
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number n is its third power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of n together. The cube of a number or any other mathematical expression is denoted by a superscript 3, for example 2 = 8 or (x + 1).
The cube is also the number multiplied by its square:
- n = n × n = n × n × n.
The cube function is the function x ↦ x (often denoted y = x) that maps a number to its cube. It is an odd function, as
- (−n) = −(n).
The volume of a geometric cube is the cube of its side length, giving rise to the name. The inverse operation that consists of finding a number whose cube is n is called extracting the cube root of n. It determines the side of the cube of a given volume. It is also n raised to the one-third power.
The graph of the cube function is known as the cubic parabola. Because the cube function is an odd function, this curve has a center of symmetry at the origin, but no axis of symmetry.
In integers
See also: Cube-free integerA cube number, or a perfect cube, or sometimes just a cube, is a number which is the cube of an integer. The non-negative perfect cubes up to 60 are (sequence A000578 in the OEIS):
| 0 = | 0 | ||||||||||
| 1 = | 1 | 11 = | 1331 | 21 = | 9261 | 31 = | 29,791 | 41 = | 68,921 | 51 = | 132,651 |
| 2 = | 8 | 12 = | 1728 | 22 = | 10,648 | 32 = | 32,768 | 42 = | 74,088 | 52 = | 140,608 |
| 3 = | 27 | 13 = | 2197 | 23 = | 12,167 | 33 = | 35,937 | 43 = | 79,507 | 53 = | 148,877 |
| 4 = | 64 | 14 = | 2744 | 24 = | 13,824 | 34 = | 39,304 | 44 = | 85,184 | 54 = | 157,464 |
| 5 = | 125 | 15 = | 3375 | 25 = | 15,625 | 35 = | 42,875 | 45 = | 91,125 | 55 = | 166,375 |
| 6 = | 216 | 16 = | 4096 | 26 = | 17,576 | 36 = | 46,656 | 46 = | 97,336 | 56 = | 175,616 |
| 7 = | 343 | 17 = | 4913 | 27 = | 19,683 | 37 = | 50,653 | 47 = | 103,823 | 57 = | 185,193 |
| 8 = | 512 | 18 = | 5832 | 28 = | 21,952 | 38 = | 54,872 | 48 = | 110,592 | 58 = | 195,112 |
| 9 = | 729 | 19 = | 6859 | 29 = | 24,389 | 39 = | 59,319 | 49 = | 117,649 | 59 = | 205,379 |
| 10 = | 1000 | 20 = | 8000 | 30 = | 27,000 | 40 = | 64,000 | 50 = | 125,000 | 60 = | 216,000 |
Geometrically speaking, a positive integer m is a perfect cube if and only if one can arrange m solid unit cubes into a larger, solid cube. For example, 27 small cubes can be arranged into one larger one with the appearance of a Rubik's Cube, since 3 × 3 × 3 = 27.
The difference between the cubes of consecutive integers can be expressed as follows:
- n − (n − 1) = 3(n − 1)n + 1.
or
- (n + 1) − n = 3(n + 1)n + 1.
There is no minimum perfect cube, since the cube of a negative integer is negative. For example, (−4) × (−4) × (−4) = −64.
Base ten
Unlike perfect squares, perfect cubes do not have a small number of possibilities for the last two digits. Except for cubes divisible by 5, where only 25, 75 and 00 can be the last two digits, any pair of digits with the last digit odd can occur as the last digits of a perfect cube. With even cubes, there is considerable restriction, for only 00, o2, e4, o6 and e8 can be the last two digits of a perfect cube (where o stands for any odd digit and e for any even digit). Some cube numbers are also square numbers; for example, 64 is a square number (8 × 8) and a cube number (4 × 4 × 4). This happens if and only if the number is a perfect sixth power (in this case 2).
The last digits of each 3rd power are:
| 0 | 1 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 9 |
It is, however, easy to show that most numbers are not perfect cubes because all perfect cubes must have digital root 1, 8 or 9. That is their values modulo 9 may be only 0, 1, and 8. Moreover, the digital root of any number's cube can be determined by the remainder the number gives when divided by 3:
- If the number x is divisible by 3, its cube has digital root 9; that is,
- If it has a remainder of 1 when divided by 3, its cube has digital root 1; that is,
- If it has a remainder of 2 when divided by 3, its cube has digital root 8; that is,
Sums of two cubes
Main article: Sum of two cubesSums of three cubes
Main article: Sums of three cubesIt is conjectured that every integer (positive or negative) not congruent to ±4 modulo 9 can be written as a sum of three (positive or negative) cubes with infinitely many ways. For example, . Integers congruent to ±4 modulo 9 are excluded because they cannot be written as the sum of three cubes.
The smallest such integer for which such a sum is not known is 114. In September 2019, the previous smallest such integer with no known 3-cube sum, 42, was found to satisfy this equation:
One solution to is given in the table below for n ≤ 78, and n not congruent to 4 or 5 modulo 9. The selected solution is the one that is primitive (gcd(x, y, z) = 1), is not of the form or (since they are infinite families of solutions), satisfies 0 ≤ |x| ≤ |y| ≤ |z|, and has minimal values for |z| and |y| (tested in this order).
Only primitive solutions are selected since the non-primitive ones can be trivially deduced from solutions for a smaller value of n. For example, for n = 24, the solution results from the solution by multiplying everything by Therefore, this is another solution that is selected. Similarly, for n = 48, the solution (x, y, z) = (-2, -2, 4) is excluded, and this is the solution (x, y, z) = (-23, -26, 31) that is selected.
| Primitive solutions for n from 1 to 78 | ||||||||
| n | x | y | z | n | x | y | z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 10 | −12 | 39 | 117367 | 134476 | −159380 | |
| 2 | 1214928 | 3480205 | −3528875 | 42 | 12602123297335631 | 80435758145817515 | −80538738812075974 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 43 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 6 | −1 | −1 | 2 | 44 | −5 | −7 | 8 | |
| 7 | 0 | −1 | 2 | 45 | 2 | −3 | 4 | |
| 8 | 9 | 15 | −16 | 46 | −2 | 3 | 3 | |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 47 | 6 | 7 | −8 | |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 48 | −23 | −26 | 31 | |
| 11 | −2 | −2 | 3 | 51 | 602 | 659 | −796 | |
| 12 | 7 | 10 | −11 | 52 | 23961292454 | 60702901317 | −61922712865 | |
| 15 | −1 | 2 | 2 | 53 | −1 | 3 | 3 | |
| 16 | −511 | −1609 | 1626 | 54 | −7 | −11 | 12 | |
| 17 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 55 | 1 | 3 | 3 | |
| 18 | −1 | −2 | 3 | 56 | −11 | −21 | 22 | |
| 19 | 0 | −2 | 3 | 57 | 1 | −2 | 4 | |
| 20 | 1 | −2 | 3 | 60 | −1 | −4 | 5 | |
| 21 | −11 | −14 | 16 | 61 | 0 | −4 | 5 | |
| 24 | −2901096694 | −15550555555 | 15584139827 | 62 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| 25 | −1 | −1 | 3 | 63 | 0 | −1 | 4 | |
| 26 | 0 | −1 | 3 | 64 | −3 | −5 | 6 | |
| 27 | −4 | −5 | 6 | 65 | 0 | 1 | 4 | |
| 28 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 66 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 29 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 69 | 2 | −4 | 5 | |
| 30 | −283059965 | −2218888517 | 2220422932 | 70 | 11 | 20 | −21 | |
| 33 | −2736111468807040 | −8778405442862239 | 8866128975287528 | 71 | −1 | 2 | 4 | |
| 34 | −1 | 2 | 3 | 72 | 7 | 9 | −10 | |
| 35 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 73 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
| 36 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 74 | 66229832190556 | 283450105697727 | −284650292555885 | |
| 37 | 0 | −3 | 4 | 75 | 4381159 | 435203083 | −435203231 | |
| 38 | 1 | −3 | 4 | 78 | 26 | 53 | −55 | |
Fermat's Last Theorem for cubes
Main article: Fermat's Last TheoremThe equation x + y = z has no non-trivial (i.e. xyz ≠ 0) solutions in integers. In fact, it has none in Eisenstein integers.
Both of these statements are also true for the equation x + y = 3z.
Sum of first n cubes
The sum of the first n cubes is the nth triangle number squared:

Proofs. Charles Wheatstone (1854) gives a particularly simple derivation, by expanding each cube in the sum into a set of consecutive odd numbers. He begins by giving the identity
That identity is related to triangular numbers in the following way:
and thus the summands forming start off just after those forming all previous values up to . Applying this property, along with another well-known identity:
we obtain the following derivation:

In the more recent mathematical literature, Stein (1971) uses the rectangle-counting interpretation of these numbers to form a geometric proof of the identity (see also Benjamin, Quinn & Wurtz 2006); he observes that it may also be proved easily (but uninformatively) by induction, and states that Toeplitz (1963) provides "an interesting old Arabic proof". Kanim (2004) provides a purely visual proof, Benjamin & Orrison (2002) provide two additional proofs, and Nelsen (1993) gives seven geometric proofs.
For example, the sum of the first 5 cubes is the square of the 5th triangular number,
A similar result can be given for the sum of the first y odd cubes,
but x, y must satisfy the negative Pell equation x − 2y = −1. For example, for y = 5 and 29, then,
and so on. Also, every even perfect number, except the lowest, is the sum of the first 2
odd cubes (p = 3, 5, 7, ...):
Sum of cubes of numbers in arithmetic progression

There are examples of cubes of numbers in arithmetic progression whose sum is a cube:
with the first one sometimes identified as the mysterious Plato's number. The formula F for finding the sum of n cubes of numbers in arithmetic progression with common difference d and initial cube a,
is given by
A parametric solution to
is known for the special case of d = 1, or consecutive cubes, as found by Pagliani in 1829.
Cubes as sums of successive odd integers
In the sequence of odd integers 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, ..., the first one is a cube (1 = 1); the sum of the next two is the next cube (3 + 5 = 2); the sum of the next three is the next cube (7 + 9 + 11 = 3); and so forth.
Waring's problem for cubes
Main article: Waring's problemEvery positive integer can be written as the sum of nine (or fewer) positive cubes. This upper limit of nine cubes cannot be reduced because, for example, 23 cannot be written as the sum of fewer than nine positive cubes:
- 23 = 2 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1.
In rational numbers
Every positive rational number is the sum of three positive rational cubes, and there are rationals that are not the sum of two rational cubes.
In real numbers, other fields, and rings
Further information: cubic function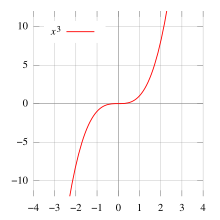
In real numbers, the cube function preserves the order: larger numbers have larger cubes. In other words, cubes (strictly) monotonically increase. Also, its codomain is the entire real line: the function x ↦ x : R → R is a surjection (takes all possible values). Only three numbers are equal to their own cubes: −1, 0, and 1. If −1 < x < 0 or 1 < x, then x > x. If x < −1 or 0 < x < 1, then x < x. All aforementioned properties pertain also to any higher odd power (x, x, ...) of real numbers. Equalities and inequalities are also true in any ordered ring.
Volumes of similar Euclidean solids are related as cubes of their linear sizes.
In complex numbers, the cube of a purely imaginary number is also purely imaginary. For example, i = −i.
The derivative of x equals 3x.
Cubes occasionally have the surjective property in other fields, such as in Fp for such prime p that p ≠ 1 (mod 3), but not necessarily: see the counterexample with rationals above. Also in F7 only three elements 0, ±1 are perfect cubes, of seven total. −1, 0, and 1 are perfect cubes anywhere and the only elements of a field equal to their own cubes: x − x = x(x − 1)(x + 1).
History
Determination of the cubes of large numbers was very common in many ancient civilizations. Mesopotamian mathematicians created cuneiform tablets with tables for calculating cubes and cube roots by the Old Babylonian period (20th to 16th centuries BC). Cubic equations were known to the ancient Greek mathematician Diophantus. Hero of Alexandria devised a method for calculating cube roots in the 1st century CE. Methods for solving cubic equations and extracting cube roots appear in The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art, a Chinese mathematical text compiled around the 2nd century BCE and commented on by Liu Hui in the 3rd century CE.
See also
- Cabtaxi number
- Cubic equation
- Doubling the cube
- Eighth power
- Euler's sum of powers conjecture
- Fifth power
- Fourth power
- Kepler's laws of planetary motion#Third law
- Monkey saddle
- Perfect power
- Seventh power
- Sixth power
- Square
- Taxicab number
References
- Huisman, Sander G. (27 Apr 2016). "Newer sums of three cubes". arXiv:1604.07746 .
- Booker, Andrew R.; Sutherland, Andrew V. (2021). "On a question of Mordell". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 118 (11). arXiv:2007.01209. Bibcode:2021PNAS..11822377B. doi:10.1073/pnas.2022377118. PMC 7980389. PMID 33692126.
- Sequences A060465, A060466 and A060467 in OEIS
- Threecubes
- n=x^3+y^3+z^3
- Hardy & Wright, Thm. 227
- Hardy & Wright, Thm. 232
- Bennett, Michael A.; Patel, Vandita; Siksek, Samir (2017), "Perfect powers that are sums of consecutive cubes", Mathematika, 63 (1): 230–249, arXiv:1603.08901, doi:10.1112/S0025579316000231, MR 3610012
- Hardy & Wright, Thm. 234
- Hardy & Wright, Thm. 233
- The multiplicative group of Fp is cyclic of order p − 1, and if it is not divisible by 3, then cubes define a group automorphism.
- Cooke, Roger (8 November 2012). The History of Mathematics. John Wiley & Sons. p. 63. ISBN 978-1-118-46029-0.
- Nemet-Nejat, Karen Rhea (1998). Daily Life in Ancient Mesopotamia. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 306. ISBN 978-0-313-29497-6.
- Van der Waerden, Geometry and Algebra of Ancient Civilizations, chapter 4, Zurich 1983 ISBN 0-387-12159-5
- Smyly, J. Gilbart (1920). "Heron's Formula for Cube Root". Hermathena. 19 (42). Trinity College Dublin: 64–67. JSTOR 23037103.
- Crossley, John; W.-C. Lun, Anthony (1999). The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art: Companion and Commentary. Oxford University Press. pp. 176, 213. ISBN 978-0-19-853936-0.
Sources
- Benjamin, Arthur T.; Orrison, Michael E. (November 2002). "Two Quick Combinatorial Proofs of Σ k = 1 n k 3 = ( \smallmatrix n+1 2 \endsmallmatrix ) 2" (PDF). The College Mathematics Journal. 33 (5): 406. doi:10.2307/1559017. JSTOR 1559017.
- Benjamin, Arthur T.; Quinn, Jennifer J.; Wurtz, Calyssa (1 November 2006). "Summing Cubes by Counting Rectangles". The College Mathematics Journal. 37 (5): 387–389. doi:10.2307/27646391. JSTOR 27646391.
- Hardy, G. H.; Wright, E. M. (1980). An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (Fifth ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-853171-5.
- Kanim, Katherine (1 October 2004). "Proof without Words: The Sum of Cubes: An Extension of Archimedes' Sum of Squares". Mathematics Magazine. 77 (4): 298–299. doi:10.2307/3219288. JSTOR 3219288.
- Nelsen, Roger B. (1993). Proofs without words : exercises in visual thinking. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-88385-700-7.
- Stein, Robert G. (1 May 1971). "A Combinatorial Proof That Σ k3 = (Σ k)2". Mathematics Magazine. 44 (3): 161–162. doi:10.2307/2688231. JSTOR 2688231.
- Toeplitz, Otto (1963). The calculus: a genetic approach. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-80667-9.
- Wheatstone, C. (1854). "On the formation of powers from arithmetical progressions". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 7: 145–151. Bibcode:1854RSPS....7..145W. doi:10.1098/rspl.1854.0036. S2CID 121885197.
| Figurate numbers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-dimensional |
| ||||||
| 3-dimensional |
| ||||||
| 4-dimensional |
| ||||||
| Higher dimensional |
| ||||||
| Classes of natural numbers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sequences and series | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integer sequences |
|  | ||||
| Properties of sequences | ||||||
| Properties of series |
| |||||
| Explicit series | ||||||
| Kinds of series | ||||||
| Hypergeometric series | ||||||



