This is an old revision of this page, as edited by This, that and the other (talk | contribs) at 10:25, 17 July 2008 (→Right triangle definitions: added section headings for sine. cosine, tangent, inverse). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 10:25, 17 July 2008 by This, that and the other (talk | contribs) (→Right triangle definitions: added section headings for sine. cosine, tangent, inverse)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) "Sine" redirects here. For other uses, see Sine (disambiguation).In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions) are functions of an angle. They are important in the study of triangles and modeling periodic phenomena, among many other applications. Trigonometric functions are commonly defined as ratios of two sides of a right triangle containing the angle, and can equivalently be defined as the lengths of various line segments from a unit circle. More modern definitions express them as infinite series or as solutions of certain differential equations, allowing their extension to arbitrary positive and negative values and even to complex numbers.
In modern usage, there are six basic trigonometric functions, which are tabulated here along with equations relating them to one another. Especially in the case of the last four, these relations are often taken as the definitions of those functions, but one can define them equally well geometrically or by other means and then derive these relations.
| Trigonometry |
|---|
 |
| Reference |
| Laws and theorems |
| Calculus |
| Mathematicians |
History
Main article: History of trigonometric functions| Function | Abbreviation | Identities (using radians) |
|---|---|---|
| Sine | sin | |
| Cosine | cos | |
| Tangent | tan (or tg) |
|
| Cosecant | csc (or cosec) |
|
| Secant | sec | |
| Cotangent | cot (or ctg or ctn) |
The notion that there should be some standard correspondence between the length of the sides of a triangle and the angles of the triangle comes as soon as one recognizes that similar triangles maintain the same ratios between their sides. That is, for any similar triangle the ratio of the hypotenuse (for example) and another of the sides remains the same. If the hypotenuse is twice as long, so are the sides. It is these ratios that the trigonometric functions express.
Trigonometric functions were studied by Hipparchus of Nicaea (180–125 BC), Ptolemy of Egypt (90–165 AD), Aryabhata (476–550), Varahamihira, Brahmagupta, Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Ḵwārizmī, Abū al-Wafā' al-Būzjānī, Omar Khayyam, Bhāskara II, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Ghiyath al-Kashi (14th century), Ulugh Beg (14th century), Regiomontanus (1464), Rheticus, and Rheticus' student Valentin Otho.
Madhava of Sangamagramma (c. 1400) made early strides in the analysis of trigonometric functions in terms of infinite series. Leonhard Euler's Introductio in analysin infinitorum (1748) was mostly responsible for establishing the analytic treatment of trigonometric functions in Europe, also defining them as infinite series and presenting "Euler's formula", as well as the near-modern abbreviations sin., cos., tang., cot., sec., and cosec.
A few functions were common historically, but are now seldom used, such as the chord (crd(θ) = 2 sin(θ/2)), the versine (versin(θ) = 1 − cos(θ) = 2 sin(θ/2)) (which appeared in the earliest tables ), the haversine (haversin(θ) = versin(θ) / 2 = sin(θ/2)), the exsecant (exsec(θ) = sec(θ) − 1) and the excosecant (excsc(θ) = exsec(π/2 − θ) = csc(θ) − 1). Many more relations between these functions are listed in the article about trigonometric identities.
Etymologically, the word sine derives from the Sanskrit word for half the chord ("jya-ardha", abbreviated to "jiva"). Arabic transliterated it to "jiba", written "jb", vowels not being written. This was mis-translated in the 12th century into Latin as "sinus," under the impression that the word was "jaib", which means "bosom" or "bay" or "fold", as does "sinus". Finally, English usage converted the word to "sine". Tangent comes from Latin "tangens" meaning "touching", since the line touches the circle of unit radius, whereas secant stems from Latin "secans" — "cutting" — since the line cuts the circle.
Right triangle definitions
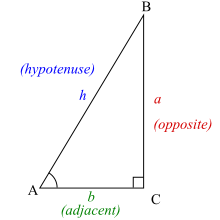


In order to define the trigonometric functions for the angle A, start with an arbitrary right triangle that contains the angle A:
We use the following names for the sides of the triangle:
- The hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle, or defined as the longest side of a right-angled triangle, in this case h.
- The opposite side is the side opposite to the angle we are interested in, in this case a.
- The adjacent side is the side that is in contact with the angle we are interested in and the right angle, hence its name. In this case the adjacent side is b.
All triangles are taken to exist in the Euclidean plane so that the inside angles of each triangle sum to π radians (or 180°); therefore, for a right triangle the two non-right angles are between zero and π/2 radians (or 90°). The reader should note that the following definitions, strictly speaking, only define the trigonometric functions for angles in this range. We extend them to the full set of real arguments by using the unit circle, or by requiring certain symmetries and that they be periodic functions.
Sine
The sine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse. In our case
Note that this ratio does not depend on the particular right triangle chosen, as long as it contains the angle A, since all those triangles are similar.
The set of zeroes of sine (i.e., the values of for which ) is
Cosine
The cosine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. In our case
The set of zeros of cosine is
Tangent
The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. In our case
The set of zeroes of tangent is
The same set of the sine function since
Inverse functions
The remaining three functions are best defined using the above three functions.
4) The cosecant csc(A) is the multiplicative inverse of sin(A), i.e. the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse to the length of the opposite side:
5) The secant sec(A) is the multiplicative inverse of cos(A), i.e. the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse to the length of the adjacent side:
6) The cotangent cot(A) is the multiplicative inverse of tan(A), i.e. the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the opposite side:
Slope definitions
Equivalent to the right-triangle definitions, the trigonometric functions can be defined in terms of the rise, run, and slope of a line segment relative to some horizontal line. The slope is commonly taught as "rise over run" or rise/run. The three main trigonometric functions are commonly taught in the order sine, cosine, tangent. With a unit circle, the following correspondence of definitions exists:
- Sine is first, rise is first. Sine takes an angle and tells the rise.
- Cosine is second, run is second. Cosine takes an angle and tells the run.
- Tangent is the slope formula that combines the rise and run. Tangent takes an angle and tells the slope.
This shows the main use of tangent and arctangent: converting between the two ways of telling the slant of a line, i.e., angles and slopes. (Note that the arctangent or "inverse tangent" is not to be confused with the cotangent, which is cos divided by sin.)
While the radius of the circle makes no difference for the slope (the slope does not depend on the length of the slanted line), it does affect rise and run. To adjust and find the actual rise and run, just multiply the sine and cosine by the radius. For instance, if the circle has radius 5, the run at an angle of 1° is 5 cos(1°)
Unit-circle definitions
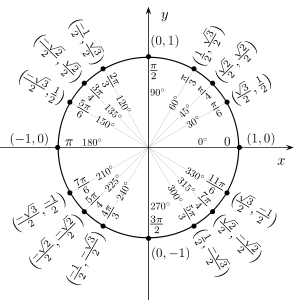
The six trigonometric functions can also be defined in terms of the unit circle, the circle of radius one centered at the origin. The unit circle definition provides little in the way of practical calculation; indeed it relies on right triangles for most angles. The unit circle definition does, however, permit the definition of the trigonometric functions for all positive and negative arguments, not just for angles between 0 and π/2 radians. It also provides a single visual picture that encapsulates at once all the important triangles. From the Pythagorean theorem the equation for the unit circle is:
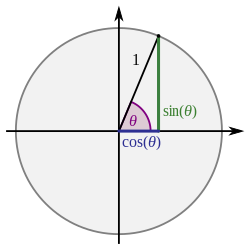
In the picture, some common angles, measured in radians, are given. Measurements in the counter clockwise direction are positive angles and measurements in the clockwise direction are negative angles. Let a line through the origin, making an angle of θ with the positive half of the x-axis, intersect the unit circle. The x- and y-coordinates of this point of intersection are equal to cos θ and sin θ, respectively. The triangle in the graphic enforces the formula; the radius is equal to the hypotenuse and has length 1, so we have sin θ = y/1 and cos θ = x/1. The unit circle can be thought of as a way of looking at an infinite number of triangles by varying the lengths of their legs but keeping the lengths of their hypotenuses equal to 1.


