| Pentagonal pyramidal molecular geometry | |
|---|---|
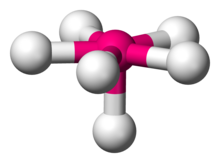 | |
| Examples | XeOF 5 |
| Point group | C5v |
| Coordination number | 6 |
| Bond angle(s) | 90°, 72° |
| μ (Polarity) | >0 |
In chemistry, pentagonal pyramidal molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where in six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands are arranged around a central atom, at the vertices of a pentagonal pyramid. It is one of the few molecular geometries with uneven bond angles.
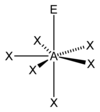
Examples
- XeOF
5 - IOF
5
References
- Baran, Enrique J. (2008). "Mean amplitudes of vibration of molecules and ions with interhalogen bonds and related species". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 129 (11): 1060–1072. Bibcode:2008JFluC.129.1060B. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2008.06.016.
- ^ Baran, E. (2000). "Mean amplitudes of vibration of the pentagonal pyramidal XeOF
5 and IOF
5 anions". J. Fluorine Chem. 101: 61–63. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(99)00194-3. - Housecroft, Catherine E.; Sharpe, Alan G. (2005). Inorganic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Pearson Prentice-Hall. p. 485. ISBN 0130-39913-2.
Pentagonal pyramid, Wolfram MathWorld
| Molecular geometry | |
|---|---|
| Coordination number 2 | |
| Coordination number 3 | |
| Coordination number 4 | |
| Coordination number 5 | |
| Coordination number 6 | |
| Coordination number 7 | |
| Coordination number 8 | |
| Coordination number 9 | |
This stereochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |