| Part of a series on |
| Classical mechanics |
|---|
| Second law of motion |
| Branches |
| Fundamentals |
| Formulations |
| Core topics |
| Rotation |
| Scientists |
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle in a single central potential field. A central force is a force (possibly negative) that points from the particle directly towards a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In a few important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.
The solution of this problem is important to classical mechanics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.
Basics
The essence of the central-force problem is to solve for the position r of a particle moving under the influence of a central force F, either as a function of time t or as a function of the angle φ relative to the center of force and an arbitrary axis.
Definition of a central force

A conservative central force F has two defining properties. First, it must drive particles either directly towards or directly away from a fixed point in space, the center of force, which is often labeled O. In other words, a central force must act along the line joining O with the present position of the particle. Second, a conservative central force depends only on the distance r between O and the moving particle; it does not depend explicitly on time or other descriptors of position.
This two-fold definition may be expressed mathematically as follows. The center of force O can be chosen as the origin of a coordinate system. The vector r joining O to the present position of the particle is known as the position vector. Therefore, a central force must have the mathematical form where r is the vector magnitude |r| (the distance to the center of force) and r̂ = r/r is the corresponding unit vector. According to Newton's second law of motion, the central force F generates a parallel acceleration a scaled by the mass m of the particle
For attractive forces, F(r) is negative, because it works to reduce the distance r to the center. Conversely, for repulsive forces, F(r) is positive.
Potential energy
See also: Kinetic energy and Potential energyIf the central force is a conservative force, then the magnitude F(r) of a central force can always be expressed as the derivative of a time-independent potential energy function U(r)
Thus, the total energy of the particle—the sum of its kinetic energy and its potential energy U—is a constant; energy is said to be conserved. To show this, it suffices that the work W done by the force depends only on initial and final positions, not on the path taken between them.
Equivalently, it suffices that the curl of the force field F is zero; using the formula for the curl in spherical coordinates, because the partial derivatives are zero for a central force; the magnitude F does not depend on the angular spherical coordinates θ and φ.
Since the scalar potential V(r) depends only on the distance r to the origin, it has spherical symmetry. In this respect, the central-force problem is analogous to the Schwarzschild geodesics in general relativity and to the quantum mechanical treatments of particles in potentials of spherical symmetry.
One-dimensional problem
If the initial velocity v of the particle is aligned with position vector r, then the motion remains forever on the line defined by r. This follows because the force—and by Newton's second law, also the acceleration a—is also aligned with r. To determine this motion, it suffices to solve the equation
One solution method is to use the conservation of total energy
Taking the reciprocal and integrating we get:
For the remainder of the article, it is assumed that the initial velocity v of the particle is not aligned with position vector r, i.e., that the angular momentum vector L = r × m v is not zero.
Uniform circular motion
Every central force can produce uniform circular motion, provided that the initial radius r and speed v satisfy the equation for the centripetal force
If this equation is satisfied at the initial moments, it will be satisfied at all later times; the particle will continue to move in a circle of radius r at speed v forever.
Relation to the classical two-body problem

The central-force problem concerns an ideal situation (a "one-body problem") in which a single particle is attracted or repelled from an immovable point O, the center of force. However, physical forces are generally between two bodies; and by Newton's third law, if the first body applies a force on the second, the second body applies an equal and opposite force on the first. Therefore, both bodies are accelerated if a force is present between them; there is no perfectly immovable center of force. However, if one body is overwhelmingly more massive than the other, its acceleration relative to the other may be neglected; the center of the more massive body may be treated as approximately fixed. For example, the Sun is overwhelmingly more massive than the planet Mercury; hence, the Sun may be approximated as an immovable center of force, reducing the problem to the motion of Mercury in response to the force applied by the Sun. In reality, however, the Sun also moves (albeit only slightly) in response to the force applied by the planet Mercury.

Such approximations are unnecessary, however. Newton's laws of motion allow any classical two-body problem to be converted into a corresponding exact one-body problem. To demonstrate this, let x1 and x2 be the positions of the two particles, and let r = x1 − x2 be their relative position. Then, by Newton's second law,
The final equation derives from Newton's third law; the force of the second body on the first body (F21) is equal and opposite to the force of the first body on the second (F12). Thus, the equation of motion for r can be written in the form where is the reduced mass
As a special case, the problem of two bodies interacting by a central force can be reduced to a central-force problem of one body.
Qualitative properties
Planar motion

The motion of a particle under a central force F always remains in the plane defined by its initial position and velocity. This may be seen by symmetry. Since the position r, velocity v and force F all lie in the same plane, there is never an acceleration perpendicular to that plane, because that would break the symmetry between "above" the plane and "below" the plane.
To demonstrate this mathematically, it suffices to show that the angular momentum of the particle is constant. This angular momentum L is defined by the equation where m is the mass of the particle and p is its linear momentum. In this equation the times symbol × indicates the vector cross product, not multiplication. Therefore, the angular momentum vector L is always perpendicular to the plane defined by the particle's position vector r and velocity vector v.
In general, the rate of change of the angular momentum L equals the net torque r × F
The first term m v × v is always zero, because the vector cross product is always zero for any two vectors pointing in the same or opposite directions. However, when F is a central force, the remaining term r × F is also zero because the vectors r and F point in the same or opposite directions. Therefore, the angular momentum vector L is constant. Then
Consequently, the particle's position r (and hence velocity v) always lies in a plane perpendicular to L.
Polar coordinates

Since the motion is planar and the force radial, it is customary to switch to polar coordinates. In these coordinates, the position vector r is represented in terms of the radial distance r and the azimuthal angle φ.
Taking the first derivative with respect to time yields the particle's velocity vector v
Similarly, the second derivative of the particle's position r equals its acceleration a
The velocity v and acceleration a can be expressed in terms of the radial and azimuthal unit vectors. The radial unit vector is obtained by dividing the position vector r by its magnitude r, as described above
The azimuthal unit vector is given by
Thus, the velocity can be written as whereas the acceleration equals
Specific angular momentum

Since F = ma by Newton's second law of motion and since F is a central force, then only the radial component of the acceleration a can be non-zero; the angular component aφ must be zero
Therefore,
This expression in parentheses is usually denoted h
which equals the speed v times r⊥, the component of the radius vector perpendicular to the velocity. h is the magnitude of the specific angular momentum because it equals the magnitude L of the angular momentum divided by the mass m of the particle.
For brevity, the angular speed is sometimes written ω
However, it should not be assumed that ω is constant. Since h is constant, ω varies with the radius r according to the formula
Since h is constant and r is positive, the angle φ changes monotonically in any central-force problem, either continuously increasing (h positive) or continuously decreasing (h negative).
Constant areal velocity
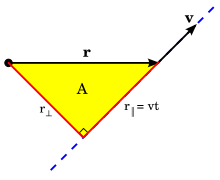
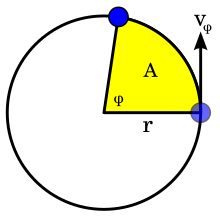
The magnitude of h also equals twice the areal velocity, which is the rate at which area is being swept out by the particle relative to the center. Thus, the areal velocity is constant for a particle acted upon by any type of central force; this is Kepler's second law. Conversely, if the motion under a conservative force F is planar and has constant areal velocity for all initial conditions of the radius r and velocity v, then the azimuthal acceleration aφ is always zero. Hence, by Newton's second law, F = ma, the force is a central force.
The constancy of areal velocity may be illustrated by uniform circular and linear motion. In uniform circular motion, the particle moves with constant speed v around the circumference of a circle of radius r. Since the angular velocity ω = v/r is constant, the area swept out in a time Δt equals ω rΔt; hence, equal areas are swept out in equal times Δt. In uniform linear motion (i.e., motion in the absence of a force, by Newton's first law of motion), the particle moves with constant velocity, that is, with constant speed v along a line. In a time Δt, the particle sweeps out an area 1⁄2vΔtr⊥ (the impact parameter). The distance r⊥ does not change as the particle moves along the line; it represents the distance of closest approach of the line to the center O (the impact parameter). Since the speed v is likewise unchanging, the areal velocity 1⁄2vr⊥ is a constant of motion; the particle sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
Equivalent parallel force field
By a transformation of variables, any central-force problem can be converted into an equivalent parallel-force problem. In place of the ordinary x and y Cartesian coordinates, two new position variables ξ = x/y and η = 1/y are defined, as is a new time coordinate τ
The corresponding equations of motion for ξ and η are given by
Since the rate of change of ξ is constant, its second derivative is zero
Since this is the acceleration in the ξ direction and since F=ma by Newton's second law, it follows that the force in the ξ direction is zero. Hence the force is only along the η direction, which is the criterion for a parallel-force problem. Explicitly, the acceleration in the η direction equals because the acceleration in the y-direction equals
Here, Fy denotes the y-component of the central force, and y/r equals the cosine of the angle between the y-axis and the radial vector r.
General solution
Binet equation
See also: Binet equationSince a central force F acts only along the radius, only the radial component of the acceleration is nonzero. By Newton's second law of motion, the magnitude of F equals the mass m of the particle times the magnitude of its radial acceleration
This equation has integration factor
Integrating yields
If h is not zero, the independent variable can be changed from t to ϕ giving the new equation of motion
Making the change of variables to the inverse radius u = 1/r yields
| 1 |
where C is a constant of integration and the function G(u) is defined by
This equation becomes quasilinear on differentiating by ϕ
This is known as the Binet equation. Integrating (1) yields the solution for ϕ where ϕ0 is another constant of integration. A central-force problem is said to be "integrable" if this final integration can be solved in terms of known functions.
Orbit of the particle
Take the scalar product of Newton's second law of motion with the particle's velocity where the force is obtained from the potential energy gives where summation is assumed over the spatial Cartesian index and we have used the fact that and used the chain rule . Rearranging The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with , the total mechanical energy. Clearly, this is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy.
Furthermore if the potential is central, and so the force is along the radial direction. In this case, the cross product of Newton's second law of motion with the particle's position vector must vanish since the cross product of two parallel vectors is zero: but (cross product of parallel vectors), so The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with the angular momentum, In particular, in polar coordinates, or Further, , so the energy equation may be simplified with the angular momentum as This indicates that the angular momentum contributes an effective potential energy Solve this equation for which may be converted to the derivative of with respect to the azimuthal angle as This is a separable first order differential equation. Integrating and yields the formula
Changing the variable of integration to the inverse radius yields the integral which expresses the above constants C = 2mEtot/L and G(u) = 2mU(1/u)/L above in terms of the total energy Etot and the potential energy U(r).
Turning points and closed orbits
Main article: Bertrand's theoremThe rate of change of r is zero whenever the effective potential energy equals the total energy
The points where this equation is satisfied are known as turning points. The orbit on either side of a turning point is symmetrical; in other words, if the azimuthal angle is defined such that φ = 0 at the turning point, then the orbit is the same in opposite directions, r(φ) = r(−φ).
If there are two turning points such that the radius r is bounded between rmin and rmax, then the motion is contained within an annulus of those radii. As the radius varies from the one turning point to the other, the change in azimuthal angle φ equals
The orbit will close upon itself provided that Δφ equals a rational fraction of 2π, i.e., where m and n are integers. In that case, the radius oscillates exactly m times while the azimuthal angle φ makes exactly n revolutions. In general, however, Δφ/2π will not be such a rational number, and thus the orbit will not be closed. In that case, the particle will eventually pass arbitrarily close to every point within the annulus. Two types of central force always produce closed orbits: F(r) = αr (a linear force) and F(r) = α/r (an inverse-square law). As shown by Bertrand, these two central forces are the only ones that guarantee closed orbits.
In general, if the angular momentum L is nonzero, the L/2mr term prevents the particle from falling into the origin, unless the effective potential energy goes to negative infinity in the limit of r going to zero. Therefore, if there is a single turning point, the orbit generally goes to infinity; the turning point corresponds to a point of minimum radius.
Specific solutions
Kepler problem

In classical physics, many important forces follow an inverse-square law, such as gravity or electrostatics. The general mathematical form of such inverse-square central forces is for a constant , which is negative for an attractive force and positive for a repulsive one.
This special case of the classical central-force problem is called the Kepler problem. For an inverse-square force, the Binet equation derived above is linear
The solution of this equation is which shows that the orbit is a conic section of eccentricity e; here, φ0 is the initial angle, and the center of force is at the focus of the conic section. Using the half-angle formula for sine, this solution can also be written as

where u1 and u2 are constants, with u2 larger than u1. The two versions of the solution are related by the equations and
Since the sin function is always greater than zero, u2 is the largest possible value of u and the inverse of the smallest possible value of r, i.e., the distance of closest approach (periapsis). Since the radial distance r cannot be a negative number, neither can its inverse u; therefore, u2 must be a positive number. If u1 is also positive, it is the smallest possible value of u, which corresponds to the largest possible value of r, the distance of furthest approach (apoapsis). If u1 is zero or negative, then the smallest possible value of u is zero (the orbit goes to infinity); in this case, the only relevant values of φ are those that make u positive.
For an attractive force (α < 0), the orbit is an ellipse, a hyperbola or parabola, depending on whether u1 is positive, negative, or zero, respectively; this corresponds to an eccentricity e less than one, greater than one, or equal to one. For a repulsive force (α > 0), u1 must be negative, since u2 is positive by definition and their sum is negative; hence, the orbit is a hyperbola. Naturally, if no force is present (α=0), the orbit is a straight line.
Central forces with exact solutions
See also: Exact solutions of classical central-force problemsThe Binet equation for u(φ) can be solved numerically for nearly any central force F(1/u). However, only a handful of forces result in formulae for u in terms of known functions. As derived above, the solution for φ can be expressed as an integral over u
A central-force problem is said to be "integrable" if this integration can be solved in terms of known functions.
If the force is a power law, i.e., if F(r) = α r, then u can be expressed in terms of circular functions and/or elliptic functions if n equals 1, -2, -3 (circular functions) and -7, -5, -4, 0, 3, 5, -3/2, -5/2, -1/3, -5/3 and -7/3 (elliptic functions). Similarly, only six possible linear combinations of power laws give solutions in terms of circular and elliptic functions
The following special cases of the first two force types always result in circular functions.
The special case was mentioned by Newton, in corollary 1 to proposition VII of the principia, as the force implied by circular orbits passing through the point of attraction.
Revolving orbits
The term r occurs in all the force laws above, indicating that the addition of the inverse-cube force does not influence the solubility of the problem in terms of known functions. Newton showed that, with adjustments in the initial conditions, the addition of such a force does not affect the radial motion of the particle, but multiplies its angular motion by a constant factor k. An extension of Newton's theorem was discovered in 2000 by Mahomed and Vawda.
Assume that a particle is moving under an arbitrary central force F1(r), and let its radius r and azimuthal angle φ be denoted as r(t) and φ1(t) as a function of time t. Now consider a second particle with the same mass m that shares the same radial motion r(t), but one whose angular speed is k times faster than that of the first particle. In other words, the azimuthal angles of the two particles are related by the equation φ2(t) = k φ1(t). Newton showed that the force acting on the second particle equals the force F1(r) acting on the first particle, plus an inverse-cube central force where L1 is the magnitude of the first particle's angular momentum.
If k is greater than one, F2−F1 is a negative number; thus, the added inverse-cube force is attractive. Conversely, if k is less than one, F2−F1 is a positive number; the added inverse-cube force is repulsive. If k is an integer such as 3, the orbit of the second particle is said to be a harmonic of the first particle's orbit; by contrast, if k is the inverse of an integer, such as 1⁄3, the second orbit is said to be a subharmonic of the first orbit.
Historical development

Newton's derivation
The classical central-force problem was solved geometrically by Isaac Newton in his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, in which Newton introduced his laws of motion. Newton used an equivalent of leapfrog integration to convert the continuous motion to a discrete one, so that geometrical methods may be applied. In this approach, the position of the particle is considered only at evenly spaced time points. For illustration, the particle in Figure 10 is located at point A at time t = 0, at point B at time t = Δt, at point C at time t = 2Δt, and so on for all times t = nΔt, where n is an integer. The velocity is assumed to be constant between these time points. Thus, the vector rAB = rB − rA equals Δt times the velocity vector vAB (red line), whereas rBC = rC − rB equals vBCΔt (blue line). Since the velocity is constant between points, the force is assumed to act instantaneously at each new position; for example, the force acting on the particle at point B instantly changes the velocity from vAB to vBC. The difference vector Δr = rBC − rAB equals ΔvΔt (green line), where Δv = vBC − vAB is the change in velocity resulting from the force at point B. Since the acceleration a is parallel to Δv and since F = ma, the force F must be parallel to Δv and Δr. If F is a central force, it must be parallel to the vector rB from the center O to the point B (dashed green line); in that case, Δr is also parallel to rB.
If no force acts at point B, the velocity is unchanged, and the particle arrives at point K at time t = 2Δt. The areas of the triangles OAB and OBK are equal, because they share the same base (rAB) and height (r⊥). If Δr is parallel to rB, the triangles OBK and OBC are likewise equal, because they share the same base (rB) and the height is unchanged. In that case, the areas of the triangles OAB and OBC are the same, and the particle sweeps out equal areas in equal time. Conversely, if the areas of all such triangles are equal, then Δr must be parallel to rB, from which it follows that F is a central force. Thus, a particle sweeps out equal areas in equal times if and only if F is a central force.
Alternative derivations of the equations of motion
Lagrangian mechanics
The formula for the radial force may also be obtained using Lagrangian mechanics. In polar coordinates, the Lagrangian L of a single particle in a potential energy field U(r) is given by
Then Lagrange's equations of motion take the form since the magnitude F(r) of the radial force equals the negative derivative of the potential energy U(r) in the radial direction.
Hamiltonian mechanics
The radial force formula may also be derived using Hamiltonian mechanics. In polar coordinates, the Hamiltonian can be written as
Since the azimuthal angle φ does not appear in the Hamiltonian, its conjugate momentum pφ is a constant of the motion. This conjugate momentum is the magnitude L of the angular momentum, as shown by the Hamiltonian equation of motion for φ
The corresponding equation of motion for r is
Taking the second derivative of r with respect to time and using Hamilton's equation of motion for pr yields the radial-force equation
Hamilton-Jacobi equation
The orbital equation can be derived directly from the Hamilton–Jacobi equation. Adopting the radial distance r and the azimuthal angle φ as the coordinates, the Hamilton-Jacobi equation for a central-force problem can be written where S = Sφ(φ) + Sr(r) − Etott is Hamilton's principal function, and Etot and t represent the total energy and time, respectively. This equation may be solved by successive integrations of ordinary differential equations, beginning with the φ equation where pφ is a constant of the motion equal to the magnitude of the angular momentum L. Thus, Sφ(φ) = Lφ and the Hamilton–Jacobi equation becomes
Integrating this equation for Sr yields
Taking the derivative of S with respect to L yields the orbital equation derived above
See also
- Schwarzschild geodesics, the analog in general relativity
- Particle in a spherically symmetric potential, the analog in quantum mechanics
- Hydrogen-like atom, the Kepler problem in quantum mechanics
- Inverse square potential
Notes
- Throughout this article, boldface type is used to indicate that quantities such as r and F are vectors, whereas ordinary numbers are written in italics. Briefly, a vector v is a quantity that has a magnitude v (also written |v|) and a direction. Vectors are often specified by their components. For example, the position vector r = (x, y) in Cartesian coordinates is described as an ordered pair of its x and y coordinates.
- In this article, Newton's notation for derivatives ("dot notation") is used sometimes to make the formulae easier to read; it has no other significance. In this notation, a single dot over a variable signifies its first derivative with respect to time, e.g., Similarly, a double dot over a variable signifies its second derivative with respect for time, e.g.,
- If a and b are three-dimensional vectors, their vector cross product c = a × b is always perpendicular to the plane defined by a and b.
- This formula for the azimuthal unit vector may be verified by calculation; its magnitude equals one and its dot-product with r equals zero Therefore, it is a unit vector perpendicular to the radial vector r.
- The area of a triangle equals one half the base times its height. In this case, the base is given by vΔt and the height equals the impact parameter r⊥.
- A parallel-force problem is one in which the force is exactly zero along one direction.
- A closed orbit is one that returns to its starting position after a finite time with exactly the same velocity. Hence, it executes exactly the same motion over and over again.
References
- Goldstein, p. 71; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 30; Sommerfeld, p. 39; Symon, p. 121.
- Landau and Lifshitz, p. 30; Symon, p. 121.
- Goldstein, p. 4; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 30; Symon, p. 122.
- Goldstein, p. 71; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 30; Whittaker, p. 77.
- Sommerfeld, p. 39; Symon, p. 123.
- Goldstein, pp. 70–71; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 29; Symon, pp. 182–185; Whittaker, pp. 76–77.
- Goldstein, p. 72; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 30; Whittaker, p. 77.
- Goldstein, pp. 2–3, 6–7.
- ^ Goldstein, p. 72.
- Goldstein, p. 73; Landau and Lifshitz, pp. 30–31; Sommerfeld, pp. 39–40; Symon, pp. 124, 127.
- Landau and Lifshitz, p. 31.
- Goldstein, p. 73; Landau and Lifshitz, pp. 30–31; Sommerfeld, pp. 36, 39; Symon, pp. 127–128.
- Goldstein, p. 73; Landau and Lifshitz, p. 31; Sommerfeld, p. 39; Symon, p. 135.
- Whittaker, pp. 93–94.
- Goldstein, p. 73.
- Goldstein, p. 75, 86.
- ^ Goldstein, p. 86.
- Whittaker, pp. 80‒81.
- Goldstein, p. 4.
- Goldstein, pp. 76–82.
- Goldstein, p. 87.
- Goldstein, p. 88.
- ^ Landau and Lifshitz, p. 32.
- Landau and Lifshitz, pp. 32–33.
- Goldstein, pp. 601–605.
- Landau and Lifshitz, p. 33.
- Whittaker, pp. 80–95.
- Broucke R (1980). "Notes on the central force r". Astrophysics and Space Science. 72 (1): 33–53. Bibcode:1980Ap&SS..72...33B. doi:10.1007/BF00642162. S2CID 123025228.
- ^ Mahomed FM, Vawda F (2000). "Application of Symmetries to Central Force Problems". Nonlinear Dynamics. 21 (4): 307–315. Bibcode:2000NonDy..21..307M. doi:10.1023/A:1008317327402. S2CID 116319304.
- Newton, Principia, section IX of Book I, Propositions 43–45, pp. 135–147.
- Goldstein, pp. 454–457; Landau and Lifshitz, pp. 149–151; Misner, Thorne, and Wheeler, pp. 644–649; Sommerfeld, pp. 235–238.
Bibliography
- Goldstein, H. (1980). Classical Mechanics (2nd ed.). Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-02918-9.
- Landau, L. D. and Lifshitz, E. M. (1976). Mechanics. Course of Theoretical Physics (3rd ed.). New York: Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-029141-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Misner, C. W., Thorne, K., and Wheeler, J. A. (1973). Gravitation. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-0344-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sommerfeld, A. (1970). Mechanics. Lectures on Theoretical Physics. Vol. I (4th ed.). New York: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-654670-5.
- Symon KR (1971). Mechanics (3rd ed.). Reading, Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-07392-7.
- Whittaker, E. T. (1937). A Treatise on the Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies, with an Introduction to the Problem of Three Bodies (4th ed.). New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-521-35883-5.
External links
- Two-body Central Force Problems by D. E. Gary of the New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Motion in a Central-Force Field Archived 2018-09-21 at the Wayback Machine by A. Brizard of Saint Michael's College
- Motion under the Influence of a Central Force by G. W. Collins, II of Case Western Reserve University
- Video lecture by W. H. G. Lewin of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology

 where r is the vector magnitude |r| (the distance to the center of force) and r̂ = r/r is the corresponding
where r is the vector magnitude |r| (the distance to the center of force) and r̂ = r/r is the corresponding 


 because the
because the 




 where
where  is the
is the 
 where m is the mass of the particle and p is its
where m is the mass of the particle and p is its 






 whereas the acceleration equals
whereas the acceleration equals










 because the acceleration in the y-direction equals
because the acceleration in the y-direction equals





 giving the new equation of motion
giving the new equation of motion




 where ϕ0 is another constant of integration. A central-force problem is said to be "integrable" if this final integration can be solved in terms of known functions.
where ϕ0 is another constant of integration. A central-force problem is said to be "integrable" if this final integration can be solved in terms of known functions.
 gives
gives
 where summation is assumed over the spatial Cartesian index
where summation is assumed over the spatial Cartesian index  and we have used the fact that
and we have used the fact that  and used the
and used the  .
Rearranging
.
Rearranging
 The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with
The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with  , the total mechanical energy. Clearly, this is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy.
, the total mechanical energy. Clearly, this is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy.
 and so the force is along the radial direction. In this case, the cross product of Newton's second law of motion with the particle's position vector
and so the force is along the radial direction. In this case, the cross product of Newton's second law of motion with the particle's position vector  must vanish since the cross product of two parallel vectors is zero:
must vanish since the cross product of two parallel vectors is zero:
 but
but  (cross product of parallel vectors), so
(cross product of parallel vectors), so
 The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with
The term in parentheses on the left hand side is a constant, label this with  the angular momentum,
In particular, in polar coordinates,
the angular momentum,
In particular, in polar coordinates,  or
or
 Further,
Further,  , so the energy equation may be simplified with the angular momentum as
, so the energy equation may be simplified with the angular momentum as
 This indicates that the angular momentum contributes an effective potential energy
This indicates that the angular momentum contributes an effective potential energy
 Solve this equation for
Solve this equation for 
 which may be converted to the derivative of
which may be converted to the derivative of  with respect to the azimuthal angle
with respect to the azimuthal angle  as
as
 This is a separable first order differential equation. Integrating and yields the formula
This is a separable first order differential equation. Integrating and yields the formula

 which expresses the above constants C = 2mEtot/L and G(u) = 2mU(1/u)/L above in terms of the total energy Etot and the potential energy U(r).
which expresses the above constants C = 2mEtot/L and G(u) = 2mU(1/u)/L above in terms of the total energy Etot and the potential energy U(r).


 where m and n are integers. In that case, the radius oscillates exactly m times while the azimuthal angle φ makes exactly n revolutions. In general, however, Δφ/2π will not be such a
where m and n are integers. In that case, the radius oscillates exactly m times while the azimuthal angle φ makes exactly n revolutions. In general, however, Δφ/2π will not be such a  for a constant
for a constant  , which is negative for an attractive force and positive for a repulsive one.
, which is negative for an attractive force and positive for a repulsive one.

 which shows that the orbit is a
which shows that the orbit is a 
 and
and










 was mentioned by Newton, in corollary 1 to proposition VII of the principia, as the force implied by circular orbits passing through the point of attraction.
was mentioned by Newton, in corollary 1 to proposition VII of the principia, as the force implied by circular orbits passing through the point of attraction.
 where L1 is the magnitude of the first particle's
where L1 is the magnitude of the first particle's 
 take the form
take the form
 since the magnitude F(r) of the radial force equals the negative derivative of the potential energy U(r) in the radial direction.
since the magnitude F(r) of the radial force equals the negative derivative of the potential energy U(r) in the radial direction.




 where S = Sφ(φ) + Sr(r) − Etott is
where S = Sφ(φ) + Sr(r) − Etott is  where pφ is a
where pφ is a 


 Similarly, a double dot over a variable signifies its second derivative with respect for time, e.g.,
Similarly, a double dot over a variable signifies its second derivative with respect for time, e.g.,

 and its dot-product with r equals zero
and its dot-product with r equals zero
 Therefore, it is a unit vector perpendicular to the radial vector r.
Therefore, it is a unit vector perpendicular to the radial vector r.