| Coronoid process of the ulna | |
|---|---|
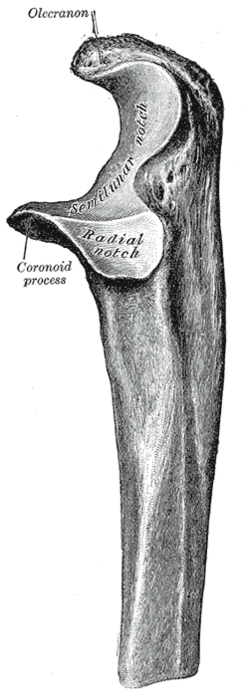 Upper extremity of left ulna. Lateral aspect. Upper extremity of left ulna. Lateral aspect. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus coronoideus ulnae |
| TA98 | A02.4.06.003 |
| TA2 | 1232 |
| FMA | 23616 |
| Anatomical terms of bone[edit on Wikidata] | |
The coronoid process of the ulna is a triangular process projecting forward from the anterior proximal portion of the ulna.
Structure
Its base is continuous with the body of the bone, and of considerable strength.
Its apex is pointed, slightly curved upward, and in flexion of the forearm is received into the coronoid fossa of the humerus.
Its upper surface is smooth, convex, and forms the lower part of the semilunar notch.
Its antero-inferior surface is concave, and marked by a rough impression for the insertion of the brachialis muscle. At the junction of this surface with the front of the body is a rough eminence, the tuberosity of the ulna, which gives insertion to a part of the brachialis; to the lateral border of this tuberosity the oblique cord is attached.
Its lateral surface presents a narrow, oblong, articular depression, the radial notch.
Its medial surface, by its prominent, free margin, serves for the attachment of part of the ulnar collateral ligament. At the front part of this surface is a small rounded eminence for the origin of one head of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle; behind the eminence is a depression for part of the origin of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle; descending from the eminence is a ridge which gives origin to one head of the pronator teres muscle.
Frequently, the flexor pollicis longus muscle arises from the lower part of the coronoid process by a rounded bundle of muscular fibers.
Function
The coronoid process stabilises the elbow joint and prevents hyperflexion.
Clinical significance
The coronoid process can be fractured from its anteromedial facet.
Additional images
-
 Bones of left forearm. Anterior aspect.
Bones of left forearm. Anterior aspect.
-
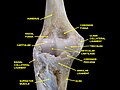 Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
Elbow joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 214 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 214 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Illustrations, Gray's (2015-05-07), "Müllerian duct anatomy - Gray's anatomy illustration", Radiopaedia.org, Radiopaedia.org, retrieved 2024-08-21
- ^ Doornberg, Job N.; de Jong, Inge M.; Lindenhovius, Anneluuk L. C.; Ring, David (2007-09-01). "The anteromedial facet of the coronoid process of the ulna". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 16 (5): 667–670. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.03.013. ISSN 1058-2746. PMID 17512221.
- Ni, Qubo; Yang, Xu; Pan, Zhengqi; Wang, Jianping (2020-05-14). "The pronator teres and the flexor carpi radialis interval approach for operative fixation of ulna coronoid process fractures". Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. 107 (2): 102610. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2020.04.004. ISSN 1877-0568. PMID 32418740.
- Sanchez-Sotelo, Joaquin; O’Driscoll, Shawn W.; Morrey, Bernard F. (2005-01-01). "Medial oblique compression fracture of the coronoid process of the ulna". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 14 (1): 60–64. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.04.012. ISSN 1058-2746. PMID 15723014.
External links
- lesson4bonesofantforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University), radiographsul at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Right ulna (anterior - proximal end) - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- X-ray at uams.edu Archived 2007-02-19 at the Wayback Machine
| Bones of the arm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder girdle, clavicle | |||||||
| Scapula |
| ||||||
| Humerus |
| ||||||
| Forearm |
| ||||||
| Hand |
| ||||||