC News. BBC. 2005-12-23. Retrieved 2006-09-28.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Religion In Britain". National Statistics. Office for National Statistics. 2003-02-13. Retrieved 2006-08-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
- See:
- J. Pedersen. "Masdjid". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Mosque". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- J. Pedersen. "Masdjid". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
- "al-Mar'a". Encyclopaedia of Islam
-
- Waines (2003) pp. 93–96
- The Oxford Dictionary of Islam (2003), p.339
- Esposito (1998) p. 79
- *"Talak". Encyclopaedia of Islam
-
- Esposito (2004), pp.95,96,235–241
- Harald Motzki. "Marriage and Divorce". Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Lori Peek. "Marriage Practices". Encyclopedia of Women & Islamic Cultures.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See:
- Adil (2002), p.288
- F. E. Peters (2003), p.67
- B. van Dalen. "Tarikh̲". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
- Ghamidi (2001): Customs and Behavioral Laws
- Friedmann (2003), pp. 14–16
- Friedmann (2003), pp. 18–19
- Friedmann (2003), p. 18
- Friedmann (2003), p. 35
- See:
- Friedmann (2003), p. 35;
- Lewis (1984), p. 39
- See:
- Lewis (1984), pp.9, 27, 36;
- Friedmann (2003), p. 37;
- Lewis (2001), p.273
- Friedmann (2003), p. 55
- "Aman", Encyclopaedia of Islam
- A woman who apostasizes is to be executed according to some jurists, or imprisoned according to others.
- "Murtadd", Encyclopedia of Islam
- Encyclopedia of Islam, "Sikhs"
- See:
- Esposito (2002b), p.2
- "Sunni and Shia Islam". Country Studies. U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-01-09.
- See:
- Esposito (2003), pp.275,306
- "Shariah". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - "Sunnite". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- See
- Lapidus (2002), p.46
- "Imam". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - "Shi'ite". Encyclopaedia Britannica Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
- Imamat, by Naser Makarem Shirazi
- See:
- Ahmed (1999), pp.44–45
- Nasr (1994), p.466
- See:
- Kramer (1987), Syria's Alawis and Shi'ism pp.237–254
- Shia branches
- Trimingham (1998), p.1
- See:
- Esposito (2003), p.302
- Malik (2006), p.3
- B. S. Turner (1998), p.145
- "Afghanistan: A Country Study". Country Studies. U. S. Library of Congress (Federal Research Division). p. 150. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- See:
- IBADI ISLAM: AN INTRODUCTION
- J. A. Williams (1994), p.173
- "al-Ibāḍiyya". Encyclopaedia of Islam Online.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)
References
2Further reading
- Arberry, A. J. (1996). The Koran Interpreted: A Translation (1st ed.). Touchstone. ISBN 978-0684825076.
- Hawting, Gerald R. (2000). The First Dynasty of Islam: The Umayyard Caliphate AD 661–750. Routledge. ISBN 0415240727.
- Khan, Muhammad Muhsin (1999). Noble Quran (1st ed.). Dar-us-Salam Publications. ISBN 978-9960740799.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Kramer (ed.), Martin (1999). The Jewish Discovery of Islam: Studies in Honor of Bernard Lewis. Syracuse University. ISBN 978-9652240408.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help) - Kuban, Dogan (1974). Muslim Religious Architecture. Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 9004038132.
- Lewis, Bernard (1993). Islam in History: Ideas, People, and Events in the Middle East. Open Court. ISBN 978-0812692174.
- Lewis, Bernard (1994). Islam and the West. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195090611.
- Lewis, Bernard (1996). Cultures in Conflict: Christians, Muslims, and Jews in the Age of Discovery. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195102833.
- Mubarkpuri, Saifur-Rahman (2002). The Sealed Nectar: Biography of the Prophet. Dar-us-Salam Publications. ISBN 978-1591440710.
- Najeebabadi, Akbar Shah (2001). History of Islam. Dar-us-Salam Publications. ISBN 978-1591440345.
- Nigosian, S. A. (2004). Islam: Its History, Teaching, and Practices (New Edition ed.). Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0253216274.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - Rahman, Fazlur (1979). Islam (2nd ed.). University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-70281-2.
- Walker, Benjamin (1998). Foundations of Islam: The Making of a World Faith. Peter Owen Publishers. ISBN 978-0720610383.
External links
- Academic resources
- University of Southern California Compendium of Muslim Texts
- Encyclopedia of Islam (Overview of World Religions)
- Unit on Islam from the NITLE Arab Culture and Civilization Online Resource
- Islam, article at Enyclopaedia Britannica Online
- Directories
- Islam in Western Europe, the United Kingdom, Germany and South Asia
- Template:Dmoz
- Islam (Bookshelf) at Project Gutenberg
- Islam - text, audio and video
- Three Translations of The Koran (Al-Qur'an) side by side
- Kur'an audio (recordings of many Qur'an recitals - easy to stream and play)
- Quranic auido downloadable or streamable by different reciters
- Qur'an audio and reading material in numerous languages
- Islam and the arts
- BBC Islam Focus
- Islamic Art at the Los Angeles County Museum of Art
- Muslim Heritage (Foundation for Science Technology and Civilisation, UK)
- Islamic Architecture (IAORG) illustrated descriptions and reviews of a large number of mosques, palaces, and monuments.
| Islam topics | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outline of Islam | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Category: