| Temporal fascia | |
|---|---|
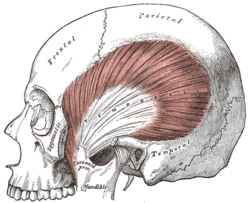 The temporalis; the zygomatic arch and masseter have been removed. The temporalis; the zygomatic arch and masseter have been removed. | |
 Muscles of the head, face, and neck. (Temporal fascia labeled at top center.) Muscles of the head, face, and neck. (Temporal fascia labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia temporalis |
| TA98 | A04.1.04.013 |
| TA2 | 2138 |
| FMA | 76863 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The temporal fascia (or deep temporal fascia) is a fascia of the head that covers the temporalis muscle and structures situated superior to the zygomatic arch.
The fascia is attached superiorly at the superior temporal line; inferiorly, it splits into two layers at the superior border of the zygomatic arch. The superficial layer then attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior border of the arch, and the deep layer to its medial aspect.
The space between the two layers is occupied by adipose tissue and contains a branch of the superficial temporal artery, and the zygomaticotemporal nerve.
Anatomy
The temporal fascia is a strong fibrous investment.
Structure
Superiorly, it is a single layer, attached to the entire extent of the superior temporal line.
Inferiorly, where it is fixed to the zygomatic arch, it consists of two layers, one of which is inserted into the lateral, and the other into the medial border of the arch.
Contents
A small quantity of fat, the orbital branch of the superficial temporal artery, and a filament from the zygomatic branch of the maxillary nerve, are contained between the two layers created by the inferior split of the fascia.
Attachments
The superficial fibers of the temporalis muscle attach onto the deep surface of the temporal fascia.
Relations
Superficial to the temporal fascia are the auricularis anterior muscle and superior auricular muscle, the galea aponeurotica and (part of) the orbicularis oculi muscle.
The superficial temporal vessels and the auriculotemporal nerve cross it inferoposteriorly.
The parotid fascia proceeds to the temporal fascia.
References
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- Fehrenbach, Margaret J.; Herring, Susan W. (2017). Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck (5th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. p. 266. ISBN 978-0-323-39634-9.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 386 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 386 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
| Muscles of the head | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraocular |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Masticatory |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Facial |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soft palate |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Tongue |
| ||||||||||||||||
This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |