| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "High Alps" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2021) |


The High Alps are the parts of the Alps unsuitable for habitation or seasonal transhumance. This includes all regions higher than 3,000 m above sea level, as well as most regions between 2,500 m and 3,000 m (Juf at 2,126 m is the highest permanently inhabited village in the Alps). Alpine pastures are typically below 2,400 m but may exceptionally be located as high as 2,800 m.
The High Alps have tundra or ice cap climate rather than the Alpine climate eponymous of the Alpine region at 1,800-2,500 m, above the tree-line but still amenable to transhumance economy.
Exploration of the High Alps began in the 18th century, with Horace-Bénédict de Saussure. The first ascent of the highest peak of the Alps, Mont Blanc, dates to 1786.
All important mountain passes in Switzerland are below 2,500 m (with Nufenen Pass as high as 2,478 m) but there are a few minor foot passes above 3,000 m: Schöllijoch at 3,343 m, Theodul Pass at 3,301 m, Zwischbergen Pass at 3,268 m, and others. Of historical interest is the Schnidejoch at 2,756 m which appears to have served as a pass since prehistoric times. In other Alpine countries there are higher road passes, such as the Col de l'Iseran (the highest paved road in Europe) in France and the Stelvio Pass in Italy.
The alpine line of perpetual snow is not fixed. The occurrence of favorable meteorological conditions during several successive seasons can increase the extent of the snowfields and lower the limit of seemingly permanent snow, while the opposite may cause the limit to rise higher on the flanks of the mountains. In some parts of the Alps the limit is about 2,400 m elevation, while in others it cannot be placed much below 2,900 m. As very little snow remains on rocks angled more than 60°, this is soon removed by the wind, some steep masses of rock remain bare even near the summits of the highest peaks, but as almost every spot offering the least hold for vegetation is covered with snow, few flowering plants are seen above 3,350 m.
The climate of the glacial region has often been compared to that of the polar regions, but they are very different. Here, intense solar radiation by day, which raises the surface when dry to a temperature approaching 27°C, alternates with severe frost by night. There, the Sun, which never sets is only able to send feeble rays that maintain a low temperature, rarely rising more than a few degrees above the freezing point. Hence the upper region of the Alps sustains a far more varied and brilliant vegetation.
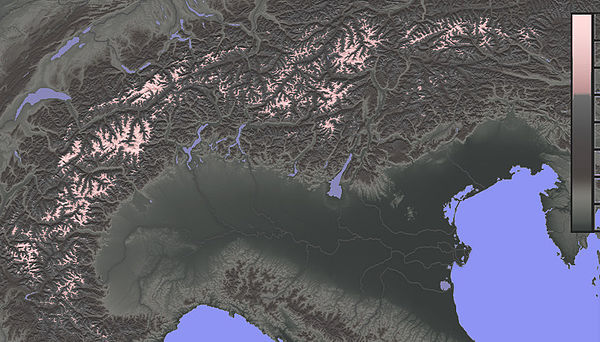
| Relief map of the Alps with altitudes above 2,500 m highlighted |
 Bernese Alps
Cottian Alps
Central Eastern Alps
Graian Alps
Dauphiné Alps
Glarus Alps
Pennine Alps
Lepontine Alps
Maritime Alps
Bernese Alps
Cottian Alps
Central Eastern Alps
Graian Alps
Dauphiné Alps
Glarus Alps
Pennine Alps
Lepontine Alps
Maritime Alps
|
See also
- Alpine foothills
- Climate of the Alps
- Geography of the Alps
- Main chain of the Alps
- Retreat of glaciers since 1850
- List of glaciers in Switzerland
- Altitudinal zonation
- High mountain tour
- White War (fighting in the high-altitude Alpine sector of the Italian front during the First World War between Kingdom of Italy and Austria-Hungary)
- List of Alpine four-thousanders
- List of mountains of the Alps above 3000 m
- List of mountains of the Alps (2500–2999 m)
- Category:Alpine three-thousanders
References
- The alp of Bréona (Valais) is among the highest, with buildings at 2,435 m and pastures reaching as high as 2,800 m.