 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alpha-Eucaine |
| Other names | α-Eucaine; Eucaine A |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
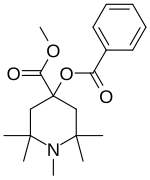
| Formula | C19H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 333.428 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
α-Eucaine (alpha-eucaine) is a drug that was previously used as a local anesthetic. It was designed as an analog of cocaine and was one of the first synthetic chemical compounds to find general use as an anesthetic.
Synthesis

The Aldol condensation between two equivalents of acetone gives Mesityl oxide (1) (isophorone is a side-product of this reaction). Ammonolysis of mesityl oxide formed diacetonamine (2). The reaction of this product with acetone then gives 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidone (3). N-methylation of the secondary amine gives 1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidin-4-one (4). Cyanohydrin formation gives CID:434556 (5). Esterification of the tertiary alcohol with benzoyl chloride gives (6). Pinner reaction of the nitrile with EtOH/H+ affords alpha-eucaine (7).
See also
- Eucaine, or β-eucaine, a related local anesthetic
References
- Sneader W (31 October 2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 127–9. ISBN 978-0-470-01552-0.
- Manske RH (12 May 2014). The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology. Elsevier. pp. 213–4. ISBN 978-1-4832-2192-2.
- Parsons, C. L. (December 1901). "THE IDENTIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF α- AND β-EUCAINE. 1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 23 (12): 885–893. doi:10.1021/ja02038a002.
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |