In mathematics, the fundamental theorem of Galois theory is a result that describes the structure of certain types of field extensions in relation to groups. It was proved by Évariste Galois in his development of Galois theory.
In its most basic form, the theorem asserts that given a field extension E/F that is finite and Galois, there is a one-to-one correspondence between its intermediate fields and subgroups of its Galois group. (Intermediate fields are fields K satisfying F ⊆ K ⊆ E; they are also called subextensions of E/F.)
Explicit description of the correspondence
For finite extensions, the correspondence can be described explicitly as follows.
- For any subgroup H of Gal(E/F), the corresponding fixed field, denoted E, is the set of those elements of E which are fixed by every automorphism in H.
- For any intermediate field K of E/F, the corresponding subgroup is Aut(E/K), that is, the set of those automorphisms in Gal(E/F) which fix every element of K.
The fundamental theorem says that this correspondence is a one-to-one correspondence if (and only if) E/F is a Galois extension. For example, the topmost field E corresponds to the trivial subgroup of Gal(E/F), and the base field F corresponds to the whole group Gal(E/F).
The notation Gal(E/F) is only used for Galois extensions. If E/F is Galois, then Gal(E/F) = Aut(E/F). If E/F is not Galois, then the "correspondence" gives only an injective (but not surjective) map from to , and a surjective (but not injective) map in the reverse direction. In particular, if E/F is not Galois, then F is not the fixed field of any subgroup of Aut(E/F).
Properties of the correspondence
The correspondence has the following useful properties.
- It is inclusion-reversing. The inclusion of subgroups H1 ⊆ H2 holds if and only if the inclusion of fields E ⊇ E holds.
- Degrees of extensions are related to orders of groups, in a manner consistent with the inclusion-reversing property. Specifically, if H is a subgroup of Gal(E/F), then |H| = and |Gal(E/F)|/|H| = .
- The field E is a normal extension of F (or, equivalently, Galois extension, since any subextension of a separable extension is separable) if and only if H is a normal subgroup of Gal(E/F). In this case, the restriction of the elements of Gal(E/F) to E induces an isomorphism between Gal(E/F) and the quotient group Gal(E/F)/H.
Example 1

Consider the field
Since K is constructed from the base field by adjoining √2, then √3, each element of K can be written as:
Its Galois group comprises the automorphisms of K which fix a. Such automorphisms must send √2 to √2 or –√2, and send √3 to √3 or –√3, since they permute the roots of any irreducible polynomial. Suppose that f exchanges √2 and –√2, so
and g exchanges √3 and –√3, so
These are clearly automorphisms of K, respecting its addition and multiplication. There is also the identity automorphism e which fixes each element, and the composition of f and g which changes the signs on both radicals:
Since the order of the Galois group is equal to the degree of the field extension, , there can be no further automorphisms:
which is isomorphic to the Klein four-group. Its five subgroups correspond to the fields intermediate between the base and the extension K.
- The trivial subgroup {1} corresponds to the entire extension field K.
- The entire group G corresponds to the base field
- The subgroup {1, f} corresponds to the subfield since f fixes √3.
- The subgroup {1, g} corresponds to the subfield since g fixes √2.
- The subgroup {1, fg} corresponds to the subfield since fg fixes √6.
Example 2
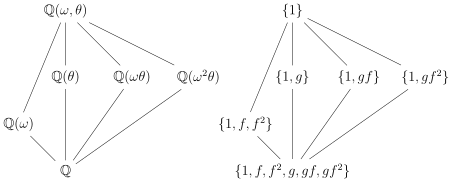
The following is the simplest case where the Galois group is not abelian.
Consider the splitting field K of the irreducible polynomial over ; that is, where θ is a cube root of 2, and ω is a cube root of 1 (but not 1 itself). If we consider K inside the complex numbers, we may take , the real cube root of 2, and Since ω has minimal polynomial , the extension has degree: with -basis as in the previous example. Therefore the Galois group has six elements, determined by all permutations of the three roots of :
Since there are only 3! = 6 such permutations, G must be isomorphic to the symmetric group of all permutations of three objects. The group can be generated by two automorphisms f and g defined by:
and , obeying the relations . Their effect as permutations of is (in cycle notation): . Also, g can be considered as the complex conjugation mapping.
The subgroups of G and corresponding subfields are as follows:
- As always, the trivial group {1} corresponds to the whole field K, while the entire group G to the base field .
- The unique subgroup of order 3, , corresponds to the subfield of degree two, since the subgroup has index two in G: i.e. . Also, this subgroup is normal, so the subfield is normal over , being the splitting field of . Its Galois group over the base field is the quotient group , where denotes the coset of g modulo H; that is, its only non-trivial automorphism is the complex conjugation g.
- There are three subgroups of order 2, and corresponding respectively to the subfields These subfields have degree 3 over since the subgroups have index 3 in G. The subgroups are not normal in G, so the subfields are not Galois or normal over . In fact, each subfield contains only a single one of the roots , so none has any non-trivial automorphisms.
Example 3
Let be the field of rational functions in the indeterminate λ, and consider the group of automorphisms:
here we denote an automorphism by its value , so that . This group is isomorphic to (see: six cross-ratios). Let be the fixed field of , so that .
If is a subgroup of , then the coefficients of the polynomial
generate the fixed field of . The Galois correspondence implies that every subfield of can be constructed this way. For example, for , the fixed field is and if then the fixed field is . The fixed field of is the base field where j is the j-invariant written in terms of the modular lambda function:
Similar examples can be constructed for each of the symmetry groups of the platonic solids as these also have faithful actions on the projective line and hence on .
Example 4
Here we give an example of a finite extension which is not Galois, and with this we show that (the fundamental theorem of) Galois theory no longer works when is not Galois.
Let and . Then is a finite extension, but not a splitting field over (since the minimal polynomials of has two complex roots that do not lie in ). Any is completely determined by and that Thus, , is the trivial group. In particular, . This shows that is not Galois.
Now, has only one subgroup, i.e., itself. The only intermediate field that contains is . It follows that the Galois correspondence fails.
Applications
The theorem classifies the intermediate fields of E/F in terms of group theory. This translation between intermediate fields and subgroups is key to showing that the general quintic equation is not solvable by radicals (see Abel–Ruffini theorem). One first determines the Galois groups of radical extensions (extensions of the form F(α) where α is an n-th root of some element of F), and then uses the fundamental theorem to show that solvable extensions correspond to solvable groups.
Theories such as Kummer theory and class field theory are predicated on the fundamental theorem.
Infinite case
Given an infinite algebraic extension we can still define it to be Galois if it is normal and separable. The problem that one encounters in the infinite case is that the bijection in the fundamental theorem does not hold as we get too many subgroups generally. More precisely if we just take every subgroup we can in general find two different subgroups that fix the same intermediate field. Therefore we amend this by introducing a topology on the Galois group.
Let be a Galois extension (possibly infinite) and let be the Galois group of the extension. Let be the set of the Galois groups of all finite intermediate Galois extensions. Note that for all we can define the maps by . We then define the Krull topology on to be weakest topology such that for all the maps are continuous, where we endow each with the discrete topology. Stated differently as an inverse limit of topological groups (where again each is endowed with the discrete topology). This makes a profinite group (in fact every profinite group can be realised as the Galois group of a Galois extension, see for example ). Note that when is finite, the Krull topology is the discrete topology.
Now that we have defined a topology on the Galois group we can restate the fundamental theorem for infinite Galois extensions.
Let denote the set of all intermediate field extensions of and let denote the set of all closed subgroups of endowed with the Krull topology. Then there exists a bijection between and given by the map
defined by and the map
defined by . One important thing one needs to check is that is a well-defined map, that is that is a closed subgroup of for all intermediate fields . This is proved in Ribes–Zalesskii, Theorem 2.11.3.
See also
References
- ^ Ribes, Zalesskii (2010). Profinite groups. Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-01641-7.
Further reading
- Milne, J. S. (2022). Fields and Galois Theory. Kea Books, Ann Arbor, MI. ISBN 979-8-218-07399-2.
External links
 Media related to Fundamental theorem of Galois theory at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fundamental theorem of Galois theory at Wikimedia Commons- proof of fundamental theorem of Galois theory at PlanetMath.
- The Stacks Project authors. "Theorem 9.21.7 (Fundamental theorem of Galois theory)".
- The Stacks Project authors. "Theorem 9.22.4 (Fundamental theorem of infinite Galois theory)".
 to
to  , and a surjective (but not injective) map in the reverse direction. In particular, if E/F is not Galois, then F is not the fixed field of any subgroup of Aut(E/F).
, and a surjective (but not injective) map in the reverse direction. In particular, if E/F is not Galois, then F is not the fixed field of any subgroup of Aut(E/F).
 and inverted
and inverted 

 by adjoining √2, then √3, each element of K can be written as:
by adjoining √2, then √3, each element of K can be written as:

 comprises the automorphisms of K which fix a. Such automorphisms must send √2 to √2 or –√2, and send √3 to √3 or –√3, since they permute the roots of any irreducible polynomial. Suppose that f exchanges √2 and –√2, so
comprises the automorphisms of K which fix a. Such automorphisms must send √2 to √2 or –√2, and send √3 to √3 or –√3, since they permute the roots of any irreducible polynomial. Suppose that f exchanges √2 and –√2, so



 , there can be no further automorphisms:
, there can be no further automorphisms:


 since f fixes √3.
since f fixes √3. since g fixes √2.
since g fixes √2. since fg fixes √6.
since fg fixes √6. over
over  where θ is a cube root of 2, and ω is a cube root of 1 (but not 1 itself). If we consider K inside the complex numbers, we may take
where θ is a cube root of 2, and ω is a cube root of 1 (but not 1 itself). If we consider K inside the complex numbers, we may take  , the real cube root of 2, and
, the real cube root of 2, and  Since ω has minimal polynomial
Since ω has minimal polynomial  , the extension
, the extension  has degree:
has degree:
 with
with  as in the previous example. Therefore the Galois group
as in the previous example. Therefore the Galois group  has six elements, determined by all permutations of the three roots of
has six elements, determined by all permutations of the three roots of 


 , obeying the relations
, obeying the relations  . Their effect as permutations of
. Their effect as permutations of  is (in
is (in  . Also, g can be considered as the
. Also, g can be considered as the  , corresponds to the subfield
, corresponds to the subfield  of degree two, since the subgroup has
of degree two, since the subgroup has  . Also, this subgroup is normal, so the subfield is normal over
. Also, this subgroup is normal, so the subfield is normal over  , where denotes the coset of g modulo H; that is, its only non-trivial automorphism is the complex conjugation g.
, where denotes the coset of g modulo H; that is, its only non-trivial automorphism is the complex conjugation g. and
and  corresponding respectively to the subfields
corresponding respectively to the subfields  These subfields have degree 3 over
These subfields have degree 3 over  be the
be the 
 by its value
by its value  , so that
, so that  . This group is isomorphic to
. This group is isomorphic to  (see:
(see:  be the fixed field of
be the fixed field of  , so that
, so that  .
.
 is a subgroup of
is a subgroup of 
 can be constructed this way. For example, for
can be constructed this way. For example, for  , the fixed field is
, the fixed field is  and if
and if  then the fixed field is
then the fixed field is  . The fixed field of
. The fixed field of  where j is the
where j is the 
 and hence on
and hence on  .
.
 and
and  . Then
. Then  has two complex roots that do not lie in
has two complex roots that do not lie in  ). Any
). Any  is completely determined by
is completely determined by  and that
and that  Thus,
Thus,  , is the trivial group. In particular,
, is the trivial group. In particular,  . This shows that
. This shows that  be the Galois group of the extension. Let
be the Galois group of the extension. Let  be the set of the Galois groups of all finite intermediate Galois extensions. Note that for all
be the set of the Galois groups of all finite intermediate Galois extensions. Note that for all  we can define the maps
we can define the maps  by
by  . We then define the Krull topology on
. We then define the Krull topology on  with the discrete topology. Stated differently
with the discrete topology. Stated differently  as an
as an  denote the set of all intermediate field extensions of
denote the set of all intermediate field extensions of  denote the set of all closed subgroups of
denote the set of all closed subgroups of 
 and the map
and the map

 . One important thing one needs to check is that
. One important thing one needs to check is that  is a well-defined map, that is that
is a well-defined map, that is that  is a closed subgroup of
is a closed subgroup of  . This is proved in Ribes–Zalesskii, Theorem 2.11.3.
. This is proved in Ribes–Zalesskii, Theorem 2.11.3.