For angles greater than 2π or less than −2π, simply continue to rotate around the circle. In this way, sine and cosine become periodic functions with period 2π:
for any angle θ and any integer k.
The smallest positive period of a periodic function is called the primitive period of the function. The primitive period of the sine, cosine, secant, or cosecant is a full circle, i.e. 2π radians or 360 degrees; the primitive period of the tangent or cotangent is only a half-circle, i.e. π radians or 180 degrees. Above, only sine and cosine were defined directly by the unit circle, but the other four trigonometric functions can be defined by:
To the right is an image that displays a noticeably different graph of the trigonometric function f(θ)= tan(θ) graphed on the cartesian plane. Note that its x-intercepts correspond to that of sin(θ) while its undefined values correspond to the x-intercepts of the cos(θ). Observe that the function's results change slowly around angles of kπ, but change rapidly at angles close to (k + 1/2)π. The graph of the tangent function also has a vertical asymptote at θ = (k + 1/2)π. This is the case because the function approaches infinity as θ approaches (k + 1/2)π from the left and minus infinity as it approaches (k + 1/2)π from the right.

Alternatively, all of the basic trigonometric functions can be defined in terms of a unit circle centered at O (as shown in the picture to the right), and similar such geometric definitions were used historically. In particular, for a chord AB of the circle, where θ is half of the subtended angle, sin(θ) is AC (half of the chord), a definition introduced in India (see above). cos(θ) is the horizontal distance OC, and versin(θ) = 1 − cos(θ) is CD. tan(θ) is the length of the segment AE of the tangent line through A, hence the word tangent for this function. cot(θ) is another tangent segment, AF. sec(θ) = OE and csc(θ) = OF are segments of secant lines (intersecting the circle at two points), and can also be viewed as projections of OA along the tangent at A to the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. DE is exsec(θ) = sec(θ) − 1 (the portion of the secant outside, or ex, the circle). From these constructions, it is easy to see that the secant and tangent functions diverge as θ approaches π/2 (90 degrees) and that the cosecant and cotangent diverge as θ approaches zero. (Many similar constructions are possible, and the basic trigonometric identities can also be proven graphically.)
Series definitions

Using only geometry and properties of limits, it can be shown that the derivative of sine is cosine and the derivative of cosine is the negative of sine. (Here, and generally in calculus, all angles are measured in radians; see also the significance of radians below.) One can then use the theory of Taylor series to show that the following identities hold for all real numbers x:
These identities are often taken as the definitions of the sine and cosine function. They are often used as the starting point in a rigorous treatment of trigonometric functions and their applications (e.g., in Fourier series), since the theory of infinite series can be developed from the foundations of the real number system, independent of any geometric considerations. The differentiability and continuity of these functions are then established from the series definitions alone.
Other series can be found:
where
- Un is the nth up/down number,
- Bn is the nth Bernoulli number, and
- En (below) is the nth Euler number.
When this is expressed in a form in which the denominators are the corresponding factorials, and the numerators, called the "tangent numbers", have a combinatorial interpretation: they enumerate alternating permutations of finite sets of odd cardinality.
When this is expressed in a form in which the denominators are the corresponding factorials, the numerators, called the "secant numbers", have a combinatorial interpretation: they enumerate alternating permutations of finite sets of even cardinality.
From a theorem in complex analysis, there is a unique analytic continuation of this real function to the domain of complex numbers. They have the same Taylor series, and so the trigonometric functions are defined on the complex numbers using the Taylor series above.
Relationship to exponential function and complex numbers
It can be shown from the series definitions that the sine and cosine functions are the imaginary and real parts, respectively, of the complex exponential function when its argument is purely imaginary:
This identity is called Euler's formula. In this way, trigonometric functions become essential in the geometric interpretation of complex analysis. For example, with the above identity, if one considers the unit circle in the complex plane, defined by e, and as above, we can parametrize this circle in terms of cosines and sines, the relationship between the complex exponential and the trigonometric functions becomes more apparent.
Furthermore, this allows for the definition of the trigonometric functions for complex arguments z:
where i
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Definitions via differential equations
Both the sine and cosine functions satisfy the differential equation
That is to say, each is the negative of its own second derivative. Within the 2-dimensional function space V consisting of all solutions of this equation, the sine function is the unique solution satisfying the initial conditions y(0) = 0 and y′(0) = 1, and the cosine function is the unique solution satisfying the initial conditions y(0) = 1 and y′(0) = 0. Since the sine and cosine functions are linearly independent, together they form a basis of V. This method of defining the sine and cosine functions is essentially equivalent to using Euler's formula. (See linear differential equation.) It turns out that this differential equation can be used not only to define the sine and cosine functions but also to prove the trigonometric identities for the sine and cosine functions. Further, the observation that sine and cosine satisfies means that they are eigenfunctions of the second-derivative operator.
The tangent function is the unique solution of the nonlinear differential equation
satisfying the initial condition y(0) = 0. There is a very interesting visual proof that the tangent function satisfies this differential equation; see Needham's Visual Complex Analysis.
The significance of radians
Radians specify an angle by measuring the length around the path of the unit circle and constitute a special argument to the sine and cosine functions. In particular, only those sines and cosines which map radians to ratios satisfy the differential equations which classically describe them. If an argument to sine or cosine in radians is scaled by frequency,
then the derivatives will scale by amplitude.
Here, k is a constant that represents a mapping between units. If x is in degrees, then
This means that the second derivative of a sine in degrees satisfies not the differential equation
but rather
The cosine's second derivative behaves similarly.
This means that these sines and cosines are different functions, and that the fourth derivative of sine will be sine again only if the argument is in radians.
Identities
Main article: List of trigonometric identitiesMany identities exist which interrelate the trigonometric functions. Among the most frequently used is the Pythagorean identity, which states that for any angle, the square of the sine plus the square of the cosine is always 1. This is easy to see by studying a right triangle of hypotenuse 1 and applying the Pythagorean theorem. In symbolic form, the Pythagorean identity reads,
which is more commonly written with the exponent "two" next to the sine and cosine symbol:
In some cases the inner parentheses may be omitted.
Other key relationships are the sum and difference formulas, which give the sine and cosine of the sum and difference of two angles in terms of sines and cosines of the angles themselves. These can be derived geometrically, using arguments which go back to Ptolemy; one can also produce them algebraically using Euler's formula.
|
|
|
When the two angles are equal, the sum formulas reduce to simpler equations known as the double-angle formulas.
These identities can also be used to derive the product-to-sum identities that were used in antiquity to transform the product of two numbers in a sum of numbers and greatly speed operations, much like the logarithm function.
Calculus
For integrals and derivatives of trigonometric functions, see the relevant sections of table of derivatives, table of integrals, and list of integrals of trigonometric functions. Below is the list of the derivatives and integrals of the six basic trigonometric functions.
Definitions using functional equations
In mathematical analysis, one can define the trigonometric functions using functional equations based on properties like the sum and difference formulas. Taking as given these formulas and the Pythagorean identity, for example, one can prove that only two real functions satisfy those conditions. Symbolically, we say that there exists exactly one pair of real functions and such that for all real numbers x and y, the following equations hold:
with the added condition that
Other derivations, starting from other functional equations, are also possible, and such derivations can be extended to the complex numbers. As an example, this derivation can be used to define trigonometry in Galois fields.
Computation
The computation of trigonometric functions is a complicated subject, which can today be avoided by most people because of the widespread availability of computers and scientific calculators that provide built-in trigonometric functions for any angle. In this section, however, we describe more details of their computation in three important contexts: the historical use of trigonometric tables, the modern techniques used by computers, and a few "important" angles where simple exact values are easily found.
The first step in computing any trigonometric function is range reduction -- reducing the given angle to a "reduced angle" inside a small range of angles, say 0 to π/2, using the periodicity and symmetries of the trigonometric functions.
Main article: Generating trigonometric tablesPrior to computers, people typically evaluated trigonometric functions by interpolating from a detailed table of their values, calculated to many significant figures. Such tables have been available for as long as trigonometric functions have been described (see History above), and were typically generated by repeated application of the half-angle and angle-addition identities starting from a known value (such as sin(π/2) = 1).
Modern computers use a variety of techniques. One common method, especially on higher-end processors with floating point units, is to combine a polynomial or rational approximation (such as Chebyshev approximation, best uniform approximation, and Padé approximation, and typically for higher or variable precisions, Taylor and Laurent series) with range reduction and a table lookup — they first look up the closest angle in a small table, and then use the polynomial to compute the correction. On simpler devices that lack hardware multipliers, there is an algorithm called CORDIC (as well as related techniques) that is more efficient, since it uses only shifts and additions. All of these methods are commonly implemented in hardware floating point units for performance reasons.
For very high precision calculations, when series expansion convergence becomes too slow, trigonometric functions can be approximated by the arithmetic-geometric mean, which itself approximates the trigonometric function by the (complex) elliptic integral.
Main article: Exact trigonometric constantsFinally, for some simple angles, the values can be easily computed by hand using the Pythagorean theorem, as in the following examples. In fact, the sine, cosine and tangent of any integer multiple of radians (3°) can be found exactly by hand.
Consider a right triangle where the two other angles are equal, and therefore are both radians (45°). Then the length of side b and the length of side a are equal; we can choose . The values of sine, cosine and tangent of an angle of radians (45°) can then be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
Therefore:
To determine the trigonometric functions for angles of π/3 radians (60 degrees) and π/6 radians (30 degrees), we start with an equilateral triangle of side length 1. All its angles are π/3 radians (60 degrees). By dividing it into two, we obtain a right triangle with π/6 radians (30 degrees) and π/3 radians (60 degrees) angles. For this triangle, the shortest side = 1/2, the next largest side =(√3)/2 and the hypotenuse = 1. This yields:
Inverse functions
Main article: Inverse trigonometric functionsThe trigonometric functions are periodic, and hence not injective, so strictly they do not have an inverse function. Therefore to define an inverse function we must restrict their domains so that the trigonometric function is bijective. In the following, the functions on the left are defined by the equation on the right; these are not proved identities. The principal inverses are usually defined as:
For inverse trigonometric functions, the notations sin and cos are often used for arcsin and arccos, etc. When this notation is used, the inverse functions could be confused with the multiplicative inverses of the functions. The notation using the "arc-" prefix avoids such confusion, though "arcsec" can be confused with "arcsecond".
Just like the sine and cosine, the inverse trigonometric functions can also be defined in terms of infinite series. For example,
These functions may also be defined by proving that they are antiderivatives of other functions. The arcsine, for example, can be written as the following integral:
Analogous formulas for the other functions can be found at Inverse trigonometric function. Using the complex logarithm, one can generalize all these functions to complex arguments:
Properties and applications
Main article: Uses of trigonometryThe trigonometric functions, as the name suggests, are of crucial importance in trigonometry, mainly because of the following two results.
Law of sines
The law of sines states that for an arbitrary triangle with sides a, b, and c and angles opposite those sides A, B and C:
or, equivalently,
where R is the radius of the triangle's circumcircle.

It can be proven by dividing the triangle into two right ones and using the above definition of sine. The law of sines is useful for computing the lengths of the unknown sides in a triangle if two angles and one side are known. This is a common situation occurring in triangulation, a technique to determine unknown distances by measuring two angles and an accessible enclosed distance.
Law of cosines
The law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula) is an extension of the Pythagorean theorem:
also known as:
In this formula the angle at C is opposite to the side c. This theorem can be proven by dividing the triangle into two right ones and using the Pythagorean theorem.
The law of cosines is mostly used to determine a side of a triangle if two sides and an angle are known, although in some cases there can be two positive solutions as in the SSA ambiguous case. And can also be used to find the cosine of an angle (and consequently the angle itself) if all the sides are known.
