| Germinal epithelium (male) | |
|---|---|
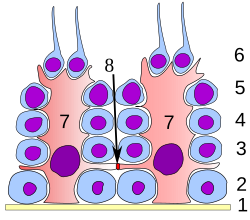 Germinal epithelium of the testicle. 1 basal lamina, 2 spermatogonia, 3 spermatocyte 1st order, 4 spermatocyte 2nd order, 5 spermatid, 6 mature spermatid, 7 Sertoli cell, 8 tight junction (blood testis barrier) Germinal epithelium of the testicle. 1 basal lamina, 2 spermatogonia, 3 spermatocyte 1st order, 4 spermatocyte 2nd order, 5 spermatid, 6 mature spermatid, 7 Sertoli cell, 8 tight junction (blood testis barrier) | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D012670 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Epithelia |
|---|
| Squamous epithelial cell |
| Columnar epithelial cell |
| Cuboidal epithelial cell |
| Specialised epithelia |
|
| Other |
The germinal epithelium is the epithelial layer of the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. It is also known as the wall of the seminiferous tubules. The cells in the epithelium are connected via tight junctions.
There are two types of cells in the germinal epithelium. The large Sertoli cells (not dividing) function as supportive cells to the developing sperm. The second cell type is the cells belonging to the spermatogenic cell lineage. These eventually develop into sperm cells (spermatozoon). Typically, the spermatogenic cells will make four to eight layers in the germinal epithelium.
References
- Junqueira's Basic Histology: Text and Atlas, Thirteenth Edition
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Histology image: 17803loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Male Reproductive System: testis, germinal epithelium"
- Anatomy Atlases – Microscopic Anatomy, plate 02.21 - "Stratified Germinal Epithelium"
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) cgametogen/spermato02
This article related to the genitourinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |