| Green-crowned brilliant | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male, Alajuela Province, Costa Rica | |

| |
| Female Both in Mount Totumas cloud forest, Panama | |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| CITES Appendix II (CITES) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Heliodoxa |
| Species: | H. jacula |
| Binomial name | |
| Heliodoxa jacula Gould, 1850 | |
| |
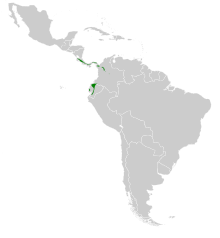
| Range of H. jacula | |
The green-crowned brilliant (Heliodoxa jacula) is species of hummingbird in the "brilliants", tribe Heliantheini in subfamily Lesbiinae. It is found in Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, and Panama. It is also known as the green-fronted brilliant.
Taxonomy and systematics
The green-crowned brilliant has three subspecies, the nominate H. j. jacula, H. j. henryi, and H. j. jamersoni.
Description
Male green-crowned brilliants are 12 to 13 cm (4.7 to 5.1 in) long and females 10.5 to 12 g (0.37 to 0.42 oz). One female weighed 7.4 g (0.26 oz). Both sexes of all subspecies have a white spot behind the eye and a forked tail, though that of the female is not as deeply indented as the male's.
Adult males of the nominate subspecies have a glittering green to blue-green head and breast with a small metallic violet-blue patch on the throat. The upperparts and belly are bronzy green, the vent area white, and the thighs also white. The tail is blue-black. Adult females' blue-green head is not shiny like the male's. They also have a short white malar stripe. Their underparts are whitish and heavily spotted with green; the spots merge on the flanks. The tail is black and the outer feathers have white tips. Immature males have a dull bronzy green crown and underparts, a bright buff chin and malar, and a shallowly forked tail. Immature females have a bright buff throat and duller green spots on the underparts than the adult.
Subspecies H. j. henryi is larger than the nominate. Males' heads have a more brilliant glitter than the nominate's and their plumage is greener with less or no blue. Females have more white on their underparts and the separate green spots extend onto the flanks. Males of H. j. jamersoni are much duller than the nominate on the head and breast; their tail is shorter and its central feathers have a green gloss.
Distribution and habitat
The nominate subspecies of green-crowned brilliant is found from Panamá Province in eastern Panama into Colombia, where it inhabits all three Andean ranges. H. j. henryi is found more northerly, from Costa Rica south and east into Panama as far as Coclé Province. H. j. jamersoni is found from Colombia's Nariño Department (and possibly from further north in Cauca Department) south along the western slope of the Andes of Ecuador at least as far as El Oro Province.
The green-crowned brilliant inhabits a variety of landscapes including the interior, edges, and clearings of humid sub-montane and montane forest; mature secondary forest; and gardens. In elevation it generally ranges between 700 and 2,200 m (2,300 and 7,200 ft) in Costa Rica, though sometimes as low as 100 m (330 ft). In Panama it is usually found between 500 and 2,100 m (1,600 and 6,900 ft), in Colombia between 300 and 1,700 m (980 and 5,600 ft), and in Ecuador between 500 and 1,550 m (1,600 and 5,100 ft). There are also records as low as 300 m (980 ft) in Ecuador.
Behavior
Movement
The low-elevation records of green-crowned brilliant in Costa Rica and Ecuador may indicate seasonal movements.
Feeding
The green-crowned brilliant usually forages in the middle and upper strata of the forest. A primary source of nectar is Marcgravia vines, and females also feed at small understory plants. Males sometimes defend Marcgravia patches, though they also nectar by trap-lining, visiting a circuit of flowering plants. The species usually clings to flowers to feed rather than hovering.
Breeding
The green-crowned brilliant's nesting season in Costa Rica is thought to span from July or August to January and in Colombia from May to September. The nest is a bulky cup of plant fibers and scales of tree ferns saddled on a thin down-sloping branch, typically between 2 and 6 m (7 and 20 ft) above the ground. The female alone incubates the two white elliptical eggs.
|
Songs and calls Listen to green-crowned brilliant on xeno-canto |
Vocalization
The green-crowned brilliant makes "a loud and squeaky kyew or tyew call". In Costa Rica, displaying males make "a tseek, tseek, tseek" call. During chases the species makes "loud sputtering notes and squeaks".
Status
The IUCN has assessed the green-crowned brilliant as being of Least Concern, though its population size is not known and is believed to be decreasing. No immediate threats have been identified. It has been recorded in several protected areas. It "shows some tolerance of habitat fragmentation, degradation and disturbance outright forest clearance is expected to cause local population declines".
Gallery
-
 Male
Male
-
 Composite showing effect of light reflection on the color of male H. j. henryi's gorget, Mount Totumas cloud forest, Panama
Composite showing effect of light reflection on the color of male H. j. henryi's gorget, Mount Totumas cloud forest, Panama
-
 Juvenile H. j. henryi
Juvenile H. j. henryi
References
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Green-crowned Brilliant Heliodoxa jacula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (January 2022). "Hummingbirds". IOC World Bird List. v 12.1. Retrieved January 15, 2022.
- HBW and BirdLife International (2020) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world Version 5. Available at: http://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v5_Dec20.zip retrieved 27 May 2021
- Stiles, F.G. (2013) . del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J.; Christie, D.A.; de Juana, E. (eds.). "Green-fronted Brilliant (Heliodoxa jacula)". Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ Taylor, J. (2020). Green-crowned Brilliant (Heliodoxa jacula), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.grcbri1.01 retrieved 7 May 2022
- Sánchez, Julio E.; Mulvihill, Robert S.; Master, Terry L. (2000). "First description of the nest and eggs of the Green-crowned Brilliant (Heliodoxa jacula), with behavioral notes" (PDF). Ornitologia Neotropical. 11 (3). Sociedad de Ornitología Neotropical: 189–196.
External links
- Green-crowned brilliant photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
