| Florida Legislature | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Bicameral |
| Chambers | Senate House of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | May 26, 1845 |
| Preceded by | Legislative Council of the Territory of Florida |
| New session started | November 19, 2024; 59 days ago (2024-11-19) |
| Leadership | |
| Senate President | Ben Albritton (R) since November 19, 2024 |
| House Speaker | Daniel Perez (R) since November 19, 2024 |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 160 voting members
|
 | |
| State Senate political groups | Majority
Minority
|
 | |
| House of Representatives political groups | Majority
Minority
|
| Salary | $18,000/year + per diem (Subsistence & Travel) |
| Elections | |
| Last State Senate election | November 5, 2024 |
| Last House of Representatives election | November 5, 2024 |
| Next State Senate election | November 3, 2026 |
| Next House of Representatives election | November 3, 2026 |
| Redistricting | Legislative control |
| Motto | |
| In God We Trust | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Florida Capitol (Old Capitol in foreground) Tallahassee | |
| Website | |
| Official Website | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of Florida | |
The Florida Legislature is the legislature of the U.S. state of Florida. It is organized as a bicameral body composed of an upper chamber, the Senate, and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. Article III, Section 1 of the Florida Constitution, adopted in 1968, defines the role of the legislature and how it is to be constituted. The legislature is composed of 160 state legislators (120 in the House and 40 in the Senate). The primary purpose of the legislature is to enact new laws and amend or repeal existing laws. It meets in the Florida State Capitol building in Tallahassee.
Florida Senate
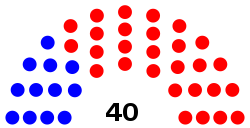
Main article: Florida SenateThe Senate is the upper house of the state legislature. As of 2024, Republicans hold the majority in the Senate with 28 seats; Democrats are in the minority with 12 seats.
Florida House of Representatives
Main article: Florida House of RepresentativesThe House of Representatives is the lower house of the state legislature. As of January 2025, Republicans hold the majority in the House of Representatives with 86 seats, and Democrats hold 33 seats. One seat is vacant.
Terms
Senate
All terms were truncated again in 2016, with all 40 Senate seats up for election, due to court-ordered redistricting.
House of Representatives
Members of the House of Representatives are elected for terms of two years in each even-numbered year.
Term limits
In 1992, voters passed Amendment 9 to amend the State Constitution to limit federal and state officials to eight-year terms. In 1995, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that states could not enact congressional term limits.
Qualifications
Florida legislators must be at least twenty-one years old, an elector and resident of their district, and must have resided in Florida for at least two years before an election.
Legislative session
Regular legislative sessions
The Florida Legislature meets in a 60-day regular legislative session each year. Regular legislative sessions in odd-numbered years must begin on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in March and on the second Tuesday after the first Monday in January of each even-numbered year.
Before 1991, the regular legislative session began in April. Senate Joint Resolution 380 (1989) proposed to the voters a constitutional amendment (approved November 1990) that shifted the starting date of regular legislative session from April to February. Subsequently, Senate Joint Resolution 2606 (1994) proposed to the voters a constitutional amendment (approved November 1994) shifting the start date to March, where it remains. In recent years, the legislature has opted to start in January to allow lawmakers to be home with their families during school spring breaks, and to give more time ahead of the legislative elections in the Fall.
Special legislative sessions
Special legislative sessions may be called by the governor, by a joint proclamation of the Senate president and House speaker, or by a three-fifths vote of all legislators. During any special session, the legislature may only address legislative business that is within the purview of the purpose or purposes stated in the special session proclamation.
Powers and process
The Florida Legislature is authorized by the Florida Constitution to create and amend the laws of the state of Florida, subject to the governor's power to veto legislation. To do so, legislators propose legislation in the forms of bills drafted by a nonpartisan, professional staff. Successful legislation must undergo committee review, three readings on the floor of each house, with appropriate voting majorities, as required, and either be signed into law by the governor or enacted through a veto override approved by two-thirds of the membership of each legislative house.
Its statutes, called "chapter laws" or generically as "slip laws" when printed separately, are compiled into the Laws of Florida and are called "session laws". The Florida Statutes are the codified statutory laws of the state.
In 2009, legislators filed 2,138 bills for consideration. On average, the legislature has passed about 300 bills into law annually.
In 2013, the legislature filed about 2,000 bills. About 1,000 of these were "member bills." The remainder are bills by committees responsible for certain functions, such as the budget. In 2016, about 15% of the bills were passed. In 2017, 1,885 lobbyists registered to represent 3,724 entities.
The legislature also has the power to propose amendments to the Florida Constitution.
Leadership
The House of Representatives is headed by the speaker of the House, while the Senate is headed by the Senate president. The House speaker and Senate president control the assignment of committees and leadership positions, along with control of the agenda in their chambers. The two leaders, along with the governor of Florida, control most of the agenda of state business in Florida.
- President of the Senate: Kathleen Passidomo (R)
- President Pro Tempore of the Florida Senate: Dennis Baxley (R)
- Majority Leader of the Florida Senate: Ben Albritton (R)
- Minority Leader of the Florida Senate: Lauren Book (D)
- Speaker of the Florida House: Paul Renner (R)
- Speaker Pro Tempore of the Florida House: Chuck Clemons (R)
- Majority Leader of the Florida House: Michael J. Grant (R)
- Minority Leader of the Florida House: Fentrice Driskell (D)
See also
- Florida House of Representatives
- Florida Senate
- Florida Senate Majority Office
- Florida State Capitol
- Government of Florida
- List of presidents of the Florida Senate
- List of speakers of the Florida House of Representatives
- List of Florida state legislatures
- The Florida Channel
References
- "The 2017 Florida Statutes F.S. 11.13 Compensation of members". Florida Legislature.
- "Constitution of the State of Florida". Florida Legislature. Archived from the original on December 8, 2008. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- "FAQ". Florida Senate.
- ^ "Constitution of the State of Florida". Florida Legislature.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "Florida Backs Article V Convention for Constitutional Amendment on Congressional Term Limits". Sunshine State News. February 11, 2016.
- Buzzacco-Foerster, Jenna (February 18, 2016). "Proposal to move 2018 session to January heads House floor". Florida Politics. Retrieved February 18, 2016.
- "The Florida Constitution". Florida Legislature.
- "The Florida Senate Handbook" (PDF). Florida Senate.
- ^ "Statutes & Constitution: Online Sunshine". Florida Legislature. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- Flemming, Paul (March 8, 2009). Capital Ideas: Lawmakers face 2,138 proposals. Florida Today.
- ^ Cotterell, Bill (March 7, 2017). "Legislative session by the numbers". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 5A.
- "Welcome : Online Sunshine". www.leg.state.fl.us.
External links
| Members of the Florida Senate | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|  | |
| Legislatures of the United States | |
|---|---|
| United States Congress | |
| State legislatures |
|
| Other legislatures | |
| Legislative elections | |

