| This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Tokyo Toden" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Tokyo Toden | |
|---|---|
 Toden cars crossing Toden cars crossing | |
| Overview | |
| Transit type | Tram |
| Number of lines | 1 |
| Line number | Arakawa Line |
| Number of stations | 30 |
| Daily ridership | 47,504 (2018) |
| Website | www |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 1903 (1903) |
| Operator(s) | Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation |
| Number of vehicles | |
| Technical | |
| System length | 12.2 km (7.6 mi) |
| Track gauge | 1,372 mm (4 ft 6 in) |
| Electrification | 600 DC (Overhead line) |
| Top speed | 40 km/h (25 mph) |
The Tokyo Toden (東京都電, Tōkyō Toden) or simply Toden, is the tram network of Tokyo, Japan. Of all its former routes, only one, the Tokyo Sakura Tram, remains in service. The Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation operates the Toden. The formal legal name is Tokyo-to Densha. Its nickname, "Toden," distinguished it from the "Kokuden" (the Japanese National Railways electrified lines).
The network had a track gauge of 1,372 mm (4 ft 6 in), except for the former Seibu Railway lines which were 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in).
History
At its peak, the Toden system boasted 41 routes with 213 kilometres (132 mi) of track. However, the increase in reliance on automobile traffic resulted in reductions in ridership, and from 1967 to 1972, 181 kilometres (112 mi) of track were abandoned as the Bureau changed its emphasis to bus and subway modes of transportation.
- 1903: The Tokyo Horse-drawn Railway changed its motive power to electricity and, under the name Tokyo Electric Railway (or Tōden, 東電) commenced operations between Shinagawa and Shimbashi.
- 1903: The Tokyo Urban Railway (or Gaitetsu, 街鉄) began operations between Sukiyabashi (in Ginza) and Kandabashi.
- 1904: The Tokyo Electric Railway (Sotobori Line) connecting Shimbashi Station and Ochanomizu opened.
- 1905: The three companies published the "Tokyo Geography Education Streetcar Song" to promote knowledge of the geography of Tokyo.
- 1906: The three companies merged to form the Tokyo Railways.
- 1911: Tokyo City purchased the Tokyo Railways, established its Electric Bureau, and inaugurated the Tokyo City Streetcar (東京市電) system.
- 1911–1922: The streetcar network expands, with various new companies and lines serving areas in the city and to the west.
- 1933: The route from Shinagawa Station to North Shinagawa Station is abandoned.
- 1933–1943: New companies, mergers, and realignments alter the network.
- 1943: Tokyo City is abolished and the larger Tokyo Prefecture assumes its administrative functions. The Tokyo City Streetcar bureau becomes the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation.
- 1944: Service is stopped on nine segments.
- 1945–1951: During the Occupation of Japan, the network evolved slowly.
- 1952: The segment of the Imai Line between Higashi-arakawa and Imaibashi Stations was replaced with trolley buses.
- 1953, 1961: Two segments (one in Shinjuku and the other connecting Shimbashi Station and Shiodome) stop operating.
- 1963: In preparation for the Tokyo Olympics, two segments (Kita-Aoyama Itchome – Miyakezaka and Hanzōmon – Kudanshita) cease operations. The Suginami Line (Shinjuku – Ogikubo) closes because it duplicates a line of the Eidan Subway.
- 1967–1972: A plan for financial restructuring is put into effect in seven stages, resulting in the closure of most of the network.
- 1974: A plan for abandoning the remaining track is cancelled. The remaining routes are consolidated into a single line, named the Arakawa Line.
- 1978: One-man operation begins.
- 1990: The 8500 Series rolling stock is introduced. It is the first new design in 28 years.
- 2000: A new station, Arakawa-itchūmae, opens between two existing stations.
- 2007: 9000 Series rolling stock was scheduled for introduction.
Former lines
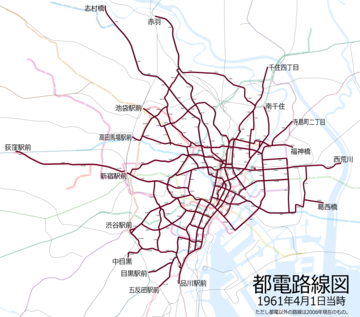
This is the list of former lines, listed according to their official names. Corresponding routes are those of 1962. The first section of the lines opened in the listed opening years, while the last section of the lines closed in the listed closing years.
| Line | Route(s) | Termini | Opened | Closed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tōkyō Electric Railway (Tōden) lines | |||||
| Azumabashi Line | 24 30 | Ueno-Ekimae – Honjo-Azumabashi | 1904 | 1972 | |
| Hondōri Line | 1 4 19 22 40 | Shimbashi – Sudachō | 1903 | 1971 | |
| Kanasugi Line | 1 4 | Mita – Shimbashi | 1903 | 1969 | |
| Kuramae Line | 22 31 | Kaminarimon – Asakusabashi | 1904 | 1971 | |
| Muromachi Line | 22 31 | Asakusabashi – Marunouchi-Itchōme | 1904 | 1971 | |
| Shinagawa Line | 1 3 7 | Kita-Shinagawa – Mita | 1903 | 1967 | Keihin Electric Railway trains (the present Keihin Electric Express Railway) operated over the Shinagawa–Kita-Shinagawa section |
| Ueno Line | 1 19 20 24 30 37 40 | Sudachō – Ueno-Ekimae | 1903 | 1972 | |
| Tōkyō Urban Railway lines | |||||
| Aoyama Line | 6 9 10 | Miyakezaka – Shibuya-Ekimae | c. 1904 | 1968 | |
| Bammachi Line | 10 | Hanzōmon – Kudanshita | c. 1905 | 1963 | |
| Chiyodabashi Line | 15 28 38 | Ōtemachi – Eitaibashi | c. 1904 | 1972 | |
| Edogawa Line | 15 39 | Kudanshita – Waseda | c. 1905 | 1968 | |
| Hamachō Line | Ningyōchō – Ryōgoku | c. 1904 | 1944 | ||
| Hanzōmon Line | 8 9 10 11 | Hibiya-Kōen – Hanzōmon | 1903 | 1968 | |
| Hongō Line | 19 | Circa Sudachō – Hakusan-ue | 1904 | 1971 | |
| Hōraibashi Line | Miharabashi – Hōraibashi | c. 1904 | c. 1909 | ||
| Ichigaya Line | 12 | c. 1905 | 1970 | ||
| Kandabashi Line | 2 5 15 25 35 37 | Hibiya-Kōen – Ogawamachi | 1903 | 1968 | |
| Kiridōshi Line | 16 39 | Bunkyō-Kuyakusho-mae – Ueno-Hirokōji | c. 1904 | 1971 | |
| Kōtōbashi Line | 25 29 38 | Ryōgoku-Nichōme – Kinshibori | c. 1905 | 1972 | |
| Kudan Line | 10 12 15 | Ogawamachi – Kudanshita | c. 1904 | 1970 | |
| Mita Line | 2 5 35 37 | Mita – Hibiya-Kōen | c. 1904 | 1968 | |
| Narihira Line | 16 23 24 | Midorichō-Itchōme – Fukujimbashi Narihirabashi – Asakusa-Ekimae (the present Tōbu Narihirabashi Station.) |
c. 1905 | 1972 | |
| Ryōgokubashi Line | 10 12 25 29 | Ogawamachi – Ryōgoku-Nichōme | 1903 | 1972 | |
| Shinjuku Line | 11 12 13 | Hanzōmon – Shinjuku-Ekimae | 1903 | 1970 | |
| Suzaki Line | 28 38 | Eitaibashi – Tōyō-Kōen-mae Fukushimabashi (Eitai-Nichōme) – Kamezumichō (Fukagawa-Itchōme) |
c. 1904 | 1972 | |
| Toranomon Line | 3 8 | Sakuradamon – Kamiyachō Toranomon – Reinanzaka |
c. 1905 | 1968 | |
| Tsukiji Line | 8 9 11 36 | Hibiya-Kōen – Kayabachō ( – Ningyōchō) | 1903 | 1971 | |
| Umayabashi Line | 16 39 | Ueno-Hirokōji – Honjo-Itchōme | c. 1905 | 1971 | |
| Tōkyō Electric Railway (Sotobori Line) lines | |||||
| Dobashi Line | 17 | Shin-Tokiwabashi – Shimbashi-eki-Kitaguchi | c. 1904 | 1968 | |
| Hiroo Line | 7 | Aoyama-Itchōme – Tengenjibashi | c. 1905 | 1969 | |
| Hōraibashi Line | 6 | Miharabashi – Toranomon | c. 1905 | 1967 | |
| Nishikichō Line | Ochanomizu – Shin-Tokiwabashi | c. 1904 | 1944 | ||
| Ochanomizu Line | 13 19 | Iidabashi – Akihabara-eki-Higashiguchi | c. 1905 | 1971 | |
| Shinanomachi Line | 7 33 | Yotsuya-Sanchōme – Kita-Aoyama-Itchōme | c. 1905 | 1969 | |
| Tameike Line | 3 6 | Toranomon – Yotsuya-Mitsuke | c. 1905 | 1967 | |
| Ushigome Line | 3 12 | Yotsuya-Mitsuke – Iidabashi | c. 1905 | 1970 | |
| Tōkyō Railways lines | |||||
| Furukawa Line | 4 5 7 8 34 | Tengenjibashi – Kanasugibashi | c. 1910 | 1969 | tracks were in a center median near Ichinohashi |
| Hakusan Line | 2 18 35 | Bunkyō-Kuyakusho-mae – Hakusan-ue | c. 1910 | 1968 | |
| Izumibashi Line | 13 21 | Doshūbashi – Ueno-Ekimae | c. 1910 | 1970 | tracks were in a center median on Shōwa Street near Ueno Station |
| Minowa Line | 21 31 | c. 1910 | 1969 | ||
| Ōtsuka Line | 16 17 | Denzūin-mae – Ōtsuka-Ekimae | c. 1910 | 1971 | |
| Senju Line | 22 | Komagata-Nichōme – Minami-Senju | c. 1910 | 1971 | |
| Sugamo Line | 2 18 35 | Hakusan-ue – Sugamo-Shako-mae | c. 1910 | 1968 | |
| Suidōbashi Line | 2 17 18 35 | Shin-Tokiwabashi – Bunkyō-Kuyakusho-mae | c. 1910 | 1968 | |
| Takahashi Line | 23 | Monzen-Nakachō – Midorichō-Itchōme | c. 1910 | 1972 | |
| Tomisaka Line | 16 17 39 | Ōmagari – Bunkyō-Kuyakusho-mae | c. 1910 | 1971 | |
| Ōji Electric Tramway lines | |||||
| Akabane Line | 27 | Ōji-Ekimae – Akabane | 1926 | 1972 | |
| Arakawa Line | 27 32 | Kumanomae – Ōji-Ekimae | 1913 | still open | present Arakawa Line |
| Mikawashima Line | 27 | Minowabashi – Kumanomae | 1913 | still open | present Arakawa Line |
| Takinogawa Line | 32 | Ōji-Ekimae – Ōtsuka-Ekimae | 1911 | still open | present Arakawa Line |
| Waseda Line | 32 | Ōtsuka-Ekimae – Waseda | 1925 | still open | present Arakawa Line |
| Jōtō Electric Tramway lines | |||||
| Ichinoe Line | 26 | Higashi-Arakawa – Imaibashi | 1925 | 1952 | commonly called Imai Line; an isolated line with no connection stations to other lines in the network |
| Komatsugawa Line | 25 29 38 | Kinshibori – Nishi-Arakawa | 1917 | 1972 | tracks were in a center median on Keiyō Road near Kameido Station |
| Sunamachi Line | 29 38 | Suijimmori – Suzaki | 1921 | 1972 | |
| Tamagawa Electric Railway lines | |||||
