| Black-girdled barbet | |
|---|---|

| |
| A male at Alta Floresta, Mato Grosso state, Brazil | |

| |
| Conservation status | |
 Near Threatened (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Capitonidae |
| Genus: | Capito |
| Species: | C. dayi |
| Binomial name | |
| Capito dayi Cherrie, 1916 | |
| |
The black-girdled barbet (Capito dayi) is a species of bird in the family Capitonidae, the New World barbets. It is found in Brazil and Bolivia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Since its description in 1916, the black-girdled barbet has almost always been recognized as a species. However, it was briefly considered to be a subspecies of black-spotted barbet (Capito niger). DNA data have shown it instead to be sister to five-colored barbet (C. quinticolor).
The black-girdled barbet is monotypic. Its specific epithet dayi honors Lee Garnet Day, one of the leaders of the expedition that discovered the bird.

Description
The black-girdled barbet is approximately 18 cm (7.1 in) long and weighs 56 to 74 g (2.0 to 2.6 oz). The adult male's entire crown and nape are scarlet, the sides of the head black, and the chin and throat various shades of brown. Its back is black. Its underparts are white or off-white on the upper breast merging to pale greenish yellow on the belly. Its flanks are black, which extends nearly across the lower breast forming the "girdle". The adult female differs in that its crown and nape are black. The immature is similar to the adult but duller overall.
Distribution and habitat
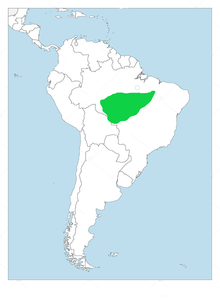
The black-girdled barbet is found in southern Amazonia. In Brazil it occurs in southeastern Amazonas, most of southern Pará, the northwestern half of Mato Grosso, and eastern Rondônia. Its range extends slightly into Santa Cruz Department of northeastern Bolivia. It inhabits the canopy of evergreen terra firme and várzea forests and also adjacent mature secondary forest.
Behavior
Feeding
Little is known about the black-girdled barbet's diet other than that it includes both fruit and arthropods. Its foraging behavior has not been described.
Breeding
Specimens of the black-girdled barbet indicate that it primarily breeds between August and November, though February and June are also implicated. It is assumed to nest in a tree cavity like other New World barbets, but its nest and eggs have not been described.
Vocalization
The black-girdled barbet's song is "a steadily accelerating series of hollow boo notes" . It has at least two calls, a series of notes "rok rok ock ock" and "a peculiar grating rattle" .
Status
The IUCN has assessed the black-girdled barbet as Vulnerable since 2012; previously it had been classed as being of Least Concern. The combination of the species' dependence on mature forest and the continued deforestation in Amazonia led to the reassessment.
References
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Capito dayi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22681917A92925988. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22681917A92925988.en. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (January 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.1)". Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 23 May 2021. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved 24 May 2021
- ^ Schulenberg, T. S. (2020). Black-girdled Barbet (Capito dayi), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.blgbar1.01 retrieved 25 May 2021