Other useful properties
There is also a law of tangents:
Periodic functions

The trigonometric functions are also important in physics. The sine and the cosine functions, for example, are used to describe the simple harmonic motion, which models many natural phenomena, such as the movement of a mass attached to a spring and, for small angles, the pendular motion of a mass hanging by a string. The sine and cosine functions are one-dimensional projections of the uniform circular motion.
Trigonometric functions also prove to be useful in the study of general periodic functions. These functions have characteristic wave patterns as graphs, useful for modeling recurring phenomena such as sound or light waves. Every signal can be written as a (typically infinite) sum of sine and cosine functions of different frequencies; this is the basic idea of Fourier analysis, where trigonometric series are used to solve a variety of boundary-value problems in partial differential equations. For example the square wave, can be written as the Fourier series
In the animation on the right it can be seen that just a few terms already produce a fairly good approximation.
See also
- Generating trigonometric tables
- Hyperbolic function
- Pythagorean theorem
- Unit vector (explains direction cosines)
- Table of Newtonian series
- List of trigonometric identities
- Proofs of trigonometric identities
- Euler's formula
- Polar sine — a generalization to vertex angles
- All Students Take Calculus — a mnemonic for recalling the signs of trigonometric functions in a particular quadrant of a Cartesian plane
- Continued fraction of Gauss A continued fraction definition for the tangent function
Notes
- ^ See Boyer (1991).
- See Maor (1998), chapter 3, regarding the etymology.
- "Clark University".
- Abramowitz; Weisstein.
- For a demonstration, see Euler's_formula#Using Taylor series
- Needham, p. .
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - Kantabutra.
- However, doing that while maintaining precision is nontrivial, and methods like Gal's accurate tables, Cody and Waite reduction, and Payne and Hanek reduction algorithms can be used.
- "R. P. Brent, "Fast Multiple-Precision Evaluation of Elementary Functions", J. ACM 23, 242 (1976)".
References
- Abramowitz, Milton and Irene A. Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, Dover, New York. (1964). ISBN 0-486-61272-4.
- Boyer, Carl B., A History of Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd edition. (1991). ISBN 0-471-54397-7.
- Joseph, George G., The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics, 2nd ed. Penguin Books, London. (2000). ISBN 0-691-00659-8.
- Kantabutra, Vitit, "On hardware for computing exponential and trigonometric functions," IEEE Trans. Computers 45 (3), 328–339 (1996).
- Maor, Eli, Trigonometric Delights, Princeton Univ. Press. (1998). Reprint edition (February 25, 2002): ISBN 0-691-09541-8.
- Needham, Tristan, "Preface"" to Visual Complex Analysis. Oxford University Press, (1999). ISBN 0-19-853446-9.
- O'Connor, J.J., and E.F. Robertson, "Trigonometric functions", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. (1996).
- O'Connor, J.J., and E.F. Robertson, "Madhava of Sangamagramma", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. (2000).
- Pearce, Ian G., "Madhava of Sangamagramma", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. (2002).
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Tangent" from MathWorld, accessed 21 January 2006.
External links
- Visionlearning Module on Wave Mathematics
- GonioLab: Visualization of the unit circle, trigonometric and hyperbolic functions
- Dave's draggable diagram. (Requires java browser plugin)
Categories:







 for which
for which  ) is
) is































 means that they are
means that they are 































 and
and  such that for all real numbers x and y, the following equations hold:
such that for all real numbers x and y, the following equations hold:





 radians (45°). Then the length of side b and the length of side a are equal; we can choose
radians (45°). Then the length of side b and the length of side a are equal; we can choose  . The values of sine, cosine and tangent of an angle of
. The values of sine, cosine and tangent of an angle of 
















