This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Mhhossein (talk | contribs) at 13:45, 1 September 2015 (Undid revision 678907851 by Anders Feder (talk) the entire section is not going to be devoted to khamenei's decree.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:45, 1 September 2015 by Mhhossein (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 678907851 by Anders Feder (talk) the entire section is not going to be devoted to khamenei's decree.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) "A-bomb" redirects here. For other uses, see A-bomb (disambiguation).

| Nuclear weapons |
|---|
 |
| Background |
| Nuclear-armed states |
|
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion (thermonuclear weapon). Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission ("atomic") bomb test released the same amount of energy as approximately 20,000 tons of TNT (see Trinity (nuclear test)). The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released the same amount of energy as approximately 10,000,000 tons of TNT.
A thermonuclear weapon weighing little more than 2,400 pounds (1,100 kg) can produce an explosive force comparable to the detonation of more than 1.2 million tons (1.1 million tonnes) of TNT. A nuclear device no larger than traditional bombs can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Nuclear weapons are considered weapons of mass destruction, and their use and control have been a major focus of international relations policy since their debut.
Nuclear weapons have been used twice in nuclear warfare, both times by the United States against Japan near the end of World War II. On 6 August 1945, the U.S. Army Air Forces detonated a uranium gun-type fission bomb codenamed "Little Boy" over the Japanese city of Hiroshima; three days later, on 9 August, the U.S. Army Air Forces detonated a plutonium implosion-type fission bomb codenamed "Fat Man" over the Japanese city of Nagasaki. The bombings resulted in the deaths of approximately 200,000 civilians and military personnel from acute injuries sustained from the explosions. The ethics of the bombings and their role in Japan's surrender remain the subject of scholarly and popular debate.
Since the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, nuclear weapons have been detonated on over two thousand occasions for the purposes of testing and demonstration. Only a few nations possess such weapons or are suspected of seeking them. The only countries known to have detonated nuclear weapons—and acknowledge possessing them—are (chronologically by date of first test) the United States, the Soviet Union (succeeded as a nuclear power by Russia), the United Kingdom, France, the People's Republic of China, India, Pakistan, and North Korea. Israel is also believed to possess nuclear weapons, though it does not acknowledge having them. One state, South Africa, fabricated nuclear weapons in the past, but as its apartheid regime was coming to an end, it disassembled its arsenal, acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, and accepted full-scope international safeguards. The Federation of American Scientists estimated there were more than 17,000 nuclear warheads worldwide as of 2012, with around 4,300 of them considered "operational" (ready for immediate use).
Types
Main article: Nuclear weapon design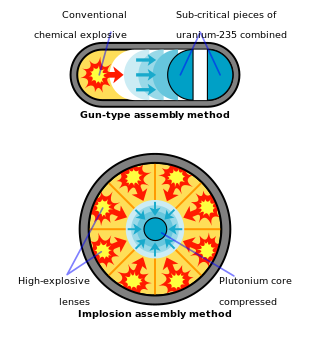
There are two basic types of nuclear weapons: those that derive the majority of their energy from nuclear fission reactions alone, and those that use fission reactions to begin nuclear fusion reactions that produce a large amount of the total energy output.
Fission weapons
All existing nuclear weapons derive some of their explosive energy from nuclear fission reactions. Weapons whose explosive output is exclusively from fission reactions are commonly referred to as atomic bombs or atom bombs (abbreviated as A-bombs). This has long been noted as something of a misnomer, as their energy comes from the nucleus of the atom, just as it does with fusion weapons.
In fission weapons, a mass of fissile material (enriched uranium or plutonium) is assembled into a supercritical mass—the amount of material needed to start an exponentially growing nuclear chain reaction—either by shooting one piece of sub-critical material into another (the "gun" method) or by compressing using explosive lenses a sub-critical sphere of material using chemical explosives to many times its original density (the "implosion" method). The latter approach is considered more sophisticated than the former and only the latter approach can be used if the fissile material is plutonium.
A major challenge in all nuclear weapon designs is to ensure that a significant fraction of the fuel is consumed before the weapon destroys itself. The amount of energy released by fission bombs can range from the equivalent of just under a ton of TNT, to upwards of 500,000 tons (500 kilotons) of TNT.
All fission reactions necessarily generate fission products, the radioactive remains of the atomic nuclei split by the fission reactions. Many fission products are either highly radioactive (but short-lived) or moderately radioactive (but long-lived), and as such are a serious form of radioactive contamination if not fully contained. Fission products are the principal radioactive component of nuclear fallout.
The most commonly used fissile materials for nuclear weapons applications have been uranium-235 and plutonium-239. Less commonly used has been uranium-233. Neptunium-237 and some isotopes of americium may be usable for nuclear explosives as well, but it is not clear that this has ever been implemented, and even their plausible use in nuclear weapons is a matter of scientific dispute.
Fusion weapons
Main article: Thermonuclear weapon
The other basic type of nuclear weapon produces a large proportion of its energy in nuclear fusion reactions. Such fusion weapons are generally referred to as thermonuclear weapons or more colloquially as hydrogen bombs (abbreviated as H-bombs), as they rely on fusion reactions between isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium). All such weapons derive a significant portion, and sometimes a majority, of their energy from fission. This is because a fission weapon is required as a "trigger" for the fusion reactions, and the fusion reactions can themselves trigger additional fission reactions.
Only six countries—United States, Russia, United Kingdom, People's Republic of China, France and India—have conducted thermonuclear weapon tests. (Whether India has detonated a "true", multi-staged thermonuclear weapon is controversial.) Thermonuclear weapons are considered much more difficult to successfully design and execute than primitive fission weapons. Almost all of the nuclear weapons deployed today use the thermonuclear design because it is more efficient.
Thermonuclear bombs work by using the energy of a fission bomb to compress and heat fusion fuel. In the Teller-Ulam design, which accounts for all multi-megaton yield hydrogen bombs, this is accomplished by placing a fission bomb and fusion fuel (tritium, deuterium, or lithium deuteride) in proximity within a special, radiation-reflecting container. When the fission bomb is detonated, gamma rays and X-rays emitted first compress the fusion fuel, then heat it to thermonuclear temperatures. The ensuing fusion reaction creates enormous numbers of high-speed neutrons, which can then induce fission in materials not normally prone to it, such as depleted uranium. Each of these components is known as a "stage", with the fission bomb as the "primary" and the fusion capsule as the "secondary". In large, megaton-range hydrogen bombs, about half of the yield comes from the final fissioning of depleted uranium.
Virtually all thermonuclear weapons deployed today use the "two-stage" design described above, but it is possible to add additional fusion stages—each stage igniting a larger amount of fusion fuel in the next stage. This technique can be used to construct thermonuclear weapons of arbitrarily large yield, in contrast to fission bombs, which are limited in their explosive force. The largest nuclear weapon ever detonated—the Tsar Bomba of the USSR, which released an energy equivalent of over 50 million tons (50 megatons) of TNT—was a three-stage weapon. Most thermonuclear weapons are considerably smaller than this, due to practical constraints from missile warhead space and weight requirements.

Fusion reactions do not create fission products, and thus contribute far less to the creation of nuclear fallout than fission reactions, but because all thermonuclear weapons contain at least one fission stage, and many high-yield thermonuclear devices have a final fission stage, thermonuclear weapons can generate at least as much nuclear fallout as fission-only weapons.
Other types
Main articles: boosted fission weapon, neutron bomb, and radiological bombThere are other types of nuclear weapons as well. For example, a boosted fission weapon is a fission bomb that increases its explosive yield through a small amount of fusion reactions, but it is not a fusion bomb. In the boosted bomb, the neutrons produced by the fusion reactions serve primarily to increase the efficiency of the fission bomb.
Some weapons are designed for special purposes; a neutron bomb is a thermonuclear weapon that yields a relatively small explosion but a relatively large amount of neutron radiation; such a device could theoretically be used to cause massive casualties while leaving infrastructure mostly intact and creating a minimal amount of fallout. The detonation of any nuclear weapon is accompanied by a blast of neutron radiation. Surrounding a nuclear weapon with suitable materials (such as cobalt or gold) creates a weapon known as a salted bomb. This device can produce exceptionally large quantities of radioactive contamination.
Research has been done into the possibility of pure fusion bombs: nuclear weapons that consist of fusion reactions without requiring a fission bomb to initiate them. Such a device might provide a simpler path to thermonuclear weapons than one that required development of fission weapons first, and pure fusion weapons would create significantly less nuclear fallout than other thermonuclear weapons, because they would not disperse fission products. In 1998, the United States Department of Energy divulged that the United States had, "...made a substantial investment" in the past to develop pure fusion weapons, but that, "The U.S. does not have and is not developing a pure fusion weapon", and that, "No credible design for a pure fusion weapon resulted from the DOE investment".
Most variation in nuclear weapon design is for the purpose of achieving different yields for different situations, and in manipulating design elements to attempt to minimize weapon size.
Antimatter, which consists of particles resembling ordinary matter particles in most of their properties but having opposite electric charge, has been considered as a trigger mechanism for nuclear weapons. A major obstacle is the difficulty of producing antimatter in large enough quantities, and there is no evidence that it is feasible beyond the military domain. However, the U.S. Air Force funded studies of the physics of antimatter in the Cold War, and began considering its possible use in weapons, not just as a trigger, but as the explosive itself. A fourth generation nuclear weapon design is related to, and relies upon, the same principle as Antimatter-catalyzed nuclear pulse propulsion.
Weapons delivery
See also: Nuclear weapons delivery, nuclear triad, Strategic bomber, Intercontinental ballistic missile, and Submarine-launched ballistic missile

Nuclear weapons delivery—the technology and systems used to bring a nuclear weapon to its target—is an important aspect of nuclear weapons relating both to nuclear weapon design and nuclear strategy. Additionally, development and maintenance of delivery options is among the most resource-intensive aspects of a nuclear weapons program: according to one estimate, deployment costs accounted for 57% of the total financial resources spent by the United States in relation to nuclear weapons since 1940.
Historically the first method of delivery, and the method used in the two nuclear weapons used in warfare, was as a gravity bomb, dropped from bomber aircraft. This is usually the first method that countries developed, as it does not place many restrictions on the size of the weapon and weapon miniaturization requires considerable weapons design knowledge. It does, however, limit attack range, response time to an impending attack, and the number of weapons that a country can field at the same time.
With the advent of miniaturization, nuclear bombs can be delivered by both strategic bombers and tactical fighter-bombers, allowing an air force to use its current fleet with little or no modification. This method may still be considered the primary means of nuclear weapons delivery; the majority of U.S. nuclear warheads, for example, are free-fall gravity bombs, namely the B61.

More preferable from a strategic point of view is a nuclear weapon mounted onto a missile, which can use a ballistic trajectory to deliver the warhead over the horizon. Although even short-range missiles allow for a faster and less vulnerable attack, the development of long-range intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) has given some nations the ability to plausibly deliver missiles anywhere on the globe with a high likelihood of success.
More advanced systems, such as multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), can launch multiple warheads at different targets from one missile, reducing the chance of a successful missile defense. Today, missiles are most common among systems designed for delivery of nuclear weapons. Making a warhead small enough to fit onto a missile, though, can be difficult.
Tactical weapons have involved the most variety of delivery types, including not only gravity bombs and missiles but also artillery shells, land mines, and nuclear depth charges and torpedoes for anti-submarine warfare. An atomic mortar was also tested at one time by the United States. Small, two-man portable tactical weapons (somewhat misleadingly referred to as suitcase bombs), such as the Special Atomic Demolition Munition, have been developed, although the difficulty of combining sufficient yield with portability limits their military utility.
Nuclear strategy
Main articles: Nuclear strategy and Deterrence theory See also: Nuclear peace, Essentials of Post–Cold War Deterrence, Single Integrated Operational Plan, nuclear warfare, and On Thermonuclear WarNuclear warfare strategy is a set of policies that deal with preventing or fighting a nuclear war. The policy of trying to prevent an attack by a nuclear weapon from another country by threatening nuclear retaliation is known as the strategy of nuclear deterrence. The goal in deterrence is to always maintain a second strike capability (the ability of a country to respond to a nuclear attack with one of its own) and potentially to strive for first strike status (the ability to completely destroy an enemy's nuclear forces before they could retaliate). During the Cold War, policy and military theorists in nuclear-enabled countries worked out models of what sorts of policies could prevent one from ever being attacked by a nuclear weapon, and developed weapon game theory models that create the greatest and most stable deterrence conditions.

Different forms of nuclear weapons delivery (see above) allow for different types of nuclear strategies. The goals of any strategy are generally to make it difficult for an enemy to launch a pre-emptive strike against the weapon system and difficult to defend against the delivery of the weapon during a potential conflict. Sometimes this has meant keeping the weapon locations hidden, such as deploying them on submarines or land mobile transporter erector launchers whose locations are very hard for an enemy to track, and other times, this means protecting them by burying them in hardened missile silo bunkers.
Other components of nuclear strategies have included using missile defense (to destroy the missiles before they land) or implementation of civil defense measures (using early-warning systems to evacuate citizens to safe areas before an attack).
Note that weapons designed to threaten large populations, or to generally deter attacks are known as strategic weapons. Weapons designed for use on a battlefield in military situations are called tactical weapons.
There are critics of the very idea of nuclear strategy for waging nuclear war who have suggested that a nuclear war between two nuclear powers would result in mutual annihilation. From this point of view, the significance of nuclear weapons is purely to deter war because any nuclear war would immediately escalate out of mutual distrust and fear, resulting in mutually assured destruction. This threat of national, if not global, destruction has been a strong motivation for anti-nuclear weapons activism.
Critics from the peace movement and within the military establishment have questioned the usefulness of such weapons in the current military climate. According to an advisory opinion issued by the International Court of Justice in 1996, the use of (or threat of use of) such weapons would generally be contrary to the rules of international law applicable in armed conflict, but the court did not reach an opinion as to whether or not the threat or use would be lawful in specific extreme circumstances such as if the survival of the state were at stake.
Another deterrence position in nuclear strategy is that nuclear proliferation can be desirable. This view argues that, unlike conventional weapons, nuclear weapons successfully deter all-out war between states, and they succeeded in doing this during the Cold War between the U.S. and the Soviet Union. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Gen. Pierre Marie Gallois of France, an adviser to Charles DeGaulle, argued in books like The Balance of Terror: Strategy for the Nuclear Age (1961) that mere possession of a nuclear arsenal, what the French called the force de frappe, was enough to ensure deterrence, and thus concluded that the spread of nuclear weapons could increase international stability. Some very prominent neo-realist scholars, such as the late Kenneth Waltz, formerly a Political Science at UC Berkeley and Adjunct Senior Research Scholar at Columbia University, and John Mearsheimer of University of Chicago, have also argued along the lines of Gallois. Specifically, these scholars have advocated some forms of nuclear proliferation, arguing that it would decrease the likelihood of total war, especially in troubled regions of the world where there exists a unipolar nuclear weapon state. Aside from the public opinion that opposes proliferation in any form, there are two schools of thought on the matter: those, like Mearsheimer, who favor selective proliferation, and those of Kenneth Waltz, who was somewhat more non-interventionist.
The threat of potentially suicidal terrorists possessing nuclear weapons (a form of nuclear terrorism) complicates the decision process. The prospect of mutually assured destruction may not deter an enemy who expects to die in the confrontation. Further, if the initial act is from a stateless terrorist instead of a sovereign nation, there is no fixed nation or fixed military targets to retaliate against. It has been argued by the New York Times, especially after the September 11, 2001 attacks, that this complication is the sign of the next age of nuclear strategy, distinct from the relative stability of the Cold War. In 1996, the United States adopted a policy of allowing the targeting of its nuclear weapons at terrorists armed with weapons of mass destruction.
Robert Gallucci, president of the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, argues that although traditional deterrence is not an effective approach toward terrorist groups bent on causing a nuclear catastrophe, Gallucci believes that “the United States should instead consider a policy of expanded deterrence, which focuses not solely on the would-be nuclear terrorists but on those states that may deliberately transfer or inadvertently lead nuclear weapons and materials to them. By threatening retaliation against those states, the United States may be able to deter that which it cannot physically prevent.”.
Graham Allison makes a similar case, arguing that the key to expanded deterrence is coming up with ways of tracing nuclear material to the country that forged the fissile material. “After a nuclear bomb detonates, nuclear forensics cops would collect debris samples and send them to a laboratory for radiological analysis. By identifying unique attributes of the fissile material, including its impurities and contaminants, one could trace the path back to its origin.” The process is analogous to identifying a criminal by fingerprints. “The goal would be twofold: first, to deter leaders of nuclear states from selling weapons to terrorists by holding them accountable for any use of their own weapons; second, to give leader every incentive to tightly secure their nuclear weapons and materials.”
Governance, control, and law
Main articles: Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, Strategic Arms Limitation Talks, Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, START I, Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty, Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty, and New START
Because of the immense military power they can confer, the political control of nuclear weapons has been a key issue for as long as they have existed; in most countries the use of nuclear force can only be authorized by the head of government or head of state.
In the late 1940s, lack of mutual trust was preventing the United States and the Soviet Union from making ground towards international arms control agreements. The Russell–Einstein Manifesto was issued in London on July 9, 1955 by Bertrand Russell in the midst of the Cold War. It highlighted the dangers posed by nuclear weapons and called for world leaders to seek peaceful resolutions to international conflict. The signatories included eleven pre-eminent intellectuals and scientists, including Albert Einstein, who signed it just days before his death on April 18, 1955. A few days after the release, philanthropist Cyrus S. Eaton offered to sponsor a conference—called for in the manifesto—in Pugwash, Nova Scotia, Eaton's birthplace. This conference was to be the first of the Pugwash Conferences on Science and World Affairs, held in July 1957.
By the 1960s steps were being taken to limit both the proliferation of nuclear weapons to other countries and the environmental effects of nuclear testing. The Partial Test Ban Treaty (1963) restricted all nuclear testing to underground nuclear testing, to prevent contamination from nuclear fallout, whereas the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (1968) attempted to place restrictions on the types of activities signatories could participate in, with the goal of allowing the transference of non-military nuclear technology to member countries without fear of proliferation.
In 1957, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was established under the mandate of the United Nations to encourage development of peaceful applications for nuclear technology, provide international safeguards against its misuse, and facilitate the application of safety measures in its use. In 1996, many nations signed the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty, which prohibits all testing of nuclear weapons. A testing ban imposes a significant hindrance to nuclear arms development by any complying country. The Treaty requires the ratification by 44 specific states before it can go into force; as of 2012, the ratification of eight of these states is still required.
Additional treaties and agreements have governed nuclear weapons stockpiles between the countries with the two largest stockpiles, the United States and the Soviet Union, and later between the United States and Russia. These include treaties such as SALT II (never ratified), START I (expired), INF, START II (never ratified), SORT, and New START, as well as non-binding agreements such as SALT I and the Presidential Nuclear Initiatives of 1991. Even when they did not enter into force, these agreements helped limit and later reduce the numbers and types of nuclear weapons between the United States and the Soviet Union/Russia.
Nuclear weapons have also been opposed by agreements between countries. Many nations have been declared Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zones, areas where nuclear weapons production and deployment are prohibited, through the use of treaties. The Treaty of Tlatelolco (1967) prohibited any production or deployment of nuclear weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean, and the Treaty of Pelindaba (1964) prohibits nuclear weapons in many African countries. As recently as 2006 a Central Asian Nuclear Weapon Free Zone was established amongst the former Soviet republics of Central Asia prohibiting nuclear weapons.
In the middle of 1996, the International Court of Justice, the highest court of the United Nations, issued an Advisory Opinion concerned with the "Legality of the Threat or Use of Nuclear Weapons". The court ruled that the use or threat of use of nuclear weapons would violate various articles of international law, including the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions, the UN Charter, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. In view of the unique, destructive characteristics of nuclear weapons, the International Committee of the Red Cross calls on States to ensure that these weapons are never used, irrespective of whether they consider them lawful or not.
Additionally, there have been other, specific actions meant to discourage countries from developing nuclear arms. In the wake of the tests by India and Pakistan in 1998, economic sanctions were (temporarily) levied against both countries, though neither were signatories with the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. One of the stated casus belli for the initiation of the 2003 Iraq War was an accusation by the United States that Iraq was actively pursuing nuclear arms (though this was soon discovered not to be the case as the program had been discontinued). In 1981, Israel had bombed a nuclear reactor being constructed in Osirak, Iraq, in what it called an attempt to halt Iraq's previous nuclear arms ambitions; in 2007, Israel bombed another reactor being constructed in Syria.
In 2013, Mark Diesendorf says that governments of France, India, North Korea, Pakistan, UK, and South Africa have used nuclear power and/or research reactors to assist nuclear weapons development or to contribute to their supplies of nuclear explosives from military reactors.
Disarmament
Main article: Nuclear disarmament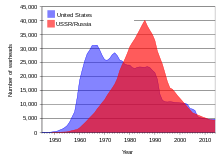
Nuclear disarmament refers to both the act of reducing or eliminating nuclear weapons and to the end state of a nuclear-free world, in which nuclear weapons are completely eliminated.
Beginning with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty and continuing through the 1996 Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty, there have been many treaties to limit or reduce nuclear weapons testing and stockpiles. The 1968 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty has as one of its explicit conditions that all signatories must "pursue negotiations in good faith" towards the long-term goal of "complete disarmament". The nuclear weapon states have largely treated that aspect of the agreement as "decorative" and without force.
Only one country—South Africa—has ever fully renounced nuclear weapons they had independently developed. The former Soviet republics of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine returned Soviet nuclear arms stationed in their countries to Russia after the collapse of the USSR.
