| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Administrative divisions of Iceland" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Icelandic. (January 2022) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| Politics of Iceland |
|---|
 |
|
Government
|
|
Legislature
|
|
Executive |
| Judiciary |
|
Elections
|
| Political parties |
| Administrative divisions |
| Foreign relations |
|
|
This article shows the administrative divisions of Iceland.
Constituencies
Main article: Constituencies of Iceland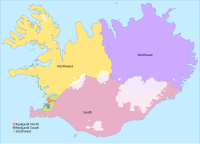
Until 2003, the constituencies for the parliament elections were the same as the regions, but by an amendment to the constitution they were changed to the current six constituencies. The change was made in order to balance the weight of different districts of the country since a vote cast in the sparsely populated areas around the country would count much more than a vote cast in the Capital Region. The imbalance between districts has been reduced by the new system, but still exists.
Regions
Main article: Regions of Iceland
There are eight regions which are primarily used for statistical purposes; the district court jurisdictions also use an older version of this division. Healthcare in Iceland is divided into 7 healthcare districts which correspond to the 8 regions of Iceland with the exception of the Northwestern Region and the Northeastern Region which are a single healthcare district.
Municipalities
Main article: Municipalities of Iceland
As of 2024, there are 63 municipalities in Iceland. These govern most local matters like kindergartens, primary schools, waste management, social services, public housing, public transport, services to senior citizens and to disabled people. They also govern zoning and can voluntarily take on additional functions if they have the budget for it. The autonomy of municipalities over their own matters is guaranteed by the constitution of Iceland.
Historical
Counties
Main article: Counties of Iceland
Historically, Iceland was divided into 23 counties. Currently, Iceland is split up amongst 24 sheriffs that represent government in various capacities. The jurisdiction of the Sheriff's Offices greatly resemble the historical county divisions. Amongst their duties are local police (except in Reykjavík, where there is a special office of police commissioner) tax collection, declaring bankruptcy and civil marriage.
Farthings
Main article: Farthings of Iceland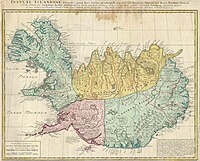
Historically, Iceland was divided into farthings that were named after the cardinal directions. These were administrative divisions established in 965 for the purpose of organising regional assemblies called farthing assemblies and for regional courts called quarter courts. Each farthing contained three local assemblies (held in spring and autumn) except the Norðlendingafjórðungur which had four.
References
- "Lýsigagnagátt". gatt.lmi.is. Retrieved 2024-11-22.
See also
- List of cities and towns in Iceland
- ISO 3166-2 codes of Iceland
- FIPS region codes of Iceland (standard withdrawn in 2008)
- NUTS of Iceland
- Subdivisions of the Nordic countries
| Iceland articles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
|  | |||||
| Geography |
| ||||||
| Politics | |||||||
| Economy | |||||||
| Society |
| ||||||
| Historical counties of Iceland | ||
|---|---|---|
| Capital Region | ||
| Southern Peninsula | ||
| Western Region | ||
| Westfjords | ||
| Northwestern Region | ||
| Northeastern Region | ||
| Eastern Region | ||
| Southern Region | ||