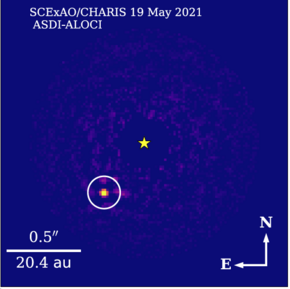
 Subaru Telescope detection of HIP 99770 b. Subaru Telescope detection of HIP 99770 b. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Currie et al. |
| Discovery site | Subaru Telescope |
| Discovery date | November 30, 2022 |
| Detection method | Direct imaging |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Semi-major axis | 16.9 −1.9AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.25 −0.16 |
| Inclination | 148+13 −11 |
| Star | HIP 99770 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mass | 16.1 −5.0 MJ |
| Temperature | 1,400 K |
HIP 99770 b is a directly imaged superjovian extrasolar planet orbiting the dusty A-type star HIP 99770 (29 Cygni), detected with Gaia/Hipparcos precision astrometry and high-contrast imaging. HIP 99770 b is the first joint direct imaging + astrometric discovery of an extrasolar planet and the first planet discovered using precision astrometry from the Gaia mission.
Discovery
HIP 99770 b was discovered by a team led by Thayne Currie, Mirek Brandt, and Tim Brandt using the Subaru Telescope on Mauna Kea. The Subaru data utilized the observatory's extreme adaptive optics system, SCExAO, to correct for atmospheric turbulence and the CHARIS integral field spectrograph to detect HIP 99770 b at 22 different near-infrared wavelength passbands from 1.1 microns to 2.4 microns. It was also detected at longer wavelengths using the NIRC2 camera on the Keck Observatory.
Atmosphere
With a spectral type of L7.5--L9, HIP 99770 b lies at the L/T transition for substellar objects, transition from cloudy atmospheres without methane absorption to clear atmospheres with methane absorption. Atmospheric modeling favors an effective temperature of 1400 K and a Jupiter-like radius. The planet is likely intermediate in cloudiness between older, more massive field brown dwarfs and young L/T transition exoplanets like HR 8799 d.
Orbit and mass
Jointly modeling relative astrometry of HIP 99770 b with absolute astrometry of the primary as measured by Gaia and Hipparcos yields precise estimates for the companion's orbit and mass. HIP 99770 b lies at about 16.9 au from its host star. The host star is significantly more luminous than the Sun: HIP 99770 b receives roughly as much light as Jupiter receives from the Sun. HIP 99770 b is a super-jovian planet with a mass of roughly 16.1 times that of Jupiter. Its mass ratio -- mass divided by the mass of the host star -- is comparable to that of many planets detected through methods such as radial velocity and transits and is similar to that of HR 8799 d.
See also
References
- ^ Direct Imaging and Astrometric Discovery of a Superjovian Planet Orbiting an Accelerating Star, 2022, arXiv:2212.00034
- Andrew Jones (April 17, 2023). "Giant exoplanet found, imaged directly thanks to star-mapping data (photos)". Space.com.
Further reading
- Nola Taylor Tillman (April 13, 2023), "New Planet-Hunting Technique Finds Worlds We Can See Directly", Scientific American
| 2022 in space | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space probe launches |
|   | |||
| Impact events | |||||
| Selected NEOs | |||||
| Discoveries |
| ||||
| Comets | |||||
| Space exploration | |||||