| Naka-Meguro Line | 8 | Shibuyabashi – Naka-Meguro | 1927 | 1967 | |
| Tengenjibashi Line | 8 34 | Shibuya-Ekimae – Tengenjibashi | 1921 | 1969 | |
| the former Seibu Railway lines | |||||
| Kōenji Line | 14 | Shinjuku-Ekimae – Kōenji-Itchōme | 1921 | 1963 | commonly called Suginami Line |
| Ogikubo Line | 14 | Kōenji-Itchōme – Ogikubo-Ekimae | 1921 | 1963 | commonly called Suginami Line |
| Other | |||||
| Asukayama Line | 19 | Komagome-Ekimae – Asukayama | c. 1920 | 1971 | |
| Awajimachi Line | 37 | Awajimachi – Soto-Kanda-Sanchōme | c. 1920 | 1967 | |
| Dōzaka Line | 20 37 40 | Ueno-Kōen – Sengoku-Itchōme | late 1910s | 1971 | private right-of-way between Ueno-Kōen-mae and Nezu-Itchōme, beside Shinobazu Pond |
| Ebisu Line | Tengenjibashi – Ebisu-Chōjamaru | 1913 | 1944 | also called Toyosawa Line or Tengenji Line | |
| Fudanotsuji Line | 3 8 | Iikura-Itchōme – Fudanotsuji | c. 1912 | 1967 | |
| Gokokuji Line | 17 20 | Sengoku-Itchōme – Gokokuji-mae | c. 1920 | 1971 | |
| Gotanda Line | 4 | Seishōkō-mae – Gotanda-Ekimae | late 1920s | 1967 | |
| Hatchōbori Line | 5 | Baba-Sakimon – Eitaibashi | c. 1920 | 1967 | |
| Ikebukuro Line | 17 | Gokokuji-mae – Ikebukuro-Ekimae | early 1930s | 1969 | |
| Isarago Line | 4 5 7 | Furukawabashi – Sengakuji | c. 1912 | 1969 | |
| Ishiwara Line | 16 | Ishiwarachō-Itchōme – Kinshichō-Ekimae (Kitaguchi) Taiheichō-Sanchōme – Kameido-Tenjimbashi |
late 1920s | 1971 | |
| Itabashi Line | 18 41 | Sugamo-Shako-mae – Itabashi-Ekimae | late 1920s | 1966 | sometimes included with the Shimura Line |
| Kachidokibashi Line | 11 | Tsukiji-Tsukishima | 1947 | 1968 | |
| Kasaibashi Line | 29 | Sakaigawa – Kasaibashi | early 1940s | 1972 | |
| Kasumichō Line | 6 | Tameike – Minami-Aoyama-Gochōme | late 1910s | 1967 | |
| Kita-Senju Line | 21 | Senju-Ōhashi – Senju-Yonchōme | late 1920s | 1968 | |
| Komagome Line | 19 | Mukōgaoka-Nichōme – Komagome-Ekimae | late 1910s | 1971 | |
| Marunouchi Line | 28 31 | Marunouchi-Itchōme – Tochō-mae | c. 1920 | 1969 | |
| Meguro Line | 4 5 | Gyoranzaka-shita – Meguro-Ekimae | c. 1912 | 1967 | |
| Mukōjima Line | 30 | Honjo-Azumabashi – Higashi-Mukōjima-Nichōme | late 1920s | 1969 | |
| Otowa Line | 20 | Gokokuji-mae – Yaraishita | late 1920s | 1971 | |
| Roppongi Line | 3 8 33 | Hamamatsuchō-Itchōme – Kita-Aoyama-Itchōme | 1912 | 1969 | |
| Ryōgoku-eki Leading Line | 12 | Ryōgoku-Nichōme – Ryōgoku-Ekimae | 1923 | 1968 | |
| Sarue Line | 28 36 | Kinshichō-Ekimae (Minamiguchi) – Tōyō-Kōen-mae | late 1920s | 1972 | |
| Senzoku Line | 31 | Kuramae-Itchōme – Minowa-Shako-mae | c. 1920 | 1969 | |
| Shibaura Line | Tōkyō-Kōguchi – Shibaura-Nichōme | 1910 | 1969 | passenger service started in the 1920s | |
| Shimura Line | 18 41 | Itabashi-Ekimae – Shimurabashi | early 1940s | 1966 | |
| Shin-Ōhashi Line | 9 36 | Kayabachō – Sumiyoshichō-Nichōme | c. 1912 | 1971 | |
| Totsuka Line | 15 | Takadanobaba-Ekimae – Omokagebashi | ? | 1968 | opening year unknown |
| Tsukishima Line | 23 | Monzen-Nakachō – Tsukishima | c. 1920 | 1972 | |
| Tsunohazu Line | 13 | Iidabashi – Yotsuya-Sankōchō | c. 1912 | 1970 | |
Routes
As of 1962, there were 41 routes in operation; the maximum for the system:
| Nº | Terminus | via | Terminus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shinagawa-Ekimae | Shinagawa Line – Kanasugi Line – Hondōri Line – Ueno Line | Ueno-Ekimae |
| 2 | Mita | Mita Line – Kandabashi Line – Suidōbashi Line – Hakusan Line – Sugamo Line | Tōyō-Daigaku-mae |
| 3 | Shinagawa-Ekimae | Shinagawa Line – Fudanotsuji Line – Roppongi Line – Toranomon Line – Tameike Line – Ushigome Line | Iidabashi |
| 4 | Gotanda-Ekimae | Gotanda Line – Meguro Line – Isarago Line – Furukawa Line – Kanasugi Line – Hondōri Line | Ginza-Nichōme |
| 5 | Meguro-Ekimae | Meguro Line – Isarago Line – Furukawa Line – Mita Line – Kandabashi Line – Hatchōbori Line | Eitaibashi |
| 6 | Shibuya-Ekimae | Aoyama Line – Kasumichō Line – Tameike Line – Hōraibashi Line | Shimbashi |
| 7 | Yotsuya-Sanchōme | Shinanomachi Line – Hiroo Line – Furukawa Line – Isarago Line – Shinagawa Line | Shinagawa-Ekimae |
| 8 | Naka-Meguro | Naka-Meguro Line – Tengenjibashi Line – Furukawa Line – Fudanotsuji Line – Roppongi Line – Toranomon Line – Hanzōmon Line – Tsukiji Line | Tsukiji |
| 9 | Shibuya-Ekimae | Aoyama Line – Hanzōmon Line – Tsukiji Line – Shin-Ōhashi Line | Hamachō-Nakanohashi |
| 10 | Shibuya-Ekimae | Aoyama Line – Hanzōmon Line – Bammachi Line – Kudanshita Line – Ryōgokubashi Line | Sudachō |
| 11 | Shinjuku-Ekimae | Shinjuku Line – Hanzōmon Line – Tsukiji Line – Kachidokibashi Line | Tsukishima |
| 12 | Shinjuku-Ekimae | Shinjuku Line – Ushigome Line – Ichigaya Line – Kudan Line – Ryōgokubashi Line – Ryōgoku-eki Leading Line | Ryōgoku-Ekimae |
| 13 | Shinjuku-Ekimae | Shinjuku Line – Tsunohazu Line – Ochanomizu Line – Izumibashi Line | Suitengū-mae |
| 14 | Shinjuku-Ekimae | Kōenji Line – Ogikubo Line | Ogikubo-Ekimae |
| 15 | Takadanobaba-Ekimae | Totsuka Line – Waseda Line – Edogawa Line – Kudan Line – Kandabashi Line – Chiyodabashi Line | Kayabachō |
| 16 | Ōtsuka-Ekimae | Ōtsuka Line – Tomisaka Line – Kiridōshi Line – Umayabashi Line – Narihira Line – Ishiwara Line | Kinshichō-Ekimae |
| 17 | Ikebukuro-Ekimae | Ikebukuro Line – Gokokuji Line – Ōtsuka Line – Tomisaka Line – Suidōbashi Line – Dobashi Line | Sukiyabashi |
| 18 | Shimura-Sakaue | Shimura Line – Itabashi Line – Sugamo Line – Hakusan Line – Suidōbashi Line | Kandabashi |
| 19 | Ōji-Ekimae | Takinogawa Line – Asukayama Line – Komagome Line – Hongō Line – Ochanomizu Line – Ueno Line – Hondōri Line | Tōri-Sanchōme |
| 20 | Edogawabashi | Otowa Line – Gokokuji Line – Dōzaka Line – Ueno Line | Sudachō |
| 21 | Senju-Yonchōme | Kita-Senju Line – Minowa Line – Izumibashi Line | Suitengū-mae |
| 22 | Minami-Senju | Senju Line – Kuramae Line – Muromachi Line – Hondōri Line | Shimbashi |
| Kaminarimon | Kuramae Line – Muromachi Line – Hondōri Line (additional service) | Shimbashi | |
| 23 | Fukujimbashi | Narihira Line – Takahashi Line – Tsukishima Line | Tsukishima |
| 24 | Fukujimbashi | Narihira Line – Azumabashi Line – Ueno Line | Sudachō |
| 25 | Nishi-Arakawa | Komatsugawa Line – Kōtōbashi Line – Ryōgokubashi Line – Kandabashi Line | Hibiya-Kōen |
| 26 | Higashi-Arakawa | Ichinoe Line | Imaibashi |
| 27 | Minowabashi | Mikawashima Line – Arakawa Line – Akabane Line | Akabane |
| 28 | Kinshichō-Ekimae | Sarue Line – Suzaki Line – Chiyodabashi Line – Marunouchi Line | Tochō-mae |
| 29 | Kasaibashi | Kasaibashi Line – Sunamachi Line – Komatsugawa Line – Kōtōbashi Line – Ryōgokubashi Line | Sudachō |
| Kasaibashi | Kasaibashi Line – Sunamachi Line – Suzaki Line – Chiyodabashi Line (morning and evening only) | Nihombashi | |
| 30 | Higashi-Mukōjima-Nichōme | Mukōjima Line – Azumabashi Line – Ueno Line | Sudachō |
| 31 | Minowabashi | Mikawashima Line – Senzoku Line – Kuramae Line – Muromachi Line – Marunouchi Line | Tochō-mae |
| 32 | Arakawa-Shako-mae | Arakawa Line – Takinogawa Line – Waseda Line | Waseda |
| 33 | Yotsuya-Sanchōme | Shinanomachi Line – Roppongi Line | Hamamatsuchō-Itchōme |
| 34 | Shibuya-Ekimae | Tengenjibashi Line | Tengenjibashi |
| 35 | Sugamo-Shako-mae | Sugamo Line – Hakusan Line – Suidōbashi Line – Kandabashi Line – Mita Line | Nishi-Shimbashi-Itchōme |
| 36 | Kinshichō-Ekimae | Sarue Line – Shin-Ōhashi Line – Tsukiji Line | Tsukiji |
| 37 | Mita | Mita Line – Kandabashi Line – Ryōgokubashi Line – Awajichō Line – Ueno Line – Dōzaka Line | Sendagi-Nichōme |
| 38 | Kishinbori-Shako-mae | Kōtōbashi Line – Komatsugawa Line – Sunamachi Line – Suzaki Line – Chiyodabashi Line | Nihombashi |
| 39 | Waseda | Edogawa Line – Tomisaka Line – Kiridōshi Line – Umayabashi Line | Umayabashi |
| 40 | Shimmeichō-Shako-mae | Dōzaka Line – Ueno Line – Hondōri Line | Ginza-Nanachōme |
| 41 | Shimurabashi | Shimura Line – Itabashi Line | Sugamo-Shako-mae |
Note: Route 26 discontinued by 1952.
Categories: