| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 Rope memory from the Apollo Guidance Computer
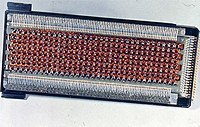
Rope memory from the Apollo Guidance Computer Photo detail of a 16Kb rope core memory board from a 1974 computer
Photo detail of a 16Kb rope core memory board from a 1974 computer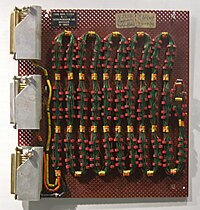 Core rope memory test sample from the Apollo program
Core rope memory test sample from the Apollo program
Core rope memory is a form of read-only memory (ROM) for computers. It was used in the UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) and the UNIVAC II, developed by the Eckert-Mauchly Computer Corporation in the 1950s, as it was a popular technology for program and data storage in that era. It was later used in the 1960s by early NASA Mars space probes and then in the Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC), which was built by Raytheon.
The software for the AGC was written by programmers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Instrumentation Lab, and was woven into core rope memory by female workers in factories. Some programmers nicknamed the finished product LOL memory, for Little Old Lady memory.
Operation
Similar to magnetic-core memory, magnetic rings (or cores) are used to determine the data of the software. Unlike magnetic-core memory, the cores themselves are not used to store the data; the way a core is wired controls whether that core represents a '0' or a '1'.
There are three main types of functions a wire can have in core rope memory:
- Set/reset: These are used to change all of the cores from one polarity to another.
- Sense: A sense wire can detect a change in a core's polarity. It can pass through a core to indicate one bit state (typically '1') or bypass it to represent the other (typically '0').
- Inhibit: Inhibit wires are used effectively to address which core to select.
To read from core rope memory, the set/reset wire is given a strong current to change the polarity of the cores. This induces a small voltage on the sense wires passing through them, which can then be used to interpret binary data. The inhibit wires pass a current in the opposite direction of the set/reset wire for all cores but the desired one, acting like a memory addressing system. This prevents the sense wires from detecting polarity changes from the other magnetic cores.
The sense wires are used to encode the data by either going through a core or bypassing it. By using many sense wires, multiple bits of data can be stored for each core. In the case of the Apollo Guidance Computer, each core had 192 sense wires passing through it, which could store 12 16-bit words per core.
Memory density
By the standards of the time, a relatively large amount of data could be stored in a small installed volume of core rope memory: 72 kilobytes per cubic foot, or roughly 2.5 megabytes per cubic meter. This was about 18 times the amount of magnetic-core memory (within two cubic feet).
| Memory technology |
Data units per cubic foot | Data units per cubic meter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bytes | Bits | Bytes | Bits | |
| Core rope ROM | 72 KB | 576 Kbit | ~2.5 MB | ~20 Mbit |
| Magnetic-core RAM | 4 KB | 32 Kbit | ~140 KB | ~1 Mbit |
References
- "Software as Hardware: Apollo's Rope Memory". Retrieved 29 Sep 2017.
- "Computer for Apollo". MIT Science Reporter. 1965. WGBH.
- Directed and Produced by: Duncan Copp, Nick Davidson, Christopher Riley (2008-07-07). "The Navigation Computer". Moon Machines. Episode 3. 22:40 minutes in. Science Channel.
- "Software woven into wire: Core rope and the Apollo Guidance Computer". Retrieved 2024-03-20.
External links
- "Computer for Apollo" NASA/MIT film from 1965 which demonstrates how rope memory was manufactured.
- Visual Introduction to the Apollo Guidance Computer, part 3: Manufacturing the Apollo Guidance Computer. Archived 2012-12-12 at archive.today – By Raytheon; hosted by the Library of the California Institute of Technology's History of Recent Science & Technology site (originally hosted by the Dibner Institute)
- Computers in Spaceflight: The NASA Experience – By James Tomayko (Chapter 2, Part 5, "The Apollo guidance computer: Hardware")
- Brent Hilpert's Core Rope & Woven-Wire Memory Systems page has a detailed explanation of pulse-transformer and switching-core techniques.
- SV3ORA's Core rope memory: A practical guide of how to build your own gives a description, schematics and photos of a simple core rope memory board using the pulse transformer technique, including a demonstration of operation.
- Software woven into wire: Core rope and the Apollo Guidance Computer, extensive blog post by computer restoration expert Ken Shirriff
- Australian 'ropes' demonstrated at MIT Letter from Ramon L. Alonso to Gordon Rose, dated 10 December 1963: "We are finding the Australian ideas on ‘ropes' to be very fruitful indeed, and we are going ahead with some development work on them."
| Magnetic storage media | |
|---|---|
|