This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

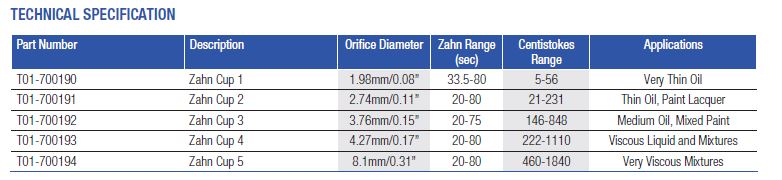
A Zahn cup is a viscosity measurement device used in the paint industry. It is commonly a stainless steel cup with a tiny hole drilled in the centre of the bottom of the cup. There is also a long handle attached to the sides. There are five cup specifications, labelled Zahn cup #x, where x is the number from one through five (see table below). Large number cup sizes are used when viscosity is high, while low number cup sizes are used when viscosity is low. They are manufactured in accordance to ASTM D 4212, ASTM D1084 and ASTM D816
To determine the viscosity of a liquid, the cup is dipped and completely filled with the substance. After lifting the cup out of the substance the user measures the time until the liquid streaming out of it breaks up, this is the corresponding "efflux time".
On paint standard specifications, one denotes viscosity in this manner: efflux time, Zahn cup number.
Conversion
One can convert efflux time to kinematic viscosity by using an equation for each cup specification number, where t is the efflux time and ν is the kinematic viscosity in centistokes.
- Zahn Cup #1: ν = 1.1(t − 29)
- Zahn Cup #2: ν = 3.5(t − 14)
- Zahn Cup #3: ν = 11.7(t − 7.5)
- Zahn Cup #4: ν = 14.8(t − 5)
- Zahn Cup #5: ν = 23t
Note the above equations are for a Brookfield series of Zahn cups.
Gardco signature Zahn cups and Gardco EZ Zahn cups use different conversions.
Ascott Zahn Cups are based on measuring the Flow of liquid in seconds. Results should be reported in Zahn-Seconds at a specified temperature for a particular cup.
To convert Zahn-Seconds to centistokes, refer to ASTM D4212, D816, and D1084
Centistokes × Specific Gravity = Centipoise
See also
References
- "Gardco :: S90 Zahn Viscosity Cups".
- Ascott Zahn Cups. "Ascott Zahn Cups" (PDF). www.ascottshop.com.
- Patton, Temple C. (1979). Paint Flow and Pigment Dispersion (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN 0-471-03272-7.