 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Potassium peroxide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.339 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | K2O2 |
| Molar mass | 110.196 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow amorphous solid |
| Melting point | 490 °C (914 °F; 763 K) |
| Solubility in water | reacts with water |
| Structure | |
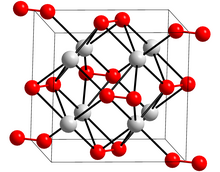
| Crystal structure | Orthorhombic |
| Space group | Cmca, oS16 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
113 J·mol·K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−496 kJ·mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H272, H315, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P220, P221, P264, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 OX |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Potassium chloride |
| Other cations | Lithium peroxide Sodium peroxide Rubidium peroxide Caesium peroxide |
| Related potassium oxides | Potassium oxide Potassium superoxide Potassium ozonide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula K2O2. It is formed as potassium reacts with oxygen in the air, along with potassium oxide (K2O) and potassium superoxide (KO2).
Potassium peroxide reacts with water to form potassium hydroxide and oxygen:
- 2 K2O2 + 2 H2O → 4 KOH + O2 ↑
Properties
Potassium peroxide is a highly reactive, oxidizing white to yellowish solid which, while not flammable itself, reacts violently with flammable materials. It decomposes violently on contact with water.
The standard enthalpy of formation of potassium peroxide is ΔH f 0 = −496 kJ/mol.
Usage
Potassium peroxide is used as an oxidizing agent and bleach (due to the peroxide), and to purify air.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 477, 520. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A22. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
| Potassium compounds | |
|---|---|
| H, (pseudo)halogens | |
| chalcogens | |
| pnictogens | |
| B, C group | |
| transition metals | |
| organic | |