| This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (August 2023) |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (S)-(+)-4,12-Bis(diphenylphosphino)--paracyclophane; (R)-(−)-4,12-Bis(diphenylphosphino)--paracyclophane | |
| Other names (S)-Phanephos; (R)-Phanephos | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.129 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C40H34P2 |
| Molar mass | 576.660 g·mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder or crystals |
| Melting point | 222 to 225 °C (432 to 437 °F; 495 to 498 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Phanephos is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (C2H4)2(C6H3PPh2)2 (Ph = C6H5). It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an example of a chiral C2-symmetric diphosphine ligand used in asymmetric hydrogenation. Many substituents have been introduced in place of the phenyl groups, e.g., i-Pr, C6H11, etc. and a variety of chiral diphosphine ligands have been reported in asymmetric catalysis since the 1960s.
Preparation
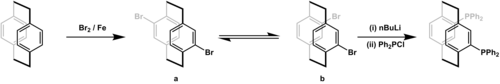
Phanephos can be prepared in two steps from paracyclophane. In the first step, paracyclophane is dibrominated to give a pseudo-para dibromide. Thermal isomerisation then gives pseudo-ortho atropisomer of the dibromide. This isomer is subjected to lithium-halogen exchange by nBuLi and the resulting dilithium compound is treated with PPh2Cl to give a racemic mixture of phanephos.
Uses
Phanephos has been used in rhodium- and ruthenium- mediated stereoselective hydrogenation of dehydro amino acid methyl esters and asymmetric reduction of various β-ketoesters with about 90% ee.
References
- G. J. Rowlands, Planar Chiral Phosphines Derived from Paracyclophane , Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 52. 60-75, doi:10.1002/ijch.201100098
- R. Gleiter, H. Hopf, Modern Cyclophane Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2005, p.449-451 doi:10.1002/3527603964