| Viscosity | |
|---|---|
 A simulation of liquids with different viscosities. The liquid on the left has lower viscosity than the liquid on the right. A simulation of liquids with different viscosities. The liquid on the left has lower viscosity than the liquid on the right. | |
| Common symbols | η, μ |
| Derivations from other quantities | μ = G·t |
| Dimension | |
| Part of a series on | |||||||
| Continuum mechanics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fick's laws of diffusion | |||||||
Laws
|
|||||||
| Solid mechanics | |||||||
Fluid mechanics
|
|||||||
Rheology
|
|||||||
| Scientists | |||||||
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of thickness; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per square meter, or pascal-seconds.
Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity.
In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is negligible in certain cases. For example, the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid does not vary significantly with the rate of deformation.
Zero viscosity (no resistance to shear stress) is observed only at very low temperatures in superfluids; otherwise, the second law of thermodynamics requires all fluids to have positive viscosity. A fluid that has zero viscosity (non-viscous) is called ideal or inviscid.
For non-Newtonian fluid's viscosity, there are pseudoplastic, plastic, and dilatant flows that are time-independent, and there are thixotropic and rheopectic flows that are time-dependent.
Etymology
The word "viscosity" is derived from the Latin viscum ("mistletoe"). Viscum also referred to a viscous glue derived from mistletoe berries.
Definitions
Dynamic viscosity
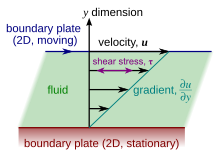

In materials science and engineering, there is often interest in understanding the forces or stresses involved in the deformation of a material. For instance, if the material were a simple spring, the answer would be given by Hooke's law, which says that the force experienced by a spring is proportional to the distance displaced from equilibrium. Stresses which can be attributed to the deformation of a material from some rest state are called elastic stresses. In other materials, stresses are present which can be attributed to the deformation rate over time. These are called viscous stresses. For instance, in a fluid such as water the stresses which arise from shearing the fluid do not depend on the distance the fluid has been sheared; rather, they depend on how quickly the shearing occurs.
Viscosity is the material property which relates the viscous stresses in a material to the rate of change of a deformation (the strain rate). Although it applies to general flows, it is easy to visualize and define in a simple shearing flow, such as a planar Couette flow.
In the Couette flow, a fluid is trapped between two infinitely large plates, one fixed and one in parallel motion at constant speed (see illustration to the right). If the speed of the top plate is low enough (to avoid turbulence), then in steady state the fluid particles move parallel to it, and their speed varies from at the bottom to at the top. Each layer of fluid moves faster than the one just below it, and friction between them gives rise to a force resisting their relative motion. In particular, the fluid applies on the top plate a force in the direction opposite to its motion, and an equal but opposite force on the bottom plate. An external force is therefore required in order to keep the top plate moving at constant speed.
In many fluids, the flow velocity is observed to vary linearly from zero at the bottom to at the top. Moreover, the magnitude of the force, , acting on the top plate is found to be proportional to the speed and the area of each plate, and inversely proportional to their separation :
The proportionality factor is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid, often simply referred to as the viscosity. It is denoted by the Greek letter mu (μ). The dynamic viscosity has the dimensions , therefore resulting in the SI units and the derived units:
The aforementioned ratio is called the rate of shear deformation or shear velocity, and is the derivative of the fluid speed in the direction parallel to the normal vector of the plates (see illustrations to the right). If the velocity does not vary linearly with , then the appropriate generalization is:
where , and is the local shear velocity. This expression is referred to as Newton's law of viscosity. In shearing flows with planar symmetry, it is what defines . It is a special case of the general definition of viscosity (see below), which can be expressed in coordinate-free form.
Use of the Greek letter mu () for the dynamic viscosity (sometimes also called the absolute viscosity) is common among mechanical and chemical engineers, as well as mathematicians and physicists. However, the Greek letter eta () is also used by chemists, physicists, and the IUPAC. The viscosity is sometimes also called the shear viscosity. However, at least one author discourages the use of this terminology, noting that can appear in non-shearing flows in addition to shearing flows.
Kinematic viscosity
In fluid dynamics, it is sometimes more appropriate to work in terms of kinematic viscosity (sometimes also called the momentum diffusivity), defined as the ratio of the dynamic viscosity (μ) over the density of the fluid (ρ). It is usually denoted by the Greek letter nu (ν):
and has the dimensions , therefore resulting in the SI units and the derived units:
- specific energy multiplied by time energy per unit mass multiplied by time.
General definition
See also: Viscous stress tensor and Volume viscosityIn very general terms, the viscous stresses in a fluid are defined as those resulting from the relative velocity of different fluid particles. As such, the viscous stresses must depend on spatial gradients of the flow velocity. If the velocity gradients are small, then to a first approximation the viscous stresses depend only on the first derivatives of the velocity. (For Newtonian fluids, this is also a linear dependence.) In Cartesian coordinates, the general relationship can then be written as
where is a viscosity tensor that maps the velocity gradient tensor onto the viscous stress tensor . Since the indices in this expression can vary from 1 to 3, there are 81 "viscosity coefficients" in total. However, assuming that the viscosity rank-2 tensor is isotropic reduces these 81 coefficients to three independent parameters , , :
and furthermore, it is assumed that no viscous forces may arise when the fluid is undergoing simple rigid-body rotation, thus , leaving only two independent parameters. The most usual decomposition is in terms of the standard (scalar) viscosity and the bulk viscosity such that and . In vector notation this appears as:
where is the unit tensor. This equation can be thought of as a generalized form of Newton's law of viscosity.
The bulk viscosity (also called volume viscosity) expresses a type of internal friction that resists the shearless compression or expansion of a fluid. Knowledge of is frequently not necessary in fluid dynamics problems. For example, an incompressible fluid satisfies and so the term containing drops out. Moreover, is often assumed to be negligible for gases since it is in a monatomic ideal gas. One situation in which can be important is the calculation of energy loss in sound and shock waves, described by Stokes' law of sound attenuation, since these phenomena involve rapid expansions and compressions.
The defining equations for viscosity are not fundamental laws of nature, so their usefulness, as well as methods for measuring or calculating the viscosity, must be established using separate means. A potential issue is that viscosity depends, in principle, on the full microscopic state of the fluid, which encompasses the positions and momenta of every particle in the system. Such highly detailed information is typically not available in realistic systems. However, under certain conditions most of this information can be shown to be negligible. In particular, for Newtonian fluids near equilibrium and far from boundaries (bulk state), the viscosity depends only space- and time-dependent macroscopic fields (such as temperature and density) defining local equilibrium.
Nevertheless, viscosity may still carry a non-negligible dependence on several system properties, such as temperature, pressure, and the amplitude and frequency of any external forcing. Therefore, precision measurements of viscosity are only defined with respect to a specific fluid state. To standardize comparisons among experiments and theoretical models, viscosity data is sometimes extrapolated to ideal limiting cases, such as the zero shear limit, or (for gases) the zero density limit.
Momentum transport
See also: Transport phenomenaTransport theory provides an alternative interpretation of viscosity in terms of momentum transport: viscosity is the material property which characterizes momentum transport within a fluid, just as thermal conductivity characterizes heat transport, and (mass) diffusivity characterizes mass transport. This perspective is implicit in Newton's law of viscosity, , because the shear stress has units equivalent to a momentum flux, i.e., momentum per unit time per unit area. Thus, can be interpreted as specifying the flow of momentum in the direction from one fluid layer to the next. Per Newton's law of viscosity, this momentum flow occurs across a velocity gradient, and the magnitude of the corresponding momentum flux is determined by the viscosity.
The analogy with heat and mass transfer can be made explicit. Just as heat flows from high temperature to low temperature and mass flows from high density to low density, momentum flows from high velocity to low velocity. These behaviors are all described by compact expressions, called constitutive relations, whose one-dimensional forms are given here:
where is the density, and are the mass and heat fluxes, and and are the mass diffusivity and thermal conductivity. The fact that mass, momentum, and energy (heat) transport are among the most relevant processes in continuum mechanics is not a coincidence: these are among the few physical quantities that are conserved at the microscopic level in interparticle collisions. Thus, rather than being dictated by the fast and complex microscopic interaction timescale, their dynamics occurs on macroscopic timescales, as described by the various equations of transport theory and hydrodynamics.
Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids
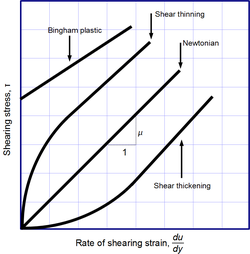
Newton's law of viscosity is not a fundamental law of nature, but rather a constitutive equation (like Hooke's law, Fick's law, and Ohm's law) which serves to define the viscosity . Its form is motivated by experiments which show that for a wide range of fluids, is independent of strain rate. Such fluids are called Newtonian. Gases, water, and many common liquids can be considered Newtonian in ordinary conditions and contexts. However, there are many non-Newtonian fluids that significantly deviate from this behavior. For example:
- Shear-thickening (dilatant) liquids, whose viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain.
- Shear-thinning liquids, whose viscosity decreases with the rate of shear strain.
- Thixotropic liquids, that become less viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed.
- Rheopectic liquids, that become more viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed.
- Bingham plastics that behave as a solid at low stresses but flow as a viscous fluid at high stresses.
Trouton's ratio is the ratio of extensional viscosity to shear viscosity. For a Newtonian fluid, the Trouton ratio is 3. Shear-thinning liquids are very commonly, but misleadingly, described as thixotropic.
Viscosity may also depend on the fluid's physical state (temperature and pressure) and other, external, factors. For gases and other compressible fluids, it depends on temperature and varies very slowly with pressure. The viscosity of some fluids may depend on other factors. A magnetorheological fluid, for example, becomes thicker when subjected to a magnetic field, possibly to the point of behaving like a solid.
In solids
The viscous forces that arise during fluid flow are distinct from the elastic forces that occur in a solid in response to shear, compression, or extension stresses. While in the latter the stress is proportional to the amount of shear deformation, in a fluid it is proportional to the rate of deformation over time. For this reason, James Clerk Maxwell used the term fugitive elasticity for fluid viscosity.
However, many liquids (including water) will briefly react like elastic solids when subjected to sudden stress. Conversely, many "solids" (even granite) will flow like liquids, albeit very slowly, even under arbitrarily small stress. Such materials are best described as viscoelastic—that is, possessing both elasticity (reaction to deformation) and viscosity (reaction to rate of deformation).
Viscoelastic solids may exhibit both shear viscosity and bulk viscosity. The extensional viscosity is a linear combination of the shear and bulk viscosities that describes the reaction of a solid elastic material to elongation. It is widely used for characterizing polymers.
In geology, earth materials that exhibit viscous deformation at least three orders of magnitude greater than their elastic deformation are sometimes called rheids.
Measurement
Main article: ViscometerViscosity is measured with various types of viscometers and rheometers. Close temperature control of the fluid is essential to obtain accurate measurements, particularly in materials like lubricants, whose viscosity can double with a change of only 5 °C. A rheometer is used for fluids that cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case for a viscometer.
For some fluids, the viscosity is constant over a wide range of shear rates (Newtonian fluids). The fluids without a constant viscosity (non-Newtonian fluids) cannot be described by a single number. Non-Newtonian fluids exhibit a variety of different correlations between shear stress and shear rate.
One of the most common instruments for measuring kinematic viscosity is the glass capillary viscometer.
In coating industries, viscosity may be measured with a cup in which the efflux time is measured. There are several sorts of cup—such as the Zahn cup and the Ford viscosity cup—with the usage of each type varying mainly according to the industry.
Also used in coatings, a Stormer viscometer employs load-based rotation to determine viscosity. The viscosity is reported in Krebs units (KU), which are unique to Stormer viscometers.
Vibrating viscometers can also be used to measure viscosity. Resonant, or vibrational viscometers work by creating shear waves within the liquid. In this method, the sensor is submerged in the fluid and is made to resonate at a specific frequency. As the surface of the sensor shears through the liquid, energy is lost due to its viscosity. This dissipated energy is then measured and converted into a viscosity reading. A higher viscosity causes a greater loss of energy.
Extensional viscosity can be measured with various rheometers that apply extensional stress.
Volume viscosity can be measured with an acoustic rheometer.
Apparent viscosity is a calculation derived from tests performed on drilling fluid used in oil or gas well development. These calculations and tests help engineers develop and maintain the properties of the drilling fluid to the specifications required.
Nanoviscosity (viscosity sensed by nanoprobes) can be measured by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy.
Units
The SI unit of dynamic viscosity is the newton-second per square meter (N·s/m), also frequently expressed in the equivalent forms pascal-second (Pa·s), kilogram per meter per second (kg·m·s) and poiseuille (Pl). The CGS unit is the poise (P, or g·cm·s = 0.1 Pa·s), named after Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille. It is commonly expressed, particularly in ASTM standards, as centipoise (cP). The centipoise is convenient because the viscosity of water at 20 °C is about 1 cP, and one centipoise is equal to the SI millipascal second (mPa·s).
The SI unit of kinematic viscosity is square meter per second (m/s), whereas the CGS unit for kinematic viscosity is the stokes (St, or cm·s = 0.0001 m·s), named after Sir George Gabriel Stokes. In U.S. usage, stoke is sometimes used as the singular form. The submultiple centistokes (cSt) is often used instead, 1 cSt = 1 mm·s = 10 m·s. 1 cSt is 1 cP divided by 1000 kg/m^3, close to the density of water. The kinematic viscosity of water at 20 °C is about 1 cSt.
The most frequently used systems of US customary, or Imperial, units are the British Gravitational (BG) and English Engineering (EE). In the BG system, dynamic viscosity has units of pound-seconds per square foot (lb·s/ft), and in the EE system it has units of pound-force-seconds per square foot (lbf·s/ft). The pound and pound-force are equivalent; the two systems differ only in how force and mass are defined. In the BG system the pound is a basic unit from which the unit of mass (the slug) is defined by Newton's Second Law, whereas in the EE system the units of force and mass (the pound-force and pound-mass respectively) are defined independently through the Second Law using the proportionality constant gc.
Kinematic viscosity has units of square feet per second (ft/s) in both the BG and EE systems.
Nonstandard units include the reyn (lbf·s/in), a British unit of dynamic viscosity. In the automotive industry the viscosity index is used to describe the change of viscosity with temperature.
The reciprocal of viscosity is fluidity, usually symbolized by or , depending on the convention used, measured in reciprocal poise (P, or cm·s·g), sometimes called the rhe. Fluidity is seldom used in engineering practice.
At one time the petroleum industry relied on measuring kinematic viscosity by means of the Saybolt viscometer, and expressing kinematic viscosity in units of Saybolt universal seconds (SUS). Other abbreviations such as SSU (Saybolt seconds universal) or SUV (Saybolt universal viscosity) are sometimes used. Kinematic viscosity in centistokes can be converted from SUS according to the arithmetic and the reference table provided in ASTM D 2161.
Molecular origins
Momentum transport in gases is mediated by discrete molecular collisions, and in liquids by attractive forces that bind molecules close together. Because of this, the dynamic viscosities of liquids are typically much larger than those of gases. In addition, viscosity tends to increase with temperature in gases and decrease with temperature in liquids.
Above the liquid-gas critical point, the liquid and gas phases are replaced by a single supercritical phase. In this regime, the mechanisms of momentum transport interpolate between liquid-like and gas-like behavior. For example, along a supercritical isobar (constant-pressure surface), the kinematic viscosity decreases at low temperature and increases at high temperature, with a minimum in between. A rough estimate for the value at the minimum is
where is the Planck constant, is the electron mass, and is the molecular mass.
In general, however, the viscosity of a system depends in detail on how the molecules constituting the system interact, and there are no simple but correct formulas for it. The simplest exact expressions are the Green–Kubo relations for the linear shear viscosity or the transient time correlation function expressions derived by Evans and Morriss in 1988. Although these expressions are each exact, calculating the viscosity of a dense fluid using these relations currently requires the use of molecular dynamics computer simulations. Somewhat more progress can be made for a dilute gas, as elementary assumptions about how gas molecules move and interact lead to a basic understanding of the molecular origins of viscosity. More sophisticated treatments can be constructed by systematically coarse-graining the equations of motion of the gas molecules. An example of such a treatment is Chapman–Enskog theory, which derives expressions for the viscosity of a dilute gas from the Boltzmann equation.
Pure gases
See also: Kinetic theory of gasesElementary calculation of viscosity for a dilute gas Consider a dilute gas moving parallel to the -axis with velocity that depends only on the coordinate. To simplify the discussion, the gas is assumed to have uniform temperature and density.
Under these assumptions, the velocity of a molecule passing through is equal to whatever velocity that molecule had when its mean free path began. Because is typically small compared with macroscopic scales, the average velocity of such a molecule has the form
where is a numerical constant on the order of . (Some authors estimate ; on the other hand, a more careful calculation for rigid elastic spheres gives .) Next, because half the molecules on either side are moving towards , and doing so on average with half the average molecular speed , the momentum flux from either side is
The net momentum flux at is the difference of the two:
According to the definition of viscosity, this momentum flux should be equal to , which leads to
Viscosity in gases arises principally from the molecular diffusion that transports momentum between layers of flow. An elementary calculation for a dilute gas at temperature and density gives
where is the Boltzmann constant, the molecular mass, and a numerical constant on the order of . The quantity , the mean free path, measures the average distance a molecule travels between collisions. Even without a priori knowledge of , this expression has nontrivial implications. In particular, since is typically inversely proportional to density and increases with temperature, itself should increase with temperature and be independent of density at fixed temperature. In fact, both of these predictions persist in more sophisticated treatments, and accurately describe experimental observations. By contrast, liquid viscosity typically decreases with temperature.
For rigid elastic spheres of diameter , can be computed, giving
In this case is independent of temperature, so . For more complicated molecular models, however, depends on temperature in a non-trivial way, and simple kinetic arguments as used here are inadequate. More fundamentally, the notion of a mean free path becomes imprecise for particles that interact over a finite range, which limits the usefulness of the concept for describing real-world gases.
Chapman–Enskog theory
Main article: Chapman–Enskog theoryA technique developed by Sydney Chapman and David Enskog in the early 1900s allows a more refined calculation of . It is based on the Boltzmann equation, which provides a statistical description of a dilute gas in terms of intermolecular interactions. The technique allows accurate calculation of for molecular models that are more realistic than rigid elastic spheres, such as those incorporating intermolecular attractions. Doing so is necessary to reproduce the correct temperature dependence of , which experiments show increases more rapidly than the trend predicted for rigid elastic spheres. Indeed, the Chapman–Enskog analysis shows that the predicted temperature dependence can be tuned by varying the parameters in various molecular models. A simple example is the Sutherland model, which describes rigid elastic spheres with weak mutual attraction. In such a case, the attractive force can be treated perturbatively, which leads to a simple expression for :
where is independent of temperature, being determined only by the parameters of the intermolecular attraction. To connect with experiment, it is convenient to rewrite as
where is the viscosity at temperature . This expression is usually named Sutherland's formula. If is known from experiments at and at least one other temperature, then can be calculated. Expressions for obtained in this way are qualitatively accurate for a number of simple gases. Slightly more sophisticated models, such as the Lennard-Jones potential, or the more flexible Mie potential, may provide better agreement with experiments, but only at the cost of a more opaque dependence on temperature. A further advantage of these more complex interaction potentials is that they can be used to develop accurate models for a wide variety of properties using the same potential parameters. In situations where little experimental data is available, this makes it possible to obtain model parameters from fitting to properties such as pure-fluid vapour-liquid equilibria, before using the parameters thus obtained to predict the viscosities of interest with reasonable accuracy.
In some systems, the assumption of spherical symmetry must be abandoned, as is the case for vapors with highly polar molecules like H2O. In these cases, the Chapman–Enskog analysis is significantly more complicated.
Bulk viscosity
See also: Bulk viscosityIn the kinetic-molecular picture, a non-zero bulk viscosity arises in gases whenever there are non-negligible relaxational timescales governing the exchange of energy between the translational energy of molecules and their internal energy, e.g. rotational and vibrational. As such, the bulk viscosity is for a monatomic ideal gas, in which the internal energy of molecules is negligible, but is nonzero for a gas like carbon dioxide, whose molecules possess both rotational and vibrational energy.
Pure liquids
See also: Temperature dependence of viscosity § LiquidsIn contrast with gases, there is no simple yet accurate picture for the molecular origins of viscosity in liquids.
At the simplest level of description, the relative motion of adjacent layers in a liquid is opposed primarily by attractive molecular forces acting across the layer boundary. In this picture, one (correctly) expects viscosity to decrease with increasing temperature. This is because increasing temperature increases the random thermal motion of the molecules, which makes it easier for them to overcome their attractive interactions.
Building on this visualization, a simple theory can be constructed in analogy with the discrete structure of a solid: groups of molecules in a liquid are visualized as forming "cages" which surround and enclose single molecules. These cages can be occupied or unoccupied, and stronger molecular attraction corresponds to stronger cages. Due to random thermal motion, a molecule "hops" between cages at a rate which varies inversely with the strength of molecular attractions. In equilibrium these "hops" are not biased in any direction. On the other hand, in order for two adjacent layers to move relative to each other, the "hops" must be biased in the direction of the relative motion. The force required to sustain this directed motion can be estimated for a given shear rate, leading to
| 1 |
where is the Avogadro constant, is the Planck constant, is the volume of a mole of liquid, and is the normal boiling point. This result has the same form as the well-known empirical relation
| 2 |
where and are constants fit from data. On the other hand, several authors express caution with respect to this model. Errors as large as 30% can be encountered using equation (1), compared with fitting equation (2) to experimental data. More fundamentally, the physical assumptions underlying equation (1) have been criticized. It has also been argued that the exponential dependence in equation (1) does not necessarily describe experimental observations more accurately than simpler, non-exponential expressions.
In light of these shortcomings, the development of a less ad hoc model is a matter of practical interest. Foregoing simplicity in favor of precision, it is possible to write rigorous expressions for viscosity starting from the fundamental equations of motion for molecules. A classic example of this approach is Irving–Kirkwood theory. On the other hand, such expressions are given as averages over multiparticle correlation functions and are therefore difficult to apply in practice.
In general, empirically derived expressions (based on existing viscosity measurements) appear to be the only consistently reliable means of calculating viscosity in liquids.
Local atomic structure changes observed in undercooled liquids on cooling below the equilibrium melting temperature either in terms of radial distribution function g(r) or structure factor S(Q) are found to be directly responsible for the liquid fragility: deviation of the temperature dependence of viscosity of the undercooled liquid from the Arrhenius equation (2) through modification of the activation energy for viscous flow. At the same time equilibrium liquids follow the Arrhenius equation.
Mixtures and blends
See also: Viscosity models for mixturesGaseous mixtures
The same molecular-kinetic picture of a single component gas can also be applied to a gaseous mixture. For instance, in the Chapman–Enskog approach the viscosity of a binary mixture of gases can be written in terms of the individual component viscosities , their respective volume fractions, and the intermolecular interactions.
As for the single-component gas, the dependence of on the parameters of the intermolecular interactions enters through various collisional integrals which may not be expressible in closed form. To obtain usable expressions for which reasonably match experimental data, the collisional integrals may be computed numerically or from correlations. In some cases, the collision integrals are regarded as fitting parameters, and are fitted directly to experimental data. This is a common approach in the development of reference equations for gas-phase viscosities. An example of such a procedure is the Sutherland approach for the single-component gas, discussed above.
For gas mixtures consisting of simple molecules, Revised Enskog Theory has been shown to accurately represent both the density- and temperature dependence of the viscosity over a wide range of conditions.
Blends of liquids
As for pure liquids, the viscosity of a blend of liquids is difficult to predict from molecular principles. One method is to extend the molecular "cage" theory presented above for a pure liquid. This can be done with varying levels of sophistication. One expression resulting from such an analysis is the Lederer–Roegiers equation for a binary mixture:
where is an empirical parameter, and and are the respective mole fractions and viscosities of the component liquids.
Since blending is an important process in the lubricating and oil industries, a variety of empirical and proprietary equations exist for predicting the viscosity of a blend.
Solutions and suspensions
Aqueous solutions
See also: Debye–Hückel theory and List of viscosities § Aqueous solutionsDepending on the solute and range of concentration, an aqueous electrolyte solution can have either a larger or smaller viscosity compared with pure water at the same temperature and pressure. For instance, a 20% saline (sodium chloride) solution has viscosity over 1.5 times that of pure water, whereas a 20% potassium iodide solution has viscosity about 0.91 times that of pure water.
An idealized model of dilute electrolytic solutions leads to the following prediction for the viscosity of a solution:
where is the viscosity of the solvent, is the concentration, and is a positive constant which depends on both solvent and solute properties. However, this expression is only valid for very dilute solutions, having less than 0.1 mol/L. For higher concentrations, additional terms are necessary which account for higher-order molecular correlations:
where and are fit from data. In particular, a negative value of is able to account for the decrease in viscosity observed in some solutions. Estimated values of these constants are shown below for sodium chloride and potassium iodide at temperature 25 °C (mol = mole, L = liter).
| Solute | (mol L) | (mol L) | (mol L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 0.0062 | 0.0793 | 0.0080 |
| Potassium iodide (KI) | 0.0047 | −0.0755 | 0.0000 |
Suspensions
In a suspension of solid particles (e.g. micron-size spheres suspended in oil), an effective viscosity can be defined in terms of stress and strain components which are averaged over a volume large compared with the distance between the suspended particles, but small with respect to macroscopic dimensions. Such suspensions generally exhibit non-Newtonian behavior. However, for dilute systems in steady flows, the behavior is Newtonian and expressions for can be derived directly from the particle dynamics. In a very dilute system, with volume fraction , interactions between the suspended particles can be ignored. In such a case one can explicitly calculate the flow field around each particle independently, and combine the results to obtain . For spheres, this results in the Einstein's effective viscosity formula:
where is the viscosity of the suspending liquid. The linear dependence on is a consequence of neglecting interparticle interactions. For dilute systems in general, one expects to take the form
where the coefficient may depend on the particle shape (e.g. spheres, rods, disks). Experimental determination of the precise value of is difficult, however: even the prediction for spheres has not been conclusively validated, with various experiments finding values in the range . This deficiency has been attributed to difficulty in controlling experimental conditions.
In denser suspensions, acquires a nonlinear dependence on , which indicates the importance of interparticle interactions. Various analytical and semi-empirical schemes exist for capturing this regime. At the most basic level, a term quadratic in is added to :
and the coefficient is fit from experimental data or approximated from the microscopic theory. However, some authors advise caution in applying such simple formulas since non-Newtonian behavior appears in dense suspensions ( for spheres), or in suspensions of elongated or flexible particles.
There is a distinction between a suspension of solid particles, described above, and an emulsion. The latter is a suspension of tiny droplets, which themselves may exhibit internal circulation. The presence of internal circulation can decrease the observed effective viscosity, and different theoretical or semi-empirical models must be used.
Amorphous materials

In the high and low temperature limits, viscous flow in amorphous materials (e.g. in glasses and melts) has the Arrhenius form:
where Q is a relevant activation energy, given in terms of molecular parameters; T is temperature; R is the molar gas constant; and A is approximately a constant. The activation energy Q takes a different value depending on whether the high or low temperature limit is being considered: it changes from a high value QH at low temperatures (in the glassy state) to a low value QL at high temperatures (in the liquid state).

For intermediate temperatures, varies nontrivially with temperature and the simple Arrhenius form fails. On the other hand, the two-exponential equation
where , , , are all constants, provides a good fit to experimental data over the entire range of temperatures, while at the same time reducing to the correct Arrhenius form in the low and high temperature limits. This expression, also known as Duouglas-Doremus-Ojovan model, can be motivated from various theoretical models of amorphous materials at the atomic level.
A two-exponential equation for the viscosity can be derived within the Dyre shoving model of supercooled liquids, where the Arrhenius energy barrier is identified with the high-frequency shear modulus times a characteristic shoving volume. Upon specifying the temperature dependence of the shear modulus via thermal expansion and via the repulsive part of the intermolecular potential, another two-exponential equation is retrieved:
where denotes the high-frequency shear modulus of the material evaluated at a temperature equal to the glass transition temperature , is the so-called shoving volume, i.e. it is the characteristic volume of the group of atoms involved in the shoving event by which an atom/molecule escapes from the cage of nearest-neighbours, typically on the order of the volume occupied by few atoms. Furthermore, is the thermal expansion coefficient of the material, is a parameter which measures the steepness of the power-law rise of the ascending flank of the first peak of the radial distribution function, and is quantitatively related to the repulsive part of the interatomic potential. Finally, denotes the Boltzmann constant.
Eddy viscosity
In the study of turbulence in fluids, a common practical strategy is to ignore the small-scale vortices (or eddies) in the motion and to calculate a large-scale motion with an effective viscosity, called the "eddy viscosity", which characterizes the transport and dissipation of energy in the smaller-scale flow (see large eddy simulation). In contrast to the viscosity of the fluid itself, which must be positive by the second law of thermodynamics, the eddy viscosity can be negative.
Prediction
Because viscosity depends continuously on temperature and pressure, it cannot be fully characterized by a finite number of experimental measurements. Predictive formulas become necessary if experimental values are not available at the temperatures and pressures of interest. This capability is important for thermophysical simulations, in which the temperature and pressure of a fluid can vary continuously with space and time. A similar situation is encountered for mixtures of pure fluids, where the viscosity depends continuously on the concentration ratios of the constituent fluids
For the simplest fluids, such as dilute monatomic gases and their mixtures, ab initio quantum mechanical computations can accurately predict viscosity in terms of fundamental atomic constants, i.e., without reference to existing viscosity measurements. For the special case of dilute helium, uncertainties in the ab initio calculated viscosity are two order of magnitudes smaller than uncertainties in experimental values.
For slightly more complex fluids and mixtures at moderate densities (i.e. sub-critical densities) Revised Enskog Theory can be used to predict viscosities with some accuracy. Revised Enskog Theory is predictive in the sense that predictions for viscosity can be obtained using parameters fitted to other, pure-fluid thermodynamic properties or transport properties, thus requiring no a priori experimental viscosity measurements.
For most fluids, high-accuracy, first-principles computations are not feasible. Rather, theoretical or empirical expressions must be fit to existing viscosity measurements. If such an expression is fit to high-fidelity data over a large range of temperatures and pressures, then it is called a "reference correlation" for that fluid. Reference correlations have been published for many pure fluids; a few examples are water, carbon dioxide, ammonia, benzene, and xenon. Many of these cover temperature and pressure ranges that encompass gas, liquid, and supercritical phases.
Thermophysical modeling software often relies on reference correlations for predicting viscosity at user-specified temperature and pressure. These correlations may be proprietary. Examples are REFPROP (proprietary) and CoolProp (open-source).
Viscosity can also be computed using formulas that express it in terms of the statistics of individual particle trajectories. These formulas include the Green–Kubo relations for the linear shear viscosity and the transient time correlation function expressions derived by Evans and Morriss in 1988. The advantage of these expressions is that they are formally exact and valid for general systems. The disadvantage is that they require detailed knowledge of particle trajectories, available only in computationally expensive simulations such as molecular dynamics. An accurate model for interparticle interactions is also required, which may be difficult to obtain for complex molecules.
Selected substances

Observed values of viscosity vary over several orders of magnitude, even for common substances (see the order of magnitude table below). For instance, a 70% sucrose (sugar) solution has a viscosity over 400 times that of water, and 26,000 times that of air. More dramatically, pitch has been estimated to have a viscosity 230 billion times that of water.
Water
The dynamic viscosity of water is about 0.89 mPa·s at room temperature (25 °C). As a function of temperature in kelvins, the viscosity can be estimated using the semi-empirical Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann equation:
where A = 0.02939 mPa·s, B = 507.88 K, and C = 149.3 K. Experimentally determined values of the viscosity are also given in the table below. The values at 20 °C are a useful reference: there, the dynamic viscosity is about 1 cP and the kinematic viscosity is about 1 cSt.
| Temperature (°C) |
Viscosity (mPa·s or cP) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 1.305 9 |
| 20 | 1.001 6 |
| 30 | 0.797 22 |
| 50 | 0.546 52 |
| 70 | 0.403 55 |
| 90 | 0.314 17 |
Air
Under standard atmospheric conditions (25 °C and pressure of 1 bar), the dynamic viscosity of air is 18.5 μPa·s, roughly 50 times smaller than the viscosity of water at the same temperature. Except at very high pressure, the viscosity of air depends mostly on the temperature. Among the many possible approximate formulas for the temperature dependence (see Temperature dependence of viscosity), one is:
which is accurate in the range −20 °C to 400 °C. For this formula to be valid, the temperature must be given in kelvins; then corresponds to the viscosity in Pa·s.

Other common substances
| Substance | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Temperature (°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 0.604 | 25 | |
| Water | 1.0016 | 20 | |
| Mercury | 1.526 | 25 | |
| Whole milk | 2.12 | 20 | |
| Dark beer | 2.53 | 20 | |
| Olive oil | 56.2 | 26 | |
| Honey | 2,000–10,000 | 20 | |
| Ketchup | 5,000–20,000 | 25 | |
| Peanut butter | 10–10 | ||
| Pitch | 2.3×10 | 10–30 (variable) |
Order of magnitude estimates
The following table illustrates the range of viscosity values observed in common substances. Unless otherwise noted, a temperature of 25 °C and a pressure of 1 atmosphere are assumed.
The values listed are representative estimates only, as they do not account for measurement uncertainties, variability in material definitions, or non-Newtonian behavior.
| Factor (Pa·s) | Description | Examples | Values (Pa·s) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Lower range of gaseous viscosity |
Butane | 7.49 × 10 | |
| Hydrogen | 8.8 × 10 | |||
| 10 | Upper range of gaseous viscosity | Krypton | 2.538 × 10 | |
| Neon | 3.175 × 10 | |||
| 10 | Lower range of liquid viscosity | Pentane | 2.24 × 10 | |
| Gasoline | 6 × 10 | |||
| Water | 8.90 × 10 | |||
| 10 | Typical range for small-molecule Newtonian liquids |
Ethanol | 1.074 × 10 | |
| Mercury | 1.526 × 10 | |||
| Whole milk (20 °C) | 2.12 × 10 | |||
| Blood | 3 × 10 to 6 × 10 | |||
| Liquid steel (1550 °C) | 6 × 10 | |||
| 10 – 10 | Oils and long-chain hydrocarbons | Linseed oil | 0.028 | |
| Oleic acid | 0.036 | |||
| Olive oil | 0.084 | |||
| SAE 10 Motor oil | 0.085 to 0.14 | |||
| Castor oil | 0.1 | |||
| SAE 20 Motor oil | 0.14 to 0.42 | |||
| SAE 30 Motor oil | 0.42 to 0.65 | |||
| SAE 40 Motor oil | 0.65 to 0.90 | |||
| Glycerine | 1.5 | |||
| Pancake syrup | 2.5 | |||
| 10 – 10 | Pastes, gels, and other semisolids (generally non-Newtonian) |
Ketchup | ≈ 10 | |
| Mustard | ||||
| Sour cream | ≈ 10 | |||
| Peanut butter | ||||
| Lard | ≈ 10 | |||
| ≈10 | Viscoelastic polymers | Pitch | 2.3×10 | |
| ≈10 | Certain solids under a viscoelastic description |
Mantle (geology) | ≈ 10 to 10 |
See also
- Dashpot
- Deborah number
- Dilatant
- Herschel–Bulkley fluid
- High viscosity mixer
- Hyperviscosity syndrome
- Intrinsic viscosity
- Inviscid flow
- Joback method (estimation of liquid viscosity from molecular structure)
- Kaye effect
- Microviscosity
- Morton number
- Oil pressure
- Quasi-solid
- Rheology
- Stokes flow
- Superfluid helium-4
- Viscoplasticity
- Viscosity models for mixtures
- Zahn cup
References
Footnotes
- The discussion which follows draws from Chapman & Cowling 1970, pp. 232–237
- ^ These materials are highly non-Newtonian.
Citations
- ^ "Viscosity". Encyclopedia Britannica. 26 June 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- Growing up with Science. Marshall Cavendish. 2006. p. 1928. ISBN 978-0-7614-7521-7.
- E. Dale Martin (1961). A Study of Laminar Compressible Viscous Pipe Flow Accelerated by an Axial Body Force, with Application to Magnetogasdynamics. NASA. p. 7.
- Balescu 1975, pp. 428–429.
- Landau & Lifshitz 1987.
- Harper, Douglas (n.d.). "viscous (adj.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 19 September 2019.
- Mewis & Wagner 2012, p. 19.
- Streeter, Wylie & Bedford 1998.
- Holman 2002.
- Incropera et al. 2007.
- Nič et al. 1997.
- ^ Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, p. 19.
- ^ Landau & Lifshitz 1987, pp. 44–45.
- Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, p. 18: This source uses an alternative sign convention, which has been reversed here.
- Landau & Lifshitz 1987, p. 45.
- ^ Balescu 1975.
- ^ Chapman & Cowling 1970.
- Millat 1996.
- ^ Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007.
- Schroeder 1999.
- Różańska et al. 2014, pp. 47–55.
- Trouton 1906, pp. 426–440.
- Mewis & Wagner 2012, pp. 228–230.
- Kumagai, Sasajima & Ito 1978, pp. 157–161.
- Scherer, Pardenek & Swiatek 1988, p. 14.
- Hannan 2007.
- Kwapiszewska et al. 2020.
- McNaught & Wilkinson 1997, poise.
- Gyllenbok 2018, p. 213.
- "What is the unit called a reyn?". sizes.com. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ASTM D2161 : Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity, ASTM, 2005, p. 1
- Trachenko & Brazhkin 2020.
- ^ Trachenko & Brazhkin 2021.
- ^ Evans & Morriss 1988.
- ^ Bellac, Mortessagne & Batrouni 2004.
- Chapman & Cowling 1970, p. 103.
- Cercignani 1975.
- Sutherland 1893, pp. 507–531.
- Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, pp. 25–27.
- Chapman & Cowling 1970, pp. 235–237.
- Chapman & Cowling 1970, pp. 197, 214–216.
- Cramer 2012, p. 066102-2.
- Reid & Sherwood 1958, p. 202.
- ^ Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, pp. 29–31.
- Reid & Sherwood 1958, pp. 203–204.
- Hildebrand 1977.
- Hildebrand 1977, p. 37.
- Egelstaff 1992, p. 264.
- Irving & Kirkwood 1949, pp. 817–829.
- Reid & Sherwood 1958, pp. 206–209.
- Louzguine-Luzgin, D. V. (2022-10-18). "Structural Changes in Metallic Glass-Forming Liquids on Cooling and Subsequent Vitrification in Relationship with Their Properties". Materials. 15 (20): 7285. Bibcode:2022Mate...15.7285L. doi:10.3390/ma15207285. ISSN 1996-1944. PMC 9610435. PMID 36295350.
- Kelton, K F (2017-01-18). "Kinetic and structural fragility—a correlation between structures and dynamics in metallic liquids and glasses". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 29 (2): 023002. Bibcode:2017JPCM...29b3002K. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/29/2/023002. ISSN 0953-8984. PMID 27841996.
- ^ Jervell, Vegard G.; Wilhelmsen, Øivind (2023-06-08). "Revised Enskog theory for Mie fluids: Prediction of diffusion coefficients, thermal diffusion coefficients, viscosities, and thermal conductivities". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 158 (22). Bibcode:2023JChPh.158v4101J. doi:10.1063/5.0149865. ISSN 0021-9606. PMID 37290070. S2CID 259119498.
- Lemmon, E. W.; Jacobsen, R. T. (2004-01-01). "Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity Equations for Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, and Air". International Journal of Thermophysics. 25 (1): 21–69. Bibcode:2004IJT....25...21L. doi:10.1023/B:IJOT.0000022327.04529.f3. ISSN 1572-9567. S2CID 119677367.
- López de Haro, M.; Cohen, E. G. D.; Kincaid, J. M. (1983-03-01). "The Enskog theory for multicomponent mixtures. I. Linear transport theory". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 78 (5): 2746–2759. Bibcode:1983JChPh..78.2746L. doi:10.1063/1.444985. ISSN 0021-9606.
- ^ Zhmud 2014, p. 22.
- ^ Viswanath et al. 2007.
- Abdulagatov, Zeinalova & Azizov 2006, pp. 75–88.
- ^ Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, pp. 31–33.
- Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, p. 32.
- ^ Mueller, Llewellin & Mader 2009, pp. 1201–1228.
- Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, p. 33.
- Fluegel 2007.
- Doremus 2002, pp. 7619–7629.
- ^ Ojovan, Travis & Hand 2007, p. 415107.
- Ojovan & Lee 2004, pp. 3803–3810.
- P. Hrma, P. Ferkl, P., A.A.Kruger. Arrhenian to non-Arrhenian crossover in glass melt viscosity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 619, 122556 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122556
- Dyre, Olsen & Christensen 1996, p. 2171.
- Hecksher & Dyre 2015.
- ^ Krausser, Samwer & Zaccone 2015, p. 13762.
- Bird, Stewart & Lightfoot 2007, p. 163.
- Lesieur 2012, pp. 2–.
- Sivashinsky & Yakhot 1985, p. 1040.
- Xie & Levchenko 2019, p. 045434.
- Sharipov & Benites 2020.
- Rowland, Al Ghafri & May 2020.
- Huber et al. 2009.
- Laesecke & Muzny 2017.
- Monogenidou, Assael & Huber 2018.
- Avgeri et al. 2014.
- Velliadou et al. 2021.
- "Refprop". NIST. Nist.gov. 18 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2022-02-09. Retrieved 2022-02-15.
- Bell et al. 2014.
- Evans & Morriss 2007.
- Maginn et al. 2019.
- ^ Edgeworth, Dalton & Parnell 1984, pp. 198–200.
- ^ Rumble 2018.
- Viswanath & Natarajan 1989, pp. 714–715.
- tec-science (2020-03-25). "Viscosity of liquids and gases". tec-science. Archived from the original on 2020-04-19. Retrieved 2020-05-07.
- ^ Fellows 2009.
- Yanniotis, Skaltsi & Karaburnioti 2006, pp. 372–377.
- ^ Koocheki et al. 2009, pp. 596–602.
- ^ Citerne, Carreau & Moan 2001, pp. 86–96.
- Kestin, Khalifa & Wakeham 1977.
- Assael et al. 2018.
- Kestin, Ro & Wakeham 1972.
- Rosenson, McCormick & Uretz 1996.
- Zhao et al. 2021.
- Sagdeev et al. 2019.
- Walzer, Hendel & Baumgardner.
Sources
- Abdulagatov, Ilmutdin M.; Zeinalova, Adelya B.; Azizov, Nazim D. (2006). "Experimental viscosity B-coefficients of aqueous LiCl solutions". Journal of Molecular Liquids. 126 (1–3): 75–88. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2005.10.006. ISSN 0167-7322.
- Assael, M. J.; et al. (2018). "Reference Values and Reference Correlations for the Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Fluids". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 47 (2): 021501. Bibcode:2018JPCRD..47b1501A. doi:10.1063/1.5036625. ISSN 0047-2689. PMC 6463310. PMID 30996494.
- Avgeri, S.; Assael, M. J.; Huber, M. L.; Perkins, R. A. (2014). "Reference Correlation of the Viscosity of Benzene from the Triple Point to 675 K and up to 300 MPa". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 43 (3). AIP Publishing: 033103. Bibcode:2014JPCRD..43c3103A. doi:10.1063/1.4892935. ISSN 0047-2689.
- Balescu, Radu (1975). Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-04600-4. Archived from the original on 2020-03-16. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Bell, Ian H.; Wronski, Jorrit; Quoilin, Sylvain; Lemort, Vincent (2014-01-27). "Pure and Pseudo-pure Fluid Thermophysical Property Evaluation and the Open-Source Thermophysical Property Library CoolProp". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 53 (6). American Chemical Society (ACS): 2498–2508. doi:10.1021/ie4033999. ISSN 0888-5885. PMC 3944605. PMID 24623957.
- Bellac, Michael; Mortessagne, Fabrice; Batrouni, G. George (2004). Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium Statistical Thermodynamics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-82143-8.
- Bird, R. Byron; Stewart, Warren E.; Lightfoot, Edwin N. (2007). Transport Phenomena (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-470-11539-8. Archived from the original on 2020-03-02. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Bird, R. Bryon; Armstrong, Robert C.; Hassager, Ole (1987), Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, Volume 1: Fluid Mechanics (2nd ed.), John Wiley & Sons
- Cercignani, Carlo (1975). Theory and Application of the Boltzmann Equation. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-444-19450-3.
- Chapman, Sydney; Cowling, T.G. (1970). The Mathematical Theory of Non-Uniform Gases (3rd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-07577-0.
- Citerne, Guillaume P.; Carreau, Pierre J.; Moan, Michel (2001). "Rheological properties of peanut butter". Rheologica Acta. 40 (1): 86–96. Bibcode:2001AcRhe..40...86C. doi:10.1007/s003970000120. S2CID 94555820.
- Cramer, M.S. (2012). "Numerical estimates for the bulk viscosity of ideal gases". Physics of Fluids. 24 (6): 066102–066102–23. Bibcode:2012PhFl...24f6102C. doi:10.1063/1.4729611. hdl:10919/47646. Archived from the original on 2022-02-15. Retrieved 2020-09-19.
- Doremus, R.H. (2002). "Viscosity of silica". J. Appl. Phys. 92 (12): 7619–7629. Bibcode:2002JAP....92.7619D. doi:10.1063/1.1515132.
- Dyre, J.C.; Olsen, N. B.; Christensen, T. (1996). "Local elastic expansion model for viscous-flow activation energies of glass-forming molecular liquids". Physical Review B. 53 (5): 2171–2174. Bibcode:1996PhRvB..53.2171D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.53.2171. PMID 9983702. S2CID 39833708.
- Edgeworth, R.; Dalton, B.J.; Parnell, T. (1984). "The pitch drop experiment". European Journal of Physics. 5 (4): 198–200. Bibcode:1984EJPh....5..198E. doi:10.1088/0143-0807/5/4/003. S2CID 250769509. Archived from the original on 2013-03-28. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- Egelstaff, P. A. (1992). An Introduction to the Liquid State (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-851012-3.
- Evans, Denis J.; Morriss, Gary P. (2007). Statistical Mechanics of Nonequilibrium Liquids. ANU Press. ISBN 978-1-921313-22-6. JSTOR j.ctt24h99q. Archived from the original on 2022-01-10. Retrieved 2022-01-10.
- Evans, Denis J.; Morriss, Gary P. (October 15, 1988). "Transient-time-correlation functions and the rheology of fluids". Physical Review A. 38 (8): 4142–4148. Bibcode:1988PhRvA..38.4142E. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.38.4142. PMID 9900865.
- Fellows, P. J. (2009). Food Processing Technology: Principles and Practice (3rd ed.). Woodhead. ISBN 978-1-84569-216-2.
- Fluegel, Alexander (2007). "Viscosity calculation of glasses". Glassproperties.com. Archived from the original on 2010-11-27. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- Gibbs, Philip (January 1997). "Is glass liquid or solid?". math.ucr.edu. Archived from the original on 29 March 2007. Retrieved 19 September 2019.
- Gyllenbok, Jan (2018). "Encyclopaedia of Historical Metrology, Weights, and Measures: Volume 1". Encyclopaedia of Historical Metrology, Weights, and Measures. Vol. 1. Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-3-319-57598-8.
- Hannan, Henry (2007). Technician's Formulation Handbook for Industrial and Household Cleaning Products. Waukesha, Wisconsin: Kyral LLC. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-615-15601-9.
- Hecksher, Tina; Dyre, Jeppe C. (2015-01-01). "A review of experiments testing the shoving model". Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 7th IDMRCS: Relaxation in Complex Systems. 407: 14–22. Bibcode:2015JNCS..407...14H. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.08.056. ISSN 0022-3093. Archived from the original on 2022-02-15. Retrieved 2021-10-17.
- Hildebrand, Joel Henry (1977). Viscosity and Diffusivity: A Predictive Treatment. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-03072-0.
- Holman, Jack Philip (2002). Heat Transfer. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-112230-6. Archived from the original on 2020-03-15. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Huber, M. L.; Perkins, R. A.; Laesecke, A.; Friend, D. G.; Sengers, J. V.; Assael, M. J.; Metaxa, I. N.; Vogel, E.; Mareš, R.; Miyagawa, K. (2009). "New International Formulation for the Viscosity of H2O". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 38 (2). AIP Publishing: 101–125. Bibcode:2009JPCRD..38..101H. doi:10.1063/1.3088050. ISSN 0047-2689.
- Incropera, Frank P.; et al. (2007). Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-45728-2. Archived from the original on 2020-03-11. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Irving, J.H.; Kirkwood, John G. (1949). "The Statistical Mechanical Theory of Transport Processes. IV. The Equations of Hydrodynamics". J. Chem. Phys. 18 (6): 817–829. doi:10.1063/1.1747782.
- Kestin, J.; Ro, S. T.; Wakeham, W. A. (1972). "Viscosity of the Noble Gases in the Temperature Range 25–700 °C". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 56 (8): 4119–4124. Bibcode:1972JChPh..56.4119K. doi:10.1063/1.1677824. ISSN 0021-9606.
- Kestin, J.; Khalifa, H.E.; Wakeham, W.A. (1977). "The viscosity of five gaseous hydrocarbons". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 66 (3): 1132. Bibcode:1977JChPh..66.1132K. doi:10.1063/1.434048.
- Koocheki, Arash; et al. (2009). "The rheological properties of ketchup as a function of different hydrocolloids and temperature". International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 44 (3): 596–602. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2008.01868.x.
- Krausser, J.; Samwer, K.; Zaccone, A. (2015). "Interatomic repulsion softness directly controls the fragility of supercooled metallic melts". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 112 (45): 13762–13767. arXiv:1510.08117. Bibcode:2015PNAS..11213762K. doi:10.1073/pnas.1503741112. PMC 4653154. PMID 26504208.
- Kumagai, Naoichi; Sasajima, Sadao; Ito, Hidebumi (15 February 1978). "Long-term Creep of Rocks: Results with Large Specimens Obtained in about 20 Years and Those with Small Specimens in about 3 Years". Journal of the Society of Materials Science (Japan). 27 (293): 157–161. NAID 110002299397. Archived from the original on 2011-05-21. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- Kwapiszewska, Karina; Szczepański, Krzysztof; Kalwarczyk, Tomasz; Michalska, Bernadeta; Patalas-Krawczyk, Paulina; Szymański, Jędrzej; Andryszewski, Tomasz; Iwan, Michalina; Duszyński, Jerzy; Hołyst, Robert (2020). "Nanoscale Viscosity of Cytoplasm Is Conserved in Human Cell Lines". The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 11 (16): 6914–6920. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01748. PMC 7450658. PMID 32787203.
- Laesecke, Arno; Muzny, Chris D. (2017). "Reference Correlation for the Viscosity of Carbon Dioxide". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 46 (1). AIP Publishing: 013107. Bibcode:2017JPCRD..46a3107L. doi:10.1063/1.4977429. ISSN 0047-2689. PMC 5514612. PMID 28736460.
- Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E.M. (1987). Fluid Mechanics (2nd ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-08-057073-0. Archived from the original on 2020-03-21. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Maginn, Edward J.; Messerly, Richard A.; Carlson, Daniel J.; Roe, Daniel R.; Elliott, J. Richard (2019). "Best Practices for Computing Transport Properties 1. Self-Diffusivity and Viscosity from Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics [Article v1.0]". Living Journal of Computational Molecular Science. 1 (1). University of Colorado at Boulder. doi:10.33011/livecoms.1.1.6324. ISSN 2575-6524. S2CID 104357320.
- Monogenidou, S. A.; Assael, M. J.; Huber, M. L. (2018). "Reference Correlation for the Viscosity of Ammonia from the Triple Point to 725 K and up to 50 MPa". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 47 (2). AIP Publishing: 023102. Bibcode:2018JPCRD..47b3102M. doi:10.1063/1.5036724. ISSN 0047-2689. PMC 6512859. PMID 31092958.
- Lesieur, Marcel (2012). Turbulence in Fluids: Stochastic and Numerical Modelling. Springer. ISBN 978-94-009-0533-7. Archived from the original on 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
- Mewis, Jan; Wagner, Norman J. (2012). Colloidal Suspension Rheology. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-51599-3. Archived from the original on 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2018-12-10.
- McNaught, A. D.; Wilkinson, A. (1997). "poise". IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the "Gold Book"). S. J. Chalk (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific. doi:10.1351/goldbook. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8.
- Millat, Jorgen (1996). Transport Properties of Fluids : Their Correlation, Prediction and Estimation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-02290-3. OCLC 668204060.
- Mueller, S.; Llewellin, E. W.; Mader, H. M. (2009). "The rheology of suspensions of solid particles". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 466 (2116): 1201–1228. doi:10.1098/rspa.2009.0445. ISSN 1364-5021.
- Nič, Miloslav; et al., eds. (1997). "dynamic viscosity, η". IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. doi:10.1351/goldbook. ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7.
- Ojovan, M.I.; Lee, W.E. (2004). "Viscosity of network liquids within Doremus approach". J. Appl. Phys. 95 (7): 3803–3810. Bibcode:2004JAP....95.3803O. doi:10.1063/1.1647260.
- Ojovan, M.I.; Travis, K. P.; Hand, R.J. (2007). "Thermodynamic parameters of bonds in glassy materials from viscosity-temperature relationships" (PDF). J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 19 (41): 415107. Bibcode:2007JPCM...19O5107O. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/19/41/415107. PMID 28192319. S2CID 24724512. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-07-25. Retrieved 2019-09-27.
- Plumb, Robert C. (1989). "Antique windowpanes and the flow of supercooled liquids". Journal of Chemical Education. 66 (12): 994. Bibcode:1989JChEd..66..994P. doi:10.1021/ed066p994. Archived from the original on 2005-08-26. Retrieved 2013-12-25.
- Rapaport, D.C. (2004). The Art of Molecular Dynamics Simulation (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-82568-9. Archived from the original on 2018-06-25. Retrieved 2022-01-10.
- Reid, Robert C.; Sherwood, Thomas K. (1958). The Properties of Gases and Liquids. McGraw-Hill.
- Reif, F. (1965), Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics, McGraw-Hill. An advanced treatment.
- Rosenson, R S; McCormick, A; Uretz, E F (1996-08-01). "Distribution of blood viscosity values and biochemical correlates in healthy adults". Clinical Chemistry. 42 (8). Oxford University Press (OUP): 1189–1195. doi:10.1093/clinchem/42.8.1189. ISSN 0009-9147. PMID 8697575.
- Rowland, Darren; Al Ghafri, Saif Z. S.; May, Eric F. (2020-03-01). "Wide-Ranging Reference Correlations for Dilute Gas Transport Properties Based on Ab Initio Calculations and Viscosity Ratio Measurements". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. 49 (1). AIP Publishing: 013101. Bibcode:2020JPCRD..49a3101X. doi:10.1063/1.5125100. ISSN 0047-2689. S2CID 213794612.
- Różańska, S.; Różański, J.; Ochowiak, M.; Mitkowski, P. T. (2014). "Extensional viscosity measurements of concentrated emulsions with the use of the opposed nozzles device" (PDF). Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 31 (1): 47–55. doi:10.1590/S0104-66322014000100006. ISSN 0104-6632. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-05-08. Retrieved 2019-09-19.
- Rumble, John R., ed. (2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-138-56163-2.
- Sagdeev, Damir; Gabitov, Il'giz; Isyanov, Chingiz; Khairutdinov, Vener; Farakhov, Mansur; Zaripov, Zufar; Abdulagatov, Ilmutdin (2019-04-22). "Densities and Viscosities of Oleic Acid at Atmospheric Pressure". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 96 (6). Wiley: 647–662. doi:10.1002/aocs.12217. ISSN 0003-021X. S2CID 150156106.
- Scherer, George W.; Pardenek, Sandra A.; Swiatek, Rose M. (1988). "Viscoelasticity in silica gel". Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 107 (1): 14. Bibcode:1988JNCS..107...14S. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(88)90086-5.
- Schroeder, Daniel V. (1999). An Introduction to Thermal Physics. Addison Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-38027-9. Archived from the original on 2020-03-10. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
- Sharipov, Felix; Benites, Victor J. (2020-07-01). "Transport coefficients of multi-component mixtures of noble gases based on ab initio potentials: Viscosity and thermal conductivity". Physics of Fluids. 32 (7). AIP Publishing: 077104. arXiv:2006.08687. Bibcode:2020PhFl...32g7104S. doi:10.1063/5.0016261. ISSN 1070-6631. S2CID 219708359.
- Sivashinsky, V.; Yakhot, G. (1985). "Negative viscosity effect in large-scale flows". The Physics of Fluids. 28 (4): 1040. Bibcode:1985PhFl...28.1040S. doi:10.1063/1.865025.
- Streeter, Victor Lyle; Wylie, E. Benjamin; Bedford, Keith W. (1998). Fluid Mechanics. WCB/McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-062537-2. Archived from the original on 2020-03-16. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Sutherland, William (1893). "LII. The viscosity of gases and molecular force" (PDF). The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science. 36 (223): 507–531. doi:10.1080/14786449308620508. ISSN 1941-5982. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-07-20. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Symon, Keith R. (1971). Mechanics (3rd ed.). Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-07392-8. Archived from the original on 2020-03-11. Retrieved 2019-09-18.
- Trachenko, K.; Brazhkin, V. V. (2020-04-22). "Minimal quantum viscosity from fundamental physical constants". Science Advances. 6 (17). American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS): eaba3747. arXiv:1912.06711. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.3747T. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba3747. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 7182420. PMID 32426470.
- Trachenko, Kostya; Brazhkin, Vadim V. (2021-12-01). "The quantum mechanics of viscosity" (PDF). Physics Today. 74 (12). AIP Publishing: 66–67. Bibcode:2021PhT....74l..66T. doi:10.1063/pt.3.4908. ISSN 0031-9228. S2CID 244831744. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-01-10. Retrieved 2022-01-10.
- Trouton, Fred. T. (1906). "On the Coefficient of Viscous Traction and Its Relation to that of Viscosity". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 77 (519): 426–440. Bibcode:1906RSPSA..77..426T. doi:10.1098/rspa.1906.0038. ISSN 1364-5021.
- Velliadou, Danai; Tasidou, Katerina A.; Antoniadis, Konstantinos D.; Assael, Marc J.; Perkins, Richard A.; Huber, Marcia L. (2021-03-25). "Reference Correlation for the Viscosity of Xenon from the Triple Point to 750 K and up to 86 MPa". International Journal of Thermophysics. 42 (5). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 74. Bibcode:2021IJT....42...74V. doi:10.1007/s10765-021-02818-9. ISSN 0195-928X. PMC 8356199. PMID 34393314.
- Viswanath, D.S.; Natarajan, G. (1989). Data Book on the Viscosity of Liquids. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation. ISBN 0-89116-778-1.
- Viswanath, Dabir S.; et al. (2007). Viscosity of Liquids: Theory, Estimation, Experiment, and Data. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-5481-5.
- Walzer, Uwe; Hendel, Roland; Baumgardner, John, "Mantle Viscosity and the Thickness of the Convective Downwellings", igw.uni-jena.de, archived from the original on 2007-06-11
- Xie, Hong-Yi; Levchenko, Alex (23 January 2019). "Negative viscosity and eddy flow of the imbalanced electron-hole liquid in graphene". Phys. Rev. B. 99 (4): 045434. arXiv:1807.04770. Bibcode:2019PhRvB..99d5434X. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.99.045434. S2CID 51792702.
- Yanniotis, S.; Skaltsi, S.; Karaburnioti, S. (February 2006). "Effect of moisture content on the viscosity of honey at different temperatures". Journal of Food Engineering. 72 (4): 372–377. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.12.017.
- Zhao, Mengjing; Wang, Yong; Yang, Shufeng; Li, Jingshe; Liu, Wei; Song, Zhaoqi (2021). "Flow behavior and heat transfer of molten steel in a two-strand tundish heated by plasma". Journal of Materials Research and Technology. 13. Elsevier BV: 561–572. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.04.069. ISSN 2238-7854. S2CID 236277034.
- Zhmud, Boris (2014). "Viscosity Blending Equations" (PDF). Lube-Tech:93. Lube. No. 121. pp. 22–27. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-12-01. Retrieved 2018-11-30.
- "NIST Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties Database (REFPROP): Version 10". NIST. 2018-01-01. Archived from the original on 2021-12-16. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- tec-science (2020-03-25). "Viscosity of liquids and gases". tec-science. Archived from the original on 2020-04-19. Retrieved 2020-05-07.
External links
- Viscosity - The Feynman Lectures on Physics
- Fluid properties – high accuracy calculation of viscosity for frequently encountered pure liquids and gases
- Fluid Characteristics Chart – a table of viscosities and vapor pressures for various fluids
- Gas Dynamics Toolbox – calculate coefficient of viscosity for mixtures of gases
- Glass Viscosity Measurement – viscosity measurement, viscosity units and fixpoints, glass viscosity calculation
- Kinematic Viscosity – conversion between kinematic and dynamic viscosity
- Physical Characteristics of Water – a table of water viscosity as a function of temperature
- Calculation of temperature-dependent dynamic viscosities for some common components
- Artificial viscosity
- Viscosity of Air, Dynamic and Kinematic, Engineers Edge
| Major branches of physics | |
|---|---|
| Divisions | |
| Approaches | |
| Classical | |
| Modern | |
| Interdisciplinary | |
| Related | |


 (see illustration to the right). If the speed of the top plate is low enough (to avoid turbulence), then in steady state the fluid particles move parallel to it, and their speed varies from
(see illustration to the right). If the speed of the top plate is low enough (to avoid turbulence), then in steady state the fluid particles move parallel to it, and their speed varies from  at the bottom to
at the bottom to  , acting on the top plate is found to be proportional to the speed
, acting on the top plate is found to be proportional to the speed  of each plate, and inversely proportional to their separation
of each plate, and inversely proportional to their separation  :
:

 , therefore resulting in the
, therefore resulting in the 
 energy per unit volume multiplied by time.
energy per unit volume multiplied by time. is called the rate of shear deformation or
is called the rate of shear deformation or 
 , and
, and  is the local shear velocity. This expression is referred to as
is the local shear velocity. This expression is referred to as  . It is a special case of the general definition of viscosity (see below), which can be expressed in coordinate-free form.
. It is a special case of the general definition of viscosity (see below), which can be expressed in coordinate-free form.
 ) is also used by chemists, physicists, and the
) is also used by chemists, physicists, and the 
 , therefore resulting in the
, therefore resulting in the 

 is a viscosity tensor that maps the
is a viscosity tensor that maps the  onto the viscous stress tensor
onto the viscous stress tensor  . Since the indices in this expression can vary from 1 to 3, there are 81 "viscosity coefficients"
. Since the indices in this expression can vary from 1 to 3, there are 81 "viscosity coefficients"  in total. However, assuming that the viscosity rank-2 tensor is
in total. However, assuming that the viscosity rank-2 tensor is  ,
,  ,
,  :
:

 , leaving only two independent parameters. The most usual decomposition is in terms of the standard (scalar) viscosity
, leaving only two independent parameters. The most usual decomposition is in terms of the standard (scalar) viscosity  such that
such that  and
and  . In vector notation this appears as:
. In vector notation this appears as:

 is the unit tensor. This equation can be thought of as a generalized form of Newton's law of viscosity.
is the unit tensor. This equation can be thought of as a generalized form of Newton's law of viscosity.
 and so the term containing
and so the term containing  , because the shear stress
, because the shear stress  has units equivalent to a momentum
has units equivalent to a momentum 
 is the density,
is the density,  and
and  are the mass and heat fluxes, and
are the mass and heat fluxes, and  and
and  are the mass diffusivity and thermal conductivity. The fact that mass, momentum, and energy (heat) transport are among the most relevant processes in continuum mechanics is not a coincidence: these are among the few physical quantities that are conserved at the microscopic level in interparticle collisions. Thus, rather than being dictated by the fast and complex microscopic interaction timescale, their dynamics occurs on macroscopic timescales, as described by the various equations of transport theory and hydrodynamics.
are the mass diffusivity and thermal conductivity. The fact that mass, momentum, and energy (heat) transport are among the most relevant processes in continuum mechanics is not a coincidence: these are among the few physical quantities that are conserved at the microscopic level in interparticle collisions. Thus, rather than being dictated by the fast and complex microscopic interaction timescale, their dynamics occurs on macroscopic timescales, as described by the various equations of transport theory and hydrodynamics.
 or
or  , depending on the convention used, measured in reciprocal poise (P, or
, depending on the convention used, measured in reciprocal poise (P, or 
 is the
is the  is the
is the  is the molecular mass.
is the molecular mass.
 -axis with velocity
-axis with velocity  that depends only on the
that depends only on the  is equal to whatever velocity that molecule had when its mean free path
is equal to whatever velocity that molecule had when its mean free path  began. Because
began. Because 
 . (Some authors estimate
. (Some authors estimate  ; on the other hand, a more careful calculation for rigid elastic spheres gives
; on the other hand, a more careful calculation for rigid elastic spheres gives  .) Next, because half the molecules on either side are moving towards
.) Next, because half the molecules on either side are moving towards  , the momentum flux from either side is
, the momentum flux from either side is


 , which leads to
, which leads to

 and density
and density 
 is the
is the  ,
, 
 . For more complicated molecular models, however,
. For more complicated molecular models, however,  trend predicted for rigid elastic spheres. Indeed, the Chapman–Enskog analysis shows that the predicted temperature dependence can be tuned by varying the parameters in various molecular models. A simple example is the Sutherland model, which describes rigid elastic spheres with weak mutual attraction. In such a case, the attractive force can be treated
trend predicted for rigid elastic spheres. Indeed, the Chapman–Enskog analysis shows that the predicted temperature dependence can be tuned by varying the parameters in various molecular models. A simple example is the Sutherland model, which describes rigid elastic spheres with weak mutual attraction. In such a case, the attractive force can be treated 
 is independent of temperature, being determined only by the parameters of the intermolecular attraction. To connect with experiment, it is convenient to rewrite as
is independent of temperature, being determined only by the parameters of the intermolecular attraction. To connect with experiment, it is convenient to rewrite as

 is the viscosity at temperature
is the viscosity at temperature  . This expression is usually named Sutherland's formula. If
. This expression is usually named Sutherland's formula. If  and at least one other temperature, then
and at least one other temperature, then 
 is the
is the  is the
is the  is the volume of a
is the volume of a  is the
is the 
 are constants fit from data. On the other hand, several authors express caution with respect to this model.
Errors as large as 30% can be encountered using equation (
are constants fit from data. On the other hand, several authors express caution with respect to this model.
Errors as large as 30% can be encountered using equation ( of a binary mixture of gases can be written in terms of the individual component viscosities
of a binary mixture of gases can be written in terms of the individual component viscosities  , their respective volume fractions, and the intermolecular interactions.
, their respective volume fractions, and the intermolecular interactions.

 and
and  of a solution:
of a solution:

 is the concentration, and
is the concentration, and 
 are fit from data. In particular, a negative value of
are fit from data. In particular, a negative value of  can be defined in terms of stress and strain components which are averaged over a volume large compared with the distance between the suspended particles, but small with respect to macroscopic dimensions. Such suspensions generally exhibit non-Newtonian behavior. However, for dilute systems in steady flows, the behavior is Newtonian and expressions for
can be defined in terms of stress and strain components which are averaged over a volume large compared with the distance between the suspended particles, but small with respect to macroscopic dimensions. Such suspensions generally exhibit non-Newtonian behavior. However, for dilute systems in steady flows, the behavior is Newtonian and expressions for  , interactions between the suspended particles can be ignored. In such a case one can explicitly calculate the flow field around each particle independently, and combine the results to obtain
, interactions between the suspended particles can be ignored. In such a case one can explicitly calculate the flow field around each particle independently, and combine the results to obtain 
 is a consequence of neglecting interparticle interactions. For dilute systems in general, one expects
is a consequence of neglecting interparticle interactions. For dilute systems in general, one expects 
 for spheres has not been conclusively validated, with various experiments finding values in the range
for spheres has not been conclusively validated, with various experiments finding values in the range  . This deficiency has been attributed to difficulty in controlling experimental conditions.
. This deficiency has been attributed to difficulty in controlling experimental conditions.

 is fit from experimental data or approximated from the microscopic theory. However, some authors advise caution in applying such simple formulas since non-Newtonian behavior appears in dense suspensions (
is fit from experimental data or approximated from the microscopic theory. However, some authors advise caution in applying such simple formulas since non-Newtonian behavior appears in dense suspensions ( for spheres), or in suspensions of elongated or flexible particles.
for spheres), or in suspensions of elongated or flexible particles.

 varies nontrivially with temperature and the simple Arrhenius form fails. On the other hand, the two-exponential equation
varies nontrivially with temperature and the simple Arrhenius form fails. On the other hand, the two-exponential equation


 denotes the high-frequency
denotes the high-frequency  ,
,  is the so-called shoving volume, i.e. it is the characteristic volume of the group of atoms involved in the shoving event by which an atom/molecule escapes from the cage of nearest-neighbours, typically on the order of the volume occupied by few atoms. Furthermore,
is the so-called shoving volume, i.e. it is the characteristic volume of the group of atoms involved in the shoving event by which an atom/molecule escapes from the cage of nearest-neighbours, typically on the order of the volume occupied by few atoms. Furthermore,  is the
is the  denotes the
denotes the 

 then corresponds to the viscosity in Pa·s.
then corresponds to the viscosity in Pa·s.
 2,000–10,000
2,000–10,000