 . Integers congruent to ±4 modulo 9 are excluded because they cannot be written as the sum of three cubes.
. Integers congruent to ±4 modulo 9 are excluded because they cannot be written as the sum of three cubes.

 is given in the table below for n ≤ 78, and n not congruent to 4 or 5 modulo 9. The selected solution is the one that is primitive (gcd(x, y, z) = 1), is not of the form
is given in the table below for n ≤ 78, and n not congruent to 4 or 5 modulo 9. The selected solution is the one that is primitive (gcd(x, y, z) = 1), is not of the form  or
or  (since they are infinite families of solutions), satisfies 0 ≤ |x| ≤ |y| ≤ |z|, and has minimal values for |z| and |y| (tested in this order).
(since they are infinite families of solutions), satisfies 0 ≤ |x| ≤ |y| ≤ |z|, and has minimal values for |z| and |y| (tested in this order).
 results from the solution
results from the solution  by multiplying everything by
by multiplying everything by  Therefore, this is another solution that is selected. Similarly, for n = 48, the solution (x, y, z) = (-2, -2, 4) is excluded, and this is the solution (x, y, z) = (-23, -26, 31) that is selected.
Therefore, this is another solution that is selected. Similarly, for n = 48, the solution (x, y, z) = (-2, -2, 4) is excluded, and this is the solution (x, y, z) = (-23, -26, 31) that is selected.


 in the following way:
in the following way:

 start off just after those forming all previous values
start off just after those forming all previous values  up to
up to  .
Applying this property, along with another well-known identity:
.
Applying this property, along with another well-known identity:














