| This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the article and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Pulmonary consolidation" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2019) |  |
| Pulmonary consolidation | |
|---|---|
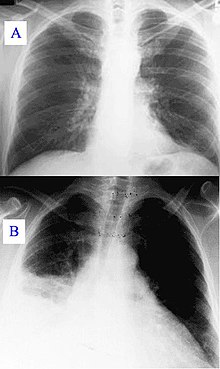 | |
| Pneumonia as seen on chest X-ray. A: Normal chest X-ray. B: Abnormal chest X-ray with consolidation from pneumonia in the right lung, middle or inferior lobe (white area, left side of image). | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. The condition is marked by induration (swelling or hardening of normally soft tissue) of a normally aerated lung. It is considered a radiologic sign. Consolidation occurs through accumulation of inflammatory cellular exudate in the alveoli and adjoining ducts. The liquid can be pulmonary edema, inflammatory exudate, pus, inhaled water, or blood (from bronchial tree or hemorrhage from a pulmonary artery). Consolidation must be present to diagnose pneumonia: the signs of lobar pneumonia are characteristic and clinically referred to as consolidation.
Signs
Signs that consolidation may have occurred include:
- Expansion of the thorax on inspiration is reduced on the affected side
- Vocal fremitus is increased on the affected side
- Percussion note is impaired in the affected area
- Breath sounds are bronchial
- Possible medium, late, or pan-inspiratory crackles
- Vocal resonance is increased. Here, the patient's voice (or whisper, as in whispered pectoriloquy) can be heard more clearly when there is consolidation, as opposed to the healthy lung where speech sounds muffled.
- A pleural rub may be present.
- A lower PAO2 than calculated in the alveolar gas equation
Diagnosis
Radiology
- Typically, an area of white lung is seen on a standard X-ray. Consolidated tissue is more radio-opaque than normally aerated lung parenchyma, so that it is clearly demonstrable in radiography and on CT scans. Consolidation is often a middle-to-late stage feature/complication in pulmonary infections.
See also
References
- "Consolidation – Definition". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- "Induration- Definition". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- Metlay JP, Kapoor WN, Fine MJ (1997). "Does this patient have community-acquired pneumonia? Diagnosing pneumonia by history and physical examination". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 278 (17): 1440–5. doi:10.1001/jama.278.17.1440. PMID 9356004.
- Talley, Nicholas Joseph (2001). Clinical Examination, a Clinical Guide to Physical Diagnosis, Wiley, 4th ed., p. 121, ISBN 0632059710.
- Corne, Jonathan; Carroll, Mary; Delany, David (2002). Chest X-Ray Made Easy. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-07008-2.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
| Diseases of the respiratory system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT (including URTIs, common cold) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower RT/ lung disease (including LRTIs) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural cavity/ mediastinum |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/general | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiologic signs | |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | |
| Respiratory | |
| Urogenital | |
| Musculoskeletal | |
| Gastrointestinal | |
| Neurological | |