Proponents of nuclear disarmament say that it would lessen the probability of nuclear war occurring, especially accidentally. Critics of nuclear disarmament say that it would undermine the present nuclear peace and deterrence and would lead to increased global instability. Various American elder statesmen, who were in office during the Cold War period, have been advocating the elimination of nuclear weapons. These officials include Henry Kissinger, George Shultz, Sam Nunn, and William Perry. In January 2010, Lawrence M. Krauss stated that "no issue carries more importance to the long-term health and security of humanity than the effort to reduce, and perhaps one day, rid the world of nuclear weapons".

In the years after the end of the Cold War, there have been numerous campaigns to urge the abolition of nuclear weapons, such as that organized by the Global Zero movement, and the goal of a "world without nuclear weapons" was advocated by United States President Barack Obama in an April 2009 speech in Prague. A CNN poll from April 2010 indicated that the American public was nearly evenly split on the issue.
Some analysts have argued that nuclear weapons have made the world relatively safer, with peace through deterrence and through the stability–instability paradox, including in south Asia. Kenneth Waltz has argued that nuclear weapons have helped keep an uneasy peace, and further nuclear weapon proliferation might even help avoid the large scale conventional wars that were so common prior to their invention at the end of World War II. But former Secretary Henry Kissinger says there is a new danger, which cannot be addressed by deterrence: "The classical notion of deterrence was that there was some consequences before which aggressors and evildoers would recoil. In a world of suicide bombers, that calculation doesn’t operate in any comparable way". George Shultz has said, "If you think of the people who are doing suicide attacks, and people like that get a nuclear weapon, they are almost by definition not deterrable".
Further information: See List of states with nuclear weapons for statistics on possession and deploymentUnited Nations
Main article: United Nations Office for Disarmament AffairsThe UN Office for Disarmament Affairs (UNODA) is a department of the United Nations Secretariat established in January 1998 as part of the United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan's plan to reform the UN as presented in his report to the General Assembly in July 1997.
Its goal is to promote nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation and the strengthening of the disarmament regimes in respect to other weapons of mass destruction, chemical and biological weapons. It also promotes disarmament efforts in the area of conventional weapons, especially land mines and small arms, which are often the weapons of choice in contemporary conflicts.
Controversy
See also: Nuclear weapons debate and History of the anti-nuclear movementEthics
Even before the first nuclear weapons had been developed, scientists involved with the Manhattan Project were divided over the use of the weapon. The role of the two atomic bombings of the country in Japan's surrender and the U.S.'s ethical justification for them has been the subject of scholarly and popular debate for decades. The question of whether nations should have nuclear weapons, or test them, has been continually and nearly universally controversial.
Notable nuclear weapons accidents
See also: United States military nuclear incident terminology- February 13, 1950: a Convair B-36B crashed in northern British Columbia after jettisoning a Mark IV atomic bomb. This was the first such nuclear weapon loss in history.
- 7 June 1960: the 1960 Fort Dix IM-99 accident destroyed a Boeing CIM-10 Bomarc nuclear missile and shelter and contaminated the BOMARC Missile Accident Site in New Jersey.
- 24 January 1961: the 1961 Goldsboro B-52 crash occurred near Goldsboro, North Carolina. A B-52 Stratofortress carrying two Mark 39 nuclear bombs broke up in mid-air, dropping its nuclear payload in the process.
- 1965 Philippine Sea A-4 crash, where a Skyhawk attack aircraft with a nuclear weapon fell into the sea. The pilot, the aircraft, and the B43 nuclear bomb were never recovered. It was not until the 1980s that the Pentagon revealed the loss of the one-megaton bomb.
- January 17, 1966: the 1966 Palomares B-52 crash occurred when a B-52G bomber of the USAF collided with a KC-135 tanker during mid-air refuelling off the coast of Spain. The KC-135 was completely destroyed when its fuel load ignited, killing all four crew members. The B-52G broke apart, killing three of the seven crew members aboard. Of the four Mk28 type hydrogen bombs the B-52G carried, three were found on land near Almería, Spain. The non-nuclear explosives in two of the weapons detonated upon impact with the ground, resulting in the contamination of a 2-square-kilometer (490-acre) (0.78 square mile) area by radioactive plutonium. The fourth, which fell into the Mediterranean Sea, was recovered intact after a 2½-month-long search.
- January 21, 1968: the 1968 Thule Air Base B-52 crash involved a United States Air Force (USAF) B-52 bomber. The aircraft was carrying four hydrogen bombs when a cabin fire forced the crew to abandon the aircraft. Six crew members ejected safely, but one who did not have an ejection seat was killed while trying to bail out. The bomber crashed onto sea ice in Greenland, causing the nuclear payload to rupture and disperse, which resulted in widespread radioactive contamination.
Nuclear fallout
Main article: Nuclear falloutOver 500 atmospheric nuclear weapons tests were conducted at various sites around the world from 1945 to 1980. Radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons testing was first drawn to public attention in 1954 when the Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb test at the Pacific Proving Grounds contaminated the crew and catch of the Japanese fishing boat Lucky Dragon. One of the fishermen died in Japan seven months later, and the fear of contaminated tuna led to a temporary boycotting of the popular staple in Japan. The incident caused widespread concern around the world, especially regarding the effects of nuclear fallout and atmospheric nuclear testing, and "provided a decisive impetus for the emergence of the anti-nuclear weapons movement in many countries".
As public awareness and concern mounted over the possible health hazards associated with exposure to the nuclear fallout, various studies were done to assess the extent of the hazard. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ National Cancer Institute study claims that fallout from atmospheric nuclear tests would lead to perhaps 11,000 excess deaths amongst people alive during atmospheric testing in the United States from all forms of cancer, including leukemia, from 1951 to well into the 21st century. As of March 2009, the U.S. is the only nation that compensates nuclear test victims. Since the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act of 1990, more than $1.38 billion in compensation has been approved. The money is going to people who took part in the tests, notably at the Nevada Test Site, and to others exposed to the radiation.
Public opposition


Peace movements emerged in Japan and in 1954 they converged to form a unified "Japanese Council Against Atomic and Hydrogen Bombs". Japanese opposition to nuclear weapons tests in the Pacific Ocean was widespread, and "an estimated 35 million signatures were collected on petitions calling for bans on nuclear weapons".
In the United Kingdom, the first Aldermaston March organised by the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament(CND) took place at Easter 1958, when, according to the CND, several thousand people marched for four days from Trafalgar Square, London, to the Atomic Weapons Research Establishment close to Aldermaston in Berkshire, England, to demonstrate their opposition to nuclear weapons. The Aldermaston marches continued into the late 1960s when tens of thousands of people took part in the four-day marches.
In 1959, a letter in the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists was the start of a successful campaign to stop the Atomic Energy Commission dumping radioactive waste in the sea 19 kilometres from Boston. In 1962, Linus Pauling won the Nobel Peace Prize for his work to stop the atmospheric testing of nuclear weapons, and the "Ban the Bomb" movement spread.
In 1963, many countries ratified the Partial Test Ban Treaty prohibiting atmospheric nuclear testing. Radioactive fallout became less of an issue and the anti-nuclear weapons movement went into decline for some years. A resurgence of interest occurred amid European and American fears of nuclear war in the 1980s.
Islamic view
See also: Khamenei's fatwa against nuclear weaponsAyatollah Ali Khamenei, the Supreme Leader of Iran, issued a decree against the acquisition, development and use of nuclear weapons dates back to the mid-1990s, though its first public announcement is reported to have occurred on October 2003, which was followed by an official statement at a meeting of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in Vienna two years later on August 2005.
Khamenei's official website specifically cites a 2010 version of these statements in the fatwa section of the website in Farsi as a fatwa on "Prohibition of Weapons of Mass Destruction:"
"We believe that besides nuclear weapons, other types of weapons of mass destruction such as chemical and biological weapons also pose a serious threat to humanity. The Iranian nation which is itself a victim of chemical weapons feels more than any other nation the danger that is caused by the production and stockpiling of such weapons and is prepared to make use of all its facilities to counter such threats. We consider the use of such weapons as haraam and believe that it is everyone's duty to make efforts to secure humanity against this great disaster."
Costs and technology spin-offs
See also: Global Positioning System, Nuclear weapons delivery, History of computers, ENIAC, and Swords to ploughsharesAccording to an audit by the Brookings Institution, between 1940 and 1996, the U.S. spent $11.3 trillion in present-day terms on nuclear weapons programs. 57 percent of which was spent on building nuclear weapons delivery systems. 6.3 percent of the total, $709 billion in present-day terms, was spent on environmental remediation and nuclear waste management, for example cleaning up the Hanford site, and 7 percent of the total, $795 billion was spent on making nuclear weapons themselves.
Non-weapons uses
Main article: Peaceful nuclear explosionsCivil engineering and energy production
See also: Athabasca oil sands § Project oilsand, and Project Gnome
Apart from their use as weapons, nuclear explosives have been tested and used, in a similar manner to chemical high explosives, for various non-military uses. These have included large-scale earth moving, isotope production and the stimulation and the closing-off of the flow of natural gas.
At the peak of the Atomic Age, the United States initiated Operation Plowshare, involving "peaceful nuclear explosions". The United States Atomic Energy Commission chairman announced that the Plowshares project was intended to "highlight the peaceful applications of nuclear explosive devices and thereby create a climate of world opinion that is more favorable to weapons development and tests". The Operation Plowshare program included 27 nuclear tests designed towards investigating these non-weapons uses from 1961 through 1973. Due to the inability of the U.S. physicists to reduce the fission fraction of small, approximately 1 kiloton, yield nuclear devices that would have been required for many civil engineering projects, when long term health and clean-up costs from fission products were included in the cost, there was virtually no economic advantage over conventional explosives, except for potentially the very largest of projects.

No route was shorter than 55 kilometers in length. Canal-cutting investigations began with the buggy salvo shot of Operation Crosstie in 1967.
The Qattara Depression Project, as developed by Professor Friedrich Bassler, who during his appointment to the West German ministry of economics in 1968, put forth a plan to create a Saharan lake and hydroelectric power station by blasting a tunnel between the Mediterranean sea and the Qattara Depression in Egypt, an area that lies below sea level. The core problem of the entire project was the water supply to the depression. Calculations by Bassler showed that digging a canal or tunnel would be too expensive, therefore Bassler determined that the use of nuclear explosive devices, to excavate the canal or tunnel, would be the most economical. The Egyptian government declined to pursue the idea.
The Soviet Union conducted a much more exhaustive program than Plowshare, with 239 nuclear tests, between 1965 and 1988. Furthermore, many of the "tests" were considered economic applications, not tests, in the Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy program.
These included one 30 kiloton explosion being used to close the Uzbekistani Urtabulak gas well in 1966 that had been blowing since 1963, and a few months later a 47 kiloton explosive was used to seal a higher pressure blowout at the nearby Pamuk gas field.
The public records for devices that produced the highest proportion of their yield via fusion-only reactions are possibly the Taiga Soviet peaceful nuclear explosions of the 1970s, with 98% of their 15 kiloton explosive yield being derived from fusion reactions, a total fission fraction of 0.3 kilotons in a 15 kt device.
The repeated detonation of nuclear devices underground in salt domes, in a somewhat analogous manner to the explosions that power a car internal combustion engine(in that it would be a heat engine) has also been proposed as a means of fusion power, in what is termed PACER. Other investigated uses for peaceful nuclear explosions were underground detonations to stimulate, by a process analogous to fracking, the flow of petroleum and natural gas in tight formations, this was most developed in the Soviet Union, with an increase in the production of many well heads being reported.
Physics

The discovery and synthesis of new chemical elements by nuclear transmutation, and their production in the necessary quantities to allow the studying of their properties, was carried out in nuclear explosive device testing. For example, the discovery of the short lived einsteinium and fermium, both created under the intense neutron flux environment within thermonuclear explosions, followed the first Teller-Ulam thermonuclear device test – Ivy Mike. The rapid capture of so many neutrons required in the synthesis of einsteinium would provide the needed direct experimental confirmation of the so-called r-process, the multiple neutron absorptions needed to explain the cosmic nucleosynthesis (production) of all heavy chemical elements heavier than nickel on the periodic table, in supernova explosions, before beta decay, with the r-process explaining the existence of many stable elements in the universe.
The worldwide presence of new isotopes from atmospheric testing beginning in the 1950s led to the 2008 development of a reliable way to detect art forgeries. Paintings created after that period may contain traces of caesium-137 and strontium-90, isotopes that did not exist in nature before 1945. (Fission products were produced in the natural nuclear fission reactor at Oklo about 1.7 billion years ago, but these decayed away before the earliest known human painting.)
Both climatology and particularly aerosol science, a subfield of atmospheric science, were largely created to answer the question of how far and wide fallout would travel. Similar to radioactive tracers used in hydrology and materials testing, fallout and the neutron activation of nitrogen gas served as a radioactive tracer that was used to measure and then help model global circulations in the atmosphere by following the movements of fallout aerosols.
After the Van Allen Belts surrounding Earth were published about in 1958, James Van Allen suggested that a nuclear detonation would be one way of probing the magnetic phenomenon, data obtained from the August 1958 Project Argus test shots, a high altitude nuclear explosion investigation, were vital to the early understanding of Earth's magnetosphere.

Soviet nuclear physicist and Nobel peace prize recipient Andrei Sakharov also proposed the idea that earthquakes could be mitigated and particle accelerators could be made by utilizing nuclear explosions, with the latter created by connecting a nuclear explosive device with another of his inventions, the explosively pumped flux compression generator, to accelerate protons to collide with each other to probe their inner workings, an endeavor that is now done at much lower energy levels with non-explosive superconducting magnets in CERN. Sakharov suggested to replace the copper coil in his MK generators by a big superconductor solenoid to magnetically compress and focus underground nuclear explosions into a shaped charge effect. He theorized this could focus 10 positively charged protons per second on a 1 mm surface, then envisaged making two such beams collide in the form of a supercollider.
Underground nuclear explosive data from peaceful nuclear explosion test shots have been used to investigate the composition of Earth's mantle, analogous to the exploration geophysics practice of mineral prospecting with chemical explosives in "deep seismic sounding" reflection seismology.
Project A119, proposed in the 1960s, which as Apollo scientist Gary Latham explained, would have been the detonating of a "smallish" nuclear device on the Moon in order to facilitate research into its geologic make-up. Analogous in concept to the comparatively low yield explosion created by the water prospecting (LCROSS)Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite mission, which launched in 2009 and released the "Centaur" kinetic energy impactor, an impactor with a mass of 2,305 kg (5,081 lb), and an impact velocity of about 9,000 km/h (5,600 mph), releasing the kinetic energy equivalent of detonating approximately 2 tons of TNT (8.86 GJ).

Propulsion use
Although likely never achieving orbit due to aerodynamic drag, the first macroscopic object to obtain Earth orbital velocity was a "manhole cover" propelled by the detonation of test shot Pascal-B, before sputnik obtained orbital velocity, and also successfully became the first satellite, in October 1957. The use of a subterranean shaft and nuclear device to propel an object to escape velocity has since been termed a "thunder well".
The direct use of nuclear explosives, by using the impact of propellant plasma from a nuclear shaped charge acting on a pusher plate, has also been seriously studied as a potential propulsion mechanism for space travel (see Project Orion).
Edward Teller, in the United States, proposed the use of a nuclear detonation to power an explosively pumped soft X-ray laser as a component of a ballistic missile defense shield, this would destroy missile components by transferring momentum to the vehicles surface by laser ablation. This ablation process is one of the damage mechanisms of a laser weapon, but it is also the basis of pulsed laser propulsion for spacecraft.
Ground flight testing by Professor Leik Myrabo, using a non-nuclear, conventionally powered pulsed laser test-bed, successfully lifted a lightcraft 72 meters in altitude by a method similar to ablative laser propulsion in 2000.
A powerful solar system based soft X-ray, to ultraviolet, laser system has been calculated to be capable of propelling an interstellar spacecraft, by the light sail principle, to 11% of the speed of light. In 1972 it was also calculated that a 1 Terawatt, 1-km diameter x-ray laser with 1 angstrom wavelength impinging on a 1-km diameter sail, could propel a spacecraft to Alpha Centauri in 10 years.

Asteroid impact avoidance
Main article: Asteroid impact avoidance See also: B83 nuclear bombA proposed means of averting an asteroid impacting with Earth, assuming low lead times between detection and Earth impact, is to detonate one, or a series, of nuclear explosive devices, on, in, or in a stand-off proximity orientation with the asteroid, with the latter method occurring far enough away from the incoming threat to prevent the potential fracturing of the near-Earth object, but still close enough to generate a high thrust laser ablation effect.
A 2007 NASA analysis of impact avoidance strategies using various technologies stated:
Nuclear stand-off explosions are assessed to be 10–100 times more effective than the non-nuclear alternatives analyzed in this study. Other techniques involving the surface or subsurface use of nuclear explosives may be more efficient, but they run an increased risk of fracturing the target near-Earth object. They also carry higher development and operations risks.
Analysis of the uncertainty involved in nuclear device asteroid deflection shows that the ability to protect the planet does not imply the ability to also target the planet, which is the case with all non-nuclear alternatives, such as the controversial gravity tractor technology. A nuclear explosion that changed an asteroid's velocity by 10 m/s (±20%) would be adequate to push it out of an Earth-impacting orbit. However, if the uncertainty of the velocity change is more than a few plus or minus percent, there would be no chance of directing the asteroid to a particular target.
However, if the need arises to use nuclear explosive devices to prevent an asteroid impact event, it may face the legal issue that the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space and the 1996 Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty ban nuclear weapons in space.
See also
History
- History of nuclear weapons
- Los Alamos National Laboratory
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
- Nuclear and radiation accidents, including nuclear weapons accidents
- Military strategy
- Weapon of mass destruction
More technical details
- Effects of nuclear explosions
- Intercontinental ballistic missile
- Neutron bomb
- Nuclear bombs and health
- Nuclear weapon yield
Popular culture
Proliferation and politics
- Agency for the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean
- Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
- International Court of Justice advisory opinion on legality of nuclear weapons
- List of states with nuclear weapons
- List of nuclear weapons
- Nth Country Experiment
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
- Nuclear weapons and the United Kingdom
- The Letters of last resort (United Kingdom)
- Nuclear weapons and Russia
- Nuclear weapons and the United States
- Paranuclear
- Strategic Arms Limitation Talks
- Three Non-Nuclear Principles, of Japan
Notes and references
- See Trinity (nuclear test) and Ivy Mike.
- Specifically the 1970 to 1980 designed and deployed US B83 nuclear bomb, with a yield of up to 1.2 megatons.
- "Frequently Asked Questions #1". Radiation Effects Research Foundation. Retrieved Sep 18, 2007.
total number of deaths is not known precisely ... acute (within two to four months) deaths ... Hiroshima ... 90,000-166,000 ... Nagasaki ... 60,000-80,000
- ^ "Federation of American Scientists: Status of World Nuclear Forces". Fas.org. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- "Nuclear Weapons – Israel". Fas.org. Jan 8, 2007. Retrieved 2010-12-15.
- See also Mordechai Vanunu
- "Nuclear Weapons – South Africa". Fas.org. May 29, 2000. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- ^ The best overall printed sources on nuclear weapons design are: Hansen, Chuck. U.S. Nuclear Weapons: The Secret History. San Antonio, TX: Aerofax, 1988; and the more-updated Hansen, Chuck, "Swords of Armageddon: U.S. Nuclear Weapons Development since 1945" (CD-ROM & download available). PDF. 2,600 pages, Sunnyvale, California, Chuklea Publications, 1995, 2007. ISBN 978-0-9791915-0-3 (2nd Ed.)
- David Albright and Kimberly Kramer (2005-08-22). "Neptunium 237 and Americium: World Inventories and Proliferation Concerns" (PDF). Institute for Science and International Security. Retrieved 2011-10-13.
- Carey Sublette, Nuclear Weapons Frequently Asked Questions: 4.5.2 "Dirty" and "Clean" Weapons, accessed 10 May 2011.
- On India's alleged hydrogen bomb test, see Carey Sublette, What Are the Real Yields of India's Test?.
- Sublette, Carey. "The Nuclear Weapon Archive". Retrieved 2007-03-07.
- U.S. Department of Energy, Restricted Data Declassification Decisions, 1946 to the Present (RDD-8) (January 1, 2002), accessed November 20, 2011.
- "Page discussing the possibility of using antimatter as a trigger for a thermonuclear explosion". Cui.unige.ch. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- Andre Gsponer; Jean-Pierre Hurni (1970). "Paper discussing the number of antiprotons required to ignite a thermonuclear weapon". In G. Velarde and E. Minguez, eds., Proceedings of the th International Conference on Emerging Nuclear Energy Systems, Madrid, June /July , (World Scientific, Singapore, 1987) 166–169. 4 (30). Arxiv.org. arXiv:physics/0507114.
- Keay Davidson, Chronicle Science Writer (2004-10-04). "Air Force pursuing antimatter weapons: Program was touted publicly, then came official gag order". Sfgate.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Fourth Generation Nuclear Weapons". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- Stephen I. Schwartz, ed., Atomic Audit: The Costs and Consequences of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Since 1940. Washington, D.C.: Brookings Institution Press, 1998. See also Estimated Minimum Incurred Costs of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Programs, 1940–1996, an excerpt from the book. Archived 2012-07-16 at the Wayback Machine
- Creveld, Martin Van (2000). "Technology and War II:Postmodern War?". The Oxford History of Modern War. New York, USA: Oxford University Press. p. 349. ISBN 0-19-285373-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - Mearsheimer, John (2006). "Conversations in International Relations: Interview with John J. Mearsheimer (Part I)" (PDF). International Relations. 20 (1): 105–123. doi:10.1177/0047117806060939.See page 116
- Kenneth Waltz, "More May Be Better," in Scott Sagan and Kenneth Waltz, eds., The Spread of Nuclear Weapons (New York: Norton, 1995).
- ^ Kenneth Waltz, "The Spread of Nuclear Weapons: More May Better," Adelphi Papers, no. 171 (London: International Institute for Strategic Studies, 1981).
- See, for example: Feldman, Noah. "Islam, Terror and the Second Nuclear Age," New York Times Magazine (29 October 2006).
- Daniel Plesch & Stephen Young, "Senseless policy", Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, November/December 1998, page 4. Fetched from URL on 18 April 2011.
- Gallucci, Robert (September 2006). "Averting Nuclear Catastrophe: Contemplating Extreme Responses to U.S. Vulnerability". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 607: pp. 51–58. doi:10.1177/0002716206290457. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
{{cite journal}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Allison, Graham (13 March 2009). "How to Keep the Bomb From Terrorists". Newsweek. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- In the United States, the President and the Secretary of Defense, acting as the National Command Authority, must jointly authorize the use of nuclear weapons.
- ^ Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (2010). "Status of Signature and Ratification". Accessed 27 May 2010. Of the "Annex 2" states whose ratification of the CTBT is required before it enters into force, China, Egypt, Iran, Israel, and the United States have signed but not ratified the Treaty. India, North Korea, and Pakistan have not signed the Treaty.
- Richelson, Jeffrey. Spying on the bomb: American nuclear intelligence from Nazi Germany to Iran and North Korea. New York: Norton, 2006.
- The Presidential Nuclear Initiatives (PNIs) on Tactical Nuclear Weapons At a Glance, Fact Sheet, Arms Control Association.
- Nuclear weapons and international humanitarian law International Committee of the Red Cross
- Mark Diesendorf (2013). "Book review: Contesting the future of nuclear power" (PDF). Energy Policy.
- Gusterson, Hugh, "Finding Article VI" Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists (8 January 2007).
- Jim Hoagland (October 6, 2011). "Nuclear energy after Fukushima". Washington Post.
- Lawrence M. Krauss. The Doomsday Clock Still Ticks, Scientific American, January 2010, p. 26.
- Graham, Nick (2009-04-05). "Obama Prague Speech On Nuclear Weapons". Huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "CNN Poll: Public divided on eliminating all nuclear weapons". Politicalticker.blogs.cnn.com. 2010-04-12. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- http://www.stimson.org/images/uploads/research-pdfs/ESCCONTROLCHAPTER1.pdf
- "Michael Krepon • The Stability-Instability Paradox". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- Ben Goddard (2010-01-27). "Cold Warriors say no nukes". The Hill.
- Hugh Gusterson (30 March 2012). "The new abolitionists". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
- ODS Team. "Renewing the United Nations: A Program for Reform (A/51/950)" (PDF). Daccess-dds-ny.un.org. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ Jerry Brown and Rinaldo Brutoco (1997). Profiles in Power: The Anti-nuclear Movement and the Dawn of the Solar Age, Twayne Publishers, pp. 191–192.
- Barry Schneider (May 1975). "Big Bangs from Little Bombs". Bulletin of Atomic Scientists: 28. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- James C. Oskins, Michael H. Maggelet (2008). Broken Arrow — The Declassified History of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Accidents. lulu.com. ISBN 1-4357-0361-8. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- "Ticonderoga Cruise Reports" (Navy.mil weblist of Aug 2003 compilation from cruise reports). Retrieved 2012-04-20.
The National Archives hold deck logs for aircraft carriers for the Vietnam Conflict.
- Broken Arrows at www.atomicarchive.com. Accessed Aug 24, 2007.
- "U.S. Confirms '65 Loss of H-Bomb Near Japanese Islands". The Washington Post. Reuters. May 9, 1989. p. A–27.
- Hayes, Ron (January 17, 2007). "H-bomb incident crippled pilot's career". Palm Beach Post. Archived from the original on 2011-06-16. Retrieved 2006-05-24.
- Maydew, Randall C. (1997). America's Lost H-Bomb: Palomares, Spain, 1966. Sunflower University Press. ISBN 978-0-89745-214-4.
- Long, Tony (January 17, 2008). "Jan. 17, 1966: H-Bombs Rain Down on a Spanish Fishing Village". WIRED. Retrieved 2008-02-16.
- ^ Wolfgang Rudig (1990). Anti-nuclear Movements: A World Survey of Opposition to Nuclear Energy, Longman, p. 54-55.
- "Report on the Health Consequences to the American Population from Nuclear Weapons Tests Conducted by the United States and Other Nations". CDC. Retrieved 7 December 2013.
- Committee to Review the CDC-NCI Feasibility Study of the Health Consequences Nuclear Weapons Tests, National Research Council. "Exposure of the American Population to Radioactive Fallout from Nuclear Weapons Tests". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ABC News. "What governments offer to victims of nuclear tests". ABC News. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- Radiation Exposure Compensation System: Claims to Date Summary of Claims Received by 06/11/2009
- ^ Jim Falk (1982). Global Fission: The Battle Over Nuclear Power, Oxford University Press, pp. 96–97.
- "A brief history of CND". Cnduk.org. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Early defections in march to Aldermaston". London: Guardian Unlimited. 1958-04-05.
- Jim Falk (1982). Global Fission: The Battle Over Nuclear Power, Oxford University Press, p. 93.
- Jim Falk (1982). Global Fission: The Battle Over Nuclear Power, Oxford University Press, p. 98.
- Spencer Weart, Nuclear Fear: A History of Images (Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1988), chapters 16 and 19.
- L Afrasiabi, Kaveh (17 March 2006). "An Iran option the US prefers to ignore". Asia Times.
- Porter, Gareth (16 October 2014). "When the Ayatollah Said No to Nukes". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 21 August 2015.
- "Iran, holder of peaceful nuclear fuel cycle technology". Mathaba.net, IRNA. 25 August 2005. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- "Supreme Leader's Message to International Conference on Nuclear Disarmament". 17 April 2010.
- ^ "حرمت سلاح کشتار جمعی". Official Website of Ayatollah Khamenei–Fatwas Section.
- 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. "Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–". Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- Brookings Institution, "Estimated Minimum Incurred Costs of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Programs, 1940–1996", at http://www.brook.edu/fp/projects/nucwcost/figure1.htm
- Declassified U.S. Nuclear Test Film #35 c. 29:30 minutes
- Guinness World Records. "Largest crater from an underground nuclear explosion". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- "The Soviet Nuclear Weapons Program". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- Russia Today documentary that visits the lake at around the 1 minute mark on YouTube
- Charles Perrow (September/October 2013 vol. 69 no. 5). "Nuclear denial: From Hiroshima to Fukushima". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Q&A with Scott Kirsch: Digging with bombs". Usnews.com. Archived from the original on January 31, 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Declassified U.S. Nuclear Test Film #35 c. 12:00 minutes
- http://www.miktechnology.com/pdf/Qattara%20Depression%20Potential%20Paper-IEEE%20Egypt%20Conference.pdf
- Nordyke, MD (2000-09-01). The Soviet Program for Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Explosions (PDF). Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. pp. 34–35. doi:10.2172/793554. Report no.: UCRL-ID-124410 Rev 2; US Department of Energy contract no.: W-7405-Eng48.
- ^ Nordyke, M. D. (2000-09-01). "Extinguishing Runaway Gas Well Fires". The Soviet Program for Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Explosions (PDF). Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. pp. 34–35. doi:10.2172/793554. Report no.: UCRL-ID-124410 Rev 2. U. S. Department of Energy contract no.: W-7405-Eng48.
- Disturbing the Universe – Freeman Dyson
- The Soviet Program for Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Explosions by Milo D. Nordyke. Science & Global Security, 1998, Volume 7, pp. 1–117. See test shot "Taiga".
- John Nuckolls, "Early Steps Toward Inertial Fusion Energy (IFE)", LLNL, 12 June 1998
- EINSTEINIUM AND FERMIUM, ALBERT GHIORSO, LAWRENCE BERKELEY NATIONAL LABORATORY
- Byrne, J. Neutrons, Nuclei, and Matter, Dover Publications, Mineola, NY, 2011, ISBN 978-0-486-48238-5 (pbk.) pp. 267.
- Cartlidge, Edwin (4 July 2008). "Nuclear fallout used to spot fake art". Physics World – the member magazine of the Institute of Physics. IOP Group. Retrieved 7 December 2014.
- "Can past nuclear explosions help detect forgeries?". Theartnewspaper.com. Archived from the original on November 13, 2010. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Emsley, John (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements (New ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- Entangled histories: Climate science and nuclear weapons research
- "Nuclear weapons' surprising contribution to climate science". Phys.org. 2012-07-13. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Going Nuclear Over the Pacific | Past Imperfect". Blogs.smithsonianmag.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- https://www.fas.org/irp/threat/mctl98-2/p2sec06.pdf SECTION VI NUCLEAR WEAPONS EFFECTS TECHNOLOGY II-6-28.
- Archived 2013-11-06 at the Wayback Machine
- Viktor Adamsky and Yuri Smirnov. 1994. "Moscow's Biggest Bomb: the 50-Megaton Test of October 1961" Cold War International History Project Bulletin, Issue 4, Fall 1994
- Sakharov, A. D. (1966). "Magnetoimplosive Generators". Soviet Physics Uspekhi. 9 (2): 294. doi:10.1070/PU1966v009n02ABEH002876.
- https://libraries.mit.edu/archives/research/collections/collections-mc/mc572.html
- "Travel time analysis of P waves arising from six underground nuclear explosion at Novaya Zemlya". Annalsofgeophysics.eu. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Upper Mantle Heterogeneities from Active and Passive Seismology". Springer.com. 1997-04-16. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "A Database Of Deep Seismic Sounding Peaceful Nuclear Explosion Recordings For Seismic Monitoring Of Northern Eurasia" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Moon madness". The Sydney Morning Herald. December 21, 1969. p. 19. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- "NASA's LCROSS Mission Changes Impact Crater". NASA. 2009-09-29. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- "Operation Plumbbob". Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- "Laser Propulsion Thrusters for Space Transportation". springer.com. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- "Roundtrip Interstellar Travel Using Laser-Pushed Lightsails. VOL. 21, NO. 2, MARCH-APRIL 1984 J. SPACECRAFT. Robert Forward et. al" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- W.E Mockel, Propulsion by impinging Laser beams. Journal of Spacecraft and rockets. 9, no 12 p 942 (1972).
- Covey et al.
- Adamsky and Smirnov, 19.
- Dillow, Clay (9 April 2012). "How it Would Work: Destroying an Incoming Killer Asteroid With a Nuclear Blast". Popular Science. Bonnier. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/neo/report2007.html Near-Earth Object Survey and Deflection Analysis of Alternatives Report to Congress March 2007
Bibliography
See also: List of books about nuclear issues- Bethe, Hans Albrecht. The Road from Los Alamos. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1991. ISBN 0-671-74012-1
- DeVolpi, Alexander, Minkov, Vladimir E., Simonenko, Vadim A., and Stanford, George S. Nuclear Shadowboxing: Contemporary Threats from Cold War Weaponry. Fidlar Doubleday, 2004 (Two volumes, both accessible on Google Book Search) (Content of both volumes is now available in the 2009 trilogy by Alexander DeVolpi: Nuclear Insights: The Cold War Legacy)
- Glasstone, Samuel and Dolan, Philip J. The Effects of Nuclear Weapons (third edition). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1977. Available online (PDF).
- NATO Handbook on the Medical Aspects of NBC Defensive Operations (Part I – Nuclear). Departments of the Army, Navy, and Air Force: Washington, D.C., 1996
- Hansen, Chuck. U.S. Nuclear Weapons: The Secret History. Arlington, TX: Aerofax, 1988
- Hansen, Chuck, "Swords of Armageddon: U.S. nuclear weapons development since 1945" (CD-ROM & download available). PDF. 2,600 pages, Sunnyvale, California, Chucklea Publications, 1995, 2007. ISBN 978-0-9791915-0-3 (2nd Ed.)
- Holloway, David. Stalin and the Bomb. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1994. ISBN 0-300-06056-4
- The Manhattan Engineer District, "The Atomic Bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki" (1946)
- Template:Fr icon Jean-Hugues Oppel, Réveillez le président, Éditions Payot et rivages, 2007 (ISBN 978-2-7436-1630-4). The book is a fiction about the nuclear weapons of France; the book also contains about ten chapters on true historical incidents involving nuclear weapons and strategy.
- Smyth, Henry DeWolf. Atomic Energy for Military Purposes. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1945. (Smyth Report – the first declassified report by the US government on nuclear weapons)
- The Effects of Nuclear War. Office of Technology Assessment, May 1979.
- Rhodes, Richard. Dark Sun: The Making of the Hydrogen Bomb. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1995. ISBN 0-684-82414-0
- Rhodes, Richard. The Making of the Atomic Bomb. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1986 ISBN 0-684-81378-5
- Weart, Spencer R. Nuclear Fear: A History of Images. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1988. ISBN 0-674-62836-5
- Weart, Spencer R. The Rise of Nuclear Fear. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012. ISBN 0-674-05233-1
External links
Listen to this article(2 parts, 15 minutes)
- Nuclear Weapon Archive from Carey Sublette is a reliable source of information and has links to other sources and an informative FAQ.
- The Federation of American Scientists provide solid information on weapons of mass destruction, including nuclear weapons and their effects
- Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues—contains many resources related to nuclear weapons, including a historical and technical overview and searchable bibliography of web and print resources.
- Video archive of US, Soviet, UK, Chinese and French Nuclear Weapon Testing at sonicbomb.com
- The National Museum of Nuclear Science & History (United States)—located in Albuquerque, New Mexico; a Smithsonian Affiliate Museum
- Nuclear Emergency and Radiation Resources
- The Manhattan Project: Making the Atomic Bomb at AtomicArchive.com
- Los Alamos National Laboratory: History (U.S. nuclear history)
- Race for the Superbomb, PBS website on the history of the H-bomb
- Recordings of recollections of the victims of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- The Woodrow Wilson Center's Nuclear Proliferation International History Project or NPIHP is a global network of individuals and institutions engaged in the study of international nuclear history through archival documents, oral history interviews and other empirical sources.
| Nuclear technology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nuclear and radioactive disasters, former facilities, tests and test sites | |
|---|---|
| Lists of disasters and incidents |
|
| Individual accidents and sites |
|
| Related topics |
|
