| Danube | |
|---|---|
 The Danube in Budapest The Danube in Budapest | |
| Course of the Danube | |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Countries |
|
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Breg |
| • location | Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany |
| • coordinates | 48°05′44″N 08°09′18″E / 48.09556°N 8.15500°E / 48.09556; 8.15500 |
| • elevation | 1,078 m (3,537 ft) |
| 2nd source | Brigach |
| • location | St. Georgen im Schwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany |
| • coordinates | 48°06′24″N 08°16′51″E / 48.10667°N 8.28083°E / 48.10667; 8.28083 |
| • elevation | 940 m (3,080 ft) |
| Source confluence | |
| • location | Donaueschingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany |
| • coordinates | 47°57′03″N 08°31′13″E / 47.95083°N 8.52028°E / 47.95083; 8.52028 |
| Mouth | Danube Delta |
| • location | Romania |
| • coordinates | 45°13′3″N 29°45′41″E / 45.21750°N 29.76139°E / 45.21750; 29.76139 |
| Length | 2,850 km (1,770 mi) |
| Basin size | 801,463 km (309,447 sq mi) |
| Width | |
| • minimum | Middle Danube (Iron Gates) 150 m (490 ft); Lower Danube (Brăila) 400 m (1,300 ft) |
| • average | Upper Danube 300 m (980 ft); Middle Danube 400–800 m (1,300–2,600 ft); Lower Danube 900–1,000 m (3,000–3,300 ft) |
| • maximum | Middle Danube 1,500 m (4,900 ft); Lower Danube 1,700 m (5,600 ft) |
| Depth | |
| • minimum | 1 m (3 ft 3 in) (Upper Danube) |
| • average | Upper Danube 8 m (26 ft); Middle Danube 6–10 m (20–33 ft), 53 m (174 ft) (Iron Gates); Lower Danube 9 m (30 ft) |
| • maximum | Middle Danube (Iron Gates) 90 m (300 ft); Lower Danube 34 m (112 ft) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Danube Delta |
| • average | (Period: 1931–2020)6,452 m/s (227,900 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 1,790 m/s (63,000 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 15,900 m/s (560,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Belgrade |
| • average | (Period: 1931–2020)5,300 m/s (190,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Budapest |
| • average | (Period: 1931–2020)2,350 m/s (83,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Vienna |
| • average | (Period: 1931–2020)1,920 m/s (68,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Passau (Bavaria, 30 km before town) |
| • average | (Period: 1931–2020)580 m/s (20,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Black Sea |
| River system | Danube River |
| Danube summary route map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: Distances are in kilometers, rounded to the nearest kilometer. Waterway distances are shown, not towpath distances. Country capitals are shown in bold. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Danube (/ˈdæn.juːb/ DAN-yoob; see also other names) is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for 2,850 km (1,770 mi), passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to 817,000 km (315,000 sq mi) and extends into nine more countries.
The Danube's longest headstream Breg rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its source confluence in the palace park in Donaueschingen onwards. Since ancient times, the Danube has been a traditional trade route in Europe. Today, 2,415 km (1,501 mi) of its total length are navigable. The Danube is linked to the North Sea via the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, connecting the Danube at Kelheim with the Main at Bamberg. The river is also an important source of hydropower and drinking water.
The Danube river basin is home to such fish species as pike, zander, huchen, Wels catfish, burbot and tench. It is also home to numerous diverse carp and sturgeon, as well as salmon and trout. A few species of euryhaline fish, such as European seabass, mullet, and eel, inhabit the Danube Delta and the lower portion of the river.
Names and etymology
Today the river carries its name from its source confluence in Donaueschingen, Germany, to its discharge into the Black Sea via the Danube Delta in Romania and Ukraine.
The river was known to the ancient Greeks as the Istros (Ἴστρος) from a root possibly also encountered in the ancient name of the Dniester (Danaster in Latin, Tiras in Greek) and akin to Iranic turos 'swift' and Sanskrit iṣiras (इषिरस्) 'swift', from the PIE *isro-, *sreu 'to flow'.
In the Middle Ages, the Greek Tiras was borrowed into Italian as Tyrlo and into Turkic languages as Tyrla; the latter was further borrowed into Romanian as a regionalism (Turlă).
The Thraco-Phrygian name was Matoas, "the bringer of luck".
The Middle Mongolian name for the Danube was transliterated as Tho-na in 1829 by Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat.
The modern languages spoken in the Danube basin all use names derived from the Latin name Danubius:
Etymology
Danube is an Old European river name derived from the Celtic 'danu' or 'don' (both Celtic gods), which itself derived from the Proto-Indo-European *deh₂nu. Other European river names from the same root include the Dunaj, Dzvina/Daugava, Don, Donets, Dnieper, Dniestr, Dysna and Tana/Deatnu. In Rigvedic Sanskrit, danu (दनु) means "fluid, dewdrop" and danuja (दनु-ज) means "born from danu" or "born from dew-drops". In Avestan, the same word means "river". The Finnish word for Danube is Tonava, which is most likely derived from the name of the river in German, Donau. Its Sámi name Deatnu means "Great River". It is possible that dānu in Scythian as in Avestan was a generic word for "river": Dnieper and Dniestr, from Danapris and Danastius, are presumed to continue Scythian *dānu apara "far river" and *dānu nazdya- "near river", respectively.
In Latin, the Danube was variously known as Danubius, Danuvius, Ister or Hister. The Latin name is masculine, as are all its Slavic names, except Slovene (the name of the Rhine is also masculine in Latin, most of the Slavic languages, as well as in German). The German Donau (Early Modern German Donaw, Tonaw, Middle High German Tuonowe) is feminine, as it has been re-interpreted as containing the suffix -ouwe "wetland".
Romanian differs from other surrounding languages in designating the river with a feminine term, Dunărea (IPA: [ˈdunəre̯a]). This form was not inherited from Latin, although Romanian is a Romance language. To explain the loss of the Latin name, scholars who suppose that Romanian developed near the large river propose that the Romanian name descends from a hypothetical Thracian *Donaris. The Proto-Indo-European root of this presumed name is related to the Iranic word "don-"/"dan-", while the supposed suffix -aris is encountered in the ancient name of the Ialomița River, Naparis, and in the unidentified Miliare river mentioned by Jordanes in his Getica. Gábor Vékony says that this hypothesis is not plausible, because the Greeks borrowed the Istros form from the native Thracians. He proposes that the Romanian name is a loanword from a Turkic language (Cuman or Pecheneg).
Geography



Classified as an international waterway, it originates in the town of Donaueschingen, in the Black Forest of Germany, at the confluence of the rivers Brigach and Breg. The Danube then flows southeast for about 2,730 km (1,700 mi), passing through four capital cities (Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade) before emptying into the Black Sea via the Danube Delta in Romania and Ukraine.
International status
Once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire, the river passes through or touches the borders of 10 countries. Its drainage basin extends into nine more (ten if Kosovo is included).
| Flow seq. |
Country | Basin area |
Local name |
Points of interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Germany | 7.0% | Donau | Donaueschingen – source |
| 2 | Austria | 10.0% | Donau | Vienna – capital |
| 3 | Slovakia | 5.9% | Dunaj | Bratislava – capital |
| 4 | Hungary | 11.6% | Duna | Budapest – capital |
| 5 | Croatia | 4.4% | Dunav | |
| 6 | Serbia | 10.2% | Dunav | Belgrade – capital |
| 7 | Romania | 29.0% | Dunărea | Danube Delta – Black Sea |
| 8 | Bulgaria | 5.9% | Dunav | |
| 9 | Moldova | 1.6% | Dunărea | |
| 10 | Ukraine | 3.8% | Дунай | Danube Delta – Black Sea |
Drainage basin
In addition to the bordering countries (see above), the drainage basin includes parts of nine more countries: Bosnia and Herzegovina (4.6% of the basin area), the Czech Republic (2.9%), Slovenia (2.0%), Montenegro (0.9%), Switzerland (0.2%), Italy (<0.15%), Poland (<0.1%), North Macedonia (<0.1%) and Albania (<0.1%). The total drainage basin is 801,463 km (309,447 sq mi) in area, and is home to 83 million people. The highest point of the drainage basin is the summit of Piz Bernina at the Italy–Switzerland border, at 4,049 m (13,284 ft). The Danube River Basin is divided into three main parts, separated by "gates" where the river is forced to cut through mountainous sections:
- Upper Basin, from the headwaters to the Devín Gate.
- Middle Basin, usually called the Pannonian basin or Carpathian Basin, between the Devín Gate and the Iron Gates. It includes the Hungarian plains Kisalföld and Alföld.
- Lower Basin, from the Iron Gates to the river mouth, including the Danube Delta.
Discharge
Mean annual discharge on the hydrological stations (period from 2000 to 2024);
| Year | Mean annual discharge in m/s (cu ft/s) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reni | Silistra | Pristol | Batina | Nagymaros Szob | Bratislava | Untergries-bach | |
| 2000 | 6,580.6 (232,390) | 6,198.1 (218,880) | 5,585.9 (197,260) | 2,669.4 (94,270) | 2,627.2 (92,780) | 2,337.9 (82,560) | 1,667.2 (58,880) |
| 2001 | 6,304.3 (222,630) | 5,919.4 (209,040) | 5,421.8 (191,470) | 2,432.5 (85,900) | 2,382.3 (84,130) | 2,231.3 (78,800) | 1,627.6 (57,480) |
| 2002 | 6,837.1 (241,450) | 6,100.1 (215,420) | 5,392 (190,400) | 2,824.9 (99,760) | 2,855.6 (100,840) | 2,683 (94,700) | 1,803.9 (63,700) |
| 2003 | 5,021 (177,300) | 4,571 (161,400) | 3,825 (135,100) | 1,786 (63,100) | 1,722 (60,800) | 1,647 (58,200) | 1,153 (40,700) |
| 2004 | 6,524 (230,400) | 6,088 (215,000) | 5,233 (184,800) | 2,025 (71,500) | 2,013 (71,100) | 1,852 (65,400) | 1,213 (42,800) |
| 2005 | 8,711 (307,600) | 7,659 (270,500) | 6,396 (225,900) | 2,420 (85,000) | 2,329 (82,200) | 2,115 (74,700) | 1,359 (48,000) |
| 2006 | 8,428 (297,600) | 7,370 (260,000) | 6,616 (233,600) | 2,110 (75,000) | 2,503 (88,400) | 2,186 (77,200) | 1,396 (49,300) |
| 2007 | 5,626 (198,700) | 5,195 (183,500) | 4,512 (159,300) | 2,182 (77,100) | 2,136 (75,400) | 1,916 (67,700) | 1,287 (45,400) |
| 2008 | 5,909 (208,700) | 5,358 (189,200) | 4,736 (167,300) | 2,163 (76,400) | 2,079 (73,400) | 1,876 (66,300) | 1,339 (47,300) |
| 2009 | 6,492 (229,300) | 5,990 (212,000) | 5,412 (191,100) | 2,607 (92,100) | 2,441 (86,200) | 2,186 (77,200) | 1,433 (50,600) |
| 2010 | 9,598 (339,000) | 8,515 (300,700) | 7,424 (262,200) | 2,879 (101,700) | 2,615 (92,300) | 2,130 (75,000) | 1,420 (50,000) |
| 2011 | 5,303 (187,300) | 2,000 (71,000) | |||||
| 2012 | 5,053 (178,400) | 2,240 (79,000) | |||||
| 2013 | 7,164 (253,000) | 6,558 (231,600) | 5,946 (210,000) | 2,863 (101,100) | 2,684 (94,800) | 2,417 (85,400) | 1,671 (59,000) |
| 2014 | 7,446 (263,000) | 6,901 (243,700) | 5,756 (203,300) | 2,198 (77,600) | 2,036 (71,900) | 1,788 (63,100) | 1,237 (43,700) |
| 2015 | 6,138 (216,800) | 5,722 (202,100) | 4,971 (175,500) | 2,030 (72,000) | 1,903 (67,200) | 1,629 (57,500) | 1,240 (44,000) |
| 2016 | 6,465 (228,300) | 5,993 (211,600) | 5,339 (188,500) | 2,261 (79,800) | 2,196 (77,600) | 1,944 (68,700) | 1,412 (49,900) |
| 2017 | 5,202 (183,700) | 4,813 (170,000) | 4,270 (151,000) | 2,143 (75,700) | 2,041 (72,100) | 1,844 (65,100) | 1,307 (46,200) |
| 2018 | 6,487.8 (229,110) | 5,875.5 (207,490) | 4,891 (172,700) | 1,906.3 (67,320) | 1,808.1 (63,850) | 1,644.1 (58,060) | 1,227.8 (43,360) |
| 2019 | 5,579 (197,000) | 5,168 (182,500) | 4,593 (162,200) | 2,253 (79,600) | 2,114 (74,700) | 1,962 (69,300) | 1,446 (51,100) |
| 2020 | 4,893.5 (172,810) | 4,659 (164,500) | 4,095 (144,600) | 2,215 (78,200) | 2,026 (71,500) | 1,841 (65,000) | 1,285 (45,400) |
| 2021 | 5,998 (211,800) | 5,505 (194,400) | 4,696 (165,800) | 2,178 (76,900) | 2,028 (71,600) | 1,838 (64,900) | 1,304 (46,100) |
| 2022 | 5,753 (203,200) | 2,180 (77,000) | |||||
| 2023 | 6,623.8 (233,920) | 2,240 (79,000) | |||||
| 2024 | 5,776.4 (203,990) | ||||||
Multiannual average, minimum and maximum discharge (water period from 1876 to 2010)
| Station | Discharge (m/s) | Discharge (cu ft/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | |
| Ceatal Izmail | 1,889 | 6,489 | 14,673 | 66,700 | 229,200 | 518,200 |
| Reni, Isaccea | 1,805 | 6,564 | 14,820 | 63,700 | 231,800 | 523,000 |
| Zimnicea, Svishtov | 1,411 | 6,018 | 14,510 | 49,800 | 212,500 | 512,000 |
| Orșova | 1,672 | 5,572 | 13,324 | 59,000 | 196,800 | 470,500 |
| Veliko Gradište | 1,461 | 5,550 | 14,152 | 51,600 | 196,000 | 499,800 |
| Pančevo | 1,454 | 5,310 | 13,080 | 51,300 | 188,000 | 462,000 |
| Bogojevo | 959 | 2,889 | 8,153 | 33,900 | 102,000 | 287,900 |
| Bezdan, Batina | 749 | 2,353 | 7,043 | 26,500 | 83,100 | 248,700 |
| Mohács | 667 | 2,336 | 7,227 | 23,600 | 82,500 | 255,200 |
| Nagymaros, Szob | 628 | 2,333 | 7,057 | 22,200 | 82,400 | 249,200 |
| Bratislava | 633 | 2,059 | 7,324 | 22,400 | 72,700 | 258,600 |
| Vienna | 506 | 1,917 | 6,062 | 17,900 | 67,700 | 214,100 |
| Krems an der Donau | 596 | 1,845 | 5,986 | 21,000 | 65,200 | 211,400 |
| Linz | 468 | 1,451 | 4,783 | 16,500 | 51,200 | 168,900 |
| Hofkirchen | 211 | 638 | 1,943 | 7,500 | 22,500 | 68,600 |
| Regensburg | 128 | 444 | 1,330 | 4,500 | 15,700 | 47,000 |
| Ingolstadt | 83 | 312 | 965 | 2,900 | 11,000 | 34,100 |
| Ulm | 6 | 38 | 153 | 210 | 1,300 | 5,400 |
Simulated water and suspended sediment results from climate-driven decadal study (with STD through specific decade):
P – Simulated average precipitation in the Danube basin; T – Simulated average temperature in the Danube basin; Q – Simulated average discharge in the Danube River at delta; S – Simulated sediment load in the Danube River at delta;
| Period (CE) | Scenario | P | T | Q | S | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | in | °C | °F | m/s | cu ft/s | metric tons (millions) |
short tons (millions) | ||
| LIA | |||||||||
| 1530–1540 | Cool/dry | 794 | 31.3 | 9.0 | 48.2 | 6,207 | 219,200 | 72.9 | 80.4 |
| 1650–1660 | Cool/wet | 885 | 34.8 | 8.4 | 47.1 | 7,929 | 280,000 | 67.3 | 74.2 |
| 1709–1719 | Warm/wet | 861 | 33.9 | 8.3 | 46.9 | 7,616 | 269,000 | 52.9 | 58.3 |
| 1770–1780 | Warm/dry | 865 | 34.1 | 8.9 | 48.0 | 7,728 | 272,900 | 74.1 | 81.7 |
| Modern | |||||||||
| 1940–1950 | Cool/dry | 778 | 30.6 | 8.9 | 48.0 | 7,209 | 254,600 | 55.0 | 60.6 |
| 1960–1970 | Cool/wet | 850 | 33 | 8.8 | 47.8 | 7,399 | 261,300 | 73.0 | 80.5 |
| 1975–1985 | Warm/wet | 818 | 32.2 | 9.0 | 48.2 | 7,186 | 253,800 | 77.8 | 85.8 |
| 1990–2000 | Warm/dry | 790 | 31 | 9.5 | 49.1 | 5,068 | 179,000 | 73.8 | 81.4 |
Discharge chronology
Historical average flow to the present day; Measured and reconstructed average water flows from 1742. The reconstructed and observed streamflow (Q – m/s) at Ceatal Izmail for the 1742 to 2022:
| Year | m/s | cu ft/s | Year | m/s | cu ft/s | Year | m/s | cu ft/s | Year | m/s | cu ft/s | Year | m/s | cu ft/s | Year | m/s | cu ft/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reconstructed | |||||||||||||||||
| 1742 | 5,780 | 204,000 | 1751 | 6,760 | 239,000 | 1761 | 6,470 | 228,000 | 1771 | 9,700 | 340,000 | 1781 | 5,830 | 206,000 | 1791 | 5,540 | 196,000 |
| 1743 | 5,355 | 189,100 | 1752 | 7,090 | 250,000 | 1762 | 6,510 | 230,000 | 1772 | 6,050 | 214,000 | 1782 | 6,470 | 228,000 | 1792 | 6,930 | 245,000 |
| 1744 | 5,370 | 190,000 | 1753 | 4,980 | 176,000 | 1763 | 5,950 | 210,000 | 1773 | 4,600 | 160,000 | 1783 | 7,930 | 280,000 | 1793 | 7,800 | 280,000 |
| 1745 | 4,940 | 174,000 | 1754 | 6,330 | 224,000 | 1764 | 6,280 | 222,000 | 1774 | 6,150 | 217,000 | 1784 | 8,400 | 300,000 | 1794 | 5,230 | 185,000 |
| 1746 | 7,140 | 252,000 | 1755 | 6,840 | 242,000 | 1765 | 6,130 | 216,000 | 1775 | 6,060 | 214,000 | 1785 | 7,610 | 269,000 | 1795 | 6,530 | 231,000 |
| 1747 | 5,850 | 207,000 | 1756 | 6,370 | 225,000 | 1766 | 8,530 | 301,000 | 1776 | 6,320 | 223,000 | 1786 | 6,570 | 232,000 | 1796 | 6,460 | 228,000 |
| 1748 | 6,840 | 242,000 | 1757 | 6,830 | 241,000 | 1767 | 6,850 | 242,000 | 1777 | 5,530 | 195,000 | 1787 | 6,980 | 246,000 | 1797 | 6,700 | 240,000 |
| 1749 | 6,690 | 236,000 | 1758 | 8,410 | 297,000 | 1768 | 8,400 | 300,000 | 1778 | 7,470 | 264,000 | 1788 | 5,860 | 207,000 | 1798 | 6,560 | 232,000 |
| 1750 | 5,180 | 183,000 | 1759 | 5,520 | 195,000 | 1769 | 5,720 | 202,000 | 1779 | 6,600 | 230,000 | 1789 | 7,190 | 254,000 | 1799 | 9,590 | 339,000 |
| 1760 | 6,840 | 242,000 | 1770 | 10,700 | 380,000 | 1780 | 6,990 | 247,000 | 1790 | 6,940 | 245,000 | 1800 | 6,150 | 217,000 | |||
| 5,905 (208,500) | 6,597 (233,000) | 7,154 (252,600) | 6,547 (231,200) | 6,978 (246,400) | 6,749 (238,300) | ||||||||||||
| 1801 | 7,310 | 258,000 | 1811 | 8,220 | 290,000 | 1821 | 6,390 | 226,000 | 1831 | 6,670 | 236,000 | 1841 | 6,210 | 219,000 | 1851 | 7,350 | 260,000 |
| 1802 | 6,590 | 233,000 | 1812 | 5,230 | 185,000 | 1822 | 5,700 | 200,000 | 1832 | 4,820 | 170,000 | 1842 | 5,340 | 189,000 | 1852 | 6,550 | 231,000 |
| 1803 | 6,870 | 243,000 | 1813 | 6,680 | 236,000 | 1823 | 6,520 | 230,000 | 1833 | 5,350 | 189,000 | 1843 | 6,710 | 237,000 | 1853 | 7,800 | 280,000 |
| 1804 | 6,220 | 220,000 | 1814 | 7,290 | 257,000 | 1824 | 6,420 | 227,000 | 1834 | 6,470 | 228,000 | 1844 | 6,960 | 246,000 | 1854 | 5,060 | 179,000 |
| 1805 | 7,010 | 248,000 | 1815 | 6,640 | 234,000 | 1825 | 8,040 | 284,000 | 1835 | 7,040 | 249,000 | 1845 | 7,440 | 263,000 | 1855 | 7,020 | 248,000 |
| 1806 | 6,830 | 241,000 | 1816 | 8,090 | 286,000 | 1826 | 5,800 | 200,000 | 1836 | 9,740 | 344,000 | 1846 | 6,750 | 238,000 | 1856 | 5,390 | 190,000 |
| 1807 | 7,000 | 250,000 | 1817 | 8,650 | 305,000 | 1827 | 6,650 | 235,000 | 1837 | 6,770 | 239,000 | 1847 | 7,070 | 250,000 | 1857 | 4,880 | 172,000 |
| 1808 | 5,600 | 200,000 | 1818 | 6,920 | 244,000 | 1828 | 8,140 | 287,000 | 1838 | 10,440 | 369,000 | 1848 | 5,620 | 198,000 | 1858 | 5,580 | 197,000 |
| 1809 | 7,150 | 252,000 | 1819 | 6,470 | 228,000 | 1829 | 8,280 | 292,000 | 1839 | 9,960 | 352,000 | 1849 | 5,360 | 189,000 | 1859 | 5,630 | 199,000 |
| 1810 | 8,430 | 298,000 | 1820 | 6,560 | 232,000 | 1830 | 7,790 | 275,000 | 1840 | 5,560 | 196,000 | 1850 | 7,360 | 260,000 | 1860 | 7,220 | 255,000 |
| 6,901 (243,700) | 7,075 (249,900) | 6,973 (246,200) | 7,282 (257,200) | 6,482 (228,900) | 6,248 (220,600) | ||||||||||||
| 1861 | 5,980 | 211,000 | 1871 | 8,860 | 313,000 | 1881 | 8,320 | 294,000 | 1891 | 5,440 | 192,000 | 1901 | 5,570 | 197,000 | 1911 | 5,120 | 181,000 |
| 1862 | 5,040 | 178,000 | 1872 | 5,970 | 211,000 | 1882 | 5,130 | 181,000 | 1892 | 5,620 | 198,000 | 1902 | 5,650 | 200,000 | 1912 | 6,940 | 245,000 |
| 1863 | 3,340 | 118,000 | 1873 | 5,150 | 182,000 | 1883 | 7,590 | 268,000 | 1893 | 5,710 | 202,000 | 1903 | 5,490 | 194,000 | 1913 | 6,410 | 226,000 |
| 1864 | 6,150 | 217,000 | 1874 | 4,680 | 165,000 | 1884 | 5,250 | 185,000 | 1894 | 4,770 | 168,000 | 1904 | 4,940 | 174,000 | 1914 | 6,560 | 232,000 |
| 1865 | 5,690 | 201,000 | 1875 | 5,360 | 189,000 | 1885 | 5,430 | 192,000 | 1895 | 6,240 | 220,000 | 1905 | 6,100 | 220,000 | 1915 | 9,540 | 337,000 |
| 1866 | 3,780 | 133,000 | 1876 | 7,520 | 266,000 | 1886 | 5,660 | 200,000 | 1896 | 6,470 | 228,000 | 1906 | 6,190 | 219,000 | 1916 | 7,550 | 267,000 |
| 1867 | 6,350 | 224,000 | 1877 | 6,660 | 235,000 | 1887 | 5,340 | 189,000 | 1897 | 7,700 | 270,000 | 1907 | 6,770 | 239,000 | 1917 | 6,410 | 226,000 |
| 1868 | 5,660 | 200,000 | 1878 | 7,040 | 249,000 | 1888 | 6,800 | 240,000 | 1898 | 4,550 | 161,000 | 1908 | 4,400 | 160,000 | 1918 | 4,300 | 150,000 |
| 1869 | 5,370 | 190,000 | 1879 | 8,300 | 290,000 | 1889 | 6,530 | 231,000 | 1899 | 4,500 | 160,000 | 1909 | 5,590 | 197,000 | 1919 | 7,410 | 262,000 |
| 1870 | 7,470 | 264,000 | 1880 | 5,660 | 200,000 | 1890 | 4,650 | 164,000 | 1900 | 6,900 | 240,000 | 1910 | 7,450 | 263,000 | 1920 | 6,720 | 237,000 |
| 5,483 (193,600) | 6,520 (230,000) | 6,070 (214,000) | 5,790 (204,000) | 5,815 (205,400) | 6,770 (239,000) | ||||||||||||
| Observed | |||||||||||||||||
| 1921 | 3,906 | 137,900 | 1931 | 6,706 | 236,800 | 1941 | 9,916 | 350,200 | 1951 | 6,368 | 224,900 | 1961 | 5,860 | 207,000 | 1971 | 5,272 | 186,200 |
| 1922 | 6,530 | 231,000 | 1932 | 6,181 | 218,300 | 1942 | 7,266 | 256,600 | 1952 | 5,850 | 207,000 | 1962 | 6,628 | 234,100 | 1972 | 6,160 | 218,000 |
| 1923 | 6,430 | 227,000 | 1933 | 6,344 | 224,000 | 1943 | 4,308 | 152,100 | 1953 | 6,117 | 216,000 | 1963 | 6,047 | 213,500 | 1973 | 5,766 | 203,600 |
| 1924 | 6,700 | 240,000 | 1934 | 5,644 | 199,300 | 1944 | 7,190 | 254,000 | 1954 | 6,168 | 217,800 | 1964 | 5,259 | 185,700 | 1974 | 7,258 | 256,300 |
| 1925 | 5,255 | 185,600 | 1935 | 5,718 | 201,900 | 1945 | 5,870 | 207,000 | 1955 | 8,834 | 312,000 | 1965 | 8,400 | 300,000 | 1975 | 7,190 | 254,000 |
| 1926 | 8,144 | 287,600 | 1936 | 6,392 | 225,700 | 1946 | 4,684 | 165,400 | 1956 | 7,100 | 250,000 | 1966 | 7,954 | 280,900 | 1976 | 6,567 | 231,900 |
| 1927 | 5,990 | 212,000 | 1937 | 8,325 | 294,000 | 1947 | 5,418 | 191,300 | 1957 | 6,254 | 220,900 | 1967 | 7,500 | 260,000 | 1977 | 7,073 | 249,800 |
| 1928 | 5,005 | 176,700 | 1938 | 6,867 | 242,500 | 1948 | 6,357 | 224,500 | 1958 | 6,340 | 224,000 | 1968 | 5,660 | 200,000 | 1978 | 7,120 | 251,000 |
| 1929 | 5,330 | 188,000 | 1939 | 6,310 | 223,000 | 1949 | 4,301 | 151,900 | 1959 | 5,375 | 189,800 | 1969 | 7,710 | 272,000 | 1979 | 7,747 | 273,600 |
| 1930 | 5,197 | 183,500 | 1940 | 9,533 | 336,700 | 1950 | 5,130 | 181,000 | 1960 | 6,514 | 230,000 | 1970 | 9,602 | 339,100 | 1980 | 8,767 | 309,600 |
| 5,888 (207,900) | 6,802 (240,200) | 6,044 (213,400) | 6,492 (229,300) | 7,062 (249,400) | 6,892 (243,400) | ||||||||||||
| 1981 | 8,172 | 288,600 | 1991 | 6,274 | 221,600 | 2001 | 6,304.3 | 222,630 | 2011 | 5,303 | 187,300 | 2021 | 6,018 | 212,500 | |||
| 1982 | 6,700 | 240,000 | 1992 | 5,710.8 | 201,670 | 2002 | 6,837.1 | 241,450 | 2012 | 5,053 | 178,400 | 2022 | 5,753 | 203,200 | |||
| 1983 | 5,543 | 195,700 | 1993 | 4,873 | 172,100 | 2003 | 5,021 | 177,300 | 2013 | 7,164 | 253,000 | 2023 | 6,623.8 | 233,920 | |||
| 1984 | 6,325 | 223,400 | 1994 | 6,031.8 | 213,010 | 2004 | 6,524 | 230,400 | 2014 | 7,446 | 263,000 | 2024 | |||||
| 1985 | 6,449 | 227,700 | 1995 | 6,223.7 | 219,790 | 2005 | 8,711 | 307,600 | 2015 | 6,138 | 216,800 | 2025 | |||||
| 1986 | 6,257 | 221,000 | 1996 | 7,035.8 | 248,470 | 2006 | 8,428 | 297,600 | 2016 | 6,465 | 228,300 | 2026 | |||||
| 1987 | 6,619 | 233,700 | 1997 | 6,684.2 | 236,050 | 2007 | 5,626 | 198,700 | 2017 | 5,202 | 183,700 | 2027 | |||||
| 1988 | 6,383 | 225,400 | 1998 | 6,804.6 | 240,300 | 2008 | 5,909 | 208,700 | 2018 | 6,487.8 | 229,110 | 2028 | |||||
| 1989 | 5,448 | 192,400 | 1999 | 7,951.5 | 280,800 | 2009 | 6,492 | 229,300 | 2019 | 5,579 | 197,000 | 2029 | |||||
| 1990 | 4,194 | 148,100 | 2000 | 6,580.6 | 232,390 | 2010 | 9,598 | 339,000 | 2020 | 4,893.5 | 172,810 | 2030 | |||||
| 6,209 (219,300) | 6,417 (226,600) | 6,945 (245,300) | 5,973 (210,900) | 6,131.6 (216,540) | |||||||||||||
| Multiannual average discharge 1742 to 2022: ~ 6,500 m/s (230,000 cu ft/s) | |||||||||||||||||
Tributaries

The land drained by the Danube extends into many other countries. Many Danubian tributaries are important rivers in their own right, navigable by barges and other shallow-draught boats. From its source to its outlet into the Black Sea, its main tributaries are (as they enter):
|
18. Tisza (entering near Titel) |
-
 The Danube's source confluence in Donaueschingen: the Donauzusammenfluss, the confluence of Breg and Brigach.
The Danube's source confluence in Donaueschingen: the Donauzusammenfluss, the confluence of Breg and Brigach.
-
0 km, Danube Delta, Ukraine
-
 Where the Danube meets the Black Sea (European Space Agency Sentinel-2 image)
Where the Danube meets the Black Sea (European Space Agency Sentinel-2 image)
-
 The Danube discharges into the Black Sea (the upper body of water in the image).
The Danube discharges into the Black Sea (the upper body of water in the image).
Cities and towns

The Danube flows through many cities, including four national capitals (shown below in bold), more than any other river in the world. Ordered from the source to the mouth they are:
- Germany
- Donaueschingen in the State of Baden-Württemberg – rivers Brigach and Breg join to form the Danube
- Möhringen an der Donau in Baden-Württemberg
- Tuttlingen in Baden-Württemberg
- Sigmaringen in Baden-Württemberg
- Riedlingen in Baden-Württemberg
- Munderkingen in Baden-Württemberg
- Ehingen in Baden-Württemberg
- Ulm in Baden-Württemberg
- Neu-Ulm in Bavaria
- Günzburg in Bavaria
- Dillingen an der Donau in Bavaria
- Donauwörth in Bavaria
- Neuburg an der Donau in Bavaria
- Ingolstadt in Bavaria
- Kelheim in Bavaria
- Regensburg in Bavaria
- Straubing in Bavaria
- Deggendorf in Bavaria
- Passau in Bavaria

- Austria
- Linz, capital of Upper Austria
- Krems in Lower Austria
- Tulln in Lower Austria
- Vienna – capital of Austria and the most populous city on the Danube, where the Danube floodplain is called the Lobau, though the Innere Stadt is situated away from the main flow of the Danube (it is bounded by the Donaukanal – 'Danube canal').

- Slovakia
- Bratislava – capital of Slovakia
- Komárno
- Štúrovo

- Hungary
- Mosonmagyaróvár
- Győr
- Komárom
- Esztergom
- Visegrád – This section of the river is also called Danube Bend.
- Vác
- Szentendre
- Göd
- Dunakeszi
- Budapest – capital of Hungary, the largest city and the largest agglomeration on Danube (about 3,300,000 people).
- Szigetszentmiklós
- Százhalombatta
- Ráckeve
- Adony
- Dunaújváros
- Dunaföldvár
- Paks
- Kalocsa
- Baja
- Mohács
- Croatia


- Serbia
- Apatin
- Bačka Palanka
- Čerević
- Futog
- Veternik
- Novi Sad – regional capital of Vojvodina
- Sremski Karlovci
- Zemun
- Belgrade – capital of Serbia
- Pančevo
- Smederevo
- Kovin
- Veliko Gradište
- Golubac
- Donji Milanovac
- Kladovo


- Romania
- Moldova
- Ukraine
 Panorama of the Danube in Vienna
Panorama of the Danube in Vienna
 The Danube Bend is a curve of the Danube in Hungary, near the city of Visegrád. The Transdanubian Mountains lie on the right bank (left side of the picture), while the North Hungarian Mountains on the left bank (right side of the picture).
The Danube Bend is a curve of the Danube in Hungary, near the city of Visegrád. The Transdanubian Mountains lie on the right bank (left side of the picture), while the North Hungarian Mountains on the left bank (right side of the picture).
 Panorama of the Danube in Budapest with the Hungarian Parliament (left)
Panorama of the Danube in Budapest with the Hungarian Parliament (left)
 Budapest at night
Budapest at night
 The confluence of the Sava into the Danube at Belgrade. Pictured from Belgrade Fortress, Serbia
The confluence of the Sava into the Danube at Belgrade. Pictured from Belgrade Fortress, Serbia
 Panoramic image of the Danube and Sava river from Kalemegdan, Belgrade Serbia
Panoramic image of the Danube and Sava river from Kalemegdan, Belgrade Serbia
 The Danube entering the Iron Gate at the South-Western end of the Carpathian Mountains. Romania on the left side, Golubac Fortress and Serbia on the right side.
The Danube entering the Iron Gate at the South-Western end of the Carpathian Mountains. Romania on the left side, Golubac Fortress and Serbia on the right side.
Islands
Further information: List of islands in the Danube


- Ada Kaleh Island
- Ostrovul Mare, Gogoșu
- Balta Ialomiței
- Belene Island
- Csepel Island
- Čakljanac Island
- Donauinsel
- Forkontumac Island
- Great Brăila Island
- Great War Island
- Island of Mohács
- Koh Chang Island, Sremski Karlovci
- Kozloduy Island
- Margaret Island
- Ostrovo (Kostolac)
- Ostrovul Ciocănești
- Ostrovul Mare, Islaz
- Paradajz Island
- Ribarsko Оstrvo [sr], Novi Sad
- Island of Šarengrad
- Szigetköz
- Island of Szentendre
- Vardim Island
- Island of Vukovar
- Žitný ostrov
Sectioning
- Upper Section: From spring to Devín Gate, at the border of Austria and Slovakia. Danube remains a characteristic mountain river until Passau, with average bottom gradient 0.0012% (12 ppm), from Passau to Devín Gate the gradient lessens to 0.0006% (6 ppm).
- Middle Section: From Devín Gate to Iron Gate, at the border of Serbia and Romania. The riverbed widens and the average bottom gradient becomes only 0.00006% (0.6 ppm).
- Lower Section: From Iron Gate to Sulina, with average gradient as little as 0.00003% (0.3 ppm).
Modern navigation
| This section needs expansion with: how the "Iron Gate" relates to ship navigation?. You can help by adding to it. (November 2022) |


The Danube is navigable by ocean ships from the Black Sea to Brăila in Romania (the maritime river sector), and further on by river ships to Kelheim, Bavaria, Germany; smaller craft can navigate further upstream to Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. About 60 of its tributaries are also navigable.
Since the completion of the German Rhine–Main–Danube Canal in 1992, the river has been part of a trans-European waterway from Rotterdam on the North Sea to Sulina on the Black Sea, a distance of 3,500 km (2,200 mi). In 1994 the Danube was declared one of ten Pan-European transport corridors, routes in Central and Eastern Europe that required major investment over the following ten to fifteen years. The amount of goods transported on the Danube increased to about 100 million tons in 1987. In 1999, transport on the river was made difficult by the NATO bombing of three bridges in Serbia during the Kosovo War. Clearance of the resulting debris was completed in 2002, and a temporary pontoon bridge that hampered navigation was removed in 2005.
At the Iron Gate, the Danube flows through a gorge that forms part of the boundary between Serbia and Romania; it contains the Iron Gate I Hydroelectric Power Station dam, followed at about 60 km (37 mi) downstream (outside the gorge) by the Iron Gate II Hydroelectric Power Station. On 13 April 2006, a record peak discharge at Iron Gate Dam reached 15,400 m/s (540,000 cu ft/s).
There are three artificial waterways built on the Danube: the Danube-Tisa-Danube Canal (DTD) in the Banat and Bačka regions (Vojvodina, northern province of Serbia); the 64 km (40 mi) Danube-Black Sea Canal, between Cernavodă and Constanța (Romania) finished in 1984, shortens the distance to the Black Sea by 400 km (250 mi); the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal is about 171 km (106 mi), finished in 1992, linking the North Sea to the Black Sea. A Danube-Aegean canal has been proposed.
Cruising on the Danube is a popular sightseeing activity, especially between Passau, Germany, to Budapest, Hungary.
Piracy
In 2010–12, shipping companies, especially from Ukraine, claimed that their vessels suffered from "regular pirate attacks" on the Serbian and the Romanian stretches of the Danube. However, the transgressions may not be considered acts of piracy, as defined according to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, but rather instances of "river robbery".
On the other hand, media reports say the crews on transport ships often steal and sell their own cargo and then blame the plundering on "pirates", and the alleged attacks are not piracy but small-time contraband theft along the river.
Danube Delta
Main article: Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (Romanian: Delta Dunării pronounced [ˈdelta ˈdunərij]; Ukrainian: Дельта Дунаю, romanized: Del'ta Dunayu) is the largest river delta in the European Union. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies in Romania (Tulcea county), while its northern part, on the left bank of the Chilia arm, is situated in Ukraine (Odesa Oblast). The approximate surface is 4,152 km (1,603 sq mi), of which 3,446 km (1,331 sq mi) are in Romania. If one includes the lagoons of Razim-Sinoe (1,015 km (392 sq mi) of which 865 km (334 sq mi) water surface), which are located south of the delta proper, but are related to it geologically and ecologically (their combined territory is part of the World Heritage Site), the total area of the Danube Delta reaches 5,165 km (1,994 sq mi).
The Danube Delta is also the best-preserved river delta in Europe, a UNESCO World Heritage Site (since 1991) and a Ramsar Site. Its lakes and marshes support 45 freshwater fish species. Its wetlands support vast flocks of migratory birds of over 300 species, including the endangered pygmy cormorant (Phalacrocorax pygmaeus). These are threatened by rival canalization and drainage schemes such as the Bystroye Canal.
International cooperation
Ecology and environment
Main article: International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River
The International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR) is an organization that consists of 14 member states (Germany, Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Montenegro, and Ukraine) and the European Union. The commission, established in 1998, deals with the whole Danube river basin, which includes tributaries and groundwater resources. Its goal is to implement the Danube River Protection Convention by promoting and coordinating sustainable and equitable water management, including conservation, improvement, and rational use of waters and the implementation of the EU Water Framework Directive and the Danube Strategy.
Navigation
Main article: Danube CommissionThe Danube Commission is concerned with the maintenance and improvement of the river's navigation conditions. It was established in 1948 by seven countries bordering the river. Members include representatives from Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Slovakia, Romania, Russia, Ukraine, and Serbia; it meets regularly twice a year. It also convenes groups of experts to consider items provided for in the commission's working plans.
The commission dates to the Paris Conferences of 1856 and 1921, which established for the first time an international regime to safeguard free navigation on the Danube. Today the Commission include riparian and non-riparian states.
Geology


Although the headwaters of the Danube are relatively small today, geologically, the Danube is much older than the Rhine, with which its catchment area competes in today's southern Germany. This has a few interesting geological complications. Since the Rhine is the only river rising in the Alps mountains which flows north towards the North Sea, an invisible line beginning at Piz Lunghin divides large parts of southern Germany, which is sometimes referred to as the European Watershed.
Before the last ice age in the Pleistocene, the Rhine started at the southwestern tip of the Black Forest, while the waters from the Alps that today feed the Rhine were carried east by the so-called Urdonau (original Danube). Parts of this ancient river's bed, which was much larger than today's Danube, can still be seen in (now waterless) canyons in today's landscape of the Swabian Alb. After the Upper Rhine valley had been eroded, most waters from the Alps changed their direction and began feeding the Rhine. Today's upper Danube is thus an underfit stream.

Since the Swabian Alb is largely shaped of porous limestone, and since the Rhine's level is much lower than the Danube's, today subsurface rivers carry much water from the Danube to the Rhine. On many days in the summer, when the Danube carries little water, it completely oozes away noisily into these underground channels at two locations in the Swabian Alb, which are referred to as the Donauversickerung (Danube Sink). Most of this water resurfaces only 12 km (7.5 mi) south at the Aachtopf, Germany's wellspring with the highest flow, an average of 8,500 L/s (300 cu ft/s), north of Lake Constance—thus feeding the Rhine. The European Water Divide applies only for those waters that pass beyond this point, and only during the days of the year when the Danube carries enough water to survive the sinkholes in the Donauversickerung.
Since such large volumes of underground water erode much of the surrounding limestone, it is estimated that the Danube upper course will one day disappear entirely in favor of the Rhine, an event called stream capturing.
The hydrological parameters of Danube are regularly monitored in Croatia at Batina, Dalj, Vukovar and Ilok.
History

The Danube basin was the site of some of the earliest human cultures. The Danubian Neolithic cultures include the Linear Pottery cultures of the mid-Danube basin. Many sites of the sixth-to-third millennium BCE Vinča culture (Vinča, Serbia), are sited along the Danube. The third millennium BCE Vučedol culture (from the Vučedol site near Vukovar, Croatia) is famous for its ceramics.
Darius the Great, king of Persia, crossed the river in the late 6th century BCE to invade European Scythia and to subdue the Scythians.
Alexander the Great defeated the Triballian king Syrmus and the northern barbarian Thracian and Illyrian tribes by advancing from Macedonia as far as the Danube in 336 BCE.
Under the Romans, the Danube formed the border of the Empire with the tribes to the north almost from its source to its mouth. At the same time, it was a route for the transport of troops and the supply of settlements downstream. From 37 CE to the reign of the Emperor Valentinian I (364–375) the Danubian Limes was the northeastern border of the Empire, with occasional interruptions such as the fall of the Danubian Limes in 259. The crossing of the Danube into Dacia was achieved by the Imperium Romanum, first in two battles in 102 and then in 106 after the construction of a bridge in 101 near the garrison town of Drobeta at the Iron Gate. This victory over Dacia under Decebalus enabled the Province of Dacia to be created, but in 271 it was abandoned by emperor Aurelian.
Avars used the river as their southeastern border in the 6th century.
-
 The oldest bridge across the Danube, constructed by Apollodorus of Damascus between 103 and 105 CE, directed by Trajan, modern Serbia and Romania
The oldest bridge across the Danube, constructed by Apollodorus of Damascus between 103 and 105 CE, directed by Trajan, modern Serbia and Romania
-
 At Esztergom and Štúrovo, the Danube separates Hungary from Slovakia.
At Esztergom and Štúrovo, the Danube separates Hungary from Slovakia.
-
 The Danube in Vienna
The Danube in Vienna
-
 The Danube between Belene and Belene Island, Bulgaria
The Danube between Belene and Belene Island, Bulgaria
-
A look upstream from the Donauinsel in Vienna, Austria during an unusually cold winter (February 2006). A frozen Danube usually occurs just once or twice in a lifetime.
-
 Bratislava does not usually suffer major floods, but the Danube sometimes overflows its right bank.
Bratislava does not usually suffer major floods, but the Danube sometimes overflows its right bank.
Ancient cultural perspectives of the lower Danube
Part of the rivers Danubius or Istros was also known as (together with the Black Sea) the Okeanos in ancient times, being called the Okeanos Potamos (Okeanos River). The lower Danube was also called the Keras Okeanoio (Gulf or Horn of Okeanos) in the Argonautica by Apollonius Rhodos (Argon. IV. 282).
At the end of the Okeanos Potamos, is the holy island of Alba (Leuke, Pytho Nisi, Isle of Snakes), sacred to the Pelasgian (and later, Greek) Apollo, greeting the sun rising in the east. Hecateus Abderitas refers to Apollo's island from the region of the Hyperboreans, in the Okeanos. It was on Leuke, in one version of his legend, that the hero Achilles was buried (to this day, one of the mouths of the Danube is called Chilia). Old Romanian folk songs recount a white monastery on a white island with nine priests.
Rivalry along the Danube
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Between the late 14th and late 19th centuries, the Ottoman Empire competed first with the Kingdom of Serbia, Second Bulgarian Empire, Kingdom of Hungary, Principality of Wallachia, Principality of Moldavia and later with the Habsburg monarchy, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Russian Empire for controlling the Danube (طونه,Tuna in Turkish), which became the northern border of the Ottoman Empire for centuries. Many of the Ottoman–Hungarian Wars (1366–1526) and Ottoman–Habsburg wars (1526–1791) were fought along the river.
The most important wars of the Ottoman Empire along the Danube include the Battle of Nicopolis (1396), the Siege of Belgrade (1456), the Battle of Mohács (1526), the first Turkish Siege of Vienna (1529), the Siege of Esztergom (1543), the Long War (1591–1606), the Battle of Vienna (1683), the Great Turkish War (1683–1699), the Crimean War (1853–1856) and the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878).
Second World War
During the 2011 renovation of the Margaret Bridge, Budapest, human remains were discovered. The mostly Jewish remains were victims of the far-right Arrow Cross Party, who briefly governed Hungary from 1944.
Economics
Drinking water
Along its course, the Danube is a source of drinking water for about 20 million people. In Baden-Württemberg, Germany, almost 30 percent (as of 2004) of the water for the area between Stuttgart, Bad Mergentheim, Aalen and Alb-Donau (district) comes from purified water of the Danube. Other cities such as Ulm and Passau also use some water from the Danube.
In Austria and Hungary, most water is drawn from ground and spring sources, and only in rare cases is water from the Danube used. Most states also find it too difficult to clean the water because of extensive pollution; only parts of Romania where the water is cleaner still obtain drinking water from the Danube on a regular basis.
Navigation and transport

In the 19th century, the Danube was an important waterway but was, as The Times of London put it, "annually swept by ice that will lift a large ship out of the water or cut her in two as if she were a carrot."
Today, as "Corridor VII" of the European Union, the Danube is an important transport route. Since the opening of the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, the river connects the Port of Rotterdam and the industrial centers of Western Europe with the Black Sea and, also, through the Danube – Black Sea Canal, with the Port of Constanța.
The waterway is designed for large-scale inland vessels (110 × 11.45 m) but it can carry much larger vessels on most of its course. The Danube has been partly canalized in Germany (5 locks) and Austria (10 locks). Proposals to build a number of new locks to improve navigation have not progressed, due in part to environmental concerns.
Downstream from the Freudenau locks in Vienna, canalization of the Danube was limited to the Gabčíkovo dam and locks near Bratislava and the two double Iron Gate locks in the border stretch of the Danube between Serbia and Romania. These locks have larger dimensions. Downstream of the Iron Gate, the river is free flowing all the way to the Black Sea, a distance of more than 860 kilometres (530 mi).
The Danube connects with the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal at Kelheim, with the Donaukanal in Vienna, and with the Danube–Black Sea Canal at Cernavodă.
Apart from a couple of secondary navigable branches, the only major navigable rivers linked to the Danube are the Drava, Sava and Tisa. In Serbia, a canal network also connects to the river; the network, known as the Danube–Tisa–Danube Canals, links sections downstream.
In the Austrian and German sections of the Danube, a type of flat-bottomed boat called a Zille was developed for use along the river. Zillen are still used today for fishing, ferrying, and other transport of goods and people in this area.
Fishing
The importance of fishing on the Danube, which was critical in the Middle Ages, has declined dramatically. Some fishermen are still active at certain points on the river, and the Danube Delta still has an important industry. However, some of the river's resources have been managed in an environmentally unsustainable manner in the past, leading to damage by pollution, alterations to the channel, and major infrastructure development, including large hydropower dams.
The sturgeon stocks associated with the Danube River basin have, over the centuries, formed the basis of a large and significant commercial fishery, renowned throughout the world. The construction of the dams, besides overfishing and river pollution, has a significant role in sturgeon population decline because it creates a barrier for fish migratory species that usually spawn in the upper parts of the river. The spawning areas of migratory fishes species has been dramatically reduced by the construction of hydropower and navigation systems at Iron Gates I (1974) and Iron Gates II (1984). The initial design of these dams has not included any fish passage facility. The possibility of building a human-made fish pass enabling migration for fish species including the sturgeon, is currently under review by projects such as We Pass.
The Upper Danube ecoregion alone has about 60 fish species and the Lower Danube–Dniester ecoregion has about twice as many. Among these are an exceptionally high diversity of sturgeon, a total of six species (beluga, Russian sturgeon, bastard sturgeon, sterlet, starry sturgeon and European sea sturgeon), but these are all threatened and have largely–or entirely in the case of the European sea sturgeon–disappeared from the river. The huchen, one of the largest species of salmon, is endemic to the Danube basin, but has been introduced elsewhere by humans.
Tourism


Important tourist and natural spots along the Danube include the Wachau Valley, the Nationalpark Donau-Auen in Austria, Gemenc in Hungary, the Naturpark Obere Donau in Germany, Kopački rit in Croatia, Iron Gate in Serbia and Romania, the Danube Delta in Romania, and the Srebarna Nature Reserve in Bulgaria.
Also, leisure and travel cruises on the river are of significance. Besides the often frequented route between Vienna and Budapest, some ships even go from Passau in Germany to the Danube Delta and back. During the peak season, more than 70 cruise liners are in use on the river, while the traffic-free upper parts can only be discovered with canoes or boats.
The Danube region is not only culturally and historically of importance, but also important for the regional tourism industry due to its fascinating landmarks and sights. With its well established infrastructure regarding cycling, hiking, and travel possibilities, the region along the Danube attracts every year an international clientele. In Austria alone, there are more than 14 million overnight stays and about 6.5 million arrivals per year.
The Danube Banks in Budapest are a part of Unesco World Heritage sites, they can be viewed from a number of sightseeing cruises offered in the city.
The Danube Bend is also a popular tourist destination.
Danube Bike Trail


The Danube Bike Trail (also called Danube Cycle Path or the Donauradweg) is a bicycle trail along the river. Especially the parts through Germany and Austria are very popular, which makes it one of the 10 most popular bike trails in Germany.
The Danube Bike Trail starts at the origin of the Danube and ends where the river flows into the Black Sea. It is divided into four sections:
- Donaueschingen–Passau (559 km or 347 mi)
- Passau–Vienna (340 km or 210 mi)
- Vienna–Budapest (306 km or 190 mi)
- Budapest–Black Sea (1,670 km or 1,040 mi)
Sultans Trail
The Sultans Trail is a hiking trail that runs along the river between Vienna and Smederevo in Serbia. From there the Sultans Trail leaves the Danube, terminating in Istanbul. Sections along the river are as follows.
Donausteig

In 2010, the Donausteig, a hiking trail from Passau to Grein, was opened. It is 450 km (280 mi) long and it is divided into 23 stages. The route passes through five Bavarian and 40 Austrian communities. A landscape and viewpoints, which are along the river, are the highlights of the Donausteig.
The Route of Emperors and Kings
The Route of Emperors and Kings is an international touristic route leading from Regensburg to Budapest, calling in Passau, Linz and Vienna. The international consortium ARGE Die Donau-Straße der Kaiser und Könige, comprising ten tourism organisations, shipping companies, and cities, strives for the conservation and touristic development of the Danube region.
In medieval Regensburg, with its maintained old town, stone bridge and cathedral, the Route of Emperors and Kings begins. It continues to Engelhartszell, with the only Trappist monastery in Austria. Further highlight-stops along the Danube, include the "Schlögener Schlinge", the city of Linz, which was European Capital of Culture in 2009 with its contemporary art richness, the Melk Abbey, the university city of Krems and the cosmopolitan city of Vienna. Before the Route of Emperors and Kings ends, you pass Bratislava and Budapest, the latter of which was seen as the twin town of Vienna during the times of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Since ancient Roman times, famous emperors and their retinue traveled on and along the Danube and used the river for travel and transportation. While traveling on the mainland was quite exhausting, most people preferred to travel by ship on the Danube. So the Route of Emperors and Kings was the setting for many important historical events, which characterize the Danube up until today.
The route got its name from the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I of Barbarossa and the crusaders as well as from Richard I of England who had been jailed in the Dürnstein Castle, which is situated above the Danube. The most imperial journeys throughout time were those of the Habsburg family. Once crowned in Frankfurt, the emperors ruled from Vienna and also held in Regensburg the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. Many famous castles, palaces, residences, and state-run convents were built by the Habsburger along the river. Nowadays they still remind us of the bold architecture of the "Donaubarock".
Today, people can not only travel by boat on the Danube but also by train, by bike on the Danube Bike Trail or walk on the "Donausteig" and visit the UNESCO World Heritage cities of Regensburg, Wachau and Vienna.
Important national parks
- Naturpark Obere Donau (Germany)
- Donauauen zwischen Neuburg und Ingolstadt (Germany) – map
- Nature protection area Donauleiten (Germany)
- Nationalpark Donau Auen (Austria) – map
- Chránená krajinná oblasť Dunajské luhy (Slovakia) – map
- Danube-Ipoly National Park (Hungary) – map
- Danube-Drava National Park (Hungary) – map
- Naturalpark Kopački Rit (Croatia) – map
- Gornje Podunavlje Nature Reserve (Serbia) – map
- Fruška Gora National Park (Serbia)
- Koviljsko-petrovaradinski rit Nature Reserve (Serbia)
- Great War Island Nature Reserve (Serbia)
- Đerdap National park (Serbia)
- Iron Gates Natural Park (Romania)
- Persina Nature Park (Bulgaria) – map
- Kalimok-Brushlen Protected Site (Bulgaria) – map
- Srebarna Nature Reserve (Bulgaria) – map
- Măcin Mountains Natural Park (Romania)
- Balta Mică a Brăilei Natural Park (Romania)
- Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve (Romania) – map
- Danube Biosphere Reserve in Ukraine
-
 Gornje Podunavlje Special Nature Reserve in Serbia
Gornje Podunavlje Special Nature Reserve in Serbia
-
 Golubac Fortress in Đerdap National park, Serbia
Golubac Fortress in Đerdap National park, Serbia
In popular culture

- The Danube is mentioned in the title of a famous waltz by Austrian composer Johann Strauss, The Blue Danube Waltz (On the Beautiful Blue Danube). This piece is well known across the world and is also used widely as a lullaby. The Waves of the Danube (Romanian: Valurile Dunării) is a waltz by the Romanian composer Iosif Ivanovici (1845–1902); as the Anniversary Song, it has been performed by many vocalists, such as Al Jolson, Rosemary Clooney, Vera Lynn, Tom Jones, and countless others. Joe Zawinul wrote a symphony about the Danube called Stories of the Danube. It was performed for the first time at the 1993 Bruckner festival, at Linz.
- The Danube figures prominently in the Bulgarian National Anthem, as a symbolic representation of the country's natural beauty. In Lithuanian folklore songs, the appearance of Danube (Dunojus, Dunojėlis) is more common than the appearance of the longest Lithuanian river Neman.
- The German tradition of landscape painting, the Danube school, was developed in the Danube valley in the 16th century.
- One of Claudio Magris's masterpieces is called Danube (ISBN 1-86046-823-3). The book, published in 1986, is a large cultural-historical essay, in which Magris travels the Danube from the first sources to the delta, tracing the rich European ethnic and cultural heritage, literary and ideological past and present along the way.
- The Great Danube Adventure(1838) is an epic travel diary.
- Jules Verne's The Danube Pilot (1908) (Le Pilote du Danube) depicts the adventures of fisherman Serge Ladko as he travels down the river.
- In the Star Trek universe, the Danube-class runabout is a type of starship used by the Federation Starfleet, featured prominently in the Deep Space Nine series.
- Miklós Jancsó's film the Blue Danube Waltz (1992)
- Algernon Blackwood's short story "The Willows" mostly takes place on the river.
See also
Portals:- 2006 European floods
- Black Sea drainage basin
- Between the Woods and the Water, a travel book telling of a Danubian journey in 1934
- Danube Monarchy
- Danubian Principalities
- Executive Agency for Exploration and Maintenance of the Danube River
- The Ister, 2004 film
- List of cities and towns on Danube river
- List of crossings of the Danube
- Steamboats on the Danube
Further reading
- Lóczy, Dénes. The Danube: Morphology, Evolution, and Environmental Issues. In Avijit Gupta, ed., Large Rivers: Geomorphology and Management. 2nd Ed. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Blackwell, 2022, pp. 335–367. ISBN 9781119412601
- SOMMERWERK, NIKE, JURG BLOESCH, CHRISTIAN BAUMGARTNER, THOMAS BITTL, DUBRAVKA CERBA, BELA CSANYI, GRIGORE DAVIDEANU, MARTIN DOKULIL, GEORG FRANK, IULIA GRECU, THOMAS HEIN, VLADIMIR KOVAC, ILULIAN NICHERSU, TIBOR MIKUSKA, KARIN PALL, MOMIR PAUNOVIC, CARMEN POSTOLACHE, MAJA RAKOVIC, CRISTINA SANDU, MARTIN SCHNEIDER-JACOBY, KATHARINA STEFKE, KLEMENT TOCKNER, ION TODERAS, AND LAURENTIA UNGUREANU. The Danube River Basin. In Klement Tockner, Christiane Zarfl, and Christopher T. Robinson (eds.), Rivers of Europe, 2nd Ed. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier, 2022, pp. 83–181. ISBN 978-0-08-102612-0
References
- "Danube River". Encyclopædia Britannica (Online ed.). Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ "ICPDR".
- ^ "Long-term Morphological Development of the Danube in Relation to the Sediment Balance".
- ^ Bondar, Constantin. "Hydromorphological balance of the Danube River Channel on the Sector between Bazias (km 1072.2) and Danube Delta Inlet (km 80.5)" (PDF). osce.org. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- "Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia".
- ^ Gâştescu, Petre; Țuchiu, Elena (2012), Gâştescu, Petre; Lewis William Jr, William; Breţcan, Petre (eds.), "The Danube River in the Pontic Sector – Hidrologycal Regime" (PDF), Water resources and wetlands: Conference Proceedings, Tulcea, Romania, p. 18, ISBN 978-606-605-038-8
- ^ "THE DANUBE RIVER AND ITS DELTA, HYDROGEOGRAPHYC CHARACTERISTICS-ACTUAL SYNTHESIS".
- "Points of view expressed by the Romanian authorities and scientific research on the Ukraine's document "Annotated Report on Scientific Research – Complex Environmental Monitoring for the Danube – Black Sea Deep Water Navigation Canal operation in 2017–2018. The Sea Approach Canal Zone"" (PDF). unece.org. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- "Herodotus, The Histories, book 4, chapter 48". www.perseus.tufts.edu.
- ^ Felecan, Oliviu; Felecan, Nicolae (2015). "Straturi etimologice reflectate în hidronimia românească" (PDF). Quaderns de Filologia: Estudis Lingüístics. 20 (1). Universitat de València: 254. doi:10.7203/qfilologia.20.7521.
- Dyer, Robert (1974). "Matoas, the Thraco-Phrygian name for the Danube, and the IE root *madų". Glotta. 52 (1/2). Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht (GmbH & Co. KG): 91–95. JSTOR 40266286.
- Šašel Kos, Marjeta (2009). "Reka kot božanstvo — Sava v antiki" [River as a Deity – The Sava in Antiquity]. In Barachini, Jožef (ed.). Ukročena lepotica: Sava in njene zgodbe [The Tamed Beauty: The Sava and Its Stories] (PDF) (in Slovenian and English). Sevnica: Javni zavod za kulturo, šport, turizem in mladinske dejavnosti. pp. 42–50. ISBN 978-961-92735-0-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
- Abel-Rémusat, Jean-Pierre (1829). Nouveaus Mélanges Asiatiques. Vol. 2. Paris: Schubart and Heidelhoff. pp. 96–97.
- ^ Vékony, Gábor (2000). Dacians, Romans, Romanians. Matthias Corvinus Publishing. p. 210. ISBN 978-1-882785-13-1.
- Kozma Vasili; Arsen Mustaqi, eds. (1981), Lirika popullore [Folk lyrics], Folklor Shqiptar (in Albanian), vol. 4, Tirana: Akademia e Shkencave e RPS te Shqiperise, Instituti i Kultures Popullore, Sektori i Prozes dhe Poezise, p. 624,
Tunë-a lumi i Danubit
- Triad 35. Bromwich, Trioedd Ynys Prydein, pp. 280–285.
- Mallory, J.P; Mair, Victor H. (2000). The Tarim Mummies: Ancient China and the Mystery of the Earliest Peoples from the West. London: Thames and Hudson. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-500-05101-6.. V. I. Adaev (1949). Осетинский язык и фольклор [Ossetian language and folklore] (PDF) (in Russian). Moscow: Publishing house of Soviet Academy of Sciences. p. 236.
- Ancient Languages of the Balkans, Part One. Paris: Mouton. 1976. p. 144.
- Tonaw in Sebastian Franck (1542). Weltbuch. p. 81. Donaw e.g. in Leonhard Thurneisser zum Thurn (1572). Pison. p. 186. Spelling Donau from the 17th century.
- Grimm. Deutsche Grammatik. p. 407.
- ^ "Countries of the Danube River Basin". International Commission for the protection of the Danube River. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- Complete table of the Bavarian Waterbody Register by the Bavarian State Office for the Environment (xls, 10.3 MB)
- "Danube River Basin District, Part A - Roof Report" (PDF). ICPDR. April 2004. p. 12.
- ^ "River Basin | ICPDR – International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River". www.icpdr.org.
- "Drainage basin of the Black Sea" (PDF). Our Waters: Joining Hands Across Borders. First Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters. United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. 2007.
- "Republički hidrometeorološki zavod".
- "ICPDR-International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River".
- ^ "DIAGNOZA ŞI PROGNOZA PENTRU DUNĂRE".
- Pekárová, Pavla; Miklánek, Pavol (2019). Flood Regime of Rivers in the Danube River Basin. doi:10.31577/2019.9788089139460. ISBN 978-80-89139-46-0. S2CID 131234947.
- "Points of view expressed by the Romanian authorities and scientific research on the Ukraine's document "Annotated Report on Scientific Research – Complex Environmental Monitoring for the Danube – Black Sea Deep Water Navigation Canal operation in 2017–2018. The Sea Approach Canal Zone"" (PDF). unece.org. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- McCarney-Castle, K.; Voulgaris, G.; Kettner, A.J.; Giosan, L. (2021). "Simulating fluvial fluxes in the Danube watershed: The "Little Ice Age" versus modern day". The Holocene. 22: 91–105. doi:10.1177/0959683611409778. S2CID 129864432.
- Nagaviciuc, Viorica; Roibu, Cătălin-Constantin; Mursa, Andrei; Ştirbu, Marian-Ionuţ; Popa, Ionel; Ionita, Monica (2023). "The first tree-ring reconstruction of streamflow variability over the last ~250 years in the Lower Danube". Journal of Hydrology. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129150. S2CID 256288140.
- "INHGA". Archived from the original on 16 December 2023.
- "Annual Reports". ICPDR. Archived from the original on 18 April 2023.
- "IPCC". Archived from the original on 21 December 2023.
- Treaty of Peace with Turkey signed at Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland: World War I Document Archive, 24 July 1923, retrieved 6 December 2014
- Bondoc, Dorel. "Ada Kaleh". The Alexis Project. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2014.
- "Danube navigation at a glance". INeS Danube. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021.
- Tzimas, Stavros (28 August 2017). "Chinese interests could make plan to link Danube and Aegean a reality". eKathimerini.com. Retrieved 11 July 2022.
- Sarna, Heidi (15 August 2019). "10 Best River Cruises". Frommer's. Archived from the original on 21 September 2023.
- Piškor, Mate (12 October 2011). "Riječni gusari u Srbiji pljačkaju hrvatske brodove". Jutarnji list (in Croatian). Archived from the original on 1 March 2020.
- "Ukrainian Danube Shipping Company Says Its Ships Are Being Attacked Frequently in Romanian Part Of River Danube". Ukrainian News. 13 January 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- Гордієва, Олена (20 January 2012). "Українські кораблі все частіше стають жертвами румунських піратів" [Romanian Pirates Attack Ukrainian Ships More Frequently]. Gazeta.ua (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 5 April 2023.
- Ingo_Eigen (27 February 2012). "Pirates on the lower Danube". rivercruiseinfo. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013.
- Tomiuc, Eugen (5 February 2012). "Reports Of 'Pirates Of The Danube' Get The Old Heave-Ho". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 9 September 2023.
- Staras, Mircea (2005). Documentation on the likely significant transboundary impact of the Ukrainian deep-water navigation canal Danube-black sea in the context of Espoo Convention, 1991 (PDF). Tulcea, Romania: Danube Delta National Institute (published February 2005). Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- "Daily hydrological report". State Hydrometeorological Bureau of the Republic of Croatia. Archived from the original on 30 May 2010. Retrieved 9 September 2010.
- Dacia Preistorica Archived 7 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Nicolae Densusianu (1913).
- "Hungary buries remains of Holocaust victims executed by Nazis on banks of the Danube River". National Post. The Associated Press. 15 April 2016. Retrieved 16 February 2022.
- "About Us". International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- "Blue River". wwf.panda.org. Archived from the original on 12 April 2021. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- "The Danube". International Association of Water Supply Companies in the Danube River Catchment Area. Archived from the original on 19 May 2012. Retrieved 28 July 2012.
- "The Times & The Sunday Times". www.thetimes.co.uk.
- Holcik, Juraj (1989). The freshwater fishes of Europe Vol.I Part II General introduction to fishes. Wiesbaden: Aula Verlag.
- Hensel, K; Holcik, J (1997). Past and current status of sturgeons in the upper and middle Danube River.
- Corda (1988). "Iron gates II design and performance of dams- geotechnical considerations" (PDF). International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering.
- Suciu Radu, Guti Gabor (2012). Have sturgeons a future in the Danube River? (PDF). 39th IAD Conference: Living Danube. Szentendre, Hungary.
- We Pass – Facilitating Fish Migration and Conservation at the Iron Gates. ICPDR. 11 November 2019. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021.
- ^ Hales, J. (2013). Upper Danube. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Hucho hucho". FishBase. February 2013 version.
- ^ "Press release of the "ARGE Donau Österreich"" (PDF) (in German). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 March 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- "Die ADFC-Radreiseanalyse 2013 – Zahlen, Daten und Fakten" (in German). Archived from the original on 18 June 2017. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- "Donausteig". Traildino.com. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- "Welcome". Straße der Kaiser und Könige.
- "The Route of Emperors and Kings". bavaria.by. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
Notes
- Flow sequence from the source confluence in Germany to final discharge into the Black Sea via the Danube Delta in Romania and Ukraine.
See also Contents > Geography. - Note that the port city of Vidin in Bulgaria is downstream from the town of Moldova Nouă in Romania.
Sources
- James, Alan G. (2020). "The Brittonic Language in the Old North, A Guide to the Place-Name Evidence, Volume 2" (PDF). Scottish Place-Name Society. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
- MacKillop, James (2004). Oxford Dictionary of Celtic Mythology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0198609674.
- Noble, Gordon; Evans, Nicholas (2022). The Picts: Scourge of Rome, Rulers of the North. Birlinn. ISBN 978-1780277783.
- Roberts, Alice (2015). The Celts: Search for a Civilisation. Heron Books. ISBN 978-1784293321.
External links
 Geographic data related to Danube at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Danube at OpenStreetMap- Danube watershed map and information from the World Resources Institute
- Danube Panorama Project Archived 23 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- сайт о Дунае (in Russian)
- Danube and the sport of rowing
- Danube image pool on Flickr
- Danube Tourist Commission Archived 6 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine (in German)
- International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River
- Bridges of Budapest over the Danube river
- Description of the Danube estuary in June 1877, The Times of London
- Old maps of the Danube, Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel
| The Danube | ||
|---|---|---|
| Countries | 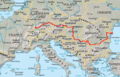 | |
| Cities | ||
| Tributaries | ||
| Canals | ||
| See also | ||
| Hydrography of Slovakia | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rivers |
|  | ||||||||||
| Lakes |
| |||||||||||
| Reservoirs |
| |||||||||||
| River islands | ||||||||||||
| Baltic Sea | |
|---|---|
| Black Sea | |
| North Sea | |
| Maas | |
| Black Sea | |
|---|---|
| Bug | |
| Danube | |
| Dnieper (Rapids) | |
| Dniester | |
| Don | |
| Pripyat | |
| San | |
| Sea of Azov | |
| Southern Bug | |
| Syvash | |
| Hydrography of Croatia | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rivers |
|  | ||||
| Lakes | ||||||
| Valleys, estuaries, canyons, wetlands | ||||||
| Waterfalls | ||||||
| Canals |
| |||||
| Adriatic Sea | ||||||
- Danube
- Danube basin
- International rivers of Europe
- Geography of Bács-Kiskun County
- Geography of Europe
- Geography of Vojvodina
- Rivers of Austria
- Rivers of Bavaria
- Rivers of Bulgaria
- Rivers of Croatia
- Rivers of Germany
- Rivers of Hungary
- Rivers of Moldova
- Rivers of Romania
- Rivers of Serbia
- Rivers of Slovakia
- Rivers of Ukraine
- Rivers of Odesa Oblast
- Rivers of Baden-Württemberg
- Rivers of Upper Austria
- Rivers of Lower Austria
- Rivers of Vienna
- Bačka
- Banat
- Syrmia
- Border rivers
- Bulgaria–Romania border
- Croatia–Serbia border
- Hungary–Slovakia border
- Romania–Ukraine border
- Romania–Serbia border
- Federal waterways in Germany