 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name -(4→6)- | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,2′R,3R,3′R,4S)-2,2′-Bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,3′,4,4′-tetrahydro-2H,2′H--3,3′,5,5′,7,7′-hexol | |
| Other names Procyanidin B5 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C30H26O12 |
| Molar mass | 578.52 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
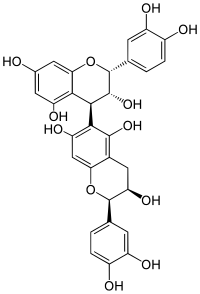
Procyanidin B5 is a B type proanthocyanidin.
Procyanidin B5 is an epicatechin-(4β → 6)-epicatechin dimer.
Natural occurrences
It can be found in grape seeds, in Hibiscus cannabinus (kenaf) root and bark, and in black chokeberries (Aronia melanocarpa).
- Presence in food
It is found in cocoa beans and chocolate.
References
- Ricardo Da Silva, Jorge M.; Rigaud, Jacques; Cheynier, Véronique; Cheminat, Annie; Moutounet, Michel (January 1991). "Procyanidin dimers and trimers from grape seeds". Phytochemistry. 30 (4): 1259–1264. Bibcode:1991PChem..30.1259R. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)95213-0.
- Van Tkhin', Fam; Makhsudova, B.; Otroshchenko, O. S. (1982). "Dimeric proanthocyanidins ofHibiscus cannabinus". Chemistry of Natural Compounds. 18 (3): 310–314. Bibcode:1982CNatC..18..310V. doi:10.1007/BF00580458.
- Esatbeyoglu, Tuba; Winterhalter, Peter (2010). "Preparation of Dimeric Procyanidins B1, B2, B5, and B7 from a Polymeric Procyanidin Fraction of Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa)". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 58 (8): 5147–5153. doi:10.1021/jf904354n. PMID 20196608.
- Esatbeyoglu, Tuba; Wray, Victor; Winterhalter, Peter (2015). "Isolation of dimeric, trimeric, tetrameric and pentameric procyanidins from unroasted cocoa beans (Theobroma cacao L.) using countercurrent chromatography". Food Chemistry. 179: 278–289. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.130. hdl:10033/346408. PMID 25722166.
- Cooper, Karen A.; Campos-Giménez, Esther; Jiménez Alvarez, Diego; Nagy, Kornél; Donovan, Jennifer L.; Williamson, Gary (2007). "Rapid Reversed Phase Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of the Major Cocoa Polyphenols and Inter-relationships of Their Concentrations in Chocolate". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 55 (8): 2841–2847. doi:10.1021/jf063277c. PMID 17362030.
| Types of procyanidins | |
|---|---|
| A-type proanthocyanidins |
|
| B type proanthocyanidins |
|
| Types | |
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |