| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Synovial bursa" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Synovial bursa | |
|---|---|
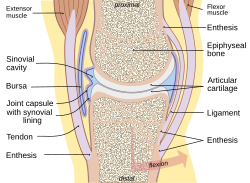 Typical joint Typical joint | |
 Within the knee joint: bursae visible top right, middle right and bottom right Within the knee joint: bursae visible top right, middle right and bottom right | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | bursa synovialis |
| MeSH | D002061 |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.039 |
| TA2 | 2028, 2027 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00039 |
| FMA | 9692 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
A synovial bursa, usually simply bursa (pl.: bursae or bursas), is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body.
Structure
Based on location, there are three types of bursa: subcutaneous, submuscular and subtendinous. A subcutaneous bursa is located between the skin and an underlying bone. It allows skin to move smoothly over the bone. Examples include the prepatellar bursa located over the kneecap and the olecranon bursa at the tip of the elbow. A submuscular bursa is found between a muscle and an underlying bone, or between adjacent muscles. These prevent rubbing of the muscle during movements. A large submuscular bursa, the trochanteric bursa, is found at the lateral hip, between the greater trochanter of the femur and the overlying gluteus maximus muscle. A subtendinous bursa is found between a tendon and a bone. Examples include the subacromial bursa that protects the tendon of shoulder muscle as it passes under the acromion of the scapula, and the suprapatellar bursa that separates the tendon of the large anterior thigh muscle from the distal femur just above the knee.
An adventitious bursa is a non-native bursa. When any surface of the body is subjected to repeated stress, an adventitious bursa develops under it. Examples are student's elbow and bunion.
Clinical significance
Infection or irritation of a bursa leads to bursitis (inflammation of a bursa). The general term for disease of bursae is "bursopathy."
Etymology
Bursa is Medieval Latin for "purse", so named for the bag-like function of an anatomical bursa. Bursae or bursas is its plural form.
See also
- Bursa of Fabricius (a lymphatic organ in birds)
- Bursectomy
- Knee bursae
- Shoulder joint#Bursae
External links
- Hirji, Zameer; Hunjun, Jaspal S; Choudur, Hema N (2 May 2011). "Imaging of the Bursae". Journal of Clinical Imaging Science. 1: 22. doi:10.4103/2156-7514.80374. PMC 3177464. PMID 21966619.
- Diagram of elbow with olecranon bursa
Reference
- Betts, J. Gordon (2013). "9.4 Synovial joints". Anatomy & physiology. Houston, Texas: OpenStax. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3. Retrieved 14 May 2023.
Source text
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY 4.0. Text taken from Anatomy and Physiology, J. Gordon Betts et al, Openstax.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY 4.0. Text taken from Anatomy and Physiology, J. Gordon Betts et al, Openstax.
| Joints | |
|---|---|
| Types |
|
| Terminology | |
| Motions |
|
| Components | |
| Synovial bursa and tendon sheaths | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synovial bursa |
| ||||
| Tendon sheaths |
| ||||