| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Hypocycloid" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

In geometry, a hypocycloid is a special plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls within a larger circle. As the radius of the larger circle is increased, the hypocycloid becomes more like the cycloid created by rolling a circle on a line.
History
The 2-cusped hypocycloid called Tusi couple was first described by the 13th-century Persian astronomer and mathematician Nasir al-Din al-Tusi in Tahrir al-Majisti (Commentary on the Almagest). German painter and German Renaissance theorist Albrecht Dürer described epitrochoids in 1525, and later Roemer and Bernoulli concentrated on some specific hypocycloids, like the astroid, in 1674 and 1691, respectively.
Properties
If the smaller circle has radius r, and the larger circle has radius R = kr, then the parametric equations for the curve can be given by either: or:
If k is an integer, then the curve is closed, and has k cusps (i.e., sharp corners, where the curve is not differentiable). Specially for k = 2 the curve is a straight line and the circles are called Tusi Couple. Nasir al-Din al-Tusi was the first to describe these hypocycloids and their applications to high-speed printing.
If k is a rational number, say k = p/q expressed in simplest terms, then the curve has p cusps.
If k is an irrational number, then the curve never closes, and fills the space between the larger circle and a circle of radius R − 2r.
Each hypocycloid (for any value of r) is a brachistochrone for the gravitational potential inside a homogeneous sphere of radius R.
The area enclosed by a hypocycloid is given by:
The arc length of a hypocycloid is given by:
Examples
- Hypocycloid Examples
-
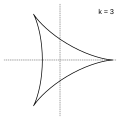 k=3 → a deltoid
k=3 → a deltoid
-
 k=4 → an astroid
k=4 → an astroid
-
 k=5 → a pentoid
k=5 → a pentoid
-
 k=6 → an exoid
k=6 → an exoid
-
 k=2.1 = 21/10
k=2.1 = 21/10
-
 k=3.8 = 19/5
k=3.8 = 19/5
-
 k=5.5 = 11/2
k=5.5 = 11/2
-
 k=7.2 = 36/5
k=7.2 = 36/5
The hypocycloid is a special kind of hypotrochoid, which is a particular kind of roulette.
A hypocycloid with three cusps is known as a deltoid.
A hypocycloid curve with four cusps is known as an astroid.
The hypocycloid with two "cusps" is a degenerate but still very interesting case, known as the Tusi couple.
Relationship to group theory

Any hypocycloid with an integral value of k, and thus k cusps, can move snugly inside another hypocycloid with k+1 cusps, such that the points of the smaller hypocycloid will always be in contact with the larger. This motion looks like 'rolling', though it is not technically rolling in the sense of classical mechanics, since it involves slipping.
Hypocycloid shapes can be related to special unitary groups, denoted SU(k), which consist of k × k unitary matrices with determinant 1. For example, the allowed values of the sum of diagonal entries for a matrix in SU(3), are precisely the points in the complex plane lying inside a hypocycloid of three cusps (a deltoid). Likewise, summing the diagonal entries of SU(4) matrices gives points inside an astroid, and so on.
Thanks to this result, one can use the fact that SU(k) fits inside SU(k+1) as a subgroup to prove that an epicycloid with k cusps moves snugly inside one with k+1 cusps.
Derived curves
The evolute of a hypocycloid is an enlarged version of the hypocycloid itself, while the involute of a hypocycloid is a reduced copy of itself.
The pedal of a hypocycloid with pole at the center of the hypocycloid is a rose curve.
The isoptic of a hypocycloid is a hypocycloid.
Hypocycloids in popular culture

Curves similar to hypocycloids can be drawn with the Spirograph toy. Specifically, the Spirograph can draw hypotrochoids and epitrochoids.
The Pittsburgh Steelers' logo, which is based on the Steelmark, includes three astroids (hypocycloids of four cusps). In his weekly NFL.com column "Tuesday Morning Quarterback," Gregg Easterbrook often refers to the Steelers as the Hypocycloids. Chilean soccer team CD Huachipato based their crest on the Steelers' logo, and as such features hypocycloids.
The first Drew Carey season of The Price Is Right's set features astroids on the three main doors, giant price tag, and the turntable area. The astroids on the doors and turntable were removed when the show switched to high definition broadcasts starting in 2008, and only the giant price tag prop still features them today.
See also
- Roulette (curve)
- Special cases: Tusi couple, Astroid, Deltoid
- List of periodic functions
- Cyclogon
- Epicycloid
- Hypotrochoid
- Epitrochoid
- Spirograph
- Flag of Portland, Oregon, featuring a hypocycloid
- Murray's Hypocycloidal Engine, utilising a tusi couple as a substitute for a crank
References
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Tusi Couple". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2023-02-27.
- Blake, Stephen P. (2016-04-08). Astronomy and Astrology in the Islamic World. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-4911-2.
- ^ "Area Enclosed by a General Hypocycloid" (PDF). Geometry Expressions. Retrieved Jan 12, 2019.
- White, G. (1988), "Epicyclic gears applied to early steam engines", Mechanism and Machine Theory, 23 (1): 25–37, doi:10.1016/0094-114X(88)90006-7,
Early experience demonstrated that the hypocycloidal mechanism was structurally unsuited to transmitting the large forces developed by the piston of a steam engine. But the mechanism had shown its ability to convert linear motion to rotary motion and so found alternative low-load applications such as the drive for printing machines and sewing machines.
- Šír, Zbyněk; Bastl, Bohumír; Lávička, Miroslav (2010), "Hermite interpolation by hypocycloids and epicycloids with rational offsets", Computer Aided Geometric Design, 27 (5): 405–417, doi:10.1016/j.cagd.2010.02.001,
G. Cardano was the first to describe applications of hypocycloids in the technology of high-speed printing press (1570).
- Rana, Narayan Chandra; Joag, Pramod Sharadchandra (2001), "7.5 Barchistochrones and tautochrones inside a gravitating homogeneous sphere", Classical Mechanics, Tata McGraw-Hill, pp. 230–2, ISBN 0-07-460315-9
- ^ "Hypocycloid". Wolfram Mathworld. Retrieved Jan 16, 2019.
- Baez, John. "Deltoid Rolling Inside Astroid". AMS Blogs. American Mathematical Society. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- Baez, John (3 December 2013). "Rolling hypocycloids". Azimuth blog. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hypocycloid Evolute". MathWorld. Wolfram Research.
- Keller, Joel (21 August 2007). "A glimpse at Drew Carey's Price is Right". TV Squad. Archived from the original on 27 May 2010.
- Trombold, John; Donahue, Peter, eds. (2006), Reading Portland: The City in Prose, Oregon Historical Society Press, p. xvi, ISBN 9780295986777,
At the center of the flag lies a star — technically, a hypocycloid — which represents the city at the confluence of the two rivers.
Further reading
- J. Dennis Lawrence (1972). A catalog of special plane curves. Dover Publications. pp. 168, 171–173. ISBN 0-486-60288-5.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hypocycloid". MathWorld.
- "Hypocycloid", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Hypocycloid", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- A free Javascript tool for generating Hypocyloid curves
- Animation of Epicycloids, Pericycloids and Hypocycloids
- Plot Hypcycloid — GeoFun
- Snyder, John. "Sphere with Tunnel Brachistochrone". Wolfram Demonstrations Project. Iterative demonstration showing the brachistochrone property of Hypocycloid
 or:
or:


